Nutation determination by means of GNSS
|
|
|
- Randall Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nutation determination by means of GNSS - Comparison with VLBI Nicole Capitaine, Kunliang Yao SYRTE - Observatoire de Paris, CNRS/UPMC, France
2 Introduction Space geodetic techniques cannot be used for a direct determination of the celestial pole offsets due to their correlations with the orbital elements of the satellite the computation of which is affected by the deficiencies in the modeling of the satellite orbits. However, as shown by Rothacher et al. (1999), GPS can be used to estimate the nutation rates, similarly to what is done on a regular basis for LOD estimation; these authors computed a series of nutation rates covering 3.5 years, which was used for the estimation of the corrections to the IERS 1996 nutation model. However, nutation rate is not part of the IGS product and no other series of nutation rates have been provided since that time. The purpose of this study, done in the framework of Kunliang Yao's PhD (2013), is to investigate the potential of GNSS observations for nutation estimation with the high precision currently achieved by this technique. We aim at developping the best use of GPS observations, independently of VLBI, for determining the nutation of the Earth s axis with the best possible accuracy. 2
3 Orbital elements and Earth orientation parameters Geometical relationships The changes in the observed orbital elements of an artificial satellite corresponding to celestial pole offsets (i.e. corrections to the coordinates, X, Y of the CIP in the GCRS), and correction to the Earth Rotation Angle (ERA) at date t can be expressed (at the 1st order of the offsets and with Keplerian approximation) by the following relationships (Capitaine & Wallace, 2007): i = dx sin Ω + dy cos Ω Ω tan i = dx cos Ω dy sin Ω cos Ω i tan i d(era) u 0 sin I = dx sin Ω + dy cos Ω, Ω, i, are the right ascension of the ascending node and inclination of the orbital plane and u 0 is the argument of the latitude of the satellite at the osculating epoch; they are affected by systematic errors due to imperfect modeling. Nutation estimation from satellite observations absolute determination of the celestial pole offsets or ERA are not possible the rates in X, Y and ERA can be estimated provided that the orbital perturbations are modeled with sufficient accuracy over the time interval of the estimation IAU definitions (see GCRS: Geocentric celestial reference system; ITRS: International Terrestrial Reference System CIP: Celestial Intermediate Pole; TIRS: Terrestrial Intermediate reference system; CIO Celestial intermediate origin; TIO: Terrestrial intermediate origin; ERA: angle from the CIO to the TIO
4 Main characteristics of the study The method used is largely based on the GNSS observations analysis strategy of the CNES-GRGS GINS multi-technique software for orbit determination and Earth dynamics studies, but with the following specificities which take advantage of the GNSS potential for estimation of the EOPs (cf. previous slide): (i) determination of the time derivatives of the GCRS CIP coordinates (X, Y), and ERA, with high temporal resolution, along with x P, y P (pole coordinates), (ii) computation of the satellite orbit in a reference system that minimizes the influence of the a priori values for precession-nutation (i.e. X, Y) and UT1-UTC (i.e. ERA), that GPS cannot determine directly. The computations are carried out by means of a new software, developed by K. Yao in Matlab environment and implementing the specificities (i) and (ii). The observations used are 3 years of GPS measurements from 1 January 2009, obtained from a dense and globally distributed reference station network.
5 The new GPS analysis software Motivation (cf. specificities (i) and (ii) of the previous slide) To obtain long time series of time derivatives of the GCRS CIP coordinates (X, Y) and the ERA To minimize the effect (on the computations) of the a priori values for (X, Y) and ERA Advantages of Matlab environment Codes easy to understand; vectorial computation are easily programmed Many scientific algorithms functions available Science programming library in C/FORTRAN can be re-used (i.e. SOFA library) Built-in tools available for the visualization and the data analysis, graphical interface etc. Calculations largely based on the GPS analysis method of GINS (see Table 1 on next slide) GPS observations analyzed day by day Calculation part 1: Determination of the station clock biases using the GPS ionosphere-free combination, P c, of the pseudo-range observations Calculation part 2 (11 successive steps; see Figure 2): Estimation of the parameters based an iterative least squares adjustment using the GPS double-differenced ionosphere-free phase observations, DDL c 5
6 The main features of the GPS analysis software Main features Inertial reference system Analysis with GINS GCRS Analysis with the new software TIRS 0 (see the figure on the next slide) EOP estimation (xp, yp, xpdot, ypdot), LOD (xp, yp), ERAdot, (Xdot, Ydot) Observations Ambiguities Solar system ephemerides GPS iono-free range and phase Resolved by GINS/DYNAMO tools chains DE405 GPS iono-free range & double-differenced phase Estimated INPOP10 Earth s potential EIGEN-Gl04S EGM2008 Station positions Antenna models Solar radiation pressure Orbit integration Parameters estimation ITRF08 igs08.atx JPL SRP model 8-order Cowell s method iterative least squares adjustment Table 1: The main features of the new analysis software as compared to the GRGS-CNES GINS software 6
7 The inertial system for orbit computation The reference system TIRS 0 in which the satellite orbit computation is performed is: based on the Terrestrial Intermediate Reference System (TIRS): cf. Figure below, defined at date t 0 = 00h of the beginning epoch of the arc under analysis. Fig. 1: Schematic representation of the TIRS 0 reference system used for the orbit integration TIRS 0 is realized by the CIP axis and the origin O on the CIP equator (Note that the distance of O from the TIO is s, i.e. ~0) 7
8 Formula for the coordinate transformation to the Terrestrial intermediate system TIRS 0 Matrix transformation between GCRS and ITRS 0 This depends on the X, Y and ERA values at epoch t 0 (including the offsets w.r.t. the a priori values) Matrix transformation between ITRS and ITRS 0 This depends on the pole coordinates x p, y p and on the variations δx, δy and δera values from epoch t 0 This is nearly not sensitive to errors in the a priori values X 0, Y 0, and ERA 0 8
9 Estimation of the parameters Observations: GPS double-differenced ionosphere-free phase observations (m: epoch; a, b: stations; i, j: satellites) (D geo : geometric distance station-satellite; M: matrix transformation from ITRS to the inertial system) Steps: iteration For example: (X,Y) corrections < 2 μas Fig. 2: The successive steps of the new GPS analysis software for the estimation of the parameters 9
