Answers to All Exercises. Appendix C ( ) ( ) Section C.1 (page C7) APPENDICES. Answers to All Exercises Ans1
|
|
|
- Abigayle Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Answers to All Eercises Ans Answers to All Eercises Appendi C Section C. (page C). Cartesian. Distance Formula. Midpoint Formula. ( h) + ( k) = r, center, radius. c. f. a. d. e. b. A: (, ); B: (, ); C: (, ); D: (, ). A: (., ); B: (, ); C: (,.); D: (, )... (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (,.) (., ) (, ) (, ). (, ) (, ) (, ) ( ), (, ) ( ), (, ) (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ). Quadrant IV. Quadrant III. Quadrant II. Quadrant I. Quadrant III or IV. Quadrant I or IV. Quadrant III. Quadrant III. Quadrant I or III. Quadrant II or IV (a),, (b) + =. (a),, (b) + =. (a),, (b) + = ( ). (a),, (b) + = ( ). ( ) + ( ) = ( ). ( ) + ( ) = ( ). Two equal sides of length. Two equal sides of length. Opposite sides have equal lengths of and.. Opposite sides have equal lengths of and.. The diagonals are of equal length ( ). The slope of the line between (, ) and (, ) is. The slope of the line between (, ) and (, ) is. The slopes are negative reciprocals, indicating perpendicular lines, which form a right angle.. The diagonals are of equal length ( ). The slope of the line between (, ) and (, ) is. The slope of the line between (, ) and (, ) is. The slopes are negative reciprocals, indicating perpendicular lines, which form a right angle.. (a) (b) (c) (, ). (a). (a). (a). (a) (, ) (, ) (, ) (b) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (c) (, ) (b) (c) (, ) (b) (, ) (c) (, ) (b) (c) (, ) APPENDICES
2 Ans Answers to All Eercises. (a) (, ) (b) (c) (, ). Center: (, ). Center: (, ) Radius: Radius:. (a) (, ) (, ) (, ) (b) (c) (, ). Center: (, ). Center: (, ) Radius: Radius:. (a) (b) (c) (, ). Center: (, ). Center: (, ) (, ) Radius: Radius:. (a). (a) (, ) (.,.) (.,.) (.,.) (.,.) (b). (c) (.,.) (b). (c) (.,.). $. million. $. million. + =. + =. ( ) + ( + ) =. ( + ) + ( ) =. ( + ) + ( ) =. ( ) + ( + ) =. ( ) + ( ) =. + =. ( + ) + ( ) =. ( ) + ( + ) =. ( ) + ( + ) =. ( + ) + =. ( ) + ( + ) =. ( + ) + ( ) =. (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ), (, ). d.. ft;. ft.. km. True. The lengths of the sides from (, ) to (, ) and from (, ) to (, ) are both.. False. It could be a rhombus.. False. You would have to use the Midpoint Formula times.. ;. No. The scales depend on the magnitudes of the quantities measured.. ( m, m ); (a) (, ) (b) (, ). ( +, + ( +, + ) ), ( +, + ), (a) (, ), (, ), (, ) (b) (, ), (, ), (, ). Proof. (a) ii (b) iii (c) iv (d) i
3 Answers to All Eercises Ans Appendi C. (page C). solution point. graph. Algebraic, graphical, numerical.. If possible, rewrite the equation so that one of the variables is isolated on one side of the equation.. Make a table of values showing several solution points.. Plot these points on a rectangular coordinate sstem.. Connect the points with a smooth curve or line.. (a) Yes (b) Yes. (a) Yes (b) Yes. (a) No (b) Yes. (a) No (b) Yes. (a) No (b) Yes. (a) No (b) Yes. (a) Yes (b) No. (a) Yes (b) No. Solution point (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). Solution point (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). b. d. c. a. e. f... Solution point (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ).. APPENDICES... Solution point (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, )..
