Tidal gravity measurements in Southeast Asia revisited.
|
|
|
- Elijah Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tidal gravity measurements in Southeast Asia revisited. Olivier Francis and Tonie van Dam Geophysics Laboratory Faculty of Science, Technology and Communication University of Luxembourg Luxembourg Abstract. In the region of Southeast Asia, there is an overall disagreement between tidal gravity observations and the tidal predictions. The predictions are based on a theoretical tidal model that calculates oceanic loading and attraction effects based on existing global ocean tides models. The loading and mass attraction effects for the M 2 tidal wave are calculated here using two recent ocean tide models. We demonstrate that the higher spatial resolution and precision of the new models still do not resolve the discrepancies between observations and predictions in this region. Introduction Almost 20 years ago, Melchior et al. (1996) reported observing large tidal residuals for the principal semi-diurnal, M2, tides in the Southeast Asia. The authors compared the observed tidal factors from 17 temporary tidal gravity stations with modeled body and ocean loading tides. In that study, the team carefully checked the calibration of the gravimeters, and rejected tidal stations for which the calibration could not be verified. Using the Schwiderski oceanic co-tidal map, Melchior et al. (1996) found that the tidal loading and direct attraction were modeled with a precision of only 2.5 microgals. This result was intriguing as one could do at least five times better anywhere else on the globe. Two explanations were put forward for the disagreement between the observations and predictions. First, a defect in the oceanic co-tidal maps could be the result of a complicated tidal regime in the adjacent seas: South China Sea, Java Sea, Arafura Sea and Coral Sea. For example, no less than ten amphidromic points are known to exist in the nearby China and Yellow seas. A second explanation for the discrepancy was the influence of a large geoid low that could induce a regional anomaly in the Earth tide deformation. To investigate the effects of the complicated tidal regime and the geoid anomaly, Melchior et al. (1996) used the newly available co-tidal maps from Grenoble, FES952, hoping to improve the agreement between the observation and the modeled ocean loading and attraction. However, the discrepancy still existed. At that time, the authors were unable to find a firm and definitive answer to the cause of the discrepancies between the observed and modeled Earth tides in this region. In this paper, we reinvestigate the discrepancy between tidal observations and predictions in Southeast Asia. New oceanic co-tidal models with greater spatial
2 resolution and precision, as compared to FES952, are available today. We restricted our analysis to the M 2 tides only. Recent Ocean Tidal Models Recently, two new global ocean tides models are available to the scientific community. The first, a new FES model FES2012 that represents an improvement over FES2004 (Lyard et al, 2006), and is widely used in satellite altimetry. FES2012 provides estimates of 33 tidal waves (instead of 15 for FES2004) with an unprecedented resolution of 1/16 x 1/16 degree. The second model is the last born from the EOT family EOT11a (Savcenko and Bosch, 2008). It contains 14 tidal waves and a resolution of 1/8 x 1/8 degree. The increased spatial resolution and the expected higher precision of these models gave us hope that the new models would resolve the discrepancy between the observed and modeled Earth tides described in the paper of Melchior et al. (1996) once for all. Oceanic Loading and Attraction Effects. The observed tidal parameters were taken from the paper of Melchior et al. (1996). An elastic ocean-less Earth model response was subtracted from these parameters. The differences should represent the oceanic attraction and loading effects at the stations. Using the notation from Melchior s (1983) in which a graphical representation can be found: the vector A(A,α) is the observed tidal response and the vector R (R,0) is the elastic oceanless Earth model response (calculated). Then we can calculate: 1. B(B, β) = A-R; L(L,λ) the oceanic attraction and loading vector (calculated with an ocean tides model); 2. X(X,χ) = B L = A R L the final residual vector. In Table 1, the vector B is given for all the stations along with the oceanic and loading vector computed for the Schwiderski model, the standard ocean tide model for many decades, and the two new models FES2012 and ETO11a. We immediately notice that two new models give similar results that are only slightly different from Scwhiderski. However, the new models do not reduce significantly the final residual vector X (Table 2) as compared to Schwiderski. In fact, the new models are not better at all on average. In Table 3, we calculate the difference between the final residuals obtained with the three ocean tide models. The residuals of the two new models differ by only 0.1+/- 0.1 microgal on average, and give almost identical results. The differences with the results based on the Schwiderski model are larger: 0.75+/-0.45 microgal. Despite the smaller residuals of the new models as compared with Schwiderski, the new models did not improve the agreement between the observed and predicted M 2 tidal loading and attraction effects in Southeast Asia. Conclusion.
3 The calculation of the loading and attraction effects of the M2 tide in the Southeast Asia using new ocean tides models does not improve the discrepancy between observations and predictions there. Despite the higher spatial resolution and precision of the new models, there is no reduction in the final residuals. Moreover, the two models give the same results. It is clear that the solutions of the global models are converging for the region of Southeast Asia. However, it appears that defects in the ocean tidal models are no longer a candidate for explaining the discrepancy between observed and predicted gravity tides in the Southeast Asia. A systematic calibration error, although highly improbable, could be verified by installing a few new tidal stations equipped with well-calibrated superconducting gravimeters. If these future observations confirm the anomaly, then the role that the geoid anomaly is playing in the discrepancy might be elucidated. In conclusion, despite our efforts to improve the loading calculation in the Southeast Asia, the mystery behind the discrepancy remains unsolved. We would like to dedicate this short paper to the late Prof. Paul Melchior who maintained a long and sincere friendship with Prof. Houze Hsu. References Lyard F., F. Lefevre, T. Letellier and O. Francis, Modelling the global ocean tides: modern insights from FES2004, Ocean Dynamics, DOI /s x, Melchior P., The Tides of the Planet Earth, Oxford, Pergamon, Melchior P., Francis O. and Ducarme B., Tidal Gravity Measurements in Southeast Asia, Bulletin d Informations des Marées Terrestres, 125, , Savcenko R. and W. Bosch, EOT08a empirical ocean tide model from multimission altimetry, DGFI Report N 81, 2008.
