Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 14
|
|
|
- Susan Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 14 Prof. Thomas Herring
2 Propagation Medium Propagation: Signal propagation from satellite to receiver Light-time iteration Basic atmospheric and ionospheric delays Propagation near receiving antenna 04/05/ Lec 14 2
3 Propagation Basics: Signal, tagged with time from satellite clock, transmitted. About 60 msec (20,000 km) later the signal arrives at GPS receiver. Satellite has moved about 66 m during the time it takes signal to propagate to receiver. Time the signal is received is given by clock in receiver. Difference between transmit time and receive time is pseudorange. During the propagation, signal passes through the ionosphere ( m of delay, phase advance), and neutral atmosphere ( m depending on elevation angle). 04/05/ Lec 14 3
4 Propagation To determine an accurate position from range data, we need to account for all these propagation effects and time offsets. In later lectures, examine ionospheric and atmospheric delays, and effects near antenna. Basic clock treatment in GPS True time of reception of signal needed True time of transmission needed (af0, af1 from broadcast ephemeris initially OK) Position of satellite when signal transmitted 04/05/ Lec 14 4
5 Times RINEX data files, tag measurements by reception time as given by the receiver clock. The error in the receiver time must be determined iteratively For linearized least squares or Kalman filter need to establish non-linear model and then estimator determines adjustments to parameters of model (e.g. receiver site coordinates) and initial clock error estimates that best match the data. 04/05/ Lec 14 5
6 Non-linear model Basics of non-linear model: Rinex data file time tags give approximate time measurement was made. Using this time initially, position of satellite can be computed Range computed from receiver and satellite position Difference between observed pseudorange and computed ranges, gives effects of satellite and receiver clock errors. In point positioning, satellite clock error is assumed known and when removed from difference, error in receiver clock determined. With new estimate of receiver clock, process can be iterated. If receiver position poorly known, then whole system can be iterated with updated receiver coordinates. 04/05/ Lec 14 6
7 Sensitivities Satellites move at about 1km/sec, therefore an error of 1 msec in time results in 1 m satellite position (and therefore in range estimate and receiver position). For pseudo-range positioning, 1 msec errors OK. For phase positioning (1 mm), times needed to 1 sec. (1 sec is about 300 m of range. Pseudorange accuracy of a few meters in fine). 04/05/ Lec 14 7
8 Light-time-iteration To compute theoretical range; two basic methods used (a) Doppler shift corrections ie. Account for rate of change of range during propagation time (b) Light-time-iteration Method most commonly used. Light time iteration: Basic process is to compute range using simple Cartesian geometry but with position of receiver at receive time and position of transmitter at transmit time. 04/05/ Lec 14 8
9 Light-time-iteration Light time iteration must be computed in a nonrotating frame Reason: Consider earth-fixed frame: one would simply compute Earth fixed coordinates at earlier time. In non-rotating frame, rotation to inertial coordinates would be done at two different time (receiver when signal received; transmitted when signal transmitted). Difference is rotation of Earth on ~60 msec. Rotation rate ~460 m/sec; therefore difference is about 30 meters. 04/05/ Lec 14 9
10 Clock errors Clock SA (ns) 1999 Clock NoSA (ns) 2000 PRN 03 (June 14) Clock error (ns) Time (hrs) /05/ Lec 14 10
11 Relativistic effects General relativity affects GPS in three ways Equations of motions of satellite Rates at which clock run Signal propagation In our GPS analysis we account for the second two items Orbits only integrated for 1-3 days and equation of motion term is considered small 04/05/ Lec 14 11
12 Clock effects GPS is controlled by MHz oscillators On the Earth s surface these oscillators are set to 10.23x( x10-10 ) MHz (39,000 ns/day rate difference) This offset accounts for the change in potential and average velocity once the satellite is launched. The first GPS satellites had a switch to turn this effect on. They were launched with Newtonian clocks 04/05/ Lec 14 12
13 Propagation and clock effects Our theoretical delay calculations are made in an Earth centered, non-rotating frame using a light-time iteration i.e., the satellite position at transmit time is differenced from ground station position at receive time. Two corrections are then applied to this calculation 04/05/ Lec 14 13
14 Corrections terms Propagation path curvature due to Earth s potential (a few centimeters) Clock effects due to changing potential For e=0.02 effect is 47 ns (14 m) 04/05/ Lec 14 14
15 Effects of General Relativity 50 PRN 03 Detrended; e=0.02 Clock - trend (ns) GR Effect (ns) Clock error (ns) Time (hrs) /05/ Lec 14 15
16 Tests of General Relativity After some back of the envelope derivations, in the parameterized post-newtonian formulation, the time delay expression* becomes: In PPN, is the gravitational curvature term. In general relativity = 1. It usually appears as (1+ )/2 but this has been modified as explained next. The clock estimates from each GPS satellite allow daily estimates of 04/05/ Lec 14 16
17 PPN formulation The clock rate correction is made of two parts: Special relativity term that depends on v 2 /2c 2 where v is the satellite velocity and c is the speed of light. General relativity contribution that depends on 2U/c 2 where U is potential The periodic variations arise from the eccentricity of the orbit: At perigee v is fastest which slows clock U is largest which also slows clock (decreasing potential increases the clock rate). The contribution to from the special relativity term is half that of the general relativity term and thus the formulation. 04/05/ Lec 14 17
18 Using GPS to determine Each day we can fit a linear trend and once-per-revolution sin and cos terms to the clock estimates of each of the GPS satellites. Comparison between the amplitude and phase (relative to sin(e)) allows and estimate of gamma to be obtained Quadrature estimates allows error bound to be assessed (cos(e) term) Problems: - Once-per-orbit perturbations are common. However should not be proportional to eccentricity. - Also possible thermal effects on the clocks in the satellites. (This is probably largest effect as we will see). - General quality of clocks in the satellites. There are multiple groups that process global GPS data using different processing software and analysis methods (double differencing versus one-way clock estimation). 04/05/ Lec 14 18