4 Ans Answers to All Eercises.... Intercepts: (, ), (, ) Intercepts: (, ), (, ) Intercepts: (, ), (, ), (, ). Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl =. Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl =. The graphs are identical. Distributive Propert. The graphs are identical. Associative Propert of Addition. The graphs are identical. Associative Propert of Multiplication. The graphs are identical. Multiplicative Inverse Propert. (a) (,.) (b) (, ). Intercepts: (, ), (, ), (, ).. (a) (, ) (b) (., ). Intercept: (, ) Intercept: (, ).. (a) (.,.) (b) (., ), (., ), (., ). Intercepts: (, ), (, ) Intercepts: (, ), (, ).. (a) (, ) (b) (.,.), (.,.), (.,.), (.,.). Intercepts: (, ), (, ) Intercepts: (, ), (, ).. =. = = =. Intercepts: (, ), (, ), Intercepts: (, ), (, ), (, ) (, ).. = + ( ). = + ( ) = ( ) = ( ) Intercepts: (, ), (, ) Intercepts: (, ), (, ). b, c, d. c, d
5 Answers to All Eercises Ans. (a),. (a) (b) $, (b). r (c). r (c) $.. (a) Year New houses (in thousands).... Year New houses (in thousands) The model fits the data well. (b).... The model fits the data well. (c) :,; :,; Yes. Answers will var. (d),. (a) The model fits the data well. (b).; The life epectanc in (c) t = or (d) About. r. False. = has two -intercepts.. False. = has an infinite number of -intercepts.. Use the equations = +. and = +. to model the situation. When the sales level equals $,, both equations ield $. Appendi C. (page C). equation. solve. etraneous. point of intersection. (a) Yes (b) No (c) No (d) No. (a) No (b) Yes (c) No (d) No. (a) Yes (b) No (c) No (d) No. (a) No (b) No (c) Yes (d) No. (a) No (b) No (c) No (d) Yes. (a) No (b) Yes (c) No (d) No. Identit. Identit. Identit. Identit. Conditional equation. Conditional equation. =. =. =. =. =. z =. =. =. z =. =. z =. =. u =. =. =. =. =. =. =. No solution. =. z =. No solution. No solution. (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). No intercepts. (, ). (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ), (,.). (, ), (, ). (, )... (, ) (, ). (, ) (, ). ( ) =. ( ) + = APPENDICES = +. = +.,,. () () + () =. () () + () = () () + () = () () + () = () () + () = () () + () =. (a) Xmin = - Xma = Xscl = Ymin = - Yma = Yscl = (b) (, ), (, ), (, ) (c) (, ): No (, ): Yes Answers will var.. + =
6 Ans Answers to All Eercises. () = =. (a) (b) and (c) =,, (d) The are the same ,...,..,....,,. ±,. ±..,... ±.,.,... (, ). (, ). (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ). (.,.), (.,.). (.,.). (, ), (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ).,. ±.,.,.,.,.,.,. a ± b. a. ±. ±.,.,. No solution. No solution. ± ;.,. ±. ;.,... ;..,.,. ±. ±. ±.,. No solution. ± ±.. ±. ±. ±. ±. ±. No solution. No solution... ±. ±. ±.,.,. No solution.. No solution. ±. ±.. ± b a. ±,. ±,.,.,., ±., ±.,,. ±, ± i. ±, ±. ±. ±, ±. ±.,..,.,.... No solution ,.,, ±..,, ±.. ±.,.,.,.,.,.,. (a). (a). (a). (a). (a). (a). (a). (a) (b) and (c) = ±, ± (d) The are the same. (b) and (c) =, (d) The are the same. (b) and (c) = (d) The are the same. (b) and (c) = (d) The are the same. (b) and (c) = (d) The are the same. (b) and (c) =, (d) The are the same. (b) and (c) =, (d) The are the same. (.,.); In, both states had the same population. (b) (.,.); In, both states had the same population. (c) Change in population per ear; Marland s population is growing faster. (d) Marland:,,; Wisconsin:,, Answers will var.
7 Ans Answers to All Eercises. (a) (b) Answers will var. (c). < <. <.. (d) (e) Answers will var.. (a) >.. (b). C (c).. (a) < >.. (b). F (c).. False. The lines could be identical.. False. See Eample.. c =. c = b. (a), (b), a lb in. Appendi C. (page C). <.... >. <. <. < <.,. <, >. < <...,. <. <. (a) (a) (b) (b). <, >.. > APPENDICES (a) (b) (a) (b)... double. a a. a, a. zeros, undefined values. No. Transitive Propert. d. a. f. b. e. c. (a) Yes (b) No (c) Yes (d) No. (a) No (b) No (c) Yes (d) Yes. (a) No (b) Yes (c) Yes (d) No. (a) Yes (b) Yes (c) Yes (d) No. >..... (a) (a) (b), (b),. >. + <. <. + + >. Positive on: (, ) (, ) Negative on: (, )
8 Ans Answers to All Eercises. Positive on: (, ) (, ) Negative on: (, ). Positive on: (, ) ( +, ) Negative on: (, + ) ). Positive on: (, + Negative on: (, ) ( +, ). Negative on: (, ). Positive on: (, ). (, ], [, ). (, ). (, ). (, ], [, )., [, ). (, ]. (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). [, ], [, ). No solution.. (, ), (, ). All real numbers. (a) = (b) (c) >. (a) =, (b), (c) <, >.. (a), (a) <, (b) (b) =, <. (, ), (, ). (, ), (, ). (, ), [, ). (, ].. (a) < (a) (b) < (b) <. [, ). [, ). [, ]. (, ], [, ). (, ], [, ). (, ). (a) (b) (, ); (, ). (a) (b) (, ); (, ). (a) sec (b) (, ). (a) sec (b) (,.), (., ). (a) (b) (, ) (c). < <.. (a) and (b) (c). lb (d) Answers will var.. t.; Starting in, there were at least Bed Bath & Beond stores.. t., t.; From to and to, there were at most Williams-Sonoma stores.. t.; In, there were about the same number of Bed Bath & Beond stores as Williams-Sonoma stores.. t.; Starting in, the number of Bed Bath & Beond stores eceeded the number of Williams-Sonoma stores.. vibrations sec.. mm.. < t <.. < v <. False.. True. + + is alwas positive.. False. Cube roots have no restrictions on the domain.. iv, ii, iii, i. (a) iv (b) ii (c) iii (d) i. (a) a, b (b) Positive on: (, a) (b, ) Negative on: (a, b) When < a or > b, the factors have the same sign so the product is positive. When a < < b, the factors have opposite signs so the product is negative. (c) = a and = b Appendi D (page D). directl proportional. constant, variation. directl proportional. inverse. combined. jointl proportional. =. =. =. =. Model: = ;. cm,. cm. Model: = ;. L,. L
9 Answers to All Eercises Ans. =.; $. =.; $.. (a). m (b) N. N.... = k = k = k = k.. mi/h. k(v) kv =.... = k = k = k = k. =. =. =. =. A = kr. V = ke. = k k s. h = s. F = kg r. z = k. P = k V. R = ks(l S). R = k(t e T). F = km m r APPENDICES
