Filling the Cosmos with (Virtual) Stars. Mark Krumholz, UC Santa Cruz HiPACC Computational Astronomy Journalism Boot Camp, June 26, 2012
|
|
|
- Christal Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Filling the Cosmos with (Virtual) Stars Mark Krumholz, UC Santa Cruz HiPACC Computational Astronomy Journalism Boot Camp, June 26, 2012
2 Outline What is the interstellar medium, and how is it related to star formation? Why is this a problem for supercomputers? What are the big questions, and how do simulations help answer them?
3 What you get if you google image search interstellar medium The black light of the interstellar medium of deep space illumines all that is not, to be seen and not to Be. To Be and not seen this is the path of the Panther woman. From the hydrogen oceans of Deep Space she condenses rain. Water precipitates from Her Vast Womb, falling onto planets open to Her Life giving moisture.
4 Hier ist wahrhaftig ein loch im Himmel!* * Here truly is a hole in Heaven! - - William Herschel, as remembered by his sister Caroline, 1784
5 Postsdam, 1904
6 Observations from Lick Observatory!
7 A Modern View of the ISM ISM made up of many phases Most H is atomic, n ~ 1 cm 3, T ~ 1,000 10,000 K Densest gas is molecular (H 2 ), n > 100 cm 3, T ~ 10 K
8 Milky Way Census Visible Stars: ~10 11 M H Atomic hydrogen: ~10 10 M CO Molecular hydrogen: ~ M
9 Evidence for Star Formation
10 Leroy Maps of HI, H 2, and SFR
11 Why Supercomputers? Clouds filled with hypersonic turbulent motions, so analytic treatment impossible Many physical processes important Gas flows, gravity, magnetic fields, radiation Large range of scales: typical GMC density ~100 cm 3, stellar density ~10 24 cm 3 Timescales too long for direct observation
12 What Does a Simulation Do? Step 1: start with the underlying equations. Example: thermal diffusion Time T t = F F = κ T = T t = κ 2 T Temperature Heat flux Thermal conductivity
13 Step 2: Discretize y L x x j = 3 (3,0) (3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (3,4) (3,5) j = 2 (2,0) (2,1) (2,2) (2,3) (2,4) (2,5) y L y j = 1 (1,0) (1,1) (1,2) (1,3) (1,4) (1,5) j = 0 (0,0) (0,1) (0,2) (0,3) (0,4) (0.5) i = 0 Discretize in space: T ij t i = 1 i = 2 i = 3 i = 4 i = 5 = κ x 2 (T i 1,j + T i+1,j + T i,j 1, +T i,j+1 4T i,j ) x
14 Step 2: Discretize y L x x j = 3 (3,0) (3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (3,4) (3,5) j = 2 (2,0) (2,1) (2,2) (2,3) (2,4) (2,5) y L y j = 1 (1,0) (1,1) (1,2) (1,3) (1,4) (1,5) j = 0 (0,0) (0,1) (0,2) (0,3) (0,4) (0.5) i = 0 Discretize in space and time: T (n+1) ij = T (n) ij i = 1 i = 2 i = 3 i = 4 i = 5 + t x 2 κ T (n) i 1,j + T (n) i+1,j + T (n) (n) i,j 1, +T i,j+1 x (n) 4T i,j
15 Step 3: Turn the Crank
16 Star Formation: The Big Questions What determines stellar masses? Does stellar mass have an upper limit? What determines the rate at which stars form?
17 The IMF Fig. 18. The measured IMF for the ONC, fitted with a log-normal dis top and bottom IMF as measured panels represent in the Orion thenebula mass distributions Cluster (da Rio+ obtained 2012) assumin respectively, whereas the center panels show the result assuming Baraffe mass has been extrapolated from their T eff (see text). The shaded areas represent the IMF of Chabrier (2003) (left panel) and Kroupa (2001) (righ
18 Challenges of the IMF IMF is universal or nearly so, yet star- forming environments vary greatly. Why? Why are stars at the right mass scale to allow nuclear fusion?