19 Example satellite clock (PRN 07) Results from different analysis groups Eccentricity is 0.011; g ~25 ns. 04/05/ Lec 14 19
20 Differences between groups RMS differences are about 0.2% of relativistic effect (measure of processing noise). Clock variation is ~4%. Eccentricity ~0.011: 25 ns 04/05/ Lec 14 20
21 PRN 28 MIT Analysis Error bars from RMS fit to clock estimates (linear, sine and cose terms only). Red line is fit to annual signal. 04/05/ Lec 14 21
22 PRN 28 GFZ analysis Results are similar but annual is slightly different 04/05/ Lec 14 22
23 Examples of receiver clock behavior Examples of satellite and station clock behaviors can be found at: IGS Time Standards are given at: Directories are by GPS week number and directories ending in W are total clock estimates; folders ending in D are differences between IGS analysis centers Now examine some examples 04/05/ Lec 14 23
24 Receiver clocks: ASC ASC1_Clk_(m) ASC1_Clk_(m) Day 04/05/ Lec 14 24
25 Receiver Clock: HOB2 Hydrogen Maser HOB2_clk_(m) HOB2_clk_(m) Day /05/ Lec 14 25
26 ASC/HOB2 Linear trends removed ASC1 detrended (m) HOB2 detrended (m) 10 Detrended (m) Day /05/ Lec 14 26
27 HOB2 only 1.0 HOB2 detrended (m) 0.5 Detrended (m) Day /05/ Lec 14 27
28 Summary of clocks In some cases; clock are well enough behaved that linear polynomials can be used. Most commonly: receiver clocks are estimated at every measurement epoch (white noise clocks) or GPS data is differenced to remove clock (as in question 2 of HW 2). Errors in receiver clocks are often thousands of km of equivalent time. More detailed analysis of gamma estimates in following slides. 04/05/ Lec 14 28
29 Analysis of result Not all satellites look like PRN 28. Only a few satellites are so well behaved. The following figures show some examples that show: Change in character when satellite changed (PRN02) Effects of change from Cs to Rb clocks (PRN10) Effects of changing eccentricity of orbit (PRN18) - change from to Period of oscillation: Draconic period: Period of orbital plane relative to sun (precession of node makes this different from days). Since all satellites in ~55 deg inclination and precess at the same rate, period is days. 04/05/ Lec 14 29
30 Change of satellite 04/05/ Lec 14 30
31 Change of clock type from Cs to Rb Change from Cs to Rb 04/05/ Lec 14 31
32 Effects of increasing eccentricity 04/05/ Lec 14 32
33 Annual versus Draconic Period 04/05/ Lec 14 33
34 MIT OpenCourseWare Principles of the Global Positioning System Spring 2012 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Mathematical models in GPS" Mathematical models used in GPS"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
Orbit Representation
 7.1 Fundamentals 223 For this purpose, code-pseudorange and carrier observations are made of all visible satellites at all monitor stations. The data are corrected for ionospheric and tropospheric delays,
7.1 Fundamentals 223 For this purpose, code-pseudorange and carrier observations are made of all visible satellites at all monitor stations. The data are corrected for ionospheric and tropospheric delays,
Earth-Centered, Earth-Fixed Coordinate System
 Fundamentals of Global Positioning System Receivers: A Software Approach James Bao-Yen Tsui Copyright 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-38154-3 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20054-9 CHAPTER FOUR Earth-Centered,
Fundamentals of Global Positioning System Receivers: A Software Approach James Bao-Yen Tsui Copyright 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-38154-3 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20054-9 CHAPTER FOUR Earth-Centered,
NGA GNSS Division Precise Ephemeris Parameters
 NGA GNSS Division Precise Ephemeris Parameters Precise Ephemeris Units. Earth-centered, Earth-fixed Coordinate system Position Velocity GPS time Trajectory interval Standard Trajectory Optional Trajectory
NGA GNSS Division Precise Ephemeris Parameters Precise Ephemeris Units. Earth-centered, Earth-fixed Coordinate system Position Velocity GPS time Trajectory interval Standard Trajectory Optional Trajectory
GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite Systems
 GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite Systems Global: today the American GPS (Global Positioning Service), http://gps.losangeles.af.mil/index.html the Russian GLONASS, http://www.glonass-center.ru/frame_e.html
GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite Systems Global: today the American GPS (Global Positioning Service), http://gps.losangeles.af.mil/index.html the Russian GLONASS, http://www.glonass-center.ru/frame_e.html
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Statistical approach to estimation Summary Look at estimation from statistical point
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Statistical approach to estimation Summary Look at estimation from statistical point
Week 02. Assist. Prof. Dr. Himmet KARAMAN
 Week 02 Assist. Prof. Dr. Himmet KARAMAN Contents Satellite Orbits Ephemerides GPS Review Accuracy & Usage Limitation Reference Systems GPS Services GPS Segments Satellite Positioning 2 Satellite Orbits
Week 02 Assist. Prof. Dr. Himmet KARAMAN Contents Satellite Orbits Ephemerides GPS Review Accuracy & Usage Limitation Reference Systems GPS Services GPS Segments Satellite Positioning 2 Satellite Orbits
Global Navigation Satellite Systems
 Global Navigation Satellite Systems GPS GLONASS Galileo BeiDou I I (COMPASS)? How Does a GNSS Work? Based on principle of triangulation Also called satellite ranging Signal travels at constant speed (3.0x10
Global Navigation Satellite Systems GPS GLONASS Galileo BeiDou I I (COMPASS)? How Does a GNSS Work? Based on principle of triangulation Also called satellite ranging Signal travels at constant speed (3.0x10
Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 12.540
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 12.540
Chapter 4. Satellite Position Estimation and Satellite Clock Error Analysis
 Chapter 4 Satellite Position Estimation and Satellite Clock Error Analysis 4.1 Introduction In satellite based navigation system, the receiver position accuracy relies on the precise knowledge of the satellite
Chapter 4 Satellite Position Estimation and Satellite Clock Error Analysis 4.1 Introduction In satellite based navigation system, the receiver position accuracy relies on the precise knowledge of the satellite
Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 20.3.3.3.3.1
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 20.3.3.3.3.1
Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Module: 2
 Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Module: 2 Dinesh Manandhar Center for Spatial Information Science The University of Tokyo Contact Information: dinesh@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Slide :
Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Module: 2 Dinesh Manandhar Center for Spatial Information Science The University of Tokyo Contact Information: dinesh@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Slide :
Satellite Navigation error sources and position estimation
 Satellite Navigation error sources and position estimation Picture: ESA AE4E08 Sandra Verhagen Course 2010 2011, lecture 6 1 Today s topics Recap: GPS measurements and error sources Signal propagation
Satellite Navigation error sources and position estimation Picture: ESA AE4E08 Sandra Verhagen Course 2010 2011, lecture 6 1 Today s topics Recap: GPS measurements and error sources Signal propagation
Real-Time Estimation of GPS Satellite Clocks Based on Global NTRIP-Streams. André Hauschild
 Real-Time Estimation of GPS Satellite Clocks Based on Global NTRIP-Streams André Hauschild Agenda Motivation Overview of the real-time clock estimation system Assessment of clock product quality a) SISRE
Real-Time Estimation of GPS Satellite Clocks Based on Global NTRIP-Streams André Hauschild Agenda Motivation Overview of the real-time clock estimation system Assessment of clock product quality a) SISRE
EESC Geodesy with the Global Positioning System. Class 4: The pseudorange and phase observables
 EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Positioning System Class 4: The pseudorange and phase observables In previous classes we had presented the equation for the pseudorange as the true range biased by the
EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Positioning System Class 4: The pseudorange and phase observables In previous classes we had presented the equation for the pseudorange as the true range biased by the
SIMPLIFIED ORBIT DETERMINATION ALGORITHM FOR LOW EARTH ORBIT SATELLITES USING SPACEBORNE GPS NAVIGATION SENSOR
 ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 49, No. 2 2014 DOI: 10.2478/arsa-2014-0007 SIMPLIFIED ORBIT DETERMINATION ALGORITHM FOR LOW EARTH ORBIT SATELLITES USING SPACEBORNE GPS NAVIGATION SENSOR ABSTRACT Sandip Tukaram
ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 49, No. 2 2014 DOI: 10.2478/arsa-2014-0007 SIMPLIFIED ORBIT DETERMINATION ALGORITHM FOR LOW EARTH ORBIT SATELLITES USING SPACEBORNE GPS NAVIGATION SENSOR ABSTRACT Sandip Tukaram
Homework #1 Solution: March 8, 2006
 12.540 Homework #1 Solution: March 8, 2006 Question 1: (a) Convert geodetic position 290 deg Long 42 deg latitude ellipsoidal height 0 m into Cartesian and geocentric coordinates. (b) How far apart on
12.540 Homework #1 Solution: March 8, 2006 Question 1: (a) Convert geodetic position 290 deg Long 42 deg latitude ellipsoidal height 0 m into Cartesian and geocentric coordinates. (b) How far apart on
E. Calais Purdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273
 E. Calais Purdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273 ecalais@purdue.edu Orbits? Satellite orbits: What for? satellite 3 satellite 2 ρr 2 ρ 3 ρ 1 satellite 1 Principle of GPS positioning: Satellite 1
E. Calais Purdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273 ecalais@purdue.edu Orbits? Satellite orbits: What for? satellite 3 satellite 2 ρr 2 ρ 3 ρ 1 satellite 1 Principle of GPS positioning: Satellite 1
Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 12.540
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 12.540
Modern Navigation
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring (tah@mit.edu), MW 10:30-12:00 Room 54-322 http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.215 Course Overview The development of the Global Positioning System (GPS) started in the
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring (tah@mit.edu), MW 10:30-12:00 Room 54-322 http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.215 Course Overview The development of the Global Positioning System (GPS) started in the
Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign
 Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign results from combined reprocessed IGS GPS orbits and EOPs assessment of IG1 orbit repeatability items to consider for next reprocessing Jake
Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign results from combined reprocessed IGS GPS orbits and EOPs assessment of IG1 orbit repeatability items to consider for next reprocessing Jake
Effects of the Theory of Relativity in the GPS
 Effects of the Theory of Relativity in the GPS Mario Haustein Chemnitz University of Technology February 5, 009 Abstract Basics of the GPS The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a world wide navigation
Effects of the Theory of Relativity in the GPS Mario Haustein Chemnitz University of Technology February 5, 009 Abstract Basics of the GPS The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a world wide navigation
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Basic Statistics Summary of last class Statistical description and parameters Probability distributions Descriptions: expectations, variances, moments Covariances
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Basic Statistics Summary of last class Statistical description and parameters Probability distributions Descriptions: expectations, variances, moments Covariances
EESC Geodesy with the Global Positioning System. Class 6: Point Positioning using Pseuduorange
 EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Positioning System Class 6: Point Positioning using Pseuduorange GPS Positioning Solutions Point Positioning: Determination of the coordinates of a point with respect
EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Positioning System Class 6: Point Positioning using Pseuduorange GPS Positioning Solutions Point Positioning: Determination of the coordinates of a point with respect
EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Posi6oning System. Class 2: Satellite orbits
 EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Posi6oning System Class 2: Satellite orbits Background The model for the pseudorange was Today, we ll develop how to calculate the vector posi6on of the satellite The
EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Posi6oning System Class 2: Satellite orbits Background The model for the pseudorange was Today, we ll develop how to calculate the vector posi6on of the satellite The
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 24
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 24 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 OVERVIEW Examination of results from Earthscope Reference frame definition: SNARF High-rate
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 24 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 OVERVIEW Examination of results from Earthscope Reference frame definition: SNARF High-rate
imin...