10 Ans Answers to All Eercises. The area of a triangle is jointl proportional to its base and height.. The surface area of a sphere varies directl as the square of its radius.. The volume of a sphere varies directl as the cube of its radius.. The volume of a right circular clinder is jointl proportional to the product of its height and the square of its radius.. Average speed is directl proportional to the distance and inversel proportional to the time.. ω varies directl as the square root of g and inversel as the square root of W.. A = πr. =. =. z =. F = rs. P =. z =. v = pq s.. ft.. in.. J. No. The -inch pizza is the best bu.. The velocit is increased b.. (a) The safe load is unchanged. (b) The safe load is eight times as great. (c) The safe load is four times as great. (d) The safe load is one-fourth as great.. (a) C Temperature (in C) Depth (in meters) (b) Yes. k =, k =, k =, k =, k = (c) C = d (d) (e) About m d. Inversel. Directl Appendi E (page E). linear. equivalent inequalities No solution. All real numbers..... <. >. <. <... >. <. <. >. <. >..... <... <.. > Appendi F Appendi F. (page F). solution. graph. linear. point, equilibrium. g. d. a. h. e. b. f. c (a) Length (in centimeters) Force (in pounds) (b) Yes. (c). lb. False. will increase if k is positive and will decrease if k is negative.. False. E is jointl proportional to the mass of an object and the square of its velocit. F....
11 Ans Answers to All Eercises (, ) (, ).. (, ) (, ). (, ) (, ) (, )... + >.. +. >. (a) Yes (b) No (c) No (d) No. (a) No (b) No (c) No (d) Yes.. APPENDICES.. (, ) (, ) (, )
12 Ans Answers to All Eercises (, ) (, ) No solution ( ),.. (, ) (, ) No solution. (, ). (, ) (, ) (, ( ) + ) (, ) (, ). (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ).. (, ) (, ) ( ), { + <.. {. { + <. + ( ) + <. + >. {... { + Consumer surplus. Producer surplus (, ) Consumer surplus: Producer surplus:.. Consumer surplus (, ) Producer surplus Consumer surplus: Producer surplus:, Consumer surplus Producer surplus, (,,, { + + Consumer surplus:,,. Producer surplus:,,. ( (, e ) (, e ) (, ) (, ). { {
13 Answers to All Eercises Ans. Consumer surplus Producer surplus (,,, ),,,,. (a) { + (b), Consumer surplus:,, Producer surplus:,,. (a) { +, (b),,,. (a) { + π (b),. (a) + { + (b),,,. (a) {π π > > (b). (a) (b),,, { + + +, (c) The line is an asmptote to the boundar. The larger the circles, the closer the radii can be and still satisf the constraint.. True. False. + is outside the parabola.. Test a point on either side.. Answers will var. Appendi F. (page F). optimization. objective function. constraints, feasible solutions. The vertices. Minimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. Minimum at (, ):, Maimum at (, ):,. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ):. Minimum at (, ):, Maimum at (, ):, APPENDICES
14 Ans Answers to All Eercises.. (, ) (, ). (, ) Minimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ): Maimum at (, ):. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) Minimum at (, ): Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):.. (, ) (, ) (, ) Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) Minimum at (, ): Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) Minimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ): Maimum at (, ): (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):.. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ): (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) Minimum at (, ): Maimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ): Minimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ): Maimum at (, ):.. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) Minimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ): Maimum at (, ): Minimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ): Maimum at (, ):
15 Answers to All Eercises Ans. Minimum at (, ): Maimum at (, ):. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ). (a) and (b) (c) (, ) + =. (, ) (, ) The constraints do not form a closed set of points. Therefore, z = + is unbounded. (, ) = + (, ) + = (, ). (a) and (b) (c) (, ) (, ) + = (, ) = + (, ) + =. (a) and (b) (c) (, ) (, ) (, ) + = + = = + (, ). (a) and (b) (, ) + = (, ) (, ) + = (c) Maimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, ). (, ) ( ) (, ), (, ) z is maimum at an point on the line segment connecting (, ) and (, )... The feasible set is empt. (, ) (, ) (, ) The constraint is etraneous. Maimum at (, ):. (a) Four audits, ta returns (b) Maimum revenue: $,. units of model A; units of model B Maimum profit: $,. (a) Three bags of brand X, si bags of brand Y (b) Minimum cost: $. Three bags of brand X; two bags of brand Y Minimum cost: $. True. True. z = +. z = +. z = +. z = +. (a) t > (b) < t <. (a) < t < (b) t > Appendi G (page G). mathematical induction. first. arithmetic. second.. (k + )(k + ) (k + )(k + ) APPENDICES
16 Ans Answers to All Eercises. k+. k (k + )! (k + )! (k ) + (k + ) (k + ) + (k + ). Answers will var..,,.,..,. Answers will var..,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Linear.,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Neither.,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Quadratic.,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Neither.,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Quadratic.,,,,, First differences:,,,, Second differences:,,, Neither.,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Linear.,,,, First differences:,,, Second differences:,, Quadratic. a n = n n +, n. a n = n n +, n. a n = n + n. a n = n n +. (a) a n = () n (b) a n = [ + n ( k= ) k ] (c) ( ) n. (a) (b) (c) a n = n (d) Answers will var.. False. Not necessaril. False. The first differences are all the same.. False. It has n second differences.. (a) P n is true for all integers n. (b) P n is true for all integers n. (c) P, P, and P are true. (d) P n is true for an positive integer n.
