ASTRONOMY. Chapter 10 EARTHLIKE PLANETS: VENUS AND MARS PowerPoint Image Slideshow
|
|
|
- Evan McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ASTRONOMY Chapter 10 EARTHLIKE PLANETS: VENUS AND MARS PowerPoint Image Slideshow
2 FIGURE 10.1 Spirit Rover on Mars. This May 2004 image shows the tracks made by the Mars Exploration Spirit rover on the surface of the red planet. Spirit was active on Mars between 2004 and 2010, twenty times longer than its planners had expected. It drove over 7.73 kilometers in the process of examining the martian landscape. (credit: modification of work by NASA/JPL/Cornell)
3 FIGURE 10.2 Venus as Photographed by the Pioneer Venus Orbiter. This ultraviolet image shows an upper-atmosphere cloud structure that would be invisible at visible wavelengths. Note that there is not even a glimpse of the planet s surface. (credit: modification of work by NASA)
4 FIGURE 10.3 Mars as Seen from Earth s Surface. These are among the best Earth-based photos of Mars, taken in 1988 when the planet was exceptionally close to Earth. The polar caps and dark surface markings are evident, but not topographic features. (credit: modification of work by Steve Larson, Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona)
5 FIGURE 10.4 Lowell s Mars Globe. One of the remarkable globes of Mars prepared by Percival Lowell, showing a network of dozens of canals, oases, and triangular water reservoirs that he claimed were visible on the red planet.
6 FIGURE 10.5 Percival Lowell ( ). This 1914 photograph shows Percival Lowell observing Venus with his 24-inch telescope at Flagstaff, Arizona.
7 FIGURE 10.6 Radar Map of Venus. This composite image has a resolution of about 3 kilometers. Colors have been added to indicate elevation, with blue meaning low and brown and white high. The large continent Aphrodite stretches around the equator, where the bright (therefore rough) surface has been deformed by tectonic forces in the crust of Venus. (credit: modification of work by NASA/JPL/USGS)
8 FIGURE 10.7 Impact Craters on Venus. (a) (b) These large impact craters are in the Lavinia region of Venus. Because they are rough, the crater rims and ejecta appear brighter in these radar images than do the smoother surrounding lava plains. The largest of these craters has a diameter of 50 kilometers. This small, complex crater is named after writer Gertrude Stein. The triple impact was caused by the breaking apart of the incoming asteroid during its passage through the thick atmosphere of Venus. The projectile had an initial diameter of between 1 and 2 kilometers. (credit a: modification of work by NASA/JPL; credit b: modification of work by NASA/JPL)
9 FIGURE 10.8 Pancake-Shaped Volcanoes on Venus. These remarkable circular domes, each about 25 kilometers across and about 2 kilometers tall, are the result of eruptions of highly viscous (sludgy) lava that spreads out evenly in all directions. (credit: modification of work by NASA/JPL)
10 FIGURE 10.9 The Miss Piggy Corona. Fotla Corona is located in the plains to the south of Aphrodite Terra. Curved fracture patterns show where the material beneath has put stress on the surface. A number of pancake and dome volcanoes are also visible. Fotla was a Celtic fertility goddess. Some students see a resemblance between this corona and Miss Piggy of the Muppets (her left ear, at the top of the picture, is the pancake volcano in the upper center of the image). (credit: NASA/JPL)
11 FIGURE Ridges and Cracks. This region of the Lakshmi Plains on Venus has been fractured by tectonic forces to produce a cross-hatched grid of cracks and ridges. Be sure to notice the fainter linear features that run perpendicular to the brighter ones. As this is a radar image, the brightness of the ridges indicates their relative height. This image shows a region about 80 kilometers wide and 37 kilometers high. Lakshmi is a Hindu goddess of prosperity. (credit: modification of work by Magellan Team, JPL, NASA)
12 FIGURE Surface of Venus. These views of the surface of Venus are from the Venera 13 spacecraft. Everything is orange because the thick atmosphere of Venus absorbs the bluer colors of light. The horizon is visible in the upper corner of each image. (credit: NASA)
13 FIGURE Venus Atmosphere. The layers of the massive atmosphere of Venus shown here are based on data from the Pioneer and Venera entry probes. Height is measured along the left axis, the bottom scale shows temperature, and the red line allows you to read off the temperature at each height. Notice how steeply the temperature rises below the clouds, thanks to the planet s huge greenhouse effect.