 Pulsar Timing For a detailed look at pulsar timing and other pulsar observing techniques, see the Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy by Duncan Lorimer and Michael Kramer. Pulsars are intrinsically interesting
Pulsar Timing For a detailed look at pulsar timing and other pulsar observing techniques, see the Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy by Duncan Lorimer and Michael Kramer. Pulsars are intrinsically interesting
IGS Reprocessing. and First Quality Assessment
 IGS Reprocessing Summary of Orbit/Clock Combination and First Quality Assessment Gerd Gendt, GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam Jake Griffiths, NOAA/National Geodetic Survey Thomas Nischan, GeoForschungsZentrum
IGS Reprocessing Summary of Orbit/Clock Combination and First Quality Assessment Gerd Gendt, GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam Jake Griffiths, NOAA/National Geodetic Survey Thomas Nischan, GeoForschungsZentrum
Orekit in NEOSAT FDS. Alexandre Janer& Pol Sola Romeu(TAS) Maxime Journot(CS) Orekit Day 2017 PROPRIETARY INFORMATION 27/11/2017
 Orekit in NEOSAT FDS Alexandre Janer& Pol Sola Romeu(TAS) Maxime Journot(CS) Orekit Day 2017 1 Modèle 83230347-DOC-TAS-FR-004 Contents TAS &the NEOSAT program NEOSAT FDS -Generalities Orekit in NEOSAT
Orekit in NEOSAT FDS Alexandre Janer& Pol Sola Romeu(TAS) Maxime Journot(CS) Orekit Day 2017 1 Modèle 83230347-DOC-TAS-FR-004 Contents TAS &the NEOSAT program NEOSAT FDS -Generalities Orekit in NEOSAT
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 23
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 23 Prof. Thomas Herring 05/12/03 12.540 Lec 23 1 OVERVIEW Run through HW 03. Final lecture: Application area and GPS results Analysis of contemporary
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 23 Prof. Thomas Herring 05/12/03 12.540 Lec 23 1 OVERVIEW Run through HW 03. Final lecture: Application area and GPS results Analysis of contemporary
Research Article Time Synchronization and Performance of BeiDou Satellite Clocks in Orbit
 Navigation and Observation Volume 213, Article ID 37145, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/37145 Research Article Time Synchronization and Performance of BeiDou Satellite Clocks in Orbit Han Chunhao,
Navigation and Observation Volume 213, Article ID 37145, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/37145 Research Article Time Synchronization and Performance of BeiDou Satellite Clocks in Orbit Han Chunhao,
STATISTICAL ORBIT DETERMINATION
 STATISTICAL ORBIT DETERMINATION Satellite Tracking Example of SNC and DMC ASEN 5070 LECTURE 6 4.08.011 1 We will develop a simple state noise compensation (SNC) algorithm. This algorithm adds process noise
STATISTICAL ORBIT DETERMINATION Satellite Tracking Example of SNC and DMC ASEN 5070 LECTURE 6 4.08.011 1 We will develop a simple state noise compensation (SNC) algorithm. This algorithm adds process noise
A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty. AVENUE project. June, 20
 Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
EESC Geodesy with the Global Positioning System. Class 7: Relative Positioning using Carrier-Beat Phase
 EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Positioning System Class 7: Relative Positioning using Carrier-Beat Phase GPS Carrier Phase The model for the carrier-beat phase observable for receiver p and satellite
EESC 9945 Geodesy with the Global Positioning System Class 7: Relative Positioning using Carrier-Beat Phase GPS Carrier Phase The model for the carrier-beat phase observable for receiver p and satellite
Orbit and Transmit Characteristics of the CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR) JPL Document No. D-29695
 Orbit and Transmit Characteristics of the CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR) JPL Document No. D-29695 Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 26 July 2004 Revised
Orbit and Transmit Characteristics of the CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR) JPL Document No. D-29695 Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 26 July 2004 Revised
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Dec 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Dec 2003 arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Dec 2003](/thumbs/93/111763098.jpg) The effective inertial acceleration due to oscillations of the gravitational potential: footprints in the solar system arxiv:physics/0309099v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Dec 2003 D.L. Khokhlov Sumy State University,
The effective inertial acceleration due to oscillations of the gravitational potential: footprints in the solar system arxiv:physics/0309099v2 [physics.gen-ph] 2 Dec 2003 D.L. Khokhlov Sumy State University,
Nutation determination by means of GNSS
 Nutation determination by means of GNSS - Comparison with VLBI Nicole Capitaine, Kunliang Yao SYRTE - Observatoire de Paris, CNRS/UPMC, France Introduction Space geodetic techniques cannot be used for
Nutation determination by means of GNSS - Comparison with VLBI Nicole Capitaine, Kunliang Yao SYRTE - Observatoire de Paris, CNRS/UPMC, France Introduction Space geodetic techniques cannot be used for
Figure 1. View of ALSAT-2A spacecraft
 ALSAT-2A TRANSFER AND FIRST YEAR OPERATIONS M. Kameche (1), A.H. Gicquel (2), D. Joalland (3) (1) CTS/ASAL, 1 Avenue de la Palestine, BP 13, Arzew 31200 Oran, Algérie, email:mo_kameche@netcourrier.com
ALSAT-2A TRANSFER AND FIRST YEAR OPERATIONS M. Kameche (1), A.H. Gicquel (2), D. Joalland (3) (1) CTS/ASAL, 1 Avenue de la Palestine, BP 13, Arzew 31200 Oran, Algérie, email:mo_kameche@netcourrier.com
Climate Monitoring with Radio Occultation Data
 Climate Monitoring with Radio Occultation Data Systematic Error Sources C. Rocken, S. Sokolovskiy, B. Schreiner, D. Hunt, B. Ho, B. Kuo, U. Foelsche Radio Occultation Claims Most stable Global Thermometer
Climate Monitoring with Radio Occultation Data Systematic Error Sources C. Rocken, S. Sokolovskiy, B. Schreiner, D. Hunt, B. Ho, B. Kuo, U. Foelsche Radio Occultation Claims Most stable Global Thermometer
CODE's multi-gnss orbit and clock solution
 source: https://doi.org/10.7892/boris.68193 downloaded: 13.3.2017 CODE's multi-gnss orbit and clock solution L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute,
source: https://doi.org/10.7892/boris.68193 downloaded: 13.3.2017 CODE's multi-gnss orbit and clock solution L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute,
DESIGN OF SYSTEM LEVEL CONCEPT FOR TERRA 25994
 DESIGN OF SYSTEM LEVEL CONCEPT FOR TERRA 25994 Prof. S.Peik Group Number : 14 Submitted by: Deepthi Poonacha Machimada : 5007754 Shridhar Reddy : 5007751 1 P a g e Table of Contents 1. Introduction...
DESIGN OF SYSTEM LEVEL CONCEPT FOR TERRA 25994 Prof. S.Peik Group Number : 14 Submitted by: Deepthi Poonacha Machimada : 5007754 Shridhar Reddy : 5007751 1 P a g e Table of Contents 1. Introduction...
