An Oceanographic Perspective on Climate State Estimation Boulder, June 2010 Carl Wunsch, MIT
|
|
|
- Alaina Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Oceanographic Perspective on Climate State Estimation Boulder, June 2010 Carl Wunsch, MIT
2 This work dates back to about 1992, when it became clear that physical oceanographers would, for the first time, have data sets near-global in scope and continuous in time (the World Ocean Circulation Experiment, WOCE). The question was how to use these new data? Data assimilation is a very sophisticated collection of numerical techniques developed primarily for prediction in the context of numerical weather prediction (NWP). Prediction and state estimation (or smoothing or interpolation) are very different problems and many methods useful for weather forecasting are not suitable for state estimation.
3 Recall the elementary problem of interpolating noisy data with a polynomial: This is too simple to be more than a metaphor---but worth remembering.
4 Let us examine the meteorological reanalyses for a bit of context. Generally speaking, these are based upon the weather forecast systems, but with the model and assimilation methodology held fixed over multidecadal intervals. They have been widely used to study the climate system for various trends. (I am indebted to David Bromwich, Ohio State, for the comparisons that follow.)
5 arrival of polar orbiters Mean annual Antarctic net precipitation (P-E) from ERA-40 reanalysis for various elevation areas. [Bromwich et al. 2007, adapted from Van de Berg et al. 2005] Spurious trends in the high latitudes resulting from changes in the observing system, especially the assimilation of satellite observations in the late 1970s. Jump in Antarctic P-E in , particularly marked at high elevations.
6 A related scenario in the 1990s-2000s? Dramatic increase in the amount and quality of satellite observations assimilated into the reanalyses (or available for assimilation). Number of observations assimilated in ERA-Interim [Dee et al., 2009, ECMWF Newsletter (119)]
7 Mean annual precipitation (P) mm y -1
8 Mean annual evaporation (E) mm y -1
9 linear trends in annual P-E (D. Bromwich, Byrd Polar Research Center, Ohio) mm y -1 decade -1
10 mm y -1 PRECIPITATION (P) Annual P, E and P-E over the grounded Antarctic Ice Sheet mm y -1 NET PRECIPITATION (P-E) mm y -1 EVAPORATION (E)
11 Precipitation and PW changes over the Southern Ocean Zonal means of precipitation and total precipitable water (PW) are examined for different latitude bands. 40 S 50 S 60 S Additional datasets are included for latitudes 40 S-60 S: Precipitation estimates from: Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) Climate Prediction Center Merged Analysis of Precipitation (CMAP) PW estimates from SSM/I (over ice-free ocean only)
12 Spurious trends in MERRA precipitation 50 S-60 S PRECIPITATION: MERRA minus ERA-Interim mm day -1 AMSU-B AMSU-A The figure shows the 2-month running average difference between forecast daily precipitation from MERRA and from ERA-Int, spatially averaged over the 50 S-60 S latitude band.
13 linear trends in annual P (Southern Hemisphere) mm y -1 decade -1
14 D. Bromwich, private comm Zonal Winds
15 Air-sea flux imbalances in analyses & reanalyses are a major problem when used as boundary conditions on the ocean circulation. Annual mean imbalances: Similar heat budget issues The reanalyses are derived from weather forecast models in which global water/heat balances are of no concern. What is the runoff rate? How much does it vary? How much is climatological ice melt? Difficult to mode the ocean state.
16 None of this would be of serious zero order concern if the estimates were accompanied by error bars.
17 Estimation (interpolation) vs. forecasting (extrapolation) Atmosphere Relatively abundant data sampling of the 3-dim. atmosphere Most DA applications target the problem of optimal forecasting find initial conditions which produce best possible forecast; dynamical consistency or property conservation *NOT* required Ocean Very sparse data sampling of the 3-dim. ocean Understanding past & present state of the ocean is a major issue all by itself, the forecasting dependent upon it use observations in an optimal way to extract max. information about oceanic changes dynamic consistency & property conservation *ESSENTIAL* over climate time scales jumps are unphysical
18 Importance of a physically consistent solution Atmospheric reanalyses contain large air-sea flux imbalances. For example, the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis has an ocean freshwater flux imbalance of 6.2 cm/yr, about 20 times larger than the observed 3 mm/yr sea level rise. They also contain discontinuities during assimilation updates. For example, standard deviation of NCEP surface pressure analysis shows that 24% of the atmosphere s mass change is physically unaccounted for (I. Fukumori, JPL). Change over 6-hours Data Increment mass conservation? mbar Contrary to atmospheric data assimilation, whose primary objective is NWP, need climate solutions satisfy model equations exactly, for example, conserving tracer properties.
19 Example tracer application: CO2 Sea Air Flux Estimate of CO2 flux during El Niño (mol/m2/yr) based on Kalman filter solution Observed estimate of CO 2 flux during El Niño (mol/m 2 /yr) Estimate based on smoothed solution McKinley, 2002 Feely et al., 1999
20 Can one predict from these solutions? IPCC AR4 scenarios for Arctic September ice cover 100 years into the future. (I. Eisenman, J. Wettlaufer, 2007) Models were all tuned to recent conditions. Climate models now contain nearly 1 million lines of computer code and have been assembled over 50 years by hundreds of individuals.
21 ECCO Origins and Goals (1992+) Origin in WOCE: first global data sets. Exploit, particularly, the satellite data (altimetry, scatterometry) plus all of the in situ observations. Directed at global climate scales (decadal+)---contrast to short-term, non-globally balanced estimates Initially, intended as a demonstration---no one had ever done anything like this in the ocean before. Computers of 1992 were not really adequate. Remains unique
22 Most so-called data assimilation efforts are based upon the experience with numerical weather forecasting. ECCO deliberately did not follow that route for several reasons: State estimation and prediction are very different goals. (Think of prediction as extrapolation, state estimation as interpolation.) NWP (as used in the reanalyses ) does not conserve global water, energy, momentum, etc. These are essential for understanding climate change. NWP methods introduce non-physical state jumps at the 6-hourly analysis times. These render impossible the calculation of budgets (freshwater, heat) essential to understanding climate. NWP methods, more generally, discard information about prior times available from formal future observations.