19 Simple Collapsing Cluster Simulation Column density Temperature Krumholz, Klein, & McKee (2011) What s included: hydrodynamics, gravity, radiation Numerical method: AMR
20 Doesn t Work
21 Adding More Physics Krumholz, Klein, & McKee (2012) What s included: hydrodynamics, gravity, radiation, protostellar jets Numerical method: AMR
22 Works Much Better
23 Do Stars Have a Mass Limit? Krumholz What s included: hydrodynamics, gravity, radiation Numerical method: AMR
24 Observational Test: The Disk
25 The Instrument Atacama Large Millimeter Array
26 The Prediction Simulated ALMA observation in CH 3 CN GHz (Krumholz+ 2007) Numerical method: long characteristics
27 Star Formation Rates: the Simplest Approach What s included: hydrodynamics, gravity Numerical method: SPH
28 SFR: The Problem in a Nutshell Simulation Bigiel Too fast by a factor of ~100 Too efficient: simulation forms a gravitationally bound cluster, but most stars not in clusters
29 Adding More Physics Simulation: Wang et al. (2009) What s included: MHD, gravity, protostellar jets Numerical method: AMR
30 Concluding Thoughts Simulations are the indispensible tool for understanding star formation Many big problems not fully solved: origin of stellar masses, star formation rates This is probably because we don t have all the necessary physics in the codes yet
From Massive Cores to Massive Stars
 From Massive Cores to Massive Stars Mark Krumholz Princeton University / UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley) Kaitlin Kratter, Christopher Matzner (U. Toronto) Jonathan
From Massive Cores to Massive Stars Mark Krumholz Princeton University / UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley) Kaitlin Kratter, Christopher Matzner (U. Toronto) Jonathan
Topics for Today s Class
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
SFEs in clusters. Final value of the SFE. For an isolated clump SFE exp. (t exp. = SFE(t exp. M ( cluster. t ) exp M clump. (t) M gas,i.
 SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
The Initial Mass Function Elisa Chisari
 The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation
 The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation Stella Offner NSF Fellow, ITC Dense Cores in Dark Clouds Oct 23 2009 Collaborators: Chris McKee (UC Berkeley), Richard Klein (UC Berkeley; LLNL),
The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation Stella Offner NSF Fellow, ITC Dense Cores in Dark Clouds Oct 23 2009 Collaborators: Chris McKee (UC Berkeley), Richard Klein (UC Berkeley; LLNL),
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview. Ulrike Kuchner
 STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview Ulrike Kuchner Remember, remember.. Outline! measurements of SFRs: - techniques to see what the SF rate is - importance of massive stars and HII regions - the
STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview Ulrike Kuchner Remember, remember.. Outline! measurements of SFRs: - techniques to see what the SF rate is - importance of massive stars and HII regions - the
The turbulent formation of stars
 The turbulent formation of stars Christoph Federrath Citation: Physics Today 71, 6, 38 (2018); doi: 10.1063/PT.3.3947 View online: https://doi.org/10.1063/pt.3.3947 View Table of Contents: http://physicstoday.scitation.org/toc/pto/71/6
The turbulent formation of stars Christoph Federrath Citation: Physics Today 71, 6, 38 (2018); doi: 10.1063/PT.3.3947 View online: https://doi.org/10.1063/pt.3.3947 View Table of Contents: http://physicstoday.scitation.org/toc/pto/71/6
Chapter 9. The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 9 The Formation and Structure of Stars The Interstellar Medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Chapter 9 The Formation and Structure of Stars The Interstellar Medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Chapter 16: Star Birth
 Chapter 16 Lecture Chapter 16: Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
Chapter 16 Lecture Chapter 16: Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
Fundamental Issues in Star Formation
 Fundamental Issues in Star Formation - Formation and statistical properties of dense molecular cloud cores (mass function of cores, scaling relations, gravitational boundedness, rotational properties)
Fundamental Issues in Star Formation - Formation and statistical properties of dense molecular cloud cores (mass function of cores, scaling relations, gravitational boundedness, rotational properties)
AST4930: Star and Planet Formation. Syllabus. AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014
 AST4930: Star and Planet Formation Lecture 1: Overview Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan jt@astro.ufl.edu Bryant 302 Syllabus AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014 Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan (jt
AST4930: Star and Planet Formation Lecture 1: Overview Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan jt@astro.ufl.edu Bryant 302 Syllabus AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014 Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan (jt
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Kiloparsec-Scale Simulations of Star Formation in Disk Galaxies. IV. Regulation of Galactic Star Formation Rates by Stellar Feedback
 Kiloparsec-Scale Simulations of Star Formation in Disk Galaxies. IV. Regulation of Galactic Star Formation Rates by Stellar Feedback Michael J. Butler Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Knigstuhl 17,
Kiloparsec-Scale Simulations of Star Formation in Disk Galaxies. IV. Regulation of Galactic Star Formation Rates by Stellar Feedback Michael J. Butler Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Knigstuhl 17,
Interstellar Dust and Gas
 Interstellar Dust and Gas In 1783 William Herschel began a survey of the heavens using an 18 ¾ inch reflector of his own construction. His goal was to discover new star clusters, nebulae, and double stars.