4 Table 1. Coordinates of each tidal gravity station in the Southeast Asia. The M 2 observed residuals vector B is compared to the oceanic attraction and loading computed with the Schwiderski, FES2013 and EOT11a ocean tide models, respectively. The amplitudes are given in microgal and the phases in degree. Observed SCHWIDERSKI FES2012 EOT11a NUM STATION LONG LAT D B β L λ L λ L λ 2460 COLOMBO 79,87 6,90 3 4, , , , CHIANG MAI 98,98 18, , , , , BANGKOK LATPRAO 100,60 13, , , , , PENANG 100,30 5,36 1 2, , , , KUALA LUMPUR 101,65 3, , , , , SAIGON 106,70 10, , , , , BANDUNG JAVA 107,63-6, , , , , DARWIN/MANTON DAM 131,13-12, , , , , BAGUIO 120,58 16, , , , , MANILA OBSERV. 121,07 14, , , , , K.KINABALU SABAH 116,07 5,95 2 1, , , , BANJAR BAR KALIM. 114,78-3, ,79-7 1, , , MANADO SULAW. 124,83 1,45 4 5,39-7 3,08 0 4,33 3 4, JAYAPURA IRIAN JAYA 140,67-2,50 5 3, , , , UJUNG PANDANG SULAW. 119,63-5, , , , , KUPANG TIMOR 123,57-10,20 1 5, , , , PORT MORESBY 147,15-9,41 5 4,92-6 1, , , D= distance to the sea in km
5 Table 2. Final residues for the M 2 tidal waves for the difference ocean tide models. The amplitudes are given in microgal and the phases in degree. Schwiderski map FES2012 map EOT11a map NUM STATION X χ X χ X χ 2460 COLOMBO 2, , , CHIANG MAI 0, , , BANGKOK LATPRAO 1, , , PENANG 1, , , KUALA LUMPUR 1, , , SAIGON 1, , , BANDUNG JAVA 2, , , DARWIN/MANTON DAM 1, , , BAGUIO 1, , , MANILA OBSERV. 1, , , K.KINABALU SABAH 1, , , BANJAR BAR KALIM. 0, , , MANADO SULAW. 2, , , JAYAPURA IRIAN JAYA 2, , , UJUNG PANDANG SULAW. 3, , , KUPANG TIMOR 1,19-8 2, , PORT MORESBY 5, , ,04 16 Average Std Dev
6 Table 3. Differences between the calculated loading and attraction effect s for the M 2 tidal waves for the difference ocean tide models. The amplitudes are given in microgal and the phases in degree. X(FES2012) X(SCHWI) X(FES2012) X(ETO11a) NUM STATION Amplitude/microgal Phase/Degree Amplitude/microgal Phase/Degree 2460 COLOMBO 0, , CHIANG MAI 0, , BANGKOK LATPRAO 0, , PENANG 0, , KUALA LUMPUR 1, , SAIGON 0, , BANDUNG JAVA 0, , DARWIN/MANTON DAM 1, , BAGUIO 0, , MANILA OBSERV. 0, , K.KINABALU SABAH 0, , BANJAR BAR KALIM. 0, , MANADO SULAW. 1, , JAYAPURA IRIAN JAYA 1, , UJUNG PANDANG SULAW. 0, , KUPANG TIMOR 1, , PORT MORESBY 0, , Mean Std Dev
ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS
 ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS AT THE CONRAD OBSERVATORIUM IN AUSTRIA IN JUNE 2012 Final Report August 2012 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication
ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS AT THE CONRAD OBSERVATORIUM IN AUSTRIA IN JUNE 2012 Final Report August 2012 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication
Intermediary Report - August Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis and Prof. Dr. Tonie Van Dam
 ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN YELLOWSTONE IN SEPTEMBER 2009 Intermediary Report - August 2010 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis and Prof. Dr. Tonie Van Dam University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology
ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN YELLOWSTONE IN SEPTEMBER 2009 Intermediary Report - August 2010 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis and Prof. Dr. Tonie Van Dam University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology
Final Report. January Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis
 ABSOLUTE AND RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN NUUK (GREENLAND) IN JULY 2005 Final Report January 2006 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication
ABSOLUTE AND RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN NUUK (GREENLAND) IN JULY 2005 Final Report January 2006 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication
Earth s free core nutation determined using C032 superconducting gravimeter at station Wuhan/China
 Journal of Geodynamics 38 (2004) 451 460 Earth s free core nutation determined using C032 superconducting gravimeter at station Wuhan/China He-Ping Sun a,, Gerhard Jentzsch b, Jian-Qiao Xu a, Hou-Ze Hsu
Journal of Geodynamics 38 (2004) 451 460 Earth s free core nutation determined using C032 superconducting gravimeter at station Wuhan/China He-Ping Sun a,, Gerhard Jentzsch b, Jian-Qiao Xu a, Hou-Ze Hsu
Absolute and Relative Gravity Measurements at the Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM) of Turin (Italy) in June 2006
 Absolute and Relative Gravity Measurements at the Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM) of Turin (Italy) in June 2006 Final Report September 2006 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg
Absolute and Relative Gravity Measurements at the Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM) of Turin (Italy) in June 2006 Final Report September 2006 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg
1. Introduction. 2. The astronomical tides
 Comparison of some tidal prediction programs and accuracy assessment of tidal gravity predictions B. Ducarme Research Associate NFSR, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Av. Circulaire 3, B-1180Brussels, Belgium
Comparison of some tidal prediction programs and accuracy assessment of tidal gravity predictions B. Ducarme Research Associate NFSR, Royal Observatory of Belgium, Av. Circulaire 3, B-1180Brussels, Belgium
Gravimetric Tide observation at Lake Nasser Region, Aswan, Egypt
 Gravimetric Tide observation at Lake Nasser Region, Aswan, Egypt R.M. Hassan, E.M. Abdelrahman, A. Tealeb, K.H. Zahran and G. Jentzsch ABSTRACT The LaCoste and Romberg gravimeter D-218 of the National
Gravimetric Tide observation at Lake Nasser Region, Aswan, Egypt R.M. Hassan, E.M. Abdelrahman, A. Tealeb, K.H. Zahran and G. Jentzsch ABSTRACT The LaCoste and Romberg gravimeter D-218 of the National
ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN LOMONOSOV, SAINT-PETERSBURG, RUSSIA
 ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN LOMONOSOV, SAINT-PETERSBURG, RUSSIA FINAL REPORT NOVEMBER 2004 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication Campus
ABSOLUTE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN LOMONOSOV, SAINT-PETERSBURG, RUSSIA FINAL REPORT NOVEMBER 2004 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication Campus
Experimental earth tidal models in considering nearly diurnal free wobble of the Earth s liquid core
 Chinese Science Bulletin 2003 Vol. 48 No. 9 935 940 Experimental earth tidal models in considering nearly diurnal free wobble of the Earth s liquid core SUN Heping 1, XU Jianqiao 1 & B. Ducarme 2 1. Key
Chinese Science Bulletin 2003 Vol. 48 No. 9 935 940 Experimental earth tidal models in considering nearly diurnal free wobble of the Earth s liquid core SUN Heping 1, XU Jianqiao 1 & B. Ducarme 2 1. Key
Cotidal Charts near Hawaii Derived from TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry Data
 606 J O U R N A L O F A T M O S P H E R I C A N D O C E A N I C T E C H N O L O G Y VOLUME 28 Cotidal Charts near Hawaii Derived from TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry Data LI-LI FAN, BIN WANG, AND XIAN-QING LV
606 J O U R N A L O F A T M O S P H E R I C A N D O C E A N I C T E C H N O L O G Y VOLUME 28 Cotidal Charts near Hawaii Derived from TOPEX/Poseidon Altimetry Data LI-LI FAN, BIN WANG, AND XIAN-QING LV
Characteristics of tidal gravity changes in Lhasa, Tibet, China
 Article Geophysics July 2012 Vol.57 No.20: 2586 2594 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5130-2 SPECIAL TOPICS: Characteristics of tidal gravity changes in Lhasa, Tibet, China XU JianQiao *, CHEN XiaoDong, ZHOU JiangCun
Article Geophysics July 2012 Vol.57 No.20: 2586 2594 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5130-2 SPECIAL TOPICS: Characteristics of tidal gravity changes in Lhasa, Tibet, China XU JianQiao *, CHEN XiaoDong, ZHOU JiangCun
Shuzo Takemoto*, Yoichi Fukuda*, Toshihiro Higashi*, Maiko Abe*, Shihori Ogasawara*, Sjafra Dwipa**, Dendi Surya Kusuma** & Achmad Andan**
 1 of 10 2/22/2011 9:32 AM Shuzo Takemoto*, Yoichi Fukuda*, Toshihiro Higashi*, Maiko Abe*, Shihori Ogasawara*, Sjafra Dwipa**, Dendi Surya Kusuma** & Achmad Andan** * Department of Geophysics, Graduate
1 of 10 2/22/2011 9:32 AM Shuzo Takemoto*, Yoichi Fukuda*, Toshihiro Higashi*, Maiko Abe*, Shihori Ogasawara*, Sjafra Dwipa**, Dendi Surya Kusuma** & Achmad Andan** * Department of Geophysics, Graduate
Gravity Monitoring with a Superconducting Gravimeter in Vienna
 1 of 10 2/18/2011 3:30 PM Gravity Monitoring with a Superconducting Gravimeter in Vienna Bruno Meurers Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Vienna Central Institute of Meteorology and
1 of 10 2/18/2011 3:30 PM Gravity Monitoring with a Superconducting Gravimeter in Vienna Bruno Meurers Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics, University of Vienna Central Institute of Meteorology and
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission
 Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS
 RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN ILULISSAT IN JULY 2013 Final Report June 2015 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication Campus Kirchberg 6, rue
RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN ILULISSAT IN JULY 2013 Final Report June 2015 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication Campus Kirchberg 6, rue
Total gravitational field is sum of contributions from all masses.
