The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges
|
|
|
- Esmond Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 The Correlation Between Supermassive Black Hole Mass and the Structure of Ellipticals and Bulges Peter Erwin 1, Alister W. Graham 2, Nicola Caon 1 (1) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna, Spain (2) Department of Astronomy, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA Abstract We demonstrate a strong correlation between supermassive black hole (SMBH) mass and the global structure of ellipticals and bulges: more centrally concentrated bulges and ellipticals (higher Sérsic index n) host higher-mass black holes. This correlation is as good as that previously found between SMBH mass and central velocity dispersion, with comparable scatter. In addition, by carefully modeling the bulges of disk galaxies so that bars, inner disks, and the like do not accidentally contribute to bulge light, we find that the correlation between SMBH mass and bulge or elliptical luminosity is similarly close. 1.1 Introduction Observations now show that supermassive black holes (SMBHs; M BH M ) are probably present at the centers of most, if not all, elliptical galaxies and bulges (collectively, bulges ). More recent studies found a strong correlation between SMBH mass and the central stellar velocity dispersion σ 0 of bulges (Ferrarese & Merritt 2000; Gebhardt et al. 2000), much stronger than the previous correlation found between bulge luminosity and SMBH mass (Magorrian et al. 1998). Graham, Trujillo, & Caon (2001a) have shown that the central concentration of bulge light C re, measured within the half-light radius r e, positively correlates with σ 0 of the bulge. In addition, Graham (2002b) found that the Sérsic (1968) index n, determined from r 1/n fits to bulge light profiles, correlated extremely well with σ 0. Taken together, this suggests that there may be a correlation between SMBH mass and the global structure of bulges. Here, we demonstrate that such a correlation does indeed exist: more concentrated bulges (higher Sersic index n) have more massive SMBHs. (A preliminary version of this correlation, using C re, was presented in Graham et al. 2001b). This correlation is as strong as that between SMBH mass and stellar velocity dispersion, and has comparable scatter. By taking care in isolating and accurately modeling the bulges of disk galaxies, it is possible to make more accurate estimates of bulge luminosity. This lets us reevaluate the relation between bulge luminosity and SMBH mass and avoid scatter introduced by, e.g., assigning a fixed fraction of a disk galaxy s light to the bulge based solely on its Hubble type. The result is that the correlation between R-band 1
2 2 Fig Sample fits to galaxy profiles. Elliptical galaxies (top) are fit by a Sérsic r 1/n model; disk-galaxy profiles (bottom) are fit with a Sérsic + exponential model. All fits incorporate seeing convolution. Most profiles are from ellipse fits; the NGC 3384 profile is a major-axis cut, almost perpendicular to the bar. luminosity and SMBH mass proves to be almost as strong as the σ 0 -M BH and n-m BH correlations, with similar scatter. 1.2 Data and Analysis We searched the public archives for R-band galaxy images which were large enough to guarantee good sky subtraction (galaxy well within the field of view) and which had no central saturation. Most of the images came from the Isaac Newton Group and Hubble Space Telescope (HST) archives; we used some I-band (F814W) images from HST if there were no R-band (F702W) images available. We found useful images for 21 of the 30 galaxies with reliable SMBH measurements (Table 1 in Merrit & Ferrarese 2001). The galaxy isophotes of the reduced, skysubtracted images were fit with ellipses. We then fit the resulting major-axis surface brightness profiles with seeing-convolved Sérsic r 1/n models for the ellipticals and a combined, seeing-convolved exponential disk + Sérsic bulge model for the disk galaxies (Figure 1.1). In several cases, fitting the global profile of disk galaxies particularly when strong bars are present can badly mismeasure the bulge; special care was needed in those cases (see Bulge-Disk Decomposition, below). We excluded the inner 100 pc from the fits, to avoid contamination of the profiles by power-law cores, stellar or active nuclei, and nuclear disks.
3 1.2 Data and Analysis 3 E N arc sec arc sec Fig An example of careful bulge-disk decomposition: the isophotes inside the bar of NGC 2787 appear at first glance to be a bulge, but 2/3 of the light is actually from an exponential inner disk, distinct from the outer disk (Erwin et al. 2003). Here, R-band isophotes show the inner-disk + bulge in context, along with an HST profile from a major-axis cut (diagonal red line in middle panel) and our Sérsic + exponential fit (right panel). Black hole masses and central velocity dispersions were taken from the compilation of Merritt & Ferrarese (2001), with updated black hole masses from Gebhardt et al. (2002). We used aperture photometry from the literature to photometrically calibrate R-band profiles for 13 galaxies. Bulge absolute magnitudes for these galaxies were then calculated using the best-fit Sérsic model and surface-brightness fluctuations distances from Tonry et al. (2001) or kinematic distances from LEDA (with H 0 = 75). The central concentration C re was calculated from the Sérsic index n (Graham et al. 2001a); preliminary results using C re were presented in Graham et al. 2001b Bulge-Disk Decomposition; Distinguishing Ellipticals from S0 s Critical to determining both the structure and luminosity of bulges in disk galaxies is the proper separation of the bulge from other galaxy components: not just from the main disk, but also from bars, lenses, and inner disks. We made a careful analysis of each disk galaxy, identifying cases where global bulge-disk decomposition would not work. In some galaxies, the existence of a lens or inner disk allowed us to make exponential + bulge decompositions without using the outer disk (e.g., NGC 2787 in Figure 1.2; see Erwin et al for a detailed discussion of this galaxy, including how a global bulge-disk decomposition mismeasures the bulge). For the Milky Way, we used the perpendicular near-ir profile of Kent, Dame, & Fazio 1991 as the bulge profile. Equally important is identifying disk galaxies which have been misclassified as ellipticals, since otherwise a disk + bulge structure will be erroneously described with a single (Sérsic) model. Using information from the literature, including the kinematic study by Rix, Carollo, & Freeman (1999), along with morphological and photometric information, we found that NGC 2778 and NGC 4564 are probably S0 galaxies, despite their previous classification as ellipticals. We follow Graham (2002a) in classifying M32 as a probable stripped S0, in which the bulge resides within a remnant exponential disk/envelope.