23 Compared to data assimilation, the ECCO choices lead to a much higher computational load as well as the necessity for a major effort to assign error estimates to the huge data sets. Our conclusion was that this price had to be paid in order to understand the climate system.
24 Ocean State Estimation Synthesize all (diverse/disparate) types of observations, taking optimal advantage of sparse observations, with best-known dynamics/physics, into dynamically consistent, time-evolving estimate, obeying known conservation laws, to enable time-varying budget calculations, and diagnostic of un-observable quantities (e.g., MOC) with quantification of posterior uncertainties
25 ECCO-GODAE estimates are from ordinary least-squares solutions obtained by adjoining the model to a model-data misfit function using an ancient mathematical trick: Lagrange multipliers: misfit to Initial conditions misfit to the observations adjustable parameters (controls) includes model error the model and seek the stationary point. vectors of Lagrange multipliers, AKA, the adjoint or dual solution In electrical engineering, called the Pontryagin Minimum Principle, in meteorology 4DVAR, in oceanography the adjoint method,. Just leastconstrained squares. Very flexible: can cope with any constraint (e.g. averages over any time and/or space span) that can be written down in ths form. R,Q can have arbitrarily complex spatial structures (if known).
26 Two major difficulties: the size of the problem, and the need to understand errors in everything. Finding the stationary point(s) of J is a (numerical) engineering problem. Not easy, but the principle is not in doubt. The Kalman filter is not a method for finding that point (was invented by Kalman to solve a prediction problem and fails to use any data in the formal future) Our particular approach has been to use automatic/algorithmic differentiation (AD) software tools. Solved by iteration relying upon knowledge of the partial derivatives of J with respect to x(t), u(t), using. Will skip all that here. After (near) optimization, the solution analyzed is from the freely running gcm---thus it satisfies the known model equations and can be used e.g., to calculate energy or heat or mass budgets.
27
28 Southern Elephant Seals as Oceanographic Samplers (SEaOS) CTD-type observations from seals in SO Sea Mammal Research Unit, University St. Andrews, UK, British Antarctic Survey Courtesy M. Meredith No animals were harmed in the making of this Powerpoint presentation
29 In round numbers, the ECCO-GODAE effort at MIT is using 2 billion observations over 16 years (including meteorological estimates), with unknowns (both state vector and control vector values). It does work (see many published papers Computationally painful.
30 EOF 1 Temperature 58% of var. Upper ocean warming trend. Warming is an artifact of the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Upper ocean observations are inadequate to preclude it---despite all the measurements!
31 Works also for the paleo problem: Example (preliminary) results from PhD thesis of Holly Dail: the ocean circulation during the last glacial maximum (LGM) Dail presentation:
32 Some Time Scales of the Climate System doubling time human population Inadequate understanding is part of the error budget.
33 How to characterize model error? Resolution issues loom largest. 1deg. mixed layer depth 1/9deg 1/54 deg. Lévy et al., Ocean Mod., 2010 meridional heat transport mean density along 72W
34 Time mean sea surface height,0.1deg,0.28deg models Smith, Maltrud, Bryan, Hecht, 2000, JPO An old-fashioned question: is numerical convergence an issue? What equations are being solved? EKE Meridional sections of the time-mean zonal velocity averaged between 35 W and 25 W for (a) the 0.1 run and (b) the 0.28 run.
35 The error estimate problem dominates the subject. Two major divisions: state estimates forecasts Classes of errors: Resolution failure coupled with inadequate subgrid-scale parameterizations Missing physics (e.g., sea-ice ocean interactions) Mis-specified data errors, including inadequate spatial/temporal covariances Erroneous initial conditions Erroneous boundary conditions (mainly in sub-system modeling, e.g., the ocean driven by an overlying atmosphere). A mixture of systematic and stochastic elements.
36 How to estimate uncertainties/errors? Several approaches: (1) Inverse Hessian (2)Fokker-Planck equation
37 (3) Singular vectors at initial times (4) Eigenvectors at initial times (5) Monte-Carlo (Ensemble methods). See e.g., T. Palmer, 2000, Rep. Prog. Phys. Dimensionality is a problem with all of them. (1) and (3) are linearizations. Ensemble sizes are minute compared to the state and control vector dimensions (thus, singular covariances and unexplored uncertainty spaces); colored (space-time) structures unaccounted for.
38 No one wants the uncertainty of the individual elements of x(t), u(t), but normally some consequences of them. But which consequences should be the focus? Stored heat content, uptake rate of carbon, sea surface temperatures, snow cover, sea ice extent in September, North Atlantic precipitation trends,. How to sort these into some priorities? Want methods that permit a fairly general application. The same issues pertain to forecasts of climate elements---but no data are involved at all (simpler?)
39 Problem Priorities: (1)Error estimates. Estimates are nearly useless without them. Forecasts are impossible to interpret. (2) Full climate system estimates (ocean; atmosphere; cryosphere--- particularly sea ice, but including glaciers; ultimately biological activity) (3) Computational efficiency improvements so resolution issues can be addressed. (4) Much better understanding of trends in key climate measurements (radiation, water vapor, etc.) (5) Efficient estimates for non-gaussian statistics (6) Model errors from lack of resolution, mis-constructed parameterizations (7) Construction of spatial covariances of data error
40 A major problem: It is clear that the atmospheric reanalyses fail as climate state products as they do not have closed budgets and exhibit discontinuities leading to unphysical trends. A self-consistent climate state estimate should be carried out using a fully coupled atmosphere-ocean-cryosphere (land and sea ice) system, and estimation methods using realistic error estimates for all data types, and producing dynamically self-consistent results. The principle is clear. The doing of it is ill-matched to a small academic group. How will this ultimately be carried out? (Probably not by the existing reanalysis groups.)
