Upper Ocean - Topographic Coupling in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution
|
|
|
- Abraham Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Upper Ocean - Topographic Coupling in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution by 1 Harley E. Hurlburt, 1 Patrick J. Hogan, 1 E. Joseph Metzger, 2 Charles E. Tilburg and 1 Jay F. Shriver 1 Naval Research Laboratory Oceanography Division Stennis Space Center, MS USA 2 University of New England Biddeford, ME USA Layered Ocean Model Workshop 2007 Bergen, Norway August, 2007
2 Kuroshio Pathway East of Japan Impact of topography and model resolution 1/8 6-layer with realistic bottom topography A=100 m 2 /s 1/8 6-layer flat bottom 1/4 6-layer with realistic bottom topography A=100 m 2 /s A=300 m 2 /s Model mean sea surface height forced by Hellerman and Rosenstein (1983, JPO) wind stress climatology From Hurlburt et al. (1996, JGR-O; 1997, Intl WOCE Newsletter)
3 Bottom Current Steering of Upper Ocean Currents In a two-layer model, the continuity equation for layer 1 is h t v 1 + h1 v = 1 + v1 h1 v The advective term in (1) can be related to the layer 2 velocity by r v r 1g h1 = v2 g h1 kˆ Since 2 f r r ( v ) 1 g v2g = g' h1 h 1 is a good measure of 1 0 (1) (2) (3) r r v 1 >> v (4) v r. From this, we see that abyssal currents affect the advection of upper layer thickness gradients and therefore upper layer currents. (Hurlburt and Thompson, 1980, JPO; Hurlburt et al., 1996, JGR-O)
4 Application of the 2-layer Theory for Abyssal Current Advection of Upper Ocean Current Pathways to Models with Higher Vertical Resolution Applies when all of the following are satisfied: a) The flow is nearly geostrophically balanced b) The barotropic and first baroclinic model are dominant c) The topography does not intrude significantly into the stratified ocean The interpretation in terms of surface currents applies when Notes: 1) The theory does not apply at low latitudes because of a) and b) 2) Abyssal current advection of upper ocean current pathways is strengthened when the currents intersect at large angles, but often the end result of this advection is near barotropy
5 Upper Ocean Topographic Coupling in the Kuroshio Extension 1/12, 20-Layer Pacific HYCOM vs. 1/8 6-Layer NLOM Mean SSH, RMS SSH, and mean abyssal currents Mean abyssal currents and bottom topography HYCOM HYCOM NLOM NLOM (in cm) depth (in m) Adapted from Hurlburt et al. (2006; DAO submitted) and Hurlburt et al. (1996; JGR-O)
6 From Hogan and Hurlburt (2000, JPO)
7 1/25, 15-layer HYCOM and 1/32, 4-layer NLOM vs Observations in the Japan/East Sea, Wind Forcing = EC10M Schematic of mean surface currents Mean abyssal currents: observed vs models HYCOM NLOM From Yanagi (2000) after Senjyu (1999) Observed currents Model currents, white at observed locations Vector correlation, model vs obs HYCOM layer 15 =.76 HYCOM layer 14 vs NLOM layer 4 NLOM layer 4 =.33 vector correlation =.72 south of 41 N
8 Mean Surface Currents: 1/25, 15-layer HYCOM vs 1/25, 4-layer NLOM using EC10M Winds HYCOM NLOM (in m) SSH correlation =.83 south of 41 N Current vector correlation =.61 south of 41 N
9 Australia NC E ECEW 145E15 0E15E 160E 165E170E 175E W170W SP 3025 S EA C 35 S TF 4540 S 50 S EACExtension ugarloaf oint TasmanSea New Zeal andnorthisland SouthIsland SC EAUCEC E Mean Sea Surface Temperature Around New Zealand - Uddstrom and Oien, JGR (1999)
10 Mean Currents and Sea Surface Height Simulated by (A,B) 1/16 Linear Barotropic Model and (c) the Surface Layer from 1/8, 6-Layer Flat Bottom NLOM A (in cm) B C -79 (A) QuikSCAT-corrected ECMWF ERA-40 climatological wind forcing (B,C) Smoothed Hellerman and Rosenstein (1983) wind stress forcing
11 1/8, 6-Layer NLOM Simulation of Mean Surface and Abyssal Currents East of South Island, New Zealand Mean currents over bottom topography Mean abyssal currents over bottom topography Mean subtropical front (STF) Mean subantarctic front (SAF) Smoothed Hellerman and Rosenstein (1983) (HRSM) wind forcing From Tilburg et al. (2002; JPO)
12 Surface Transport Streamfunctions T = 0 years T = 3 years T = 7 years T = 80 years
13 Development of an Upper Ocean Western Boundary Current due to Remote Topographic Forcing T = 0 years T = 0 years T = 3 years T = 3 years T = 7 years T = 7 years Centered at 177 E, a northward abyssal layer current along an escarpment is turned on at T=0. The model has two layers with topography confined to the bottom layer. A meridional plateau to the west slopes to deeper depths near 177 E. Surface layer transport streamfunction is shown. From Tilburg et al. (2002, JPO) T = 80 years T = 80 years
14 Mean currents simulated by 1/12, 32-layer global HYCOM in the New Zealand Region 8.6 m depth Black line segments mark vertical cross-sections shown on the next slide South Island, NZ Chatham Rise ~ 2000 m depth ~ 400 m depth Campbell Plateau Currents overlaid on bottom topography From Hurlburt et al. (2006, DAO submitted)
15 Mean velocity cross-sections simulated by 1/12, 32-layer global HYCOM southeast of New Zealand Velocity contour interval = 5 cm/s + = N or E, yellow red S Transport = 75.5 Sv 177 E Transport = 51.7 Sv S Transport = 20.1 Sv 46.5 S Southland Current Southland Current transports Observed steric = 8.3 Sv (Sutton, 2003; NZJMFR) HYCOM steric = 7.8 Sv HYCOM nonsteric = 16.2 Sv HYCOM total = 24.0 Sv 173 E Cross-sections are marked on the previous slide
16 Mean sea surface height in the New Zealand region 42 S 46 S 50 S 54 S Observation based Maximenko and Niiler (2005) 1/12 global HYCOM 42 S 46 S 50 S 54 S 1/8 global NLOM 1/32 global NLOM 160 E 170 E W 170 E W (in cm)
Abyssal Current Steering of Upper Ocean Current Pathways in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution
 Abyssal Current Steering of Upper Ocean Current Pathways in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution by 1 Harley E. Hurlburt, 1 E. Joseph Metzger, 1 Patrick J. Hogan, 2 Charles E. Tilburg and 1 Jay
Abyssal Current Steering of Upper Ocean Current Pathways in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution by 1 Harley E. Hurlburt, 1 E. Joseph Metzger, 1 Patrick J. Hogan, 2 Charles E. Tilburg and 1 Jay
Abyssal Current Steering of Upper Ocean Current Pathways in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution
 Abyssal Current Steering of Upper Ocean Current Pathways in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution by 1 Harley E. Hurlburt, 1 E. Joseph Metzger, 1 Patrick J. Hogan, 2 Charles E. Tilburg and 1 Jay
