Fermilab FERMILAB-Conf-00/339-A January 2001
|
|
|
- Garey Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fermilab FERMILAB-Conf-00/339-A January 2001 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **PUBLICATION YEAR** **EDITORS** Precision Galactic Structure Stephen Kent Fermilab, P. O. Box 500, Batavia, IL For the SDSS Collaboration Abstract. Optical and IR surveys in progress or in the planning stages will lead to substantial improvements in our picture of the Milky Way as a consequence of their providing large volumes of data with much improved photometric and positional measurements compared with existing datasets. 1. Introduction The structure of the Milky Way can be described to rst order by a canonical model that is the sum of a circularly symmetric disk (or two disks, one thick, one thin), a bulge (either an oblate spheroid or a triaxial bar), and an oblate spheroidal halo; each component hascharacteristic shape parameters, stellar populations, and kinematic properties. While the major features of each component are reasonably well known, gaps remain (e.g. the mass function for low mass stars); further, in detail the Milky Way has a more complex structure than that of the canonical model. Existing and future optical and near IR surveys such as SDSS and 2MASS will provide a wealth of new data on the Milky Way, and it would seem that it should be possible to improve our models of the Milky Way immensely. However, interpretation of the data is not necessarily straightforward, and this paper will discuss how precision Galactic Structure requires data of high quality, not just large quantity. The data sets provided by the photometric surveys typically consist of star counts as a function of position, apparent magnitude, and mulitple colors. The rst problem one encounters is that interpretation of these data requires that one model the galaxy in equal detail; a study of Galactic structure ends up being as much an exercise in modeling stellar populations as it is in modeling the structure itself. If one wishes to probe the structure of the disk at large distances from the sun, one must additionally deal with problems of confusion due to high star densities and extinction by dust. Fortunately the dust seems to follow the total gas content of the Galaxy, so maps can be contructed based on HI and CO surveys (Kent, Dame and Fazio 1991). Finally, to probe the kinematic properties of the Galaxy, one would like tocombine radial velocity and proper motion surveys to obtain 3-dimensional velocities of large samples of stars. 1
2 2 Kent STELLAR POPULATIONS u-g m l g-r k r-i k = temperature/spectral type l = metallicity/gravity m = unresolved Figure 1. Stellar locus in two SDSS colors (left) and three colors (right) 2. Stellar Populations The observable properties of a population of stars can be expressed as a multidimensional function of luminosity and color. Stars do not uniformly ll this space, but are concentrated in a narrow locus. Figure 1 shows a typical projection of the stellar locus in two SDSS colors On the right is a schematic representation of a section of the locus in a 3 dimensional color space. Newberg et al (1997, APJS, 113, 89) have shown that the locus is remarkably well behaved. If one denes principal axes k; l; m as shown, then the k axis primarily measures temperature, l measures a mix of metallicity and gravity, while the m dimension is essentially unresolved. The widths in the l and m direction are.07 mag and.03 mag respectively (FWHM). Newberg et al. have shown that it is possible to measure metallicities of F and G main sequence stars with an accuracy of 0.13 dex. In a typical magnitude-limited sample of stars, stars with the same apparent magnitude but dierent colors can a wide range of intrinsic luminosity, making it dicult analyze such samples as a single set. Often it is possible to select a subset of stars based on color alone that have a narrow range in luminosity compared with the ensemble of all stars, esaing the task of making detailed structure maps Two features that will be used in the next section include the main sequence turno, which is readily identied in any histogram of stars vs. color, and the blue horizontal branch, which can be picked out using u; g; r colors or their equivalent. Color alone cannot distinguish blue horizontal branch stars from blue stragglers, however.
3 Precision Galactic Structure 3 3. Halo Properties of the halo that are not yet well known include: 1. Radial density prole: (r). 2. Metallicity vs. radius. 3. Triaxiality: a : b : c, which may be a signature of the underlying dark matter distribution. 4. Substructure. Figure 2 is a plot from Yanny et al. (2000) of the distribution of BHB stars along the equator in early SDSS data. The most notable feature is the presence of bands of stars between 19th and 21st mag (g) in both the Northern and Southern Galactic hemispheres. The double band seen in the North (lower right part of the gure) is thought to be a single structure seen in BHB's at 19th mag and blue stragglers at 21st mag. The bands are thought to be the tidally disrupted remnants of companion galaxies of the Milky Way captured at some previous time. The masses are a few million solar masses. 4. Disk/Halo Transition Figure 3 is a color/apparent-magnitude diagram for stars from the SDSS commissioning data covering approximately 8 square degrees of sky in the South Galactic Hemisphere. This line-of-sight is close to perpendicular to the Galactic disk and thus samples primarly the old disk and the nearby halo. The near-vertical band on the left side of the gure arises from stars at the main sequence turno; the band fainter than g = 18 on the right side of the diagram arises from K and M dwarfs in the Galactic disk. The turno stars show an abrupt change in color from g, r = 0:4 to g, r = 0:25 at around g = 18. This change reects the transition from the metal-decient thick disk to the even more metal-poor halo (Chen et al. 2000). The vertical extent of the thick disk has been notoriously tricky to measure; with accurate photometry, its separation from the halo is straightforward. 5. Precision Dynamics Measurement of dynamical quantities such as the local mass density in the solar neighborhood proves to be perniciously dicult when one attempts to attains accuracies of better than a factor 2. In principle the problem is well dened: one only needs to measure the density and velocity dispersions, including their gradients, for a homogeneous subpopulation of stars. In practice, the amount of data required to do a complete job is prohibitive, and virtually all analyses introduce simplifying assumptions, at the cost of possibly introducing biases in the results (e.g., Kuijken and Gilmore 1989). Limiting factors include the lack of combined radial velocity/proper motion data for large samples of stars that are needed to construct 3-dimensional velocity ellipsoids. Future proper motion
4 4 Kent Figure 2. Distribution of horizontal branch stars on the celestial e- quator.