Interstellar Dust and Gas In 1783 William Herschel began a survey of the heavens using an 18 ¾ inch reflector of his own construction. His goal was to discover new star clusters, nebulae, and double stars.
Star-Forming Clouds. Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space. The gas between the stars is called the interstellar medium.
 Star Birth Chapter 16 Lecture 16.1 Stellar Nurseries The Cosmic Perspective Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Seventh Edition Star Birth Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Star Birth Chapter 16 Lecture 16.1 Stellar Nurseries The Cosmic Perspective Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Seventh Edition Star Birth Where do stars form? Star-Forming
SFEs in clusters. Final value of the SFE. For an isolated clump SFE exp. (t exp. = SFE(t exp. M ( cluster. t ) exp M clump. (t) M gas,i.
 SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay)
 Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Interstellar Dust and Gas
 Interstellar Dust and Gas In 1783 William Herschel began a survey of the heavens using an 18 ¾ inch reflector of his own construction. His goal was to discover new star clusters, nebulae, and double stars.
Interstellar Dust and Gas In 1783 William Herschel began a survey of the heavens using an 18 ¾ inch reflector of his own construction. His goal was to discover new star clusters, nebulae, and double stars.
Chapter 11 Review. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
 Chapter 11 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
Chapter 11 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
Where do Stars Form?
 Where do Stars Form? Coldest spots in the galaxy: T ~ 10 K Composition: Mainly molecular hydrogen 1% dust EGGs = Evaporating Gaseous Globules ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1995/95-190.txt Slide
Where do Stars Form? Coldest spots in the galaxy: T ~ 10 K Composition: Mainly molecular hydrogen 1% dust EGGs = Evaporating Gaseous Globules ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1995/95-190.txt Slide
PART 3 Galaxies. Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way
 PART 3 Galaxies Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way The Interstellar Medium The Sombrero Galaxy Space is far from empty! Clouds of cold gas Clouds of dust In a galaxy, gravity pulls the dust
PART 3 Galaxies Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way The Interstellar Medium The Sombrero Galaxy Space is far from empty! Clouds of cold gas Clouds of dust In a galaxy, gravity pulls the dust
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^
 Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Other stellar types. Open and globular clusters: chemical compositions
 Other stellar types Some clusters have hotter stars than we find in the solar neighbourhood -- O, B, A stars -- as well as F stars, and cooler stars (G, K, M) Hence we can establish intrinsic values (M
Other stellar types Some clusters have hotter stars than we find in the solar neighbourhood -- O, B, A stars -- as well as F stars, and cooler stars (G, K, M) Hence we can establish intrinsic values (M
21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO
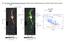 21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO Spitzer YSO JCMT prestellar core prestellar core JCMT protostellar core protostellar core surface
21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO Spitzer YSO JCMT prestellar core prestellar core JCMT protostellar core protostellar core surface
Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales
 Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales Suzanne N. Shaske1 and Dr. Jonathan C. Tan2 1 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida Departments of
Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales Suzanne N. Shaske1 and Dr. Jonathan C. Tan2 1 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida Departments of
Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved
 Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
CHAPTER 29: STARS BELL RINGER:
 CHAPTER 29: STARS BELL RINGER: Where does the energy of the Sun come from? Compare the size of the Sun to the size of Earth. 1 CHAPTER 29.1: THE SUN What are the properties of the Sun? What are the layers
CHAPTER 29: STARS BELL RINGER: Where does the energy of the Sun come from? Compare the size of the Sun to the size of Earth. 1 CHAPTER 29.1: THE SUN What are the properties of the Sun? What are the layers
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
 The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2])
![Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2])](/thumbs/81/83160044.jpg) Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Massive interstellar gas clouds Up to ~10 5 M 100 s of LY in diameter. Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) defined to be M > 10 4 M High
Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Massive interstellar gas clouds Up to ~10 5 M 100 s of LY in diameter. Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) defined to be M > 10 4 M High
Clicker Question: Clicker Question: What is the expected lifetime for a G2 star (one just like our Sun)?