41 Thank you.
An Oceanographer's View of Data Assimilation and Reanalysis
 An Oceanographer's View of Data Assimilation and Reanalysis Carl Wunsch, MIT and AOPP, Oxford (George Eastman Visiting Professor, Balliol College) University of Reading, February 2012 The World Ocean Circulation
An Oceanographer's View of Data Assimilation and Reanalysis Carl Wunsch, MIT and AOPP, Oxford (George Eastman Visiting Professor, Balliol College) University of Reading, February 2012 The World Ocean Circulation
Innovation, increments, and residuals: Definitions and examples. Patrick Heimbach MIT, EAPS, Cambridge, MA
 Innovation, increments, and residuals: Definitions and examples Patrick Heimbach MIT, EAPS, Cambridge, MA Outline 1. Why should we / do we care? 2. How does (re- )analysis really work? 3. Conclusions Balance
Innovation, increments, and residuals: Definitions and examples Patrick Heimbach MIT, EAPS, Cambridge, MA Outline 1. Why should we / do we care? 2. How does (re- )analysis really work? 3. Conclusions Balance
An Overview of Atmospheric Analyses and Reanalyses for Climate
 An Overview of Atmospheric Analyses and Reanalyses for Climate Kevin E. Trenberth NCAR Boulder CO Analysis Data Assimilation merges observations & model predictions to provide a superior state estimate.
An Overview of Atmospheric Analyses and Reanalyses for Climate Kevin E. Trenberth NCAR Boulder CO Analysis Data Assimilation merges observations & model predictions to provide a superior state estimate.
Overview of data assimilation in oceanography or how best to initialize the ocean?
 Overview of data assimilation in oceanography or how best to initialize the ocean? T. Janjic Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research Bremerhaven, Germany Outline Ocean observing system Ocean
Overview of data assimilation in oceanography or how best to initialize the ocean? T. Janjic Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research Bremerhaven, Germany Outline Ocean observing system Ocean
Modeling the Arctic Climate System
 Modeling the Arctic Climate System General model types Single-column models: Processes in a single column Land Surface Models (LSMs): Interactions between the land surface, atmosphere and underlying surface
Modeling the Arctic Climate System General model types Single-column models: Processes in a single column Land Surface Models (LSMs): Interactions between the land surface, atmosphere and underlying surface
An Assessment of Contemporary Global Reanalyses in the Polar Regions
 An Assessment of Contemporary Global Reanalyses in the Polar Regions David H. Bromwich Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center and Atmospheric Sciences Program, Department of Geography The
An Assessment of Contemporary Global Reanalyses in the Polar Regions David H. Bromwich Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center and Atmospheric Sciences Program, Department of Geography The
The Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF) Eric Kostelich. Main topics
 The Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF) Eric Kostelich Arizona State University Co-workers: Istvan Szunyogh, Brian Hunt, Ed Ott, Eugenia Kalnay, Jim Yorke, and many others http://www.weatherchaos.umd.edu
The Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF) Eric Kostelich Arizona State University Co-workers: Istvan Szunyogh, Brian Hunt, Ed Ott, Eugenia Kalnay, Jim Yorke, and many others http://www.weatherchaos.umd.edu
Why build a climate model
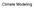 Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
The ECMWF coupled data assimilation system
 The ECMWF coupled data assimilation system Patrick Laloyaux Acknowledgments: Magdalena Balmaseda, Kristian Mogensen, Peter Janssen, Dick Dee August 21, 214 Patrick Laloyaux (ECMWF) CERA August 21, 214
The ECMWF coupled data assimilation system Patrick Laloyaux Acknowledgments: Magdalena Balmaseda, Kristian Mogensen, Peter Janssen, Dick Dee August 21, 214 Patrick Laloyaux (ECMWF) CERA August 21, 214
ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community
 ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community (and a few myth-busters) Paul Poli European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Shinfield Park, RG2 9AX, Reading, UK paul.poli
ECMWF global reanalyses: Resources for the wind energy community (and a few myth-busters) Paul Poli European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Shinfield Park, RG2 9AX, Reading, UK paul.poli
The Oceans in a Warming World
 The Oceans in a Warming World John Marshall Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences 1. Review global observations of warming trends. Ocean temperature trends key part of the puzzle. 2. Discuss timing
The Oceans in a Warming World John Marshall Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences 1. Review global observations of warming trends. Ocean temperature trends key part of the puzzle. 2. Discuss timing
1. Current atmospheric DA systems 2. Coupling surface/atmospheric DA 3. Trends & ideas
 1 Current issues in atmospheric data assimilation and its relationship with surfaces François Bouttier GAME/CNRM Météo-France 2nd workshop on remote sensing and modeling of surface properties, Toulouse,
1 Current issues in atmospheric data assimilation and its relationship with surfaces François Bouttier GAME/CNRM Météo-France 2nd workshop on remote sensing and modeling of surface properties, Toulouse,
The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges
 The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges Kevin E Trenberth and John T. Fasullo NCAR, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu INTRODUCTION Weather
The flow of Energy through the Earth s Climate System: Land and Ocean Exchanges Kevin E Trenberth and John T. Fasullo NCAR, Boulder, CO, USA Correspondence: Contact trenbert@ucar.edu INTRODUCTION Weather
Coupled data assimilation for climate reanalysis
 Coupled data assimilation for climate reanalysis Dick Dee Climate reanalysis Coupled data assimilation CERA: Incremental 4D-Var ECMWF June 26, 2015 Tools from numerical weather prediction Weather prediction
Coupled data assimilation for climate reanalysis Dick Dee Climate reanalysis Coupled data assimilation CERA: Incremental 4D-Var ECMWF June 26, 2015 Tools from numerical weather prediction Weather prediction
GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems
 GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems Jim Carton (UMD) With help from Gennady Chepurin, Ben Giese (TAMU), David Behringer (NCEP), Matt Harrison & Tony Rosati (GFDL) Description Goals Products
GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems Jim Carton (UMD) With help from Gennady Chepurin, Ben Giese (TAMU), David Behringer (NCEP), Matt Harrison & Tony Rosati (GFDL) Description Goals Products
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
4C.4 TRENDS IN LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATIONS AND THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURES IN THE TROPICS DERIVED FROM ATMOSPHERIC REANALYSES AND CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENTS
 4C.4 TRENDS IN LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATIONS AND THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURES IN THE TROPICS DERIVED FROM ATMOSPHERIC REANALYSES AND CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENTS Junichi Tsutsui Central Research Institute of Electric
4C.4 TRENDS IN LARGE-SCALE CIRCULATIONS AND THERMODYNAMIC STRUCTURES IN THE TROPICS DERIVED FROM ATMOSPHERIC REANALYSES AND CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENTS Junichi Tsutsui Central Research Institute of Electric
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
The impact of polar mesoscale storms on northeast Atlantic Ocean circulation
 The impact of polar mesoscale storms on northeast Atlantic Ocean circulation Influence of polar mesoscale storms on ocean circulation in the Nordic Seas Supplementary Methods and Discussion Atmospheric
The impact of polar mesoscale storms on northeast Atlantic Ocean circulation Influence of polar mesoscale storms on ocean circulation in the Nordic Seas Supplementary Methods and Discussion Atmospheric
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons?