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models...................... Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................. Section
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models...................... Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................. Section
CHAPTER 3 Polynomial Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
CHAPTER 2 Solving Equations and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
6.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing Algebra 2
 10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing Algebra Goal 1: Write functions in quadratic form Goal : Graph quadratic functions Goal 3: Solve quadratic equations b graphing. Quadratic Function: Eample 1:
10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Graphing Algebra Goal 1: Write functions in quadratic form Goal : Graph quadratic functions Goal 3: Solve quadratic equations b graphing. Quadratic Function: Eample 1:
Graphs of Rational Functions. 386 Chapter 7 Linear Models and Graphs of Nonlinear Models Equation of ellipse ab
 Chapter 7 Linear Models and Graphs of Nonlinear Models. Equation of ellipse or.9 7.9 7 feet 7..9 ab.9 ab a b A ab 9 ab 9 a a a a 9 a a 9 a a a b a b b a 9. The four tpes of conics are circles, parabolas,
Chapter 7 Linear Models and Graphs of Nonlinear Models. Equation of ellipse or.9 7.9 7 feet 7..9 ab.9 ab a b A ab 9 ab 9 a a a a 9 a a 9 a a a b a b b a 9. The four tpes of conics are circles, parabolas,
CHAPTER 3 Graphs and Functions
 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
CHAPTER 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
( ) ( ) SECTION 1.1, Page ( x 3) 5 = 4( x 5) = 7. x = = = x x+ 0.12(4000 x) = 432
 CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
Chapter P Prerequisites
 ch0p_p_8 /8/0 :8 PM Page Section P. Real Numbers Chapter P Prerequisites Section P. Real Numbers Quick Review P.. {,,,,, 6}. {,, 0,,,,,, 6}. {,, }. {,,, }. (a) 87.7 (b).7 6. (a) 0.6 (b) 0.0 7. ( ) -( )+
ch0p_p_8 /8/0 :8 PM Page Section P. Real Numbers Chapter P Prerequisites Section P. Real Numbers Quick Review P.. {,,,,, 6}. {,, 0,,,,,, 6}. {,, }. {,,, }. (a) 87.7 (b).7 6. (a) 0.6 (b) 0.0 7. ( ) -( )+
Chapter P Prerequisites
 Section P. Real Numbers Chapter P Prerequisites Section P. Real Numbers Quick Review P.. {,,,,, 6}. {,, 0,,,,,, 6}. {,, }. {,,, }. (a) 87.7 (b).7 6. (a) 0.6 (b) 0.0 7. ( ) -( )+ ; (.) -(.)+.7 8. ( ) +(
Section P. Real Numbers Chapter P Prerequisites Section P. Real Numbers Quick Review P.. {,,,,, 6}. {,, 0,,,,,, 6}. {,, }. {,,, }. (a) 87.7 (b).7 6. (a) 0.6 (b) 0.0 7. ( ) -( )+ ; (.) -(.)+.7 8. ( ) +(
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
Graphing Calculator Computations 2
 Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Graphing Calculator Computations A) Write the graphing calculator notation and B) Evaluate each epression. 4 1) 15 43 8 e) 15 - -4 * 3^ + 8 ^ 4/ - 1) ) 5 ) 8 3 3) 3 4 1 8 3) 7 9 4) 1 3 5 4) 5) 5 5) 6)
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 0390) Final Exam Oct 2009
 Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
Review for Intermediate Algebra (MATD 090) Final Eam Oct 009 Students are epected to know all relevant formulas, including: All special factoring formulas Equation of a circle All formulas for linear equations
( 1 3, 3 4 ) Selected Answers SECTION P.2. Quick Review P.1. Exercises P.1. Quick Review P.2. Exercises P.2 SELECTED ANSWERS 895
 44_Demana_SEANS_pp89-04 /4/06 8:00 AM Page 89 SELECTED ANSWERS 89 Selected Answers Quick Review P.. {,,, 4,, 6}. {,, }. (a) 87.7 (b) 4.7 7. ;.7 9. 0,,,, 4,, 6 Eercises P.. 4.6 (terminating)..6 (repeating).