NPL Time and Frequency Section: NPL S CONTRIBUTION TO TUGGS
 NPL Time & Frequency NPL Time and Frequency Section: NPL S CONTRIBUTION TO TUGGS J A Davis, P W Stacey, R Hlavac, and P B Whibberley. Date: 21st April 2004 THALES UK-BASED GNSS GROUND SEGMENT (TUGGS) Aim
NPL Time & Frequency NPL Time and Frequency Section: NPL S CONTRIBUTION TO TUGGS J A Davis, P W Stacey, R Hlavac, and P B Whibberley. Date: 21st April 2004 THALES UK-BASED GNSS GROUND SEGMENT (TUGGS) Aim
The ACES Mission. Fundamental Physics Tests with Cold Atom Clocks in Space. L. Cacciapuoti European Space Agency
 The ACES Mission Fundamental Physics Tests with Cold Atom Clocks in Space L. Cacciapuoti European Space Agency La Thuile, 20-27 March 2011 Gravitational Waves and Experimental Gravity 1 ACES Mission Concept
The ACES Mission Fundamental Physics Tests with Cold Atom Clocks in Space L. Cacciapuoti European Space Agency La Thuile, 20-27 March 2011 Gravitational Waves and Experimental Gravity 1 ACES Mission Concept
Research of Satellite and Ground Time Synchronization Based on a New Navigation System
 Research of Satellite and Ground Time Synchronization Based on a New Navigation System Yang Yang, Yufei Yang, Kun Zheng and Yongjun Jia Abstract The new navigation time synchronization method is a breakthrough
Research of Satellite and Ground Time Synchronization Based on a New Navigation System Yang Yang, Yufei Yang, Kun Zheng and Yongjun Jia Abstract The new navigation time synchronization method is a breakthrough
VELOX-CI: Advanced Application of GPS for Radio Occultation and Satellite Attitude Determination
 VELOX-CI: Advanced Application of GPS for Radio Occultation and Satellite Attitude Determination Yung-Fu Tsai, Guo Xiong Lee and Kay Soon Low Satellite Research Centre (SaRC) School of Electrical and Electronic
VELOX-CI: Advanced Application of GPS for Radio Occultation and Satellite Attitude Determination Yung-Fu Tsai, Guo Xiong Lee and Kay Soon Low Satellite Research Centre (SaRC) School of Electrical and Electronic
SPACECRAFT NAVIGATION AND MISSION SIMULATION
 TianQin Space-borne gravitational wave detector SPACECRAFT NAVIGATION AND MISSION SIMULATION December 9, 2015 - Prepared by Viktor T. Toth A PERSPECTIVE Precision navigation End-to-end mission simulation
TianQin Space-borne gravitational wave detector SPACECRAFT NAVIGATION AND MISSION SIMULATION December 9, 2015 - Prepared by Viktor T. Toth A PERSPECTIVE Precision navigation End-to-end mission simulation
Impact of the SRP model on CODE's 5- system orbit and clock solution for the MGEX
 Impact of the SRP model on CODE's 5- system orbit and clock solution for the MGEX L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Switzerland
Impact of the SRP model on CODE's 5- system orbit and clock solution for the MGEX L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Switzerland
RINEX Extensions to Handle Clock Information ********************************************
 RINEX Extensions to Handle Clock Information ******************************************** Jim Ray, US Naval Observatory Werner Gurtner, University of Berne (Initial version, 27 August 1998) (Error in example
RINEX Extensions to Handle Clock Information ******************************************** Jim Ray, US Naval Observatory Werner Gurtner, University of Berne (Initial version, 27 August 1998) (Error in example
Improved GNSS-Based Precise Orbit Determination by using highly accurate clocks
 Improved GNSS-Based Precise Orbit Determination by using highly accurate clocks A. Susnik 1, R. Dach 1, K. Wang 2, M. Meindl 2, M. Rothacher 2, D. Koch 2, T. Romanyuk 3, I. Selmke 3, U. Hugentobler 3,
Improved GNSS-Based Precise Orbit Determination by using highly accurate clocks A. Susnik 1, R. Dach 1, K. Wang 2, M. Meindl 2, M. Rothacher 2, D. Koch 2, T. Romanyuk 3, I. Selmke 3, U. Hugentobler 3,
What s Not Wrong With Faster-Than-Light Neutrinos
 What s Not Wrong With Faster-Than-Light Neutrinos Care and Feeding of Relativistic Measurements Eric L. Michelsen (emichels/physics.ucsd.edu) UCSD CASS Journal Club Topics The problem The size of the problem
What s Not Wrong With Faster-Than-Light Neutrinos Care and Feeding of Relativistic Measurements Eric L. Michelsen (emichels/physics.ucsd.edu) UCSD CASS Journal Club Topics The problem The size of the problem
APPENDIX B SUMMARY OF ORBITAL MECHANICS RELEVANT TO REMOTE SENSING
 APPENDIX B SUMMARY OF ORBITAL MECHANICS RELEVANT TO REMOTE SENSING Orbit selection and sensor characteristics are closely related to the strategy required to achieve the desired results. Different types
APPENDIX B SUMMARY OF ORBITAL MECHANICS RELEVANT TO REMOTE SENSING Orbit selection and sensor characteristics are closely related to the strategy required to achieve the desired results. Different types
Workshop on GNSS Data Application to Low Latitude Ionospheric Research May Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation
 2458-6 Workshop on GNSS Data Application to Low Latitude Ionospheric Research 6-17 May 2013 Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation HEGARTY Christopher The MITRE Corporation 202 Burlington Rd. / Rte 62 Bedford
2458-6 Workshop on GNSS Data Application to Low Latitude Ionospheric Research 6-17 May 2013 Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation HEGARTY Christopher The MITRE Corporation 202 Burlington Rd. / Rte 62 Bedford
ERTH 455 / GEOP 555 Geodetic Methods. Lecture 04: GPS Overview, Coordinate Systems
 ERTH 455 / GEOP 555 Geodetic Methods Lecture 04: GPS Overview, Coordinate Systems Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356 x5924 August 30, 2017 1 / 22 2 / 22 GPS Overview 1973: Architecture approved 1978:
ERTH 455 / GEOP 555 Geodetic Methods Lecture 04: GPS Overview, Coordinate Systems Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356 x5924 August 30, 2017 1 / 22 2 / 22 GPS Overview 1973: Architecture approved 1978:
Hourly Updated Precise Orbit Products of Quad-constellation
 Hourly Updated Precise Orbit Products of Quad-constellation Satellites in IGS Analysis Center at Wuhan University Qile Zhao; Hongyang Ma; Xiaolong Xu; Jing Guo; Min Li Wuhan University Jul.05 2017 Paris
Hourly Updated Precise Orbit Products of Quad-constellation Satellites in IGS Analysis Center at Wuhan University Qile Zhao; Hongyang Ma; Xiaolong Xu; Jing Guo; Min Li Wuhan University Jul.05 2017 Paris
Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks
 Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks Pierre Waller, Francisco Gonzalez, Stefano Binda, ESA/ESTEC Ilaria Sesia, Patrizia Tavella, INRiM Irene Hidalgo, Guillermo Tobias, GMV Abstract The Galileo
Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks Pierre Waller, Francisco Gonzalez, Stefano Binda, ESA/ESTEC Ilaria Sesia, Patrizia Tavella, INRiM Irene Hidalgo, Guillermo Tobias, GMV Abstract The Galileo
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 04"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 04" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Review" So far we have looked at measuring
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 04" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Review" So far we have looked at measuring
10 General Relativistic Models for Space-time Coordinates and Equations of Motion
 10 General Relativistic Models for Space-time Coordinates and Equations of Motion 10.1 Time Coordinates IAU resolution A4 (1991) set the framework presently used to define the barycentric reference system
10 General Relativistic Models for Space-time Coordinates and Equations of Motion 10.1 Time Coordinates IAU resolution A4 (1991) set the framework presently used to define the barycentric reference system
Estimating Atmospheric Water Vapor with Groundbased. Lecture 12
 Estimating Atmospheric Water Vapor with Groundbased GPS Lecture 12 Overview This lecture covers metrological applica4ons of GPS Some of the material has already been presented and is shown here for completeness.