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar Energy and the global Heat Budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation Should we talk about this? What causes the seasons? Before you answer, think. What
Earth s Heat Budget Solar Energy and the global Heat Budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation Should we talk about this? What causes the seasons? Before you answer, think. What
Ocean data assimilation for reanalysis
 Ocean data assimilation for reanalysis Matt Martin. ERA-CLIM2 Symposium, University of Bern, 14 th December 2017. Contents Introduction. On-going developments to improve ocean data assimilation for reanalysis.
Ocean data assimilation for reanalysis Matt Martin. ERA-CLIM2 Symposium, University of Bern, 14 th December 2017. Contents Introduction. On-going developments to improve ocean data assimilation for reanalysis.
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
CERA-SAT: A coupled reanalysis at higher resolution (WP1)
 CERA-SAT: A coupled reanalysis at higher resolution (WP1) ERA-CLIM2 General assembly Dinand Schepers 16 Jan 2017 Contributors: Eric de Boisseson, Per Dahlgren, Patrick Lalolyaux, Iain Miller and many others
CERA-SAT: A coupled reanalysis at higher resolution (WP1) ERA-CLIM2 General assembly Dinand Schepers 16 Jan 2017 Contributors: Eric de Boisseson, Per Dahlgren, Patrick Lalolyaux, Iain Miller and many others
Near-surface observations for coupled atmosphere-ocean reanalysis
 Near-surface observations for coupled atmosphere-ocean reanalysis Patrick Laloyaux Acknowledgement: Clément Albergel, Magdalena Balmaseda, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Dick Dee, Paul Poli, Patricia de Rosnay, Adrian
Near-surface observations for coupled atmosphere-ocean reanalysis Patrick Laloyaux Acknowledgement: Clément Albergel, Magdalena Balmaseda, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Dick Dee, Paul Poli, Patricia de Rosnay, Adrian
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS. Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 1850
 CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water. Kevin E Trenberth NCAR
 Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Tracking Earth s Global Energy Where has global warming from increased GHGs gone? Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Where did the heat
Aspects of a climate observing system: energy and water Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Tracking Earth s Global Energy Where has global warming from increased GHGs gone? Kevin E Trenberth NCAR Where did the heat
Relative Merits of 4D-Var and Ensemble Kalman Filter
 Relative Merits of 4D-Var and Ensemble Kalman Filter Andrew Lorenc Met Office, Exeter International summer school on Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (ISSAOS) "Atmospheric Data Assimilation". August 29
Relative Merits of 4D-Var and Ensemble Kalman Filter Andrew Lorenc Met Office, Exeter International summer school on Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (ISSAOS) "Atmospheric Data Assimilation". August 29
The Canadian approach to ensemble prediction
 The Canadian approach to ensemble prediction ECMWF 2017 Annual seminar: Ensemble prediction : past, present and future. Pieter Houtekamer Montreal, Canada Overview. The Canadian approach. What are the
The Canadian approach to ensemble prediction ECMWF 2017 Annual seminar: Ensemble prediction : past, present and future. Pieter Houtekamer Montreal, Canada Overview. The Canadian approach. What are the
Fast and Slow Response of Sea ice and the Southern Ocean to Ozone Depletion
 Fast and Slow Response of Sea ice and the Southern Ocean to Ozone Depletion Annual Minimum Sea ice extent 1979-2013 10 6 km 2 Arctic September Antarctic February Data from in passive microwave satellite
Fast and Slow Response of Sea ice and the Southern Ocean to Ozone Depletion Annual Minimum Sea ice extent 1979-2013 10 6 km 2 Arctic September Antarctic February Data from in passive microwave satellite
Recent Developments in Climate Information Services at JMA. Koichi Kurihara Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency
 Recent Developments in Climate Information Services at JMA Koichi Kurihara Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency 1 Topics 1. Diagnosis of the Northern Hemispheric circulation in December
Recent Developments in Climate Information Services at JMA Koichi Kurihara Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency 1 Topics 1. Diagnosis of the Northern Hemispheric circulation in December
Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044988, 2010 Arctic sea ice response to atmospheric forcings with varying levels of anthropogenic warming and climate variability Jinlun Zhang,
Validation of satellite derived snow cover data records with surface networks and m ulti-dataset inter-comparisons
 Validation of satellite derived snow cover data records with surface networks and m ulti-dataset inter-comparisons Chris Derksen Climate Research Division Environment Canada Thanks to our data providers:
Validation of satellite derived snow cover data records with surface networks and m ulti-dataset inter-comparisons Chris Derksen Climate Research Division Environment Canada Thanks to our data providers:
Second-Order Draft Chapter 10 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
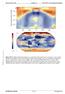 Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis
 Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Extended abstract for the 3 rd WCRP International Conference on Reanalysis held in Tokyo, Japan, on Jan. 28 Feb. 1, 2008 Global Ocean Monitoring: A Synthesis of Atmospheric and Oceanic Analysis Yan Xue,
Applications of Data Assimilation in Earth System Science. Alan O Neill University of Reading, UK
 Applications of Data Assimilation in Earth System Science Alan O Neill University of Reading, UK NCEO Early Career Science Conference 16th 18th April 2012 Introduction to data assimilation Page 2 of 20
Applications of Data Assimilation in Earth System Science Alan O Neill University of Reading, UK NCEO Early Career Science Conference 16th 18th April 2012 Introduction to data assimilation Page 2 of 20
Climate Modeling and Downscaling
 Climate Modeling and Downscaling Types of climate-change experiments: a preview 1) What-if sensitivity experiments increase the optically active gases and aerosols according to an assumed scenario, and
Climate Modeling and Downscaling Types of climate-change experiments: a preview 1) What-if sensitivity experiments increase the optically active gases and aerosols according to an assumed scenario, and