 How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass
How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass
The Formation of Star Clusters
 The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of ngvla Working Group 2
 Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Low mass star formation. Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...
 Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
First Detection of an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Candidate in the Milky Way
 Press Release September 27, 2017 Keio University First Detection of an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Candidate in the Milky Way Professor Tomoharu Oka of the Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and
Press Release September 27, 2017 Keio University First Detection of an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Candidate in the Milky Way Professor Tomoharu Oka of the Department of Physics, Faculty of Science and
Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
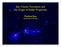 Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties Matthew Bate University of Exeter Typical molecular cloud (Bate et al. 2003) Denser cloud (Bate & Bonnell 2005) Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit
Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties Matthew Bate University of Exeter Typical molecular cloud (Bate et al. 2003) Denser cloud (Bate & Bonnell 2005) Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit
IX. Star and planet formation. h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html
 IX. Star and planet formation h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 1. The ISM Most of the volume of space around us contains the diffuse ISM at 10 4-10 6 K with densities of only a few atoms per
IX. Star and planet formation h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 1. The ISM Most of the volume of space around us contains the diffuse ISM at 10 4-10 6 K with densities of only a few atoms per
ISM Structure: Order from Chaos
 ISM Structure: Order from Chaos Philip Hopkins with Eliot Quataert, Norm Murray, Lars Hernquist, Dusan Keres, Todd Thompson, Desika Narayanan, Dan Kasen, T. J. Cox, Chris Hayward, Kevin Bundy, & more The
ISM Structure: Order from Chaos Philip Hopkins with Eliot Quataert, Norm Murray, Lars Hernquist, Dusan Keres, Todd Thompson, Desika Narayanan, Dan Kasen, T. J. Cox, Chris Hayward, Kevin Bundy, & more The
Chapter 15 Star Birth. Star-Forming Clouds. Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space
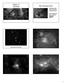 Chapter 15 Star Birth Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space The gas between the stars is called the interstellar medium Visible light (Hubble Space Telescope)
Chapter 15 Star Birth Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space The gas between the stars is called the interstellar medium Visible light (Hubble Space Telescope)
Early Phases of Star Formation
 Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Star Formation. Eagle Nebula, Lagoon Nebula, and Orion Nebula
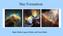 Star Formation Eagle Nebula, Lagoon Nebula, and Orion Nebula By the late 18 th century astronomers understood that there were changes in the starry realm. Occasionally, new stars appeared, then faded away.
Star Formation Eagle Nebula, Lagoon Nebula, and Orion Nebula By the late 18 th century astronomers understood that there were changes in the starry realm. Occasionally, new stars appeared, then faded away.
SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG)
 SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG) WITH PATRICK HENNEBELLE JUAN SOLER AND RALF KLESSEN Credit: Lost Valley Observatory Star formation is self regulating HII HII regions, regions, supernovae supernovae Molecular
SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG) WITH PATRICK HENNEBELLE JUAN SOLER AND RALF KLESSEN Credit: Lost Valley Observatory Star formation is self regulating HII HII regions, regions, supernovae supernovae Molecular
(Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core
 (Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core Benoît Commerçon Supervisors: E. Audit, G. Chabrier and P. Hennebelle Collaborator: R. Teyssier (3D - AMR) CEA/DSM/IRFU/SAp
(Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core Benoît Commerçon Supervisors: E. Audit, G. Chabrier and P. Hennebelle Collaborator: R. Teyssier (3D - AMR) CEA/DSM/IRFU/SAp
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ M gas / dyn. Log SFR. Kennicutt Log. gas / dyn
 Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates.