5 Precision Galactic Structure 5 Figure 3. g-r color vs. apparent g magnitude for a sample of stars near the SGP
6 6 Kent surveys (e.g., as might be constructed by combining scans of plates from the two Palomar Sky Surveys) could have a major impact. A classic problem is measurement of the tilt of the velocity ellipsoid for a population of stars as one moves out of the Galactic plane (Kent and De Zeeuw 1991). For stars in the plane of the disk, the velocity dispersion in the radial direction is about twice that perpendicular to the disk. If the mass of the Galaxy is spherically symmetric, then as one moves out of the plane, the major axis of the velocity distribution function rotates so as to continue pointing to the Galactic center, but if the mass is primarily in the disk, the major axis will remain parallel to the disk. A measurement of this direction gives information on the ratio of disk to (dark) halo mass. Halo stars, for example, have a characteristic velocity dispersion of 150 km s,1, so measurement of the tilt term at a height of10kpc above the plane requires accurate radial velocities combined with proper motions that have errors of order 3 milliarcseconds per year. 6. Conclusions The eld of Galactic Structure will benet greatly from the new generation of surveys, both because of their completeness and their accuracy. The problems and possibilities discussed above are just a fraction of the total that one can imagine. Full utilization of these surveys will require joint analyses of combined data sets. Acknowledgement: The Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) is a joint project of The University of Chicago, Fermilab, the Institute for Advanced Study, the Japan Participation Group, The Johns Hopkins University, the Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy, Princeton University, the United States Naval Observatory, and the University of Washington. Apache Point Observatory, site of the SDSS, is operated by the Astrophysical Research Consortium. Funding for the project has been provided by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the SDSS member institutions, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy, and Monbusho. The SDSS Web site is References Chen, B. Stoughton, C., Smith, J. A., Uomoto, A., Pier, J. R., Yanny, B., & Ivezic, Z. 2000, (in preparation) Kent, S. M., Dame, T., & Fazio, G. 1991, ApJ, 378, 131 Kent, S. M., & de Zeeuw, T. 1991, AJ, 102, 1994 Kuijken, K, &Gilmore, G. MNRAS, 239, 605 Newberg, H. J., & Yanny, B ApJS, 113, 89 Yanny, B., Newberg, H. J., Kent, S., Laurent-Muehleisen, S. A., Pier, J. R., Richards, G. T., Stoughton, C., Anderson, J. E., Annis, J., Brinkmann, J., Chen, B., Csabai, I., Doi, M., Fukugita, M., Hennessy, G. S., Ivezic, Z., Knapp, G. R., Lupton, R., Munn, J. A., Nash, T., Rockosi, C. M., Schneider, D. P., Smith, J. A., & York, D. G. 2000, ApJ, (in press)
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM. Brian Yanny Fermilab. DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug
 Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Sebastian Jester Experimental Astrophysics Group Fermilab
 The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Sebastian Jester Experimental Astrophysics Group Fermilab SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY Sloan Digital Sky Survey Goals: 1. Image ¼ of sky in 5 bands 2. Measure parameters of objects
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Sebastian Jester Experimental Astrophysics Group Fermilab SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY Sloan Digital Sky Survey Goals: 1. Image ¼ of sky in 5 bands 2. Measure parameters of objects
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future
 JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
(a) B-V 6 V. (b) B-V
 721 TOWARDS AN IMPROVED MODEL OF THE GALAXY Johan Holmberg 1, Chris Flynn 2, Lennart Lindegren 1 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-22100 Lund, Sweden 2 Tuorla Observatory, Vaisalantie 20, FI-21500 Piikkio,
721 TOWARDS AN IMPROVED MODEL OF THE GALAXY Johan Holmberg 1, Chris Flynn 2, Lennart Lindegren 1 1 Lund Observatory, Box 43, SE-22100 Lund, Sweden 2 Tuorla Observatory, Vaisalantie 20, FI-21500 Piikkio,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009](/thumbs/90/104342312.jpg) Discovery of a New, Polar-Orbiting Debris Stream in the Milky Way Stellar Halo Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, & Benjamin A. Willett 1 arxiv:0906.3291v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009 ABSTRACT We show that
Discovery of a New, Polar-Orbiting Debris Stream in the Milky Way Stellar Halo Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, & Benjamin A. Willett 1 arxiv:0906.3291v1 [astro-ph.ga] 17 Jun 2009 ABSTRACT We show that
New insights into the Sagittarius stream
 New insights into the Sagittarius stream EWASS, Turku July 8th, 213 Martin C. Smith Shanghai Astronomical Observatory http://hubble.shao.ac.cn/~msmith/ Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal(ish) Since its discovery
New insights into the Sagittarius stream EWASS, Turku July 8th, 213 Martin C. Smith Shanghai Astronomical Observatory http://hubble.shao.ac.cn/~msmith/ Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal(ish) Since its discovery
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
 Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way What kinds of stars are present in the Solar neighborhood, and in what numbers? How are they distributed spatially? How do we know? How can we measure this?
