Mapping the Surface of Mars Prelab. 1. Explain in your own words what you think a "geologic history" for a planet or moon is?
|
|
|
- Sarah Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prelab 1. Explain in your own words what you think a "geologic history" for a planet or moon is? 2. Describe some of the major features seen on the Martian surface by various spacecraft missions over the past 30 years. Include observations from Mariner 1, Viking 1 & 2, Pathfinder/Sojourner, Mars Global Surveyor, etc Describe the similarities between Mars and Earth. Describe the differences. Why is Venus often called Earth's sister planet while Mars is not? 4. What evidence has been found that suggests water was once on Mars? Is there evidence for water on Mars today? 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 1 of 1
2 MAPPING THE SURFACE OF MARS What will you learn in this lab? How can we determine the geologic history of a planet or satellite without travelling to the planetary body? In this lab you will create a simple feature map of a region of Mars in a similar way used by photogeologists. Using this map of the surface you will hypothesize a geologic history of a part of the Martian surface. What do I need to bring to the Class with me to do this Lab? A copy of this lab script Pencil and eraser Scientific calculator Introduction: What is a geologic history? When looking at a planetary body a scientist wants to know how certain features were developed, what the sequence of events was, the age of certain features, etc. After gathering facts, data, and evidence, a geologic scientist can piece together a geologic history of the planet. A geologic history is just a story of how a planetary body formed from beginning to end. A geologic history can include many different things. It can include a geologic map of the planet similar to a map of Arizona that tells us where things are and what things might look like. The history can also include a geologic timeline that includes both relative time and absolute time. Relative time is where one determines the ages of events by comparing them against other events. The events are then ordered by when they occurred. With relative dating no exact date is identified (e.g. WWI and WWII). Absolute time is where the exact time or date of an event can be identified (e.g. 65 million years ago). A geologic history can also include pictures, fossils, practically anything that will help us determine the life story of the planet. What types of things would you include in a geologic history of the Earth? When geologists want to determine the geologic history of another planet what do they do? What instruments can be used? If we had a geologic map of a planet this would give us a large amount of data and evidence and allow us to determine a geologic history. It would tell us how the planet looks in the present and from that we can arrive at hypotheses of how those features came to be. But how do we make geologic maps? Let's first think about how we 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 1 of 14
3 would map the Earth s surface. What instruments would we use? What information would we want to try to find? Geologic maps are made of a planet or moon by looking at present day features land masses, bodies of water, volcanoes, channels, impact craters, etc. This can be done both by using photographs taken by orbiting satellites and from human physical research of the surface. The maps can give geologic scientists a relative time for the planet - show if the features were formed earlier or later than each other - but not any absolute times (specific dates). For example, early in the solar system there was a heavy bombardment period when many of the largest craters were formed. Most of the smaller craters were formed later when only smaller bodies were left over from the debris disk that formed the planets. When geologic scientists just look at the appearance of features on a planet or moon without denoting the relative time on the map then they are looking at the geomorphology of the region. A map that only looks at the appearance of features is called a geomorphic map. What happens if we can't travel to and physically stand on a planet s surface to conduct research? So far in space travel we have only been able to stand on the Earth and the Moon. What can we use to tell us the geologic history of a planet like Mars or Venus? In such cases, all we can do is rely on the geologic map of the planet determined from images taken by orbiting satellites (remote sensing) or rovers that land on the surface for us. Photogeologists examine the images carefully and use all available data to make a representative map of the surface. In this lab you will use images of the Chryse Planitia and Tiu Valles regions of Mars taken by the THEMIS Camera on the Mars Odyssey orbiter to make your own simple geomorphic map. You will need to distinguish between and identify a few different features: craters and channels. The images and descriptions in the following sections define examples of these features. Part I: Looking at Mars Globally In this section, we will use the MOLA map (the large colorful map). The MOLA (Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter) map shows the whole surface of Mars with colors representing elevation. Red and white colors indicate high elevation while blue and purple colors indicate low elevation. Like maps of Earth, Latitude is indicated by the numbers along the vertical axis while Longitude is indicated by numbers on the horizontal axis. 1. Look at the locations of craters on Mars. a. Does the Northern or Southern Hemisphere have more craters? b. Does the Northern or Southern Hemisphere have an older surface? Explain Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 2 of 14
4 We can classify impact craters into three general categories or classifications based on their appearance. These three categories give clues about the history (or relative age) of the crater. We cannot identify the exact age of a crater on Mars, but relative ages for different craters can help us develop a sequential history. I. Preserved Craters: Near perfect craters Raised rims Look new Can sometimes see ejecta blanket or central peak Young crater Crater rim Central peak (not all craters have a central peak.) II. Modified Craters: Craters that have been changed or modified by: o Erosion (wind, water or lava) o Other impacts Sometimes crater ejecta is visible but looks eroded Crater may have smooth floor (partially filled in with material or sediment) Middle-aged craters Ejecta blanket (not all craters have ejecta blankets.) III. Destroyed Craters: Look very worn away Rims are broken Have been severely changed or modified Crater has been filled in almost completely by sediment Very old craters 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 3 of 14
5 Scientists use two basic rules or principles to help determine the relative age of craters or other features on a surface. They are as follows: I. Cross-Cutting Relationships: A crater (or any other feature) can be cut by another feature. The feature cut is older than the feature that cut it. Crater shown here is older than the fracture (crack) that cut through it. II. Principle of Superposition When one feature is on top of another feature, the feature on top is younger. The feature on the bottom is the older feature. Crater #1 is partly covered by crater #2, so crater #1 is older Crater #2 is partly covered by crater #3, which makes crater #2 older than #3. By inference then, crater #1 is the oldest and crater #3 is the youngest Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 4 of 14