 1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
1. Star: A object made of gas found in outer space that radiates. 2. Stars produce extremely great quantities of energy through the process of. The chemical formula for nuclear fusion looks like this:
The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18)
 The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18) The interstellar medium (ISM) is all the gas (and about 1% dust) that fills our Galaxy and others. It is the raw material from which stars form, and into which stars eject
The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18) The interstellar medium (ISM) is all the gas (and about 1% dust) that fills our Galaxy and others. It is the raw material from which stars form, and into which stars eject
Implications of protostellar disk fragmentation
 Implications of protostellar disk fragmentation Eduard Vorobyov: The Institute of Astronomy, The University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Collaborators: Shantanu Basu, The University of Western Ontario, Canada
Implications of protostellar disk fragmentation Eduard Vorobyov: The Institute of Astronomy, The University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Collaborators: Shantanu Basu, The University of Western Ontario, Canada
Chapter 11 The Formation of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky.
Chapter 11 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky.
Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: Date: 09/21/2017
 Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR7.2017.Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: 243920 Date: 09/21/2017 Section 1.1 - According to the Doppler Effect, what happens to the wavelength of light as galaxies
Test Name: 09.LCW.0352.SCIENCE.GR7.2017.Q1.S.THEUNIVERSE-SOLARSYSTEMHONORS Test ID: 243920 Date: 09/21/2017 Section 1.1 - According to the Doppler Effect, what happens to the wavelength of light as galaxies
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation
 Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Physics and chemistry of the interstellar medium. Lecturers: Simon Glover, Rowan Smith Tutor: Raquel Chicharro
 Physics and chemistry of the interstellar medium Lecturers: Simon Glover, Rowan Smith Tutor: Raquel Chicharro This course consists of three components: Lectures Exercises Seminar [Wed., 2-4] [Thu., 4-5]
Physics and chemistry of the interstellar medium Lecturers: Simon Glover, Rowan Smith Tutor: Raquel Chicharro This course consists of three components: Lectures Exercises Seminar [Wed., 2-4] [Thu., 4-5]
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Examination 3 Review Problems Multiple Choice Questions: The first eight questions are multiple choice. Except where explicitly noted, only one answer is correct for each
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016
 Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Lecture11; November 1, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to stars Measuring distances Inverse square law: luminosity vs brightness Colors and spectral types, the H-R diagram
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Lecture11; November 1, 2016 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to stars Measuring distances Inverse square law: luminosity vs brightness Colors and spectral types, the H-R diagram
V. Astronomy Section
 EAS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines V. Astronomy Section 1. Introduction, Astronomical Distances, Solar System Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of Earth s position in the solar
EAS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines V. Astronomy Section 1. Introduction, Astronomical Distances, Solar System Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of Earth s position in the solar
Energy. mosquito lands on your arm = 1 erg. Firecracker = 5 x 10 9 ergs. 1 stick of dynamite = 2 x ergs. 1 ton of TNT = 4 x ergs
 Energy mosquito lands on your arm = 1 erg Firecracker = 5 x 10 9 ergs 1 stick of dynamite = 2 x 10 13 ergs 1 ton of TNT = 4 x 10 16 ergs 1 atomic bomb = 1 x 10 21 ergs Magnitude 8 earthquake = 1 x 10 26
Energy mosquito lands on your arm = 1 erg Firecracker = 5 x 10 9 ergs 1 stick of dynamite = 2 x 10 13 ergs 1 ton of TNT = 4 x 10 16 ergs 1 atomic bomb = 1 x 10 21 ergs Magnitude 8 earthquake = 1 x 10 26
Unveiling the Birth of Stars and Galaxies
 Unveiling the Birth of Stars and Galaxies Robert Kennicutt Institute of Astronomy University of Cambridge Cosmic Origins: A Grand Challenge for 21 st Century Astrophysics We are in the midst of a revolution
Unveiling the Birth of Stars and Galaxies Robert Kennicutt Institute of Astronomy University of Cambridge Cosmic Origins: A Grand Challenge for 21 st Century Astrophysics We are in the midst of a revolution
Chapter 19: Our Galaxy
