Redshift-Distance Relationships
|
|
|
- Magdalene Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Redshift-Distance Relationships George Jones April 4, 0. Distances in Cosmology This note considers two conceptually important definitions of cosmological distances, look-back distance and proper distance. Definitions of distance more directly related to observations, luminosity distance and angular diameter distance, are not treated in this note. Look-back distance is the time difference between when a galaxy emits light and when we receive the light, multiplied by the speed of light. Proper distance at time t is the distance between where the galaxy is at time t and where we are at time t.. Flat FLRW Universe The metric for a spatially flat Friedmann-Lemaitre-Robertson-Walker (FLRW) universe gives (omitting angular coordinates) the spacetime interval ds = c a (t) dr. () Here, t is cosmological time since the Big Bang, r is a comoving spatial coordinate, and a (t) is the scale factor of the universe. Just as in special relativity, the spacetime interval is: timelike if ds > 0; lightlike if ds = 0; and spacelikelike if ds < 0. To help understand comoving coordinates and scale factors, consider the surface of the Earth, with points on the surface located by their latitude and longitude coordinates. Suppose the Earth expands. Because latitude and longitude coordinates for points do not change as the Earth expands, they are examples of comoving coordinates. The distance between any two points, however, increases as the Earth expands. This can be represented by scale factor that increases as time goes on, i.e., the scale factor is a function of time. Just as points on an expanding Earth have fixed values of latitude and longitude, galaxies in our expanding universe have fixed values of the comoving coordinate r. For convenience, assume that our Milky Way galaxy has the fixed value r = 0. The expansion of the universe is given by the change in the scale factor a (t). The proper distance d (t) at time t between the Milky Way and a galaxy that has comoving coordinate is d (t) = a (t) r. Spatially flat spacetime universes are often called flat universes, but this is somewhat misleading, as (spatially) flat universes have non-zero spacetime curvature! For a flat universe that contains matter (including dark matter), dark energy, and no radiation, the scale factor a (t) of
2 the universe is (see exercise 5. from General Relativity: An Introduction for Physicists by Hobson, Efstathiou, and Lasenby) ( ΩΛ0 a (t) = Ω Λ0 ) sinh ( ) ΩΛ0 H 0 t. Here, Ω Λ0 is the (normalized) present density of dark energy, Ω Λ0 is the (normalized) density of matter, and the scale factor a (t) is normalized such that a (t 0 ) =, where t 0 is the present age of the universe. This is a very good approximation to the best fit to cosmological observations. (This expression for the scale factor is obtained by solving the Friedmann equation, which itself comes from the Einstein equation.) Take the present dark energy density to be Ω Λ0 = 0.69, and the present value of the Hubble parameter to be (latest PLANCK satellite results). Then, where H 0 = km / s /Mpc = s = s a (t) = A sinh (Bt), () ( ΩΛ0 A = Ω Λ0 ( 0.69 = 0.69 = 0.765, ) ) B = ΩΛ0 H 0 = s = s. Inverting () gives (exercise: show that this is equivalent to equation (9.9) in Carroll and Ostlie, where their R (t) is my a (t)) t = [ ( a ) ] B sinh, () A which can be used to find t 0, the present age of the universe from the PLANCK parameters. To
3 do this, set a = in (), which gives ( ) t 0 = sinh = s = y. Plot of scale factor a (t) versus t measured in billions of years: a t. Cosmological Redshift As light travels from a galaxy to us, the universe expands, and the wavelength of the light stretches in proportion to the amount of expansion of the universe. This means that if λ e is the wavelenth of the emitted light and λ o is the wavelength of the light that we observe, then λ o λ e = a (t 0) a (t e ), where t e is the time at which the galaxy emitted the light. Redshift is quantified by the relative change in wavelength z, which is expressed as z = λ o λ e λ e = λ o λ e = a (t 0). (4) a (t e )
4 4. Look-Back Time and Distance Given z, the redshift of a galaxy that we observe now, we can find t e, + z = a (t 0) a (t e ) a (t e ) = a (t 0) + z A sinh (Bte ) = a (t 0) + z sinh (Bt e ) = ( a (t0 ) A ( + z) ) t e = B sinh ( [ a (t0 ) A ( + z) ] ). The time of travel for the light is the difference t 0 t e between the time at which the light is observed and the time at which the light was emitted, and is called the look-back time. Plot of look-back distance (in billions of light-years) versus redshift z: For example, for an observed z = 0.4, light was emitted at cosmological time ( [ ] ) t e = sinh s ( + 0.4) the look-back time is = s = y, t 0 t e = (.8 9.4) 0 9 y = y, and the look-back distance is 4.4 billion light-years. z
5 5. Proper Distance The time t e can be used to find the comoving coordinate r e of the object that emitted the light. Since the light follows a lightlike path, the spacetime interval all along its path is ds = 0, so () gives 0 = c a (t) dr a (t) dr = c. The negative sign arises because the light starts at positive r e and is observed by us at r = 0. Integrating this gives 0 t0 dr = c r e a (t) r e = c t e t0 t e a (t). The proper distance between where we are now (t = t 0 ) and where the galaxy is now (i.e., not where the galaxy was when the light was emitted) d (t 0 ) is given by d (t 0 ) = a (t 0 ) r e = r e, since a (t 0 ) =. Plot of present proper distance (in billions of light-years) versus redshift z: z
6 For light observed at z = 0.4, the present proper distance to the galaxy is d (t 0 ) = r e = c = t0 t e c a (t) s s = c s = c y = light years. sinh ( s t) (5) 6. Cosmological Horizon Because both the age of the universe and the speed of light are finite, there is a cosmological horizon, beyond which we cannot see. The farthest we can look back is the present age of the universe,.8 billion years, which is the look-back distance of the cosmic horizon. Where are the ojects now that were then on the cosmic horizon, i.e., what is the current proper distance of something on the cosmic horizon? This is found by setting t e = 0 in (5) t0 d horizon = c 0 = c a (t) s 0 s = c s = c y = light years. sinh ( s t) Using t e = 0 in () and (4) shows that the cosmic horizon is a surface of infinite redshift. The calculated value for d horizon is somewhat larger than the accepted value of 46 billion light-years because t e should actually be the time from which we receive the Comic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation.