Abyssal Current Steering of Upper Ocean Current Pathways in an Ocean Model with High Vertical Resolution by 1 Harley E. Hurlburt, 1 E. Joseph Metzger, 1 Patrick J. Hogan, 2 Charles E. Tilburg and 1 Jay
Dynamical Evaluation of Gulf Stream Simulations in Models with High Vertical Resolution
 Dynamical Evaluation of Gulf Stream Simulations in Models with High Vertical Resolution Harley E. Hurlburt 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, E. Joseph Metzger 1, James G. Richman 1, William J. Schmitz, Jr. 3, Jay
Dynamical Evaluation of Gulf Stream Simulations in Models with High Vertical Resolution Harley E. Hurlburt 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, E. Joseph Metzger 1, James G. Richman 1, William J. Schmitz, Jr. 3, Jay
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans. Steering of upper ocean currents and fronts by the topographically constrained abyssal circulation
 Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 45 (2008) 102-134 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dynatmoce Steering of upper ocean
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 45 (2008) 102-134 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dynatmoce Steering of upper ocean
Pacific HYCOM. E. Joseph Metzger, Harley E. Hurlburt, Alan J. Wallcraft, Luis Zamudio and Patrick J. Hogan
 Pacific HYCOM E. Joseph Metzger, Harley E. Hurlburt, Alan J. Wallcraft, Luis Zamudio and Patrick J. Hogan Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies,
Pacific HYCOM E. Joseph Metzger, Harley E. Hurlburt, Alan J. Wallcraft, Luis Zamudio and Patrick J. Hogan Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies,
HYCOM and GODAE in Relation to Navy Ocean Prediction
 HYCOM and GODAE in Relation to Navy Ocean Prediction An Overview Presented by Harley Hurlburt Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 5004 HYCOM Meeting Naval Research Laboratory
HYCOM and GODAE in Relation to Navy Ocean Prediction An Overview Presented by Harley Hurlburt Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 5004 HYCOM Meeting Naval Research Laboratory
Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM
 Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM James G. Richman Oceanography Division Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS In collaboration with Brian Arbic, Univ. Michigan Joe Metzger, Jay Shriver &
Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM James G. Richman Oceanography Division Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS In collaboration with Brian Arbic, Univ. Michigan Joe Metzger, Jay Shriver &
Status of 1/25 Global HYCOM Simulations
 Status of 1/25 Global HYCOM Simulations Luis Zamudio 1 & Joe Metzger 2 1 Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Florida State University 2 Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, Mississippi
Status of 1/25 Global HYCOM Simulations Luis Zamudio 1 & Joe Metzger 2 1 Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Florida State University 2 Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, Mississippi
An Update on the 1/12 Global HYCOM Effort
 An Update on the 1/12 Global HYCOM Effort E. Joseph Metzger, Alan J. Wallcraft, Jay F. Shriver and Harley E. Hurlburt Naval Research Laboratory 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting 7-99 November 2006 FSU-COAPS,
An Update on the 1/12 Global HYCOM Effort E. Joseph Metzger, Alan J. Wallcraft, Jay F. Shriver and Harley E. Hurlburt Naval Research Laboratory 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting 7-99 November 2006 FSU-COAPS,
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 45 (2008)71-101 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dynatmoce The Gulf Stream pathway
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans 45 (2008)71-101 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dynatmoce The Gulf Stream pathway
Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM
 Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM James G. Richman Oceanography Division Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS In collaboration with Brian Arbic, Univ. Michigan Joe Metzger, Jay Shriver &
Forecasting Tides in Global HYCOM James G. Richman Oceanography Division Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS In collaboration with Brian Arbic, Univ. Michigan Joe Metzger, Jay Shriver &
C
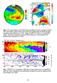 C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/25, and 1/50
 North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/2, and 1/ Xiaobiao Xu and Eric Chassignet Center for ocean-atmospheric prediction studies Florida State University Motivation Numerical models
North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/2, and 1/ Xiaobiao Xu and Eric Chassignet Center for ocean-atmospheric prediction studies Florida State University Motivation Numerical models
1/12 Pacific HYCOM: The End Of A Long Simulation
 1/12 Pacific HYCOM: The End Of A Long Simulation E. Joseph Metzger,, Harley E. Hurlburt and Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM NOPP GODAE Meeting 27-29 29 October
1/12 Pacific HYCOM: The End Of A Long Simulation E. Joseph Metzger,, Harley E. Hurlburt and Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM NOPP GODAE Meeting 27-29 29 October
Concurrent simulation of the eddying general circulation and tides in a global ocean model
 Concurrent simulation of the eddying general circulation and tides in a global ocean model Brian K. Arbic 1 E. Joseph Metzger 2 Alan J. Wallcraft 2 1 Department of Oceanography and Center for Ocean-Atmospheric
Concurrent simulation of the eddying general circulation and tides in a global ocean model Brian K. Arbic 1 E. Joseph Metzger 2 Alan J. Wallcraft 2 1 Department of Oceanography and Center for Ocean-Atmospheric
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM
 An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
Energetics of a global ocean circulation model compared to observations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl048347, 2011 Energetics of a global ocean circulation model compared to observations Prasad G. Thoppil, 1 James G. Richman, 1 and Patrick J. Hogan
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl048347, 2011 Energetics of a global ocean circulation model compared to observations Prasad G. Thoppil, 1 James G. Richman, 1 and Patrick J. Hogan