 Chapter 19 Lecture Chapter 19: Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Chapter 19 Lecture Chapter 19: Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
NUMERICAL METHODS IN ASTROPHYSICS An Introduction
 -1 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics NUMERICAL METHODS IN ASTROPHYSICS An Introduction Peter Bodenheimer University of California Santa Cruz, USA Gregory P. Laughlin University of California Santa Cruz,
-1 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics NUMERICAL METHODS IN ASTROPHYSICS An Introduction Peter Bodenheimer University of California Santa Cruz, USA Gregory P. Laughlin University of California Santa Cruz,
Textbook Chapters 24 - Stars Textbook Chapter 25 - Universe. Regents Earth Science with Ms. Connery
 Textbook Chapters 24 - Stars Textbook Chapter 25 - Universe Regents Earth Science with Ms. Connery SPECTROSCOPY is the study of light. Read to learn - textbook pages 674-677 STAR LIGHT gives us characteristics
Textbook Chapters 24 - Stars Textbook Chapter 25 - Universe Regents Earth Science with Ms. Connery SPECTROSCOPY is the study of light. Read to learn - textbook pages 674-677 STAR LIGHT gives us characteristics
10/26/ Star Birth. Chapter 13: Star Stuff. How do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds. Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud. Gravity Versus Pressure
 10/26/16 Lecture Outline 13.1 Star Birth Chapter 13: Star Stuff How do stars form? Our goals for learning: How do stars form? How massive are newborn stars? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
10/26/16 Lecture Outline 13.1 Star Birth Chapter 13: Star Stuff How do stars form? Our goals for learning: How do stars form? How massive are newborn stars? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
Late Stages of Stellar Evolution. Late Stages of Stellar Evolution
 Late Stages of Stellar Evolution The star enters the Asymptotic Giant Branch with an active helium shell burning and an almost dormant hydrogen shell Again the stars size and luminosity increase, leading
Late Stages of Stellar Evolution The star enters the Asymptotic Giant Branch with an active helium shell burning and an almost dormant hydrogen shell Again the stars size and luminosity increase, leading
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Gravitational collapse of gas
 Gravitational collapse of gas Assume a gas cloud of mass M and diameter D Sound speed for ideal gas is c s = γ P ρ = γ nkt ρ = γ kt m Time for sound wave to cross the cloud t sound = D == D m c s γ kt
Gravitational collapse of gas Assume a gas cloud of mass M and diameter D Sound speed for ideal gas is c s = γ P ρ = γ nkt ρ = γ kt m Time for sound wave to cross the cloud t sound = D == D m c s γ kt
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS. η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith)
 THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee HIPACC, UCSC August 8, 2013 with Andrew Cunningham Richard Klein Mark Krumholz Andrew Myers
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee HIPACC, UCSC August 8, 2013 with Andrew Cunningham Richard Klein Mark Krumholz Andrew Myers
Astronomy across the spectrum: telescopes and where we put them. Martha Haynes Exploring Early Galaxies with the CCAT June 28, 2012
 Astronomy across the spectrum: telescopes and where we put them Martha Haynes Exploring Early Galaxies with the CCAT June 28, 2012 CCAT: 25 meter submm telescope CCAT Site on C. Chajnantor Me, at 18,400
Astronomy across the spectrum: telescopes and where we put them Martha Haynes Exploring Early Galaxies with the CCAT June 28, 2012 CCAT: 25 meter submm telescope CCAT Site on C. Chajnantor Me, at 18,400
Stellar Death. Final Phases
 Stellar Death Final Phases After the post-agb phase, the death of the star is close at hand. Function of Mass (For stars < ~ 4 solar masses) 1. Lowest mass stars will never have sufficient pressure and
Stellar Death Final Phases After the post-agb phase, the death of the star is close at hand. Function of Mass (For stars < ~ 4 solar masses) 1. Lowest mass stars will never have sufficient pressure and
The Night Sky. The Universe. The Celestial Sphere. Stars. Chapter 14
 The Night Sky The Universe Chapter 14 Homework: All the multiple choice questions in Applying the Concepts and Group A questions in Parallel Exercises. Celestial observation dates to ancient civilizations
The Night Sky The Universe Chapter 14 Homework: All the multiple choice questions in Applying the Concepts and Group A questions in Parallel Exercises. Celestial observation dates to ancient civilizations
Chapter 33 The History of a Star. Introduction. Radio telescopes allow us to look into the center of the galaxy. The milky way
 Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
The Content of the Universe, and how we get heavy elements.