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes
 High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
Project of Strategic Interest NEXTDATA. Deliverables D1.3.B and 1.3.C. Final Report on the quality of Reconstruction/Reanalysis products
 Project of Strategic Interest NEXTDATA Deliverables D1.3.B and 1.3.C Final Report on the quality of Reconstruction/Reanalysis products WP Coordinator: Nadia Pinardi INGV, Bologna Deliverable authors Claudia
Project of Strategic Interest NEXTDATA Deliverables D1.3.B and 1.3.C Final Report on the quality of Reconstruction/Reanalysis products WP Coordinator: Nadia Pinardi INGV, Bologna Deliverable authors Claudia
T2.2: Development of assimilation techniques for improved use of surface observations
 WP2 T2.2: Development of assimilation techniques for improved use of surface observations Matt Martin, Rob King, Dan Lea, James While, Charles-Emmanuel Testut November 2014, ECMWF, Reading, UK. Contents
WP2 T2.2: Development of assimilation techniques for improved use of surface observations Matt Martin, Rob King, Dan Lea, James While, Charles-Emmanuel Testut November 2014, ECMWF, Reading, UK. Contents
ERA-CLIM: Developing reanalyses of the coupled climate system
 ERA-CLIM: Developing reanalyses of the coupled climate system Dick Dee Acknowledgements: Reanalysis team and many others at ECMWF, ERA-CLIM project partners at Met Office, Météo France, EUMETSAT, Un. Bern,
ERA-CLIM: Developing reanalyses of the coupled climate system Dick Dee Acknowledgements: Reanalysis team and many others at ECMWF, ERA-CLIM project partners at Met Office, Météo France, EUMETSAT, Un. Bern,
Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models
 Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models Robert Marsh, Beverly de Cuevas, Andrew Coward & Simon Josey (+ contributions by
Recent warming and changes of circulation in the North Atlantic - simulated with eddy-permitting & eddy-resolving models Robert Marsh, Beverly de Cuevas, Andrew Coward & Simon Josey (+ contributions by
A Global Atmospheric Model. Joe Tribbia NCAR Turbulence Summer School July 2008
 A Global Atmospheric Model Joe Tribbia NCAR Turbulence Summer School July 2008 Outline Broad overview of what is in a global climate/weather model of the atmosphere Spectral dynamical core Some results-climate
A Global Atmospheric Model Joe Tribbia NCAR Turbulence Summer School July 2008 Outline Broad overview of what is in a global climate/weather model of the atmosphere Spectral dynamical core Some results-climate
Environment and Climate Change Canada / GPC Montreal
 Environment and Climate Change Canada / GPC Montreal Assessment, research and development Bill Merryfield Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis (CCCma) with contributions from colleagues at
Environment and Climate Change Canada / GPC Montreal Assessment, research and development Bill Merryfield Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis (CCCma) with contributions from colleagues at
Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center. Current Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Capabilities
 Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center Current Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Capabilities presented at Workshop on Metrics, Post-Processing, and Products for S2S 28 Feb 2018 Chuck Skupniewicz Modeling
Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center Current Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Capabilities presented at Workshop on Metrics, Post-Processing, and Products for S2S 28 Feb 2018 Chuck Skupniewicz Modeling
Oceans and Climate. Caroline Katsman. KNMI Global Climate Division
 Oceans and Climate Caroline Katsman KNMI Global Climate Division Aimée Slangen, Roderik van de Wal (IMAU, Utrecht University) Sybren Drijfhout, Wilco Hazeleger (KNMI, Global Climate) Bert Vermeersen (NIOZ/Delft
Oceans and Climate Caroline Katsman KNMI Global Climate Division Aimée Slangen, Roderik van de Wal (IMAU, Utrecht University) Sybren Drijfhout, Wilco Hazeleger (KNMI, Global Climate) Bert Vermeersen (NIOZ/Delft
The global oceanic freshwater cycle: A state-of-the-art quantification
 Journal of Marine Research, 68, 569 595, 2010 The global oceanic freshwater cycle: A state-of-the-art quantification by J. J. Schanze 1, R. W. Schmitt 2 and L. L. Yu 2 ABSTRACT The current capabilities
Journal of Marine Research, 68, 569 595, 2010 The global oceanic freshwater cycle: A state-of-the-art quantification by J. J. Schanze 1, R. W. Schmitt 2 and L. L. Yu 2 ABSTRACT The current capabilities
Improving numerical sea ice predictions in the Arctic Ocean by data assimilation using satellite observations
 Okhotsk Sea and Polar Oceans Research 1 (2017) 7-11 Okhotsk Sea and Polar Oceans Research Association Article Improving numerical sea ice predictions in the Arctic Ocean by data assimilation using satellite
Okhotsk Sea and Polar Oceans Research 1 (2017) 7-11 Okhotsk Sea and Polar Oceans Research Association Article Improving numerical sea ice predictions in the Arctic Ocean by data assimilation using satellite
Analysis of the Relationship between a Change in Wind Field Curl Rate and Sea Surface Height within the Beaufort Gyre Region of the Arctic
 Analysis of the Relationship between a Change in Wind Field Curl Rate and Sea Surface Height within the Beaufort Gyre Region of the Arctic Tyler Pelle (Advisement from Pedro Elosegui) MIT Haystack Observatory
Analysis of the Relationship between a Change in Wind Field Curl Rate and Sea Surface Height within the Beaufort Gyre Region of the Arctic Tyler Pelle (Advisement from Pedro Elosegui) MIT Haystack Observatory
Global reanalysis: Some lessons learned and future plans
 Global reanalysis: Some lessons learned and future plans Adrian Simmons and Sakari Uppala European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts With thanks to Per Kållberg and many other colleagues from ECMWF
Global reanalysis: Some lessons learned and future plans Adrian Simmons and Sakari Uppala European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts With thanks to Per Kållberg and many other colleagues from ECMWF
Intercomparison of the Arctic sea ice cover in global ocean-sea ice reanalyses
 Intercomparison of the Arctic sea ice cover in global ocean-sea ice reanalyses Matthieu Chevallier (CNRM, Météo France/CNRS) Greg Smith, Frédéric Dupont, Jean-François Lemieux (ECC Canada), Gilles Garric
Intercomparison of the Arctic sea ice cover in global ocean-sea ice reanalyses Matthieu Chevallier (CNRM, Météo France/CNRS) Greg Smith, Frédéric Dupont, Jean-François Lemieux (ECC Canada), Gilles Garric