10 IAU 2000 semi-analytical model for the time derivative of the X, Y quantities sin. coef. cos. coef. Argument period (mas/d) (mas/d) l l' F D Ω (days) Table 2: Semi-analytical development of the time derivative of X corresponding to IAU 2000 nutation: largest terms
11 Test of the efficiency of the GPS analysis software for nutation rate estimation Data set: GPS data over 200 days from 01/01/2009 with ~115 IGS core stations, and ~32 satellites A priori values: IERS C04 polar motion and LOD; nutation rates equal to zero Results: estimated X, Y rates in very good agreement with the IAU 2000A nutation model Estimation errors: mostly within 0.1μas/s = 8.64 mas/day; will be reduced if better a priori values Xdot -----model estimated Ydot -----model estimated in uas/sec in uas/sec estimation error estimation error Fig. 3: The X, Y rates estimated from GPS observations using the new analysis software and the IAU 2000 nutation 1 point = 6 hours; interval 200 days 11
12 Computation of the time series of the parameters Validation of the computations: Evaluation of the observations fitting residuals (RMS ~ 8 mm) Comparison of the zenith tropospheric delay with the IGS product Evaluation of the 3D orbit difference in the ITRF w.r.t. the IGS final orbit (typically < 5 cm) Comparison of the polar coordinates to those obtained by GINS (typically < 50 µas)) Data set: GPS data from 2009 to 2011 (3 years; observation epochs) About 115 IGS core stations, and almost 32 satellites have been used A priori values Polar motion and LOD : IERS C04 Xdot, Ydot : IAU2006/2000A model Results 3-year time series of corrections (every 6 hours) δxdot, δydot: i.e. nutation rates 3-year time series of corrections to ERAdot (i.e. δlod) 3-year time series of polar motion corrections (i.e. dx p, dy p ) correlations bettween EOPs included between 0.02 and 0.23 (Xdot or Ydot and ERAdot) 12
13 Time series of nutation rate corrections δxdot estimation in uas/day δydot estimation in uas/day Fig. 4: Example of nutation rates corrections (dxdot, dydot) during the 100 days interval starting on 01/01/
14 Spectral analysis of the time series for nutation rate corrections in uas/day Fig. 5: Spectrum of 3-year time series for dxdot + idydot Periods in days 14
15 Nutation estimation from the Xdot and Ydot time series The 3-year ( ) time series (δxdot, δydot) are used as pseudo observations weighted LS harmonic adjustment of 28 circular nutation terms based on the equations enclosed in blue Amplitudes to estimate 15
16 GPS-estimated corrections to the IAU 2000A nutation Table 3: List of the corrections to the largest terms with periods shorter than 16 days 16
17 Comparison between the GPS and VLBI nutation estimations Corrections to IAU 2000 IITable 4: GPS estimations from time series ( ) of the corrections to the IAU 2006/2000 X and Y rates. VLBI estimations from time series ( ) of corrections to IAU 2006/2000 X, Y
18 Conclusions and perspectives GPS observations covering a 3-yr interval have been analyzed for estimating corrections to the short periodic terms of nutation. The computations have been carried out by means of a new GPS analysis software, developed by K. Yao in the framework of his PhD (2013) in Matlab environment. In this analysis, the satellite orbit has been integrated in an appropriate inertial system which reduces the influence of the error in the a priori values of the precession-nutation and ERA. This analysis has provided a 3-year time series of nutation rates corrections (dxdot, dydot) to IAU2006/2000A a priori values along with corrections to ERAdot and pole coordinates. The time series have been used to estimate corrections to the 28 largest nutation terms with period less than 20 days with an accuracy of about 10 μas. This study proves that the GNSS technique alone (i.e. without any use of VLBI estimates) has the potential to determine the short-period terms of nutation. The corrections obtained by GPS for the short periodic terms of nutation has been compared with those obtained by VLBI. The two set of corrections are of the same order of magnitude, but they are not perfectly consistent this discrerpancy requires further research. 18
ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS
 ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard Beutler Astronomical Institute, University of Berne CH-3012 Berne, Switzerland ABSTRACT Satellite space-geodetic measurements have been
ESTIMATION OF NUTATION TERMS USING GPS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard Beutler Astronomical Institute, University of Berne CH-3012 Berne, Switzerland ABSTRACT Satellite space-geodetic measurements have been
Evaluation of the accuracy of the IAU 2006/2000 precession-nutation
 Evaluation of the accuracy of the IAU 2006/2000 precession-nutation Nicole Capitaine (1), Sébastien Lambert (1), Kunliang Yao (1), Jia-cheng Liu (1)(2) (1) SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, France (2) Nanjing
Evaluation of the accuracy of the IAU 2006/2000 precession-nutation Nicole Capitaine (1), Sébastien Lambert (1), Kunliang Yao (1), Jia-cheng Liu (1)(2) (1) SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris, France (2) Nanjing
On the definition and use of the ecliptic in modern astronomy
 On the definition and use of the ecliptic in modern astronomy Nicole Capitaine (1), Michael Soffel (2) (1) : Observatoire de Paris / SYRTE (2) : Lohrmann Observatory, Dresden Technical University Introduction
On the definition and use of the ecliptic in modern astronomy Nicole Capitaine (1), Michael Soffel (2) (1) : Observatoire de Paris / SYRTE (2) : Lohrmann Observatory, Dresden Technical University Introduction
NGA GNSS Division Precise Ephemeris Parameters
 NGA GNSS Division Precise Ephemeris Parameters Precise Ephemeris Units. Earth-centered, Earth-fixed Coordinate system Position Velocity GPS time Trajectory interval Standard Trajectory Optional Trajectory
NGA GNSS Division Precise Ephemeris Parameters Precise Ephemeris Units. Earth-centered, Earth-fixed Coordinate system Position Velocity GPS time Trajectory interval Standard Trajectory Optional Trajectory
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry
 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME. Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON
 Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol.2, No.3 (139), 87-94, 2005 COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON Department of Galaxies
Acta Geodyn. Geomater., Vol.2, No.3 (139), 87-94, 2005 COMBINING GPS AND VLBI MEASUREMENTS OF CELESTIAL MOTION OF THE EARTH S SPIN AXIS AND UNIVERSAL TIME Jan VONDRÁK* and Cyril RON Department of Galaxies
IAU 2006 NFA GLOSSARY
 IAU 2006 NFA GLOSSARY Prepared by the IAU Division I Working Group Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy'' (latest revision: 20 November 2007) Those definitions corresponding to the IAU 2000 resolutions
IAU 2006 NFA GLOSSARY Prepared by the IAU Division I Working Group Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy'' (latest revision: 20 November 2007) Those definitions corresponding to the IAU 2000 resolutions