44_Demana_SEANS_pp89-04 /4/06 8:00 AM Page 89 SELECTED ANSWERS 89 Selected Answers Quick Review P.. {,,, 4,, 6}. {,, }. (a) 87.7 (b) 4.7 7. ;.7 9. 0,,,, 4,, 6 Eercises P.. 4.6 (terminating)..6 (repeating).
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
The standard form of the equation of a circle is based on the distance formula. The distance formula, in turn, is based on the Pythagorean Theorem.
 Unit, Lesson. Deriving the Equation of a Circle The graph of an equation in and is the set of all points (, ) in a coordinate plane that satisf the equation. Some equations have graphs with precise geometric
Unit, Lesson. Deriving the Equation of a Circle The graph of an equation in and is the set of all points (, ) in a coordinate plane that satisf the equation. Some equations have graphs with precise geometric
P.4 Lines in the Plane
 28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
CHAPTER 0: Preliminary Topics
 (Exercises for Chapter 0: Preliminary Topics) E.0.1 CHAPTER 0: Preliminary Topics (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. (Calculator) means use a calculator. Otherwise, do not use a
(Exercises for Chapter 0: Preliminary Topics) E.0.1 CHAPTER 0: Preliminary Topics (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. (Calculator) means use a calculator. Otherwise, do not use a
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Practice for the Final Eam MAC 1 Sullivan Version 1 (2007) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
Practice for the Final Eam MAC 1 Sullivan Version 1 (2007) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2) between the points
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
Appendix D: Variation
 A96 Appendi D Variation Appendi D: Variation Direct Variation There are two basic types of linear models. The more general model has a y-intercept that is nonzero. y m b, b 0 The simpler model y k has
A96 Appendi D Variation Appendi D: Variation Direct Variation There are two basic types of linear models. The more general model has a y-intercept that is nonzero. y m b, b 0 The simpler model y k has
CHAPTER 8 Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
CHAPTER Quadratic Equations, Functions, and Inequalities Section. Solving Quadratic Equations: Factoring and Special Forms..................... 7 Section. Completing the Square................... 9 Section.
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
y = f(x + 4) a) Example: A repeating X by using two linear equations y = ±x. b) Example: y = f(x - 3). The translation is
 Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
For Thought. 3.1 Exercises 142 CHAPTER 3 POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. 1. False, the range of y = x 2 is [0, ).
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A) 5 B) 277 C) 126 D) 115
 MAC 1 Sullivan Practice for Chapter 2 Test (Kincade) Name Date Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2)
MAC 1 Sullivan Practice for Chapter 2 Test (Kincade) Name Date Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(p1, P2)
2.2 Equations of Lines
 660_ch0pp07668.qd 10/16/08 4:1 PM Page 96 96 CHAPTER Linear Functions and Equations. Equations of Lines Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms Find the intercepts of a line Write equations for
660_ch0pp07668.qd 10/16/08 4:1 PM Page 96 96 CHAPTER Linear Functions and Equations. Equations of Lines Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms Find the intercepts of a line Write equations for
Answer Explanations. The SAT Subject Tests. Mathematics Level 1 & 2 TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE
 The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
Mathematics Placement Examination (MPE)
 Practice Problems for Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Revised June, 011 When ou come to New Meico State Universit, ou ma be asked to take the Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Your inital placement
Practice Problems for Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Revised June, 011 When ou come to New Meico State Universit, ou ma be asked to take the Mathematics Placement Eamination (MPE) Your inital placement
Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus
 Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Copyrighted by Gabriel Tang B.Ed., B.Sc. Page 1.
 Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions -: Points and Lines Sstem of Linear Equations: - two or more linear equations on the same coordinate grid. Solution of
Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter : Linear and Quadratic Functions -: Points and Lines Sstem of Linear Equations: - two or more linear equations on the same coordinate grid. Solution of
Advanced Algebra 2 Final Review Packet KG Page 1 of Find the slope of the line passing through (3, -1) and (6, 4).
 Advanced Algebra Final Review Packet KG 0 Page of 8. Evaluate (7 ) 0 when and. 7 7. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation. 6. An awards dinner costs $ plus $ for each person making
Advanced Algebra Final Review Packet KG 0 Page of 8. Evaluate (7 ) 0 when and. 7 7. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation.. Solve the equation. 6. An awards dinner costs $ plus $ for each person making
CHAPTER 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
PART I CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Section. Lines in the Plane....................... Section. Functions........................... Section. Graphs of Functions..................... Section. Shifting,
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
Find the distance between the pair of points. 2) (7, -7) and (3, -5) A) 12 3 units B) 2 5 units C) 6 units D) 12 units B) 8 C) 63 2
 Sample Departmental Final - Math 9 Write the first five terms of the sequence whose general term is given. 1) a n = n 2 - n 0, 2,, 12, 20 B) 2,, 12, 20, 30 C) 0, 3, 8, 1, 2 D) 1,, 9, 1, 2 Find the distance
Sample Departmental Final - Math 9 Write the first five terms of the sequence whose general term is given. 1) a n = n 2 - n 0, 2,, 12, 20 B) 2,, 12, 20, 30 C) 0, 3, 8, 1, 2 D) 1,, 9, 1, 2 Find the distance
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Test 1-0312-Chap. 2.4,2.7, 3.1-3.6,4.1,.4,. Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write an inequalit statement involving the
Practice Test 1-0312-Chap. 2.4,2.7, 3.1-3.6,4.1,.4,. Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write an inequalit statement involving the
x and y, called the coordinates of the point.