 Gravity force (acceleration) vs potential (energy) acceleration (g) => GM/r 2 Potential => - GM/r G is Newton s gravitational constant 6.67x10-11 (S.I. units) you should determine what the S.I. units are
Gravity force (acceleration) vs potential (energy) acceleration (g) => GM/r 2 Potential => - GM/r G is Newton s gravitational constant 6.67x10-11 (S.I. units) you should determine what the S.I. units are
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations. Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis
 Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Contribution of non-tidal oceanic mass variations to Earth rotation determined from space geodesy and ocean data
 Earth FOR584 rotation Earth and rotation global and dynamic global processes dynamic processes Contribution of non-tidal oceanic mass variations to Earth rotation determined from space geodesy and ocean
Earth FOR584 rotation Earth and rotation global and dynamic global processes dynamic processes Contribution of non-tidal oceanic mass variations to Earth rotation determined from space geodesy and ocean
Search for the Gravitational Absorption Effect Using Spring and Super-conducting Gravimeters during the Total Solar Eclipse of August 11, 1999
 Bulletin d Information de Marees Terrestres (BIM) 138 (2003) 10967 http://www.astro.oma.be/icet/bim/bim138/vanruymbeke2.htm Search for the Gravitational Absorption Effect Using Spring and Super-conducting
Bulletin d Information de Marees Terrestres (BIM) 138 (2003) 10967 http://www.astro.oma.be/icet/bim/bim138/vanruymbeke2.htm Search for the Gravitational Absorption Effect Using Spring and Super-conducting
Call for space geodetic solutions corrected for non-tidal atmospheric loading (NT-ATML) at the observation level
 Call for space geodetic solutions corrected for non-tidal atmospheric loading (NT-ATML) at the observation level Xavier Collilieux, Tonie van Dam, Zuheir Altamimi Outline: Context Why correcting for non-tidal
Call for space geodetic solutions corrected for non-tidal atmospheric loading (NT-ATML) at the observation level Xavier Collilieux, Tonie van Dam, Zuheir Altamimi Outline: Context Why correcting for non-tidal
DERIVATION OF SEA LEVEL ANOMALY USING SATELLITE ALTIMETER. Ami Hassan Md Din, Kamaludin Mohd Omar
 DERIVATION OF SEA LEVEL ANOMALY USING SATELLITE ALTIMETER Ami Hassan Md Din, Kamaludin Mohd Omar Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Skudai, Johor E-mail: amihassan@utm.my
DERIVATION OF SEA LEVEL ANOMALY USING SATELLITE ALTIMETER Ami Hassan Md Din, Kamaludin Mohd Omar Faculty of Geoinformation Science and Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Skudai, Johor E-mail: amihassan@utm.my
Rigorous Combination of Superconducting and Absolute Gravity Measurements with Respect to Instrumental Properties
 Rigorous Combination of Superconducting and Absolute Gravity Measurements with Respect to Instrumental Properties H. Wziontek, R. Falk, H. Wilmes, P. Wolf Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie (BKG),
Rigorous Combination of Superconducting and Absolute Gravity Measurements with Respect to Instrumental Properties H. Wziontek, R. Falk, H. Wilmes, P. Wolf Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie (BKG),
Tides Supplement. Brian Arbic
 Tides Supplement Brian Arbic OVERVIEW QUESTIONS What causes the tides? How is a lunar day different from a solar day? Which body creates a larger tidal influence on Earth: the Moon or the Sun? How do the
Tides Supplement Brian Arbic OVERVIEW QUESTIONS What causes the tides? How is a lunar day different from a solar day? Which body creates a larger tidal influence on Earth: the Moon or the Sun? How do the
RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS
 RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN KELLYVILLE AND KANGERLUSSUAQ IN JULY 2013 Final Report June 2015 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication Campus
RELATIVE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN KELLYVILLE AND KANGERLUSSUAQ IN JULY 2013 Final Report June 2015 Prof. Dr. Olivier Francis University of Luxembourg Faculty of Sciences, Technology and Communication Campus
ONE YEAR WITH OUR ABSOLUTE GRAVIMETER
 ONE YEAR WITH OUR ABSOLUTE GRAVIMETER Mikael Lilje, Jonas Ågren, Andreas Engfeldt, Per-Anders Olsson Lantmäteriet, Sweden Introduction In Sweden, a new generation of reference systems has been introduced.
ONE YEAR WITH OUR ABSOLUTE GRAVIMETER Mikael Lilje, Jonas Ågren, Andreas Engfeldt, Per-Anders Olsson Lantmäteriet, Sweden Introduction In Sweden, a new generation of reference systems has been introduced.