The VLBI contribution to precession (present and future)
 The VLBI contribution to precession (present and future) N.Capitaine (1) and P. Wallace (2) (1) Observatoire de Paris/Syrte (2) RAL, HMNAO Precession-nutation parameters Classical: equinox-based fixed
The VLBI contribution to precession (present and future) N.Capitaine (1) and P. Wallace (2) (1) Observatoire de Paris/Syrte (2) RAL, HMNAO Precession-nutation parameters Classical: equinox-based fixed
Introduction to geodetic VLBI
 Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Orbit Representation
 7.1 Fundamentals 223 For this purpose, code-pseudorange and carrier observations are made of all visible satellites at all monitor stations. The data are corrected for ionospheric and tropospheric delays,
7.1 Fundamentals 223 For this purpose, code-pseudorange and carrier observations are made of all visible satellites at all monitor stations. The data are corrected for ionospheric and tropospheric delays,
Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions. J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM
 Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM IERS Conventions update: electronic access http://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/listupdt.html Introduction Add a set of
Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM IERS Conventions update: electronic access http://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/listupdt.html Introduction Add a set of
Comparison between high precision precession models for the ecliptic and the equator
 A&A 421, 365 379 (2004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035942 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Comparison between high precision precession models for the ecliptic and the equator N. Capitaine 1,P.T.Wallace
A&A 421, 365 379 (2004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035942 c ESO 2004 Astronomy & Astrophysics Comparison between high precision precession models for the ecliptic and the equator N. Capitaine 1,P.T.Wallace
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry
 VieVS User-Workshop 2017 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm VLBI How does it work? VLBI a flowchart SINEX skd vex2 drudge drudge snp/prc snp/prc NGS Mark4 Mark4
VieVS User-Workshop 2017 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm VLBI How does it work? VLBI a flowchart SINEX skd vex2 drudge drudge snp/prc snp/prc NGS Mark4 Mark4
ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES, ASTROMETRIC TECHNIQUES AND CATALOGS
 1 ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES, ASTROMETRIC TECHNIQUES AND CATALOGS Jan Vondrák, Astronomical Institute Prague P PART 1: Reference systems and frames used in astronomy:! Historical outline,
1 ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES, ASTROMETRIC TECHNIQUES AND CATALOGS Jan Vondrák, Astronomical Institute Prague P PART 1: Reference systems and frames used in astronomy:! Historical outline,
Report of the IAU WORKING GROUP "Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy" (NFA)
 Report of the IAU WORKING GROUP "Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy" (NFA) Nicole Capitaine, Observatoire de Paris, France Membership Nicole CAPITAINE (Paris Observatory, France), Chair Catherine HOHENKERK
Report of the IAU WORKING GROUP "Nomenclature for Fundamental Astronomy" (NFA) Nicole Capitaine, Observatoire de Paris, France Membership Nicole CAPITAINE (Paris Observatory, France), Chair Catherine HOHENKERK
Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign
 Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign results from combined reprocessed IGS GPS orbits and EOPs assessment of IG1 orbit repeatability items to consider for next reprocessing Jake
Assessment of the orbits from the 1st IGS reprocessing campaign results from combined reprocessed IGS GPS orbits and EOPs assessment of IG1 orbit repeatability items to consider for next reprocessing Jake
Proposed terminology for Fundamental Astronomy based on IAU 2000 resolutions
 Proposed terminology for Fundamental Astronomy based on IAU 2000 resolutions N. Capitaine and A. H. Andrei, M. Calabretta, V. Dehant, T. Fukushima, B. Guinot, C. Hohenkerk, G. Kaplan, S. Klioner, J. Kovalevsky,
Proposed terminology for Fundamental Astronomy based on IAU 2000 resolutions N. Capitaine and A. H. Andrei, M. Calabretta, V. Dehant, T. Fukushima, B. Guinot, C. Hohenkerk, G. Kaplan, S. Klioner, J. Kovalevsky,
IGS POLAR MOTION MEASUREMENTS
 STATUS & PROSPECTS FOR IGS POLAR MOTION MEASUREMENTS Why does the IGS care about EOPs? observations, predictions, & IGS product table Recent pole & pole rate accuracies & error sources Rapid & Final products
STATUS & PROSPECTS FOR IGS POLAR MOTION MEASUREMENTS Why does the IGS care about EOPs? observations, predictions, & IGS product table Recent pole & pole rate accuracies & error sources Rapid & Final products
The 3D representation of the new transformation from the terrestrial to the celestial system.
 The 3D representation of the new transformation from the terrestrial to the celestial system. Véronique Dehant, Olivier de Viron Royal Observatory of Belgium Nicole Capitaine Observatoire de Paris, France
The 3D representation of the new transformation from the terrestrial to the celestial system. Véronique Dehant, Olivier de Viron Royal Observatory of Belgium Nicole Capitaine Observatoire de Paris, France
GGOS Bureau for Standards and Conventions
 GGOS D. Angermann (1), T. Gruber (2), J. Bouman (1), M. Gerstl (1), R. Heinkelmann (1), U. Hugentobler (2), L. Sánchez (1), P. Steigenberger (2) (1) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI), München
GGOS D. Angermann (1), T. Gruber (2), J. Bouman (1), M. Gerstl (1), R. Heinkelmann (1), U. Hugentobler (2), L. Sánchez (1), P. Steigenberger (2) (1) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI), München
Workshop on GNSS Data Application to Low Latitude Ionospheric Research May Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation
 2458-6 Workshop on GNSS Data Application to Low Latitude Ionospheric Research 6-17 May 2013 Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation HEGARTY Christopher The MITRE Corporation 202 Burlington Rd. / Rte 62 Bedford
2458-6 Workshop on GNSS Data Application to Low Latitude Ionospheric Research 6-17 May 2013 Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation HEGARTY Christopher The MITRE Corporation 202 Burlington Rd. / Rte 62 Bedford
Mutual comparison of the combinations of the Earth orientation parameters obtained by different techniques
 Mutual comparison of the combinations of the Earth orientation parameters obtained by different techniques C. Ron, J. Vondrák Astronomical Institute, Boční II 141, 141 31 Praha 4, Czech Republic Abstract.
Mutual comparison of the combinations of the Earth orientation parameters obtained by different techniques C. Ron, J. Vondrák Astronomical Institute, Boční II 141, 141 31 Praha 4, Czech Republic Abstract.