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology Lecture 4; January 15 2014 Previously The dominant force on the scale of the Universe is gravity Gravity is accurately described by the theory of general
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy ad Cosmology Lecture 4; January 15 2014 Previously The dominant force on the scale of the Universe is gravity Gravity is accurately described by the theory of general
3.1 Cosmological Parameters
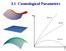 3.1 Cosmological Parameters 1 Cosmological Parameters Cosmological models are typically defined through several handy key parameters: Hubble Constant Defines the Scale of the Universe R 0 H 0 = slope at
3.1 Cosmological Parameters 1 Cosmological Parameters Cosmological models are typically defined through several handy key parameters: Hubble Constant Defines the Scale of the Universe R 0 H 0 = slope at
Cosmology ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Hubble Ultra-Deep Field
 Cosmology ASTR 2120 Sarazin Hubble Ultra-Deep Field Cosmology - Da Facts! 1) Big Universe of Galaxies 2) Sky is Dark at Night 3) Isotropy of Universe Cosmological Principle = Universe Homogeneous 4) Hubble
Cosmology ASTR 2120 Sarazin Hubble Ultra-Deep Field Cosmology - Da Facts! 1) Big Universe of Galaxies 2) Sky is Dark at Night 3) Isotropy of Universe Cosmological Principle = Universe Homogeneous 4) Hubble
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang. Expansion of the Universe. Big Bang Theory. Age of the Universe. Hubble s Law. Hubble s Law
 Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
12. Relativistic Cosmology I. Simple Solutions to the Einstein Equations
 12. Relativistic Cosmology I. Simple Solutions to the Einstein Equations 1. Minkowski space Initial assumptions:! no matter (T µν = 0)! no gravitation (R σ µνρ = 0; i.e., zero curvature) Not realistic!
12. Relativistic Cosmology I. Simple Solutions to the Einstein Equations 1. Minkowski space Initial assumptions:! no matter (T µν = 0)! no gravitation (R σ µνρ = 0; i.e., zero curvature) Not realistic!
Cosmology. Assumptions in cosmology Olber s paradox Cosmology à la Newton Cosmology à la Einstein Cosmological constant Evolution of the Universe
 Cosmology Assumptions in cosmology Olber s paradox Cosmology à la Newton Cosmology à la Einstein Cosmological constant Evolution of the Universe Assumptions in Cosmology Copernican principle: We do not
Cosmology Assumptions in cosmology Olber s paradox Cosmology à la Newton Cosmology à la Einstein Cosmological constant Evolution of the Universe Assumptions in Cosmology Copernican principle: We do not
Cosmology: An Introduction. Eung Jin Chun
 Cosmology: An Introduction Eung Jin Chun Cosmology Hot Big Bang + Inflation. Theory of the evolution of the Universe described by General relativity (spacetime) Thermodynamics, Particle/nuclear physics
Cosmology: An Introduction Eung Jin Chun Cosmology Hot Big Bang + Inflation. Theory of the evolution of the Universe described by General relativity (spacetime) Thermodynamics, Particle/nuclear physics
Introduction to Cosmology (in 5 lectures) Licia Verde
 Introduction to Cosmology (in 5 lectures) Licia Verde http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde Program: Cosmology Introduction, Hubble law, Freedman- Robertson Walker metric Dark matter and large-scale cosmological
Introduction to Cosmology (in 5 lectures) Licia Verde http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde Program: Cosmology Introduction, Hubble law, Freedman- Robertson Walker metric Dark matter and large-scale cosmological
Modern Cosmology Solutions 4: LCDM Universe
 Modern Cosmology Solutions 4: LCDM Universe Max Camenzind October 29, 200. LCDM Models The ansatz solves the Friedmann equation, since ȧ = C cosh() Ωm sinh /3 H 0 () () ȧ 2 = C 2 cosh2 () sinh 2/3 () (
Modern Cosmology Solutions 4: LCDM Universe Max Camenzind October 29, 200. LCDM Models The ansatz solves the Friedmann equation, since ȧ = C cosh() Ωm sinh /3 H 0 () () ȧ 2 = C 2 cosh2 () sinh 2/3 () (
VU lecture Introduction to Particle Physics. Thomas Gajdosik, FI & VU. Big Bang (model)
 Big Bang (model) What can be seen / measured? basically only light _ (and a few particles: e ±, p, p, ν x ) in different wave lengths: microwave to γ-rays in different intensities (measured in magnitudes)
Big Bang (model) What can be seen / measured? basically only light _ (and a few particles: e ±, p, p, ν x ) in different wave lengths: microwave to γ-rays in different intensities (measured in magnitudes)
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 2 Spring 2018 Previously: Empirical foundations of the Big Bang theory. II: Hubble s Law ==> Expanding Universe CMB Radiation ==> Universe was hot
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 2 Spring 2018 Previously: Empirical foundations of the Big Bang theory. II: Hubble s Law ==> Expanding Universe CMB Radiation ==> Universe was hot
Cosmology: The Origin and Evolution of the Universe Chapter Twenty-Eight. Guiding Questions
 Cosmology: The Origin and Evolution of the Universe Chapter Twenty-Eight Guiding Questions 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands,
Cosmology: The Origin and Evolution of the Universe Chapter Twenty-Eight Guiding Questions 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands,
Modeling the Universe A Summary
 Modeling the Universe A Summary Questions to Consider 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands, what, if anything, is it expanding
Modeling the Universe A Summary Questions to Consider 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands, what, if anything, is it expanding
PAPER 73 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday 4 June 2008 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 73 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday 4 June 2008 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 73 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
Lecture 05. Cosmology. Part I
 Cosmology Part I What is Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole It asks the biggest questions in nature What is the content of the universe: Today? Long ago? In the far future? How
Cosmology Part I What is Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole It asks the biggest questions in nature What is the content of the universe: Today? Long ago? In the far future? How
Ay1 Lecture 17. The Expanding Universe Introduction to Cosmology