 P.1 The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane (also called the rectangular coordinate system) is the plane that allows you to represent ordered pairs of real numbers by points. It is
P.1 The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane (also called the rectangular coordinate system) is the plane that allows you to represent ordered pairs of real numbers by points. It is
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
 Review Eercises for Chapter 7 Review Eercises for Chapter. (a) Vertical stretch Vertical stretch and a reflection in the -ais Vertical shift two units upward (a) Horizontal shift two units to the left.
Review Eercises for Chapter 7 Review Eercises for Chapter. (a) Vertical stretch Vertical stretch and a reflection in the -ais Vertical shift two units upward (a) Horizontal shift two units to the left.
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
N x. You should know how to decompose a rational function into partial fractions.
 Section.7 Partial Fractions Section.7 Partial Fractions N You should know how to decompose a rational function into partial fractions. D (a) If the fraction is improper, divide to obtain N D p N D (a)
Section.7 Partial Fractions Section.7 Partial Fractions N You should know how to decompose a rational function into partial fractions. D (a) If the fraction is improper, divide to obtain N D p N D (a)
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
UNIT 6 MODELING GEOMETRY Lesson 1: Deriving Equations Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: appling the Pthagorean Theorem representing horizontal and vertical distances in a coordinate plane simplifing square roots writing
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: appling the Pthagorean Theorem representing horizontal and vertical distances in a coordinate plane simplifing square roots writing
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
Unit 9: Rational Functions
 Date Period Unit 9: Rational Functions DAY TOPIC Direct, Inverse and Combined Variation Graphs of Inverse Variation Page 484 In Class 3 Rational Epressions Multipling and Dividing 4 Adding and Subtracting
Date Period Unit 9: Rational Functions DAY TOPIC Direct, Inverse and Combined Variation Graphs of Inverse Variation Page 484 In Class 3 Rational Epressions Multipling and Dividing 4 Adding and Subtracting
1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to
 SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
Test # 2 Review Sections (2.4,2.5,2.6, & ch. 3) Math 1314 Name
 Test # Review Sections (.,.,., & ch. 3) Math 131 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the equation of the line. 1) -intercept,
Test # Review Sections (.,.,., & ch. 3) Math 131 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the equation of the line. 1) -intercept,
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide
 The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root. Ans. (D) x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
Graph and Write Equations of Circles
 TEKS 9.3 a.5, A.5.B Graph and Write Equations of Circles Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas. Now You will graph and write equations of circles. Wh? So ou can model transmission ranges,
TEKS 9.3 a.5, A.5.B Graph and Write Equations of Circles Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas. Now You will graph and write equations of circles. Wh? So ou can model transmission ranges,
Chapter 2 Polynomial, Power, and Rational Functions
 Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
Area Formulas. Linear
 Math Vocabulary and Formulas Approximate Area Arithmetic Sequences Average Rate of Change Axis of Symmetry Base Behavior of the Graph Bell Curve Bi-annually(with Compound Interest) Binomials Boundary Lines
Math Vocabulary and Formulas Approximate Area Arithmetic Sequences Average Rate of Change Axis of Symmetry Base Behavior of the Graph Bell Curve Bi-annually(with Compound Interest) Binomials Boundary Lines
Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions
 Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
Answers. Chapter Warm Up. Sample answer: The graph of h is a translation. 3 units right of the parent linear function.
 Chapter. Start Thinking As the string V gets wider, the points on the string move closer to the -ais. This activit mimics a vertical shrink of a parabola... Warm Up.. Sample answer: The graph of f is a
Chapter. Start Thinking As the string V gets wider, the points on the string move closer to the -ais. This activit mimics a vertical shrink of a parabola... Warm Up.. Sample answer: The graph of f is a
6 p p } 5. x 26 x 5 x 3 5 x Product of powers property x4 y x 3 y 2 6
 Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions Copright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan. All rights reserved. Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Polnomials and Polnomial Functions. and. 4. a b
Chapter 1: Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter : Linear Equations and Functions Eercise.. 7 8+ 7+ 7 8 8+ + 7 8. + 8 8( + ) + 8 8+ 8 8 8 8 7 0 0. 8( ) ( ) 8 8 8 8 + 0 8 8 0 7. ( ) 8. 8. ( 7) ( + ) + + +. 7 7 7 7 7 7 ( ). 8 8 0 0 7. + + + 8 +
Chapter : Linear Equations and Functions Eercise.. 7 8+ 7+ 7 8 8+ + 7 8. + 8 8( + ) + 8 8+ 8 8 8 8 7 0 0. 8( ) ( ) 8 8 8 8 + 0 8 8 0 7. ( ) 8. 8. ( 7) ( + ) + + +. 7 7 7 7 7 7 ( ). 8 8 0 0 7. + + + 8 +
C H A P T E R 3 Polynomial Functions
 C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
C H A P T E R Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ 8 Section.