Bifurcation of the Pacific North Equatorial Current in a wind-driven model: response to climatological winds
 Ocean Dynamics (2011) 61:1329 1344 DOI 10.1007/s10236-011-0427-2 Bifurcation of the Pacific North Equatorial Current in a wind-driven model: response to climatological winds Tommy G. Jensen Received: 23
Ocean Dynamics (2011) 61:1329 1344 DOI 10.1007/s10236-011-0427-2 Bifurcation of the Pacific North Equatorial Current in a wind-driven model: response to climatological winds Tommy G. Jensen Received: 23
Effects of Eddy Variability on the Circulation of the Japan/ East Sea
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 55, pp. 247 to 256. 1999 Effects of Eddy Variability on the Circulation of the Japan/ East Sea G. A. JACOBS 1, P. J. HOGAN 1 AND K. R. WHITMER 2 1 Naval Research Laboratory,
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 55, pp. 247 to 256. 1999 Effects of Eddy Variability on the Circulation of the Japan/ East Sea G. A. JACOBS 1, P. J. HOGAN 1 AND K. R. WHITMER 2 1 Naval Research Laboratory,
Nested Gulf of Mexico Modeling with HYCOM
 Nested Gulf of Mexico Modeling with HYCOM Patrick J. Hogan Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM Meeting December 6-8, 2005 University of Miami, Miami, FL 1/25 (~4
Nested Gulf of Mexico Modeling with HYCOM Patrick J. Hogan Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM Meeting December 6-8, 2005 University of Miami, Miami, FL 1/25 (~4
Impact of Upper Ocean Topographical Coupling and Isopycnal Outcropping in Japan/East Sea Models with 1 8 to 1 64 Resolution*
 2535 Impact of Upper Ocean Topographical Coupling and Isopycnal Outcropping in Japan/East Sea Models with 1 8 to 1 64 Resolution* PATRICK J. HOGAN AND HARLEY E. HURLBURT Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis
2535 Impact of Upper Ocean Topographical Coupling and Isopycnal Outcropping in Japan/East Sea Models with 1 8 to 1 64 Resolution* PATRICK J. HOGAN AND HARLEY E. HURLBURT Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis
Water mass transport associated with the oceanic fronts in the northwestern Pacific Ocean HIDEYUKI NAKANO (METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE)
 Water mass transport associated with the oceanic fronts in the northwestern Pacific Ocean HIDEYUKI NAKANO (METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE) How is the Kuroshio-origin water distributed in the subtropical
Water mass transport associated with the oceanic fronts in the northwestern Pacific Ocean HIDEYUKI NAKANO (METEOROLOGICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE) How is the Kuroshio-origin water distributed in the subtropical
Eddy-resolving global ocean prediction
 Eddy-resolving global ocean prediction Harley E. Hurlburt 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, James A. Cummings 1, A. Birol Kara 1, E. Joseph Metzger 1, Jay F. Shriver 1, Ole Martin Smedstad 3, Alan J. Wallcraft
Eddy-resolving global ocean prediction Harley E. Hurlburt 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, James A. Cummings 1, A. Birol Kara 1, E. Joseph Metzger 1, Jay F. Shriver 1, Ole Martin Smedstad 3, Alan J. Wallcraft
ACC transport sensitivity to air-sea fluxes. Matt Mazloff SIO-UCSD
 ACC transport sensitivity to air-sea fluxes Matt Mazloff SIO-UCSD Southern Ocean State estimate (SOSE): Adjoint, (4d-var) method optimization non-sequential no nudging J = (obs model) 2-2 solve for IC
ACC transport sensitivity to air-sea fluxes Matt Mazloff SIO-UCSD Southern Ocean State estimate (SOSE): Adjoint, (4d-var) method optimization non-sequential no nudging J = (obs model) 2-2 solve for IC
Depth Distribution of the Subtropical Gyre in the North Pacific
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 58, pp. 525 to 529, 2002 Short Contribution Depth Distribution of the Subtropical Gyre in the North Pacific TANGDONG QU* International Pacific Research Center, SOEST, University
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 58, pp. 525 to 529, 2002 Short Contribution Depth Distribution of the Subtropical Gyre in the North Pacific TANGDONG QU* International Pacific Research Center, SOEST, University
Annual Variation of the Kuroshio Transport in a Two-Layer Numerical Model with a Ridge
 994 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 32 Annual Variation of the Kuroshio Transport in a Two-Layer Numerical Model with a Ridge ATSUHIKO ISOBE Department of Earth System Science and Technology, Interdisciplinary
994 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 32 Annual Variation of the Kuroshio Transport in a Two-Layer Numerical Model with a Ridge ATSUHIKO ISOBE Department of Earth System Science and Technology, Interdisciplinary
Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea
 Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea Olga Trusenkova V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia PICES 2014 Annual Meeting, 16-26 October 2014, Korea, Yeosu Deep
Modeling of deep currents in the Japan/East Sea Olga Trusenkova V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia PICES 2014 Annual Meeting, 16-26 October 2014, Korea, Yeosu Deep
1/12 Pacific HYCOM: The End Of A Long Simulation
 1/12 Pacific HYCOM: The End Of A Long Simulation E. Joseph Metzger,, Harley E. Hurlburt and Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM NOPP GODAE Meeting 27-29 29 October
1/12 Pacific HYCOM: The End Of A Long Simulation E. Joseph Metzger,, Harley E. Hurlburt and Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM NOPP GODAE Meeting 27-29 29 October
Chapter 6. Antarctic oceanography
 Chapter 6 Antarctic oceanography The region of the world ocean bordering on Antarctica is unique in many respects. First of all, it is the only region where the flow of water can continue all around the
Chapter 6 Antarctic oceanography The region of the world ocean bordering on Antarctica is unique in many respects. First of all, it is the only region where the flow of water can continue all around the
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM
 An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
Non-linear patterns of eddy kinetic energy in the Japan/East Sea
 Non-linear patterns of eddy kinetic energy in the Japan/East Sea O.O. Trusenkova, D.D. Kaplunenko, S.Yu. Ladychenko, V.B. Lobanov V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia
Non-linear patterns of eddy kinetic energy in the Japan/East Sea O.O. Trusenkova, D.D. Kaplunenko, S.Yu. Ladychenko, V.B. Lobanov V.I.Il ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute, FEB RAS Vladivostok, Russia
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, U. Miami, Miami, FL 33149
 1/25 Atlantic Ocean Simulation Using HYCOM Alan J. Wallcraft1, Eric P. Chassignet2, Harley E. Hurlburt1, and Tamara L. Townsend1 1 2 Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 Rosenstiel
1/25 Atlantic Ocean Simulation Using HYCOM Alan J. Wallcraft1, Eric P. Chassignet2, Harley E. Hurlburt1, and Tamara L. Townsend1 1 2 Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 Rosenstiel
Sea Level Variability in the Western North Pacific during the 20th Century
 Sea Level Variability in the Western North Pacific during the 20th Century Yoshi N. Sasaki (sasakiyo@sci.hokudai.ac.jp), R. Washizu, S. Minobe Hokkaido University, Japan T. Yasuda: Japan Meteorological
Sea Level Variability in the Western North Pacific during the 20th Century Yoshi N. Sasaki (sasakiyo@sci.hokudai.ac.jp), R. Washizu, S. Minobe Hokkaido University, Japan T. Yasuda: Japan Meteorological
Results from High Resolution North Atlantic HYCOM Simulations
 Results from High Resolution North Atlantic HYCOM Simulations Patrick Hogan, Alan Wallcraft, Harley Hurlburt, Tammy Townsend Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS Eric Chassignet RSMAS, University
Results from High Resolution North Atlantic HYCOM Simulations Patrick Hogan, Alan Wallcraft, Harley Hurlburt, Tammy Townsend Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS Eric Chassignet RSMAS, University
Tracer transport and meridional overturn in the equatorial ocean
 OFES workshops, February 2006 Tracer transport and meridional overturn in the equatorial ocean Akio Ishida with Yoshikazu Sasai, Yasuhiro Yamanaka, Hideharu Sasaki, and the OFES members Chlorofluorocarbon
OFES workshops, February 2006 Tracer transport and meridional overturn in the equatorial ocean Akio Ishida with Yoshikazu Sasai, Yasuhiro Yamanaka, Hideharu Sasaki, and the OFES members Chlorofluorocarbon
Enhancing predictability of the Loop Current variability using Gulf of Mexico Hycom
 Enhancing predictability of the Loop Current variability using Gulf of Mexico Hycom Matthieu Le Hénaff (1) Villy Kourafalou (1) Ashwanth Srinivasan (1) Collaborators: O. M. Smedstad (2), P. Hogan (2),
Enhancing predictability of the Loop Current variability using Gulf of Mexico Hycom Matthieu Le Hénaff (1) Villy Kourafalou (1) Ashwanth Srinivasan (1) Collaborators: O. M. Smedstad (2), P. Hogan (2),
Observation and dynamics of baroclinic eddies southeast of Okinawa Island
 Observation and dynamics of baroclinic eddies southeast of Okinawa Island Xiao-Hua Zhu 1, Jea-Hun Park 2 and Daji Huang 1 1 Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, China 2 Graduate
Observation and dynamics of baroclinic eddies southeast of Okinawa Island Xiao-Hua Zhu 1, Jea-Hun Park 2 and Daji Huang 1 1 Second Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, China 2 Graduate
Response of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to Atmospheric Variability
 3020 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 Response of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to Atmospheric Variability J. B. SALLÉE LEGOS, Toulouse, France K. SPEER Oceanography Department, The Florida
3020 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 Response of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to Atmospheric Variability J. B. SALLÉE LEGOS, Toulouse, France K. SPEER Oceanography Department, The Florida
Circumpolar structure and distribution of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current fronts: 1. Mean circumpolar paths
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jc005108, 2009 Circumpolar structure and distribution of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current fronts: 1. Mean circumpolar paths Serguei Sokolov
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jc005108, 2009 Circumpolar structure and distribution of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current fronts: 1. Mean circumpolar paths Serguei Sokolov
Toward Accurate Coastal Ocean Modeling
 Toward Accurate Coastal Ocean Modeling Peter C. Chu Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943, USA Email: pcchu@nps.edu http://www.oc.nps.navy.mil/~chu International Council for Sciences, Scientific
Toward Accurate Coastal Ocean Modeling Peter C. Chu Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943, USA Email: pcchu@nps.edu http://www.oc.nps.navy.mil/~chu International Council for Sciences, Scientific
Numerical Experiments of the Influences of the Transport Variation through the Korea Strait on the Japan/ East Sea Upper Layer Circulation
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 61, pp. 155 to 165, 2005 Numerical Experiments of the Influences of the Transport Variation through the Korea Strait on the Japan/ East Sea Upper Layer Circulation SUNGHYEA
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 61, pp. 155 to 165, 2005 Numerical Experiments of the Influences of the Transport Variation through the Korea Strait on the Japan/ East Sea Upper Layer Circulation SUNGHYEA
Western Boundary Currents. Global Distribution of Western Boundary Currents and their importance
 Western Boundary Currents In previous chapters you have learned about the processes that cause the intensification of currents along the western boundaries of the oceans. In this chapter we will examine
Western Boundary Currents In previous chapters you have learned about the processes that cause the intensification of currents along the western boundaries of the oceans. In this chapter we will examine
O.M Smedstad 1, E.J. Metzger 2, R.A. Allard 2, R. Broome 1, D.S. Franklin 1 and A.J. Wallcraft 2. QinetiQ North America 2. Naval Research Laboratory
 An eddy-resolving ocean reanalysis using the 1/12 global HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) and the Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation (NCODA) scheme O.M Smedstad 1, E.J. Metzger 2, R.A. Allard 2,
An eddy-resolving ocean reanalysis using the 1/12 global HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) and the Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation (NCODA) scheme O.M Smedstad 1, E.J. Metzger 2, R.A. Allard 2,
Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.
![Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz. Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.](/thumbs/88/117265944.jpg) Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
EI Nino Induced Ocean Eddies in the Gulf of Alaska
 EI Nino Induced Ocean Eddies in the Gulf of Alaska Arne Melsom, Harley E. Hurlburt, E. Joseph Metzger, Steven D. Meyers and James J. O'Brien Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida
EI Nino Induced Ocean Eddies in the Gulf of Alaska Arne Melsom, Harley E. Hurlburt, E. Joseph Metzger, Steven D. Meyers and James J. O'Brien Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida
Currents and Mixing in the Southern Ocean. Sarah Gille
 Currents and Mixing in the Southern Ocean Sarah Gille Scripps Institution of Oceanography and Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering UCSD, La Jolla, CA Where might AVISO gridded fields fall
Currents and Mixing in the Southern Ocean Sarah Gille Scripps Institution of Oceanography and Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering UCSD, La Jolla, CA Where might AVISO gridded fields fall
Regional eddy-permitting state estimation of the circulation in the Northern Philippine Sea
 Regional eddy-permitting state estimation of the circulation in the Northern Philippine Sea Bruce D. Cornuelle, Ganesh Gopalakrishnan, Peter F. Worcester, Matthew A. Dzieciuch, and Matthew Mazloff Scripps
Regional eddy-permitting state estimation of the circulation in the Northern Philippine Sea Bruce D. Cornuelle, Ganesh Gopalakrishnan, Peter F. Worcester, Matthew A. Dzieciuch, and Matthew Mazloff Scripps
A Regional HYCOM Model for the US West Coast
 A Regional HYCOM Model for the US West Coast John Kindle Sergio derada,, Josefina Olascoaga Brad Penta Acknowledgments: Joe Metzger, Alan Wallcraft,, Harley Hurlburt,, Pat Hogan Stephanie Anderson( Cayula),
A Regional HYCOM Model for the US West Coast John Kindle Sergio derada,, Josefina Olascoaga Brad Penta Acknowledgments: Joe Metzger, Alan Wallcraft,, Harley Hurlburt,, Pat Hogan Stephanie Anderson( Cayula),
Global HYCOM and Advanced Data Assimilation
 Global HYCOM and Advanced Data Assimilation Harley E. Hurlburt, Robert C. Rhodes, Gregg A. Jacobs Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 phone: (228) 688-4626 fax:(228) 688-4759
Global HYCOM and Advanced Data Assimilation Harley E. Hurlburt, Robert C. Rhodes, Gregg A. Jacobs Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 39529-5004 phone: (228) 688-4626 fax:(228) 688-4759
Tropical wave-induced oceanic eddies at Cabo Corrientes and the María Islands, Mexico
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jc004018, 2007 Tropical wave-induced oceanic eddies at Cabo Corrientes and the María Islands, Mexico Luis Zamudio,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jc004018, 2007 Tropical wave-induced oceanic eddies at Cabo Corrientes and the María Islands, Mexico Luis Zamudio,
Three-Dimensional Pathways of the Northern Deep Waters to the Southern Ocean Surface
 Three-Dimensional Pathways of the Northern Deep Waters to the Southern Ocean Surface Lynne Talley Scripps Institution of Oceanography Workshop: Southern Ocean Dynamics and Biogeochemistry Caltech Linde
Three-Dimensional Pathways of the Northern Deep Waters to the Southern Ocean Surface Lynne Talley Scripps Institution of Oceanography Workshop: Southern Ocean Dynamics and Biogeochemistry Caltech Linde
Generation and Evolution of Internal Waves in Luzon Strait
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Generation and Evolution of Internal Waves in Luzon Strait Ren-Chieh Lien Applied Physics Laboratory University of Washington
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Generation and Evolution of Internal Waves in Luzon Strait Ren-Chieh Lien Applied Physics Laboratory University of Washington
(chose the sign to ensure that it is evaporative)
 SIO 210 (2-3:20 class) Problem Set 2 ANSWER KEY October 17, 2016 Due October 31, 2016 (10 points) 1. The salinity of the inflow to the Mediterranean Sea at the Strait of Gibraltar is about 36.1. The salinity
SIO 210 (2-3:20 class) Problem Set 2 ANSWER KEY October 17, 2016 Due October 31, 2016 (10 points) 1. The salinity of the inflow to the Mediterranean Sea at the Strait of Gibraltar is about 36.1. The salinity
Diagnostics for variability on HYCOM 1/12º Atlantic data assimilative simulations. Z.D.Garraffo, E.P.Chassignet, R.Baraille, O.M.Smedstad, M.