Estimating Atmospheric Water Vapor with Groundbased GPS Lecture 12 Overview This lecture covers metrological applica4ons of GPS Some of the material has already been presented and is shown here for completeness.
IGS-MGEX: QZSS Orbit and Clock Determination
 IGS-MGEX: QZSS Orbit and Clock Determination P. Steigenberger (1), S. Kogure (2) (1) DLR/GSOC, (2) JAXA Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) Japanese regional augmentation System for GPS in the Asia and
IGS-MGEX: QZSS Orbit and Clock Determination P. Steigenberger (1), S. Kogure (2) (1) DLR/GSOC, (2) JAXA Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) Japanese regional augmentation System for GPS in the Asia and
GPS-BASED NAVIGATION AND ORBIT DETERMINATION FOR THE AMSAT AO-40 SATELLITE
 GPS-BASED NAVIGATION AND ORBIT DETERMINATION FOR THE AMSAT AO-4 SATELLITE George Davis Emergent Space Technologies, LLC Michael Moreau, Russell Carpenter, Frank Bauer NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Abstract
GPS-BASED NAVIGATION AND ORBIT DETERMINATION FOR THE AMSAT AO-4 SATELLITE George Davis Emergent Space Technologies, LLC Michael Moreau, Russell Carpenter, Frank Bauer NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Abstract
ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY)
 ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY) J. Paul Collins and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory Department of Geodesy and Geomatics
ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY) J. Paul Collins and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory Department of Geodesy and Geomatics
Information in Radio Waves
 Teacher Notes for the Geodesy Presentation: Possible discussion questions before presentation: - If you didn t know the size and shape of the Earth, how would you go about figuring it out? Slide 1: Geodesy
Teacher Notes for the Geodesy Presentation: Possible discussion questions before presentation: - If you didn t know the size and shape of the Earth, how would you go about figuring it out? Slide 1: Geodesy
TOWARDS ROBUST LOCALIZATION OF RTK-GPS TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEYS 23
 TOWARDS ROBUST LOCALIZATION OF RTK-GPS TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEYS Jerry W. Nave, North Carolina A&T University; Tarig A. Ali, American University of Sharjah Abstract Localization is performed to fit the observed
TOWARDS ROBUST LOCALIZATION OF RTK-GPS TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEYS Jerry W. Nave, North Carolina A&T University; Tarig A. Ali, American University of Sharjah Abstract Localization is performed to fit the observed
General Relativity and Black Holes
 General Relativity and Black Holes Lecture 19 1 Lecture Topics General Relativity The Principal of Equivalence Consequences of General Relativity slowing of clocks curvature of space-time Tests of GR Escape
General Relativity and Black Holes Lecture 19 1 Lecture Topics General Relativity The Principal of Equivalence Consequences of General Relativity slowing of clocks curvature of space-time Tests of GR Escape
Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI)
 Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) A brief Note compiled by: Prof. Madhav N. Kulkarni, IIT Bombay Since the inception of the Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) system in 1967, this
Geodetic Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) A brief Note compiled by: Prof. Madhav N. Kulkarni, IIT Bombay Since the inception of the Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) system in 1967, this
Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr
 Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, Graz University of Technology WG Theoretical Geodesy and Satellite Geodesy Geodetic Week 2015, Stuttgart, Germany Sebastian Strasser 16.09.2015
Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, Graz University of Technology WG Theoretical Geodesy and Satellite Geodesy Geodetic Week 2015, Stuttgart, Germany Sebastian Strasser 16.09.2015
Understanding the Differences between LS Algorithms and Sequential Filters
 Understanding the Differences between LS Algorithms and Sequential Filters In order to perform meaningful comparisons between outputs from a least squares (LS) orbit determination algorithm and orbit determination
Understanding the Differences between LS Algorithms and Sequential Filters In order to perform meaningful comparisons between outputs from a least squares (LS) orbit determination algorithm and orbit determination
Introduction to Pulsar Timing. David Nice Lafayette College. International Pulsar Timing Array Student Workshop Banff, Alberta 16 June 2014
 Introduction to Pulsar Timing David Nice Lafayette College International Pulsar Timing Array Student Workshop Banff, Alberta 16 June 2014 1. Extremely short overview 2. Measuring TOAs 3. What s in a timing
Introduction to Pulsar Timing David Nice Lafayette College International Pulsar Timing Array Student Workshop Banff, Alberta 16 June 2014 1. Extremely short overview 2. Measuring TOAs 3. What s in a timing
2. GNSS Measurements
 Abstract: With the development of the International GNSS Service, whose primary object is to provide highest products for research, education and multidisciplinary application, the concept of Precise Point
Abstract: With the development of the International GNSS Service, whose primary object is to provide highest products for research, education and multidisciplinary application, the concept of Precise Point
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study
 Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
ASEN 6008: Interplanetary Mission Design Lab Spring, 2015
 ASEN 6008: Interplanetary Mission Design Lab Spring, 2015 Lab 4: Targeting Mars using the B-Plane Name: I d like to give credit to Scott Mitchell who developed this lab exercise. He is the lead Astrodynamicist
ASEN 6008: Interplanetary Mission Design Lab Spring, 2015 Lab 4: Targeting Mars using the B-Plane Name: I d like to give credit to Scott Mitchell who developed this lab exercise. He is the lead Astrodynamicist
Test Computations
 158 7. Test Computations.3.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 2.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 2.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 3.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 3.2.1 -.1 -.2 -.3 Fourier index 4.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 4.2.1