 Ay1 Lecture 17 The Expanding Universe Introduction to Cosmology 17.1 The Expanding Universe General Relativity (1915) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, and matter/energy Postulates
Ay1 Lecture 17 The Expanding Universe Introduction to Cosmology 17.1 The Expanding Universe General Relativity (1915) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, and matter/energy Postulates
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 2913 ASTROPHYSICS AND RELATIVITY (ADVANCED) ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN
 CC0937 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 2913 ASTROPHYSICS AND RELATIVITY (ADVANCED) SEMESTER 2, 2014 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN INSTRUCTIONS:
CC0937 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY FACULTY OF SCIENCE INTERMEDIATE PHYSICS PHYS 2913 ASTROPHYSICS AND RELATIVITY (ADVANCED) SEMESTER 2, 2014 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS ALL QUESTIONS HAVE THE VALUE SHOWN INSTRUCTIONS:
Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles
 Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles The basic Cosmological Principles The geometry of the Universe The scale factor R and curvature constant k Comoving coordinates Einstein s initial solutions 3/28/11
Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles The basic Cosmological Principles The geometry of the Universe The scale factor R and curvature constant k Comoving coordinates Einstein s initial solutions 3/28/11
Lecture 1 General relativity and cosmology. Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU
 A Superfluid Universe Lecture 1 General relativity and cosmology Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU Lecture 1. General relativity and cosmology Mathematics and physics Big bang Dark energy Dark matter Robertson-Walker
A Superfluid Universe Lecture 1 General relativity and cosmology Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU Lecture 1. General relativity and cosmology Mathematics and physics Big bang Dark energy Dark matter Robertson-Walker
PHY 475/375. Lecture 5. (April 9, 2012)
 PHY 475/375 Lecture 5 (April 9, 2012) Describing Curvature (contd.) So far, we have studied homogenous and isotropic surfaces in 2-dimensions. The results can be extended easily to three dimensions. As
PHY 475/375 Lecture 5 (April 9, 2012) Describing Curvature (contd.) So far, we have studied homogenous and isotropic surfaces in 2-dimensions. The results can be extended easily to three dimensions. As
Tuesday: Special epochs of the universe (recombination, nucleosynthesis, inflation) Wednesday: Structure formation
 Introduction to Cosmology Professor Barbara Ryden Department of Astronomy The Ohio State University ICTP Summer School on Cosmology 2016 June 6 Today: Observational evidence for the standard model of cosmology
Introduction to Cosmology Professor Barbara Ryden Department of Astronomy The Ohio State University ICTP Summer School on Cosmology 2016 June 6 Today: Observational evidence for the standard model of cosmology
The early and late time acceleration of the Universe
 The early and late time acceleration of the Universe Tomo Takahashi (Saga University) March 7, 2016 New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and Chemistry- @Kyoto University The early
The early and late time acceleration of the Universe Tomo Takahashi (Saga University) March 7, 2016 New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and Chemistry- @Kyoto University The early
Cosmology. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16
 Cosmology Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16 Expansion of the Universe 1923 - Edwin Hubble resolved Andromeda Nebula into separate stars. 1929 - Hubble compared radial velocity versus distance for 18 nearest galaxies.
Cosmology Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16 Expansion of the Universe 1923 - Edwin Hubble resolved Andromeda Nebula into separate stars. 1929 - Hubble compared radial velocity versus distance for 18 nearest galaxies.
The Friedmann Equation R = GM R 2. R(t) R R = GM R GM R. d dt. = d dt 1 2 R 2 = GM R + K. Kinetic + potential energy per unit mass = constant
 The Friedmann Equation R = GM R R R = GM R R R(t) d dt 1 R = d dt GM R M 1 R = GM R + K Kinetic + potential energy per unit mass = constant The Friedmann Equation 1 R = GM R + K M = ρ 4 3 π R3 1 R = 4πGρR
The Friedmann Equation R = GM R R R = GM R R R(t) d dt 1 R = d dt GM R M 1 R = GM R + K Kinetic + potential energy per unit mass = constant The Friedmann Equation 1 R = GM R + K M = ρ 4 3 π R3 1 R = 4πGρR
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 7 Oct. 30, 2015 Today Relativistic Cosmology Dark Side of the Universe I: Dark Matter Assignments This week: read Hawley and
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 7 Oct. 30, 2015 Today Relativistic Cosmology Dark Side of the Universe I: Dark Matter Assignments This week: read Hawley and
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Friday 8 June 2001 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 41 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Answer any THREE questions. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to read the questions printed on
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Friday 8 June 2001 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 41 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Answer any THREE questions. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to read the questions printed on
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Lecture #24: Plan. Cosmology. Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe
 Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
Lecture #24: Plan Cosmology Expansion of the Universe Olber s Paradox Birth of our Universe Reminder: Redshifts and the Expansion of the Universe Early 20 th century astronomers noted: Spectra from most
THE DARK SIDE OF THE COSMOLOGICAL CONSTANT
 THE DARK SIDE OF THE COSMOLOGICAL CONSTANT CAMILO POSADA AGUIRRE University of South Carolina Department of Physics and Astronomy 09/23/11 Outline 1 Einstein s Greatest Blunder 2 The FLRW Universe 3 A
THE DARK SIDE OF THE COSMOLOGICAL CONSTANT CAMILO POSADA AGUIRRE University of South Carolina Department of Physics and Astronomy 09/23/11 Outline 1 Einstein s Greatest Blunder 2 The FLRW Universe 3 A
Cosmology. Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick.
 Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
In the expanding Universe, a comoving volume element expands along with the cosmological flow, getting physically larger over time.
 Cosmological models In the expanding Universe, a comoving volume element expands along with the cosmological flow, getting physically larger over time. The expansion is described by the scale factor R(t).
Cosmological models In the expanding Universe, a comoving volume element expands along with the cosmological flow, getting physically larger over time. The expansion is described by the scale factor R(t).
Introduction to Cosmology
 Introduction to Cosmology João G. Rosa joao.rosa@ua.pt http://gravitation.web.ua.pt/cosmo LECTURE 2 - Newtonian cosmology I As a first approach to the Hot Big Bang model, in this lecture we will consider
Introduction to Cosmology João G. Rosa joao.rosa@ua.pt http://gravitation.web.ua.pt/cosmo LECTURE 2 - Newtonian cosmology I As a first approach to the Hot Big Bang model, in this lecture we will consider
2.1 Basics of the Relativistic Cosmology: Global Geometry and the Dynamics of the Universe Part I
 1 2.1 Basics of the Relativistic Cosmology: Global Geometry and the Dynamics of the Universe Part I 2 Special Relativity (1905) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, now unified
1 2.1 Basics of the Relativistic Cosmology: Global Geometry and the Dynamics of the Universe Part I 2 Special Relativity (1905) A fundamental change in viewing the physical space and time, now unified
Introduction. How did the universe evolve to what it is today?
 Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Cosmology 8 1 Introduction 8 2 Cosmology: science of the universe as a whole How did the universe evolve to what it is today? Based on four basic facts: The universe expands, is isotropic, and is homogeneous.
Astro-2: History of the Universe
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 8; May 7 2013 Previously on astro-2 Wherever we look in the sky there is a background of microwaves, the CMB. The CMB is very close to isotropic better than 0.001%
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 8; May 7 2013 Previously on astro-2 Wherever we look in the sky there is a background of microwaves, the CMB. The CMB is very close to isotropic better than 0.001%
with Matter and Radiation By: Michael Solway
 Interactions of Dark Energy with Matter and Radiation By: Michael Solway Advisor: Professor Mike Berger What is Dark Energy? Dark energy is the energy needed to explain the observed accelerated expansion
Interactions of Dark Energy with Matter and Radiation By: Michael Solway Advisor: Professor Mike Berger What is Dark Energy? Dark energy is the energy needed to explain the observed accelerated expansion
Licia Verde. Introduction to cosmology. Lecture 4. Inflation
 Licia Verde Introduction to cosmology Lecture 4 Inflation Dividing line We see them like temperature On scales larger than a degree, fluctuations were outside the Hubble horizon at decoupling Potential
Licia Verde Introduction to cosmology Lecture 4 Inflation Dividing line We see them like temperature On scales larger than a degree, fluctuations were outside the Hubble horizon at decoupling Potential
Cosmic Confusion. common misconceptions about the big bang, the expansion of the universe and cosmic horizons.
 The basics Cosmic Confusion common misconceptions about the big bang, the expansion of the universe and cosmic horizons. What is the expansion of space? Is there an edge to space? What is the universe
The basics Cosmic Confusion common misconceptions about the big bang, the expansion of the universe and cosmic horizons. What is the expansion of space? Is there an edge to space? What is the universe
Licia Verde. ICREA & ICC-UB-IEEC CERN Theory Division.