Advances in Ground-based Gravity for Hydrologic Studies
 Advances in Ground-based Gravity for Hydrologic Studies L. Longuevergne (1,2), C.R. Wilson 1, B.R. Scanlon 2 1 Department of Geological Sciences, UT Austin 2 Bureau of Economic Geology, UT Austin What
Advances in Ground-based Gravity for Hydrologic Studies L. Longuevergne (1,2), C.R. Wilson 1, B.R. Scanlon 2 1 Department of Geological Sciences, UT Austin 2 Bureau of Economic Geology, UT Austin What
Application of Satellite Laser Ranging for Long- Wavelength Gravity Field Determination
 Application of Satellite Laser Ranging for Long- Wavelength Gravity Field Determination J. C. Ries Center for Space Research The University of Texas at Austin Low Degree Gravity Variations from SLR GRACE
Application of Satellite Laser Ranging for Long- Wavelength Gravity Field Determination J. C. Ries Center for Space Research The University of Texas at Austin Low Degree Gravity Variations from SLR GRACE
A new ocean tide loading model in the Canary Islands region
 Journal of Geodynamics 41 (2006) 100 111 A new ocean tide loading model in the Canary Islands region J. Arnoso a,, M. Benavent a, B. Ducarme b, F.G. Montesinos a a Instituto de Astronomía y Geodesia (CSIC-UCM),
Journal of Geodynamics 41 (2006) 100 111 A new ocean tide loading model in the Canary Islands region J. Arnoso a,, M. Benavent a, B. Ducarme b, F.G. Montesinos a a Instituto de Astronomía y Geodesia (CSIC-UCM),
2. THE TIDAL POTENTIAL AND TIDE GENERATED DISPLACEMENTS. The reference system: the vertical axis points to the centre of the Earth
 1 of 10 2/22/2011 9:21 AM Varga P., Mentes Gy. & Eperne Papai I. GEODETIC AND GEOPHYSICAL RESEARH INSTITUTE OF THE HUNGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Sopron, Csatkai Endre u. 6-8,H-9400, Hungary. E-mail:varga@seismology.hu
1 of 10 2/22/2011 9:21 AM Varga P., Mentes Gy. & Eperne Papai I. GEODETIC AND GEOPHYSICAL RESEARH INSTITUTE OF THE HUNGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Sopron, Csatkai Endre u. 6-8,H-9400, Hungary. E-mail:varga@seismology.hu
Introduction to the use of gravity measurements in Ge111A
 Introduction to the use of gravity measurements in Ge111A Background & basic intuition Data reduction Use of the instrument See Reynolds for detailed quantitative discussion What and Why Gravity measures
Introduction to the use of gravity measurements in Ge111A Background & basic intuition Data reduction Use of the instrument See Reynolds for detailed quantitative discussion What and Why Gravity measures
To the best of our knowledge, the FG5 gravimeter represents the current state-of-the-art in the measurement of absolute gravity.
 FG5 gravity meter To the best of our knowledge, the FG5 gravimeter represents the current state-of-the-art in the measurement of absolute gravity. American Geophysical Union, EOS Journal Since its introduction
FG5 gravity meter To the best of our knowledge, the FG5 gravimeter represents the current state-of-the-art in the measurement of absolute gravity. American Geophysical Union, EOS Journal Since its introduction
2.2 Gravity surveys. Gravity survey
 2.2 Gravity surveys Gravity survey The effect of latitude The effect of elevation The Bouguer effect Topographic effect The effect of tides Summary of corrections Gravity in boreholes Gravity survey In
2.2 Gravity surveys Gravity survey The effect of latitude The effect of elevation The Bouguer effect Topographic effect The effect of tides Summary of corrections Gravity in boreholes Gravity survey In
Comparison of Sea Surface Heights Observed by TOPEX Altimeter with Sea Level Data at Chichijima
 Journal of Oceanography Vol. 52, pp. 259 to 273. 1996 Comparison of Sea Surface Heights Observed by TOPEX Altimeter with Sea Level Data at Chichijima NAOTO EBUCHI 1 and KIMIO HANAWA 2 1 Center for Atmospheric
Journal of Oceanography Vol. 52, pp. 259 to 273. 1996 Comparison of Sea Surface Heights Observed by TOPEX Altimeter with Sea Level Data at Chichijima NAOTO EBUCHI 1 and KIMIO HANAWA 2 1 Center for Atmospheric
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Paper ID: 9253 (Peer Review) By: Amalina Izzati Abdul Hamid, Ami Hassan Md Din & Kamaludin Mohd Omar Geomatic Innovation Research
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Paper ID: 9253 (Peer Review) By: Amalina Izzati Abdul Hamid, Ami Hassan Md Din & Kamaludin Mohd Omar Geomatic Innovation Research
Test of theoretical solid earth and ocean gravity tides
 Geophys. J. Int. (1996) 125, 106-1 14 Test of theoretical solid earth and ocean gravity tides John M. Goodkind University ofcalifornia, Sun Diego, 9500 Gilrnan Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093-0319, USA Accepted
Geophys. J. Int. (1996) 125, 106-1 14 Test of theoretical solid earth and ocean gravity tides John M. Goodkind University ofcalifornia, Sun Diego, 9500 Gilrnan Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093-0319, USA Accepted
Tidal gravity observations at Mt. Etna and Stromboli: results concerning the modeled and observed tidal factors
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 51, N. 1, February 2008 Tidal gravity observations at Mt. Etna and Stromboli: results concerning the modeled and observed tidal factors Stefano Panepinto ( 1 )( 3 ), Filippo
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 51, N. 1, February 2008 Tidal gravity observations at Mt. Etna and Stromboli: results concerning the modeled and observed tidal factors Stefano Panepinto ( 1 )( 3 ), Filippo
Chapter 24 Test on Southeast Asia
 Name Score Chapter 24 Test on Southeast Asia Part 1 - Multiple Choice (24 pts.) Read the following statements carefully. Select and circle the most correct choice from among the choices provided. 1. Which
Name Score Chapter 24 Test on Southeast Asia Part 1 - Multiple Choice (24 pts.) Read the following statements carefully. Select and circle the most correct choice from among the choices provided. 1. Which
Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations
 Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations Hans-Peter Plag(1), Geoff Blewitt, Tom A. Herring (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University
Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations Hans-Peter Plag(1), Geoff Blewitt, Tom A. Herring (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University
Active microwave systems (2) Satellite Altimetry * the movie * applications
 Remote Sensing: John Wilkin wilkin@marine.rutgers.edu IMCS Building Room 211C 732-932-6555 ext 251 Active microwave systems (2) Satellite Altimetry * the movie * applications Altimeters (nadir pointing
Remote Sensing: John Wilkin wilkin@marine.rutgers.edu IMCS Building Room 211C 732-932-6555 ext 251 Active microwave systems (2) Satellite Altimetry * the movie * applications Altimeters (nadir pointing
Studies of Tides and Instrumental Performance of Three Gravimeters at Cueva de los Verdes (Lanzarote, Spain)
 ijiijjjjj"f:~~, ;ti 47 ~, ;ti 1 % (2001), 70-75 Jií: Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan Vol. 47, No. 1, (2001), pp. 70-75 Studies of Tides and Instrumental Performance of Three Gravimeters at Cueva
ijiijjjjj"f:~~, ;ti 47 ~, ;ti 1 % (2001), 70-75 Jií: Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan Vol. 47, No. 1, (2001), pp. 70-75 Studies of Tides and Instrumental Performance of Three Gravimeters at Cueva
Comparison between measurements with the superconducting gravimeter T020 and the absolute gravimeter FG5-221 at Metsähovi, Finland in
 Comparison between measurements with the superconducting gravimeter T020 and the absolute gravimeter FG5-221 at Metsähovi, Finland in 2003-2012 H. Virtanen,, M. Bilker-Koivula, J. Mäkinen J. Näränen, A.