4 4 Fig Correlations between SMBH mass M BH and: Sérsic index n (upper left), central concentration C re (upper right), central velocity dispersion (lower left), and bulge R-band luminosity (lower right). The straight lines are fits made with the bisector linear-regression routine from Akritas & Bershady (1996). We also show the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient r s and the Pearson linear correlation coefficient r. (The Spearman coefficient is more robust to outliers and does not presuppose a linear relation.) Filled circles are elliptical galaxies; open circles are bulges of disk galaxies. 1.3 Results and Discussion We find a strong correlation between the central SMBH mass M BH and its host galaxy s bulge structure, as measured by the Sérsic index n (or by central concentration C re ; Graham et al. 2001b), such that more centrally concentrated galaxies (higher n) have more massive black holes. This correlation is as good as that previously found between M BH and the central velocity dispersion, when the same galaxies are compared (Figure 1.3). In addition, by identifying S0 galaxies misclassified as ellipticals and making careful bulge-disk decompositions including the avoidance of bars and the accomodation of other components such as inner disks we find bulge luminosities for these galaxies which also correlate well with SMBH mass (McLure & Dunlop 2002 found a similary tight correlation by considering only elliptcal galaxies.). The scatter in log(m BH ) for these three relations is comparable ( dex). We thus have four closely-linked quantities M BH, central velocity dispersion, bulge luminosity, and global bulge structure which are well correlated at least over the range M BH M. Models which explain SMBH formation and growth ultimately need to address all three SMBH-bulge relations; explanations which rely
5 1.3 Results and Discussion 5 primarly on one quantity (e.g., bulge mass or central velocity dispersion) need to explain why the other quantities correlate so well. It is worth noting that using the n-m BH relation to estimate SMBH masses or to study SMBH-bulge evolution with redshift has several advantages over the σ 0 -M BH and L bulge -M BH relations. Measurements of n require only (uncalibrated) images, and are thus less expensive in terms of telescope time than the spectroscopic observations needed to determine σ 0. Measurements of n are also not sensitive to uncertainties in, e.g., distance or Galactic extinction. Finally, the existence of a clear relation between n and SMBH mass is further proof that bulges are not homologous: not all ellipticals have de Vaucouleurs (n =4) profiles, and spiral and S0 bulges cannot simply be classified as either de Vaucouleurs or exponential (n =1). References Akritas, M. G., & Bershady, M. A. 1996, ApJ, 470, 706 Erwin, P., Vega Beltrán, J. C., Graham, A. W., & Beckman, J. E. 2003, ApJ, submitted Ferrarese, L., & Merritt, D. 2000, ApJ, 539, L9 Gebhardt, K., et al. 2000, ApJ, 539, L13 Gebhardt, K., et al. 2002, ApJ, in press Graham, A. W., Trujillo, I., & Caon, N. 2001a, AJ, 122, 1707 Graham, A. W., Erwin, P., Caon, N., & Trujillo, I. 2001b, ApJ, 563, L11 Graham, A. W. 2002a ApJ, 568, L13 Graham, A. W. 2002b, MNRAS, 334, 859 Kent, S. M., Dame, T., & Fazio, G. 1991, ApJ, 378, 131 Magorrian, J., et al. 1998, AJ, 115, 2285 McLure, R. J., & Dunlop, J. S. 2002, MNRAS, 331, 795 Merritt D., & Ferrarese, L. 2001, in The Central Kpc of Starbursts and AGN: the La Palma Connection, eds. J. H. Knapen, J. E. Beckman, I. Shlosman, & T. J. Mahoney (San Francisco: ASP), 85 Rix, H.-W., Carollo, C. M., & Freeman, K. 1999, ApJ, 513, L25 Sérsic, J.-L. 1968, Atlas de Galaxias Australes (Cordoba: Obs. Astron.) Tonry, J. L., et al. 2001, ApJ, 546, 681
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory
 A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
Scaling Correlations Among Central Massive Objects and Their Host Galaxies
 Scaling Correlations Among Central Massive Objects and Their Host Galaxies I. Tosta e Melo 1, R. Capuzzo-Dolcetta 1, 1 Sapienza-Università di Roma, P.le A. Moro 5, I-00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: iara.tosta.melo@gmail.com
Scaling Correlations Among Central Massive Objects and Their Host Galaxies I. Tosta e Melo 1, R. Capuzzo-Dolcetta 1, 1 Sapienza-Università di Roma, P.le A. Moro 5, I-00185 Roma, Italy E-mail: iara.tosta.melo@gmail.com
The Redshift Evolution of Bulges and Disks of Spiral Galaxies in COSMOS
 Pathways through an Eclectic Universe ASP Conference Series, Vol. 390, c 2008 J. H. Knapen, T. J. Mahoney, and A. Vazdekis, eds. The Redshift Evolution of Bulges and Disks of Spiral Galaxies in COSMOS
Pathways through an Eclectic Universe ASP Conference Series, Vol. 390, c 2008 J. H. Knapen, T. J. Mahoney, and A. Vazdekis, eds. The Redshift Evolution of Bulges and Disks of Spiral Galaxies in COSMOS
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2013W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 GALAXIES Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2013W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 GALAXIES Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the
Thus Far. Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies. Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies
 Thus Far Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies Stars Gas Dust Black Holes Dark Matter Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies Components of Galaxies:
Thus Far Intro / Some Definitions Hubble Classification Components of Galaxies Stars Gas Dust Black Holes Dark Matter Specific Galaxy Types Star Formation Clusters of Galaxies Components of Galaxies:
Black hole demographics from the M X 2 s relation
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 320, L30±L34 (2001) Black hole demographics from the M X 2 s relation David Merritt w and Laura Ferrarese Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, New Brunswick,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 320, L30±L34 (2001) Black hole demographics from the M X 2 s relation David Merritt w and Laura Ferrarese Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers University, New Brunswick,
The growth of supermassive black holes in bulges and elliptical galaxies
 The growth of supermassive black holes in bulges and elliptical galaxies in collaboration with Guinevere Kauffmann Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Outline Work with two main observables: 1. M Bulge
The growth of supermassive black holes in bulges and elliptical galaxies in collaboration with Guinevere Kauffmann Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Outline Work with two main observables: 1. M Bulge
The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations
 The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations Nicola Bennert UCSB in collaboration with Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Jong-Hak Woo (UCLA), Alexandre Le Bris (UCSB), Matthew A. Malkan (UCLA), Matthew W. Auger (UCSB),
The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations Nicola Bennert UCSB in collaboration with Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Jong-Hak Woo (UCLA), Alexandre Le Bris (UCSB), Matthew A. Malkan (UCLA), Matthew W. Auger (UCSB),
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 10 Sep 1999
 THE INFLUENCE OF BULGE PROFILE SHAPES ON CLAIMS FOR A SCALE-FREE HUBBLE SEQUENCE FOR SPIRAL GALAXIES arxiv:astro-ph/9908131 v2 10 Sep 1999 Alister W. Graham 1 and Mercedes Prieto Instituto de Astrofísica
THE INFLUENCE OF BULGE PROFILE SHAPES ON CLAIMS FOR A SCALE-FREE HUBBLE SEQUENCE FOR SPIRAL GALAXIES arxiv:astro-ph/9908131 v2 10 Sep 1999 Alister W. Graham 1 and Mercedes Prieto Instituto de Astrofísica
Optical surface photometry of a sample of disk galaxies
 A&A 367, 405 427 (01) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:0004 c ESO 01 Astronomy & Astrophysics Optical surface photometry of a sample of galaxies II. Structural components M. Prieto 1,J.A.L.Aguerri 1,2,A.M.Varela
A&A 367, 405 427 (01) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:0004 c ESO 01 Astronomy & Astrophysics Optical surface photometry of a sample of galaxies II. Structural components M. Prieto 1,J.A.L.Aguerri 1,2,A.M.Varela
Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
 ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
THE OUTER STRUCTURE OF GALACTIC DISCS. 1 Introduction
 THE OUTER STRUCTURE OF GALACTIC DISCS J.E. Beckman 1,2,L.Gutiérrez 1,3,P.Erwin 1,4,R.Aladro 5,6,M.Pohlen 1,7, I. Trujillo 1 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias. La Laguna, Tenerife 2CSIC 3 Universidad
THE OUTER STRUCTURE OF GALACTIC DISCS J.E. Beckman 1,2,L.Gutiérrez 1,3,P.Erwin 1,4,R.Aladro 5,6,M.Pohlen 1,7, I. Trujillo 1 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias. La Laguna, Tenerife 2CSIC 3 Universidad
12.1 Elliptical Galaxies
 12.1 Elliptical Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies Old view: ellipticals are boring, simple systems Ellipticals contain no gas & dust Ellipticals are composed of old stars Ellipticals formed in a monolithic
12.1 Elliptical Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies Old view: ellipticals are boring, simple systems Ellipticals contain no gas & dust Ellipticals are composed of old stars Ellipticals formed in a monolithic
Correlation between kinematics and Hubble Sequence in disk galaxies?
 Correlation between kinematics and Hubble Sequence in disk galaxies? J.C. Vega Beltrán (jvega@pd.astro.it) and E. Pignatelli (pignatelli@pd.astro.it) Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, vicolo dell Osservatorio
Correlation between kinematics and Hubble Sequence in disk galaxies? J.C. Vega Beltrán (jvega@pd.astro.it) and E. Pignatelli (pignatelli@pd.astro.it) Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, vicolo dell Osservatorio
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy. 2. Classification
 ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Classification Morphological classification Elliptical (E) galaxies Lenticular (SO) galaxies Spiral (S) galaxies Irregular (Im) galaxies The realm of nebulae Hubble
ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Classification Morphological classification Elliptical (E) galaxies Lenticular (SO) galaxies Spiral (S) galaxies Irregular (Im) galaxies The realm of nebulae Hubble
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy. From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation
 ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation Second Lecture Reverberation Mapping experiments & virial BH masses estimations Estimating AGN black hole
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation Second Lecture Reverberation Mapping experiments & virial BH masses estimations Estimating AGN black hole
Galaxy Morphology. - a description of the structure of galaxies
 Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Clearly astronomical
Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Galaxy Morphology - a description of the structure of galaxies Clearly astronomical
The growth of supermassive black holes in pseudo-bulges, classical bulges and elliptical galaxies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (2008 Printed 30 June 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2 The growth of supermassive black holes in pseudo-bulges, classical bulges and elliptical galaxies Dimitri A. Gadotti
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 7 (2008 Printed 30 June 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2 The growth of supermassive black holes in pseudo-bulges, classical bulges and elliptical galaxies Dimitri A. Gadotti
Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope
 Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope S.N. Kemp (skemp@ll.iac.es) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La
Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope S.N. Kemp (skemp@ll.iac.es) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies
 Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
The parsec scale of. ac-ve galac-c nuclei. Mar Mezcua. International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics
 The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HST/NICMOS. II. ISOPHOTAL FITS AND NUCLEAR CUSP SLOPES 1 Marc Seigar 2. C. Marcella Carollo 3. Massimo Stiavelli. P.
 The Astronomical Journal, 123:184 194, 2002 January # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HST/NICMOS. II. ISOPHOTAL FITS AND NUCLEAR CUSP
The Astronomical Journal, 123:184 194, 2002 January # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HST/NICMOS. II. ISOPHOTAL FITS AND NUCLEAR CUSP
arxiv:astro-ph/ Jan 2000
 A NEAR INFRARED PHOTOMETRIC PLANE FOR ELLIPTICALS AND BULGES OF SPIRALS Habib G. Khosroshahi 1;2,Yogesh Wadadekar 1, Ajit Kembhavi 1 and Bahram Mobasher 3 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0001373 21 Jan 2000 We
A NEAR INFRARED PHOTOMETRIC PLANE FOR ELLIPTICALS AND BULGES OF SPIRALS Habib G. Khosroshahi 1;2,Yogesh Wadadekar 1, Ajit Kembhavi 1 and Bahram Mobasher 3 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0001373 21 Jan 2000 We
The Role of Dissipation in Spheroid Formation
 The Role of Dissipation in Spheroid Formation Philip Hopkins 4/08/08 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, John Kormendy, Tod Lauer, Suvendra Dutta, Dusan Keres, Volker Springel Ellipticals & Bulges: Formation in Mergers?
The Role of Dissipation in Spheroid Formation Philip Hopkins 4/08/08 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, John Kormendy, Tod Lauer, Suvendra Dutta, Dusan Keres, Volker Springel Ellipticals & Bulges: Formation in Mergers?
Frequency of Seyfert Type Transitions in a Sample of 102 Local Active Galactic Nuclei
 Frequency of Seyfert Type Transitions in a Sample of 102 Local Active Galactic Nuclei Jordan Runco A Thesis presented for the degree of Physics Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University
Frequency of Seyfert Type Transitions in a Sample of 102 Local Active Galactic Nuclei Jordan Runco A Thesis presented for the degree of Physics Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University
Double-Barred Galaxies
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Double-Barred Galaxies Peter Erwin 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrasse, D-85748 Garching, Germany 2 Universitäts-Sternwarte
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Double-Barred Galaxies Peter Erwin 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrasse, D-85748 Garching, Germany 2 Universitäts-Sternwarte
GAMA-SIGMA: Exploring Galaxy Structure Through Modelling
 GAMA-SIGMA: Exploring Galaxy Structure Through Modelling University of St Andrews / ICRAR (UWA) Science Goals Do galaxies form in two phases: bulge disk? Are ellipticals and bulges essentially the same?
GAMA-SIGMA: Exploring Galaxy Structure Through Modelling University of St Andrews / ICRAR (UWA) Science Goals Do galaxies form in two phases: bulge disk? Are ellipticals and bulges essentially the same?
A New Mass Estimate of the Central Supermassive Black Hole in NGC with Reverberation Mapping
 A New Mass Estimate of the Central Supermassive Black Hole in NGC 4051 with Reverberation Mapping Kelly D. Denney 1 ABSTRACT There is increasingly strong evidence from observations of the local universe
A New Mass Estimate of the Central Supermassive Black Hole in NGC 4051 with Reverberation Mapping Kelly D. Denney 1 ABSTRACT There is increasingly strong evidence from observations of the local universe
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes
 In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
Central supermassive black holes from SINFONI observations
 Central supermassive black holes from SINFONI observations R.P Saglia, MPE with R.Bender, N.Nowak, P. Erwin, J. Thomas Gas and stars in Galaxies A Multi-Wavelength 3D Perspective Garching, 10th June 2008
Central supermassive black holes from SINFONI observations R.P Saglia, MPE with R.Bender, N.Nowak, P. Erwin, J. Thomas Gas and stars in Galaxies A Multi-Wavelength 3D Perspective Garching, 10th June 2008
The Formation of Galaxy Nuclei
 The Formation of Galaxy Nuclei Anil Seth (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA University of Utah) Collaborators: Nadine Neumayer (ESO) Michele Cappellari (Oxford) Nelson Caldwell (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA), Bob Blum
The Formation of Galaxy Nuclei Anil Seth (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA University of Utah) Collaborators: Nadine Neumayer (ESO) Michele Cappellari (Oxford) Nelson Caldwell (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA), Bob Blum
The AGN / host galaxy connection in nearby galaxies.
 The AGN / host galaxy connection in nearby galaxies. A new view of the origin of the radio-quiet / radio-loud dichotomy? Alessandro Capetti & Barbara Balmaverde (Observatory of Torino Italy) The radio-quiet
The AGN / host galaxy connection in nearby galaxies. A new view of the origin of the radio-quiet / radio-loud dichotomy? Alessandro Capetti & Barbara Balmaverde (Observatory of Torino Italy) The radio-quiet
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Dec 2004
 arxiv:astro-ph/0412433v1 16 Dec 2004 The Nuclear Orbital Distribution in Galaxies as Fossil Record of Black Hole Formation from Integral-Field Spectroscopy Michele Cappellari and Richard McDermid Leiden
arxiv:astro-ph/0412433v1 16 Dec 2004 The Nuclear Orbital Distribution in Galaxies as Fossil Record of Black Hole Formation from Integral-Field Spectroscopy Michele Cappellari and Richard McDermid Leiden
Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology. Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology
 Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology Galaxy structure contains clues about galaxy formation and evolution Point
Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology Galaxy structure contains clues about galaxy formation and evolution Point
Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation
 Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation Philip Hopkins, NoviCosmo 2007 Fundamental Planes = Scaling Laws Obeyed by Galaxies vs Origin of scaling laws: Ideally, we d understand every galaxy as an individual:
Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation Philip Hopkins, NoviCosmo 2007 Fundamental Planes = Scaling Laws Obeyed by Galaxies vs Origin of scaling laws: Ideally, we d understand every galaxy as an individual:
The Classification of Galaxies
 Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Relazioni di scala tra Buchi Neri e Galassie Ospiti. Lezione 7
 Relazioni di scala tra Buchi Neri e Galassie Ospiti Lezione 7 First hints of BH-galaxy relations Kormendy & Richstone (1995) suggest the existence of a correlation between the total blue magnitude of the
Relazioni di scala tra Buchi Neri e Galassie Ospiti Lezione 7 First hints of BH-galaxy relations Kormendy & Richstone (1995) suggest the existence of a correlation between the total blue magnitude of the
Antitruncated stellar light profiles in the outer regions of STAGES spiral galaxies: bulge or disc related?
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 420, 2475 2479 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20211.x Antitruncated stellar light profiles in the outer regions of STAGES spiral galaxies: bulge or disc related? David T.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 420, 2475 2479 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20211.x Antitruncated stellar light profiles in the outer regions of STAGES spiral galaxies: bulge or disc related? David T.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Jan 1997
 Globular Clusters in the Sombrero Galaxy (NGC 4594) 1,2 arxiv:astro-ph/9701144v1 20 Jan 1997 Duncan A. Forbes Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064 and School of Physics and
Globular Clusters in the Sombrero Galaxy (NGC 4594) 1,2 arxiv:astro-ph/9701144v1 20 Jan 1997 Duncan A. Forbes Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064 and School of Physics and
Black Holes in Hibernation
 Black Holes in Hibernation Black Holes in Hibernation Only about 1 in 100 galaxies contains an active nucleus. This however does not mean that most galaxies do no have SMBHs since activity also requires
Black Holes in Hibernation Black Holes in Hibernation Only about 1 in 100 galaxies contains an active nucleus. This however does not mean that most galaxies do no have SMBHs since activity also requires
The radial distribution of supernovae in nuclear starbursts
 Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation
 Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation 1 Università Roma Tre F. Ricci 1, F. Onori, F. La Franca 1, E. Sani, M. Brusa et al. Hidden Monsters,
Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation 1 Università Roma Tre F. Ricci 1, F. Onori, F. La Franca 1, E. Sani, M. Brusa et al. Hidden Monsters,
University of Groningen. The outer disks of galaxies Pohlen, M.; Trujillo, I. Published in: The Astrophysical Journal
 University of Groningen The outer disks of galaxies Pohlen, M.; Trujillo, I. Published in: The Astrophysical Journal IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen The outer disks of galaxies Pohlen, M.; Trujillo, I. Published in: The Astrophysical Journal IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Underneath the Monster: In which galaxies are black holes growing?
 Underneath the Monster: In which galaxies are black holes growing? Mauricio Cisternas Ins:tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias, Spain + Nacho Trujillo Jürgen Fliri Johan Knapen dagalnetwork.eu ESO San:ago,
Underneath the Monster: In which galaxies are black holes growing? Mauricio Cisternas Ins:tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias, Spain + Nacho Trujillo Jürgen Fliri Johan Knapen dagalnetwork.eu ESO San:ago,
Galaxy evolution through resolved stellar populations: from the Local Group to Coma
 Galaxy evolution through resolved stellar populations: from the Local Group to Coma Isabel Pérez Kapteyn Institute & Universidad de Granada Brief summary of the science cases presented at the Local Universe
Galaxy evolution through resolved stellar populations: from the Local Group to Coma Isabel Pérez Kapteyn Institute & Universidad de Granada Brief summary of the science cases presented at the Local Universe
This figure "stiavelli.fig1a.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
 This figure "stiavelli.fig1a.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from: http://arxiv.org/ps/astro-ph/0012170v1 This figure "stiavelli.fig1b.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from: http://arxiv.org/ps/astro-ph/0012170v1
This figure "stiavelli.fig1a.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from: http://arxiv.org/ps/astro-ph/0012170v1 This figure "stiavelli.fig1b.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from: http://arxiv.org/ps/astro-ph/0012170v1
THE CENTERS OF EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE. VI. BIMODAL CENTRAL SURFACE BRIGHTNESS PROFILES 1
 The Astrophysical Journal, 664:226Y256, 2007 July 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A THE CENTERS OF EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE.
The Astrophysical Journal, 664:226Y256, 2007 July 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A THE CENTERS OF EARLY-TYPE GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE.
TEMA 3. Host Galaxies & Environment
 TEMA 3. Host Galaxies & Environment AGN Dr. Juan Pablo Torres-Papaqui Departamento de Astronomía Universidad de Guanajuato DA-UG (México) papaqui@astro.ugto.mx División de Ciencias Naturales y Exactas,
TEMA 3. Host Galaxies & Environment AGN Dr. Juan Pablo Torres-Papaqui Departamento de Astronomía Universidad de Guanajuato DA-UG (México) papaqui@astro.ugto.mx División de Ciencias Naturales y Exactas,
Gas and Stellar Dynamical Black Hole Mass Measurements:
 Gas and Stellar Dynamical Black Hole Mass Measurements: Revisiting M84 and a Consistency Test with NGC 3998 Jonelle Walsh (UC Irvine/UT Austin) Aaron Barth (UC Irvine) Remco van den Bosch (MPIA) Marc Sarzi
Gas and Stellar Dynamical Black Hole Mass Measurements: Revisiting M84 and a Consistency Test with NGC 3998 Jonelle Walsh (UC Irvine/UT Austin) Aaron Barth (UC Irvine) Remco van den Bosch (MPIA) Marc Sarzi
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Image decomposition of barred galaxies and AGN hosts
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 384, 40 439 (008) doi:0./j.365-966.007.73.x Image decomposition of barred galaxies and AGN hosts Dimitri Alexei Gadotti Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 384, 40 439 (008) doi:0./j.365-966.007.73.x Image decomposition of barred galaxies and AGN hosts Dimitri Alexei Gadotti Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.,
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE BLACK HOLE -BULGE MASS CORRELATION? By Curtis McCully
 WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE BLACK HOLE -BULGE MASS CORRELATION? By Curtis McCully OUTLINE What is the Black hole-bulge mass correlation Observations Possible Theoretical Explanations BH - BULGE MASS CORRELATION
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE BLACK HOLE -BULGE MASS CORRELATION? By Curtis McCully OUTLINE What is the Black hole-bulge mass correlation Observations Possible Theoretical Explanations BH - BULGE MASS CORRELATION
Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Galaxies
 Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Galaxies Luis C. Ho ( 何子山 ) The Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science Ho 2008, ARA&A Nuclear Activity in Nearby Galaxies Kormendy &
Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Galaxies Luis C. Ho ( 何子山 ) The Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science Ho 2008, ARA&A Nuclear Activity in Nearby Galaxies Kormendy &
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
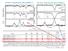 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Feb 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Feb 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Feb 2010](/thumbs/88/117192372.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 30 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Photometric scaling relations of lenticular and spiral galaxies arxiv:1002.4370v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Feb 2010
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 30 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Photometric scaling relations of lenticular and spiral galaxies arxiv:1002.4370v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Feb 2010
A triple nucleus in the brightest cluster galaxy in Abell 193
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 44, 0 4 (00) A triple nucleus in the brightest cluster galaxy in Abell 9 Marc S. Seigar, Paul D. Lynam and Nicole E. Chorney, Joint Astronomy Centre, 660 N. A ohōkū Place, Hilo,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 44, 0 4 (00) A triple nucleus in the brightest cluster galaxy in Abell 9 Marc S. Seigar, Paul D. Lynam and Nicole E. Chorney, Joint Astronomy Centre, 660 N. A ohōkū Place, Hilo,
GLOBAL PROPERTIES OF THE GLOBULAR CLUSTER SYSTEMS OF FOUR SPIRAL GALAXIES
 The Astronomical Journal, 134:1403 1418, 2007 October # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. GLOBAL PROPERTIES OF THE GLOBULAR CLUSTER SYSTEMS OF FOUR SPIRAL
The Astronomical Journal, 134:1403 1418, 2007 October # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. GLOBAL PROPERTIES OF THE GLOBULAR CLUSTER SYSTEMS OF FOUR SPIRAL
Module 3: Astronomy The Universe Topic 2 Content: The Milky Way Galaxy Presentation Notes
 On a clear night, you can go outside and view the Moon and the stars scattered throughout the night sky. At times, you can also see neighboring planets. When you look at the sky and these objects, almost
On a clear night, you can go outside and view the Moon and the stars scattered throughout the night sky. At times, you can also see neighboring planets. When you look at the sky and these objects, almost
The Milky Way nuclear star cluster beyond 1 pc
 The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 303, 2013 c International Astronomical Union 2014 L. O. Sjouwerman, C. C. Lang & J. Ott doi:10.1017/s1743921314000611
The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 303, 2013 c International Astronomical Union 2014 L. O. Sjouwerman, C. C. Lang & J. Ott doi:10.1017/s1743921314000611
AUTOMATIC MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GALAXIES. 1. Introduction
 AUTOMATIC MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GALAXIES ZSOLT FREI Institute of Physics, Eötvös University, Budapest, Pázmány P. s. 1/A, H-1117, Hungary; E-mail: frei@alcyone.elte.hu Abstract. Sky-survey projects
AUTOMATIC MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF GALAXIES ZSOLT FREI Institute of Physics, Eötvös University, Budapest, Pázmány P. s. 1/A, H-1117, Hungary; E-mail: frei@alcyone.elte.hu Abstract. Sky-survey projects
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 25 Apr 2005
 Structural Parameters of Dwarf Galaxies in the Coma Cluster: On the Origin of ds0 Galaxies. J. A. L. Aguerri Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, C/ Vía Láctea s/n, 38205 La Laguna, Spain arxiv:astro-ph/0504549v1
Structural Parameters of Dwarf Galaxies in the Coma Cluster: On the Origin of ds0 Galaxies. J. A. L. Aguerri Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, C/ Vía Láctea s/n, 38205 La Laguna, Spain arxiv:astro-ph/0504549v1
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Oct 2018](/thumbs/89/98754765.jpg) Draft version October 12, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 Black Hole Mass Scaling Relations for Spiral Galaxies. II. M BH M,tot and M BH M,disk Benjamin L. Davis, 1 Alister W. Graham,
Draft version October 12, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 Black Hole Mass Scaling Relations for Spiral Galaxies. II. M BH M,tot and M BH M,disk Benjamin L. Davis, 1 Alister W. Graham,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Sep 2006
 Stars and Gas in the Inner Parts of Galaxies seen in SAURON Integral Field Observations R.F. Peletier a, K. Fathi a, arxiv:astro-ph/0609551v1 19 Sep 2006 a Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of
Stars and Gas in the Inner Parts of Galaxies seen in SAURON Integral Field Observations R.F. Peletier a, K. Fathi a, arxiv:astro-ph/0609551v1 19 Sep 2006 a Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of
FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera
 FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera In this presentation the different theories that can explain the formation of Supermassive Black Holes (SMBH) are presented. Before focus on
FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera In this presentation the different theories that can explain the formation of Supermassive Black Holes (SMBH) are presented. Before focus on
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SEPTEMBER 1996, PAGE 557 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 118, (1996)
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SEPTEMBER 1996, PAGE 557 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 118, 557-573 (1996) Near-infrared and optical broadband surface photometry of 86 face-on disk dominated
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS SEPTEMBER 1996, PAGE 557 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 118, 557-573 (1996) Near-infrared and optical broadband surface photometry of 86 face-on disk dominated
ASTRO 310: Galac/c & Extragalac/c Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney. Class 17 Mar 30, 2016 Starlight Distribu/ons in Disk Galaxies
 ASTRO 310: Galac/c & Extragalac/c Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 17 Mar 30, 2016 Starlight Distribu/ons in Disk Galaxies reminder no class next Monday, April 3!! 3 Color op/cal image of spiral galaxy
ASTRO 310: Galac/c & Extragalac/c Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 17 Mar 30, 2016 Starlight Distribu/ons in Disk Galaxies reminder no class next Monday, April 3!! 3 Color op/cal image of spiral galaxy
DYNAMICAL MODELS OF ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES IN z = 0.5 CLUSTERS. II. MASS-TO-LIGHT RATIO EVOLUTION WITHOUT FUNDAMENTAL PLANE ASSUMPTIONS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 668:756Y771, 2007 October 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DYNAMICAL MODELS OF ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES IN z = 0.5 CLUSTERS. II.
The Astrophysical Journal, 668:756Y771, 2007 October 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. DYNAMICAL MODELS OF ELLIPTICAL GALAXIES IN z = 0.5 CLUSTERS. II.
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 8 Apr 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 8 Apr 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 8 Apr 2013](/thumbs/91/106490569.jpg) Draft version April 9, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 A SPITZER STUDY OF PSEUDOBULGES IN S0 GALAXIES : SECULAR EVOLUTION OF DISKS Kaustubh Vaghmare 1, Sudhanshu Barway 2
Draft version April 9, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 A SPITZER STUDY OF PSEUDOBULGES IN S0 GALAXIES : SECULAR EVOLUTION OF DISKS Kaustubh Vaghmare 1, Sudhanshu Barway 2
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared
 Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses. E. Pian, R. Falomo, A.
 Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses E. Pian, R. Falomo, A. Treves 1 Outline Extra Background Introduction Sample Selection Data Analysis
Hubble Space Telescope ultraviolet spectroscopy of blazars: emission lines properties and black hole masses E. Pian, R. Falomo, A. Treves 1 Outline Extra Background Introduction Sample Selection Data Analysis
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics
 Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics Claire Max Anne Medling Mark Ammons UC Santa Cruz Ric Davies Hauke Engel MPE-Garching Image of NGC 6240: Bush et al.
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics Claire Max Anne Medling Mark Ammons UC Santa Cruz Ric Davies Hauke Engel MPE-Garching Image of NGC 6240: Bush et al.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 27 May 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 27 May 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 27 May 2008](/thumbs/94/118298853.jpg) SUBMITTED TO APJ Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 08/13/06 arxiv:0805.4206v1 [astro-ph] 27 May 2008 THE STRUCTURE OF CLASSICAL BULGES AND PSEUDOBULGES: THE LINK BETWEEN PSEUDOBULGES AND
SUBMITTED TO APJ Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 08/13/06 arxiv:0805.4206v1 [astro-ph] 27 May 2008 THE STRUCTURE OF CLASSICAL BULGES AND PSEUDOBULGES: THE LINK BETWEEN PSEUDOBULGES AND
Lecture 30. The Galactic Center
 Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS IN 228 SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE
 Inter-Departmental Science Workshop Aranjuez, Spain, 20 October 2013 NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS IN 228 SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE Iskren Georgiev International Research Fellow ESTEC, Noordwijk, Netherlands
Inter-Departmental Science Workshop Aranjuez, Spain, 20 October 2013 NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS IN 228 SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE Iskren Georgiev International Research Fellow ESTEC, Noordwijk, Netherlands
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Jan 2002
 The Central kpc of Starbursts and AGN ASP Conference Series, Vol. xxx, 2001 J. H. Knapen, J. E. Beckman, I. Shlosman, and T. J. Mahoney Molecular Gas in The Central Kpc of Starbursts and AGN Shardha Jogee
The Central kpc of Starbursts and AGN ASP Conference Series, Vol. xxx, 2001 J. H. Knapen, J. E. Beckman, I. Shlosman, and T. J. Mahoney Molecular Gas in The Central Kpc of Starbursts and AGN Shardha Jogee
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Mar 2001
 A MORPHOLOGICAL-TYPE DEPENDENCE IN THE µ 0 log h PLANE OF SPIRAL GALAXY DISKS arxiv:astro-ph/0103405v1 24 Mar 2001 Alister W. Graham Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna, E-38200, Tenerife,
A MORPHOLOGICAL-TYPE DEPENDENCE IN THE µ 0 log h PLANE OF SPIRAL GALAXY DISKS arxiv:astro-ph/0103405v1 24 Mar 2001 Alister W. Graham Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, La Laguna, E-38200, Tenerife,
Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 5. SPIRAL GALAXIES
 Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 1 : Preliminaries 6 : Dynamics I 11 : Star Formation 16 : Cosmology : Morphology 7 : Ellipticals 1 : Interactions 17 : Structure Growth 3 : Surveys 8 : Dynamics II 13
Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 1 : Preliminaries 6 : Dynamics I 11 : Star Formation 16 : Cosmology : Morphology 7 : Ellipticals 1 : Interactions 17 : Structure Growth 3 : Surveys 8 : Dynamics II 13
Galaxy photometry. The surface brightness of a galaxy I(x) is the amount of light on the sky at a particular point x on the image.
 Galaxy photometry The surface brightness of a galaxy I(x) is the amount of light on the sky at a particular point x on the image. A small patch of side D in a galaxy located at a distance d, will subtend
Galaxy photometry The surface brightness of a galaxy I(x) is the amount of light on the sky at a particular point x on the image. A small patch of side D in a galaxy located at a distance d, will subtend
Galaxies. Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations
 Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
The nature of late-type spiral galaxies: structural parameters, optical and near-infrared colour profiles and dust extinction
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 1669 1694 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14658.x The nature of late-type spiral galaxies: structural parameters, optical and near-infrared colour profiles and dust extinction
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 1669 1694 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.14658.x The nature of late-type spiral galaxies: structural parameters, optical and near-infrared colour profiles and dust extinction
The supermassive black hole in NGC 4486a detected with SINFONI at the Very Large Telescope
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 379, 99 94 (7) doi:./j.365-966.7.949.x The supermassive black hole in NGC 4486a detected with SINFONI at the Very Large Telescope N. Nowak, R. P. Saglia, J. Thomas, R. Bender,,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 379, 99 94 (7) doi:./j.365-966.7.949.x The supermassive black hole in NGC 4486a detected with SINFONI at the Very Large Telescope N. Nowak, R. P. Saglia, J. Thomas, R. Bender,,
Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations
 Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations Vardha Nicola Bennert Assistant Professor California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo in collaboration with Tommaso Treu, Chelsea E. Harris
Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations Vardha Nicola Bennert Assistant Professor California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo in collaboration with Tommaso Treu, Chelsea E. Harris
On the Role of Minor Galaxy Mergers in the. Formation of Active Galactic Nuclei
 On the Role of Minor Galaxy Mergers in the Formation of Active Galactic Nuclei Michael R. Corbin Steward Observatory The University of Arizona Tucson, AZ, 85721; mcorbin@as.arizona.edu 2 ABSTRACT The large-scale
On the Role of Minor Galaxy Mergers in the Formation of Active Galactic Nuclei Michael R. Corbin Steward Observatory The University of Arizona Tucson, AZ, 85721; mcorbin@as.arizona.edu 2 ABSTRACT The large-scale
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 14 Mar 1996
 A Counter-rotating Bulge in the Sb Galaxy NGC 7331 F. Prada 1 C.M. Gutiérrez 1,2 arxiv:astro-ph/9602142v2 14 Mar 1996 R.F. Peletier 3,1 and C. D. McKeith 4 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, 38200
A Counter-rotating Bulge in the Sb Galaxy NGC 7331 F. Prada 1 C.M. Gutiérrez 1,2 arxiv:astro-ph/9602142v2 14 Mar 1996 R.F. Peletier 3,1 and C. D. McKeith 4 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, 38200
The nature of late-type spiral galaxies Ganda, Katia; Peletier, Reynier; Balcells, Marc; Falcón-Barroso, Jesús
 University of Groningen The nature of late-type spiral galaxies Ganda, Katia; Peletier, Reynier; Balcells, Marc; Falcón-Barroso, Jesús Published in: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society DOI:
University of Groningen The nature of late-type spiral galaxies Ganda, Katia; Peletier, Reynier; Balcells, Marc; Falcón-Barroso, Jesús Published in: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society DOI:
On the morphology of sigma-drop galaxies ABSTRACT
 A&A 485, 695 705 (2008) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20079161 c ESO 2008 Astronomy & Astrophysics On the morphology of sigma-drop galaxies S. Comerón 1,J.H.Knapen 1, and J. E. Beckman 1,2 1 Instituto de Astrofísica
A&A 485, 695 705 (2008) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20079161 c ESO 2008 Astronomy & Astrophysics On the morphology of sigma-drop galaxies S. Comerón 1,J.H.Knapen 1, and J. E. Beckman 1,2 1 Instituto de Astrofísica
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 2 May 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 2 May 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 2 May 2008](/thumbs/85/91344090.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. sigma v10 June 3, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) On the morphology of sigma-drop galaxies S. Comerón 1, J. H. Knapen 1, and J. E. Beckman 1,2 arxiv:0805.0222v1
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. sigma v10 June 3, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) On the morphology of sigma-drop galaxies S. Comerón 1, J. H. Knapen 1, and J. E. Beckman 1,2 arxiv:0805.0222v1
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs): A type of AGNs: Quasars. Whatever is powering these QSO s must be very small!!
 Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs): Galaxies with lots of activity AST 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Some galaxies at high redshift (large lookback times) have extremely active centers More than 1000
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGNs): Galaxies with lots of activity AST 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Some galaxies at high redshift (large lookback times) have extremely active centers More than 1000
GALAXIES. I. Morphologies and classification 2. Successes of Hubble scheme 3. Problems with Hubble scheme 4. Galaxies in other wavelengths
 GALAXIES I. Morphologies and classification 2. Successes of Hubble scheme 3. Problems with Hubble scheme 4. Galaxies in other wavelengths 5. Properties of spirals and Irregulars. Hubble tuning-fork diagram.
GALAXIES I. Morphologies and classification 2. Successes of Hubble scheme 3. Problems with Hubble scheme 4. Galaxies in other wavelengths 5. Properties of spirals and Irregulars. Hubble tuning-fork diagram.
The Milky Way. Finding the Center. Milky Way Composite Photo. Finding the Center. Milky Way : A band of and a. Milky Way
 The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
KINEMATIC MEASUREMENTS OF GAS AND STARS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES. 1 Basic galactic kinematics: observational method
 KINEMATIC MEASUREMENTS OF GAS AND STARS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES JOHN E. BECKMAN Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La Laguna, SPAIN Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, SPAIN ALMUDENA
KINEMATIC MEASUREMENTS OF GAS AND STARS IN SPIRAL GALAXIES JOHN E. BECKMAN Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La Laguna, SPAIN Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, SPAIN ALMUDENA
A PRELIMINARY CLASSIFICATION SCHEME FOR THE CENTRAL REGIONS OF LATE-TYPE GALAXIES
 A PRELIMINARY CLASSIFICATION SCHEME FOR THE CENTRAL REGIONS OF LATE-TYPE GALAXIES SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH* Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, National Research Council 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria, B.C.,
A PRELIMINARY CLASSIFICATION SCHEME FOR THE CENTRAL REGIONS OF LATE-TYPE GALAXIES SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH* Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, National Research Council 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria, B.C.,
Galaxy Luminosity Function. Galaxy Luminosity Function. Schechter Function. Schechter Function by environment. Schechter (1976) found that
 Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