 Licia Verde ICREA & ICC-UB-IEEC CERN Theory Division http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde AIMS and GOALS Observational cosmology has been evolving very rapidly over the past few years Theoretical cosmology is
Licia Verde ICREA & ICC-UB-IEEC CERN Theory Division http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde AIMS and GOALS Observational cosmology has been evolving very rapidly over the past few years Theoretical cosmology is
Is inflation really necessary in a closed Universe? Branislav Vlahovic, Maxim Eingorn. Please see also arxiv:
 Is inflation really necessary in a closed Universe? Branislav Vlahovic, Maxim Eingorn North Carolina Central University NASA University Research Centers, Durham NC Please see also arxiv:1303.3203 Chicago
Is inflation really necessary in a closed Universe? Branislav Vlahovic, Maxim Eingorn North Carolina Central University NASA University Research Centers, Durham NC Please see also arxiv:1303.3203 Chicago
Short introduction to the accelerating Universe
 SEMINAR Short introduction to the accelerating Universe Gašper Kukec Mezek Our expanding Universe Albert Einstein general relativity (1917): Our expanding Universe Curvature = Energy Our expanding Universe
SEMINAR Short introduction to the accelerating Universe Gašper Kukec Mezek Our expanding Universe Albert Einstein general relativity (1917): Our expanding Universe Curvature = Energy Our expanding Universe
Visit for more fantastic resources. Edexcel. A Level. A Level Physics. Astrophysics 2 (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30
 Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. Edexcel A Level A Level Physics Astrophysics 2 (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. The Doppler
Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. Edexcel A Level A Level Physics Astrophysics 2 (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. The Doppler
Watching The Big Bang
 Watching The Big Bang Have Primordial Gravitational Waves Been Detected? Robert H. Gowdy Virginia Commonwealth University September 5, 2014 R. H. Gowdy (VCU) Cosmology 09/05 1 / 12 Summary Picturing the
Watching The Big Bang Have Primordial Gravitational Waves Been Detected? Robert H. Gowdy Virginia Commonwealth University September 5, 2014 R. H. Gowdy (VCU) Cosmology 09/05 1 / 12 Summary Picturing the
26. Cosmology. Significance of a dark night sky. The Universe Is Expanding
 26. Cosmology Significance of a dark night sky The Universe is expanding The Big Bang initiated the expanding Universe Microwave radiation evidence of the Big Bang The Universe was initially hot & opaque
26. Cosmology Significance of a dark night sky The Universe is expanding The Big Bang initiated the expanding Universe Microwave radiation evidence of the Big Bang The Universe was initially hot & opaque
Chapter 1 Introduction. Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS
 Chapter 1 Introduction Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS 2008 1 Ptolemäus (85 165 b.c.) Kopernicus (1473 1543) Kepler (1571 1630) Newton (1643 1727) Kant (1724 1630) Herschel (1738 1822) Einstein (1917)
Chapter 1 Introduction Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS 2008 1 Ptolemäus (85 165 b.c.) Kopernicus (1473 1543) Kepler (1571 1630) Newton (1643 1727) Kant (1724 1630) Herschel (1738 1822) Einstein (1917)
A Bit of History. Hubble s original redshiftdistance
 XKCD: April 7, 2014 Cosmology Galaxies are lighthouses that trace the evolution of the universe with time We will concentrate primarily on observational cosmology (how do we measure important cosmological
XKCD: April 7, 2014 Cosmology Galaxies are lighthouses that trace the evolution of the universe with time We will concentrate primarily on observational cosmology (how do we measure important cosmological
Astronomy 114. Lecture35:TheBigBang. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture35:TheBigBang Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 35 09 May 2005 Read: Ch. 28,29 Astronomy 114 1/18 Announcements PS#8 due Monday!
Astronomy 114 Lecture35:TheBigBang Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 35 09 May 2005 Read: Ch. 28,29 Astronomy 114 1/18 Announcements PS#8 due Monday!
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 26. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 26 Cosmology Units of Chapter 26 26.1 The Universe on the Largest Scales 26.2 The Expanding Universe 26.3 The Fate of the
Lecture Outlines Chapter 26 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 26 Cosmology Units of Chapter 26 26.1 The Universe on the Largest Scales 26.2 The Expanding Universe 26.3 The Fate of the
Derivation of parametric equations of the expansion of a closed universe with torsion. Prastik Mohanraj
 Derivation of parametric equations of the expansion of a closed universe with torsion Prastik Mohanraj Big Bang Cosmology We observe redshift, where galaxies become redder in color over time. This means
Derivation of parametric equations of the expansion of a closed universe with torsion Prastik Mohanraj Big Bang Cosmology We observe redshift, where galaxies become redder in color over time. This means
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence
 CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
3 The Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric
 3 The Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric 3.1 Three dimensions The most general isotropic and homogeneous metric in three dimensions is similar to the two dimensional result of eq. (43): ( ) dr ds 2 = a
3 The Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric 3.1 Three dimensions The most general isotropic and homogeneous metric in three dimensions is similar to the two dimensional result of eq. (43): ( ) dr ds 2 = a
Inflation; the Concordance Model
 Duke Physics 55 Spring 2007 Inflation; the Concordance Model Lecture #31: OUTLINE BDSV Chapter 23.3, 23.4 Inflation of the Early Universe: Solving the structure problem Solving the horizon problem Solving
Duke Physics 55 Spring 2007 Inflation; the Concordance Model Lecture #31: OUTLINE BDSV Chapter 23.3, 23.4 Inflation of the Early Universe: Solving the structure problem Solving the horizon problem Solving
The Cosmological Constant and the Vacuum Catastrophe
 The Cosmological Constant and the Vacuum Catastrophe Jason Emory Andrews Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 98195 (Dated: December 18 th, 2010) General relativity
The Cosmological Constant and the Vacuum Catastrophe Jason Emory Andrews Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 98195 (Dated: December 18 th, 2010) General relativity
Third Year: General Relativity and Cosmology. 1 Problem Sheet 1 - Newtonian Gravity and the Equivalence Principle
 Third Year: General Relativity and Cosmology 2011/2012 Problem Sheets (Version 2) Prof. Pedro Ferreira: p.ferreira1@physics.ox.ac.uk 1 Problem Sheet 1 - Newtonian Gravity and the Equivalence Principle
Third Year: General Relativity and Cosmology 2011/2012 Problem Sheets (Version 2) Prof. Pedro Ferreira: p.ferreira1@physics.ox.ac.uk 1 Problem Sheet 1 - Newtonian Gravity and the Equivalence Principle
Hubble's Law. H o = 71 km/s / Mpc. The further a galaxy is away, the faster it s moving away from us. V = H 0 D. Modern Data.