14 FIGURE Mars Photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope. This is one of the best photos of Mars taken from our planet, obtained in June 2001 when Mars was only 68 million kilometers away. The resolution is about 20 kilometers much better than can be obtained with ground-based telescopes but still insufficient to reveal the underlying geology of Mars. (credit: modification of work by NASA and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA))
15 FIGURE Surface View from Mars Pathfinder. The scene from the Pathfinder lander shows a windswept plain, sculpted long ago when water flowed out of the martian highlands and into the depression where the spacecraft landed. The Sojourner rover, the first wheeled vehicle on Mars, is about the size of a microwave oven. Its flat top contains solar cells that provided electricity to run the vehicle. You can see the ramp from the lander and the path the rover took to the larger rock that the mission team nicknamed Yogi. (credit: NASA/JPL)
16 FIGURE Victoria Crater. (a) (b) This crater in Meridiani Planum is 800 meters wide, making it slightly smaller than Meteor crater on Earth. Note the dune field in the interior. This image shows the view from the Opportunity rover as it scouted the rim of Victoria crater looking for a safe route down into the interior. (credit a: modification of work by NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/Cornell/Phio State University; credit b: modification of work by NASA/JPL/Cornell)
17 FIGURE Martian Meteorite. This fragment of basalt, ejected from Mars in a crater-forming impact, eventually arrived on Earth s surface. (credit: NASA)
18 FIGURE Mars Map from Laser Ranging. These globes are highly precise topographic maps, reconstructed from millions of individual elevation measurements made with the Mars Global Surveyor. Color is used to indicate elevation. The hemisphere on the left includes the Tharsis bulge and Olympus Mons, the highest mountain on Mars; the hemisphere on the right includes the Hellas basin, which has the lowest elevation on Mars. (credit: modification of work by NASA/JPL)
19 FIGURE Olympus Mons. The largest volcano on Mars, and probably the largest in the solar system, is Olympus Mons, illustrated in this computer-generated rendering based on data from the Mars Global Surveyor s laser altimeter. Placed on Earth, the base of Olympus Mons would completely cover the state of Missouri; the caldera, the circular opening at the top, is 65 kilometers across, about the size of Los Angeles. (credit: NASA/Corbis)
20 FIGURE Heavily Eroded Canyonlands on Mars. This image shows the Valles Marineris canyon complex, which is 3000 kilometers wide and 8 kilometers deep. (credit: NASA/JPL/USGS)
21 FIGURE Martian Landslides. This Viking orbiter image shows Ophir Chasma, one of the connected valleys of the Valles Marineris canyon system. Look carefully and you can see enormous landslides whose debris is piled up underneath the cliff wall, which tower up to 10 kilometers above the canyon floor. (credit: modification of work by NASA/JPL/USGS)
22 FIGURE Three Martian Landing Sites. The Mars landers Viking 1 in Chryse, Pathfinder in Ares Valley, and Viking 2 in Utopia, all photographed their immediate surroundings. It is apparent from the similarity of these three photos that each spacecraft touched down on a flat, windswept plain littered with rocks ranging from tiny pebbles up to meter-size boulders. It is probable that most of Mars looks like this on the surface. (credit Viking 1 : modification of work by Van der Hoorn/NASA; credit Pathfinder : modification of work by NASA; credit Viking 2 : modification of work by NASA; credit Mars: modification of work by NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center)
23 FIGURE Water Frost in Utopia. This image of surface frost was photographed at the Viking 2 landing site during late winter. (credit: NASA/JPL)
24 FIGURE Dust Devil Tracks and Sand Dunes. (a) This high-resolution photo from the Mars Global Surveyor shows the dark tracks of several dust devils that have stripped away a thin coating of light-colored dust. This view is of an area about 3 kilometers across. Dust devils are one of the most important ways that dust gets redistributed by the martian winds. They may also help keep the solar panels of our rovers free of dust. (b) These windblown sand dunes on Mars overlay a lighter sandy surface. Each dune in this high-resolution view is about 1 kilometer across. (credit a: modification of work by NASA/JPL/University of Arizona; credit b: modification of work by NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
25 FIGURE Wind Erosion on Mars. These long straight ridges, called yardangs, are aligned with the dominant wind direction. This is a high-resolution image from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and is about 1 kilometer wide. (credit: NASA/JPL- Caltech/University of Arizona)
26 FIGURE Martian North Polar Cap. (a) This is a composite image of the north pole in summer, obtained in October 2006 by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. It shows the mostly water-ice residual cap sitting atop light, tan-colored, layered sediments. Note that although the border of this photo is circular, it shows only a small part of the planet. (b) Here we see a small section of the layered terrain near the martian north pole. There is a mound about 40 meters high that is sticking out of a trough in the center of the picture. (credit a: modification of work by NASA/JPL/MSSS; credit b: modification of work by NASA/JPL- Caltech/University of Arizona)
27 FIGURE Evaporating Ice on Mars. We see a trench dug by the Phoenix lander in the north polar region four martian days apart in June If you look at the shadowed region in the bottom left of the trench, you can see three spots of ice in the left image which have sublimated away in the right image. (credit: modification of work by NASA/JPL- Caltech/University of Arizona/Texas A&M University)
28 FIGURE Runoff and Outflow Channels. (a) (b) These runoff channels in the old martian highlands are interpreted as the valleys of ancient rivers fed by either rain or underground springs. The width of this image is about 200 kilometers. This intriguing channel, called Nanedi Valles, resembles Earth riverbeds in some (but not all) ways. The tight curves and terraces seen in the channel certainly suggest the sustained flow of a fluid like water. The channel is about 2.5 kilometers across. (credit a: modification of work by Jim Secosky/NASA; credit b: modification of work by Jim Secosky/NASA)
29 FIGURE Gullies on the Wall of Garni Crater. This high-resolution image is from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The dark streaks, which are each several hundred meters long, change in a seasonal pattern that suggests they are caused by the temporary flow of surface water. (credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
30 FIGURE Evidence for Liquid Water on Mars. The dark streaks in Horowitz crater, which move downslope, have been called recurring slope lineae. The streaks in the center of the image go down the wall of the crater for about a distance of 100 meters. Spectra taken of this region indicate that these are locations where salty liquid water flows on or just below the surface of Mars. (The vertical dimension is exaggerated by a factor of 1.5 compared to horizontal dimensions.) (credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
31 FIGURE Gale Crater. (a) (b) This scene, photographed by the Curiosity rover, shows an ancient lakebed of cracked mudstones. Geologists working with the Curiosity rover interpret this image of cross-bedded sandstone in Gale crater as evidence of liquid water passing over a loose bed of sediment at the time this rock formed. (credit a: modification of work by NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS; credit b: modification of work by NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
32 FIGURE Face on Mars. The so-called Face on Mars is seen (a) in low resolution from Viking (the face is in the upper part of the picture) and (b) with 20 times better resolution from the Mars Global Surveyor. (credit a: modification of work NASA/JPL; credit b: modification of work by NASA/JPL/MSSS)
33 PRINTED FOR WIKIVERSITY This OpenStax ancillary resource is Rice University under a CC-BY 4.0 International license; it may be reproduced or modified but must be attributed to OpenStax, Rice University and any changes must be noted.