SDSS spectroscopic survey of stars
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 1057 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della SDSS spectroscopic survey of stars Ž. Ivezić 1, D. Schlegel 2, A. Uomoto 3, N. Bond 4, T. Beers 5, C. Allende Prieto 6, R. Wilhelm 7, Y. Sun Lee 5,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 77, 1057 c SAIt 2006 Memorie della SDSS spectroscopic survey of stars Ž. Ivezić 1, D. Schlegel 2, A. Uomoto 3, N. Bond 4, T. Beers 5, C. Allende Prieto 6, R. Wilhelm 7, Y. Sun Lee 5,
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo
 Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) The punch line... When looking for something, sometimes what
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) The punch line... When looking for something, sometimes what
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo
 Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) When looking for something, sometimes what you get, is not
Chasing Ghosts in the Galactic Halo L. Aguilar, A. Brown & H. Velázquez Inst. de Astronomía, UNAM (México) & Leiden Observatory (Netherlands) When looking for something, sometimes what you get, is not
AN IMPROVED PROPER-MOTION CATALOG COMBINING USNO-B AND THE SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY
 The Astronomical Journal, 127:3034 3042, 2004 May # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. AN IMPROVED PROPER-MOTION CATALOG COMBINING USNO-B AND THE SLOAN DIGITAL
The Astronomical Journal, 127:3034 3042, 2004 May # 2004. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. AN IMPROVED PROPER-MOTION CATALOG COMBINING USNO-B AND THE SLOAN DIGITAL
Mario Juric Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton
 Mapping Galactic density, metallicity and kinematics. Mario Juric Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton with Zeljko Ivezic, Nick Bond, Branimir Sesar, Robert Lupton and the SDSS Collaboration Dissecting
Mapping Galactic density, metallicity and kinematics. Mario Juric Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton with Zeljko Ivezic, Nick Bond, Branimir Sesar, Robert Lupton and the SDSS Collaboration Dissecting
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey
 The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Robert Lupton Xiaohui Fan Jim Gunn Željko Ivezić Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation Group, Johns
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Robert Lupton Xiaohui Fan Jim Gunn Željko Ivezić Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation Group, Johns
Searching for Needles in the Sloan Digital Haystack
 Searching for Needles in the Sloan Digital Haystack Robert Lupton Željko Ivezić Jim Gunn Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation
Searching for Needles in the Sloan Digital Haystack Robert Lupton Željko Ivezić Jim Gunn Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation
1. INTRODUCTION 2. SDSS OBSERVATIONS OF ASTEROIDS. The Astronomical Journal, 124: , 2002 November
 The Astronomical Journal, 124:2943 2948, 2002 November # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. COLOR CONFIRMATION OF ASTEROID FAMILIES Željko Ivezić, 1 Robert
The Astronomical Journal, 124:2943 2948, 2002 November # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. COLOR CONFIRMATION OF ASTEROID FAMILIES Željko Ivezić, 1 Robert
Exploring the Structure of the Milky Way with WFIRST
 Exploring the Structure of the Milky Way with WFIRST Heidi Jo Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Simulation: Stefan Gottlöber/AIP Image Credit: Heidi Newberg Milky Way Structure we want it all: The
Exploring the Structure of the Milky Way with WFIRST Heidi Jo Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Simulation: Stefan Gottlöber/AIP Image Credit: Heidi Newberg Milky Way Structure we want it all: The
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Aug 2001
 TRACING LUMINOUS AND DARK MATTER WITH THE SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY J. LOVEDAY 1, for the SDSS collaboration 1 Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Falmer, Brighton, BN1 9QJ, England arxiv:astro-ph/18488v1
TRACING LUMINOUS AND DARK MATTER WITH THE SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY J. LOVEDAY 1, for the SDSS collaboration 1 Astronomy Centre, University of Sussex, Falmer, Brighton, BN1 9QJ, England arxiv:astro-ph/18488v1
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
(Present and) Future Surveys for Metal-Poor Stars
 (Present and) Future Surveys for Metal-Poor Stars Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics SDSS 1 Why the Fascination
(Present and) Future Surveys for Metal-Poor Stars Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics SDSS 1 Why the Fascination
Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using Sloan Digital Sky Survey ugriz Magnitudes
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Martin Gaskell Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-1-2007 Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Martin Gaskell Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-1-2007 Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Jul 2001
 Mass Outflow in Active Galactic Nuclei: New Perspectives ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 D.M. Crenshaw, S.B. Kraemer, and I.M. George Extreme BAL Quasars from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Patrick
Mass Outflow in Active Galactic Nuclei: New Perspectives ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 D.M. Crenshaw, S.B. Kraemer, and I.M. George Extreme BAL Quasars from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Patrick
Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia
 Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Chengqun Yang Contents 1 Stellar Halo
Milky Way s Anisotropy Profile with LAMOST/SDSS and Gaia Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Chengqun Yang Contents 1 Stellar Halo
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
THE OVERDENSITY IN VIRGO, SAGITTARIUS DEBRIS, AND THE ASYMMETRIC SPHEROID
 The Astrophysical Journal, 668:221Y235, 2007 October 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE OVERDENSITY IN VIRGO, SAGITTARIUS DEBRIS, AND THE ASYMMETRIC
The Astrophysical Journal, 668:221Y235, 2007 October 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE OVERDENSITY IN VIRGO, SAGITTARIUS DEBRIS, AND THE ASYMMETRIC
The halo is specially interesting because gravitational potential becomes dominated by the dark matter halo
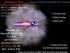 Evidence for dark matter in the Milky Way Astr 511: Galactic Astronomy Winter Quarter 2015 University of Washington Željko Ivezić The halo is specially interesting because gravitational potential becomes
Evidence for dark matter in the Milky Way Astr 511: Galactic Astronomy Winter Quarter 2015 University of Washington Željko Ivezić The halo is specially interesting because gravitational potential becomes
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
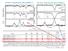 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2000) 21, 53-59 Scale Length of the Galactic Thin Disk D. Κ. Ojha, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400 005, India Received 1999 September 14; accepted
THE ASYMMETRIC THICK DISK: A STAR-COUNT AND KINEMATIC ANALYSIS. I. THE STAR COUNTS Jennifer E. Parker and Roberta M. Humphreys. and Jeffrey A.