 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Outline. Covers chapter 2 + half of chapter 3 in Ryden
 Outline Covers chapter + half of chapter 3 in Ryden The Cosmological Principle I The cosmological principle The Cosmological Principle II Voids typically 70 Mpc across The Perfect Cosmological Principle
Outline Covers chapter + half of chapter 3 in Ryden The Cosmological Principle I The cosmological principle The Cosmological Principle II Voids typically 70 Mpc across The Perfect Cosmological Principle
Cosmology. Clusters of galaxies. Redshift. Late 1920 s: Hubble plots distances versus velocities of galaxies. λ λ. redshift =
 Cosmology Study of the structure and origin of the universe Observational science The large-scale distribution of galaxies Looking out to extremely large distances The motions of galaxies Clusters of galaxies
Cosmology Study of the structure and origin of the universe Observational science The large-scale distribution of galaxies Looking out to extremely large distances The motions of galaxies Clusters of galaxies
PHY326/426:Lecture 19
 PHY326/426:Lecture 19 Dark Energy Finish WIMP signals Evidence for Dark Energy Type Ia Supernovae What is Dark Energy The fate of the Universe The Distance-Redshift relation Recall from lecture 2: The
PHY326/426:Lecture 19 Dark Energy Finish WIMP signals Evidence for Dark Energy Type Ia Supernovae What is Dark Energy The fate of the Universe The Distance-Redshift relation Recall from lecture 2: The
If there is an edge to the universe, we should be able to see our way out of the woods. Olber s Paradox. This is called Olber s Paradox
 Suppose the Universe were not expanding, but was in some kind of steady state. How should galaxy recession velocities correlate with distance? They should a) be directly proportional to distance. b) reverse
Suppose the Universe were not expanding, but was in some kind of steady state. How should galaxy recession velocities correlate with distance? They should a) be directly proportional to distance. b) reverse
IoP. An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology. Derek Raine. Ted Thomas. Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics
 Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology Derek Raine Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Leicester, UK Ted Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy
Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics An Introduction to the Science of Cosmology Derek Raine Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Leicester, UK Ted Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy
The Expanding Universe
 Announcements (this page posted as part of lecture notes on Angel) Homework 7 due late at night Monday April 23 (6:30AM Apr 24) Homework 8 now available on Angel Due late at night Friday April 27 (6:30AM
Announcements (this page posted as part of lecture notes on Angel) Homework 7 due late at night Monday April 23 (6:30AM Apr 24) Homework 8 now available on Angel Due late at night Friday April 27 (6:30AM
Structure. Subodh Patil NBIA Nov Formation in the Universe From the Big Bang to the Big Rip?
 Structure Subodh Patil NBIA Nov 19 2018 Formation in the Universe From the Big Bang to the Big Rip? Physicists like to think in terms of characteristic scales the `typical size of something or some process.
Structure Subodh Patil NBIA Nov 19 2018 Formation in the Universe From the Big Bang to the Big Rip? Physicists like to think in terms of characteristic scales the `typical size of something or some process.
Expanding Universe. 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe. Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium
 Expanding Universe November 20, 2002 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium NOTE THIS!!! not UPL Dec. 11, 2002 10am-noon Review
Expanding Universe November 20, 2002 1) Hubble s Law 2) Expanding Universe 3) Fate of the Universe Final Exam will be held in Ruby Diamond Auditorium NOTE THIS!!! not UPL Dec. 11, 2002 10am-noon Review
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
Lecture 10: Cosmology and the Future of Astronomical Research
 Lecture 10: Cosmology and the Future of Astronomical Research 1 ! The study of the Universe " Origin " Evolution " Eventual Fate! Physical Cosmology " Includes studies of large-scale structure and dynamics
Lecture 10: Cosmology and the Future of Astronomical Research 1 ! The study of the Universe " Origin " Evolution " Eventual Fate! Physical Cosmology " Includes studies of large-scale structure and dynamics
3 Spacetime metrics. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Flat spacetime
 3 Spacetime metrics 3.1 Introduction The efforts to generalize physical laws under different coordinate transformations would probably not have been very successful without differential calculus. Riemann
3 Spacetime metrics 3.1 Introduction The efforts to generalize physical laws under different coordinate transformations would probably not have been very successful without differential calculus. Riemann
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008
 Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
D.V. Fursaev JINR, Dubna. Mysteries of. the Universe. Problems of the Modern Cosmology
 Mysteries of D.V. Fursaev JINR, Dubna the Universe Problems of the Modern Cosmology plan of the lecture facts about our Universe mathematical model, Friedman universe consequences, the Big Bang recent
Mysteries of D.V. Fursaev JINR, Dubna the Universe Problems of the Modern Cosmology plan of the lecture facts about our Universe mathematical model, Friedman universe consequences, the Big Bang recent
Cosmology. Big Bang and Inflation
 Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Olbers Paradox. Lecture 14: Cosmology. Resolutions of Olbers paradox. Cosmic redshift
 Lecture 14: Cosmology Olbers paradox Redshift and the expansion of the Universe The Cosmological Principle Ω and the curvature of space The Big Bang model Primordial nucleosynthesis The Cosmic Microwave
Lecture 14: Cosmology Olbers paradox Redshift and the expansion of the Universe The Cosmological Principle Ω and the curvature of space The Big Bang model Primordial nucleosynthesis The Cosmic Microwave
Why is the Universe Expanding?
 Why is the Universe Expanding? In general relativity, mass warps space. Warped space makes matter move, which changes the structure of space. Thus the universe should be dynamic! Gravity tries to collapse
Why is the Universe Expanding? In general relativity, mass warps space. Warped space makes matter move, which changes the structure of space. Thus the universe should be dynamic! Gravity tries to collapse
Cosmology AS
 Cosmology AS7009 2011 Exercises to be solved in class 1. Olbers paradox: Why is the sky dark at night? Let s assume that the universe is static and of infinite extent. The number density of stars is n,
Cosmology AS7009 2011 Exercises to be solved in class 1. Olbers paradox: Why is the sky dark at night? Let s assume that the universe is static and of infinite extent. The number density of stars is n,
PROBLEM SET 10 (The Last!)