Common Realization of Terrestrial and Celestial Reference Frame
 Common Realization of Terrestrial and Celestial Reference Frame M. Seitz, R. Heinkelmann, P. Steigenberger, T. Artz Abstract The realization of the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) and the
Common Realization of Terrestrial and Celestial Reference Frame M. Seitz, R. Heinkelmann, P. Steigenberger, T. Artz Abstract The realization of the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) and the
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part II : ITRS & ETRS89 relationship
 The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part II : ITRS & ETRS89 relationship Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part II : ITRS & ETRS89 relationship Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière
High precision methods for locating the celestial intermediate pole and origin ABSTRACT
 A&A 45, 855 872 (26) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:25455 c ESO 26 Astronomy & Astrophysics High precision methods for locating the celestial intermediate pole and origin N. Capitaine 1 and P. T. Wallace 2 1 Observatoire
A&A 45, 855 872 (26) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:25455 c ESO 26 Astronomy & Astrophysics High precision methods for locating the celestial intermediate pole and origin N. Capitaine 1 and P. T. Wallace 2 1 Observatoire
Global reference systems and Earth rotation
 current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
current realizations and scientific problems Aleksander Brzeziński 1,2, Tomasz Liwosz 1, Jerzy Rogowski 1, Jan Kryński 3 1 Department of Geodesy and Geodetic Astronomy Warsaw University of Technology 2
THE FREE CORE NUTATION
 THE FREE CORE NUTATION D.D. MCCARTHY U. S. Naval Observatory Washington, DC 20392 USA e-mail: dmc@maia.usno.navy.mil ABSTRACT. The International Earth rotation and Reference system Service (IERS) provides
THE FREE CORE NUTATION D.D. MCCARTHY U. S. Naval Observatory Washington, DC 20392 USA e-mail: dmc@maia.usno.navy.mil ABSTRACT. The International Earth rotation and Reference system Service (IERS) provides
GRACE. Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment. JPL Level-2 Processing Standards Document. For Level-2 Product Release 05.1
 GRACE Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment JPL Level-2 Processing Standards Document For Level-2 Product Release 05.1 Michael M. Watkins and Dah-Ning Yuan Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute
GRACE Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment JPL Level-2 Processing Standards Document For Level-2 Product Release 05.1 Michael M. Watkins and Dah-Ning Yuan Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites
 13-01-08 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Christian Baumann (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
13-01-08 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Christian Baumann (1), Rolf Dach (1), Gerhard
GINS: a new tool for VLBI Geodesy and Astrometry
 GINS: a new tool for VLBI Geodesy and Astrometry G. Bourda, P. Charlot, R. Biancale 2 () Observatoire Aquitain des Sciences de l Univers - Université Bordeaux I Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux
GINS: a new tool for VLBI Geodesy and Astrometry G. Bourda, P. Charlot, R. Biancale 2 () Observatoire Aquitain des Sciences de l Univers - Université Bordeaux I Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux
IGS Reprocessing. and First Quality Assessment
 IGS Reprocessing Summary of Orbit/Clock Combination and First Quality Assessment Gerd Gendt, GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam Jake Griffiths, NOAA/National Geodetic Survey Thomas Nischan, GeoForschungsZentrum
IGS Reprocessing Summary of Orbit/Clock Combination and First Quality Assessment Gerd Gendt, GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam Jake Griffiths, NOAA/National Geodetic Survey Thomas Nischan, GeoForschungsZentrum
THE PERTURBATION OF THE ORBITAL ELEMENTS OF GPS AND Y-BIAS. GPS satellite and each arc of one to three days on top of the a priori radiation pressure
 THE PERTURATION OF THE ORITAL ELEMENTS OF GPS SATELLITES THROUGH DIRET RADIATION PRESSURE AND Y-IAS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard eutler, Leos Mervart Astronomical Institute, University of erne H-3 ern, Switzerland
THE PERTURATION OF THE ORITAL ELEMENTS OF GPS SATELLITES THROUGH DIRET RADIATION PRESSURE AND Y-IAS Markus Rothacher, Gerhard eutler, Leos Mervart Astronomical Institute, University of erne H-3 ern, Switzerland
Estimation of polar motion, polar motion rates, and GNSS orbits in the IGS
 Estimation of polar motion, polar motion rates, and GNSS orbits in the IGS G. Beutler, M. Meindl, S. Lutz, R. Dach, S. Scaramuzza, A. Sušnik, D. Arnold, A. Jäggi IGS Analysis Center Workshop Plenary #03
Estimation of polar motion, polar motion rates, and GNSS orbits in the IGS G. Beutler, M. Meindl, S. Lutz, R. Dach, S. Scaramuzza, A. Sušnik, D. Arnold, A. Jäggi IGS Analysis Center Workshop Plenary #03
DRAFT OF NOMENCLATURE & TERMINOLOGY FOR IAU WG 1
 s TIO terrestrial intermediate origin DRAFT OF NOMENCLATURE & TERMINOLOGY FOR IAU WG 1 This is not a complete list. Symbols are not, and need not necessarily be unique, eg φ is used for latitude, both
s TIO terrestrial intermediate origin DRAFT OF NOMENCLATURE & TERMINOLOGY FOR IAU WG 1 This is not a complete list. Symbols are not, and need not necessarily be unique, eg φ is used for latitude, both
ROCZNIK ASTRONOMICZNY (ASTRONOMICAL ALMANAC) OF THE INSTITUTE OF GEODESY AND CARTOGRAPHY AGAINST THE IAU 2000 RESOLUTIONS
 ROCZNIK ASTRONOMICZNY (ASTRONOMICAL ALMANAC) OF THE INSTITUTE OF GEODESY AND CARTOGRAPHY AGAINST THE IAU 2000 RESOLUTIONS M. SĘKOWSKI Institute of Geodesy and Cartography ul. Modzelewskiego 27, Warsaw,
ROCZNIK ASTRONOMICZNY (ASTRONOMICAL ALMANAC) OF THE INSTITUTE OF GEODESY AND CARTOGRAPHY AGAINST THE IAU 2000 RESOLUTIONS M. SĘKOWSKI Institute of Geodesy and Cartography ul. Modzelewskiego 27, Warsaw,
Toward a direct combination of space-geodetic techniques at the measurement level: Methodology and main issues
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004336, 2007 Toward a direct combination of space-geodetic techniques at the measurement level: Methodology and
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004336, 2007 Toward a direct combination of space-geodetic techniques at the measurement level: Methodology and
Week 02. Assist. Prof. Dr. Himmet KARAMAN
 Week 02 Assist. Prof. Dr. Himmet KARAMAN Contents Satellite Orbits Ephemerides GPS Review Accuracy & Usage Limitation Reference Systems GPS Services GPS Segments Satellite Positioning 2 Satellite Orbits
Week 02 Assist. Prof. Dr. Himmet KARAMAN Contents Satellite Orbits Ephemerides GPS Review Accuracy & Usage Limitation Reference Systems GPS Services GPS Segments Satellite Positioning 2 Satellite Orbits
Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques
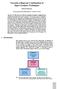 Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques Markus Rothacher Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodäsie, TU Munich, Germany Abstract: The with all its different components and products, ranging
Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques Markus Rothacher Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodäsie, TU Munich, Germany Abstract: The with all its different components and products, ranging
CALCULATION OF POSITION AND VELOCITY OF GLONASS SATELLITE BASED ON ANALYTICAL THEORY OF MOTION
 ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 50, No. 3 2015 DOI: 10.1515/arsa-2015-0008 CALCULATION OF POSITION AND VELOCITY OF GLONASS SATELLITE BASED ON ANALYTICAL THEORY OF MOTION W. Góral, B. Skorupa AGH University
ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 50, No. 3 2015 DOI: 10.1515/arsa-2015-0008 CALCULATION OF POSITION AND VELOCITY OF GLONASS SATELLITE BASED ON ANALYTICAL THEORY OF MOTION W. Góral, B. Skorupa AGH University
Improvement of the CNES/CLS IDS Analysis Center solution for the contribution to the next ITRF
 IDS Workshop Ponta Delgada, September 2018 Improvement of the CNES/CLS IDS Analysis Center solution for the contribution to the next ITRF Hugues Capdeville, Jean-Michel Lemoine CNES/CLS AC (GRG) Outline
IDS Workshop Ponta Delgada, September 2018 Improvement of the CNES/CLS IDS Analysis Center solution for the contribution to the next ITRF Hugues Capdeville, Jean-Michel Lemoine CNES/CLS AC (GRG) Outline
Astrodynamics (AERO0024)
 Astrodynamics (AERO0024) 3B. The Orbit in Space and Time Gaëtan Kerschen Space Structures & Systems Lab (S3L) Previous Lecture: The Orbit in Time 3.1 ORBITAL POSITION AS A FUNCTION OF TIME 3.1.1 Kepler
Astrodynamics (AERO0024) 3B. The Orbit in Space and Time Gaëtan Kerschen Space Structures & Systems Lab (S3L) Previous Lecture: The Orbit in Time 3.1 ORBITAL POSITION AS A FUNCTION OF TIME 3.1.1 Kepler
Recent and Anticipated Changes to the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) Conventions
 Recent and Anticipated Changes to the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) Conventions Brian Luzum, U.S. Naval Observatory BIOGRAPHY Brian Luzum began full-time employment
Recent and Anticipated Changes to the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) Conventions Brian Luzum, U.S. Naval Observatory BIOGRAPHY Brian Luzum began full-time employment
5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems
 No. 32 5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems The coordinate transformation to be used to transform from the terrestrial reference system (TRS) to the celestial reference system
No. 32 5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems The coordinate transformation to be used to transform from the terrestrial reference system (TRS) to the celestial reference system
Astrodynamics (AERO0024)
 Astrodynamics (AERO0024) 3. The Orbit in Space Gaëtan Kerschen Space Structures & Systems Lab (S3L) Motivation: Space We need means of describing orbits in three-dimensional space. Example: Earth s oblateness
Astrodynamics (AERO0024) 3. The Orbit in Space Gaëtan Kerschen Space Structures & Systems Lab (S3L) Motivation: Space We need means of describing orbits in three-dimensional space. Example: Earth s oblateness
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Mathematical models in GPS" Mathematical models used in GPS"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
Long-Term Evolution of High Earth Orbits: Effects of Direct Solar Radiation Pressure and Comparison of Trajectory Propagators
 Long-Term Evolution of High Earth Orbits: Effects of Direct Solar Radiation Pressure and Comparison of Trajectory Propagators by L. Anselmo and C. Pardini (Luciano.Anselmo@isti.cnr.it & Carmen.Pardini@isti.cnr.it)
Long-Term Evolution of High Earth Orbits: Effects of Direct Solar Radiation Pressure and Comparison of Trajectory Propagators by L. Anselmo and C. Pardini (Luciano.Anselmo@isti.cnr.it & Carmen.Pardini@isti.cnr.it)
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 14
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 14 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Propagation Medium Propagation: Signal propagation from satellite to receiver Light-time
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 14 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Propagation Medium Propagation: Signal propagation from satellite to receiver Light-time
Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
Test Computations
 158 7. Test Computations.3.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 2.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 2.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 3.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 3.2.1 -.1 -.2 -.3 Fourier index 4.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 4.2.1
158 7. Test Computations.3.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 2.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 2.2.1 -.1 -.2 Fourier index 3.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 3.2.1 -.1 -.2 -.3 Fourier index 4.8.4 -.4 -.8 Fourier index 4.2.1
Celestial Mechanics III. Time and reference frames Orbital elements Calculation of ephemerides Orbit determination
 Celestial Mechanics III Time and reference frames Orbital elements Calculation of ephemerides Orbit determination Orbital position versus time: The choice of units Gravitational constant: SI units ([m],[kg],[s])
Celestial Mechanics III Time and reference frames Orbital elements Calculation of ephemerides Orbit determination Orbital position versus time: The choice of units Gravitational constant: SI units ([m],[kg],[s])
Numerical evidence for the inconsistent separation of the ITRF-ICRF transformation into precession-nutation, diurnal rotation and polar motion
 Numerical evidence for the inconsistent separation of the ITRF-ICRF transformation into precession-nutation, diurnal rotation and polar motion Athanasios Dermanis and Dimitrios Tsoulis Aristotle University
Numerical evidence for the inconsistent separation of the ITRF-ICRF transformation into precession-nutation, diurnal rotation and polar motion Athanasios Dermanis and Dimitrios Tsoulis Aristotle University
Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
 Russian Academy of Sciences Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo IAU XXVIII General Assembly, Joint Discussion 7, Beijing, China, August 28, 2012 Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
Russian Academy of Sciences Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo IAU XXVIII General Assembly, Joint Discussion 7, Beijing, China, August 28, 2012 Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites
 Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Gerhard Beutler (1), Rolf Dach (1) (1) Astronomical Institute,
Earth gravity field recovery using GPS, GLONASS, and SLR satellites Krzysztof Sośnica (1), Adrian Jäggi (1), Daniela Thaller (2), Ulrich Meyer (1), Gerhard Beutler (1), Rolf Dach (1) (1) Astronomical Institute,
New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts
 Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2)
 Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2) S. Loyer (1), J.-M. Lemoine (2) and F. Perosanz (2) (1) Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France) (2) Centre National
Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2) S. Loyer (1), J.-M. Lemoine (2) and F. Perosanz (2) (1) Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France) (2) Centre National