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
On assessing temporal variability and trends of coupled arctic energy budgets. Michael Mayer Leo Haimberger
 On assessing temporal variability and trends of coupled arctic energy budgets Michael Mayer Leo Haimberger Motivation and outline Arctic climate system is subject to rapid changes and large interannual
On assessing temporal variability and trends of coupled arctic energy budgets Michael Mayer Leo Haimberger Motivation and outline Arctic climate system is subject to rapid changes and large interannual
Sea level variability in the North Indian Ocean
 Sea level variability in the North Indian Ocean M. Ravichandran ESSO-National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR) (Ministry of Earth Sciences, Govt. of India) Goa mravi@ncaor.gov.in U.Srinivasu
Sea level variability in the North Indian Ocean M. Ravichandran ESSO-National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (NCAOR) (Ministry of Earth Sciences, Govt. of India) Goa mravi@ncaor.gov.in U.Srinivasu
Regional eddy-permitting state estimation of the circulation in the Northern Philippine Sea
 Regional eddy-permitting state estimation of the circulation in the Northern Philippine Sea Bruce D. Cornuelle, Ganesh Gopalakrishnan, Peter F. Worcester, Matthew A. Dzieciuch, and Matthew Mazloff Scripps
Regional eddy-permitting state estimation of the circulation in the Northern Philippine Sea Bruce D. Cornuelle, Ganesh Gopalakrishnan, Peter F. Worcester, Matthew A. Dzieciuch, and Matthew Mazloff Scripps
The Hydrologic Cycle
 The Hydrologic Cycle Monthly precipitation for the central Arctic Ocean based on data from the Russian North Pole manned camps with daily bias adjustments. Raw precipitation totals are shown along with
The Hydrologic Cycle Monthly precipitation for the central Arctic Ocean based on data from the Russian North Pole manned camps with daily bias adjustments. Raw precipitation totals are shown along with
Experiences of using ECV datasets in ECMWF reanalyses including CCI applications. David Tan and colleagues ECMWF, Reading, UK
 Experiences of using ECV datasets in ECMWF reanalyses including CCI applications David Tan and colleagues ECMWF, Reading, UK Slide 1 Main points Experience shows benefit of integrated & iterative approach
Experiences of using ECV datasets in ECMWF reanalyses including CCI applications David Tan and colleagues ECMWF, Reading, UK Slide 1 Main points Experience shows benefit of integrated & iterative approach
Atmospheric origins of variability in the South Atlantic meridional overturning circulation
 Atmospheric origins of variability in the South Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Timothy Smith Patrick Heimbach July 3, 2018 INSTITUTE FOR COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING & SCIENCES The South Atlantic
Atmospheric origins of variability in the South Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Timothy Smith Patrick Heimbach July 3, 2018 INSTITUTE FOR COMPUTATIONAL ENGINEERING & SCIENCES The South Atlantic
Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list)
 Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list) Snow/ice Sea ice motion (sat): experimental, climate model Sea ice extent (sat): operational, U.S. Navy PIPs model; Canada; others? Sea ice concentration
Assimilation of Snow and Ice Data (Incomplete list) Snow/ice Sea ice motion (sat): experimental, climate model Sea ice extent (sat): operational, U.S. Navy PIPs model; Canada; others? Sea ice concentration
Arctic System Reanalysis *
 Arctic System Reanalysis * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1 and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center 2 Atmospheric Sciences Program, Dept. of Geography The Ohio State
Arctic System Reanalysis * David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1 and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center 2 Atmospheric Sciences Program, Dept. of Geography The Ohio State
Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio
 JP2.14 ON ADAPTING A NEXT-GENERATION MESOSCALE MODEL FOR THE POLAR REGIONS* Keith M. Hines 1 and David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University,
JP2.14 ON ADAPTING A NEXT-GENERATION MESOSCALE MODEL FOR THE POLAR REGIONS* Keith M. Hines 1 and David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University,
is the coefficient of degree 2, order 0 of the non-dimensional spherical harmonic
 Materials and Methods J is the coefficient of degree, order 0 of the non-dimensional spherical harmonic representation of the mass distribution of the Earth system. It is directly related to the diagonal
Materials and Methods J is the coefficient of degree, order 0 of the non-dimensional spherical harmonic representation of the mass distribution of the Earth system. It is directly related to the diagonal
Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L20601, doi:10.1029/2008gl035490, 2008 Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean Denis L. Volkov, 1 Tong Lee, 1 and Lee-Lueng Fu 1 Received 28 July 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L20601, doi:10.1029/2008gl035490, 2008 Eddy-induced meridional heat transport in the ocean Denis L. Volkov, 1 Tong Lee, 1 and Lee-Lueng Fu 1 Received 28 July 2008;
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker
 Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
Arctic sea ice in IPCC climate scenarios in view of the 2007 record low sea ice event A comment by Ralf Döscher, Michael Karcher and Frank Kauker Fig. 1: Arctic September sea ice extent in observations
The JRA-55 Reanalysis: quality control and reprocessing of observational data
 The JRA-55 Reanalysis: quality control and reprocessing of observational data Kazutoshi Onogi On behalf of JRA group Japan Meteorological Agency 29 October 2014 EASCOF 1 1. Introduction 1. Introduction
The JRA-55 Reanalysis: quality control and reprocessing of observational data Kazutoshi Onogi On behalf of JRA group Japan Meteorological Agency 29 October 2014 EASCOF 1 1. Introduction 1. Introduction
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic
 Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Changes in Frequency of Extreme Wind Events in the Arctic John E. Walsh Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois 105 S. Gregory Avenue Urbana, IL 61801 phone: (217) 333-7521 fax: (217)
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture
 Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Improved Fields of Satellite-Derived Ocean Surface Turbulent Fluxes of Energy and Moisture First year report on NASA grant NNX09AJ49G PI: Mark A. Bourassa Co-Is: Carol Anne Clayson, Shawn Smith, and Gary