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.286: The Early Universe December 8, 2016 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 10 (The Last!) DUE DATE: Wednesday, December 14, 2016, at 4:00 pm.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.286: The Early Universe December 8, 2016 Prof. Alan Guth PROBLEM SET 10 (The Last!) DUE DATE: Wednesday, December 14, 2016, at 4:00 pm.
Gravitation: Cosmology
 An Introduction to General Relativity Center for Relativistic Astrophysics School of Physics Georgia Institute of Technology Notes based on textbook: Spacetime and Geometry by S.M. Carroll Spring 2013
An Introduction to General Relativity Center for Relativistic Astrophysics School of Physics Georgia Institute of Technology Notes based on textbook: Spacetime and Geometry by S.M. Carroll Spring 2013
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters. I. A Cosmological Primer
 Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters I. A Cosmological Primer Timetable Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 4pm 4pm 4pm 4pm no lecture 4pm Can we have lectures from 16.00-16.50? Timetable shows problems
Cosmology with Galaxy Clusters I. A Cosmological Primer Timetable Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 4pm 4pm 4pm 4pm no lecture 4pm Can we have lectures from 16.00-16.50? Timetable shows problems
Lecture 34. General relativity
 Lecture 34 The Shape of Space General Relativity Curvature of Space Critical Density Dark Energy Apr 17, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 34 1 General relativity So far, just needed simple Newton's Gravity. Because
Lecture 34 The Shape of Space General Relativity Curvature of Space Critical Density Dark Energy Apr 17, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 34 1 General relativity So far, just needed simple Newton's Gravity. Because
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 3 June, 2004 9 to 12 PAPER 67 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 3 June, 2004 9 to 12 PAPER 67 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to
Astronomy 1 Winter Lecture 24; March
 Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 24; March 7 2011 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to special relativity Introduction to general relativity Introduction to black holes, stellar and supermassive Today..
Astronomy 1 Winter 2011 Lecture 24; March 7 2011 Previously on Astro-1 Introduction to special relativity Introduction to general relativity Introduction to black holes, stellar and supermassive Today..
Zero-energy space cancels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola
 Short notes on Zero-energy space cancels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola, Faculty of Science of Eötvös University, Budapest 7 9.9.2007 Zero-energy space cancels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola,
Short notes on Zero-energy space cancels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola, Faculty of Science of Eötvös University, Budapest 7 9.9.2007 Zero-energy space cancels the need for dark energy Tuomo Suntola,
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
Physics Nobel Prize 2006
 Physics Nobel Prize 2006 Ghanashyam Date The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai http://www.imsc.res.in shyam@imsc.res.in Nov 4, 2006. Organization of the Talk Organization of the Talk Nobel Laureates
Physics Nobel Prize 2006 Ghanashyam Date The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai http://www.imsc.res.in shyam@imsc.res.in Nov 4, 2006. Organization of the Talk Organization of the Talk Nobel Laureates
General Relativity and Cosmology. The End of Absolute Space Cosmological Principle Black Holes CBMR and Big Bang
 General Relativity and Cosmology The End of Absolute Space Cosmological Principle Black Holes CBMR and Big Bang The End of Absolute Space (AS) Special Relativity (SR) abolished AS only for the special
General Relativity and Cosmology The End of Absolute Space Cosmological Principle Black Holes CBMR and Big Bang The End of Absolute Space (AS) Special Relativity (SR) abolished AS only for the special
Cosmology. An Analogy 11/28/2010. Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe
 Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
HOMEWORK 10. Applications: special relativity, Newtonian limit, gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, cosmology, 1 black holes
 General Relativity 8.96 (Petters, spring 003) HOMEWORK 10. Applications: special relativity, Newtonian limit, gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, cosmology, 1 black holes 1. Special Relativity
General Relativity 8.96 (Petters, spring 003) HOMEWORK 10. Applications: special relativity, Newtonian limit, gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, cosmology, 1 black holes 1. Special Relativity
3 Friedmann Robertson Walker Universe
 3 Friedmann Robertson Walker Universe 3. Kinematics 3.. Robertson Walker metric We adopt now the cosmological principle, and discuss the homogeneous and isotropic model for the universe. This is called
3 Friedmann Robertson Walker Universe 3. Kinematics 3.. Robertson Walker metric We adopt now the cosmological principle, and discuss the homogeneous and isotropic model for the universe. This is called
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST1100 Lecture Notes 23-24: Cosmology: models of the universe 1 The FRW-metric Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole. In the lectures on cosmology we will look at current theories of how the
AST1100 Lecture Notes 23-24: Cosmology: models of the universe 1 The FRW-metric Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole. In the lectures on cosmology we will look at current theories of how the
The Origin of the Halton Arp Quantized Inherent Redshift
 Copyright 2017 by Sylwester Kornowski All rights reserved The Origin of the Halton Arp Quantized Inherent Redshift Sylwester Kornowski Abstract: The Scale-Symmetric Theory (SST) shows that the Halton Arp
Copyright 2017 by Sylwester Kornowski All rights reserved The Origin of the Halton Arp Quantized Inherent Redshift Sylwester Kornowski Abstract: The Scale-Symmetric Theory (SST) shows that the Halton Arp
The State of the Universe [2010] There is only data and the interpretation of data (green text = assumptions)
![The State of the Universe [2010] There is only data and the interpretation of data (green text = assumptions) The State of the Universe [2010] There is only data and the interpretation of data (green text = assumptions)](/thumbs/89/97484015.jpg) The State of the Universe [2010] There is only data and the interpretation of data (green text = assumptions) Current thinking in cosmology says that the universe is filled with dark matter and dark energy.