Comparison between measurements with the superconducting gravimeter T020 and the absolute gravimeter FG5-221 at Metsähovi, Finland in 2003-2012 H. Virtanen,, M. Bilker-Koivula, J. Mäkinen J. Näränen, A.
Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2)
 Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2) S. Loyer (1), J.-M. Lemoine (2) and F. Perosanz (2) (1) Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France) (2) Centre National
Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2) S. Loyer (1), J.-M. Lemoine (2) and F. Perosanz (2) (1) Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France) (2) Centre National
YOKOYAMA (1977) have recently reported the oceanic effects in the coastal
 J. Phys. Earth, 27, 481-496, 1979 TIDAL CORRECTIONS FOR PRECISE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN IZU PENINSULA Hideo HANADA* Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan (Received June 18, 1979)
J. Phys. Earth, 27, 481-496, 1979 TIDAL CORRECTIONS FOR PRECISE GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS IN IZU PENINSULA Hideo HANADA* Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan (Received June 18, 1979)
(2007), Ocean tidal solutions in Antarctica from GRACE intersatellite
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L21607, doi:10.1029/2007gl031540, 2007 Ocean tidal solutions in Antarctica from GRACE inter-satellite tracking data Shin-Chan Han, 1,2 Richard D. Ray, 1 and Scott
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L21607, doi:10.1029/2007gl031540, 2007 Ocean tidal solutions in Antarctica from GRACE inter-satellite tracking data Shin-Chan Han, 1,2 Richard D. Ray, 1 and Scott
Gravity data reduction
 Gravity data reduction REDUCTION: raw data à gravity anomaly data Temporal corrections tides and instrument drift Spatial corrections latitude and elevation GRS67 = gravity variation with latitude at sea
Gravity data reduction REDUCTION: raw data à gravity anomaly data Temporal corrections tides and instrument drift Spatial corrections latitude and elevation GRS67 = gravity variation with latitude at sea
Timofeev V.Y.*, Ducarme B.**, Saricheva Y.K*, Vandercoilden L.***
 1 of 7 2/18/2011 2:59 PM Timofeev V.Y.*, Ducarme B.**, Saricheva Y.K*, Vandercoilden L.*** *Institute of Geophysics UIGGM SB RAS Koptiug pr.,3,630090 Novosibirsk, Russia (e-mail: sari@uiggm.nsc.ru) **Chercheur
1 of 7 2/18/2011 2:59 PM Timofeev V.Y.*, Ducarme B.**, Saricheva Y.K*, Vandercoilden L.*** *Institute of Geophysics UIGGM SB RAS Koptiug pr.,3,630090 Novosibirsk, Russia (e-mail: sari@uiggm.nsc.ru) **Chercheur
Application of ECGS to host the direction of the
 Président d honneur: Son Altesse Royale Le Grand Duc Henri Président Secrétaire J-M. Goerens E. Buttini ECGS 19, Rue Josy Welter L-7256 Walferdange http://www.ecgs.lu To the International Association of
Président d honneur: Son Altesse Royale Le Grand Duc Henri Président Secrétaire J-M. Goerens E. Buttini ECGS 19, Rue Josy Welter L-7256 Walferdange http://www.ecgs.lu To the International Association of
GEOID UNDULATIONS OF SUDAN USING ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHTS COMPARED WITH THE EGM96 ANG EGM2008
 GEOID UNDULATIONS OF SUDAN USING ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHTS COMPARED Dr. Abdelrahim Elgizouli Mohamed Ahmed* WITH THE EGM96 ANG EGM2008 Abstract: Positioning by satellite system determine the normal height above
GEOID UNDULATIONS OF SUDAN USING ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHTS COMPARED Dr. Abdelrahim Elgizouli Mohamed Ahmed* WITH THE EGM96 ANG EGM2008 Abstract: Positioning by satellite system determine the normal height above
GEOID UNDULATION DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GEOPOTENTIAL. RICHARD H. RAPP and YAN MING WANG
 GEOID UNDULATION DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GEOPOTENTIAL MODELS RICHARD H. RAPP and YAN MING WANG Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, U.S.A. (Received 15 September,
GEOID UNDULATION DIFFERENCES BETWEEN GEOPOTENTIAL MODELS RICHARD H. RAPP and YAN MING WANG Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, U.S.A. (Received 15 September,
The GOCE Geoid in Support to Sea Level Analysis
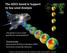 The GOCE Geoid in Support to Sea Level Analysis The geoid is a very useful quantity for oceanographers Thomas Gruber Astronomical & Physical Geodesy (IAPG) Technische Universität München 1. Characteristics
The GOCE Geoid in Support to Sea Level Analysis The geoid is a very useful quantity for oceanographers Thomas Gruber Astronomical & Physical Geodesy (IAPG) Technische Universität München 1. Characteristics
The Earth s time-variable gravity field observed by GOCE
 The Earth s time-variable gravity field observed by GOCE GOCE+ Time-Variations, part of STSE (Theme 4, Innovative Feasibility Studies) J. Bouman, M. Fuchs, C. Haberkorn, V. Lieb, M. Schmidt T. Broerse,
The Earth s time-variable gravity field observed by GOCE GOCE+ Time-Variations, part of STSE (Theme 4, Innovative Feasibility Studies) J. Bouman, M. Fuchs, C. Haberkorn, V. Lieb, M. Schmidt T. Broerse,
Tides: this is what we see
 Last time Wind generated waves and Tsunami These are wind and earthquake generated waves Today: Tides These are Gravity waves How are they generated What are their intersting complexities? Low tide (decrease
Last time Wind generated waves and Tsunami These are wind and earthquake generated waves Today: Tides These are Gravity waves How are they generated What are their intersting complexities? Low tide (decrease
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra.