 The Astronomical Journal, 126:1346 1361, 2003 September # 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE ASYMMETRIC THICK DISK: A STAR-COUNT AND KINEMATIC ANALYSIS.
The Astronomical Journal, 126:1346 1361, 2003 September # 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE ASYMMETRIC THICK DISK: A STAR-COUNT AND KINEMATIC ANALYSIS.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Aug 2002
 Accepted by Astronomical Journal Color Confirmation of Asteroid Families arxiv:astro-ph/0208098v1 5 Aug 2002 Željko Ivezić 1, Robert H. Lupton 1, Mario Jurić 1,2,3, Serge Tabachnik 1, Tom Quinn 4, James
Accepted by Astronomical Journal Color Confirmation of Asteroid Families arxiv:astro-ph/0208098v1 5 Aug 2002 Željko Ivezić 1, Robert H. Lupton 1, Mario Jurić 1,2,3, Serge Tabachnik 1, Tom Quinn 4, James
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Astronomy 330 Lecture 7 24 Sep 2010 Outline Review Counts: A(m), Euclidean slope, Olbers paradox Stellar Luminosity Function: Φ(M,S) Structure of the Milky Way: disk, bulge, halo Milky Way kinematics Rotation
Determining the Membership of Globular Cluster, M2 with APOGEE Data
 Determining the Membership of Globular Cluster, M2 with APOGEE Data VA-NC Alliance Summer Research Program The Leadership Alliance National Symposium July 29 th, 2017 BY: ZANIYAH DOCK What s the point?
Determining the Membership of Globular Cluster, M2 with APOGEE Data VA-NC Alliance Summer Research Program The Leadership Alliance National Symposium July 29 th, 2017 BY: ZANIYAH DOCK What s the point?
Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars
 EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
Radial Velocity Surveys. Matthias Steinmetz (AIP)
 Radial Velocity Surveys Matthias Steinmetz (AIP) The Galactic case for RV surveys Information on how galaxies form is locked in n the phase-space (position,velocities) Information is locked in stars (abundances)
Radial Velocity Surveys Matthias Steinmetz (AIP) The Galactic case for RV surveys Information on how galaxies form is locked in n the phase-space (position,velocities) Information is locked in stars (abundances)
This week at Astro Lecture 06, Sep 13, Pick up PE#6. Please turn in HW#2. HW#3 is posted
 This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk
 Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk omas Bensby Lund Observatory, Department of Astronomy and eoretical Physics Discovery of thick disks (Burstein 1979, ApJ, 234, 829) Discovery of the Galactic
Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk omas Bensby Lund Observatory, Department of Astronomy and eoretical Physics Discovery of thick disks (Burstein 1979, ApJ, 234, 829) Discovery of the Galactic
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Jun 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Jun 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 22 Jun 2007](/thumbs/80/81793328.jpg) The Overdensity in Virgo, Sagittarius Debris, and the Asymmetric Spheroid Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, Nate Cole 1, Timothy C. Beers 3, Paola Re Fiorentin 4, Donald P. Schneider 5, Ron Wilhelm 6
The Overdensity in Virgo, Sagittarius Debris, and the Asymmetric Spheroid Heidi Jo Newberg 1, Brian Yanny 2, Nate Cole 1, Timothy C. Beers 3, Paola Re Fiorentin 4, Donald P. Schneider 5, Ron Wilhelm 6
Scale height and Luminosity
 The Milky Way I suggest to consult the excellent lectures held at Saas-Fee by Gilmore, King and van der Kruit in the Book The Milky Way as a Galaxy edited by Buser & King and published by the University
The Milky Way I suggest to consult the excellent lectures held at Saas-Fee by Gilmore, King and van der Kruit in the Book The Milky Way as a Galaxy edited by Buser & King and published by the University
Absolute magnitudes for late-type dwarf stars for Sloan photometry
 Astron. Nachr./AN 32X (200X) X, XXX XXX Absolute magnitudes for late-type dwarf stars for Sloan photometry S. BILIR, S. KARAALI, and S. TUNÇEL Istanbul University Science Faculty, Department of Astronomy
Astron. Nachr./AN 32X (200X) X, XXX XXX Absolute magnitudes for late-type dwarf stars for Sloan photometry S. BILIR, S. KARAALI, and S. TUNÇEL Istanbul University Science Faculty, Department of Astronomy
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney
 ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
A New Milky Way Companion: Unusual Globular Cluster or Extreme Dwarf Satellite?