The State of the Universe [2010] There is only data and the interpretation of data (green text = assumptions) Current thinking in cosmology says that the universe is filled with dark matter and dark energy.
Energy Source for Active Galactic Nuclei
 Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
Quasars Quasars are small, extremely luminous, extremely distant galactic nuclei Bright radio sources Name comes from Quasi-Stellar Radio Source, as they appeared to be stars! Can have clouds of gas near
baryons+dm radiation+neutrinos vacuum curvature
 baryons+dm radiation+neutrinos vacuum curvature DENSITY ISN T DESTINY! The cosmologist T-shirt (if Λ>0): ΩM,0=0.9 Ω Λ,0 =1.6 ΩM,0=2.5 ΩM,0=2.0 Ω Λ,0 =0.1 ΩM,0=2.0 http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/resources/camb_tool/cmb_plot.swf
baryons+dm radiation+neutrinos vacuum curvature DENSITY ISN T DESTINY! The cosmologist T-shirt (if Λ>0): ΩM,0=0.9 Ω Λ,0 =1.6 ΩM,0=2.5 ΩM,0=2.0 Ω Λ,0 =0.1 ΩM,0=2.0 http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/resources/camb_tool/cmb_plot.swf
Computational Physics and Astrophysics
 Cosmological Inflation Kostas Kokkotas University of Tübingen, Germany and Pablo Laguna Georgia Institute of Technology, USA Spring 2012 Our Universe Cosmic Expansion Co-moving coordinates expand at exactly
Cosmological Inflation Kostas Kokkotas University of Tübingen, Germany and Pablo Laguna Georgia Institute of Technology, USA Spring 2012 Our Universe Cosmic Expansion Co-moving coordinates expand at exactly
Cosmology & the CMB - Cosmology: Overview - Cosmic Microwave Background - Large Scale Structure (Wed) - CMB Fluctuations (Wed)
 Oct 16, 2017 Cosmology & the CMB - Cosmology: Overview - Cosmic Microwave Background - Large Scale Structure (Wed) - CMB Fluctuations (Wed) Wednesday: HW#5 due History of the universe Discovery of Quasars
Oct 16, 2017 Cosmology & the CMB - Cosmology: Overview - Cosmic Microwave Background - Large Scale Structure (Wed) - CMB Fluctuations (Wed) Wednesday: HW#5 due History of the universe Discovery of Quasars
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 10 Nov. 11, 2015 Today Hot Big Bang I: Cosmic Microwave Background Assignments This week: read Hawley and Holcomb, Chapter
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 10 Nov. 11, 2015 Today Hot Big Bang I: Cosmic Microwave Background Assignments This week: read Hawley and Holcomb, Chapter
Lecture 2: Cosmological Background
 Lecture 2: Cosmological Background Houjun Mo January 27, 2004 Goal: To establish the space-time frame within which cosmic events are to be described. The development of spacetime concept Absolute flat
Lecture 2: Cosmological Background Houjun Mo January 27, 2004 Goal: To establish the space-time frame within which cosmic events are to be described. The development of spacetime concept Absolute flat
Cosmology Dark Energy Models ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Cosmology Dark Energy Models ASTR 2120 Sarazin Late Homeworks Last day Wednesday, May 1 My mail box in ASTR 204 Maximum credit 50% unless excused (but, better than nothing) Final Exam Thursday, May 2,
Cosmology Dark Energy Models ASTR 2120 Sarazin Late Homeworks Last day Wednesday, May 1 My mail box in ASTR 204 Maximum credit 50% unless excused (but, better than nothing) Final Exam Thursday, May 2,
Observational evidence and cosmological constant. Kazuya Koyama University of Portsmouth
 Observational evidence and cosmological constant Kazuya Koyama University of Portsmouth Basic assumptions (1) Isotropy and homogeneity Isotropy CMB fluctuation ESA Planck T 5 10 T Homogeneity galaxy distribution
Observational evidence and cosmological constant Kazuya Koyama University of Portsmouth Basic assumptions (1) Isotropy and homogeneity Isotropy CMB fluctuation ESA Planck T 5 10 T Homogeneity galaxy distribution
3 Friedmann Robertson Walker Universe
 28 3 Friedmann Robertson Walker Universe 3. Kinematics 3.. Robertson Walker metric We adopt now the cosmological principle, and discuss the homogeneous and isotropic model for the universe. This is called
28 3 Friedmann Robertson Walker Universe 3. Kinematics 3.. Robertson Walker metric We adopt now the cosmological principle, and discuss the homogeneous and isotropic model for the universe. This is called
Cosmology ESP. Kevin Janeiro. May 26, 2015
 Cosmology ESP Kevin Janeiro May 26, 2015 1 Contents 1 Abstract 2 2 Fundamental Assumptions and Principles 2 2.1 The Cosmological Principle................... 2 2.2 Olbers Paradox..........................
Cosmology ESP Kevin Janeiro May 26, 2015 1 Contents 1 Abstract 2 2 Fundamental Assumptions and Principles 2 2.1 The Cosmological Principle................... 2 2.2 Olbers Paradox..........................
The homogeneous and isotropic universe
 1 The homogeneous and isotropic universe Notation In this book we denote the derivative with respect to physical time by a prime, and the derivative with respect to conformal time by a dot, dx τ = physical
1 The homogeneous and isotropic universe Notation In this book we denote the derivative with respect to physical time by a prime, and the derivative with respect to conformal time by a dot, dx τ = physical