158 7. Test Computations.3.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 2.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 2.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 3.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 3.2.1 -.1 -.2 -.3 Fourier index 4.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 4.2.1
GRACE processing at TU Graz
 S C I E N C E P A S S I O N T E C H N O L O G Y GRACE processing at TU Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr, Saniya Behzadpour, Andreas Kvas, Matthias Ellmer, Beate Klinger, Norbert Zehentner, and Sebastian Strasser
S C I E N C E P A S S I O N T E C H N O L O G Y GRACE processing at TU Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr, Saniya Behzadpour, Andreas Kvas, Matthias Ellmer, Beate Klinger, Norbert Zehentner, and Sebastian Strasser
Satellite communications and the environment of space. V 1.1 Swiss Space Summer Camp 2016 Images: NASA 1
 Satellite communications and the environment of space Swiss Space Summer Camp 2016 Images: NASA 1 Can you name these satellites? Sputnik The first man made satellite Launched in 1957 by The USSR Mass 84kg,
Satellite communications and the environment of space Swiss Space Summer Camp 2016 Images: NASA 1 Can you name these satellites? Sputnik The first man made satellite Launched in 1957 by The USSR Mass 84kg,
ACCURACY ASSESSMENT OF GEOSTATIONARY-EARTH-ORBIT WITH SIMPLIFIED PERTURBATIONS MODELS
 ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 51, No. 2 2016 DOI: 10.1515/arsa-2016-0005 ACCURACY ASSESSMENT OF GEOSTATIONARY-EARTH-ORBIT WITH SIMPLIFIED PERTURBATIONS MODELS Lihua Ma, Xiaojun Xu, Feng Pang National Astronomical
ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 51, No. 2 2016 DOI: 10.1515/arsa-2016-0005 ACCURACY ASSESSMENT OF GEOSTATIONARY-EARTH-ORBIT WITH SIMPLIFIED PERTURBATIONS MODELS Lihua Ma, Xiaojun Xu, Feng Pang National Astronomical
Homework #2 Due Monday, April 18, 2012
 12.540 Homework #2 Due Monday, April 18, 2012 Matlab solution codes are given in HW02_2012.m This code uses cells and contains the solutions to all the questions. Question 1: Non-linear estimation problem
12.540 Homework #2 Due Monday, April 18, 2012 Matlab solution codes are given in HW02_2012.m This code uses cells and contains the solutions to all the questions. Question 1: Non-linear estimation problem
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy
 Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
Accelerometers for GNSS Orbit Determination
 Accelerometers for GNSS Orbit Determination Urs Hugentobler, Anja Schlicht Technische Universität München 5th International Colloquium on Scientific and Fundamental Aspects of the Galileo Programme October
Accelerometers for GNSS Orbit Determination Urs Hugentobler, Anja Schlicht Technische Universität München 5th International Colloquium on Scientific and Fundamental Aspects of the Galileo Programme October
Satellite Navigation GPS measurements and error sources
 Satellite Navigation GPS measrements and error sorces Pictre: ESA AE4E08 Sandra Verhagen Corse 2010 2011, lectre 4 1 Today s topics Recap: GPS signal components Code Phase measrements psedoranges Carrier
Satellite Navigation GPS measrements and error sorces Pictre: ESA AE4E08 Sandra Verhagen Corse 2010 2011, lectre 4 1 Today s topics Recap: GPS signal components Code Phase measrements psedoranges Carrier
TIMEKEEPING AND TIME DISSEMINATION IN A DISTRIBUTED SPACE-BASED CLOCK ENSEMBLE
 TIMEKEEPING AND TIME DISSEMINATION IN A DISTRIBUTED SPACE-BASED CLOCK ENSEMBLE S. Francis Zeta Associates Incorporated B. Ramsey and S. Stein Timing Solutions Corporation J. Leitner, M. Moreau, and R.
TIMEKEEPING AND TIME DISSEMINATION IN A DISTRIBUTED SPACE-BASED CLOCK ENSEMBLE S. Francis Zeta Associates Incorporated B. Ramsey and S. Stein Timing Solutions Corporation J. Leitner, M. Moreau, and R.
Creating Satellite Orbits
 Exercises using Satellite ToolKit (STK) vivarad@ait.ac.th Creating Satellite Orbits 1. What You Will Do Create a low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite Create a medium-earth orbit (MEO) satellite Create a highly
Exercises using Satellite ToolKit (STK) vivarad@ait.ac.th Creating Satellite Orbits 1. What You Will Do Create a low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite Create a medium-earth orbit (MEO) satellite Create a highly
Space Surveillance with Star Trackers. Part II: Orbit Estimation
 AAS -3 Space Surveillance with Star Trackers. Part II: Orbit Estimation Ossama Abdelkhalik, Daniele Mortari, and John L. Junkins Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 7783-3 Abstract The problem
AAS -3 Space Surveillance with Star Trackers. Part II: Orbit Estimation Ossama Abdelkhalik, Daniele Mortari, and John L. Junkins Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas 7783-3 Abstract The problem
ORBIT PERIOD FREQUENCY VARIATIONS IN THE GPS SATELLITE CLOCKS
 ORBIT PERIOD FREQUENCY VARIATIONS IN THE GPS SATELLITE CLOCKS Everett R. Swift Bruce. R. Hermann Space and Surface Systems Division (K10) Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren, Virginia 22448, USA Abstract
ORBIT PERIOD FREQUENCY VARIATIONS IN THE GPS SATELLITE CLOCKS Everett R. Swift Bruce. R. Hermann Space and Surface Systems Division (K10) Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren, Virginia 22448, USA Abstract
Long-Term Evolution of High Earth Orbits: Effects of Direct Solar Radiation Pressure and Comparison of Trajectory Propagators
 Long-Term Evolution of High Earth Orbits: Effects of Direct Solar Radiation Pressure and Comparison of Trajectory Propagators by L. Anselmo and C. Pardini (Luciano.Anselmo@isti.cnr.it & Carmen.Pardini@isti.cnr.it)
Long-Term Evolution of High Earth Orbits: Effects of Direct Solar Radiation Pressure and Comparison of Trajectory Propagators by L. Anselmo and C. Pardini (Luciano.Anselmo@isti.cnr.it & Carmen.Pardini@isti.cnr.it)
This is an author-deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 16117
 Open Archive TOULOUSE Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Open Archive TOULOUSE Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Monday s Class Spherical Trigonometry Review plane trigonometry Concepts in Spherical Trigonometry Distance measures Azimuths and bearings Basic formulas:
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Review of Monday s Class Spherical Trigonometry Review plane trigonometry Concepts in Spherical Trigonometry Distance measures Azimuths and bearings Basic formulas:
CHAPTER 25 SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS # DEFINITIONS TERMS. Satellite. 1) A celestial body that orbits around a planet.