Lawrence High School s AP Calculus AB 2018 Summer Assignment
 s AP Calculus AB 2018 Summer Assignment To incoming AP Calculus AB students, To be best prepared for your AP Calculus AB course, you will complete this summer review assignment, which you will submit on
s AP Calculus AB 2018 Summer Assignment To incoming AP Calculus AB students, To be best prepared for your AP Calculus AB course, you will complete this summer review assignment, which you will submit on
Benchmark Test Modules 1 7
 . What is the solution of 50 = x 3?. Does each equation have at least one solution? A 8x + = 8x 4 x = 5x + C 6x + 9 = 6x + 9 D 5 x = 0 x 3. Solve x + 7= 9 x. What is the value of x? 4. A living room of
. What is the solution of 50 = x 3?. Does each equation have at least one solution? A 8x + = 8x 4 x = 5x + C 6x + 9 = 6x + 9 D 5 x = 0 x 3. Solve x + 7= 9 x. What is the value of x? 4. A living room of
Use the slope-intercept form to graph the equation. 8) 6x + y = 0
 03 Review Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution set and write it in interval notation. 1) -2(4-9) < - + 2 Use the slope-intercept form to graph the equation. 8) 6 + = 0 Objective: (2.8) Solve Linear
03 Review Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution set and write it in interval notation. 1) -2(4-9) < - + 2 Use the slope-intercept form to graph the equation. 8) 6 + = 0 Objective: (2.8) Solve Linear
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
Algebra 1 (cp) Midterm Review Name: Date: Period:
 Algebra 1 (cp) Midterm Review Name: Date: Period: Chapter 1 1. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. j 44 [1] 2. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. 24 j [2] 3. Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
Algebra 1 (cp) Midterm Review Name: Date: Period: Chapter 1 1. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. j 44 [1] 2. Evaluate the variable expression when j 4. 24 j [2] 3. Find the perimeter of the rectangle.
Precalculus Notes: Unit P Prerequisite Skills
 Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
APPENDIXES. B Coordinate Geometry and Lines C. D Trigonometry E F. G The Logarithm Defined as an Integral H Complex Numbers I
 APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
Coordinate geometry. + bx + c. Vertical asymptote. Sketch graphs of hyperbolas (including asymptotic behaviour) from the general
 A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
c) domain {x R, x 3}, range {y R}
 Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions. Quadratic functions are of the form.
 3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Quadratic Functions Completing the Square Quadratic functions are of the form. 3. It is easiest to graph quadratic functions when the are in the form using transformations.
3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Quadratic Functions Completing the Square Quadratic functions are of the form. 3. It is easiest to graph quadratic functions when the are in the form using transformations.
Equations Quadratic in Form NOT AVAILABLE FOR ELECTRONIC VIEWING. B x = 0 u = x 1 3
 SECTION.4 Equations Quadratic in Form 785 In Eercises, without solving the equation, determine the number and type of solutions... In Eercises 3 4, write a quadratic equation in standard form with the
SECTION.4 Equations Quadratic in Form 785 In Eercises, without solving the equation, determine the number and type of solutions... In Eercises 3 4, write a quadratic equation in standard form with the
Algebra 2 Semester Exam Review
 Algebra Semester Eam Review 7 Graph the numbers,,,, and 0 on a number line Identif the propert shown rs rs r when r and s Evaluate What is the value of k k when k? Simplif the epression 7 7 Solve the equation
Algebra Semester Eam Review 7 Graph the numbers,,,, and 0 on a number line Identif the propert shown rs rs r when r and s Evaluate What is the value of k k when k? Simplif the epression 7 7 Solve the equation
Divide and simplify. Assume that all variables are positive. Rationalize the denominator of the expression if necessary. pg.