GOCE High Level Processing Facility. GOCE Standards. Doc. No.: GO-TN-HPF-GS-0111 Issue: 4 Revision: 0 Date: 14 / 05 / 2014
 15.2014 1 of 81 GOCE High Level Processing Facility GOCE Standards Doc. No.: 4 Revision: 0 14 / 05 / 2014 Prepared by: The European GOCE Gravity Consortium EGG-C 1 15.2014 2 of 81 Document Information
15.2014 1 of 81 GOCE High Level Processing Facility GOCE Standards Doc. No.: 4 Revision: 0 14 / 05 / 2014 Prepared by: The European GOCE Gravity Consortium EGG-C 1 15.2014 2 of 81 Document Information
Space-Time Reference Systems
 Space-Time Reference Systems Bearbeitet von Michael Soffel, Ralf Langhans 1. Auflage 2012. Buch. xiv, 314 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 642 30225 1 Format (B x L): 15,5 x 23,5 cm Gewicht: 654 g Weitere Fachgebiete
Space-Time Reference Systems Bearbeitet von Michael Soffel, Ralf Langhans 1. Auflage 2012. Buch. xiv, 314 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 642 30225 1 Format (B x L): 15,5 x 23,5 cm Gewicht: 654 g Weitere Fachgebiete
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Seitz M., Steigenberger P., Artz T. (2xx) Consistent adjustment of combined terrestrial and celestial reference frames, Earth on the Edge: Science for a Sustainable Planet, IAG
Originally published as: Seitz M., Steigenberger P., Artz T. (2xx) Consistent adjustment of combined terrestrial and celestial reference frames, Earth on the Edge: Science for a Sustainable Planet, IAG
A new Solar Radiation Pressure Model for the GPS Satellites
 A new Solar Radiation Pressure Model for the GPS Satellites T.A. Springer, G. Beutler, M. Rothacher Astronomical Institute, University of Bern Sidlerstrasse 5, CH-32 Bern, Switzerland Abstract The largest
A new Solar Radiation Pressure Model for the GPS Satellites T.A. Springer, G. Beutler, M. Rothacher Astronomical Institute, University of Bern Sidlerstrasse 5, CH-32 Bern, Switzerland Abstract The largest
Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz
 GGOS and Reference Systems Introduction 2015-10-12 Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr 1 Course and exam Lecture Monday 14:00 16:00, A111 (ST01044)
GGOS and Reference Systems Introduction 2015-10-12 Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, NAWI Graz Technische Universität Graz Torsten Mayer-Gürr 1 Course and exam Lecture Monday 14:00 16:00, A111 (ST01044)
A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty. AVENUE project. June, 20
 Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
DETERMINATION OF THE STATION COORDINATES FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING DATA S.
 DETERMINATION OF THE STATION COORDINATES FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING DATA S. Schillak Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Astrogeodynamic Observatory, Borowiec
DETERMINATION OF THE STATION COORDINATES FOR QUALITY CONTROL OF THE SATELLITE LASER RANGING DATA S. Schillak Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Astrogeodynamic Observatory, Borowiec
Reference system and non-rotating origin: the NRO for the rest of us Olivier de Viron, Véronique Dehant, and Nicole Capitaine
 Reference system and non-rotating origin: the NRO for the rest of us Olivier de Viron, Véronique Dehant, and Nicole Capitaine Abstract The concept of Non Rotating Origin has been introduced in the method
Reference system and non-rotating origin: the NRO for the rest of us Olivier de Viron, Véronique Dehant, and Nicole Capitaine Abstract The concept of Non Rotating Origin has been introduced in the method
Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 12.540
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.540 Principles of Global Positioning Systems Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 12.540
MAE 180A: Spacecraft Guidance I, Summer 2009 Homework 2 Due Tuesday, July 14, in class.
 MAE 180A: Spacecraft Guidance I, Summer 2009 Homework 2 Due Tuesday, July 14, in class. Guidelines: Please turn in a neat and clean homework that gives all the formulae that you have used as well as details
MAE 180A: Spacecraft Guidance I, Summer 2009 Homework 2 Due Tuesday, July 14, in class. Guidelines: Please turn in a neat and clean homework that gives all the formulae that you have used as well as details
Impact of the SRP model on CODE's 5- system orbit and clock solution for the MGEX
 Impact of the SRP model on CODE's 5- system orbit and clock solution for the MGEX L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Switzerland
Impact of the SRP model on CODE's 5- system orbit and clock solution for the MGEX L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Switzerland
GNSS Estimates of Short-period Nutation
 GNSS Estimates of Short-period Nutation Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler Technische Universität München Daniela Thaller, Simon Lutz, Rolf Dach Astronomisches Institut, Universität Bern Sarah Böckmann
GNSS Estimates of Short-period Nutation Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler Technische Universität München Daniela Thaller, Simon Lutz, Rolf Dach Astronomisches Institut, Universität Bern Sarah Böckmann
GOCE High Level Processing Facility. GOCE Standards. Doc. No.: GO-TN-HPF-GS-0111 Issue: 3 Revision: 1 Date: 30 / 04 / 2009
 1 of 81 GOCE High Level Processing Facility GOCE Standards Doc. No.: 3 Revision: 1 30 / 04 / 2009 Prepared by: The European GOCE Gravity Consortium EGG-C 1 2 of 81 Document Information Sheet Document Name
1 of 81 GOCE High Level Processing Facility GOCE Standards Doc. No.: 3 Revision: 1 30 / 04 / 2009 Prepared by: The European GOCE Gravity Consortium EGG-C 1 2 of 81 Document Information Sheet Document Name
Challenges and perspectives for CRF and TRF determination
 Challenges and perspectives for CRF and TRF determination J. Böhm, Z. Malkin, S. Lambert, C. Ma with contributions by H. Spicakova, L. Plank, and H. Schuh Consistency TRF EOP CRF ITRF2008 from VLBI/GNSS/SLR/DORIS
Challenges and perspectives for CRF and TRF determination J. Böhm, Z. Malkin, S. Lambert, C. Ma with contributions by H. Spicakova, L. Plank, and H. Schuh Consistency TRF EOP CRF ITRF2008 from VLBI/GNSS/SLR/DORIS
A new Solar Radiation Pressure Model for the GPS Satellites
 A new Solar Radiation Pressure Model for the GPS Satellites T.A. Springer, G. Beutler, M. Rothacher Astronomical Institute, University of Bern Sidlerstrasse 5, CH-3012 Bern, Switzerland Abstract The largest
A new Solar Radiation Pressure Model for the GPS Satellites T.A. Springer, G. Beutler, M. Rothacher Astronomical Institute, University of Bern Sidlerstrasse 5, CH-3012 Bern, Switzerland Abstract The largest
DIVISION I WORKING GROUP on NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA)
 Transactions IAU, Volume XXVIB Proc. XXVIth IAU General Assembly, August 2006 K.A. van der Hucht, ed. c 2007 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X DIVISION I WORKING GROUP on
Transactions IAU, Volume XXVIB Proc. XXVIth IAU General Assembly, August 2006 K.A. van der Hucht, ed. c 2007 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X DIVISION I WORKING GROUP on
Consistent realization of Celestial and Terrestrial Reference Frames