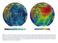 Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Figure 3.1: Illustration showing the bathymetry s role for the tsunami propagation following the earth quake 26 December 2004 outside of Sumatra. The left globe shows the seafloor bathymetry as portrayed
Intercomparison of Relative and Absolute Gravimeters. Olivier FRANCIS
 Intercomparison of Relative and Absolute Gravimeters Olivier FRANCIS The right gravimeter for the right job (signal to be detected) Absolute/relative Stability (accuracy)/precision (repetability) Spatial
Intercomparison of Relative and Absolute Gravimeters Olivier FRANCIS The right gravimeter for the right job (signal to be detected) Absolute/relative Stability (accuracy)/precision (repetability) Spatial
Effect of coastal resolution on global estimates of tidal energy dissipation
 Effect of coastal resolution on global estimates of tidal energy dissipation Maialen Irazoqui Apecechea, Martin Verlaan Contents The GTSMv2.0 model Characteristics Major developments Applications Coastal
Effect of coastal resolution on global estimates of tidal energy dissipation Maialen Irazoqui Apecechea, Martin Verlaan Contents The GTSMv2.0 model Characteristics Major developments Applications Coastal
Mechanical energy input to the world oceans due to. atmospheric loading
 Mechanical energy input to the world oceans due to atmospheric loading Wei Wang +, Cheng Chun Qian +, & Rui Xin Huang * +Physical Oceanography Laboratory, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, Shandong,
Mechanical energy input to the world oceans due to atmospheric loading Wei Wang +, Cheng Chun Qian +, & Rui Xin Huang * +Physical Oceanography Laboratory, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, Shandong,
Mount Stromlo Gravity Station Gravimetry at the ANU
 ANU COLLEGE OF SCIENCE RESEARCH SCHOOL OF EARTH SCIENCES Canberra ACT 0200 Australia Mount Stromlo Gravity Station Gravimetry at the ANU Background Terrestrial observing has been conducted at Mount Stromlo
ANU COLLEGE OF SCIENCE RESEARCH SCHOOL OF EARTH SCIENCES Canberra ACT 0200 Australia Mount Stromlo Gravity Station Gravimetry at the ANU Background Terrestrial observing has been conducted at Mount Stromlo
Love Numbers and Gravimetric Factor for Diurnal Tides. Piravonu M. Mathews
 Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan Vol. 46, No. 4, (2001), pp. 231-236 Love Numbers and Gravimetric Factor for Diurnal Tides Piravonu M. Mathews Department of Theoretical Physics, University of Madras
Journal of the Geodetic Society of Japan Vol. 46, No. 4, (2001), pp. 231-236 Love Numbers and Gravimetric Factor for Diurnal Tides Piravonu M. Mathews Department of Theoretical Physics, University of Madras
The Effect of Ocean Tide Loading on Tides of the Solid Earth Observed with the Superconducting Gravimeter
 Geophys. J. R. astr. (1975) 43,707-720 The Effect of Ocean Tide Loading on Tides of the Solid Earth Observed with the Superconducting Gravimeter Richard J. Warburton, Christopher Beaumont* and John M.
Geophys. J. R. astr. (1975) 43,707-720 The Effect of Ocean Tide Loading on Tides of the Solid Earth Observed with the Superconducting Gravimeter Richard J. Warburton, Christopher Beaumont* and John M.
Assessment of the International Terrestrial Reference System 2014 realizations by Precise Orbit Determination of SLR Satellites
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Assessment of the International Terrestrial Reference System 2014 realizations by Precise Orbit Determination of SLR
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Assessment of the International Terrestrial Reference System 2014 realizations by Precise Orbit Determination of SLR
CONTINUOUS GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS FOR RESERVOIR MONITORING. M. Sugihara
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 CONTINUOUS GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS FOR RESERVOIR MONITORING
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 25-27, 1999 SGP-TR-162 CONTINUOUS GRAVITY MEASUREMENTS FOR RESERVOIR MONITORING
Tides ( gravity waves ): this is what we see. (bay of Fundy, CAN)
 Tides ( gravity waves ): this is what we see (bay of Fundy, CAN) Which of the following are correct? A. Coastlines experience two high tides each day. B. Tides are 12 hours apart. C. High tide occurs simultaneously
Tides ( gravity waves ): this is what we see (bay of Fundy, CAN) Which of the following are correct? A. Coastlines experience two high tides each day. B. Tides are 12 hours apart. C. High tide occurs simultaneously
MAREES TERRESTRES BULLETIN D'INFORMATIONS
 MAREES TERRESTRES BULLETIN D'INFORMATIONS INTERNATIONAL CENTER FOR EARTH TIDES CENTRE INTERNATIONAL DES MAREES TERRESTRES International Association of Geodesy - International Gravity Field Service (IAG
MAREES TERRESTRES BULLETIN D'INFORMATIONS INTERNATIONAL CENTER FOR EARTH TIDES CENTRE INTERNATIONAL DES MAREES TERRESTRES International Association of Geodesy - International Gravity Field Service (IAG
About the impelling force by composition of centrifugal force
 About the impelling force by composition of centrifugal force 2011.SEP.22 First edition Gravity Engineering Corporation CEO Takashi Tsuda 1. Introduction Since centrifugal force and gravity balanced, Newton
About the impelling force by composition of centrifugal force 2011.SEP.22 First edition Gravity Engineering Corporation CEO Takashi Tsuda 1. Introduction Since centrifugal force and gravity balanced, Newton
Past, present and future
 Southern New Jersey and Delaware sea levels: Past, present and future Benjamin P. Horton Sea Level Research Department of Marine and Coastal Science Rutgers University bphorton@marine.rutgers.edu DRIVERS
Southern New Jersey and Delaware sea levels: Past, present and future Benjamin P. Horton Sea Level Research Department of Marine and Coastal Science Rutgers University bphorton@marine.rutgers.edu DRIVERS
GRAVITY. Reading Practice
 Reading Practice GRAVITY A. Without forces of gravitation, Earth and other planets would be unable to stay in their orbits around the Sun. the Moon would be unable to orbit the Earth, tidal waves would
Reading Practice GRAVITY A. Without forces of gravitation, Earth and other planets would be unable to stay in their orbits around the Sun. the Moon would be unable to orbit the Earth, tidal waves would
Tides. Q: What do we want to know about tides for? A: So we can use them as a calibration signal for the BSM s.
 Tides Q: What do we want to know about tides for? A: So we can use them as a calibration signal for the BSM s. The aim is thus to model the tides as well as we can, rather than to analyze them to understand
Tides Q: What do we want to know about tides for? A: So we can use them as a calibration signal for the BSM s. The aim is thus to model the tides as well as we can, rather than to analyze them to understand
Tidal Effects on Earth s Surface
 Tidal Effects on Earth s Surface Tom Murphy February, 1 This treatment follows the conventions of F. D. Stacey s Physics of the Earth, and is largely an elaboration on this work. 1 Tidal Potential The
Tidal Effects on Earth s Surface Tom Murphy February, 1 This treatment follows the conventions of F. D. Stacey s Physics of the Earth, and is largely an elaboration on this work. 1 Tidal Potential The
Satellite ALTimetry. SALT applications and use of data base for SE-Asia region. SEAMERGES kick-off meeting, Bangkok, Thailand.