 Spring 011 Final Exam Review Show all work and answers on SEPARATE PAPER The review for the final must be completed b the date of the original final exam in order to be eligible for a reassessment in the
Spring 011 Final Exam Review Show all work and answers on SEPARATE PAPER The review for the final must be completed b the date of the original final exam in order to be eligible for a reassessment in the
Unit 4 Practice Problem ANSWERS
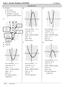 Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
Unit Practice Problem ANSWERS SECTION.1A 1) Parabola ) a. Root, Zeros b. Ais of smmetr c. Substitute = 0 into the equation to find the value of. -int 6) 7 6 1 - - - - -1-1 1 - - - - -6-7 - ) ) Maimum )
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form (general form) of a quadratic function (.1) parabola (.1) leading coefficient (.) second differences (.) vertical motion model (.3) zeros (.3) interval (.3) open interval
Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form (general form) of a quadratic function (.1) parabola (.1) leading coefficient (.) second differences (.) vertical motion model (.3) zeros (.3) interval (.3) open interval
APPLIED ALGEBRA II SEMESTER 1 EXAM ITEM SPECIFICATION SHEET & KEY
 APPLIED ALGEBRA II SEMESTER 1 EXAM ITEM SPECIFICATION SHEET & KEY Constructed Response # Objective Sllabus Objective NV State Standard 1 Graph a polnomial function. 1.1.7.1 Analze graphs of polnomial functions
APPLIED ALGEBRA II SEMESTER 1 EXAM ITEM SPECIFICATION SHEET & KEY Constructed Response # Objective Sllabus Objective NV State Standard 1 Graph a polnomial function. 1.1.7.1 Analze graphs of polnomial functions
Algebra 2 End of Term Final REVIEW
 Algebra End of Term Final REVIEW DO NOT WRITE IN TEST BOOKLET. 1. Graph. a. c. x x x x. Express as a single logarithm. Simplif, if possible. a. 5 c. 3 3. The volume V of a clinder varies jointl with the
Algebra End of Term Final REVIEW DO NOT WRITE IN TEST BOOKLET. 1. Graph. a. c. x x x x. Express as a single logarithm. Simplif, if possible. a. 5 c. 3 3. The volume V of a clinder varies jointl with the
Model Inverse Variation. p Write and graph inverse variation equations. VOCABULARY. Inverse variation. Constant of variation. Branches of a hyperbola
 12.1 Model Inverse Variation Goal p Write and graph inverse variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Inverse variation Constant of variation Hperbola Branches of a hperbola Asmptotes of a hperbola Eample
12.1 Model Inverse Variation Goal p Write and graph inverse variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Inverse variation Constant of variation Hperbola Branches of a hperbola Asmptotes of a hperbola Eample
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Section 5.4. Check Point Exercises
 Chapter : Systems of Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Eercises. = y y = Solve the first equation for y. y = + Substitute the epression + for y in the second equation and solve for. ( + )
Chapter : Systems of Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Eercises. = y y = Solve the first equation for y. y = + Substitute the epression + for y in the second equation and solve for. ( + )
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
Chapter P. Prerequisites. Slide P- 1. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Chapter 11 Exponential and Logarithmic Function
 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Function - Page 69.. Real Eponents. a m a n a mn. (a m ) n a mn. a b m a b m m, when b 0 Graphing Calculator Eploration Page 700 Check for Understanding. The quantities
Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Function - Page 69.. Real Eponents. a m a n a mn. (a m ) n a mn. a b m a b m m, when b 0 Graphing Calculator Eploration Page 700 Check for Understanding. The quantities
CHAPTER 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
CHAPTER Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs......... Section. Properties of Logarithms..................
INVESTIGATE the Math
 . Graphs of Reciprocal Functions YOU WILL NEED graph paper coloured pencils or pens graphing calculator or graphing software f() = GOAL Sketch the graphs of reciprocals of linear and quadratic functions.
. Graphs of Reciprocal Functions YOU WILL NEED graph paper coloured pencils or pens graphing calculator or graphing software f() = GOAL Sketch the graphs of reciprocals of linear and quadratic functions.
Summary and Vocabulary
 Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Summar and Vocabular The functions studied in this chapter are all based on direct and inverse variation. When k and n >, formulas of the form = k n define direct-variation functions,
Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Summar and Vocabular The functions studied in this chapter are all based on direct and inverse variation. When k and n >, formulas of the form = k n define direct-variation functions,
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
Since x + we get x² + 2x = 4, or simplifying it, x² = 4. Therefore, x² + = 4 2 = 2. Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
CHAPTER 3 : QUADRARIC FUNCTIONS MODULE CONCEPT MAP Eercise 1 3. Recognizing the quadratic functions Graphs of quadratic functions 4 Eercis
 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS MODULE 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS CHAPTER 3 : QUADRARIC FUNCTIONS MODULE 5 3.1 CONCEPT MAP Eercise 1 3. Recognizing the quadratic functions 3 3.3 Graphs of quadratic functions 4 Eercise
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS MODULE 5 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS CHAPTER 3 : QUADRARIC FUNCTIONS MODULE 5 3.1 CONCEPT MAP Eercise 1 3. Recognizing the quadratic functions 3 3.3 Graphs of quadratic functions 4 Eercise
Ordered pair: Domain: Range:
 Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space. Coordinates in Space
 0_110.qd 11//0 : PM Page 77 SECTION 11. Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space 77 -plane Section 11. -plane -plane The three-dimensional coordinate sstem Figure 11.1 Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space
0_110.qd 11//0 : PM Page 77 SECTION 11. Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space 77 -plane Section 11. -plane -plane The three-dimensional coordinate sstem Figure 11.1 Space Coordinates and Vectors in Space
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT. Dear future Calculus AB student
 AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
Algebra I. Administered May 2013 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: 9th Grade Final Test Review160 pts Class: Date: Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an
Name: 9th Grade Final Test Review160 pts Class: Date: Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the Distributive Property to write each expression as an
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
C) x m A) 260 sq. m B) 26 sq. m C) 40 sq. m D) 364 sq. m. 7) x x - (6x + 24) = -4 A) 0 B) all real numbers C) 4 D) no solution
 Sample Departmental Final - Math 46 Perform the indicated operation. Simplif if possible. 1) 7 - - 2-2 + 3 2 - A) + - 2 B) - + 4-2 C) + 4-2 D) - + - 2 Solve the problem. 2) The sum of a number and its
Sample Departmental Final - Math 46 Perform the indicated operation. Simplif if possible. 1) 7 - - 2-2 + 3 2 - A) + - 2 B) - + 4-2 C) + 4-2 D) - + - 2 Solve the problem. 2) The sum of a number and its
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