 The Content of the Universe, and how we get heavy elements http://www.lbl.gov/science-articles/archive/sabl/2006/jan/pie-chart.jpg 1 Outline The content of the universe How structure forms Elements heavier
The Content of the Universe, and how we get heavy elements http://www.lbl.gov/science-articles/archive/sabl/2006/jan/pie-chart.jpg 1 Outline The content of the universe How structure forms Elements heavier
The Galaxy. (The Milky Way Galaxy)
 The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
The Dusty Universe. Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy
 The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
Chapter 0 Introduction X-RAY BINARIES
 X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
The Formation of Stars
 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
Nucleus Hydrogen nucleus. hydrogen. helium
 1. (a) Once formed, a star can have a stable life for billions of years. Describe the two main forces at work in the star during this period of stability. 1.... 2.... What happens to a star once this stable
1. (a) Once formed, a star can have a stable life for billions of years. Describe the two main forces at work in the star during this period of stability. 1.... 2.... What happens to a star once this stable
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Apr 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Apr 2017](/thumbs/96/128270441.jpg) Draft version November 6, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 KILOPARSEC-SCALE SIMULATIONS OF STAR FORMATION IN DISK GALAXIES. IV. REGULATION OF GALACTIC STAR FORMATION RATES
Draft version November 6, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 KILOPARSEC-SCALE SIMULATIONS OF STAR FORMATION IN DISK GALAXIES. IV. REGULATION OF GALACTIC STAR FORMATION RATES
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION
 MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
The Formation of Massive Stars
 The Formation of Massive Stars Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Chris McKee, Stella Offner (UC Berkeley) Andrew Cunningham (LLNL) Kaitlin Kratter, Chris Matzner (U. Toronto) Jim
The Formation of Massive Stars Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Chris McKee, Stella Offner (UC Berkeley) Andrew Cunningham (LLNL) Kaitlin Kratter, Chris Matzner (U. Toronto) Jim
Observational signatures of proto brown dwarf formation in protostellar disks
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 88 c SAIt 213 Memorie della Observational signatures of proto brown dwarf formation in protostellar disks O. V. Zakhozhay 1, E. I. Vorobyov 2,3, and M. M. Dunham 4 1 Main Astronomical
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 88 c SAIt 213 Memorie della Observational signatures of proto brown dwarf formation in protostellar disks O. V. Zakhozhay 1, E. I. Vorobyov 2,3, and M. M. Dunham 4 1 Main Astronomical
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 23. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Lecture 20: Deuterium Burning and Hydrogen Burning
 Lecture 20: Deuterium Burning and Hydrogen Burning G Star M Dwarf L Dwarf T Dwarf Hydrogen Burning Deuterium Burning Only Decreasing Luminosity Increasing Time Protostars: Accretes mass throughout protostellar
Lecture 20: Deuterium Burning and Hydrogen Burning G Star M Dwarf L Dwarf T Dwarf Hydrogen Burning Deuterium Burning Only Decreasing Luminosity Increasing Time Protostars: Accretes mass throughout protostellar
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments. S. Oey
 The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
Recall what you know about the Big Bang.
