arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Aug 2007
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dark Galaxies and Lost Baryons Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 244, 2007 J. Davies et al., eds. c 2007 International Astronomical Union DOI: /X X The Local Void is Really Empty R. Brent Tully Institure for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA tully@ifa.hawaii.edu Abstract. Are voids in the distribution of galaxies only places with reduced matter density and low star formation efficiency or are they empty of matter? There is now compelling evidence of expansion away from the Local Void at very high velocities. The motion is most reasonably interpreted as an evacuation of the void, which requires that the void be very large and very empty. arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Aug 2007 Keywords. Galaxies: distances and redshifts, intergalactic medium, large-scale structure of universe 1. Introduction The dipole pattern in the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) gives precise information about our motion with respect to the mean expansion of the universe. What is the cause of this motion? Several component influences are well known. The Sun orbits in our Milky Way Galaxy at 220 km/s. The Milky Way is falling toward Andromeda Galaxy at 135 km/s. The neighborhood of our Galaxy is retarded from the cosmic expansion by the Virgo Cluster by 185 km/s, and by large-scale structure in the direction of the Centaurus constellation by 455 km/s. But there must be something else. The pattern of motions of nearby galaxies reveals the extra component. We are moving together with all our neighbors within 7 Mpc, the Local Sheet, but there is a discontinuity in the pattern of velocities as one passes beyond 7 Mpc. It will be argued that our Local Sheet is repelling from the Local Void at 260 km/s! In a ΛCDM universe with the energy density parameter Ω Λ = 0.7, a spherical void in an otherwise homogeneous universe evacuates with expansion velocities of 16 km/s/mpc. The Local Void is inferred to be at least 45 Mpc across and really empty. The following pages will contain a brief outline of the evidence for these claims. A more complete discussion has been submitted to the Astrophysical Journal by Tully, Shaya, Karachentsev, Courtois, Kocevski, Rizzi, and Peel (Tully et al. 2007). 2. Observations An accurate distance, d, for a galaxy allows us to separate the radial component of deviant motions, V pec, from the cosmic expansion: V pec = V obs H 0 d, where a galaxy has an observed motion V obs and H 0 is the Hubble Constant (taken to be 74 km/s/mpc). The present analysis is based on 1797 measured distances for galaxies in 743 groups within 3000 km/s. In 601 cases, the distance estimates are based on Cepheid Period-Luminosity (CPL: Freedman et al. 2001), Tip of the Red Giant Branch (TRGB: Sakai et al. 1996), or Surface Brightness Fluctuation (SBF: Tonry et al. 2001) methods. The rest are provided by the correlation between the luminosity of a galaxy and its line width (Tully & Fisher 1977; Tully & Pierce 2000; Karachentsev et al. 2002). The large number of accurate TRGB distances to nearby galaxies demonstrates clearly 1
2 2 Tully Figure 1. Peculiar velocities in the vicinity of the Local Sheet. Peculiar velocities < 100 km/s are coded solid purple (black), peculiar velocities > +100 km/s are coded solid orange (grey), and peculiar velocities within 100 km/s of zero are coded green (grey) with open symbols. Our Galaxy lies at SGY=SGZ=0 and the dense clump of galaxies at the right is the Virgo Cluster. that the Local Sheet of galaxies within 7 Mpc has very low internal motions in co-moving coordinates (Karachentsev et al. 2003). It is shown in Figure 1 that our Milky Way Galaxy has an insignificant random motion with respect to 159 galaxies outside the Local Group but within 7 Mpc. We are travelling with the Local Sheet as a unit. However it is seen in Figure 1 and the pan to Figure 2 that there is a discontinuity in velocities between the Local Sheet and the next nearest structures. The nature of this discontinuity provides a clue to the origin of our relative motion. The vector of the motion of the Local Sheet with respect to the other galaxies with distance measures within 3000 km/s but beyond 7 Mpc has an amplitude of 323 km/s, toward SGL=80, SGB= 52. Part of this motion is suspected to be due to the influence of the Virgo Cluster, 17 Mpc away (Mohayaee & Tully 2005). The component of the Local Sheet vector toward the Virgo Cluster in the direction SGL=102.7, SGB= 2.3 is 185 km/s, consistent with expectations. The residual is a vector of 259 km/s toward SGL=11. SGB= 72. This vector is not directed toward anything of interest, but it is directed away from the Local Void. Following on with this decomposition of the vectors of our motion, we take note that in the Local Sheet rest frame the CMB dipole vector is 631 km/s toward SGL=139, SGB= 37. If the motion of the Local Sheet with respect to galaxies within 3000 km/s is subtracted from the CMB vector, the residual is 455 km/s toward SGL=162, SGB= 16. This motion must be attributed to influences on scales larger than 3000 km/s. The vectors described above are graphically illustrated in Figures 3 and 4.