 Satellite ALTimetry SALT applications and use of data base for SE-Asia region SEAMERGES kick-off meeting, Bangkok, Thailand Marc Naeije 4 March 2004 1 Faculty of Aerospace Engineering DEOS/AS SEAMERGES
Satellite ALTimetry SALT applications and use of data base for SE-Asia region SEAMERGES kick-off meeting, Bangkok, Thailand Marc Naeije 4 March 2004 1 Faculty of Aerospace Engineering DEOS/AS SEAMERGES
Centre International des Marées Terrestres International Centre for Earth Tides
 Centre International des Marées Terrestres International Centre for Earth Tides SCIENTIFIC ACTIVITY REPORT for the period 2003-2007 by B.Ducarme, ICET Director ducarme@oma.be The staff of ICET, which is
Centre International des Marées Terrestres International Centre for Earth Tides SCIENTIFIC ACTIVITY REPORT for the period 2003-2007 by B.Ducarme, ICET Director ducarme@oma.be The staff of ICET, which is
Shape of the Earth. Data Output by the Receiver
 It is quite common for confusion to arise about the process used during a hydrographic survey when GPS-derived water surface elevation is incorporated into the data as an RTK Tide correction. This article
It is quite common for confusion to arise about the process used during a hydrographic survey when GPS-derived water surface elevation is incorporated into the data as an RTK Tide correction. This article
Improving the long-term stability of the GDR orbit solutions
 Improving the long-term stability of the GDR orbit solutions L. Cerri 1, A. Couhert 1, S. Houry 1, F. Mercier 1 (1) CNES Toulouse OSTST Meeting 19-21 Oct. 2011 POD Splinter Session Status of the POD standards
Improving the long-term stability of the GDR orbit solutions L. Cerri 1, A. Couhert 1, S. Houry 1, F. Mercier 1 (1) CNES Toulouse OSTST Meeting 19-21 Oct. 2011 POD Splinter Session Status of the POD standards
DEFLECTIONS AND GEOIDAL HEIGHTS ACROSS A SEAMOUNT
 DEFLECTIONS AND GEOIDAL HEIGHTS ACROSS A SEAMOUNT by Irene F i s c h e r Defense Mapping Agency Topographic Center, W ashington (*> Paper presented at the General Assem bly of the In te rn a tio n a l
DEFLECTIONS AND GEOIDAL HEIGHTS ACROSS A SEAMOUNT by Irene F i s c h e r Defense Mapping Agency Topographic Center, W ashington (*> Paper presented at the General Assem bly of the In te rn a tio n a l
Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM
 Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM James G. Richman Oceanography Division Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS In collaboration with Brian Arbic, Univ. Michigan Joe Metzger, Jay Shriver &
Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM James G. Richman Oceanography Division Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS In collaboration with Brian Arbic, Univ. Michigan Joe Metzger, Jay Shriver &
mdu G = Fdr = mgdr Dr. Clint Conrad POST 804 Gravity, the Geoid, and Mantle Dynamics Lecture: Gravity and the Geoid U G = G M r
 GG 611 Big Gulp Fall 2014 Gravity, the Geoid, and Mantle Dynamics Lecture: Gravity and the Geoid Dr. Clint Conrad POST 804 clintc@hawaii.edu Gravitational Potential For a point mass: Newton s law of gravitation:
GG 611 Big Gulp Fall 2014 Gravity, the Geoid, and Mantle Dynamics Lecture: Gravity and the Geoid Dr. Clint Conrad POST 804 clintc@hawaii.edu Gravitational Potential For a point mass: Newton s law of gravitation:
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Bosch, W., Savcenko, R., Flechtner, F., Dahle, C., Mayer-Gürr, T., Stammer, D., Taguchi, E., Ilk, K. H. (2009): Residual ocean tide signals from satellite altimetry, GRACE gravity
Originally published as: Bosch, W., Savcenko, R., Flechtner, F., Dahle, C., Mayer-Gürr, T., Stammer, D., Taguchi, E., Ilk, K. H. (2009): Residual ocean tide signals from satellite altimetry, GRACE gravity
Sea level changes around Thailand
 Final symposium 27 May Bangkok, Thailand Sea level changes around Thailand Marc Naeije Contents GEO2TECDI- SONG: measuring sea level around Thailand Concept of satellite altimetry Concept of tide gauges
Final symposium 27 May Bangkok, Thailand Sea level changes around Thailand Marc Naeije Contents GEO2TECDI- SONG: measuring sea level around Thailand Concept of satellite altimetry Concept of tide gauges
Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from GRACE observations
 Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from GRACE observations P. Tregoning 1 and S.C. McClusky 1 1 Research School of Earth Sciences, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, 0200, Australia,
Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from GRACE observations P. Tregoning 1 and S.C. McClusky 1 1 Research School of Earth Sciences, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, 0200, Australia,
A Preliminary Attempt of a Quasi-Geoid for Saudi Arabia
 A Preliminary Attempt of a Quasi-Geoid for Saudi Arabia Saad MOGREN, Saudi Arabia Key words: Geoid, Saudi Arabia, SUMMARY This proposal describes the need to undertake a national geoid (quasi-geoid) model
A Preliminary Attempt of a Quasi-Geoid for Saudi Arabia Saad MOGREN, Saudi Arabia Key words: Geoid, Saudi Arabia, SUMMARY This proposal describes the need to undertake a national geoid (quasi-geoid) model
Comparison of variations in air mass attraction derived from radiosonde data and a meteorological weather model
 Comparison of variations in air mass attraction derived from radiosonde data and a meteorological weather model D. Simon 1, Th. Klügel 2, and C. Kroner 3 1 Frankensteinstr.4, D-36469 Tiefenort, Germany,
Comparison of variations in air mass attraction derived from radiosonde data and a meteorological weather model D. Simon 1, Th. Klügel 2, and C. Kroner 3 1 Frankensteinstr.4, D-36469 Tiefenort, Germany,
Dependences in the pillar Earth s gravity field of
 Reports on Geodesy, vol. 92, no. 1, 2012 Dependences in the pillar Earth s gravity field of GGOS - description using UML notation Małgorzata Paśnicka 1, Karolina Szafranek 2, Agnieszka Zwirowicz Rutkowska
Reports on Geodesy, vol. 92, no. 1, 2012 Dependences in the pillar Earth s gravity field of GGOS - description using UML notation Małgorzata Paśnicka 1, Karolina Szafranek 2, Agnieszka Zwirowicz Rutkowska
GROUND VIBRATIONS AND TILTS
 IV/336 GROUND VIBRATIONS AND TILTS Hideo Hanada National Astronomical Observatory, Mizusawa, Iwate, JAPAN 1. INTRODUCTION We cannot avoid effects of ground vibrations or tilts so far as we make some kind
IV/336 GROUND VIBRATIONS AND TILTS Hideo Hanada National Astronomical Observatory, Mizusawa, Iwate, JAPAN 1. INTRODUCTION We cannot avoid effects of ground vibrations or tilts so far as we make some kind
Global Edited Soundings for Gravity/Bathymetry Calibration
 Global Edited Soundings for Gravity/Bathymetry Calibration David Sandwell, Walter Smith, JJ Becker, Karen Marks, Megan Jones, Adrienne Apacile, Seung-Hee Kim, Scott Nelson Rob Beaman,... Objective - construct
Global Edited Soundings for Gravity/Bathymetry Calibration David Sandwell, Walter Smith, JJ Becker, Karen Marks, Megan Jones, Adrienne Apacile, Seung-Hee Kim, Scott Nelson Rob Beaman,... Objective - construct
A gravimetric quasi-geoid evaluation in the Northern region of Algeria using EGM96 and GPS/Levelling
 A gravimetric quasi-geoid evaluation in the Northern region of Algeria using EGM96 and GPS/Levelling Mohamed Aissa MESLEM Laboratory of geodesy Department of Research and Development National Institute
A gravimetric quasi-geoid evaluation in the Northern region of Algeria using EGM96 and GPS/Levelling Mohamed Aissa MESLEM Laboratory of geodesy Department of Research and Development National Institute
3.3 Analysis Coordinator
 1. Introduction 2. Analysis of ITRF2014 post-seismic parameterization In this report we outline the activities of the Analysis Coordinator during 2015. The main activities were analysis of the ITRF2014
1. Introduction 2. Analysis of ITRF2014 post-seismic parameterization In this report we outline the activities of the Analysis Coordinator during 2015. The main activities were analysis of the ITRF2014
Assessment of atmospheric reductions for terrestrial gravity observations
 Assessment of atmospheric reductions for terrestrial gravity observations 1) 1) M.Abe, C.Kroner, J.Neumeyer, X.D. Chen 2) 1) Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ), Gravity Field and Gravimetry 2) Institute
Assessment of atmospheric reductions for terrestrial gravity observations 1) 1) M.Abe, C.Kroner, J.Neumeyer, X.D. Chen 2) 1) Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ), Gravity Field and Gravimetry 2) Institute
A new method for in-situ calibration of rod extensometers
 A new method for in-situ calibration of rod extensometers Gyula Mentes Geodetic and Geophysical Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences Abstract At the Geodetic and Geophysical Research
A new method for in-situ calibration of rod extensometers Gyula Mentes Geodetic and Geophysical Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences Abstract At the Geodetic and Geophysical Research
Lab 8: Gravity and Isostasy (35 points)
 it's not the most important thing in your life right now. But what is important is gravity. Arnold Schwarzenegger as Colonel John Matrix, Commando (Check out this classic of American cinema!) Lab 8: Gravity
it's not the most important thing in your life right now. But what is important is gravity. Arnold Schwarzenegger as Colonel John Matrix, Commando (Check out this classic of American cinema!) Lab 8: Gravity
The Application of POM to the Operational Tidal Forecast for the Sea around Taiwan
 The Application of POM to the Operational Tidal Forecast for the Sea around Taiwan Shan-Pei YEH 1 Hwa CHIEN Sen JAN 3 and Chia Chuen KAO 4 1 Coastal Ocean Monitoring Center, National Cheng Kung University,
The Application of POM to the Operational Tidal Forecast for the Sea around Taiwan Shan-Pei YEH 1 Hwa CHIEN Sen JAN 3 and Chia Chuen KAO 4 1 Coastal Ocean Monitoring Center, National Cheng Kung University,
Recent Climate History - The Instrumental Era.