 Diagnostics for variability on HYCOM 1/12º Atlantic data assimilative simulations Z.D.Garraffo, E.P.Chassignet, R.Baraille, O.M.Smedstad, M.Gavart Motivation What is the Impact of data assimilation on
Diagnostics for variability on HYCOM 1/12º Atlantic data assimilative simulations Z.D.Garraffo, E.P.Chassignet, R.Baraille, O.M.Smedstad, M.Gavart Motivation What is the Impact of data assimilation on
The Structure of the Wind-Driven Circulation in the Subtropical South Pacific Ocean*
 JUNE 1998 HUANG AND QIU 1173 The Structure of the Wind-Driven Circulation in the Subtropical South Pacific Ocean* RUI XIN HUANG Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution,
JUNE 1998 HUANG AND QIU 1173 The Structure of the Wind-Driven Circulation in the Subtropical South Pacific Ocean* RUI XIN HUANG Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution,
Shallow, Intermediate, and Deep Overturning Components of the Global Heat Budget
 530 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Shallow, Intermediate, and Deep Overturning Components of the Global Heat Budget LYNNE D. TALLEY Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San
530 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Shallow, Intermediate, and Deep Overturning Components of the Global Heat Budget LYNNE D. TALLEY Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California, San
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey 1. Dynamics: rotation (a) Draw the direction of an inertial current in (i) the northern hemisphere and (ii) the southern hemisphere and
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey 1. Dynamics: rotation (a) Draw the direction of an inertial current in (i) the northern hemisphere and (ii) the southern hemisphere and
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. Effect of Sea Surface Temperature Wind Stress Coupling on Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean
 1092 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 37 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Effect of Sea Surface Temperature Wind Stress Coupling on Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean MICHAEL A.
1092 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 37 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE Effect of Sea Surface Temperature Wind Stress Coupling on Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean MICHAEL A.
S11. Indian Ocean: Supplementary Materials
 C H A P T E R S11 Indian Ocean: Supplementary Materials FIGURE S11.1 Indian Ocean surface circulation (Tables S11.1, S11.2 and Figure 11.1). Surface height (cm). Data from Niiler, Maximenko, and McWilliams
C H A P T E R S11 Indian Ocean: Supplementary Materials FIGURE S11.1 Indian Ocean surface circulation (Tables S11.1, S11.2 and Figure 11.1). Surface height (cm). Data from Niiler, Maximenko, and McWilliams
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP023750 TITLE: Global Ocean Prediction Using HYCOM DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited This paper
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP023750 TITLE: Global Ocean Prediction Using HYCOM DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited This paper
Answer the following questions using letters A through H :
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 10, 2014 Due Nov. 24, 2014 Answer key 1. 10 total 6 points (a) The following kinds of wave motion were mentioned in class A. light 3 x 10 9 m/sec B. sound in air (340 m/sec)
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 10, 2014 Due Nov. 24, 2014 Answer key 1. 10 total 6 points (a) The following kinds of wave motion were mentioned in class A. light 3 x 10 9 m/sec B. sound in air (340 m/sec)
Seafloor Topography and Ocean Circulation
 Special Issue Bathymetry from Space Seafloor Topography and Ocean Circulation Sarah T. Gille Scripps Institution of Oceanography and Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California
Special Issue Bathymetry from Space Seafloor Topography and Ocean Circulation Sarah T. Gille Scripps Institution of Oceanography and Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California
Equilibrium surface elevation distribution in a baroclinic ocean with realistic bottom topography
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 08, NO. C0, 330, doi:0.029/2002jc00579, 2003 Equilibrium surface elevation distribution in a baroclinic ocean with realistic bottom topography Srdjan Dobricic Institute
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 08, NO. C0, 330, doi:0.029/2002jc00579, 2003 Equilibrium surface elevation distribution in a baroclinic ocean with realistic bottom topography Srdjan Dobricic Institute
SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 12, :30-2:30 Eckart 227 Name:
 SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 12, 2018 11:30-2:30 Eckart 227 Name: Please put your initials or name on each page, especially if you pull pages apart. Turn off all phones, ipods, etc. and
SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 12, 2018 11:30-2:30 Eckart 227 Name: Please put your initials or name on each page, especially if you pull pages apart. Turn off all phones, ipods, etc. and
New Development in Coastal Ocean Analysis and Prediction. Peter C. Chu Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943, USA
 New Development in Coastal Ocean Analysis and Prediction Peter C. Chu Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943, USA Coastal Model Major Problems in Coastal Modeling (1) Discretization (2) Sigma Error
New Development in Coastal Ocean Analysis and Prediction Peter C. Chu Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943, USA Coastal Model Major Problems in Coastal Modeling (1) Discretization (2) Sigma Error
The Nondeterministic Nature of Kuroshio Penetration and Eddy Shedding in the South China Sea*
 1712 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY The Nondeterministic Nature of Kuroshio Penetration and Eddy Shedding in the South China Sea* E. JOSEPH METZGER AND HARLEY E. HURLBURT Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis
1712 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY The Nondeterministic Nature of Kuroshio Penetration and Eddy Shedding in the South China Sea* E. JOSEPH METZGER AND HARLEY E. HURLBURT Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation. Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B
 Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
isopycnal outcrop w < 0 (downwelling), v < 0 L.I. V. P.
 Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
On the Atlantic inflow to the Caribbean Sea
 Deep-Sea Research I 49 (2002) 211 243 On the Atlantic inflow to the Caribbean Sea William E. Johns a, *, Tamara L. Townsend b, David M. Fratantoni c, W. Douglas Wilson d a Rosenstiel School of Marine and
Deep-Sea Research I 49 (2002) 211 243 On the Atlantic inflow to the Caribbean Sea William E. Johns a, *, Tamara L. Townsend b, David M. Fratantoni c, W. Douglas Wilson d a Rosenstiel School of Marine and
Large-Scale Circulations Forced by Localized Mixing over a Sloping Bottom*
 AUGUST 001 SPALL 369 Large-Scale Circulations Forced by Localized Miing over a Sloping Bottom* MICHAEL A. SPALL Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts
AUGUST 001 SPALL 369 Large-Scale Circulations Forced by Localized Miing over a Sloping Bottom* MICHAEL A. SPALL Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts
Upper Ocean Circulation
 Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Summer generation of the Southern Gulf of California eddy train
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jc004467, 2008 Summer generation of the Southern Gulf of California eddy train Luis Zamudio, 1 Patrick Hogan, 2 and
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jc004467, 2008 Summer generation of the Southern Gulf of California eddy train Luis Zamudio, 1 Patrick Hogan, 2 and
The first operational weather prediction
 HPC AND N ATIONAL S ECURITY REAL-TIME OCEAN MODELING SYSTEMS The Naval Research Laboratory has developed the world s first eddy-resolving global ocean nowcast and forecast system. It uses satellite observations
HPC AND N ATIONAL S ECURITY REAL-TIME OCEAN MODELING SYSTEMS The Naval Research Laboratory has developed the world s first eddy-resolving global ocean nowcast and forecast system. It uses satellite observations
Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator
 Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator Group Representative Hideharu
Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator Group Representative Hideharu
Deep-ocean observatories, biogeochemical & biophysical time-series data: NZ-Australia & international linkages
 Deep-ocean observatories, biogeochemical & biophysical time-series data: NZ-Australia & international linkages Scott Nodder (NIWA), Tom Trull (ACE-CRC, UTas, CSIRO) & Eric Schulz (BoM) IMOS NZ-Australia
Deep-ocean observatories, biogeochemical & biophysical time-series data: NZ-Australia & international linkages Scott Nodder (NIWA), Tom Trull (ACE-CRC, UTas, CSIRO) & Eric Schulz (BoM) IMOS NZ-Australia
Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, U. Miami, Miami, FL 33149
 1/25 Atlantic Ocean Simulation Using HYCOM Alan J. Wallcraft 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, Harley E. Hurlburt 1, and Tamara L. Townsend 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 2 Rosenstiel
1/25 Atlantic Ocean Simulation Using HYCOM Alan J. Wallcraft 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, Harley E. Hurlburt 1, and Tamara L. Townsend 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS 39529 2 Rosenstiel
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
Decadal Variation of the Geostrophic Vorticity West of the Luzon Strait
 144 The Open Oceanography Journal, 2010, 4, 144-149 Open Access Decadal Variation of the Geostrophic Vorticity West of the Luzon Strait Yinglai Jia *,1, Qinyu Liu 1 and Haibo Hu 2 1 Physical Oceanography
144 The Open Oceanography Journal, 2010, 4, 144-149 Open Access Decadal Variation of the Geostrophic Vorticity West of the Luzon Strait Yinglai Jia *,1, Qinyu Liu 1 and Haibo Hu 2 1 Physical Oceanography
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO3053 1 2 Contribution of topographically-generated submesoscale turbulence to Southern Ocean overturning 3
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO3053 1 2 Contribution of topographically-generated submesoscale turbulence to Southern Ocean overturning 3
Eddy Shedding from the Kuroshio Bend at Luzon Strait
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 60, pp. 1063 to 1069, 2004 Short Contribution Eddy Shedding from the Kuroshio Bend at Luzon Strait YINGLAI JIA* and QINYU LIU Physical Oceanography Laboratory and Ocean-Atmosphere
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 60, pp. 1063 to 1069, 2004 Short Contribution Eddy Shedding from the Kuroshio Bend at Luzon Strait YINGLAI JIA* and QINYU LIU Physical Oceanography Laboratory and Ocean-Atmosphere
Processes Coupling the Upper and Deep Ocean on the Continental Slope
 Processes Coupling the Upper and Deep Ocean on the Continental Slope D. Randolph Watts Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island South Ferry Road Narragansett, RI 02882 phone:(401) 874-6507;
Processes Coupling the Upper and Deep Ocean on the Continental Slope D. Randolph Watts Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island South Ferry Road Narragansett, RI 02882 phone:(401) 874-6507;
Lecture 8. Lecture 1. Wind-driven gyres. Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk
 Lecture 8 Lecture 1 Wind-driven gyres Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk wek > 0 VEk wek < 0 VEk 1 8.1 Vorticity and circulation The vorticity of a parcel is a measure of its
Lecture 8 Lecture 1 Wind-driven gyres Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk wek > 0 VEk wek < 0 VEk 1 8.1 Vorticity and circulation The vorticity of a parcel is a measure of its
Ocean surface circulation
 Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region
 Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
The Center for Ocean Atmospheric Prediction Studies, FSU, Tallahassee, FL 32306
 Global Ocean Prediction Using HYCOM E. Joseph Metzger 1 joe.metzger@nrlssc.navy.mil Eric P. Chassignet 2 echassignet@coaps.fsu.edu James A. Cummings 3 james.cummings@nrlmry.navy.mil Harley E. Hurlburt
Global Ocean Prediction Using HYCOM E. Joseph Metzger 1 joe.metzger@nrlssc.navy.mil Eric P. Chassignet 2 echassignet@coaps.fsu.edu James A. Cummings 3 james.cummings@nrlmry.navy.mil Harley E. Hurlburt
Characteristics of Sea Surface Circulation and Eddy Field in the South China Sea Revealed by Satellite Altimetric Data
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 331 to 344, 2000 Characteristics of Sea Surface Circulation and Eddy Field in the South China Sea Revealed by Satellite Altimetric Data AKIHIKO MORIMOTO 1 *, KOICHI