3 The Local Void is Really Empty 3 Figure 2. Pan to view peculiar velocities within the Local Supercluster. Symbol code is the same as in previous figure. 3. The Local Void The Local Void was first identified in the Nearby Galaxies Atlas (Tully & Fisher 1987). It is poorly defined because so much of it lies behind the plane of the Milky Way, but recent surveys such as the HI Parkes All Sky Survey (HIPASS: Meyer et al. 2004) confirm its general properties. There is an underabundance, though not a total lack, of galaxies in a very large part of the sky at low redshifts. The empty region begins at the edge of the Local Group, with the Local Sheet a bounding surface. Figure 5 represents an attempt to illustrate the Local Void. In detail, there are wispy filaments of galaxies that lace through the underdense region, causing us to disect it into a nearby part and more distant north and south parts. Analytic calculations of the expansion of an underdense spherical region in an otherwise uniform distribution of matter are discussed in the refereed article. It is found that an entirely empty region is evacuated at 16 km/s/mpc. N-body models provide confirmation (Schaap 2007). To generate the observed motion of 260 km/s away from the Local Void, we infer that the void at our doorstep must have a diameter of at least 45 Mpc and be very empty. It may seem incredible that the CMB dipole motion of the Local Group can be de-
4 4 Tully Figure 3. Vectors of the motion of the Local Sheet superposed on the data of Figure 1. The motion of the Local Sheet with respect to galaxies with measured distances within 3000 km/s is indicated by the orange (grey) bar pointing toward the lower right. A component of this motion is directed toward the Virgo Cluster, indicated by the blue (black) horizontal bar. The residual if the component toward Virgo is subtracted from the observed motion is the red (black) bar directed downward. composed into just three primary contributions: one away from the Local Void, a second toward the Virgo Cluster, and a third toward large-scale structure in the direction of Centaurus. Of course, this is a simplification. The reason the three contributions are distinct is because they arise on distinct scales and are almost orthogonal in direction. Our attention here is on the nearest component, the motion away from the Local Void. There is ongoing discussion about whether places where nothing is seen are truly empty. The Local Void generates a push of 260 km/s. Perhaps we are seeing here the best evidence available that voids in the distribution of galaxies are really empty. Acknowledgements My collaborators in this research are Ed Shaya, Igor Karachentsev, Hélène Courtois, Dale Kocevski, Luca Rizzi, and Alan Peel. Support has been provided by grants from Space Telescope Science Institute and the US National Science Foundation. The motion of our Galaxy with respect to the structure in the distribution of galaxies is illustrated in videos at tully/ References Freedman, W.L., et al. 2001, ApJ, 553, 47 Karachentsev, I.D. et al. 2003, A&A, 398, 479
5 The Local Void is Really Empty 5 Figure 4. Decomposition of the CMB vector, shown in cyan (grey) and directed from the origin toward the lower left, into the component with respect to galaxies with velocities < 3000 km/s, shown in orange (grey) and directed downward from the origin, and the residual component associated with structure on scales larger than 3000 km/s, shown in brown (black) and directed almost horizontal toward the left from the origin. Symbols for individual galaxies with distance measures follow the scheme used in previous figures. The Centaurus Cluster is at SGX= 2800 km/s, SGZ= 500 km/s. Karachentsev, I.D., Mitronova, S.N., Karachentseva, V.E., Kudrya, Y.N., Jarrett, T.H. 2002, A&A, 396, 431 Meyer, M.J. et al. 2004, MNRAS, 350, 1195 Mohayaee, R., Tully, R.B. 2005, ApJ, 635, L113 Sakai, S., Madore, B.F, Freedman, W.L. 1996, ApJ, 461, 713 Schaap, W. 2007, PhD Thesis, Groningen U. Tonry, J.L. et al. 2001, ApJ, 546, 681 Tully, R.B., Fisher, J.R. 1977, A&A, 54, 661 Tully, R.B., Fisher, J.R. 1987, Nearby Galaxies Atlas, Cambridge University Press, 1987 Tully, R.B., Pierce, M.J. 2000, ApJ, 533, 744 Tully, R.B., Shaya, E.J., Karachentsev, I.D., Courtois, H., Kocevski, D.D., Rizzi, L., Peel, A. 2007, ApJ, submitted (astro-ph/ )
6 6 Tully Figure 5. The region of the Local Void. The ellipses outline three apparent sectors of the Local Void. The solid dark blue ellipse shows the projection of the nearest part of the Local Void, bounded at our location by the Local Sheet. North and South extensions of the Local Void are identified by the light blue short dashed ellipse and the green long dashed ellipse, respectively. These sectors are separated by bridges of wispy filaments. The red vector indicates the direction and amplitude of our motion away from the void.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 17 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 17 Aug 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 17 Aug 2007](/thumbs/92/110401404.jpg) The Local Velocity Anomaly R. Brent Tully arxiv:0708.2449v1 [astro-ph] 17 Aug 2007 Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, USA 1 Historical Notes 1.1 What is the Local Velocity Anomaly?
The Local Velocity Anomaly R. Brent Tully arxiv:0708.2449v1 [astro-ph] 17 Aug 2007 Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, USA 1 Historical Notes 1.1 What is the Local Velocity Anomaly?
Cosmicflows-2. Laniakea Supercluster
 Cosmicflows-2 Laniakea Supercluster Cosmic Flows Program Measure distances d Peculiar velocities: V pec = V obs - H 0 d Infer 3D velocities and density field Project to initial conditions Simulate evolution
Cosmicflows-2 Laniakea Supercluster Cosmic Flows Program Measure distances d Peculiar velocities: V pec = V obs - H 0 d Infer 3D velocities and density field Project to initial conditions Simulate evolution
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 14 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 14 Dec 2007 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 14 Dec 2007](/thumbs/74/69991882.jpg) Our Peculiar Motion Away from the Local Void R. Brent Tully, Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, 2680 Woodlawn Drive, Honolulu, HI 96822 and arxiv:0705.4139v2 [astro-ph] 14 Dec 2007 Edward J.
Our Peculiar Motion Away from the Local Void R. Brent Tully, Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, 2680 Woodlawn Drive, Honolulu, HI 96822 and arxiv:0705.4139v2 [astro-ph] 14 Dec 2007 Edward J.
Hubble s Law. Tully-Fisher relation. The redshift. λ λ0. Are there other ways to estimate distances? Yes.
 Distances to galaxies Cepheids used by Hubble, 1924 to show that spiral nebulae like M31 were further from the Sun than any part of the Milky Way, therefore galaxies in their own right. Review of Cepheids
Distances to galaxies Cepheids used by Hubble, 1924 to show that spiral nebulae like M31 were further from the Sun than any part of the Milky Way, therefore galaxies in their own right. Review of Cepheids
Learning Objectives. distances to objects in our Galaxy and to other galaxies? apparent magnitude key to measuring distances?
 The Distance Ladder Learning Objectives! What is the distance ladder? How do we measure distances to objects in our Galaxy and to other galaxies?! How are the concepts of absolute magnitude and apparent
The Distance Ladder Learning Objectives! What is the distance ladder? How do we measure distances to objects in our Galaxy and to other galaxies?! How are the concepts of absolute magnitude and apparent
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Symbolically: E0.E7.. S0..Sa..Sb..Sc..Sd..Irr
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Cepheid Distance Measurement. Clusters of Galaxies. The Nature of Galaxies
 Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology
 Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
Galaxies & Introduction to Cosmology Other Galaxies: How many are there? Hubble Deep Field Project 100 hour exposures over 10 days Covered an area of the sky about 1/100 the size of the full moon Probably
The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background The Cosmic Microwave Background Key Concepts 1) The universe is filled with a Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). 2) The microwave radiation that fills the universe is nearly
The Cosmic Microwave Background The Cosmic Microwave Background Key Concepts 1) The universe is filled with a Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). 2) The microwave radiation that fills the universe is nearly
The Cosmic Flows project : voyage to the Great Attractor and beyond second episode
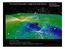 The Cosmic Flows project : voyage to the Great Attractor and beyond second episode Hélėne Courtois Ass. Prof University of Lyon, France Affiliate Researcher, Institute for Astronomy, Hawaii, USA Dwingeloo,
The Cosmic Flows project : voyage to the Great Attractor and beyond second episode Hélėne Courtois Ass. Prof University of Lyon, France Affiliate Researcher, Institute for Astronomy, Hawaii, USA Dwingeloo,
Large-Scale Structure
 Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale
 Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Set 5: Expansion of the Universe
 Set 5: Expansion of the Universe Cosmology Study of the origin, contents and evolution of the universe as a whole Expansion rate and history Space-time geometry Energy density composition Origin of structure
Set 5: Expansion of the Universe Cosmology Study of the origin, contents and evolution of the universe as a whole Expansion rate and history Space-time geometry Energy density composition Origin of structure
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Lecture 32: The Expanding Universe Readings: Sections 26-5 and 28-2
 Lecture 32: The Expanding Universe Readings: Sections 26-5 and 28-2 Key Ideas Measuring the Distances to Galaxies and Determining the Scale of the Universe Distance Methods: Trigonometric Parallaxes Spectroscopic
Lecture 32: The Expanding Universe Readings: Sections 26-5 and 28-2 Key Ideas Measuring the Distances to Galaxies and Determining the Scale of the Universe Distance Methods: Trigonometric Parallaxes Spectroscopic
Calibration of the Mid-Infrared Tully-Fisher relation
 Calibration of the Mid-Infrared Tully-Fisher relation The Tully-Fisher at 35 Workshop April 1 st 2012 Jenny Sorce University of Lyon / IPNL - University of Hawaii / IFA Jenny Sorce (IPNL) L band TFR 2012
Calibration of the Mid-Infrared Tully-Fisher relation The Tully-Fisher at 35 Workshop April 1 st 2012 Jenny Sorce University of Lyon / IPNL - University of Hawaii / IFA Jenny Sorce (IPNL) L band TFR 2012
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Sample variance in the local measurements of H 0. Heidi Wu (Caltech OSU) with Dragan Huterer (U. Michigan) arxiv: , MNRAS accepted
 Sample variance in the al measurements of H 0 Heidi Wu (Caltech OSU) with Dragan Huterer (U. Michigan) arxiv:1706.09723, MNRAS accepted 1 Tension in H 0 measurements Beaton (2016); Freedman (2017) 2 H
Sample variance in the al measurements of H 0 Heidi Wu (Caltech OSU) with Dragan Huterer (U. Michigan) arxiv:1706.09723, MNRAS accepted 1 Tension in H 0 measurements Beaton (2016); Freedman (2017) 2 H
Chapter 25 (and end of 24): Lecture Notes
 Chapter 25 (and end of 24): Lecture Notes In order to understand the Hubble Law and its implications both for estimating distances and for interpreting the evolution of the universe, you have to be comfortable
Chapter 25 (and end of 24): Lecture Notes In order to understand the Hubble Law and its implications both for estimating distances and for interpreting the evolution of the universe, you have to be comfortable
XII. The distance scale. h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html
 XII. The distance scale h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. How far away are galaxies? We discussed galaxies without thinking about how we know the distances to these galaxies. Only in the past
XII. The distance scale h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. How far away are galaxies? We discussed galaxies without thinking about how we know the distances to these galaxies. Only in the past
ASTRONOMY 2 Overview of the Universe Second Practice Problem Set Solutions
 ASTRONOMY 2 Overview of the Universe Second Practice Problem Set Solutions 1. Consider a 2 M neutron star. The mass of a neutron is 1.67 10 24 g, and 1 M = 2 10 33 g. (i) How many neutrons are in this
ASTRONOMY 2 Overview of the Universe Second Practice Problem Set Solutions 1. Consider a 2 M neutron star. The mass of a neutron is 1.67 10 24 g, and 1 M = 2 10 33 g. (i) How many neutrons are in this
Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies
 Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies You will access your textbook for this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: As we began to talk about stars beyond the Sun, one of the most important pieces of information
Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies You will access your textbook for this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: As we began to talk about stars beyond the Sun, one of the most important pieces of information
Cosmology. Clusters of galaxies. Redshift. Late 1920 s: Hubble plots distances versus velocities of galaxies. λ λ. redshift =
 Cosmology Study of the structure and origin of the universe Observational science The large-scale distribution of galaxies Looking out to extremely large distances The motions of galaxies Clusters of galaxies
Cosmology Study of the structure and origin of the universe Observational science The large-scale distribution of galaxies Looking out to extremely large distances The motions of galaxies Clusters of galaxies
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Oct 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Oct 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Oct 2010](/thumbs/93/113955093.jpg) Lighthouses in the Shoals of Dark Halos. Conference Honoring Ken Freeman s 70th Birthday: Galaxies and their Masks, Sossusvlei, Namibia 12-16 April, 2010 arxiv:1010.3787v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Oct 2010 R.
Lighthouses in the Shoals of Dark Halos. Conference Honoring Ken Freeman s 70th Birthday: Galaxies and their Masks, Sossusvlei, Namibia 12-16 April, 2010 arxiv:1010.3787v1 [astro-ph.co] 19 Oct 2010 R.
THE ARROWHEAD MINI-SUPERCLUSTER OF GALAXIES
 2015. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/812/1/17 THE ARROWHEAD MINI-SUPERCLUSTER OF GALAXIES Daniel Pomarède 1, R. Brent Tully 2, Yehuda Hoffman 3, and Hélène
2015. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/812/1/17 THE ARROWHEAD MINI-SUPERCLUSTER OF GALAXIES Daniel Pomarède 1, R. Brent Tully 2, Yehuda Hoffman 3, and Hélène
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Astronomy 330 Lecture Dec 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
The Milky Way. Finding the Center. Milky Way Composite Photo. Finding the Center. Milky Way : A band of and a. Milky Way
 The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
Set 1: Expansion of the Universe
 Set 1: Expansion of the Universe Syllabus Course text book: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd edition Olber s paradox, expansion of the universe: Ch 2 Cosmic geometry, expansion rate, acceleration:
Set 1: Expansion of the Universe Syllabus Course text book: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd edition Olber s paradox, expansion of the universe: Ch 2 Cosmic geometry, expansion rate, acceleration:
Campus Observatory. 7pm. you are here
 Announcements Homework #9 is due today Course Evaluations available on line now Post-test Survey for At Play in the Cosmos now ready For extra credit: - must complete all 8 missions by Dec 10 - must complete
Announcements Homework #9 is due today Course Evaluations available on line now Post-test Survey for At Play in the Cosmos now ready For extra credit: - must complete all 8 missions by Dec 10 - must complete
Addition to the Lecture on Galactic Evolution
 Addition to the Lecture on Galactic Evolution Rapid Encounters In case the encounter of two galaxies is quite fast, there will be not much dynamical friction due to lack of the density enhancement The
Addition to the Lecture on Galactic Evolution Rapid Encounters In case the encounter of two galaxies is quite fast, there will be not much dynamical friction due to lack of the density enhancement The
Astro Assignment 1 on course web page (due 15 Feb) Instructors: Jim Cordes & Shami Chatterjee
 Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 4 This time: Redshifts and the Hubble Law Hubble law and the expanding universe The cosmic microwave background (CMB) The elements and the periodic
Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 4 This time: Redshifts and the Hubble Law Hubble law and the expanding universe The cosmic microwave background (CMB) The elements and the periodic
Cosmic Distance Determinations
 Cosmic Distance Determinations Radar (works for inner solar system) Parallax D(pc) = 1 p(arcsec) GAIA satellite (2013) 20 micro-arcsec resolution! Thus D < 10 kpc Beyond Parallax: Standard Candles Use
Cosmic Distance Determinations Radar (works for inner solar system) Parallax D(pc) = 1 p(arcsec) GAIA satellite (2013) 20 micro-arcsec resolution! Thus D < 10 kpc Beyond Parallax: Standard Candles Use
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
Chapter 20 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology 20.1 Islands of Stars Our goals for learning: How do galaxies evolve? What are the three major
Chapter 20 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology 20.1 Islands of Stars Our goals for learning: How do galaxies evolve? What are the three major
The Cosmological Redshift. Cepheid Variables. Hubble s Diagram
 SOME NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF THE EXPANSION OF THE UNIVERSE. Lecture 22 Hubble s Law and the Large Scale Structure of the Universe PRS: According to modern ideas and observations, what can be said about the
SOME NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF THE EXPANSION OF THE UNIVERSE. Lecture 22 Hubble s Law and the Large Scale Structure of the Universe PRS: According to modern ideas and observations, what can be said about the
Astronomy 422. Lecture 15: Expansion and Large Scale Structure of the Universe
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 15: Expansion and Large Scale Structure of the Universe Key concepts: Hubble Flow Clusters and Large scale structure Gravitational Lensing Sunyaev-Zeldovich Effect Expansion and age
Astronomy 422 Lecture 15: Expansion and Large Scale Structure of the Universe Key concepts: Hubble Flow Clusters and Large scale structure Gravitational Lensing Sunyaev-Zeldovich Effect Expansion and age
A 103 Notes, Week 14, Kaufmann-Comins Chapter 15
 NEARBY GALAXIES I. Brief History A 103 Notes, Week 14, Kaufmann-Comins Chapter 15 A. Kant B. Curtis-Shapley debate C. Distance to Andromeda II. Classification of nearby galaxies: Spirals, Ellipticals,
NEARBY GALAXIES I. Brief History A 103 Notes, Week 14, Kaufmann-Comins Chapter 15 A. Kant B. Curtis-Shapley debate C. Distance to Andromeda II. Classification of nearby galaxies: Spirals, Ellipticals,
Structure. Subodh Patil NBIA Nov Formation in the Universe From the Big Bang to the Big Rip?
 Structure Subodh Patil NBIA Nov 19 2018 Formation in the Universe From the Big Bang to the Big Rip? Physicists like to think in terms of characteristic scales the `typical size of something or some process.
Structure Subodh Patil NBIA Nov 19 2018 Formation in the Universe From the Big Bang to the Big Rip? Physicists like to think in terms of characteristic scales the `typical size of something or some process.
Galaxies Guiding Questions
 Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Allan Sandage and the Cosmic Expansion
 Allan Sandage and the Cosmic Expansion The Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Conference, Naples May 2 6, 2011 G. A. Tammann Allan Sandage a mentor, a collaborator, a friend for 47 years G. A. Tammann A.
Allan Sandage and the Cosmic Expansion The Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Conference, Naples May 2 6, 2011 G. A. Tammann Allan Sandage a mentor, a collaborator, a friend for 47 years G. A. Tammann A.
PHY 475/375. Lecture 2. (March 28, 2012) The Scale of the Universe: The Shapley-Curtis Debate
 PHY 475/375 Lecture 2 (March 28, 2012) The Scale of the Universe: The Shapley-Curtis Debate By the 1920 s a debate had developed over whether some of the spiral nebulae catalogued in the 18th century by
PHY 475/375 Lecture 2 (March 28, 2012) The Scale of the Universe: The Shapley-Curtis Debate By the 1920 s a debate had developed over whether some of the spiral nebulae catalogued in the 18th century by
Chapter 20 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology 20.1 Islands of Stars Our goals for learning: How
Chapter 20 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology Galaxies and the Foundation of Modern Cosmology 20.1 Islands of Stars Our goals for learning: How
Class 5 Cosmology Large-Scale Structure of the Universe What do we see? Big Bang Cosmology What model explains what we see?
 Class 1 Introduction, Background History of Modern Astronomy The Night Sky, Eclipses and the Seasons Kepler's Laws Newtonian Gravity General Relativity Matter and Light Telescopes Class 2 Solar System
Class 1 Introduction, Background History of Modern Astronomy The Night Sky, Eclipses and the Seasons Kepler's Laws Newtonian Gravity General Relativity Matter and Light Telescopes Class 2 Solar System
Arguments for a Hubble Constant near H 0 =55
 Arguments for a Hubble Constant near H 0 =55 H. Arp Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Garching 85741, Germany ABSTRACT Recent analyses of Cepheid distances to spiral galaxies have led to an announcement
Arguments for a Hubble Constant near H 0 =55 H. Arp Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Garching 85741, Germany ABSTRACT Recent analyses of Cepheid distances to spiral galaxies have led to an announcement
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 3 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 3 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 3 May 2017](/thumbs/93/111167622.jpg) 1 NEARBY GROUPS OF GALAXIES IN THE HERCULES BOOTES CONSTELLATIONS I.D.Karachentsev 1, (*), O.G.Kashibadze 1, V.E.Karachentseva 2 1 Special Astrophysical Observatory of Russian AS, Nizhnij Arkhyz 369167,
1 NEARBY GROUPS OF GALAXIES IN THE HERCULES BOOTES CONSTELLATIONS I.D.Karachentsev 1, (*), O.G.Kashibadze 1, V.E.Karachentseva 2 1 Special Astrophysical Observatory of Russian AS, Nizhnij Arkhyz 369167,
1. This question is about Hubble s law. The light received from many distant galaxies is red-shifted. (a) State the cause of this red-shift (1)
 ROUND 2 - QUESTIONS 1. This question is about Hubble s law. The light received from many distant galaxies is red-shifted. (a) State the cause of this red-shift (1) expanding universe (b) State Hubble s
ROUND 2 - QUESTIONS 1. This question is about Hubble s law. The light received from many distant galaxies is red-shifted. (a) State the cause of this red-shift (1) expanding universe (b) State Hubble s
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Sample Review Test for Examination 3
 October 28, 2003 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Sample Review Test for Examination 3 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. No
October 28, 2003 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Sample Review Test for Examination 3 Do not open the test until instructed to begin. Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided. No
Galaxies. Ed Shaya (U. of. Maryland) &
 The Formation of the Local Group of Galaxies Wherein Numerical Action Method and Backward Integration are used to Model the Trajectories of LG Galaxies Ed Shaya (U. of Maryland) & R. B. Tully (U. of Hawaii)
The Formation of the Local Group of Galaxies Wherein Numerical Action Method and Backward Integration are used to Model the Trajectories of LG Galaxies Ed Shaya (U. of Maryland) & R. B. Tully (U. of Hawaii)
Cosmology in the Very Local Universe - Why Flow Models Matter
 Cosmology in the Very Local Universe - Why Flow Models Matter Karen L. Masters Department of Astronomy, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 14853, USA While much of the focus of observational cosmology is
Cosmology in the Very Local Universe - Why Flow Models Matter Karen L. Masters Department of Astronomy, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 14853, USA While much of the focus of observational cosmology is
LARGE QUASAR GROUPS. Kevin Rahill Astrophysics
 LARGE QUASAR GROUPS Kevin Rahill Astrophysics QUASARS Quasi-stellar Radio Sources Subset of Active Galactic Nuclei AGNs are compact and extremely luminous regions at the center of galaxies Identified as
LARGE QUASAR GROUPS Kevin Rahill Astrophysics QUASARS Quasi-stellar Radio Sources Subset of Active Galactic Nuclei AGNs are compact and extremely luminous regions at the center of galaxies Identified as
Outline. Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks
 Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
Island Universes. Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe.
 Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
The Extragalactic Distance Scale
 One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Supernovae and cosmology
 Supernovae and cosmology Gavin Lawes Wayne State University David Cinabro Wayne State University Johanna-Laina Fischer Outline Structure of the universe Dynamics of the universe Type 1a supernova Michigan
Supernovae and cosmology Gavin Lawes Wayne State University David Cinabro Wayne State University Johanna-Laina Fischer Outline Structure of the universe Dynamics of the universe Type 1a supernova Michigan
Galaxies and Cosmology
 Galaxies and Cosmology Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) Cosmetology? Like hair and nails and makeup? Next Tuesday, 5/30: Dr. Jorge Moreno is unavailable, so class will be cancelled
Galaxies and Cosmology Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) Cosmetology? Like hair and nails and makeup? Next Tuesday, 5/30: Dr. Jorge Moreno is unavailable, so class will be cancelled
The Extragalactic Distance Scale
 One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments
 The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
The oldest science? One of the most rapidly evolving fields of modern research. Driven by observations and instruments Intersection of physics (fundamental laws) and astronomy (contents of the universe)
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence
 CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
CH 14 MODERN COSMOLOGY The Study of Nature, origin and evolution of the universe Does the Universe have a center and an edge? What is the evidence that the Universe began with a Big Bang? How has the Universe
arxiv: v2 [physics.hist-ph] 9 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v2 [physics.hist-ph] 9 Oct 2014 arxiv: v2 [physics.hist-ph] 9 Oct 2014](/thumbs/76/73256269.jpg) arxiv:1312.0472v2 [physics.hist-ph] 9 Oct 2014 Solar-motion correction in early extragalactic astrophysics Domingos Soares and Luiz Paulo R. Vaz Departamento de Física, ICEx, UFMG C.P. 702 30123-970, Belo
arxiv:1312.0472v2 [physics.hist-ph] 9 Oct 2014 Solar-motion correction in early extragalactic astrophysics Domingos Soares and Luiz Paulo R. Vaz Departamento de Física, ICEx, UFMG C.P. 702 30123-970, Belo
Today: Start Ch. 18: Cosmology. Homework # 5 due next Wed. (HW #6 is online)
 Today: Start Ch. 18: Cosmology Homework # 5 due next Wed. (HW #6 is online) Dark Matter! A rotation curve is a graph of how fast a something is rotating, as a function of distance from the center.! We
Today: Start Ch. 18: Cosmology Homework # 5 due next Wed. (HW #6 is online) Dark Matter! A rotation curve is a graph of how fast a something is rotating, as a function of distance from the center.! We
Astronomy 114. Lecture35:TheBigBang. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture35:TheBigBang Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 35 09 May 2005 Read: Ch. 28,29 Astronomy 114 1/18 Announcements PS#8 due Monday!
Astronomy 114 Lecture35:TheBigBang Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 35 09 May 2005 Read: Ch. 28,29 Astronomy 114 1/18 Announcements PS#8 due Monday!
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the Universe
 Outline Homework due on Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Style Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the
Outline Homework due on Friday 11:50 am Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. THE FINAL IS DECEMBER 15 th : 7-10pm! Style Galaxies are the Fundamental Ecosystems of the
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3
 October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
The King's University College Astronomy 201 Mid-Term Exam Solutions
 The King's University College Astronomy 201 Mid-Term Exam Solutions Instructions: The exam consists of two sections. Part A is 20 multiple choice questions - please record answers on the sheet provided.
The King's University College Astronomy 201 Mid-Term Exam Solutions Instructions: The exam consists of two sections. Part A is 20 multiple choice questions - please record answers on the sheet provided.
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 25: Beyond our Solar System The Universe pp
 Chapter 25: Beyond our Solar System 25.3 The Universe pp 715-721 The Milky Way Galaxy On a clear and moonless night, away from city lights, you might see a a band of light in the sky. This band is The
Chapter 25: Beyond our Solar System 25.3 The Universe pp 715-721 The Milky Way Galaxy On a clear and moonless night, away from city lights, you might see a a band of light in the sky. This band is The
Cosmology at a Crossroads: Tension With the Hubble Constant
 Cosmology at a Crossroads: Tension With the Hubble Constant Wendy L. Freedman We are at an interesting juncture in cosmology. With new methods and technology, the accuracy in measurement of the Hubble
Cosmology at a Crossroads: Tension With the Hubble Constant Wendy L. Freedman We are at an interesting juncture in cosmology. With new methods and technology, the accuracy in measurement of the Hubble
The dipole repeller SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Yehuda Hoffman, Daniel Pomarède, R. Brent Tully and Hélène M. Courtois
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0036 The dipole repeller Yehuda Hoffman, Daniel Pomarède, R. Brent Tully and Hélène M. Courtois NATURE
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0036 The dipole repeller Yehuda Hoffman, Daniel Pomarède, R. Brent Tully and Hélène M. Courtois NATURE
Clustering of Galaxies in an Expanding Universe IAS School January 26, 2012 Nanyang Technological University Singapore
 Clustering of Galaxies in an Expanding Universe IAS School January 26, 2012 Nanyang Technological University Singapore Naseer Iqbal University of Kashmir Srinagar, India IUCAA, Pune India Astronomy and
Clustering of Galaxies in an Expanding Universe IAS School January 26, 2012 Nanyang Technological University Singapore Naseer Iqbal University of Kashmir Srinagar, India IUCAA, Pune India Astronomy and
Review of Lecture 15 3/17/10. Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath
 Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
Cosmology with Peculiar Velocity Surveys
 Cosmology with Peculiar Velocity Surveys Simulations Fest, Sydney 2011 Morag I Scrimgeour Supervisors: Lister Staveley-Smith, Tamara Davis, Peter Quinn Collaborators: Chris Blake, Brian Schmidt What are
Cosmology with Peculiar Velocity Surveys Simulations Fest, Sydney 2011 Morag I Scrimgeour Supervisors: Lister Staveley-Smith, Tamara Davis, Peter Quinn Collaborators: Chris Blake, Brian Schmidt What are
Obtain one of the laminated sheets, and classify the numbered objects by color (hopefully obvious) and by shape:
 Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 8: Galaxies and the Hubble Law The large-scale structure of the universe is governed by gravity. The Sun orbits the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The Milky Way, in
Astronomy 100 Name(s): Exercise 8: Galaxies and the Hubble Law The large-scale structure of the universe is governed by gravity. The Sun orbits the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The Milky Way, in
24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification
 Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble s Law 24.4 XXActive Galactic Nuclei XXRelativistic Redshifts and Look-Back
Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble s Law 24.4 XXActive Galactic Nuclei XXRelativistic Redshifts and Look-Back
Modeling the Universe Chapter 11 Hawley/Holcomb. Adapted from Dr. Dennis Papadopoulos UMCP
 Modeling the Universe Chapter 11 Hawley/Holcomb Adapted from Dr. Dennis Papadopoulos UMCP Spectral Lines - Doppler λ λ em 1+ z = obs z = λ obs λ λ em em Doppler Examples Doppler Examples Expansion Redshifts
Modeling the Universe Chapter 11 Hawley/Holcomb Adapted from Dr. Dennis Papadopoulos UMCP Spectral Lines - Doppler λ λ em 1+ z = obs z = λ obs λ λ em em Doppler Examples Doppler Examples Expansion Redshifts
The Milky Way. Mass of the Galaxy, Part 2. Mass of the Galaxy, Part 1. Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya
 Foundations Chapter of Astronomy 15 13e Our Milky Way Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Selected Topics in Chapter 15 A view our Milky Way? The Size of our Milky Way The Mass of
Foundations Chapter of Astronomy 15 13e Our Milky Way Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Selected Topics in Chapter 15 A view our Milky Way? The Size of our Milky Way The Mass of
Frontiers: Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect
 Frontiers: Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect An effect predicted more than four decades ago, the S-Z effect has come into its own as a probe of cosmological conditions, due to instrumental advances and a certain
Frontiers: Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect An effect predicted more than four decades ago, the S-Z effect has come into its own as a probe of cosmological conditions, due to instrumental advances and a certain
11/9/2010. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Sky & Telescope s Week at a Glance. iphone App available now.
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #11 Wednesday Mix of questions from today s lecture & reading for Wed. on active galaxies HW#10 in ICON due Friday (11/12) by 5 pm - available
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #11 Wednesday Mix of questions from today s lecture & reading for Wed. on active galaxies HW#10 in ICON due Friday (11/12) by 5 pm - available
Cosmic Microwave Background
 Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Cosmic Microwave Background Following recombination, photons that were coupled to the matter have had very little subsequent interaction with matter. Now observed as the cosmic microwave background. Arguably
Lecture 11. The standard Model
 Lecture 11 The standard Model Standard Model The standard model assumes that the universe is filled with matter and other forms of energy (photons) but that matter is dominant today. The standard model
Lecture 11 The standard Model Standard Model The standard model assumes that the universe is filled with matter and other forms of energy (photons) but that matter is dominant today. The standard model
Measuring Distances to Galaxies. Galaxies in Motion. Hubble s Law. Galaxy Redshifts. Type Ia Supernovae. Supernovae are Good Standard Candles
 Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances
 Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances Final Results from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant Freedman, Madore, Gibson, et al., Astrophysical Journal
Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances Final Results from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant Freedman, Madore, Gibson, et al., Astrophysical Journal
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!NNOUNCEMENTS HOMEWORK #6 DUE TODAY, by 5pm HOMEWORK #7 DUE Nov. 10, by 5pm Dark matter halo for galaxies Dark matter extends beyond visible part of the galaxy
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!NNOUNCEMENTS HOMEWORK #6 DUE TODAY, by 5pm HOMEWORK #7 DUE Nov. 10, by 5pm Dark matter halo for galaxies Dark matter extends beyond visible part of the galaxy
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration
 ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 3: Our Place in the Universe [1/19/07] Announcements Scale in the
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 3: Our Place in the Universe [1/19/07] Announcements Scale in the
Dark Matter / Dark Energy
 Dark Matter / Dark Energy 2 different things! The first hints of Dark Matter arose with observations of large motions in clusters of galaxies in the 1930 s. The case became compelling in the 1970 s with
Dark Matter / Dark Energy 2 different things! The first hints of Dark Matter arose with observations of large motions in clusters of galaxies in the 1930 s. The case became compelling in the 1970 s with
Chapter 15 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline Hubble s Galaxy Classification. Normal and Active Galaxies Hubble s Galaxy Classification
 Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Spiral galaxies are classified according to the size of their central bulge. Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Type Sa has the largest central
Lecture Outline Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Spiral galaxies are classified according to the size of their central bulge. Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies Type Sa has the largest central
PHY323:Lecture 7 Dark Matter with Gravitational Lensing
 PHY323:Lecture 7 Dark Matter with Gravitational Lensing Strong Gravitational Lensing Theory of Gravitational Lensing Weak Gravitational Lensing Large Scale Structure Experimental Evidence for Dark Matter
PHY323:Lecture 7 Dark Matter with Gravitational Lensing Strong Gravitational Lensing Theory of Gravitational Lensing Weak Gravitational Lensing Large Scale Structure Experimental Evidence for Dark Matter
According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a. Chapter 34: Cosmology. Cosmology: How the Universe Works
 Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 23 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
Chapter 23 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe Curvature of the Universe The Density Parameter of the Universe Ω 0 is defined as the ratio
The Millennium Simulation: cosmic evolution in a supercomputer. Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
 The Millennium Simulation: cosmic evolution in a supercomputer Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The COBE satellite (1989-1993) Two instruments made maps of the whole sky in microwaves
The Millennium Simulation: cosmic evolution in a supercomputer Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The COBE satellite (1989-1993) Two instruments made maps of the whole sky in microwaves
Large Scale Structure
 Large Scale Structure Measuring Distance in Universe-- a ladder of steps, building from nearby Redshift distance Redshift = z = (λ observed - λ rest )/ λ rest Every part of a distant spectrum has same
Large Scale Structure Measuring Distance in Universe-- a ladder of steps, building from nearby Redshift distance Redshift = z = (λ observed - λ rest )/ λ rest Every part of a distant spectrum has same
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!NNOUNCEMENTS HOMEWORK #6 DUE TODAY, by 5pm HOMEWORK #7 DUE Nov. 10, by 5pm Dark matter halo for galaxies REVIEW Dark matter extends beyond visible part of
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!NNOUNCEMENTS HOMEWORK #6 DUE TODAY, by 5pm HOMEWORK #7 DUE Nov. 10, by 5pm Dark matter halo for galaxies REVIEW Dark matter extends beyond visible part of
Galaxies and Star Systems
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Ned Wright's Cosmology Tutorial
 Sunday, September 5, 1999 Ned Wright's Cosmology Tutorial - Part 1 Page: 1 Ned Wright's Cosmology Tutorial Part 1: Observations of Global Properties Part 2: Homogeneity and Isotropy; Many Distances; Scale
Sunday, September 5, 1999 Ned Wright's Cosmology Tutorial - Part 1 Page: 1 Ned Wright's Cosmology Tutorial Part 1: Observations of Global Properties Part 2: Homogeneity and Isotropy; Many Distances; Scale
A5682: Introduction to Cosmology Course Notes. 11. CMB Anisotropy
 Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
Reading: Chapter 8, sections 8.4 and 8.5 11. CMB Anisotropy Gravitational instability and structure formation Today s universe shows structure on scales from individual galaxies to galaxy groups and clusters
 COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 OBSERVING THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - January 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 OBSERVING THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - January 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters. Formation and Evolution Hubble s Law
 The American astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1924, according to appearance of galaxies categorized them into four basic types. Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters Masses Formation and Evolution
The American astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1924, according to appearance of galaxies categorized them into four basic types. Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters Masses Formation and Evolution
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Sep 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Sep 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Sep 2011](/thumbs/73/69040556.jpg) 3D Velocity and Density Reconstructions of the Local Universe with Cosmicflows-1 arxiv:1109.3856v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Sep 2011 Hélène M. Courtois 1,2 1 Institute for Astronomy (IFA), University of Hawaii,
3D Velocity and Density Reconstructions of the Local Universe with Cosmicflows-1 arxiv:1109.3856v1 [astro-ph.co] 18 Sep 2011 Hélène M. Courtois 1,2 1 Institute for Astronomy (IFA), University of Hawaii,