 Journal of Geodesy manuscript - accepted version (minor errata corrected) The official publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1130-6 Consistent realization of Celestial
Journal of Geodesy manuscript - accepted version (minor errata corrected) The official publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1130-6 Consistent realization of Celestial
REPORT OF THE IAU DIVISION 1 WORKING GROUP ON NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA)
 REPORT OF THE IAU DIVISION 1 WORKING GROUP ON NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA) N. CAPITAINE, Observatoire de Paris, France and C. HOHENKERK, HMNAO, UK; A.H. ANDREI, Observatorio Nacional, Brazil;
REPORT OF THE IAU DIVISION 1 WORKING GROUP ON NOMENCLATURE FOR FUNDAMENTAL ASTRONOMY (NFA) N. CAPITAINE, Observatoire de Paris, France and C. HOHENKERK, HMNAO, UK; A.H. ANDREI, Observatorio Nacional, Brazil;
PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION OF GPS SATELLITES FOR REAL TIME APPLICATIONS
 J. Astron. Space Sci. 18(2), 129 136 (2001) GPS,,,, PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION OF GPS SATELLITES FOR REAL TIME APPLICATIONS Hyung-Chul Lim, Pil-Ho Park, Jong-Uk Park, Jung-Ho Cho, Yong-Won Ahn GPS Research
J. Astron. Space Sci. 18(2), 129 136 (2001) GPS,,,, PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION OF GPS SATELLITES FOR REAL TIME APPLICATIONS Hyung-Chul Lim, Pil-Ho Park, Jong-Uk Park, Jung-Ho Cho, Yong-Won Ahn GPS Research
The conversion of Universal Time to Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time is rigorously possible and is given by a series development with time defined by
 2.2 Time Systems 23 A = LAST - GAST = LMST -GMST. (2.5) LAST is detennined from astronomical observations to fixed stars and extragalactic radio sources. The mean sidereal time scale is still affected
2.2 Time Systems 23 A = LAST - GAST = LMST -GMST. (2.5) LAST is detennined from astronomical observations to fixed stars and extragalactic radio sources. The mean sidereal time scale is still affected
Time Systems. Ludwig Combrinck. Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory. AVN training 9 March 2017
 Time Systems Ludwig Combrinck Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory ludwig@hartrao.ac.za AVN training 9 March 2017 What is time? AVN Training March 2017 2 The Critique of Pure Reason, by Immanuel
Time Systems Ludwig Combrinck Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory ludwig@hartrao.ac.za AVN training 9 March 2017 What is time? AVN Training March 2017 2 The Critique of Pure Reason, by Immanuel
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study
 Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Module: 2
 Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Module: 2 Dinesh Manandhar Center for Spatial Information Science The University of Tokyo Contact Information: dinesh@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Slide :
Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Module: 2 Dinesh Manandhar Center for Spatial Information Science The University of Tokyo Contact Information: dinesh@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Slide :
Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications
 Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications Third Edition David A. Vallado with technical contributions by Wayne D. McClain Space Technology Library Published Jointly by Microcosm Press Hawthorne, CA
Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications Third Edition David A. Vallado with technical contributions by Wayne D. McClain Space Technology Library Published Jointly by Microcosm Press Hawthorne, CA
Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr
 Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, Graz University of Technology WG Theoretical Geodesy and Satellite Geodesy Geodetic Week 2015, Stuttgart, Germany Sebastian Strasser 16.09.2015
Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, Graz University of Technology WG Theoretical Geodesy and Satellite Geodesy Geodetic Week 2015, Stuttgart, Germany Sebastian Strasser 16.09.2015
GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell
 GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler, Ralf Schmid Technische Universität München (TUM) Uwe Hessels, Thomas Klügel Bundesamt für Kartographie
GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler, Ralf Schmid Technische Universität München (TUM) Uwe Hessels, Thomas Klügel Bundesamt für Kartographie
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
3.6 ITRS Combination Centres
 3 Reports of IERS components 3.6.1 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) In 2010, the focus of the ITRS Combination Centre at DGFI was on the finalization of the ITRS realization DTRF2008, internal
3 Reports of IERS components 3.6.1 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI) In 2010, the focus of the ITRS Combination Centre at DGFI was on the finalization of the ITRS realization DTRF2008, internal
Real-Time Estimation of GPS Satellite Clocks Based on Global NTRIP-Streams. André Hauschild
 Real-Time Estimation of GPS Satellite Clocks Based on Global NTRIP-Streams André Hauschild Agenda Motivation Overview of the real-time clock estimation system Assessment of clock product quality a) SISRE
Real-Time Estimation of GPS Satellite Clocks Based on Global NTRIP-Streams André Hauschild Agenda Motivation Overview of the real-time clock estimation system Assessment of clock product quality a) SISRE
Analysis Strategies And Software For Geodetic VLBI
 Analysis Strategies And Software For Geodetic VLBI Rüdiger Haas Presentation at the 7th EVN Symposium, Toledo, 2004 Outline: Observing stategies and observables Data analysis strategies Data analysis software
Analysis Strategies And Software For Geodetic VLBI Rüdiger Haas Presentation at the 7th EVN Symposium, Toledo, 2004 Outline: Observing stategies and observables Data analysis strategies Data analysis software
Application of the new concepts and definitions (ICRS, CIP and CEO) in fundamental astronomy. P. K. Seidelmann and J. Kovalevsky
 A&A 392, 341 351 (2002) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20020931 c ESO 2002 Astronomy & Astrophysics Application of the new concepts and definitions (ICRS, CIP and CEO) in fundamental astronomy P. K. Seidelmann
A&A 392, 341 351 (2002) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20020931 c ESO 2002 Astronomy & Astrophysics Application of the new concepts and definitions (ICRS, CIP and CEO) in fundamental astronomy P. K. Seidelmann
GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite Systems
 GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite Systems Global: today the American GPS (Global Positioning Service), http://gps.losangeles.af.mil/index.html the Russian GLONASS, http://www.glonass-center.ru/frame_e.html
GNSS: Global Navigation Satellite Systems Global: today the American GPS (Global Positioning Service), http://gps.losangeles.af.mil/index.html the Russian GLONASS, http://www.glonass-center.ru/frame_e.html
Sub-Daily Parameter Estimation in VLBI Data Analysis
 Dissertation Sub-Daily Parameter Estimation in VLBI Data Analysis Supervisors o.univ.-prof. Dipl.-Ing. Dr.techn. Harald Schuh Priv.-Doz. Dr.-Ing. Axel Nothnagel Examiners Prof. Dr. Hansjörg Kutterer Dr.