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 56, pp. 331 to 344, 2000 Characteristics of Sea Surface Circulation and Eddy Field in the South China Sea Revealed by Satellite Altimetric Data AKIHIKO MORIMOTO 1 *, KOICHI
Causes for Large-Scale Hydrographic Changes at the Hawaii Ocean Time Series Station
 SEPTEMBER 2008 S T A M M E R E T A L. 1931 Causes for Large-Scale Hydrographic Changes at the Hawaii Ocean Time Series Station D. STAMMER Institut für Meereskunde, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
SEPTEMBER 2008 S T A M M E R E T A L. 1931 Causes for Large-Scale Hydrographic Changes at the Hawaii Ocean Time Series Station D. STAMMER Institut für Meereskunde, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Topographic Control of Basin and Channel Flows: The Role of Bottom Pressure Torques and Friction
 1786 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 36 Topographic Control of Basin and Channel Flows: The Role of Bottom Pressure Torques and Friction LAURA JACKSON* Department of Earth
1786 J O U R N A L O F P H Y S I C A L O C E A N O G R A P H Y VOLUME 36 Topographic Control of Basin and Channel Flows: The Role of Bottom Pressure Torques and Friction LAURA JACKSON* Department of Earth
Improvements to the Wind Driven Component of the OSCAR Surface Current Product
 OVWST Meeting May 18-2, 29 p. 1 Improvements to the Wind Driven Component of the OSCAR Surface Current Product Kathleen Dohan, Gary S. E. Lagerloef, and John T. Gunn Earth & Space Research Seattle, Washington
OVWST Meeting May 18-2, 29 p. 1 Improvements to the Wind Driven Component of the OSCAR Surface Current Product Kathleen Dohan, Gary S. E. Lagerloef, and John T. Gunn Earth & Space Research Seattle, Washington
What governs the location of the Southern Ocean deep winter mixing in CESM
 NSF NCAR WYOMING SUPERCOMPUTER CENTER DOE SCIDAC FUNDED PROJECT What governs the location of the Southern Ocean deep winter mixing in CESM Justin Small Dan Whitt Alice DuVivier Matt Long Acknowledging:
NSF NCAR WYOMING SUPERCOMPUTER CENTER DOE SCIDAC FUNDED PROJECT What governs the location of the Southern Ocean deep winter mixing in CESM Justin Small Dan Whitt Alice DuVivier Matt Long Acknowledging:
Comparison between vertical shear mixing and surface wave-induced mixing in the global ocean
 Comparison between vertical shear mixing and surface wave-induced mixing in the global ocean Fangli Qiao and Chuanjiang Huang Key Laboratory of Marine Science and Numerical Modeling First Institute of
Comparison between vertical shear mixing and surface wave-induced mixing in the global ocean Fangli Qiao and Chuanjiang Huang Key Laboratory of Marine Science and Numerical Modeling First Institute of
Marginal Sea - Open Ocean Exchange
 Marginal Sea - Open Ocean Exchange Michael A. Spall Mail Stop 21 Department of Physical Oceanography Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543-1541 phone: (508) 289-3342 fax: (508) 457-2181
Marginal Sea - Open Ocean Exchange Michael A. Spall Mail Stop 21 Department of Physical Oceanography Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543-1541 phone: (508) 289-3342 fax: (508) 457-2181
Interactions between the Indonesian Throughflow and circulations in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Abstract
 Interactions between the Indonesian Throughflow and circulations in the Indian and Pacific Oceans Julian P. McCreary, 1 Ryo Furue, Tommy Jensen, Hyoun-Woo Kang, 2 Bohyun Bang, Tangdong Qu International
Interactions between the Indonesian Throughflow and circulations in the Indian and Pacific Oceans Julian P. McCreary, 1 Ryo Furue, Tommy Jensen, Hyoun-Woo Kang, 2 Bohyun Bang, Tangdong Qu International
On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time
 Hamburg Workshop 215 On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time Xiaoming Zhai Centre for Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia With David Marshall,
Hamburg Workshop 215 On the Wind Power Input and Eddy Residence Time Xiaoming Zhai Centre for Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia With David Marshall,
Why Western Boundary Currents in Realistic Oceans are Inviscid: A Link between Form Stress and Bottom Pressure Torques
 2871 Why Western Boundary Currents in Realistic Oceans are Inviscid: A Link between Form Stress and Bottom Pressure Torques CHRIS W. HUGHES Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, Bidston Observatory, Prenton,
2871 Why Western Boundary Currents in Realistic Oceans are Inviscid: A Link between Form Stress and Bottom Pressure Torques CHRIS W. HUGHES Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, Bidston Observatory, Prenton,
Evaluation of HYCOM in the Kuroshio Extension region using new metrics
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jc003614, 2007 Evaluation of HYCOM in the Kuroshio Extension region using new metrics Kathryn A. Kelly, 1 LuAnne
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jc003614, 2007 Evaluation of HYCOM in the Kuroshio Extension region using new metrics Kathryn A. Kelly, 1 LuAnne
Proposed draft marine bioregions
 Proposed draft marine bioregions 1. PROPOSED PELAGIC BIOREGIONS Map 1. Proposed draft pelagic bioregions List of proposed pelagic bioregions: 1. Agulhas Current 2. Antarctic 3. Antarctic Polar Front 4.
Proposed draft marine bioregions 1. PROPOSED PELAGIC BIOREGIONS Map 1. Proposed draft pelagic bioregions List of proposed pelagic bioregions: 1. Agulhas Current 2. Antarctic 3. Antarctic Polar Front 4.
Flow structure and variability in the Subtropical Indian Ocean
 Chapter 4 Flow structure and variability in the Subtropical Indian Ocean 4.1 Introduction It is well known from satellite altimetry that the variability of the South Indian Ocean comprises a range of frequencies
Chapter 4 Flow structure and variability in the Subtropical Indian Ocean 4.1 Introduction It is well known from satellite altimetry that the variability of the South Indian Ocean comprises a range of frequencies
Note that Rossby waves are tranverse waves, that is the particles move perpendicular to the direction of propagation. f up, down (clockwise)
 Ocean 423 Rossby waves 1 Rossby waves: Restoring force is the north-south gradient of background potential vorticity (f/h). That gradient can be due to either the variation in f with latitude, or to a
Ocean 423 Rossby waves 1 Rossby waves: Restoring force is the north-south gradient of background potential vorticity (f/h). That gradient can be due to either the variation in f with latitude, or to a