 Haverford College Haverford Scholarship Faculty Publications Astronomy 2005 A New Milky Way Companion: Unusual Globular Cluster or Extreme Dwarf Satellite? Beth Willman Haverford College, bwillman@haverford.edu
Haverford College Haverford Scholarship Faculty Publications Astronomy 2005 A New Milky Way Companion: Unusual Globular Cluster or Extreme Dwarf Satellite? Beth Willman Haverford College, bwillman@haverford.edu
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Milky Way. 20 March The Shape of the Galaxy Stellar Populations and Motions Stars as a Gas. University of Rochester
 The Milky Way The Shape of the Galaxy Stellar Populations and Motions Stars as a Gas 20 March 2018 University of Rochester The Milky Way Today s lecture: The shape of the Galaxy Stellar populations and
The Milky Way The Shape of the Galaxy Stellar Populations and Motions Stars as a Gas 20 March 2018 University of Rochester The Milky Way Today s lecture: The shape of the Galaxy Stellar populations and
SkyMapper and the Southern Sky Survey
 SkyMapper and the Southern Sky Survey Stefan Keller Mt. Stromlo Observatory Brian Schmidt, Mike Bessell and Patrick Tisserand SkyMapper 1.35m telescope with a 5.7 sq. degree field of view located at Siding
SkyMapper and the Southern Sky Survey Stefan Keller Mt. Stromlo Observatory Brian Schmidt, Mike Bessell and Patrick Tisserand SkyMapper 1.35m telescope with a 5.7 sq. degree field of view located at Siding
Today in Astronomy 142: the Milky Way
 Today in Astronomy 142: the Milky Way The shape of the Galaxy Stellar populations and motions Stars as a gas: Scale height, velocities and the mass per area of the disk Missing mass in the Solar neighborhood
Today in Astronomy 142: the Milky Way The shape of the Galaxy Stellar populations and motions Stars as a gas: Scale height, velocities and the mass per area of the disk Missing mass in the Solar neighborhood
Properties of the Milky Way stellar disks in the direction of the Draco dsph galaxy.
 The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context IAU Symposium No. 254, 2008 J. Andersen, J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. c 2008 International Astronomical Union Properties of the Milky Way stellar disks
The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context IAU Symposium No. 254, 2008 J. Andersen, J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. c 2008 International Astronomical Union Properties of the Milky Way stellar disks
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23)
 The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 May 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 May 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 May 2013](/thumbs/94/121058460.jpg) Astron. Nachr. / AN Volume, No. Issue, 1 4 (212) / DOI DOI Photo-Met: a non-parametric method for estimating stellar metallicity from photometric observations Gyöngyi Kerekes 1, István Csabai 1, László
Astron. Nachr. / AN Volume, No. Issue, 1 4 (212) / DOI DOI Photo-Met: a non-parametric method for estimating stellar metallicity from photometric observations Gyöngyi Kerekes 1, István Csabai 1, László
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Jan 2007
 THE FUTURE OF PHOTOMETRIC, SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC AND POLARIMETRIC STANDARDIZATION ASP Conference Series, Vol. 999, 27 C. Sterken A Comparison of SDSS Standard Star Catalog for Stripe 82 with Stetson s Photometric
THE FUTURE OF PHOTOMETRIC, SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC AND POLARIMETRIC STANDARDIZATION ASP Conference Series, Vol. 999, 27 C. Sterken A Comparison of SDSS Standard Star Catalog for Stripe 82 with Stetson s Photometric
Stellar Streams and Their Importance to Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Department of Physics, Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Queen s University Stellar Streams and Their Importance to Galaxy Formation and Evolution Nicholas Fantin December 9th, 2014 ABSTRACT The Sloan
Department of Physics, Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Queen s University Stellar Streams and Their Importance to Galaxy Formation and Evolution Nicholas Fantin December 9th, 2014 ABSTRACT The Sloan
Photometric Separation of Physical Properties of Stars
 Photometric Separation of Physical Properties of Stars Miranda K. Nordhaus 1, Heidi Jo Newberg 1, James P. Bagrow 2, Timothy Beers 3,Jamie Kern 1,CristinRider 4,J.AllynSmith 5, Douglas Tucker 4,BrianYanny
Photometric Separation of Physical Properties of Stars Miranda K. Nordhaus 1, Heidi Jo Newberg 1, James P. Bagrow 2, Timothy Beers 3,Jamie Kern 1,CristinRider 4,J.AllynSmith 5, Douglas Tucker 4,BrianYanny
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf
 The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8
 The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
The Milky Way Part 3 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2011 part 8 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s continue with the rotation of the Galaxy, this time from the point of view of the stars First,
Gaia & Ultra-Cool Dwarfs: a high-denition picture of the Milky Way
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 699 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Gaia & Ultra-Cool Dwarfs: a high-denition picture of the Milky Way J. Bochanski 1,2 1 Haverford College, 370 Lancaster Avenue, Haverford, PA 19041, USA