Dissertation Sub-Daily Parameter Estimation in VLBI Data Analysis Supervisors o.univ.-prof. Dipl.-Ing. Dr.techn. Harald Schuh Priv.-Doz. Dr.-Ing. Axel Nothnagel Examiners Prof. Dr. Hansjörg Kutterer Dr.
CODE's multi-gnss orbit and clock solution
 source: https://doi.org/10.7892/boris.68193 downloaded: 13.3.2017 CODE's multi-gnss orbit and clock solution L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute,
source: https://doi.org/10.7892/boris.68193 downloaded: 13.3.2017 CODE's multi-gnss orbit and clock solution L. Prange, E. Orliac, R. Dach, D. Arnold, G. Beutler, S. Schaer, A. Jäggi Astronomical Institute,
Introduction to geodetic VLBI and VieVS software
 Introduction to geodetic VLBI and VieVS software Hana Krásná and colleagues April 15, 2014 Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory, South Africa Introduction to geodetic VLBI Introduction to VieVS Our
Introduction to geodetic VLBI and VieVS software Hana Krásná and colleagues April 15, 2014 Hartebeesthoek Radio Astronomy Observatory, South Africa Introduction to geodetic VLBI Introduction to VieVS Our
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Expressions for IAU 2000 precession quantities. N. Capitaine 1,P.T.Wallace 2, and J. Chapront 1. 1.
 A&A 42, 567 586 (2003) DOI: 0.05/0004-636:2003539 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Expressions for IAU 2000 precession quantities N. Capitaine,P.T.Wallace 2, and J. Chapront Observatoire de Paris, SYRTE/UMR8630-CNRS,
A&A 42, 567 586 (2003) DOI: 0.05/0004-636:2003539 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics Expressions for IAU 2000 precession quantities N. Capitaine,P.T.Wallace 2, and J. Chapront Observatoire de Paris, SYRTE/UMR8630-CNRS,
SOFA Tools for Earth Attitude
 International Astronomical Union Standards Of Fundamental Astronomy SOFA Tools for Earth Attitude Software version 13 Document revision 1.6 Version for C programming language http://www.iausofa.org 2017
International Astronomical Union Standards Of Fundamental Astronomy SOFA Tools for Earth Attitude Software version 13 Document revision 1.6 Version for C programming language http://www.iausofa.org 2017
ESA/ESOC Status. T. Springer, E. Schoenmann, W. Enderle. ESA/ESOC Navigation Support Office. ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use
 ESA/ESOC Status T. Springer, E. Schoenmann, W. Enderle ESA/ESOC Navigation Support Office ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Content Issues in BIAS PP Status regarding future ILRS plans Other ILRS/SLR
ESA/ESOC Status T. Springer, E. Schoenmann, W. Enderle ESA/ESOC Navigation Support Office ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Content Issues in BIAS PP Status regarding future ILRS plans Other ILRS/SLR
Orbit Determination Using Satellite-to-Satellite Tracking Data
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 1, No. 3, (2001 281 286 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Orbit Determination Using Satellite-to-Satellite
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 1, No. 3, (2001 281 286 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Orbit Determination Using Satellite-to-Satellite
RELATIVISTIC ASPECTS IN ASTRONOMICAL STANDARDS AND THE IERS CONVENTIONS
 RELATIVISTIC ASPECTS IN ASTRONOMICAL STANDARDS AND THE IERS CONVENTIONS G. PETIT Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 92312 Sèvres France e-mail: gpetit@bipm.org ABSTRACT. In the last years, the definition
RELATIVISTIC ASPECTS IN ASTRONOMICAL STANDARDS AND THE IERS CONVENTIONS G. PETIT Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 92312 Sèvres France e-mail: gpetit@bipm.org ABSTRACT. In the last years, the definition
Earth-Centered, Earth-Fixed Coordinate System
 Fundamentals of Global Positioning System Receivers: A Software Approach James Bao-Yen Tsui Copyright 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-38154-3 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20054-9 CHAPTER FOUR Earth-Centered,
Fundamentals of Global Positioning System Receivers: A Software Approach James Bao-Yen Tsui Copyright 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-38154-3 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20054-9 CHAPTER FOUR Earth-Centered,
Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks
 Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks Jan Vondrák and Cyril Ron, Astronomical Inst., Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague Contents: Introduction; Description
Earth orientation parameters: excitation by atmosphere, oceans and geomagnetic jerks Jan Vondrák and Cyril Ron, Astronomical Inst., Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague Contents: Introduction; Description
Astrometric Interferometry. P. Charlot Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux
 Astrometric Interferometry P. Charlot Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux Outline VLBI observables for astrometry VLBI modeling Reference frames and surveys (ICRF, VCS) Organisation for data acquisition
Astrometric Interferometry P. Charlot Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux Outline VLBI observables for astrometry VLBI modeling Reference frames and surveys (ICRF, VCS) Organisation for data acquisition
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 04"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 04" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Review" So far we have looked at measuring
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 04" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Review" So far we have looked at measuring