 CHAPTER 25 SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) A celestial body that orbits around a planet. Satellite 2) Man-made satellites that orbit earth, providing a multitude of communication functions
CHAPTER 25 SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) A celestial body that orbits around a planet. Satellite 2) Man-made satellites that orbit earth, providing a multitude of communication functions
INTRODUCTION TO ORBITAL MECHANICS - MODEL & SIMULATION SOFTWARE (OM-MSS) Earth, Sun, Moon & Satellites Motion in Orbit - Model & Simulation Software
 Return to Website INTRODUCTION TO ORBITAL MECHANICS - MODEL & SIMULATION SOFTWARE (OM-MSS) Earth, Sun, Moon & Satellites Motion in Orbit - Model & Simulation Software RC Chakraborty (Retd), Former Director,
Return to Website INTRODUCTION TO ORBITAL MECHANICS - MODEL & SIMULATION SOFTWARE (OM-MSS) Earth, Sun, Moon & Satellites Motion in Orbit - Model & Simulation Software RC Chakraborty (Retd), Former Director,
MEETING ORBIT DETERMINATION REQUIREMENTS FOR A SMALL SATELLITE MISSION
 MEETING ORBIT DETERMINATION REQUIREMENTS FOR A SMALL SATELLITE MISSION Adonis Pimienta-Peñalver, Richard Linares, and John L. Crassidis University at Buffalo, State University of New York, Amherst, NY,
MEETING ORBIT DETERMINATION REQUIREMENTS FOR A SMALL SATELLITE MISSION Adonis Pimienta-Peñalver, Richard Linares, and John L. Crassidis University at Buffalo, State University of New York, Amherst, NY,
Velocity and Acceleration of NavIC Satellites using Broadcast Ephemeris
 Velocity and Acceleration of NavIC Satellites using Broadcast Ephemeris Bidyut B. Gogoi *, Akhilesh Kumar, A. Kartik, Nirmala S. Space Navigation Group Indian Space Research Organisation Satellite Center
Velocity and Acceleration of NavIC Satellites using Broadcast Ephemeris Bidyut B. Gogoi *, Akhilesh Kumar, A. Kartik, Nirmala S. Space Navigation Group Indian Space Research Organisation Satellite Center
We have processed RO data for climate research and for validation of weather data since 1995 as illustrated in Figure 1.
 Real-time Analysis of COSMIC Data Christian Rocken, Doug Hunt, Bill Schreiner University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) COSMIC Project Office Boulder, CO Abstract UCAR has analyzed GPS radio
Real-time Analysis of COSMIC Data Christian Rocken, Doug Hunt, Bill Schreiner University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) COSMIC Project Office Boulder, CO Abstract UCAR has analyzed GPS radio
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate
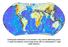 Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
MORE Orbit Determination Software status
 MORE Orbit Determination Software status Celestial Mechanics Group University of Pisa Department of Mathematics Progress Meeting MORE, October 15th 2009 1/ 25 Outline 1. Current status of the Orbit14 software
MORE Orbit Determination Software status Celestial Mechanics Group University of Pisa Department of Mathematics Progress Meeting MORE, October 15th 2009 1/ 25 Outline 1. Current status of the Orbit14 software
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Living Rev. Relativity, 6, (2003), 1 L I V I N G in relativity REVIEWS Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Dept. of Physics, University of Colorado Boulder, CO 80309 0390 U.S.A. email:
Living Rev. Relativity, 6, (2003), 1 L I V I N G in relativity REVIEWS Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Dept. of Physics, University of Colorado Boulder, CO 80309 0390 U.S.A. email:
Attitude Determination using Infrared Earth Horizon Sensors
 Attitude Determination using Infrared Earth Horizon Sensors Tam N. T. Nguyen Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology 28 th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites
Attitude Determination using Infrared Earth Horizon Sensors Tam N. T. Nguyen Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology 28 th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites
Autonomous satellite orbit prediction
 Autonomous satellite orbit prediction Mari Seppänen Department of Mathematics Tampere University of Technology P.O. Box 553, FI-33101 Tampere, Finland e-mail: mari.j.seppanen@tut.fi Abstract A method to
Autonomous satellite orbit prediction Mari Seppänen Department of Mathematics Tampere University of Technology P.O. Box 553, FI-33101 Tampere, Finland e-mail: mari.j.seppanen@tut.fi Abstract A method to
Lecture 2c: Satellite Orbits
 Lecture 2c: Satellite Orbits Outline 1. Newton s Laws of Mo3on 2. Newton s Law of Universal Gravita3on 3. Kepler s Laws 4. Pu>ng Newton and Kepler s Laws together and applying them to the Earth-satellite
Lecture 2c: Satellite Orbits Outline 1. Newton s Laws of Mo3on 2. Newton s Law of Universal Gravita3on 3. Kepler s Laws 4. Pu>ng Newton and Kepler s Laws together and applying them to the Earth-satellite
The Orbit Control of ERS-1 and ERS-2 for a Very Accurate Tandem Configuration
 The Orbit Control of ERS-1 and ERS-2 for a Very Accurate Tandem Configuration Mats Rosengren European Space Operations Centre Robert Bosch Str 5 D64293 Darmstadt Germany Email: mrosengr@esoc.esa.de Abstract
The Orbit Control of ERS-1 and ERS-2 for a Very Accurate Tandem Configuration Mats Rosengren European Space Operations Centre Robert Bosch Str 5 D64293 Darmstadt Germany Email: mrosengr@esoc.esa.de Abstract
INTEGRATED OPERATIONAL PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION FOR LEO
 INTEGRATED OPERATIONAL PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION FOR LEO J. Fernández Sánchez, F. M. Martínez Fadrique, A. Águeda Maté, D. Escobar Antón GMV S.A., Isaac Newton, 8760 Tres Cantos, Spain, Email: jfernandez@gmv.com,
INTEGRATED OPERATIONAL PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION FOR LEO J. Fernández Sánchez, F. M. Martínez Fadrique, A. Águeda Maté, D. Escobar Antón GMV S.A., Isaac Newton, 8760 Tres Cantos, Spain, Email: jfernandez@gmv.com,
Interferometer Circuits. Professor David H. Staelin
 Interferometer Circuits Professor David H. Staelin Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lec18.5-1 Basic Aperture Synthesis Equation Recall: E( ) E r,t,t E E λ = λ { } Ι ( Ψ ) E R E τ φ τ Ψ,t,T E A Ψ 2
Interferometer Circuits Professor David H. Staelin Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lec18.5-1 Basic Aperture Synthesis Equation Recall: E( ) E r,t,t E E λ = λ { } Ι ( Ψ ) E R E τ φ τ Ψ,t,T E A Ψ 2