 What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
BUT, what happens when atoms, with electrons attached, are packed really close together? The electrons from the neighboring atoms can have a small
 Quiz #5 There are two stars, star A and star B. Star A is approaching the Earth at 100 km/s and Star B is moving away from the Earth at 200 km/s. Compare the Doppler shift for these two stars by explaining
Quiz #5 There are two stars, star A and star B. Star A is approaching the Earth at 100 km/s and Star B is moving away from the Earth at 200 km/s. Compare the Doppler shift for these two stars by explaining
Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = solar masses
 Quasars Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = 10 6 10 9 solar masses Stars and gas fall into the black hole and shine in an accrecon disk billion
Quasars Quasars are supermassive black holes, found in the centers of galaxies Mass of quasar black holes = 10 6 10 9 solar masses Stars and gas fall into the black hole and shine in an accrecon disk billion
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation
 Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
ASTR-101 4/4/2018 Stellar Evolution: Part II Lecture 19
 ASTR-101 4/4/2018 Stellar Evolution: Part II Lecture 19 WHEN S THE NEXT TEST?!?!?!? If anyone is following the syllabus, you know that it says there is a test today. The test will be on April 11 th (a
ASTR-101 4/4/2018 Stellar Evolution: Part II Lecture 19 WHEN S THE NEXT TEST?!?!?!? If anyone is following the syllabus, you know that it says there is a test today. The test will be on April 11 th (a
Radio astronomy, Lecture 14
 Radio astronomy, Lecture 14 1) Molecular clouds 2) Dust 3) ALMA 1937 1 Laboratory tour Helmholtzweg 3 (rotes Haus), Montag 05.02.18 12-00 1937 2 The whole sky (by eyes) Lund observatory 3 The whole sky
Radio astronomy, Lecture 14 1) Molecular clouds 2) Dust 3) ALMA 1937 1 Laboratory tour Helmholtzweg 3 (rotes Haus), Montag 05.02.18 12-00 1937 2 The whole sky (by eyes) Lund observatory 3 The whole sky
Numerical Simulations. Duncan Christie
 Numerical Simulations Duncan Christie Motivation There isn t enough time to derive the necessary methods to do numerical simulations, but there is enough time to survey what methods and codes are available
Numerical Simulations Duncan Christie Motivation There isn t enough time to derive the necessary methods to do numerical simulations, but there is enough time to survey what methods and codes are available
Physics HW Set 3 Spring 2015
 1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
The Milky Way Galaxy. Some thoughts. How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of?
 Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Formation of massive stars : a review
 Formation of massive stars : a review Patrick Hennebelle (a former «star formation ignorant» Ant s postdoc) Benoit Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi, Gilles Chabrier One of the Constellation network
Formation of massive stars : a review Patrick Hennebelle (a former «star formation ignorant» Ant s postdoc) Benoit Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi, Gilles Chabrier One of the Constellation network
The formation of super-stellar clusters
 The formation of super-stellar clusters François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Cynthia Herrera, Edith Falgarone, Pierre Guillard, Nicole Nesvadba, Guillaume Pineau des Forets Outline How
The formation of super-stellar clusters François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Cynthia Herrera, Edith Falgarone, Pierre Guillard, Nicole Nesvadba, Guillaume Pineau des Forets Outline How
Chapter 12: The Lives of Stars. How do we know it s there? Three Kinds of Nebulae 11/7/11. 1) Emission Nebulae 2) Reflection Nebulae 3) Dark Nebulae
 11/7/11 Chapter 12: The Lives of Stars Space is Not Empty The Constellation Orion The Orion Nebula This material between the stars is called the Interstellar Medium It is very diffuse and thin. In fact
11/7/11 Chapter 12: The Lives of Stars Space is Not Empty The Constellation Orion The Orion Nebula This material between the stars is called the Interstellar Medium It is very diffuse and thin. In fact
Stellar Evolution. Stars are chemical factories The Earth and all life on the Earth are made of elements forged in stars
 Lecture 11 Stellar Evolution Stars are chemical factories The Earth and all life on the Earth are made of elements forged in stars A Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way Type) 120,000 ly A few hundred billion stars
Lecture 11 Stellar Evolution Stars are chemical factories The Earth and all life on the Earth are made of elements forged in stars A Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way Type) 120,000 ly A few hundred billion stars
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks. Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany
 Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