 2002 Recent Climate History - The Instrumental Era. Figure 1. Reconstructed surface temperature record. Strong warming in the first and late part of the century. El Ninos and major volcanic eruptions are
2002 Recent Climate History - The Instrumental Era. Figure 1. Reconstructed surface temperature record. Strong warming in the first and late part of the century. El Ninos and major volcanic eruptions are
PGM2016: A new geoid model for the. Philippines
 PGM2016: A new geoid model for the Philippines United Nations/Nepal Workshop on the Applications of Global Navigation Satellite Systems Kathmandu, Nepal December 12-16, 2016 Ronaldo Gatchalian, Chief Geodesy
PGM2016: A new geoid model for the Philippines United Nations/Nepal Workshop on the Applications of Global Navigation Satellite Systems Kathmandu, Nepal December 12-16, 2016 Ronaldo Gatchalian, Chief Geodesy
An Arctic Perspective on Climate Change
 An Arctic Perspective on Climate Change 23 Oct 2012 Gifford Miller (and many others) University of Colorado Boulder The Earth is warming How do we know? Temperature Anomaly ( C) It s a fact Global Land
An Arctic Perspective on Climate Change 23 Oct 2012 Gifford Miller (and many others) University of Colorado Boulder The Earth is warming How do we know? Temperature Anomaly ( C) It s a fact Global Land
GSA DATA REPOSITORY D. Livsey and A.R. Simms
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013273 D. Livsey and A.R. Simms Supplementary Information The supplementary information is divided into three sections: (1) Tide model and datums, (2) Vertical error calculation, and
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013273 D. Livsey and A.R. Simms Supplementary Information The supplementary information is divided into three sections: (1) Tide model and datums, (2) Vertical error calculation, and
PRACTICAL UNCERTAINTY BUDGETS FOR SPECTRAL MEASUREMENTS OF LEDS
 PRACTICAL UNCERTAINTY BUDGETS FOR SPECTRAL MEASUREMENTS OF LEDS ABSTRACT LEDs are used in many applications, ranging from signalling to ambient lighting to displays. Specifications and tolerances are used
PRACTICAL UNCERTAINTY BUDGETS FOR SPECTRAL MEASUREMENTS OF LEDS ABSTRACT LEDs are used in many applications, ranging from signalling to ambient lighting to displays. Specifications and tolerances are used
GRAVITY EXPLORATION (Gph 301) Chokri Jallouli 2014/2015
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCES Department of Geology and Geophysics GRAVITY EXPLORATION (Gph 301) Chokri Jallouli 2014/2015 INTRODUCTION Definition Gravity method consists of measuring, studying
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCES Department of Geology and Geophysics GRAVITY EXPLORATION (Gph 301) Chokri Jallouli 2014/2015 INTRODUCTION Definition Gravity method consists of measuring, studying
The Malaysian Seas: Variation of Sea Level Observed by Tide Gauges and Satellite Altimetry. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Skudai, Johor
 The Malaysian Seas: Variation of Sea Level Observed by Tide Gauges and Satellite Altimetry Kamaludin Omar 1, Shahrum Ses 1, Marc Naeije 2, Mohamad Asrul Mustafar 1 1 Faculty of Geoinformation Science and
The Malaysian Seas: Variation of Sea Level Observed by Tide Gauges and Satellite Altimetry Kamaludin Omar 1, Shahrum Ses 1, Marc Naeije 2, Mohamad Asrul Mustafar 1 1 Faculty of Geoinformation Science and
On the calibration of a superconducting gravimeter using absolute gravity measurements
 Geophys. J. Int. (1991) 106, 491-497 On the calibration of a superconducting gravimeter using absolute gravity measurements J. Hinderer,' N. Florsch,2 J. Maki~~en,~ H. Legros' and J. E. Faller4 Laboratoire
Geophys. J. Int. (1991) 106, 491-497 On the calibration of a superconducting gravimeter using absolute gravity measurements J. Hinderer,' N. Florsch,2 J. Maki~~en,~ H. Legros' and J. E. Faller4 Laboratoire
Lesson 9. Luis Anchordoqui. Physics 168. Tuesday, October 24, 17
 Lesson 9 Physics 168 1 Static Equilibrium 2 Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it but that is not moving is said to be in equilibrium 3 Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) First
Lesson 9 Physics 168 1 Static Equilibrium 2 Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it but that is not moving is said to be in equilibrium 3 Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) First
An Assessment of the Gravity Data Collected at the Mohe Observation Center in China during the March 9, 1997 Total Solar Eclipse
 An Assessment of the Gravity Data Collected at the Mohe Observation Center in China during the March 9, 1997 Total Solar Eclipse William L. Stubbs 1961 SW Davis Street, Port St. Lucie, FL 34953 e-mail:
An Assessment of the Gravity Data Collected at the Mohe Observation Center in China during the March 9, 1997 Total Solar Eclipse William L. Stubbs 1961 SW Davis Street, Port St. Lucie, FL 34953 e-mail:
The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity
 The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity Pulls all points on Earth toward Moon s center of mass. near side of Earth is attracted more than far side because force of gravity decreases with increasing distance.
The Tides: Consider Moon s Gravity Pulls all points on Earth toward Moon s center of mass. near side of Earth is attracted more than far side because force of gravity decreases with increasing distance.