6 Based on the Crater Classification information sheet, classify the craters at the bottom of the page. Be sure to explain your reasoning for each classification. CRATER IMAGE CRATER CLASSIFICATION (Preserved, Modified or Destroyed) REASONS Crater A Crater B Crater C Crater D Crater A Crater B Crater C Crater D 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 5 of 14
7 Based on the two relative age dating principles (cross-cutting relationships and superposition), write your interpretation of the relative ages of the features in the following images: Oldest Feature: Younger Feature: Youngest Feature: Please explain your answers: Which principle(s) did you use to choose your answer? Oldest Feature: Younger Feature: Youngest Feature: Please explain your answers: Which principle(s) did you use to choose your answer? 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 6 of 14
8 Now you know how to classify craters and are familiar with relative age dating principles. You can now create a feature map of your region of Mars that will help you interpret the geologic history. In order to create your feature map, you will need to put a piece of transparency paper over your THEMIS mosaic image. Using paper clips, secure the THEMIS image and your paper together. Using your observations and erasable markers, identify the features listed below to create your map. Keep in mind that some features may be too small to map. Use your best judgment to decide what may be too small to map and in determining how to the outline or color features. Outline or color the features as indicated below. 1. Preserved Craters: Carefully outline the rims and ejecta (if visible) of all preserved craters in BLACK. Feature Colored Feature 2. Modified Craters: Carefully outline the uneven, or eroded rims and ejecta (if visible) of the modified craters in GREEN. 3. Destroyed Craters: Carefully outline the very eroded crater rims in RED. 4. Channels: Outline all channels in BLUE Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 7 of 14
9 Part II: Interpreting Your Geological Maps Using the map you made of Chryse Planitia, answer the following questions. 1. Which is older the channel(s) (blue) or the destroyed (red) craters? How do you know? 2. Which is older the channel(s) (blue) or the modified (green) craters? How do you know? 3. Which is older the channel(s) (blue) or the preserved (black) craters? How do you know? 4. Which are older most larger craters or smaller craters? How do you know? Why do you think this is? 5. Which features are oldest, youngest, and of medium age? 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 8 of 14
10 Using the map you made of Tiu Valles, answer the following questions. 1. Which is older the channel(s) (blue) or the destroyed (red) craters? How do you know? 2. Which is older the channel(s) (blue) or the modified (green) craters? How do you know? 3. Which is older the channel(s) (blue) or the preserved (black) craters? How do you know? 4. Which are older most larger craters or smaller craters? How do you know? Why do you think this is? 5. Which features are oldest, youngest, and of medium age? 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 9 of 14
11 Part III: Examining Crater Sizes Focus now on the craters only. Fill in the tables below with the number of craters that fall into each bin. Remember, a quick measurement to see which data bin your crater falls into is all that is necessary. Precise measurements, in this case, are not important. Chryse Planitia Crater Diameter (cm) or larger Preserved (black) Modified (green) Destroyed (red) Tiu Valles Crater Diameter (cm) or larger Preserved (black) Modified (green) Destroyed (red) Answer the following using the data from your tables: 1. Which crater type is most frequent? 2. Which crater type is the largest? 3. Which crater type is the smallest? 4. Which crater type is the youngest? 5. Which crater type is the oldest? 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 10 of 14
12 Now that you have information about the Martian regions you have mapped determine a geologic history for these regions. This should be a simple description of what happened, in what order, and how it affected the surrounding region. Be sure to state your evidence to support your hypothesis. Geologic History for Chryse Planitia: Geologic History for Tiu Valles: 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 11 of 14
13 Wrap-up questions: 1.a. Describe the process used to determine a geologic history for a terrestrial planet. 1.b. What steps does a scientist take? 1.c. What evidence does a scientist look for? 1.d. What instruments can help retrieve supporting data? 2.a. Using the latitude and longitude listed on the images of the Chryse Planitia and Tiu Valles, plot and label those locations on the MOLA map using the markers provided. 2.b. Describe the general area where these images were taken (include information about elevation and topography) Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 12 of 14
14 3.a. Do both regions (Chryse and Tiu) look similar? 3.b. Do they give a similar geologic history for Mars? 3.c. What are the similarities and differences? 3.d. Why might there be differences between the two regions you looked at? 3.e. Are these two regions the correct ones to use to make a global geologic history for Mars? 4. Was Mars a geologically active planet based on the two regions you mapped? Explain Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 13 of 14
15 5.a. Out of the four geologic processes that affect the surface of a terrestrial planet (erosion, tectonic activity, impact cratering, & volcanism) which are evident in the regions you looked at? 5.b. How can you tell? Summarize what you have learned in tonight s lab: 2014 Arizona State University & NASA Mars Education Group Page 14 of 14
MAPPING THE SURFACE OF MARS
 MAPPING THE SURFACE OF MARS What will you learn in this lab? How can we determine the geologic history of a planet or satellite without travelling to the planetary body? In this lab you will create a simple
MAPPING THE SURFACE OF MARS What will you learn in this lab? How can we determine the geologic history of a planet or satellite without travelling to the planetary body? In this lab you will create a simple
Initial Observations and Strategies
 STUDENT WORKSHEET 1 Initial Observations and Strategies Name(s) Date Look at the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) Daytime Infrared (IR) image mosaic your teacher has given you. You will be investigating
STUDENT WORKSHEET 1 Initial Observations and Strategies Name(s) Date Look at the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) Daytime Infrared (IR) image mosaic your teacher has given you. You will be investigating
Introduction. Background
 Introduction In introducing our research on mars we have asked the question: Is there a correlation between the width of an impact crater and the depth of that crater? This will lead to answering the question:
Introduction In introducing our research on mars we have asked the question: Is there a correlation between the width of an impact crater and the depth of that crater? This will lead to answering the question:
LUNAR OBSERVING. What will you learn in this lab?