The Main Points. The View from the Surface. Geology of Mars. Lecture #20: Reading:
 Surface of Mars Lecture #20: Geology and Geologic Processes View from the Surface History/Evolution of the surface Reading: Chapter 9.4 The Main Points Mars has had a geologically active past that has
Surface of Mars Lecture #20: Geology and Geologic Processes View from the Surface History/Evolution of the surface Reading: Chapter 9.4 The Main Points Mars has had a geologically active past that has
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 10. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 10 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 10 Mars Units of Chapter 10 10.1 Orbital Properties 10.2 Physical Properties 10.3 Long-Distance Observations of Mars 10.4
Lecture Outlines Chapter 10 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 10 Mars Units of Chapter 10 10.1 Orbital Properties 10.2 Physical Properties 10.3 Long-Distance Observations of Mars 10.4
What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. Seismic Waves.
 Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Seismic Waves Vibrations that travel through Earth s interior tell us what Earth is
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Seismic Waves Vibrations that travel through Earth s interior tell us what Earth is
Chapter 17: Mercury, Venus and Mars
 Chapter 17: Mercury, Venus and Mars Mercury Very similar to Earth s moon in several ways: Small; no atmosphere lowlands flooded by ancient lava flows heavily cratered surfaces Most of our knowledge based
Chapter 17: Mercury, Venus and Mars Mercury Very similar to Earth s moon in several ways: Small; no atmosphere lowlands flooded by ancient lava flows heavily cratered surfaces Most of our knowledge based
11/4/2015. Venus and Mars. Chapter 13. Venus and Mars. The Rotation of Venus. The Atmosphere of Venus. The Surface of Venus
 Venus and Mars Two most similar planets to Earth: Chapter 13 Venus and Mars Similar in size and mass Same part of the solar system Atmosphere Similar interior structure The Rotation of Venus Almost all
Venus and Mars Two most similar planets to Earth: Chapter 13 Venus and Mars Similar in size and mass Same part of the solar system Atmosphere Similar interior structure The Rotation of Venus Almost all
Mars: The Red Planet. Roman God of war Blood Reflects 30% of its incident sunlight 2 small moons : Phobos and Deimos
 Mars: The Red Planet Roman God of war Blood Reflects 30% of its incident sunlight 2 small moons : Phobos and Deimos Property Earth Mars Radius 6378km 3394km ~ 0.51R E Mass 5.97x10 24 kg 6.42x10 23 kg =
Mars: The Red Planet Roman God of war Blood Reflects 30% of its incident sunlight 2 small moons : Phobos and Deimos Property Earth Mars Radius 6378km 3394km ~ 0.51R E Mass 5.97x10 24 kg 6.42x10 23 kg =
Examining the Terrestrial Planets (Chapter 20)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Examining the Terrestrial Planets (Chapter 20) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and your geology
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Examining the Terrestrial Planets (Chapter 20) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and your geology
Mars ( ) The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Spring Semester 2018 Prof Dr Ravit Helled
 The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Spring Semester 2018 Prof Dr Ravit Helled Mars ( ) Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost terrestrial planet. It has a density of 3.93 g/cm3, which
The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Spring Semester 2018 Prof Dr Ravit Helled Mars ( ) Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost terrestrial planet. It has a density of 3.93 g/cm3, which
Geologic Features of Mars
 Name Purpose Geologic Features of Mars To learn to identify landforms on the surface of Mars and the geological processes that produced them. Introduction In many ways, Mars is similar to Earth. The same
Name Purpose Geologic Features of Mars To learn to identify landforms on the surface of Mars and the geological processes that produced them. Introduction In many ways, Mars is similar to Earth. The same
The Planets. The Terrestrial Planets. Admin. 9/19/17. Key Concepts: Lecture 13. Formulae (will be displayed for you in Midterm 1):
 Admin. 9/19/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.35pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Admin. 9/19/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.35pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
 Mars Math National Aeronautics and Space Administration Table of Contents ii Acknowledgments Table of Contents Mathematics Topic Matrix How to use this Book Alignment with Standards Teacher Comments Grade
Mars Math National Aeronautics and Space Administration Table of Contents ii Acknowledgments Table of Contents Mathematics Topic Matrix How to use this Book Alignment with Standards Teacher Comments Grade
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 9.1 Connecting Planetary Interiors and Surfaces Our goals for learning What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? What causes geological
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 9.1 Connecting Planetary Interiors and Surfaces Our goals for learning What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? What causes geological
Opposition and Conjunction
 Opposition and Conjunction Summary 1. Mars is 52% further the Sun having an orbital period of nearly 2 Earth years 2. Mars is much smaller than the Earth being roughly 53% the size, 11% the mass of the
Opposition and Conjunction Summary 1. Mars is 52% further the Sun having an orbital period of nearly 2 Earth years 2. Mars is much smaller than the Earth being roughly 53% the size, 11% the mass of the
Jovian Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
 The Inner Planets The Inner Planets Terrestrial Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars Rocky Surfaces No rings No or Few Moons Jovian Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Gas Surfaces rings Many
The Inner Planets The Inner Planets Terrestrial Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars Rocky Surfaces No rings No or Few Moons Jovian Planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Gas Surfaces rings Many
Scale: Mars is 6,787 km in diameter. Image 1. What is the feature across the middle? What do you think the circles on the left side are?
 Image Set Scale: Mars is 6,787 km in diameter. Image 1 What is the feature across the middle? What do you think the circles on the left side are? Image 2 On Earth, what are some things about the size of
Image Set Scale: Mars is 6,787 km in diameter. Image 1 What is the feature across the middle? What do you think the circles on the left side are? Image 2 On Earth, what are some things about the size of
What You Already Know
 Mars: The Red Planet What You Already Know The Sun is a star, a huge ball of very hot gas that gives off energy. Our Sun is an average star. It is located at the center of the solar system, which consists
Mars: The Red Planet What You Already Know The Sun is a star, a huge ball of very hot gas that gives off energy. Our Sun is an average star. It is located at the center of the solar system, which consists
Red Planet Mars. Chapter Thirteen
 Red Planet Mars Chapter Thirteen ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 11 Nov. 13, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch7: Comparative Planetology
Red Planet Mars Chapter Thirteen ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 11 Nov. 13, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch7: Comparative Planetology
Chapter 9 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 9.1 Connecting Planetary Interiors
Chapter 9 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 9.1 Connecting Planetary Interiors
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 9.1 Apollo 11 Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin on the Surface of the Moon. Because there is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity
ASTRONOMY Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 9.1 Apollo 11 Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin on the Surface of the Moon. Because there is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity
Highs and Lows Floods and Flows
 Highs and Lows Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Facilitator Guide Becky Nelson Education Specialist The Lunar and Planetary Institute Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Overview In this
Highs and Lows Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Facilitator Guide Becky Nelson Education Specialist The Lunar and Planetary Institute Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Overview In this
Mars. PHYS Week 4, Part 2
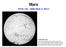 Mars PHYS 178 2008 Week 4, Part 2 Lowell s Mars Globe One of the remarkable globes of Mars prepared by Percival Lowell, showing a network of dozens of canals, oases, and triangular water reservoirs that
Mars PHYS 178 2008 Week 4, Part 2 Lowell s Mars Globe One of the remarkable globes of Mars prepared by Percival Lowell, showing a network of dozens of canals, oases, and triangular water reservoirs that
Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows PLANETARY MAPPING
 Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows PLANETARY MAPPING OVERVIEW Teams of students become familiar with the topography of Mars, its geologic features, and patterns of features using a color-coded topographic
Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows PLANETARY MAPPING OVERVIEW Teams of students become familiar with the topography of Mars, its geologic features, and patterns of features using a color-coded topographic
Orbit of Mars. Exploration of Mars
 Mars 1 Orbit of Mars Exploration of Mars First visits were by Mariners 4, 6, and 7. A major step forward was achieved in 1971, when Mariner 9 became the first spacecraft to orbit another planet. The Mariner
Mars 1 Orbit of Mars Exploration of Mars First visits were by Mariners 4, 6, and 7. A major step forward was achieved in 1971, when Mariner 9 became the first spacecraft to orbit another planet. The Mariner
Venus Earth s Sister Planet
 Venus Earth s Sister Planet 9 9.1 Orbital Properties 3rd brightest object in the sky, after Sun and Moon. Can even be seen in broad daylight Often called the morning star or the evening star, as it is
Venus Earth s Sister Planet 9 9.1 Orbital Properties 3rd brightest object in the sky, after Sun and Moon. Can even be seen in broad daylight Often called the morning star or the evening star, as it is
WHAT DO THESE IMAGES SHOW?
 Background Information The Mariner and Viking missions to Mars have taken thousands of pictures of Mars from orbit and from the surface, and new missions will provide many more images. These images are
Background Information The Mariner and Viking missions to Mars have taken thousands of pictures of Mars from orbit and from the surface, and new missions will provide many more images. These images are
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 7 OTHER WORLDS: AN INTRODUCTION TO THE SOLAR SYSTEM PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 7 OTHER WORLDS: AN INTRODUCTION TO THE SOLAR SYSTEM PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 7.1 Self-Portrait of Mars. This picture was taken by the Curiosity Rover on Mars in 2012. The image
ASTRONOMY Chapter 7 OTHER WORLDS: AN INTRODUCTION TO THE SOLAR SYSTEM PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 7.1 Self-Portrait of Mars. This picture was taken by the Curiosity Rover on Mars in 2012. The image
Mars. Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost of the four terrestrial worlds in the Solar System. It lies outside Earth s orbit.
 Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost of the four terrestrial worlds in the Solar System. It lies outside Earth s orbit. Mars s orbital eccentricity is 0.093, much larger than that
Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost of the four terrestrial worlds in the Solar System. It lies outside Earth s orbit. Mars s orbital eccentricity is 0.093, much larger than that
InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars
 InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars InSight is a robotic scientific explorer to investigate the deep interior of Mars set to launch May 5, 2018. It is scheduled to land on Mars November
InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars InSight is a robotic scientific explorer to investigate the deep interior of Mars set to launch May 5, 2018. It is scheduled to land on Mars November
This evening s announcements
 This evening s announcements Homework 3 is graded and available for pickup at entry Quiz 4 will be held this Wednesday, March 12. Coverage: Feb. 25: origin of the solar system (chapter 6) Feb. 27: Earth,
This evening s announcements Homework 3 is graded and available for pickup at entry Quiz 4 will be held this Wednesday, March 12. Coverage: Feb. 25: origin of the solar system (chapter 6) Feb. 27: Earth,
Physics Homework Set 3 Fall 2015
 1) Mercury presents the same side to the Sun 1) A) every third orbit. B) every 12 hours. C) all the time, just like our Moon. D) every other orbit. E) Twice every orbit. 2) Both the Moon and Mercury are
1) Mercury presents the same side to the Sun 1) A) every third orbit. B) every 12 hours. C) all the time, just like our Moon. D) every other orbit. E) Twice every orbit. 2) Both the Moon and Mercury are
Activity #1 - Getting Started in Mars Exploration
 Materials Activity #1 - Getting Started in Mars Exploration Paper, staples, glue, tape, markers, a collection of Mars images, etc., to construct a journal Preparation Collect newspaper or magazine articles
Materials Activity #1 - Getting Started in Mars Exploration Paper, staples, glue, tape, markers, a collection of Mars images, etc., to construct a journal Preparation Collect newspaper or magazine articles
10/31/2010. Opposition and Conjunction. Opposition occurs every 2 years. Best opposition at perihelion. Percival Lowell
 Opposition and Conjunction Opposition occurs every 2 years Best opposition at perihelion Percival Lowell 1 Canals on Mars? Martians? Orson Welle s Broadcast (1938) The War of the Worlds H G Wells (1898)
Opposition and Conjunction Opposition occurs every 2 years Best opposition at perihelion Percival Lowell 1 Canals on Mars? Martians? Orson Welle s Broadcast (1938) The War of the Worlds H G Wells (1898)
Terrestrial Atmospheres
 Terrestrial Atmospheres Why Is There Air? An atmosphere is a layer of gas trapped by the gravity of a planet or moon. Here s Earth s atmosphere viewed from orbit: Why Is There Air? If atoms move faster
Terrestrial Atmospheres Why Is There Air? An atmosphere is a layer of gas trapped by the gravity of a planet or moon. Here s Earth s atmosphere viewed from orbit: Why Is There Air? If atoms move faster
Image of the Moon from the Galileo Space Craft
 Image of the Moon from the Galileo Space Craft Moon: Overview Due to its size (diameter 3476 km, Mercury s diameter is 4880 km) and composition, the moon is sometimes considered as a terrestrial planet
Image of the Moon from the Galileo Space Craft Moon: Overview Due to its size (diameter 3476 km, Mercury s diameter is 4880 km) and composition, the moon is sometimes considered as a terrestrial planet
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases. The Early Archean Earth
 Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases
 Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Q. Some rays cross maria. What does this imply about the relative age of the rays and the maria?
 Page 184 7.1 The Surface of the Moon Surface Features To the naked eye, the Moon is a world of grays. Some patches are darker than others, creating a vague impression of what some see as a face ( the man
Page 184 7.1 The Surface of the Moon Surface Features To the naked eye, the Moon is a world of grays. Some patches are darker than others, creating a vague impression of what some see as a face ( the man
Unit 3 Lesson 4 The Terrestrial Planets. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.5 Analyze the methods used to develop a scientific explanation as seen in different fields of science. SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets
Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.5 Analyze the methods used to develop a scientific explanation as seen in different fields of science. SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets
Venus. Appearance. Earth s Sister? Venus is very bright.
 Venus Earth s Sister? Appearance Venus is very bright. It goes through phases, although full cannot be seen. Angular size varies from 10 to 64 arcsec. Venus is at its greatest brilliance when it is a crescent,
Venus Earth s Sister? Appearance Venus is very bright. It goes through phases, although full cannot be seen. Angular size varies from 10 to 64 arcsec. Venus is at its greatest brilliance when it is a crescent,
Hubble Telescope Picture of Mars
 Information of Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and is commonly referred to as the Red Planet. The rocks and soil have a red or pink hue due to the iron oxiode (rust) they contain. Hubble Telescope
Information of Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and is commonly referred to as the Red Planet. The rocks and soil have a red or pink hue due to the iron oxiode (rust) they contain. Hubble Telescope
Quiz 3 is available for pickup in front
 Quiz 3 is available for pickup in front Extra credit corrections: for up to 4 of the questions you missed: Look up or figure out the correct answer. Write a sentence or two explaining what you did wrong
Quiz 3 is available for pickup in front Extra credit corrections: for up to 4 of the questions you missed: Look up or figure out the correct answer. Write a sentence or two explaining what you did wrong
Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky Ages on Mars. Martian Surface Age Exploration
 Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 Ages on Mars Martian Surface Age Exploration You have now learned some very important things about various planets and moons in our Solar
Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 Ages on Mars Martian Surface Age Exploration You have now learned some very important things about various planets and moons in our Solar
Mapping the Surface of Mars Prelab. 1. Explain in your own words what you think a "geologic history" for a planet or moon is?
 Prelab 1. Explain in your own words what you think a "geologic history" for a planet or moon is? 2. Describe some of the major features seen on the Martian surface by various spacecraft missions over the
Prelab 1. Explain in your own words what you think a "geologic history" for a planet or moon is? 2. Describe some of the major features seen on the Martian surface by various spacecraft missions over the
Astronomy Ch. 10 Mars Review. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 10 Mars Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Why was the summer of 2003 a fine time for Mars
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 10 Mars Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Why was the summer of 2003 a fine time for Mars
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
Earth, the Lively* Planet. * not counting the life on the planet!
 Earth, the Lively* Planet * not counting the life on the planet! What We Will Learn Today What are planet Earth s features? What processes shape planetary surfaces? How does Earth s surface move? How did
Earth, the Lively* Planet * not counting the life on the planet! What We Will Learn Today What are planet Earth s features? What processes shape planetary surfaces? How does Earth s surface move? How did
The Latest from Mars: Recent Results and the Next Decade of Exploration
 The Latest from Mars: Recent Results and the Next Decade of Exploration Brian M. Hynek Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics & Department of Geological Sciences, University of Colorado Mars ½ diameter
The Latest from Mars: Recent Results and the Next Decade of Exploration Brian M. Hynek Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics & Department of Geological Sciences, University of Colorado Mars ½ diameter
Venus: Key Ideas: A Warm Up Exercise. Venus at a Glance -- Orbit. Venus at a Glance Planetary Data
 Venus A Warm Up Exercise Because Mercury has a high average density despite its relatively low mass, it is thought to a) Have a subsurface ocean b) Have a large iron core c) Be made largely of lead d)
Venus A Warm Up Exercise Because Mercury has a high average density despite its relatively low mass, it is thought to a) Have a subsurface ocean b) Have a large iron core c) Be made largely of lead d)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009
 Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
Today s Class. Results for Exam #2 11/7/2017. Today s Class: Robotic & Human Exploration of Mars
 11/7/2017 Today s Class: Robotic & Human Exploration of Mars Results for Exam #2 Homework: 1. Reading for Earth as a Planet: Section 9.4 of Cosmic Perspective. 2. Meet at Fiske on Thursday! Average Median
11/7/2017 Today s Class: Robotic & Human Exploration of Mars Results for Exam #2 Homework: 1. Reading for Earth as a Planet: Section 9.4 of Cosmic Perspective. 2. Meet at Fiske on Thursday! Average Median
Earth. Physical Properties of Earth kg. Average Density g/cm 2. Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s o C to 50 o C. Surface Temperature
 Earth Physical Properties of Earth Equatorial Diameter Mass 12,756 km 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 5.497 g/cm 2 Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s 2 Escape Velocity Surface Temperature 11.2 km/s -50 o C to 50 o
Earth Physical Properties of Earth Equatorial Diameter Mass 12,756 km 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 5.497 g/cm 2 Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s 2 Escape Velocity Surface Temperature 11.2 km/s -50 o C to 50 o
PTYS/ASTR Section 2 - Spring 2007 Practice Exam 2
 PTYS/ASTR 206 - Section 2 - Spring 2007 Practice Exam 2 Note: The exam is scheduled for Thursday, March 29, 2007. It will be held in-class; you will have 75 minutes to finish the exam, though many of you
PTYS/ASTR 206 - Section 2 - Spring 2007 Practice Exam 2 Note: The exam is scheduled for Thursday, March 29, 2007. It will be held in-class; you will have 75 minutes to finish the exam, though many of you
The Moon. Tides. Tides. Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = MEarth. = 0.27 REarth. (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth
 The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6.
 The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Lecture 6 Venus 1 Spring Semester 2017 Prof Dr Ravit Helled Cover photo: Venus in true color (Courtesy of NASA) Venus Properties Venus is the second brightest natural
The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Lecture 6 Venus 1 Spring Semester 2017 Prof Dr Ravit Helled Cover photo: Venus in true color (Courtesy of NASA) Venus Properties Venus is the second brightest natural
Meeting the neighbors. The exploration of Mars
 Meeting the neighbors The exploration of Mars An angry red star It s distinctive red hue has marked Mars has a notable world throughout human history. Recorded observations stretch back more than 3,500
Meeting the neighbors The exploration of Mars An angry red star It s distinctive red hue has marked Mars has a notable world throughout human history. Recorded observations stretch back more than 3,500
Rotation and Orbital Motion
 Venus Rotation and Orbital Motion The interior orbit of Venus means that it never strays far from the Sun in the sky. Because of its highly reflective cloud cover, Venus is brighter than any star in the
Venus Rotation and Orbital Motion The interior orbit of Venus means that it never strays far from the Sun in the sky. Because of its highly reflective cloud cover, Venus is brighter than any star in the
Exam# 2 Review. Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280
 Exam# 2 Review Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the
Exam# 2 Review Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the
The Solar System. Tour of the Solar System
 The Solar System Tour of the Solar System The Sun more later 8 planets Mercury Venus Earth more later Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Various other objects Asteroids Comets Pluto The Terrestrial Planets
The Solar System Tour of the Solar System The Sun more later 8 planets Mercury Venus Earth more later Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Various other objects Asteroids Comets Pluto The Terrestrial Planets
Impact Cratering. David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM
 Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
Lunar Cratering and Surface Composition
 Lunar Cratering and Surface Composition Earth vs. Moon On Earth, the combined actions of wind and water erode our planet s surface and reshape its appearance almost daily Most of the ancient history of
Lunar Cratering and Surface Composition Earth vs. Moon On Earth, the combined actions of wind and water erode our planet s surface and reshape its appearance almost daily Most of the ancient history of
Outline. Astronomy 122. What s this Picture of? It s not your parent s Solar System
 Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 10): The Solar System Next Class: The Sun Homework #4 is posted. Review of the Solar System Music: Venus Bjork What s this Picture of? It s not your parent s Solar
Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 10): The Solar System Next Class: The Sun Homework #4 is posted. Review of the Solar System Music: Venus Bjork What s this Picture of? It s not your parent s Solar
10/24/2010. Venus Roman goddess of love. Bulk Properties. Summary. Venus is easier to observe than Mercury! Venus and Earth
 Venus Roman goddess of love Birth of Venus Botticelli (1485) Bulk Properties Summary 1. Venus is 28% closer to the Sun having an orbital period of 225 Earth days 2. Venus is roughly 95% the size, 82% the
Venus Roman goddess of love Birth of Venus Botticelli (1485) Bulk Properties Summary 1. Venus is 28% closer to the Sun having an orbital period of 225 Earth days 2. Venus is roughly 95% the size, 82% the
Missions mars. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 Imagine that you are part of a team designing a new Mars rover. An area of the planet has been found that has ice and possibly liquid water. It seems like a great spot to locate life on Mars! Your job
Imagine that you are part of a team designing a new Mars rover. An area of the planet has been found that has ice and possibly liquid water. It seems like a great spot to locate life on Mars! Your job
ESCI 110: Planetary Surfaces Page 3-1. Exercise 3. Surfaces of the Planets and Moons
 ESCI 110: Planetary Surfaces Page 3-1 Introduction Exercise 3 Surfaces of the Planets and Moons Our knowledge of the solar system has exploded with the space exploration programs of the last 40 years.
ESCI 110: Planetary Surfaces Page 3-1 Introduction Exercise 3 Surfaces of the Planets and Moons Our knowledge of the solar system has exploded with the space exploration programs of the last 40 years.
Welcome to Class 12: Mars Geology & History. Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room
 Welcome to Class 12: Mars Geology & History Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What are we going to discuss today? How easily could humans live on Mars? Is there water on Mars? PRS: If
Welcome to Class 12: Mars Geology & History Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What are we going to discuss today? How easily could humans live on Mars? Is there water on Mars? PRS: If
1.2: Observing the Surfaces of Mars and Earth
 GEOLOGY ON MARS Unit 1 - Chapter 1-2 Comparing Rocky Planets 1.2: Observing the Surfaces of Mars and Earth Log on to Amplify Geology on Mars Chapter 1.2 In a moment, you will watch a video made by other
GEOLOGY ON MARS Unit 1 - Chapter 1-2 Comparing Rocky Planets 1.2: Observing the Surfaces of Mars and Earth Log on to Amplify Geology on Mars Chapter 1.2 In a moment, you will watch a video made by other
The Main Point. Lecture #21: Mars ~3 billion years ago? The Martian Climate
 Lecture #21: The Martian Climate Evidence for climate change Did it rain on Mars? Can you have a snowball fight on Mars? Similarities to variations in Earth's climate... Reading: Chapter 10.4 The Main
Lecture #21: The Martian Climate Evidence for climate change Did it rain on Mars? Can you have a snowball fight on Mars? Similarities to variations in Earth's climate... Reading: Chapter 10.4 The Main
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets
 page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
Page Mars. Figure 9.17 Picture of Mars made by the Hubble Space Telescope.
 Page 236 9.3 Mars Mars is named for the Roman god of war, presumably because of its distinctly reddish color. Compared with Mercury and Venus, Mars seems positively Earth like. Although its diameter is
Page 236 9.3 Mars Mars is named for the Roman god of war, presumably because of its distinctly reddish color. Compared with Mercury and Venus, Mars seems positively Earth like. Although its diameter is
Lecture #11: Plan. Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets
 Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Venus Venus The atmosphere of Venus is very dense and an opaque layer of clouds covers the planet, such that we cannot
Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Venus Venus The atmosphere of Venus is very dense and an opaque layer of clouds covers the planet, such that we cannot
The Main Point. Basic Properties of Mars. Observations. Lecture #19: Mars
 Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
Introduction to Mars PTYS/ASTR 206 3/22/07
 Introduction to Reading Assignment Finish Chapter 13 Announcements Quiz today Will cover all material since the last exam. This is Chapters 9-12 and the part of 13 covered today. Exam #2 next Thursday
Introduction to Reading Assignment Finish Chapter 13 Announcements Quiz today Will cover all material since the last exam. This is Chapters 9-12 and the part of 13 covered today. Exam #2 next Thursday
EXPLORING THE GEOLOGY OF SEVERAL WORLDS FROM SPACE
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) EXPLORING THE GEOLOGY OF SEVERAL WORLDS FROM SPACE We have investigated to understand how scientists can map the sea floor and land surfaces of the Earth. Now let=s extend our vision
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) EXPLORING THE GEOLOGY OF SEVERAL WORLDS FROM SPACE We have investigated to understand how scientists can map the sea floor and land surfaces of the Earth. Now let=s extend our vision
Mercury and Venus 3/20/07
 Announcements Reading Assignment Chapter 13 4 th Homework due today Quiz on Thursday (3/22) Will cover all material since the last exam. This is Chapters 9-12 and the part of 13 covered in the lecture
Announcements Reading Assignment Chapter 13 4 th Homework due today Quiz on Thursday (3/22) Will cover all material since the last exam. This is Chapters 9-12 and the part of 13 covered in the lecture
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018
 Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
CHANNELS ON MARS. KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity
 CHANNELS ON MARS KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity In your small group, brainstorm ideas about what you think you know about channels and what questions you have about channels on Mars. You will
CHANNELS ON MARS KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity In your small group, brainstorm ideas about what you think you know about channels and what questions you have about channels on Mars. You will
PLATO - 4. The terrestrial planets, planetology
 PLATO - 4 The terrestrial planets, planetology 1 Disk Formation Why does the contracting cloud form a disk?! As matter rotates faster and faster, it feels more and more centrifugal force, resisting gravity!
PLATO - 4 The terrestrial planets, planetology 1 Disk Formation Why does the contracting cloud form a disk?! As matter rotates faster and faster, it feels more and more centrifugal force, resisting gravity!
Mars Update. Presented by NASA/JPL Solar System Educator Don W. Brown
 Mars Update Presented by NASA/JPL Solar System Educator Don W. Brown http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2010/01/gallery-mars/6/ Mariner Mars Climate Orbiter Mars Exploration Rovers Mars Global Surveyor
Mars Update Presented by NASA/JPL Solar System Educator Don W. Brown http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2010/01/gallery-mars/6/ Mariner Mars Climate Orbiter Mars Exploration Rovers Mars Global Surveyor
Life in the Inner Solar System!
 Life in the Inner Solar System Life in the Solar System 1. Study processes that produce current conditions on planets (n e ) 2. Life elsewhere in Solar System? (f l ) Greenhouse effect Planet Temperatures
Life in the Inner Solar System Life in the Solar System 1. Study processes that produce current conditions on planets (n e ) 2. Life elsewhere in Solar System? (f l ) Greenhouse effect Planet Temperatures
Part 1: the terrestrial planets
 Mercury close up Part 1: the terrestrial planets The weird day on Mercury Weirdness is due to the fact that the rota:on period is comparable to period of revolu:on, and that they are related by the ra:o
Mercury close up Part 1: the terrestrial planets The weird day on Mercury Weirdness is due to the fact that the rota:on period is comparable to period of revolu:on, and that they are related by the ra:o
Planetary Geology. Geology Colloquium. Tucker County Research Assistants
 Planetary Geology Geology Colloquium Dr. Peter Sak, Dickinson College Interseismic Coupling, Quaternary Uplift Rates, and Fore Arc Deformation along the Costa Rican Segment of the Middle American Trench
Planetary Geology Geology Colloquium Dr. Peter Sak, Dickinson College Interseismic Coupling, Quaternary Uplift Rates, and Fore Arc Deformation along the Costa Rican Segment of the Middle American Trench
Name: Period: Mars. 1.Where does Mars get its name? 2. How does the atmosphere of Mars compare to Earth s? 3. Why is Mars different than Earth?
 Question 1.Where does get its name? Name: Period: Answer 2. How does the atmosphere of compare to Earth s? 3. Why is different than Earth? 4. What is different about the orbit of? 5. How does the length
Question 1.Where does get its name? Name: Period: Answer 2. How does the atmosphere of compare to Earth s? 3. Why is different than Earth? 4. What is different about the orbit of? 5. How does the length
Extraterrestrial Volcanism
 Extraterrestrial Volcanism What does it take to create volcanic activity? How do different planetary conditions influence volcanism? Venus Volcanism in our solar system. Io Europa Mercury Venus Earth/Moon
Extraterrestrial Volcanism What does it take to create volcanic activity? How do different planetary conditions influence volcanism? Venus Volcanism in our solar system. Io Europa Mercury Venus Earth/Moon
Utilizing a trial-and-error approach to studying the orbit of Mars and adjusting as needed, Kepler formulated three laws of planetary motion:
 2006 NSO Finals/Solar System Event Mars: The Fourth Rock Directions: Record all answers on the Student Response Sheet. Do not write on the map. You may write on this exam, and you may separate the pages.
2006 NSO Finals/Solar System Event Mars: The Fourth Rock Directions: Record all answers on the Student Response Sheet. Do not write on the map. You may write on this exam, and you may separate the pages.
1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation
 Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Loulousis 1 Describe the structure of the moon 2. Describe its surface features 3. Summarize the hypothesis of moon formation moon -a body that revolves around a planet and that has less mass than the
Distance of Mercury to the Sun or the Orbital Radius
 Distance of Mercury to the Sun or the Orbital Radius The minimum distance from the Sun to Mercury is about 45866304 kilometers and the maximum distance is about 70006464 kilometers. Space Station One Day
Distance of Mercury to the Sun or the Orbital Radius The minimum distance from the Sun to Mercury is about 45866304 kilometers and the maximum distance is about 70006464 kilometers. Space Station One Day
Mars Exploration Script
 Mars Exploration Script By Michael Hardegree-Ullman 8/14/15 Revised: 8/12/16 Script Bulletpoints Sphere Flatscreens/ Mars has been known as a planet for thousands of years. The first records come from
Mars Exploration Script By Michael Hardegree-Ullman 8/14/15 Revised: 8/12/16 Script Bulletpoints Sphere Flatscreens/ Mars has been known as a planet for thousands of years. The first records come from
9. Moon, Mercury, Venus
 9. Moon, Mercury, Venus All the heavier elements were manufactured by stars later, either by thermonuclear fusion reactions deep in their interiors or by the violent explosions that mark the end of massive
9. Moon, Mercury, Venus All the heavier elements were manufactured by stars later, either by thermonuclear fusion reactions deep in their interiors or by the violent explosions that mark the end of massive
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT. Mars Cratering. Crater count isochrons of Arsia and Pavonis Mons
 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT Mars Cratering Crater count isochrons of Arsia and Pavonis Mons Paul Hearding and Ben McIlwain 5/21/2007 Imagery of Arsia and Pavonis Mons taken by Mars Global
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT Mars Cratering Crater count isochrons of Arsia and Pavonis Mons Paul Hearding and Ben McIlwain 5/21/2007 Imagery of Arsia and Pavonis Mons taken by Mars Global
Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF B6 Eng Hall. Outline. Midterm. Review I. Midterm Discussion Venus. Mars
 Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 16): Life in the Solar System Next Class: Life in the Solar System Part II Midterm is March 12! The Exam will be in the Astronomy
Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 106 B6 Eng Hall This Class (Lecture 16): Life in the Solar System Next Class: Life in the Solar System Part II Midterm is March 12! The Exam will be in the Astronomy
Activity 7 At a Glance
 At a Glance Where Would You Search for Water on Mars? Purpose To help students develop an ongoing connection to the Mars missions Overview Students generate questions based on their module experiences
At a Glance Where Would You Search for Water on Mars? Purpose To help students develop an ongoing connection to the Mars missions Overview Students generate questions based on their module experiences
2. Terrestrial Planet G 9. Coulomb Force C 16. Babcock model Q. 3. Continuous Spectrum K 10. Large-impact hypothesis I 17.
 Astronomy 1 S 16 Exam 1 Name Identify terms Label each term with the appropriate letter of a definition listed 1. Spectral line R 8. Albedo H 15. helioseismology E 2. Terrestrial Planet G 9. Coulomb Force
Astronomy 1 S 16 Exam 1 Name Identify terms Label each term with the appropriate letter of a definition listed 1. Spectral line R 8. Albedo H 15. helioseismology E 2. Terrestrial Planet G 9. Coulomb Force
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 12 RINGS, MOONS, AND PLUTO PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 12 RINGS, MOONS, AND PLUTO PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 12.1 Jupiter Family. This montage, assembled from individual Galileo and Voyager images, shows a family portrait of Jupiter
ASTRONOMY Chapter 12 RINGS, MOONS, AND PLUTO PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 12.1 Jupiter Family. This montage, assembled from individual Galileo and Voyager images, shows a family portrait of Jupiter
ASTRONOMY 340 FALL September 2007 Class #6-#7
 ASTRONOMY 340 FALL 2007 25 September 2007 Class #6-#7 Review Physical basis of spectroscopy Einstein A,B coefficients probabilities of transistions Absorption/emission coefficients are functions of ρ,
ASTRONOMY 340 FALL 2007 25 September 2007 Class #6-#7 Review Physical basis of spectroscopy Einstein A,B coefficients probabilities of transistions Absorption/emission coefficients are functions of ρ,
Learning Objectives. they differ in density, composition, atmosphere, surface age, size, geological activity, magnetic field?
 The Red Planet Learning Objectives! Contrast the Terrestrial Planets and the Moon. Do they differ in density, composition, atmosphere, surface age, size, geological activity, magnetic field?! Why is Mars
The Red Planet Learning Objectives! Contrast the Terrestrial Planets and the Moon. Do they differ in density, composition, atmosphere, surface age, size, geological activity, magnetic field?! Why is Mars
AST 248, Lecture 19. James Lattimer. Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University. October 22, 2018
 AST 248, Lecture 19 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University October 22, 2018 The Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu
AST 248, Lecture 19 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University October 22, 2018 The Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu
October 30, Chapter 8. Terrestrial Planet Overview. The Terrestrial Planets. Terrestrial Planet Overview. Terrestrial Planet Overview 10/29/2008
 October 30, 2008 Reminder: Online quizzes due by test date Observation tonight, weather permitting, dress warmly! Chapter 8 Planetary distances Exercise Chapter 8 The Terrestrial Planets Copyright (c)
October 30, 2008 Reminder: Online quizzes due by test date Observation tonight, weather permitting, dress warmly! Chapter 8 Planetary distances Exercise Chapter 8 The Terrestrial Planets Copyright (c)
Lunar Geology ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Lunar Geology ASTR 2120 Sarazin Interior of the Moon Density low (3.3 gm/cc), very little iron No iron core Very small heat flow out of interior Little radioactive heating No magnetic field No molten iron
Lunar Geology ASTR 2120 Sarazin Interior of the Moon Density low (3.3 gm/cc), very little iron No iron core Very small heat flow out of interior Little radioactive heating No magnetic field No molten iron