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest
 Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
Trends in Climate Teleconnections and Effects on the Midwest Don Wuebbles Zachary Zobel Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Illinois, Urbana November 11, 2015 Date Name of Meeting 1 Arctic
3. Climate Change. 3.1 Observations 3.2 Theory of Climate Change 3.3 Climate Change Prediction 3.4 The IPCC Process
 3. Climate Change 3.1 Observations 3.2 Theory of Climate Change 3.3 Climate Change Prediction 3.4 The IPCC Process 3.1 Observations Need to consider: Instrumental climate record of the last century or
3. Climate Change 3.1 Observations 3.2 Theory of Climate Change 3.3 Climate Change Prediction 3.4 The IPCC Process 3.1 Observations Need to consider: Instrumental climate record of the last century or
Biogeochemical modelling and data assimilation: status in Australia
 Biogeochemical modelling and data assimilation: status in Australia Richard Matear, Andrew Lenton, Matt Chamberlain, Mathieu Mongin, Emlyn Jones, Mark Baird www.cmar.csiro.au/staff/oke/ Biogeochemical
Biogeochemical modelling and data assimilation: status in Australia Richard Matear, Andrew Lenton, Matt Chamberlain, Mathieu Mongin, Emlyn Jones, Mark Baird www.cmar.csiro.au/staff/oke/ Biogeochemical
Constraining simulated atmospheric states by sparse empirical information
 Constraining simulated atmospheric states by sparse empirical information Martin Widmann University of Birmingham Hugues Goosse University of Louvain-la-Neuve NCAR workshop Data assimilation and climate
Constraining simulated atmospheric states by sparse empirical information Martin Widmann University of Birmingham Hugues Goosse University of Louvain-la-Neuve NCAR workshop Data assimilation and climate
Development and Validation of Polar WRF
 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Development and Validation of Polar WRF David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1, and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar
Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio Development and Validation of Polar WRF David H. Bromwich 1,2, Keith M. Hines 1, and Le-Sheng Bai 1 1 Polar
A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC
 National Snow and Ice Data Center ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH'S FROZEN REGIONS Special Report #18 06 July 2016 A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC W. Meier NASA GSFC i 2 Contents List of Figures... 4 List of
National Snow and Ice Data Center ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH'S FROZEN REGIONS Special Report #18 06 July 2016 A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC W. Meier NASA GSFC i 2 Contents List of Figures... 4 List of
Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... )
 Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... ) 4 Land, biosphere, cryosphere 1. Introduction 2. Atmosphere 3. Ocean 4. Land, biosphere, cryosphere 4.1 Land
Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... ) 4 Land, biosphere, cryosphere 1. Introduction 2. Atmosphere 3. Ocean 4. Land, biosphere, cryosphere 4.1 Land
Presentation of met.no s experience and expertise related to high resolution reanalysis
 Presentation of met.no s experience and expertise related to high resolution reanalysis Oyvind Saetra, Ole Einar Tveito, Harald Schyberg and Lars Anders Breivik Norwegian Meteorological Institute Daily
Presentation of met.no s experience and expertise related to high resolution reanalysis Oyvind Saetra, Ole Einar Tveito, Harald Schyberg and Lars Anders Breivik Norwegian Meteorological Institute Daily
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM. Marika Holland NCAR
 Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Arctic climate projections and progress towards a new CCSM Marika Holland NCAR The Arctic is changing! Loss of Sept Arctic Sea Ice 2002 Loss of about 8% per decade Or >20% since 1979 (Courtesy I. Rigor
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons? Seasons
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean
 Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
Air sea satellite flux datasets and what they do (and don't) tell us about the air sea interface in the Southern Ocean Carol Anne Clayson Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Southern Ocean Workshop Seattle,
What makes the Arctic hot?
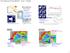 1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
Francis O. 1, David H. Bromwich 1,2
 Impact of assimilating COSMIC GPS RO moisture and temperature profiles on Polar WRF simulations of West Antarctic cyclones Francis O. O@eno 1, David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group BPRC 2 Atmospheric
Impact of assimilating COSMIC GPS RO moisture and temperature profiles on Polar WRF simulations of West Antarctic cyclones Francis O. O@eno 1, David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group BPRC 2 Atmospheric
Assessing the Climate-Scale Variability and Seasonal Predictability of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America
 Assessing the Climate-Scale Variability and Seasonal Predictability of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Alexander Gershunov, Tamara Shulgina, Marty Ralph, David Lavers CW3E
Assessing the Climate-Scale Variability and Seasonal Predictability of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Alexander Gershunov, Tamara Shulgina, Marty Ralph, David Lavers CW3E
Importance of physics, resolution and forcing in hindcast simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice variability and trends
 WCRP Workshop on Seasonal to Multi-Decadal Predictability of Polar Climate Bergen, 25-29 October 2010 Importance of physics, resolution and forcing in hindcast simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice
WCRP Workshop on Seasonal to Multi-Decadal Predictability of Polar Climate Bergen, 25-29 October 2010 Importance of physics, resolution and forcing in hindcast simulations of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice
Predicting Climate Change
 Predicting Climate Change Dave Frame Climate Dynamics Group, Department of Physics, Predicting climate change Simple model of climate system, used as the basis of a probabilistic forecast Generating a
Predicting Climate Change Dave Frame Climate Dynamics Group, Department of Physics, Predicting climate change Simple model of climate system, used as the basis of a probabilistic forecast Generating a
Polar WRF. Polar Meteorology Group Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center The Ohio State University Columbus Ohio