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 699 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Gaia & Ultra-Cool Dwarfs: a high-denition picture of the Milky Way J. Bochanski 1,2 1 Haverford College, 370 Lancaster Avenue, Haverford, PA 19041, USA
THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA
 143 THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA C. Reylé 1, A.C. Robin 1, M. Schultheis 1, S. Picaud 2 1 Observatoire de Besançon, CNRS UMR 6091, BP 1615, 25010 Besançon cedex, France 2 IAG/USP Departamento de
143 THE GALACTIC BULGE AS SEEN BY GAIA C. Reylé 1, A.C. Robin 1, M. Schultheis 1, S. Picaud 2 1 Observatoire de Besançon, CNRS UMR 6091, BP 1615, 25010 Besançon cedex, France 2 IAG/USP Departamento de
489 THE METALLICITY DISTRIBUTION OF LATE-TYPE DWARFS AND THE HIPPARCOS HR DIAGRAM M. Haywood, J. Palasi, A. Gomez, L. Meillon DASGAL, URA 335 du CNRS
 489 THE METALLICITY DISTRIBUTION OF LATE-TYPE DWARFS AND THE HIPPARCOS HR DIAGRAM M. Haywood, J. Palasi, A. Gomez, L. Meillon DASGAL, URA 335 du CNRS Observatoire de Paris - Meudon, France ABSTRACT The
489 THE METALLICITY DISTRIBUTION OF LATE-TYPE DWARFS AND THE HIPPARCOS HR DIAGRAM M. Haywood, J. Palasi, A. Gomez, L. Meillon DASGAL, URA 335 du CNRS Observatoire de Paris - Meudon, France ABSTRACT The
SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY: RECENT RESULTS
 SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY: RECENT RESULTS Stephen Kent Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory M.S. 127, P.O. Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510 for the SDSS Collaboration ABSTRACT The status of and recent results
SLOAN DIGITAL SKY SURVEY: RECENT RESULTS Stephen Kent Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory M.S. 127, P.O. Box 500, Batavia, IL 60510 for the SDSS Collaboration ABSTRACT The status of and recent results
Outline. c.f. Zhao et al. 2006, ChJA&A, 6, 265. Stellar Abundance and Galactic Chemical Evolution through LAMOST Spectroscopic Survey
 KIAA-CambridgeJoint Workshop on Near-Field Cosmology and Galactic Archeology ZHAO Gang National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences Dec 1-5, 2008 Beijing Outline LAMOST stellar spectroscopic
KIAA-CambridgeJoint Workshop on Near-Field Cosmology and Galactic Archeology ZHAO Gang National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences Dec 1-5, 2008 Beijing Outline LAMOST stellar spectroscopic
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7
 The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
The Milky Way Part 2 Stellar kinematics Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 7 1 Stellar motions in the MW disk Let s look at the rotation of the Galactic disk First, we need to introduce the concept of the Local
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 29 Jun 2006
 submitted to Astrophysical Journal Letters Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 A FAINT NEW MILKY WAY SATELLITE IN BOÖTES V. Belokurov 1, D. B. Zucker 1, N. W. Evans 1, M. I. Wilkinson
submitted to Astrophysical Journal Letters Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 A FAINT NEW MILKY WAY SATELLITE IN BOÖTES V. Belokurov 1, D. B. Zucker 1, N. W. Evans 1, M. I. Wilkinson
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Resolved Star Formation Surface Density and Stellar Mass Density of Galaxies in the Local Universe. Abstract
 Resolved Star Formation Surface Density and Stellar Mass Density of Galaxies in the Local Universe Abdurrouf Astronomical Institute of Tohoku University Abstract In order to understand how the stellar
Resolved Star Formation Surface Density and Stellar Mass Density of Galaxies in the Local Universe Abdurrouf Astronomical Institute of Tohoku University Abstract In order to understand how the stellar
ABSTRACT. Title: The Accuracy of the Photometric Redshift of Galaxy Clusters
 ABSTRACT Name: Elizabeth A. Holden Department: Physics Title: The Accuracy of the Photometric Redshift of Galaxy Clusters Major: Physics Degree: Master of Science Approved by: Date: Thesis Director NORTHERN
ABSTRACT Name: Elizabeth A. Holden Department: Physics Title: The Accuracy of the Photometric Redshift of Galaxy Clusters Major: Physics Degree: Master of Science Approved by: Date: Thesis Director NORTHERN
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE
 THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
Gamma-Ray Bursts from High. Velocity Neutron Stars. Tomasz Bulik and Donald Q. Lamb. Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics. University of Chicago
 Gamma-Ray Bursts from High Velocity Neutron Stars Tomasz Bulik and Donald Q. Lamb Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago 5640 South Ellis Avenue Chicago, IL 60637 We investigate
Gamma-Ray Bursts from High Velocity Neutron Stars Tomasz Bulik and Donald Q. Lamb Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics University of Chicago 5640 South Ellis Avenue Chicago, IL 60637 We investigate
Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale
 Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center Kailash C. Sahu Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center Kailash C. Sahu Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure
 Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
astro-ph/ May 94
 Invited talk at 4th DAEC meeting \Unveiling Large-Scale Structure behind the Milky-Way", ed. C. Balkowski & R. Kraan-Korteweg (San Fransisco: A.S.P.), in press. How well should the DENIS Survey probe through
Invited talk at 4th DAEC meeting \Unveiling Large-Scale Structure behind the Milky-Way", ed. C. Balkowski & R. Kraan-Korteweg (San Fransisco: A.S.P.), in press. How well should the DENIS Survey probe through
The Milky Way Tomography with SDSS. I. Stellar Number Density Distribution
 The Milky Way Tomography with SDSS. I. Stellar Number Density Distribution The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
The Milky Way Tomography with SDSS. I. Stellar Number Density Distribution The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution
 Name Pd Date BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution This lab comes from http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~zirbel/ast21/homework/hw-8.pdf (Tufts University) The word galaxy, having been used in English
Name Pd Date BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution This lab comes from http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~zirbel/ast21/homework/hw-8.pdf (Tufts University) The word galaxy, having been used in English
The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges
 1 The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges Peter Erwin 1, Alister W. Graham 2, Nicola Caon 1 (1) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna,
1 The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges Peter Erwin 1, Alister W. Graham 2, Nicola Caon 1 (1) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna,
Search for streams in thick disk and halo of the Milky Way
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Search for streams in thick disk and halo of the Milky Way To cite this article: Dian Puspita Triani and M Ikbal Arifyanto 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Search for streams in thick disk and halo of the Milky Way To cite this article: Dian Puspita Triani and M Ikbal Arifyanto 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Hubble Sequence. Environment! Globular Clusters in Milky Way. kpc
 Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Probing the history of star formation in the Local Group using the galactic fossil record
 Probing the history of star formation in the Local Group using the galactic fossil record Brian O Shea (Michigan State University) Collaborators: Tim Beers, Carolyn Peruta, Monica Derris (MSU), Jason Tumlinson
Probing the history of star formation in the Local Group using the galactic fossil record Brian O Shea (Michigan State University) Collaborators: Tim Beers, Carolyn Peruta, Monica Derris (MSU), Jason Tumlinson
Quasar Selection from Combined Radio and Optical Surveys using Neural Networks
 Quasar Selection from Combined Radio and Optical Surveys using Neural Networks Ruth Carballo and Antonio Santiago Cofiño Dpto. de Matemática Aplicada y C. Computación. Universidad de Cantabria, Avda de
Quasar Selection from Combined Radio and Optical Surveys using Neural Networks Ruth Carballo and Antonio Santiago Cofiño Dpto. de Matemática Aplicada y C. Computación. Universidad de Cantabria, Avda de
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 16 Aug 2004
 Andromeda IX: A New Dwarf Spheroidal Satellite of M31 arxiv:astro-ph/0404268v2 16 Aug 2004 Daniel B. Zucker 1,10, Alexei Y. Kniazev 1, Eric F. Bell 1, David Martínez-Delgado 1, Eva K. Grebel 1,2, Hans-Walter
Andromeda IX: A New Dwarf Spheroidal Satellite of M31 arxiv:astro-ph/0404268v2 16 Aug 2004 Daniel B. Zucker 1,10, Alexei Y. Kniazev 1, Eric F. Bell 1, David Martínez-Delgado 1, Eva K. Grebel 1,2, Hans-Walter
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007](/thumbs/79/78965434.jpg) A Pair of Boötes: A New Milky Way Satellite S. M. Walsh 1, H. Jerjen 1, B. Willman 2 arxiv:0705.1378v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007 ABSTRACT As part of preparations for a southern sky search for faint Milky
A Pair of Boötes: A New Milky Way Satellite S. M. Walsh 1, H. Jerjen 1, B. Willman 2 arxiv:0705.1378v1 [astro-ph] 10 May 2007 ABSTRACT As part of preparations for a southern sky search for faint Milky
Review of the Bulge Stellar Population And Comparison to the Nuclear Bulge
 Review of the Bulge Stellar Population And Comparison to the Nuclear Bulge David M. Nataf, Australian National University 22 July, 2016 IAU Symposium 322, 'The Multi- Messenger Astrophysics of the Galactic
Review of the Bulge Stellar Population And Comparison to the Nuclear Bulge David M. Nataf, Australian National University 22 July, 2016 IAU Symposium 322, 'The Multi- Messenger Astrophysics of the Galactic
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Hertzprung-Russel and colormagnitude. ASTR320 Wednesday January 31, 2018
 Hertzprung-Russel and colormagnitude diagrams ASTR320 Wednesday January 31, 2018 H-R diagram vs. Color- Magnitude Diagram (CMD) H-R diagram: Plot of Luminosity vs. Temperature CMD: Plot of magnitude vs.
Hertzprung-Russel and colormagnitude diagrams ASTR320 Wednesday January 31, 2018 H-R diagram vs. Color- Magnitude Diagram (CMD) H-R diagram: Plot of Luminosity vs. Temperature CMD: Plot of magnitude vs.
Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway. More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy
 Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy "What good are Mercator's North Poles and Equators Tropics, Zones, and Meridian Lines?" So the Bellman would cry, and the
Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy "What good are Mercator's North Poles and Equators Tropics, Zones, and Meridian Lines?" So the Bellman would cry, and the
Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 5. SPIRAL GALAXIES
 Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 1 : Preliminaries 6 : Dynamics I 11 : Star Formation 16 : Cosmology : Morphology 7 : Ellipticals 1 : Interactions 17 : Structure Growth 3 : Surveys 8 : Dynamics II 13
Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 1 : Preliminaries 6 : Dynamics I 11 : Star Formation 16 : Cosmology : Morphology 7 : Ellipticals 1 : Interactions 17 : Structure Growth 3 : Surveys 8 : Dynamics II 13
2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 By tracing their orbits and using our understanding of gravity, we can conclude that the object these stars are orbiting (shown here as a 5- pointed star) must have a mass over 2.5 million times greater
By tracing their orbits and using our understanding of gravity, we can conclude that the object these stars are orbiting (shown here as a 5- pointed star) must have a mass over 2.5 million times greater
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 4 Dec 2003
 Last modified June 8, 2018 The Richness-Dependent Cluster Correlation Function: Early SDSS Data arxiv:astro-ph/0307102v2 4 Dec 2003 Neta A. Bahcall 1, Feng Dong 1, Lei Hao 1, Paul Bode 1, Jim Annis 2,
Last modified June 8, 2018 The Richness-Dependent Cluster Correlation Function: Early SDSS Data arxiv:astro-ph/0307102v2 4 Dec 2003 Neta A. Bahcall 1, Feng Dong 1, Lei Hao 1, Paul Bode 1, Jim Annis 2,
MEMBERSHIP ANALYSIS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTER M92 WITH APOGEE (APACHE POINT OBSERVATORY GALACTIC EVOLUTION EXPERIMENT) DATA
 MEMBERSHIP ANALYSIS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTER M92 WITH APOGEE (APACHE POINT OBSERVATORY GALACTIC EVOLUTION EXPERIMENT) DATA TEMI OLATINWO-SPELMAN COLLEGE VA-NC ALLIANCE LEADERSHIP ALLIANCE NATIONAL SYMPOSIUM
MEMBERSHIP ANALYSIS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTER M92 WITH APOGEE (APACHE POINT OBSERVATORY GALACTIC EVOLUTION EXPERIMENT) DATA TEMI OLATINWO-SPELMAN COLLEGE VA-NC ALLIANCE LEADERSHIP ALLIANCE NATIONAL SYMPOSIUM
distribution of mass! The rotation curve of the Galaxy ! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk
 Today in Astronomy 142:! The local standard of rest the Milky Way, continued! Rotation curves and the! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk distribution
Today in Astronomy 142:! The local standard of rest the Milky Way, continued! Rotation curves and the! Stellar relaxation time! Virial theorem! Differential rotation of the stars in the disk distribution
Preparing Red-Green-Blue (RGB) Images from CCD Data
 Preparing Red-Green-Blue (RGB) Images from CCD Data Robert Lupton 1,2 Michael R. Blanton 3, George Fekete 4, David W. Hogg 3, Wil O Mullane 4, Alex Szalay 4, N. Wherry 3 1 Princeton University Observatory,
Preparing Red-Green-Blue (RGB) Images from CCD Data Robert Lupton 1,2 Michael R. Blanton 3, George Fekete 4, David W. Hogg 3, Wil O Mullane 4, Alex Szalay 4, N. Wherry 3 1 Princeton University Observatory,
AUTOMATIC MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GALAXIES. 1. Introduction
 AUTOMATIC MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GALAXIES ZSOLT FREI Institute of Physics, Eötvös University, Budapest, Pázmány P. s. 1/A, H-1117, Hungary; E-mail: frei@alcyone.elte.hu Abstract. Sky-survey projects
AUTOMATIC MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GALAXIES ZSOLT FREI Institute of Physics, Eötvös University, Budapest, Pázmány P. s. 1/A, H-1117, Hungary; E-mail: frei@alcyone.elte.hu Abstract. Sky-survey projects
The Stellar Low-Mass IMF: SDSS Observations of 15 Million M Dwarfs
 The Stellar Low-Mass IMF: SDSS Observations of 15 Million M Dwarfs John Bochanski (Penn State) Origins of Stellar Masses October 21st, 2010 Suzanne Hawley (UW), Kevin Covey (Cornell), Andrew West (BU),
The Stellar Low-Mass IMF: SDSS Observations of 15 Million M Dwarfs John Bochanski (Penn State) Origins of Stellar Masses October 21st, 2010 Suzanne Hawley (UW), Kevin Covey (Cornell), Andrew West (BU),
LAMOST Sky Survey --Site limitations and survey planning
 LAMOST Sky Survey --Site limitations and survey planning Chao Liu, Licai Deng National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Heidi Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Overview Site limitations that strictly
LAMOST Sky Survey --Site limitations and survey planning Chao Liu, Licai Deng National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Heidi Newberg Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Overview Site limitations that strictly
The Milky Way. Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location. First ideas about MW structure. Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way
 Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Overview of Gaia-ESO Survey results based on high-resolution spectra of FGK-type stars Rodolfo Smiljanic! (Gaia-ESO WG11 co-coordinator)
 Overview of Gaia-ESO Survey results based on high-resolution spectra of FGK-type stars Rodolfo Smiljanic! (Gaia-ESO WG11 co-coordinator) The Gaia-ESO Survey http://www.gaia-eso.eu Public spectroscopic
Overview of Gaia-ESO Survey results based on high-resolution spectra of FGK-type stars Rodolfo Smiljanic! (Gaia-ESO WG11 co-coordinator) The Gaia-ESO Survey http://www.gaia-eso.eu Public spectroscopic
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Galaxy Morphology. - a description of the structure of galaxies
 Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Clearly astronomical
Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Clearly astronomical
474 randomly chosen star has a radial velocity increases strongly with its proper motion because high-proper motion stars are preferentially put on ra
 473 THE KINEMATICS OF MAIN-SEQUENCE STARS FROM HIPPARCOS DATA J.J. Binney 1, W. Dehnen 1, N. Houk 2, C.A. Murray 3, M.J. Penston 4 1 Theoretical Physics, Keble Road, Oxford OX1 3NP, UK 2 Dept. of Astronomy,
473 THE KINEMATICS OF MAIN-SEQUENCE STARS FROM HIPPARCOS DATA J.J. Binney 1, W. Dehnen 1, N. Houk 2, C.A. Murray 3, M.J. Penston 4 1 Theoretical Physics, Keble Road, Oxford OX1 3NP, UK 2 Dept. of Astronomy,