 LUNAR OBSERVING What will you learn in this lab? The Moon is the second most noticeable object in the sky. This lab will first introduce you to observing the Moon with a telescope. You will be looking
LUNAR OBSERVING What will you learn in this lab? The Moon is the second most noticeable object in the sky. This lab will first introduce you to observing the Moon with a telescope. You will be looking
Highs and Lows Floods and Flows
 Highs and Lows Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Facilitator Guide Becky Nelson Education Specialist The Lunar and Planetary Institute Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Overview In this
Highs and Lows Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Facilitator Guide Becky Nelson Education Specialist The Lunar and Planetary Institute Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows Planetary Mapping Overview In this
We will apply two of these principles to features on the lunar surface in the following activities.
 STUDENT ACTIVITY 4 Studying the Geologic Past Scientists who study the processes that shape the surface of Earth are called geologists. They have scientific rules, which help them figure out the history
STUDENT ACTIVITY 4 Studying the Geologic Past Scientists who study the processes that shape the surface of Earth are called geologists. They have scientific rules, which help them figure out the history
Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows PLANETARY MAPPING
 Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows PLANETARY MAPPING OVERVIEW Teams of students become familiar with the topography of Mars, its geologic features, and patterns of features using a color-coded topographic
Highs and Lows, Floods and Flows PLANETARY MAPPING OVERVIEW Teams of students become familiar with the topography of Mars, its geologic features, and patterns of features using a color-coded topographic
CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds
 CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds PART 1: OBSERVATIONS AND PRELIMINARY QUESTIONS The images below are of impact craters from different planetary worlds
CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds PART 1: OBSERVATIONS AND PRELIMINARY QUESTIONS The images below are of impact craters from different planetary worlds
Type of Exercise: In-Class Activity or Laboratory Exercise.
 Using Lava Flows & Volcanic Structures on Mars to Introduce the Concept of Relative Dating in Introductory Courses Audeliz Matias Skidmore College, Saratoga Springs, NY 12866 amatias@skidmore.edu Type
Using Lava Flows & Volcanic Structures on Mars to Introduce the Concept of Relative Dating in Introductory Courses Audeliz Matias Skidmore College, Saratoga Springs, NY 12866 amatias@skidmore.edu Type
Geologic Features of Mars
 Name Purpose Geologic Features of Mars To learn to identify landforms on the surface of Mars and the geological processes that produced them. Introduction In many ways, Mars is similar to Earth. The same
Name Purpose Geologic Features of Mars To learn to identify landforms on the surface of Mars and the geological processes that produced them. Introduction In many ways, Mars is similar to Earth. The same
MSIP Proposal Milks Period 4
 part of Hebrus Vallis, V11030007, probably lava-formed (http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20041203a) Tinjar Vallis, V11030007, maybe water-formed? ( http://themis.asu.edu/ zoom-20040519a) MSIP Proposal Milks
part of Hebrus Vallis, V11030007, probably lava-formed (http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20041203a) Tinjar Vallis, V11030007, maybe water-formed? ( http://themis.asu.edu/ zoom-20040519a) MSIP Proposal Milks
ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can we use the Mars Map and photographs of Mars to learn about the geologic history of the planet?
 GRADE LEVEL(S) 4 6 LENGTH 60 minutes MATERIALS Giant Destination Mars Map Mars Mapping Student Sheet Colored Markers (red, green, blue) VOCABULARY Crater Erode Ejecta Channel Sun Angle Sequence ESSENTIAL
GRADE LEVEL(S) 4 6 LENGTH 60 minutes MATERIALS Giant Destination Mars Map Mars Mapping Student Sheet Colored Markers (red, green, blue) VOCABULARY Crater Erode Ejecta Channel Sun Angle Sequence ESSENTIAL
Examining the Terrestrial Planets (Chapter 20)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Examining the Terrestrial Planets (Chapter 20) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and your geology
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Examining the Terrestrial Planets (Chapter 20) For this assignment you will require: a calculator, colored pencils, a metric ruler, and your geology
I. Introduction: II. Background:
 I. Introduction: Is there a difference between the size of the crater and the ejecta blanket? This question could lead to many different discoveries. When you think about the thousands of craters on mars,
I. Introduction: Is there a difference between the size of the crater and the ejecta blanket? This question could lead to many different discoveries. When you think about the thousands of craters on mars,
The Main Points. The View from the Surface. Geology of Mars. Lecture #20: Reading:
 Surface of Mars Lecture #20: Geology and Geologic Processes View from the Surface History/Evolution of the surface Reading: Chapter 9.4 The Main Points Mars has had a geologically active past that has
Surface of Mars Lecture #20: Geology and Geologic Processes View from the Surface History/Evolution of the surface Reading: Chapter 9.4 The Main Points Mars has had a geologically active past that has
Problem Set 3: Crater Counting
 Problem Set 3: Crater Counting Introduction Impact craters are the dominant landforms on most of the solid surfaces in our solar system. These impact craters have formed on the surfaces over the 4.6 billion
Problem Set 3: Crater Counting Introduction Impact craters are the dominant landforms on most of the solid surfaces in our solar system. These impact craters have formed on the surfaces over the 4.6 billion
Question. Which volcano on the Tharsis region of Mars is the youngest?
 Question Which volcano on the Tharsis region of Mars is the youngest? Importance We believe that this question is important and interesting because we don t have any evidence of recent tectonic activity
Question Which volcano on the Tharsis region of Mars is the youngest? Importance We believe that this question is important and interesting because we don t have any evidence of recent tectonic activity
Photogeologic Mapping of Mars
 Exercise Two and Fifteen are suggested as introductory exercises. 2.0 hours Exercise Seventeen Photogeologic Mapping of Mars Instructor Notes Suggested Correlation of Topics Deductive reasoning, geologic
Exercise Two and Fifteen are suggested as introductory exercises. 2.0 hours Exercise Seventeen Photogeologic Mapping of Mars Instructor Notes Suggested Correlation of Topics Deductive reasoning, geologic
Where do they come from?
 Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
STUDENT GUIDE. Written and Developed by:
 CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds STUDENT GUIDE Written and Developed by: Paige Valderrama Graff Science Education Specialist, Jacobs Astromaterials Research
CRATER COMPARISONS Investigating Impact Craters on Earth and Other Planetary Worlds STUDENT GUIDE Written and Developed by: Paige Valderrama Graff Science Education Specialist, Jacobs Astromaterials Research
Activity #1 - Getting Started in Mars Exploration
 Materials Activity #1 - Getting Started in Mars Exploration Paper, staples, glue, tape, markers, a collection of Mars images, etc., to construct a journal Preparation Collect newspaper or magazine articles
Materials Activity #1 - Getting Started in Mars Exploration Paper, staples, glue, tape, markers, a collection of Mars images, etc., to construct a journal Preparation Collect newspaper or magazine articles
Scale: Mars is 6,787 km in diameter. Image 1. What is the feature across the middle? What do you think the circles on the left side are?
 Image Set Scale: Mars is 6,787 km in diameter. Image 1 What is the feature across the middle? What do you think the circles on the left side are? Image 2 On Earth, what are some things about the size of
Image Set Scale: Mars is 6,787 km in diameter. Image 1 What is the feature across the middle? What do you think the circles on the left side are? Image 2 On Earth, what are some things about the size of
15 Surface Water Flow Features on Mars
 Name: Date: 15 Surface Water Flow Features on Mars 15.1 Introduction In this lab you will be making measurements of some valleys and channels on Mars. The main goal of this lab is to be able to distinguish
Name: Date: 15 Surface Water Flow Features on Mars 15.1 Introduction In this lab you will be making measurements of some valleys and channels on Mars. The main goal of this lab is to be able to distinguish
Martian Crater Dating through Isochrons. The universe is a vast and seemingly-endless array of space and matter that
 Gary Studen ASTR 498 5/13/05 Martian Crater Dating through Isochrons Introduction The universe is a vast and seemingly-endless array of space and matter that harbors many mysteries. Through advances in
Gary Studen ASTR 498 5/13/05 Martian Crater Dating through Isochrons Introduction The universe is a vast and seemingly-endless array of space and matter that harbors many mysteries. Through advances in
COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009
 Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2009 Geologic landforms Purpose: By studying aerial photographs you will learn to identify different kinds of geologic features based on their different morphologies and learn
Assignment 2. Due March 4, 2019
 Assignment 2 Due March 4, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
Assignment 2 Due March 4, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
Craters. Part 1: What should we measure?
 When a meteoroid (called the impactor ) hits the surface of a planet or moon, it creates an impact crater. As the impactor s kinetic energy is dissipated, the resulting explosive energy release carves
When a meteoroid (called the impactor ) hits the surface of a planet or moon, it creates an impact crater. As the impactor s kinetic energy is dissipated, the resulting explosive energy release carves
Assignment 4. Due TBD
 Assignment 4 Due TBD Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your work is
Assignment 4 Due TBD Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your work is
1.2: Observing the Surfaces of Mars and Earth
 GEOLOGY ON MARS Unit 1 - Chapter 1-2 Comparing Rocky Planets 1.2: Observing the Surfaces of Mars and Earth Log on to Amplify Geology on Mars Chapter 1.2 In a moment, you will watch a video made by other
GEOLOGY ON MARS Unit 1 - Chapter 1-2 Comparing Rocky Planets 1.2: Observing the Surfaces of Mars and Earth Log on to Amplify Geology on Mars Chapter 1.2 In a moment, you will watch a video made by other
Impact Cratering. David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM
 Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
CHANNELS ON MARS. KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity
 CHANNELS ON MARS KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity In your small group, brainstorm ideas about what you think you know about channels and what questions you have about channels on Mars. You will
CHANNELS ON MARS KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity In your small group, brainstorm ideas about what you think you know about channels and what questions you have about channels on Mars. You will
Grading Summary: Question 1: 80 points. Question 2: 20 points. Total: 100 points
 HOMEWORK #5 Mars & Mercury Due Friday, May 26 th IN CLASS Answers to the questions must be given in complete sentences (except where indicated), using correct grammar and spelling. Please be as brief and
HOMEWORK #5 Mars & Mercury Due Friday, May 26 th IN CLASS Answers to the questions must be given in complete sentences (except where indicated), using correct grammar and spelling. Please be as brief and
Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores
 Earths History Reu2.notebook November 14, 2013 Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores One goal of geology is to develop a timeline of Earth's past, including both geological and biological events.
Earths History Reu2.notebook November 14, 2013 Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores One goal of geology is to develop a timeline of Earth's past, including both geological and biological events.
Moon 101. Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi
 Moon 101 Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi Part I Formation of the Moon Planetary Formation In the solar nebula, dust particles coalesced to form smaller planetesimals and
Moon 101 Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi Part I Formation of the Moon Planetary Formation In the solar nebula, dust particles coalesced to form smaller planetesimals and
Introduction. Background
 Introduction Our question was What is the affect of the elevation of an area on the state of the crater found there?. This question is important because it shows us how the weather at each elevation affects
Introduction Our question was What is the affect of the elevation of an area on the state of the crater found there?. This question is important because it shows us how the weather at each elevation affects
Student Guide to Moon 101
 Student Guide to Moon 101 LINKS TO WEBSITES AND DOCUMENTS NECESSARY TO COMPLETE MOON 101 CAN BE FOUND AT: 1) Read the following articles: PART 1 - FORMATION OF THE MOON a) The Scientific Legacy of Apollo,
Student Guide to Moon 101 LINKS TO WEBSITES AND DOCUMENTS NECESSARY TO COMPLETE MOON 101 CAN BE FOUND AT: 1) Read the following articles: PART 1 - FORMATION OF THE MOON a) The Scientific Legacy of Apollo,
Resources for Treasure Hunt In Earth s Attic Try This!
 Try This! Work in groups or as a family to determine the order of events that in the history of the Earth and Moon. More information and graphics are available at http://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/timeline/introduction.shtml
Try This! Work in groups or as a family to determine the order of events that in the history of the Earth and Moon. More information and graphics are available at http://www.lpi.usra.edu/education/timeline/introduction.shtml
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 10. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 10 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 10 Mars Units of Chapter 10 10.1 Orbital Properties 10.2 Physical Properties 10.3 Long-Distance Observations of Mars 10.4
Lecture Outlines Chapter 10 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 10 Mars Units of Chapter 10 10.1 Orbital Properties 10.2 Physical Properties 10.3 Long-Distance Observations of Mars 10.4
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT. Mars Cratering. Crater count isochrons of Arsia and Pavonis Mons
 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT Mars Cratering Crater count isochrons of Arsia and Pavonis Mons Paul Hearding and Ben McIlwain 5/21/2007 Imagery of Arsia and Pavonis Mons taken by Mars Global
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT Mars Cratering Crater count isochrons of Arsia and Pavonis Mons Paul Hearding and Ben McIlwain 5/21/2007 Imagery of Arsia and Pavonis Mons taken by Mars Global
Mars: The Red Planet. Roman God of war Blood Reflects 30% of its incident sunlight 2 small moons : Phobos and Deimos
 Mars: The Red Planet Roman God of war Blood Reflects 30% of its incident sunlight 2 small moons : Phobos and Deimos Property Earth Mars Radius 6378km 3394km ~ 0.51R E Mass 5.97x10 24 kg 6.42x10 23 kg =
Mars: The Red Planet Roman God of war Blood Reflects 30% of its incident sunlight 2 small moons : Phobos and Deimos Property Earth Mars Radius 6378km 3394km ~ 0.51R E Mass 5.97x10 24 kg 6.42x10 23 kg =
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets
 page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
ESCI 110: Planetary Surfaces Page 3-1. Exercise 3. Surfaces of the Planets and Moons
 ESCI 110: Planetary Surfaces Page 3-1 Introduction Exercise 3 Surfaces of the Planets and Moons Our knowledge of the solar system has exploded with the space exploration programs of the last 40 years.
ESCI 110: Planetary Surfaces Page 3-1 Introduction Exercise 3 Surfaces of the Planets and Moons Our knowledge of the solar system has exploded with the space exploration programs of the last 40 years.
Relative Dating. The Rock Cycle. Key Concept Scientists can interpret the sequence of events in Earth s history by studying rock layers.
 2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
Name Date. Partners. Comparative Planetology by Mary Lou West after Paul Johnson and Ron Canterna
 Name Date Partners Comparative Planetology by Mary Lou West after Paul Johnson and Ron Canterna Purpose : to become familiar with the major features of the planets of the solar system, especially the Earth,
Name Date Partners Comparative Planetology by Mary Lou West after Paul Johnson and Ron Canterna Purpose : to become familiar with the major features of the planets of the solar system, especially the Earth,
What is Crater Number Density?
 Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 What is Crater Number Density? REAL Curriculum Crater Number Density Today we will learn some math that is necessary in order to learn important
Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 What is Crater Number Density? REAL Curriculum Crater Number Density Today we will learn some math that is necessary in order to learn important
4 th Grade PSI. Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107. Slide 3 / 107. Slide 4 / 107. Slide 5 / 107. Slide 6 / 107. The History of Planet Earth
 Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107 4 th Grade PSI The History of Planet Earth 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 107 Slide 4 / 107 The History of Planet Earth The Structure of Earth Rock Layers Fossils and Relative
Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107 4 th Grade PSI The History of Planet Earth 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 107 Slide 4 / 107 The History of Planet Earth The Structure of Earth Rock Layers Fossils and Relative
MARS INSIDE AND OUT.
 GEOLOGIC SCENE INVESTIGATOR JOURNAL MARS INSIDE AND OUT Explore! Mars Inside and Out Investigator Name www.lpi.usra.edu/education PART I: SCRATCHING THE SURFACE GSI: INSIDE MARS COOLING CUPCAKES AND PLANETS
GEOLOGIC SCENE INVESTIGATOR JOURNAL MARS INSIDE AND OUT Explore! Mars Inside and Out Investigator Name www.lpi.usra.edu/education PART I: SCRATCHING THE SURFACE GSI: INSIDE MARS COOLING CUPCAKES AND PLANETS
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Strange New Planet. Time Budget: 1 hour
 Strange New Planet Grade Range: 5-8 G.L.E Focus: Time Budget: 1 hour WASL Vocabulary: Overview: This activity develops insight into the processes involved in learning about planetary exploration. Students
Strange New Planet Grade Range: 5-8 G.L.E Focus: Time Budget: 1 hour WASL Vocabulary: Overview: This activity develops insight into the processes involved in learning about planetary exploration. Students
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
Erosional Features. What processes shaped this landscape?
 Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered what processes shaped what you see? Perhaps you see mountains, valleys, rivers, or canyons. Do you know how long these geologic features have been
Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered what processes shaped what you see? Perhaps you see mountains, valleys, rivers, or canyons. Do you know how long these geologic features have been
MARS STUDENT IMAGING PROJECT FINAL REPORT ASU MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Waubonsie Valley High School Period School Year
 I. Introduction What is your science question? What effect do the polar ice caps have on craters in the rock strata? Why is this question important and interesting? This question is important for the following
I. Introduction What is your science question? What effect do the polar ice caps have on craters in the rock strata? Why is this question important and interesting? This question is important for the following
EROSIONAL FEATURES. reflect
 reflect Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered what processes shaped what you see? Perhaps you see mountains, valleys, rivers, or canyons. Do you know how long these geologic features
reflect Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered what processes shaped what you see? Perhaps you see mountains, valleys, rivers, or canyons. Do you know how long these geologic features
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
SOLAR SYSTEM B Division
 SOLAR SYSTEM B Division Team Name: Team #: Student Names: IMAGE SHEET A E B C D F G H Spectrum I Spectrum II SS2014 Spectrum III Spectrum IV Spectrum V Spectrum VI 1. A. What satellite is pictured in Image
SOLAR SYSTEM B Division Team Name: Team #: Student Names: IMAGE SHEET A E B C D F G H Spectrum I Spectrum II SS2014 Spectrum III Spectrum IV Spectrum V Spectrum VI 1. A. What satellite is pictured in Image
MAPPING THE SURFACE OF A PLANET
 Written and Developed by: Keith Watt, ASU Mars Education Program Editing by: Paige Valderrama Graff Assistant Director ASU Mars Education Program Sheri Klug Director ASU Mars Education Program SG-SG4 2002
Written and Developed by: Keith Watt, ASU Mars Education Program Editing by: Paige Valderrama Graff Assistant Director ASU Mars Education Program Sheri Klug Director ASU Mars Education Program SG-SG4 2002
MARS PUBLIC MAPPING PROJECT (MP)2
 KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity In your small group, brainstorm ideas about what you think you know about geologic features that may be found on Mars. Also include what questions you have about
KWL Prior Knowledge/Engagement Activity In your small group, brainstorm ideas about what you think you know about geologic features that may be found on Mars. Also include what questions you have about
Write Up #3. 3a) Given a picture of the moon I need to give an age sequence at least three maybe more
 Brad O Neal Professor Wilhelm AST 191 001 21 September Write Up #3 3a) Given a picture of the moon I need to give an age sequence at least three maybe more of the formations present in the picture. This
Brad O Neal Professor Wilhelm AST 191 001 21 September Write Up #3 3a) Given a picture of the moon I need to give an age sequence at least three maybe more of the formations present in the picture. This
Impact Age Dating. ASTRO 202 Lecture Thursday, February 14, Review. What is relative age dating? What is relative age dating?
 Review Impact Age Dating ASTRO 202 Lecture Thursday, February 14, 2008 Carbon-14, Potassium-Argon isotopic age determination: (1) Parent decays to daughter at some predictable rate (2) How much now? (3)
Review Impact Age Dating ASTRO 202 Lecture Thursday, February 14, 2008 Carbon-14, Potassium-Argon isotopic age determination: (1) Parent decays to daughter at some predictable rate (2) How much now? (3)
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST GRADE 8 SCIENCE. Student Name
 Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST GRADE 8 SCIENCE Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability in employment
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST GRADE 8 SCIENCE Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability in employment
Signature: Name: Banner ID#:
 1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
Name: Lab Instructor: Lab Section: GEO104: Planetary Geology LAB 10: MARS GEOLOGIC MAPPING
 Name: Lab Instructor: Lab Section: GEO104: Planetary Geology LAB 10: MARS GEOLOGIC MAPPING OBJECTIVES: I. Apply our understanding of relative age dating and geologic processes to the Moon II. Develop an
Name: Lab Instructor: Lab Section: GEO104: Planetary Geology LAB 10: MARS GEOLOGIC MAPPING OBJECTIVES: I. Apply our understanding of relative age dating and geologic processes to the Moon II. Develop an
Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky Ages on Mars. Martian Surface Age Exploration
 Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 Ages on Mars Martian Surface Age Exploration You have now learned some very important things about various planets and moons in our Solar
Ronald Wilhelm & Jennifer Wilhelm, University of Kentucky 2008 Ages on Mars Martian Surface Age Exploration You have now learned some very important things about various planets and moons in our Solar
Lunar Crater Activity - Teacher Pages
 Adapted from: http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/180572main_etm.impact.craters.pdf I took the activity and simplified it so that there was just one independent variable: the drop height, and one dependent variable:
Adapted from: http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/180572main_etm.impact.craters.pdf I took the activity and simplified it so that there was just one independent variable: the drop height, and one dependent variable:
Unit 3 Lesson 4 The Terrestrial Planets. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.5 Analyze the methods used to develop a scientific explanation as seen in different fields of science. SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets
Florida Benchmarks SC.8.N.1.5 Analyze the methods used to develop a scientific explanation as seen in different fields of science. SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets
Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with
 Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with complete sentences. How old is the Earth? The Earth is
Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with complete sentences. How old is the Earth? The Earth is
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST LARGE PRINT GRADE 8 SCIENCE. Student Name
 Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST LARGE PRINT GRADE 8 SCIENCE Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability
Ohio s State Tests PRACTICE TEST LARGE PRINT GRADE 8 SCIENCE Student Name The Ohio Department of Education does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, religion, age, or disability
Finding Impact Craters with Landsat
 Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
GOOD VIBRATIONS Remote Sensing Data Collection: Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES)
 TEACHER PAGE Background: Thermal emission spectroscopy is a technique currently being used by a Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft instrument called TES (Thermal Emission Spectrometer). The purpose of TES
TEACHER PAGE Background: Thermal emission spectroscopy is a technique currently being used by a Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft instrument called TES (Thermal Emission Spectrometer). The purpose of TES
Lesson 2 The Inner Planets
 Lesson 2 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 School to Home 32 Key Concept Builders 33 Enrichment
Lesson 2 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 School to Home 32 Key Concept Builders 33 Enrichment
State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks.
 Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. Seismic Waves.
 Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Seismic Waves Vibrations that travel through Earth s interior tell us what Earth is
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Seismic Waves Vibrations that travel through Earth s interior tell us what Earth is
The Moon. Tides. Tides. Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = MEarth. = 0.27 REarth. (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth
 The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2012
 Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2012 Geologic mapping Goals: To recognize the similarities and differences in the processes affecting the outer planet satellites, and in the resulting landforms. To demonstrate
Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2012 Geologic mapping Goals: To recognize the similarities and differences in the processes affecting the outer planet satellites, and in the resulting landforms. To demonstrate
Mars. Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost of the four terrestrial worlds in the Solar System. It lies outside Earth s orbit.
 Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost of the four terrestrial worlds in the Solar System. It lies outside Earth s orbit. Mars s orbital eccentricity is 0.093, much larger than that
Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost of the four terrestrial worlds in the Solar System. It lies outside Earth s orbit. Mars s orbital eccentricity is 0.093, much larger than that
Eleva&on vs. Wind Streaks
 Eleva&on vs. Wind Streaks Scien&fic Ques&on Are wind streaks more common in higher or lower eleva&ons on the Southern Hemisphere of Mars? Why This Is Important o Answering this ques&on may help give us
Eleva&on vs. Wind Streaks Scien&fic Ques&on Are wind streaks more common in higher or lower eleva&ons on the Southern Hemisphere of Mars? Why This Is Important o Answering this ques&on may help give us
11 Surface of the Moon
 Name: Date: 11 Surface of the Moon 11.1 Introduction One can learn a lot about the Moon by looking at the lunar surface. Even before astronauts landed on the Moon, scientists had enough data to formulate
Name: Date: 11 Surface of the Moon 11.1 Introduction One can learn a lot about the Moon by looking at the lunar surface. Even before astronauts landed on the Moon, scientists had enough data to formulate
Mars for Earthlings. Purpose: Recognize the purpose and need for understanding the scale and context of various remote sensing imaging techniques.
 LESSON 4: Remote Sensing Mars In-Class Activity 1 Scale and Context Purpose: Recognize the purpose and need for understanding the scale and context of various remote sensing imaging techniques. Study the
LESSON 4: Remote Sensing Mars In-Class Activity 1 Scale and Context Purpose: Recognize the purpose and need for understanding the scale and context of various remote sensing imaging techniques. Study the
Outflow Channels May Make a Case for a Bygone Ocean on Mars Written by Linda M.V. Martel Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology
 1 of 5 posted June 14, 2001 Outflow Channels May Make a Case for a Bygone Ocean on Mars Written by Linda M.V. Martel Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology High-resolution elevation data from
1 of 5 posted June 14, 2001 Outflow Channels May Make a Case for a Bygone Ocean on Mars Written by Linda M.V. Martel Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology High-resolution elevation data from
Writing Earth s History
 Earths History Writing Earth s History How is Earths History like writing in your Journal? Everyday, something happens and, with a pen, it is written down in the pages of your journal. As you continue,
Earths History Writing Earth s History How is Earths History like writing in your Journal? Everyday, something happens and, with a pen, it is written down in the pages of your journal. As you continue,
A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology
 Impact Cratering: Physics and Chronology A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology Impact features are common All solar system bodies with solid surfaces show evidence
Impact Cratering: Physics and Chronology A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology Impact features are common All solar system bodies with solid surfaces show evidence
Welcome to Class 12: Mars Geology & History. Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room
 Welcome to Class 12: Mars Geology & History Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What are we going to discuss today? How easily could humans live on Mars? Is there water on Mars? PRS: If
Welcome to Class 12: Mars Geology & History Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What are we going to discuss today? How easily could humans live on Mars? Is there water on Mars? PRS: If
EXERCISE 2 (16 POINTS): LUNAR EVOLUTION & APOLLO EXPLORATION
 1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
Unconformities, Geologic Time Scale, and Uniformitarianism. Ms. P Science 2016
 Unconformities, Geologic Time Scale, and Uniformitarianism Ms. P Science 2016 Do Now due tomorrow! 1. Compare and contrast relative dating to absolute dating. 2. The Law of Superposition states that younger
Unconformities, Geologic Time Scale, and Uniformitarianism Ms. P Science 2016 Do Now due tomorrow! 1. Compare and contrast relative dating to absolute dating. 2. The Law of Superposition states that younger
Opposition and Conjunction
 Opposition and Conjunction Summary 1. Mars is 52% further the Sun having an orbital period of nearly 2 Earth years 2. Mars is much smaller than the Earth being roughly 53% the size, 11% the mass of the
Opposition and Conjunction Summary 1. Mars is 52% further the Sun having an orbital period of nearly 2 Earth years 2. Mars is much smaller than the Earth being roughly 53% the size, 11% the mass of the
LESSON 2 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM. Chapter 8 Astronomy
 LESSON 2 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM Chapter 8 Astronomy OBJECTIVES Investigate how the interaction of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun causes lunar phases. Describe conditions that produce lunar and solar eclipses.
LESSON 2 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM Chapter 8 Astronomy OBJECTIVES Investigate how the interaction of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun causes lunar phases. Describe conditions that produce lunar and solar eclipses.
Age Dating and the Oceans
 Age Dating and the Oceans 1. Age dating of geologic materials reveals (a) the age of the Earth, and (b) how long oceans have been on Earth. 2. Relative dating of fossils from the seafloor allows us to
Age Dating and the Oceans 1. Age dating of geologic materials reveals (a) the age of the Earth, and (b) how long oceans have been on Earth. 2. Relative dating of fossils from the seafloor allows us to
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Earth History Teacher Rubrics and Directions
 Earth History Teacher Rubrics and Directions 1.a. Using the tools provided, observe the three rock samples, A, B, and C. One is sandstone, one is shale, and one is limestone. Make a chart to record your
Earth History Teacher Rubrics and Directions 1.a. Using the tools provided, observe the three rock samples, A, B, and C. One is sandstone, one is shale, and one is limestone. Make a chart to record your
Part 1: the terrestrial planets
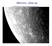 Mercury close up Part 1: the terrestrial planets The weird day on Mercury Weirdness is due to the fact that the rota:on period is comparable to period of revolu:on, and that they are related by the ra:o
Mercury close up Part 1: the terrestrial planets The weird day on Mercury Weirdness is due to the fact that the rota:on period is comparable to period of revolu:on, and that they are related by the ra:o
Directed Reading page
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading page 185-190 Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading page 185-190 Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the
Kind of plate boundary (convergent or divergent?)
 19B Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
19B Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
Exam# 2 Review. Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280
 Exam# 2 Review Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the
Exam# 2 Review Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the
Mars ( ) The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Spring Semester 2018 Prof Dr Ravit Helled
 The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Spring Semester 2018 Prof Dr Ravit Helled Mars ( ) Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost terrestrial planet. It has a density of 3.93 g/cm3, which
The Sun and Planets Lecture Notes 6. Spring Semester 2018 Prof Dr Ravit Helled Mars ( ) Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the outermost terrestrial planet. It has a density of 3.93 g/cm3, which
10/31/2010. Opposition and Conjunction. Opposition occurs every 2 years. Best opposition at perihelion. Percival Lowell
 Opposition and Conjunction Opposition occurs every 2 years Best opposition at perihelion Percival Lowell 1 Canals on Mars? Martians? Orson Welle s Broadcast (1938) The War of the Worlds H G Wells (1898)
Opposition and Conjunction Opposition occurs every 2 years Best opposition at perihelion Percival Lowell 1 Canals on Mars? Martians? Orson Welle s Broadcast (1938) The War of the Worlds H G Wells (1898)
Activity 7 At a Glance
 At a Glance Where Would You Search for Water on Mars? Purpose To help students develop an ongoing connection to the Mars missions Overview Students generate questions based on their module experiences
At a Glance Where Would You Search for Water on Mars? Purpose To help students develop an ongoing connection to the Mars missions Overview Students generate questions based on their module experiences
What Craters Can Tell Us about a Planet
 C16 What Craters Can Tell Us about a Planet Activity C16 Grade Level: 6 12 Source: This activity comes from the MarsQuest On Line web site. It was developed by TERC, with funding from the National Science
C16 What Craters Can Tell Us about a Planet Activity C16 Grade Level: 6 12 Source: This activity comes from the MarsQuest On Line web site. It was developed by TERC, with funding from the National Science
AT A GLANCE. Content Goals Sand grains contain clues about their origin and history. A sand sample reflects the geology of its watershed
 AT A GLANCE Overview This activity introduces students to one of the main geologic reasons why the mouth of Ares Vallis is such a desirable landing site. By examining sand samples from different locations,
AT A GLANCE Overview This activity introduces students to one of the main geologic reasons why the mouth of Ares Vallis is such a desirable landing site. By examining sand samples from different locations,
Jupiter & Saturn. Moons of the Planets. Jupiter s Galilean satellites are easily seen with Earth-based telescopes. The Moons
 The Moons Jupiter & Saturn Earth 1 Mars 2 Jupiter 63 Saturn 47 Uranus 27 Neptune 13 Pluto 3 Moons of the Planets Galileo (1610) found the first four moons of Jupiter. Total 156 (as of Nov. 8, 2005) Shortened
The Moons Jupiter & Saturn Earth 1 Mars 2 Jupiter 63 Saturn 47 Uranus 27 Neptune 13 Pluto 3 Moons of the Planets Galileo (1610) found the first four moons of Jupiter. Total 156 (as of Nov. 8, 2005) Shortened
Latitude and Longitude
 Seafloor Magnetism, Seafloor Spreading: Developing the Theory of Plate Tectonics Graphics: (top) Earth topography, (bottom) Garrison, Fig. 3.14. Earthquakes and the Dynamic Earth The Earth is not entirely
Seafloor Magnetism, Seafloor Spreading: Developing the Theory of Plate Tectonics Graphics: (top) Earth topography, (bottom) Garrison, Fig. 3.14. Earthquakes and the Dynamic Earth The Earth is not entirely