 Polar WRF David H. Bromwich, Keith M. Hines, Lesheng Bai and Sheng-Hung Wang Polar Meteorology Group Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center The Ohio State University Columbus Ohio Byrd Polar and Climate
Polar WRF David H. Bromwich, Keith M. Hines, Lesheng Bai and Sheng-Hung Wang Polar Meteorology Group Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center The Ohio State University Columbus Ohio Byrd Polar and Climate
The Oceanic Component of CFSR
 1 The Oceanic Component of CFSR Yan Xue 1, David Behringer 2, Boyin Huang 1,Caihong Wen 1,Arun Kumar 1 1 Climate Prediction Center, NCEP/NOAA, 2 Environmental Modeling Center, NCEP/NOAA, The 34 th Annual
1 The Oceanic Component of CFSR Yan Xue 1, David Behringer 2, Boyin Huang 1,Caihong Wen 1,Arun Kumar 1 1 Climate Prediction Center, NCEP/NOAA, 2 Environmental Modeling Center, NCEP/NOAA, The 34 th Annual
MOTIVATION. New view of Arctic cyclone activity from the Arctic System Reanalysis
 New view of Arctic cyclone activity from the Arctic System Reanalysis Natalia Tilinina 1, Sergey Gulev 1 and David H.Bromwich 2 1) P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Moscow 2) Byrd Polar Research Center,
New view of Arctic cyclone activity from the Arctic System Reanalysis Natalia Tilinina 1, Sergey Gulev 1 and David H.Bromwich 2 1) P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Moscow 2) Byrd Polar Research Center,
EVALUATION OF THE GLOBAL OCEAN DATA ASSIMILATION SYSTEM AT NCEP: THE PACIFIC OCEAN
 2.3 Eighth Symposium on Integrated Observing and Assimilation Systems for Atmosphere, Oceans, and Land Surface, AMS 84th Annual Meeting, Washington State Convention and Trade Center, Seattle, Washington,
2.3 Eighth Symposium on Integrated Observing and Assimilation Systems for Atmosphere, Oceans, and Land Surface, AMS 84th Annual Meeting, Washington State Convention and Trade Center, Seattle, Washington,
Ice sheet freshwater forcing
 Jan Lenaerts Utrecht University University of Colorado Ice sheet freshwater forcing Photo: Reijmer, 2011 Sea level meeting 5 to ~6 pm, South Bay Goal: Sea level rise and its impacts on coastal populations
Jan Lenaerts Utrecht University University of Colorado Ice sheet freshwater forcing Photo: Reijmer, 2011 Sea level meeting 5 to ~6 pm, South Bay Goal: Sea level rise and its impacts on coastal populations
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Atmosphere-ocean interactions and dynamic response of the Southern Ocean to climate variability and trends. Mike Meredith BAS, Cambridge, UK
 Atmosphere-ocean interactions and dynamic response of the Southern Ocean to climate variability and trends. Mike Meredith BAS, Cambridge, UK Structure Preliminary random thoughts Brief examples demonstrating
Atmosphere-ocean interactions and dynamic response of the Southern Ocean to climate variability and trends. Mike Meredith BAS, Cambridge, UK Structure Preliminary random thoughts Brief examples demonstrating
Adrian Simmons & Re-analysis by David Burridge (pay-back time!) Credits: Dick Dee, Hans Hersbach,Adrian and a cast of thousands
 Adrian Simmons & Re-analysis by David Burridge (pay-back time!) Credits: Dick Dee, Hans Hersbach,Adrian and a cast of thousands A brief history of atmospheric reanalysis productions at ECMWF 1990 2000
Adrian Simmons & Re-analysis by David Burridge (pay-back time!) Credits: Dick Dee, Hans Hersbach,Adrian and a cast of thousands A brief history of atmospheric reanalysis productions at ECMWF 1990 2000
Turbulent fluxes. Sensible heat flux. Momentum flux = Wind stress ρc D (U-U s ) 2. Latent heat flux. ρc p C H (U-U s ) (T s -T a )
 Intertropical ocean-atmosphere coupling in a state of the art Earth System Model: Evaluating the representation of turbulent air-sea fluxes in IPSL-CM5A Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Pascale Braconnot Laboratoire
Intertropical ocean-atmosphere coupling in a state of the art Earth System Model: Evaluating the representation of turbulent air-sea fluxes in IPSL-CM5A Alina Găinuşă-Bogdan, Pascale Braconnot Laboratoire
The Arctic Energy Budget
 The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
The Arctic Energy Budget The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth, NCAR]. Differential solar heating between low and high latitudes gives rise to a circulation of the atmosphere and ocean that
New Insights into the January 2016 West Antarctic Melt Event from the AWARE Campaign and Climate Model Simulations
 New Insights into the January 2016 West Antarctic Melt Event from the AWARE Campaign and Climate Model Simulations Julien P. Nicolas 1, Andrew M. Vogelmann 2, Ryan C. Scott 3, Aaron B. Wilson 1, Maria
New Insights into the January 2016 West Antarctic Melt Event from the AWARE Campaign and Climate Model Simulations Julien P. Nicolas 1, Andrew M. Vogelmann 2, Ryan C. Scott 3, Aaron B. Wilson 1, Maria
Observed State of the Global Climate
 WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
WMO Observed State of the Global Climate Jerry Lengoasa WMO June 2013 WMO Observations of Changes of the physical state of the climate ESSENTIAL CLIMATE VARIABLES OCEANIC ATMOSPHERIC TERRESTRIAL Surface
2. DYNAMICS OF CLIMATIC AND GEOPHYSICAL INDICES
 4 2. DYNAMICS OF CLIMATIC AND GEOPHYSICAL INDICES Regular and reliable climate observations with measurement and calculation of principal climatic indices were started only about 150 years ago, when organized
4 2. DYNAMICS OF CLIMATIC AND GEOPHYSICAL INDICES Regular and reliable climate observations with measurement and calculation of principal climatic indices were started only about 150 years ago, when organized
Numerical Weather prediction at the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
 Numerical Weather prediction at the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Time series curves 500hPa geopotential Correlation coefficent of forecast anomaly N Hemisphere Lat 20.0 to 90.0 Lon
Numerical Weather prediction at the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Time series curves 500hPa geopotential Correlation coefficent of forecast anomaly N Hemisphere Lat 20.0 to 90.0 Lon
NSF Expeditions in Computing. Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach. Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota
 NSF Expeditions in Computing Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota kumar@cs.umn.edu www.cs.umn.edu/~kumar Vipin Kumar UCC Aug 15, 2011 Climate Change:
NSF Expeditions in Computing Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota kumar@cs.umn.edu www.cs.umn.edu/~kumar Vipin Kumar UCC Aug 15, 2011 Climate Change:
