The Detection and Characterization of Extrasolar Planets. gregory laughlin - uco/lick observatory
|
|
|
- George Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Detection and Characterization of Extrasolar Planets gregory laughlin - uco/lick observatory
2 Collaborators Fred Adams, Mark Ammons, Peter Bodenheimer, Paul Butler, Debra Fischer, Greg Henry Shigeru Ida, Geoff Marcy, Sally Robinson, Jay Strader, Bunei Sato, Steve Vogt, Aaron Wolf Funding from the NASA TPF Program and the NSF CAREER Program
3
4 Simulation showing infall onto a massive protostellar disk AU
5 The Gravitational Instability Paradigm Two basic requirements for gravitational disk instability to work: 1. Q = c sκ πgσ 1 somewhere in the disk 2. The cooling time for fragments must be less than half an orbital period (Gammie (2001). Kuiper 1951 Cameron 1978 DeCampli & Cameron 1979 Boss 1998 Boss 2000 Mayer et al Pickett et al Rice et al 2003a Rice et al 2003b Boss 2003 Cai et al 2004 Boss 2004 Mayer et al 2004 Mejia et al 2005
6 Text Laughlin, Korchagin & Adams 1997 Ttime TexAnother Text unresolved issue for G.I. is the feasibility of having a highly gravitationally unstable axisymmetric disk.t
7 The Core Accretion Paradigm Perri & Cameron 1974, Mizuno et al 1978, Mizuno 1980, Bodenheimer & Pollack 1986, Pollack et al 1996 During Phase 1, the growing planet consists mostly of solid material. The planet experiences runaway accretion until the feeding zone is depleted. Solid accretion occurs much faster than gas accretion during this phase. During Phase 2, both solid and gas accretion rates are small and are nearly independent of time. This phase dictates the overall evolutionary time-scale. During Phase 3, runaway gas accretion occurs. Runaway gas accretion starts when the solid and gas masses are roughly equal.
8 The Core Accretion Paradigm During Phase 1, the mass increase of the planet depends on the planetary radius, and the ratio of the gravitational to geometric cross section: dm p dt (Pollack et al 1996) = πr 2 cσωf g Because the escape velocity from the planetary surface is much faster than the relative velocity of planetesimals, this phase is characterized by a runaway growth of the solid core which ends when the core depletes its feeding zone, defined by: a f = ( 12 + e 2 h )R H Hill Radius R H = a( M P 3M ) 1/3
9 As runaway solid accretion proceeds through several Earth masses, the gas envelope becomes increasingly significant. Modeling of this stage requires computation of the hydrodynamic structure and effect of the gas envelope. 1. Stellar Evolution code for the quasiequilibrium envelope: dp dr = gρ dm dr = 4πR2 ρ dt dr = 3κρ 16σT 3 2. Planetesimal dissolution routine: v encounter = ( 5e 2 L 4πR 2 L core = GM coreṁcore R core 8 + i2 )v kepler - numerical integration in envelope - energy deposition into envelope
10 Earth Masses Pollack et al baseline Jupiter formation model. isolation mass reached Total Mass Gas Mass Core Mass Millions of Years d = 5.2 AU T neb = 150 K σ solids = 10 g cm 2 ρ neb = gcm 3
11 ngc 2024 trapezium Haisch et al 2001 ic 348 Observed disk lifetimes tend to be shorter than the ~8 Myr required in the Pollack et al. (1996) standard case model ngc 2362
12 The standard model of Pollack et al 1996 predicts: 1. A planet with a core mass that seems too high. 2. A timescale to reach runaway gas accretion that seems too long. A great deal of work has been done from to refine core accretion. Examples include: 1. Improved physics: equation of state (reviewed by Saumon & Guillot 2004) envelope opacity (Ikoma et al 2000, Podolak 2003) 2. Additional physics: migration of the cores (Papaloizou & Terquem 1999, Alibert et al 2004, Ida & Lin 2004) turbulence in the disk (Rice and Armitage 2003) competition between embryos (Hubickyj, Bodenheimer & Lissauer 2005) time evolution of the disk (Alibert et al 2004, Ida & Lin 2004, Laughlin,Bodenheimer & Adams)
13 non-ideal gas ideal gas log κ 4 2 interstellar opacity 0 envelope opacity log T Grain opacities are a key issue. Original studies (e.g Pollack et al 1996) used envelope opacities with an interstellar size distribution. But material that enters a giant planet envelope has been modified from the original interstellar grains by coagulation and fragmentation. Calculations by Podolak (2003) indicate that once grains enter the protoplanetary envelope, they coagulate and settle out quickly into warmer regions where they are destroyed. Podolak argues that true opacities are ~50x smaller than interstellar.
14 40 Reduced grain opacity greatly speeds up the gas accretion timescale. -2 total mass mass (earth masses) gas mass core mass log L/Lsun time (millions of years) -10 (Hubickyj et al. 2005) time (millions of years)
15 A key (and well established) result of standard core accretion theory is the extraordinary sensitivity of the time of onset of rapid gas accretion to the surface density of solids in the disk. Recent calculations by Hubickyj et al (2005), illustrate that decreasing the solid surface density from 10 to 6 gm/cm 2 causes a 12 Myr delay in the onset of rapid gas accretion.
16 Percentage of Stars with Planets Fischer & Valenti solar 0.5 [Fe/H] The extrasolar planet - host star metallicity connection is one of the most remarkable results to have emerged from the radial velocity surveys. This correlation certainly provides an important clue to the planet formation process.
17 The metallicity -- planet connection suggests that giant planet formation is a threshold phenomenon that depends sensitively on the surface density of solids (planetesimals) in the disk. This is a characteristic and generic property of core-accretion. The metallicity connection is very hard to understand within the gravitational instability paradigm (e.g. Boss 2002).
18 orbital eccentricity e=0.80 e=0.50 e= planets 171 planets Semi-Major Axis (AU)
19
20 51 Peg shows a strong residual peak at 356 days. Is this peak an alias?
21 51 Peg Residuals folded at days
22 The 51 Peg day peak is not an alias peak.
23 Fischer & Valenti 2005 [Fe/H] The extrasolar planet - host star metallicity connection is one of the most remarkable results to have emerged from the radial velocity surveys. This correlation is saying something important about planet formation. It also shows how to efficiently find planets.
24 candy for breakfast A quick-look Doppler velocity survey that searches metal-rich stars for planets will certainly skew the overall statistical census of extrasolar planets. Why is it important to quickly find more hot-jupiter type planets?
25 Brown et al Short-period planets have a high probability of transiting. When a planet transits a bright star, a tremendous amount can be learned.
26 Statistical Anomalies A curious concentration (11 out of 26) planets with periods 0<P<10 days have periods between 3 and 4 days. All of the short-period planets are solar or higher metallicity. A possible relation (of negative slope) exists between the mass of transiting planets and their periods. Planets with periods P<10 days have an average mass M<1MJup. Planets with periods 10<P<200 days have an average mass M~5Mjup (this is not due to an observational bias). Furthermore, the mass-period relation for planets appears to be different for the cases of single parent stars and binary parent stars.
27 As more planets with periods of approximately one week are discovered, the tidal quality factor, Q, which in general should depend on Mass, Teff, and composition will become better constrained. Right now, the circularization boundary suggests <Q>~10^6 * multiple planet systems circularization boundary occurs at a period of about one week. τ circ = ė e = ( 4QP 63n ) ( ) ( MP a M R p ) 5
28
29 Over half of the short-period planets that have been discovered show evidence for detectable additional companions. Multiple-planet systems can tell us much more about the formation and evolutionary processes that are sculpting the galactic planetary census. hd HD gj 876 hd
30 The N2K Survey - An international Consortium to survey the next two thousand metal rich stars (identified via broadband photometric calibrations). - Our strategy is to obtain 3+1 Doppler velocities for each star. Stars with scatter characteristic of a Hot Jupiter sent to Keck for follow-up stars have been surveyed so far. - Fischer, Laughlin, Butler, Marcy, Henry (US: NASA / NOAO Keck); Ida, Sato (Japan: Subaru); Minniti (Chile: Magellan)
31 Broadband calibrations: Fischer & Valenti (2005) have derived accurate physical properties (Fe/H, log g, Teff) from uniformly obtained high-resolution spectra of 1330 stars in the Keck, Lick, and AAT surveys. All of these stars have Tycho B and V photometry, and 2-Mass J, H, and K photometry. Use the Levenberg-Marquardt method to derive empirical calibrations (by varying the coefficients of polynomials constructed from the broadband colors) to calibrate Fe/H, etc. Ammons et al. (2006)
32 no hot jupiter spectroscopic binary rms= 6.87 m/s; sig=5.43 m/s rms= 3354 m/s; sig=65.3 m/s time (days) hot jupiter candidate time (years) no hot jupiter rms= 24.7 m/s; sig=3.99 m/s rms= 3.85 m/s; sig=4.61 m/s velocity m/s velocity m/s velocity m/s velocity m/s time (days) time (days)
33 A Hot-Saturn Orbiting HD Tp=3.41ext P=3.41 d, e=0, Msini= 0.29 MJup
34 Photometry from Greg Henry, using a 0.8 m automated telescope, shows no evidence of transit for HD88133b.Tex
35 Velocity (m/s) HD Filled symbols: Keck, Open symbols: Subaru Orbital Phase HD R 1.45 (0.1) Rsun M 1.3 (0.1) Msun L 2.7 (0.5) Lsun d 79 (7) pc Teff 6147 (50) K Age 2.0 (0.8) Gyr Type G0 IV V 8.15 vsini 6.0 (0.5) km/s [Fe/H] 0.36 (0.05) dex dec +30 HD b P (0.001) d e 0.00 (fixed) K 43.3 (1.2) m/s Msini 0.36 (0.03) Mjup
36 1.005 Three millimagnitude transit depth! JD Flux JD JD Three telescope average Orbital Phase
37 HD b A Year in a Weekend! Viewed from above Sat. 7:45 am transit ends Sat. 4:45 am transit begins View from Earth (scale reduced by 1/2) Orbital path (to scale) Planet location Sun. 5:00 am HD (to scale) Line of sight to the Earth The diameter of the orbit is only six times the diameter of the star. The diameter of the star is 19.6 times the diameter of the planet. (All times UT) HD b (to scale) Orbital direction shown counterclockwise Planet location at Noon, Fri. July 01, 2005 Planet location at 9:01 am, Mon. July 04, 2005 HD b completes one orbit in days. If we start tracking the planet at Noon on Friday, we find that it has returned to its starting position by 9:01 am on Monday morning.
38 R/Rjup R/Rjup Mcore 10.5 gm/cc 5.5 gm/cc
39 Radial Velocity Rossiter-McLaughlin effect velocities from June 25th Phased Period (d)
40 stellar spin axis radial velocity (m/s) transit chord time (days)
41 25 Radial Velocity (m/s) In-transit radial velocities indicate no significant misalignment between spin axis of the star and the orbital angular momentum vector of the planet Phased Period (d)
42 10,000 bootstrap trials (Wolf et al. 2006)
43 The Known Transiting Planets Model Predictions HD b and HD b too large HD b too small
44 Amateur astronomer Ron Bissinger observed the transit from his backyard in Pleasanton as soon as the transit was announced
45 c.transits.txt Predicted Transit times for GJ 876 "c" (The INNER planet) Predicted Central transit duration is 152 minutes These are the predicted ingress and egress times for a central transit of GJ 876 "c", from ( ) as computed using the three-body dynamical model of Laughlin et al (ApJ In Press). Uncertainty for transit opportunities during is approximately 0.2 days. ingres (JD) egress (JD) UT (ingress) M D Y UT : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :22 The website provides ephemeris tables for the predicted transit times and uncertainties for all of the known extrasolar planets. As new velocities are published, new self-consistent (n-body) radial velocity fits and transit windows are computed. A cron job updates the table every night.
46
47
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground
 The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
Outline. RV Planet Searches Improving Doppler Precision Population Synthesis Planet Formation Models Eta-Earth Survey Future Directions
 The NASA-UC Eta-Earth Survey: A Systematic Search for Low-mass Planets From Keck Observatory - Andrew Howard - Townes Post-doctoral Fellow, UC Berkeley HD 7924b Collaborators Geoff Marcy Debra Fischer
The NASA-UC Eta-Earth Survey: A Systematic Search for Low-mass Planets From Keck Observatory - Andrew Howard - Townes Post-doctoral Fellow, UC Berkeley HD 7924b Collaborators Geoff Marcy Debra Fischer
II. Results from Transiting Planets. 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect
 II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks. Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany
 Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 30 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 30 Oct 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 30 Oct 2007](/thumbs/76/74278284.jpg) **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Giant Planet Formation by Core Accretion arxiv:0710.5667v1 [astro-ph] 30 Oct 2007 Christoph Mordasini,
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Giant Planet Formation by Core Accretion arxiv:0710.5667v1 [astro-ph] 30 Oct 2007 Christoph Mordasini,
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Migration. Phil Armitage (University of Colorado) 4Migration regimes 4Time scale for massive planet formation 4Observational signatures
 Phil Armitage (University of Colorado) Migration 4Migration regimes 4Time scale for massive planet formation 4Observational signatures Ken Rice (UC Riverside) Dimitri Veras (Colorado) + Mario Livio, Steve
Phil Armitage (University of Colorado) Migration 4Migration regimes 4Time scale for massive planet formation 4Observational signatures Ken Rice (UC Riverside) Dimitri Veras (Colorado) + Mario Livio, Steve
How do we model each process of planet formation? How do results depend on the model parameters?
 How do we model each process of planet formation? How do results depend on the model parameters? Planetary Population Synthesis: The Predictive Power of Planet Formation Theory, Ringberg, Nov 29, 2010
How do we model each process of planet formation? How do results depend on the model parameters? Planetary Population Synthesis: The Predictive Power of Planet Formation Theory, Ringberg, Nov 29, 2010
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census
 Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia.
 Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Searching for planets around other stars. Searching for planets around other stars. Searching for other planetary systems this is a hard problem!
 Reading: Chap. 21, Sect.21.4-21.6 Final Exam: Tuesday, December 12; 4:30-6:30PM Homework 10: Due in recitation Dec. 1,4 1 Brief review of last time: Formation of Planetary Systems Observational Clues:
Reading: Chap. 21, Sect.21.4-21.6 Final Exam: Tuesday, December 12; 4:30-6:30PM Homework 10: Due in recitation Dec. 1,4 1 Brief review of last time: Formation of Planetary Systems Observational Clues:
Definitions. Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H. Brown dwarfs: M<0.07M s No Burning. Planets No Burning. Dwarf planets. cosmic composition (H+He)
 Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
hd b greg laughlin jonathan langton ucsc
 hd 80606 b greg laughlin jonathan langton ucsc The success of the planet detection programs has enabled the comparative study of populations of planets, as well as the detailed investigation of individual
hd 80606 b greg laughlin jonathan langton ucsc The success of the planet detection programs has enabled the comparative study of populations of planets, as well as the detailed investigation of individual
Planet Formation: theory and observations. Sean Raymond University of Colorado (until Friday) Observatoire de Bordeaux
 Planet Formation: theory and observations Sean Raymond University of Colorado (until Friday) Observatoire de Bordeaux Outline Stages of Planet Formation Solar System Formation Cores to disks (c2d) Observational
Planet Formation: theory and observations Sean Raymond University of Colorado (until Friday) Observatoire de Bordeaux Outline Stages of Planet Formation Solar System Formation Cores to disks (c2d) Observational
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Oct 2006
 Planet Formation with Migration J. E. Chambers 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0610905v1 30 Oct 2006 In the core-accretion model, gas-giant planets form solid cores which then accrete gaseous envelopes. Tidal
Planet Formation with Migration J. E. Chambers 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0610905v1 30 Oct 2006 In the core-accretion model, gas-giant planets form solid cores which then accrete gaseous envelopes. Tidal
C. Mordasini & G. Bryden. Sagan Summer School 2015
 Hands-on Session I C. Mordasini & G. Bryden Sagan Summer School 2015 Population synthesis Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Thursday GlobalPFE model Minimum physical processes to consider GlobalPFE: Toy
Hands-on Session I C. Mordasini & G. Bryden Sagan Summer School 2015 Population synthesis Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Thursday GlobalPFE model Minimum physical processes to consider GlobalPFE: Toy
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 20 Apr 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 20 Apr 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 20 Apr 2014](/thumbs/83/87285854.jpg) The Formation of Uranus & Neptune: Challenges and Implications For Intermediate-Mass Exoplanets Ravit Helled 1 and Peter Bodenheimer 2 1 Department of Geophysical, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences,
The Formation of Uranus & Neptune: Challenges and Implications For Intermediate-Mass Exoplanets Ravit Helled 1 and Peter Bodenheimer 2 1 Department of Geophysical, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences,
Planetary Systems in Stellar Clusters
 Planetary Systems in Stellar Clusters Melvyn B. Davies Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics Lund Observatory Collaborators: John Chambers, Ross Church, Francesca de Angeli, Douglas Heggie, Thijs
Planetary Systems in Stellar Clusters Melvyn B. Davies Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics Lund Observatory Collaborators: John Chambers, Ross Church, Francesca de Angeli, Douglas Heggie, Thijs
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems
 Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Heavy meteal rules. Vardan Adibekyan Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences. The star-planet connection. 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo
 The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara
 A Diversity of Worlds: Toward a Theoretical Framework for the Structures of Planetary Systems Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara Strange New Worlds. Slide credit: Scott Gaudi ~1500
A Diversity of Worlds: Toward a Theoretical Framework for the Structures of Planetary Systems Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara Strange New Worlds. Slide credit: Scott Gaudi ~1500
Practical Numerical Training UKNum
 Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions PD. Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4) Bachelor/Masterarbeiten
Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions PD. Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4) Bachelor/Masterarbeiten
Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance
 Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance Intermediate Graduate Physics Seminar Waqas Bhatti May 1, 2007 Abstract Over 200 extrasolar planets have been discovered since the first confirmed observation
Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance Intermediate Graduate Physics Seminar Waqas Bhatti May 1, 2007 Abstract Over 200 extrasolar planets have been discovered since the first confirmed observation
[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)
![[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)](/thumbs/86/94788164.jpg) 1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
EXOPLANET LECTURE PLANET FORMATION. Dr. Judit Szulagyi - ETH Fellow
 EXOPLANET LECTURE PLANET FORMATION Dr. Judit Szulagyi - ETH Fellow (judits@ethz.ch) I. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS AND THEIR DISKS (YSOs) Star Formation Young stars born in 10 4 10 6 M Sun Giant Molecular Clouds.
EXOPLANET LECTURE PLANET FORMATION Dr. Judit Szulagyi - ETH Fellow (judits@ethz.ch) I. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS AND THEIR DISKS (YSOs) Star Formation Young stars born in 10 4 10 6 M Sun Giant Molecular Clouds.
A Long-Period Jupiter-Mass Planet Orbiting the Nearby M Dwarf GJ 849 1
 Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 118: 1685 1689, 2006 December 2006. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A Long-Period Jupiter-Mass Planet
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 118: 1685 1689, 2006 December 2006. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A Long-Period Jupiter-Mass Planet
Sta%s%cal Proper%es of Exoplanets
 Sta%s%cal Proper%es of Exoplanets Mordasini et al. 2009, A&A, 501, 1139 Next: Popula%on Synthesis 1 Goals of Population Synthesis: incorporate essential planet formation processes, with simplifying approximation
Sta%s%cal Proper%es of Exoplanets Mordasini et al. 2009, A&A, 501, 1139 Next: Popula%on Synthesis 1 Goals of Population Synthesis: incorporate essential planet formation processes, with simplifying approximation
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems
 Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Formation of the Solar System 15.3 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets 15.4 Interplanetary Debris 15.5 Solar
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Formation of the Solar System 15.3 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets 15.4 Interplanetary Debris 15.5 Solar
TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack
 Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Transiting Extrasolar Planets Workshop ASP Conference Series, Vol. 366, 2007 C. Afonso, D. Weldrake and Th. Henning TrES Exoplanets and False Positives: Finding the Needle in the Haystack F. T. O Donovan
Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets
 Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture
Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture
Substellar companions and isolated planetary-mass objects from protostellar disc fragmentation
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 346, L36 L40 (2003) Substellar companions and isolated planetary-mass objects from protostellar disc fragmentation W. K. M. Rice, 1 P. J. Armitage, 2,3 I. A. Bonnell, 1 M. R.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 346, L36 L40 (2003) Substellar companions and isolated planetary-mass objects from protostellar disc fragmentation W. K. M. Rice, 1 P. J. Armitage, 2,3 I. A. Bonnell, 1 M. R.
Substellar companions and isolated planetary-mass objects from protostellar disc fragmentation
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 346, L36 L40 (2003) Substellar companions and isolated planetary-mass objects from protostellar disc fragmentation W. K. M. Rice, 1 P. J. Armitage, 2,3 I. A. Bonnell, 1 M. R.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 346, L36 L40 (2003) Substellar companions and isolated planetary-mass objects from protostellar disc fragmentation W. K. M. Rice, 1 P. J. Armitage, 2,3 I. A. Bonnell, 1 M. R.
Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones
 Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
II Planet Finding.
 II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
Giant Planet Formation
 Giant Planet Formation Overview Observations: Meteorites to Extrasolar Planets Our Solar System Dynamics Meteorites Geology Planetary composition & structure Other Stars Circumstellar disks Extrasolar
Giant Planet Formation Overview Observations: Meteorites to Extrasolar Planets Our Solar System Dynamics Meteorites Geology Planetary composition & structure Other Stars Circumstellar disks Extrasolar
Formation of Planets around M & L dwarfs
 Formation of Planets around & L dwarfs D.N.C. Lin University of California with S. Ida, H. Li, S.L.Li, E. Thommes, I. Dobbs-Dixon, S.T. Lee,P. Garaud,. Nagasawa AAS Washington Jan 11th, 006 17 slides Disk
Formation of Planets around & L dwarfs D.N.C. Lin University of California with S. Ida, H. Li, S.L.Li, E. Thommes, I. Dobbs-Dixon, S.T. Lee,P. Garaud,. Nagasawa AAS Washington Jan 11th, 006 17 slides Disk
Research paper assignment
 Research paper assignment Review of research that interests you, more focused than discussions in class Include references and figures Final format should be PDF (try LaTeX!) Concise! < 5000 words Steps:
Research paper assignment Review of research that interests you, more focused than discussions in class Include references and figures Final format should be PDF (try LaTeX!) Concise! < 5000 words Steps:
10/16/ Detecting Planets Around Other Stars. Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds
 10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
Finding Other Earths. Jason H. Steffen. Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009
 Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Observations of Extrasolar Planets
 Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler. William Cochran McDonald Observatory
 Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
OGLE-TR-56. Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha INTRODUCTION
 OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
OGLE-TR-56 Guillermo Torres, Maciej Konacki, Dimitar D. Sasselov and Saurabh Jha Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Caltech, Department of Geological and Planetary Sciences University of California
EUROPEAN SOUTHERN OBSERVATORY
 EUROPEAN SOUTHERN OBSERVATORY Organisation Européenne pour des Recherches Astronomiques dans l Hémisphère Austral Europäische Organisation für astronomische Forschung in der südlichen Hemisphäre VISITING
EUROPEAN SOUTHERN OBSERVATORY Organisation Européenne pour des Recherches Astronomiques dans l Hémisphère Austral Europäische Organisation für astronomische Forschung in der südlichen Hemisphäre VISITING
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Introduction. Convergence of the fragmentation boundary in self-gravitating discs
 Convergence of the fragmentation boundary in self-gravitating discs Collaborators : Phil Armitage - University of Colorado Duncan Forgan- University of St Andrews Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Queen Mary, University
Convergence of the fragmentation boundary in self-gravitating discs Collaborators : Phil Armitage - University of Colorado Duncan Forgan- University of St Andrews Sijme-Jan Paardekooper Queen Mary, University
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Planets and Brown Dwarfs
 Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
The Rossiter effect of transiting extra-solar planets Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo
 The Rossiter effect of transiting extra-solar planets λ λ = 4 o.4 ± 1 o.4 Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo International Workshop on on the 10th Gravitational Microlensing and Related
The Rossiter effect of transiting extra-solar planets λ λ = 4 o.4 ± 1 o.4 Yasushi Suto Department of Physics, University of Tokyo International Workshop on on the 10th Gravitational Microlensing and Related
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Young Solar-like Systems
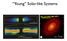 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa<ons of Transi<ng Systems
 June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
June. 4, 215 @ NAOJ Probing the Dynamical History of Exoplanets: Spectroscopic Observa
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Planets: Name Distance from Sun Satellites Year Day Mercury 0.4AU yr 60 days Venus yr 243 days* Earth 1 1 yr 1 day Mars 1.
 The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
Planetary System Stability and Evolution. N. Jeremy Kasdin Princeton University
 Planetary System Stability and Evolution N. Jeremy Kasdin Princeton University (Lots of help from Eric Ford, Florida and Robert Vanderbei, Princeton) KISS Exoplanet Workshop 10 November 2009 Motivation
Planetary System Stability and Evolution N. Jeremy Kasdin Princeton University (Lots of help from Eric Ford, Florida and Robert Vanderbei, Princeton) KISS Exoplanet Workshop 10 November 2009 Motivation
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Testing Theories of Planet Formation & Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems using Orbital Properties of Exoplanets
 Testing Theories of Planet Formation & Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems using Orbital Properties of Exoplanets Eric B. Ford Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (Starting at UF in August
Testing Theories of Planet Formation & Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems using Orbital Properties of Exoplanets Eric B. Ford Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (Starting at UF in August
Extrasolar Planets. Properties Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Dynamically Unstable Planetary Systems Emerging Out of Gas Disks
 EXTREME SOLAR SYSTEMS ASP Conference Series, Vol. 398, 2008 D. Fischer, F. A. Rasio, S. E. Thorsett, and A. Wolszczan Dynamically Unstable Planetary Systems Emerging Out of Gas Disks Soko Matsumura, Edward
EXTREME SOLAR SYSTEMS ASP Conference Series, Vol. 398, 2008 D. Fischer, F. A. Rasio, S. E. Thorsett, and A. Wolszczan Dynamically Unstable Planetary Systems Emerging Out of Gas Disks Soko Matsumura, Edward
Lecture 16. How did it happen? How long did it take? Where did it occur? Was there more than 1 process?
 Planet formation in the Solar System Lecture 16 How did it happen? How long did it take? Where did it occur? Was there more than 1 process? Planet formation How do planets form?? By what mechanism? Planet
Planet formation in the Solar System Lecture 16 How did it happen? How long did it take? Where did it occur? Was there more than 1 process? Planet formation How do planets form?? By what mechanism? Planet
PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona. Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015
 PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015 PLANET FORMATION BY in GAS! GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of
PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015 PLANET FORMATION BY in GAS! GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity. PHY 688, Lecture 11
 Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity PHY 688, Lecture 11 Outline Review of previous lecture binary stars and brown dwarfs (sub)stellar dynamical masses and radii Surface gravity stars,
Fundamental (Sub)stellar Parameters: Surface Gravity PHY 688, Lecture 11 Outline Review of previous lecture binary stars and brown dwarfs (sub)stellar dynamical masses and radii Surface gravity stars,
Kozai-Lidov oscillations
 Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Disc-Planet Interactions during Planet Formation
 Disc-Planet Interactions during Planet Formation Richard Nelson Queen Mary, University of London Collaborators: Paul Cresswell (QMUL), Martin Ilgner (QMUL), Sebastien Fromang (DAMTP), John Papaloizou (DAMTP),
Disc-Planet Interactions during Planet Formation Richard Nelson Queen Mary, University of London Collaborators: Paul Cresswell (QMUL), Martin Ilgner (QMUL), Sebastien Fromang (DAMTP), John Papaloizou (DAMTP),
F. Marzari, Dept. Physics, Padova Univ. Planetary migration
 F. Marzari, Dept. Physics, Padova Univ. Planetary migration Standard model of planet formation based on Solar system exploration Small semimajor axes Large eccentricities The standard model Protostar +Disk
F. Marzari, Dept. Physics, Padova Univ. Planetary migration Standard model of planet formation based on Solar system exploration Small semimajor axes Large eccentricities The standard model Protostar +Disk
Theory of planet formation C. Mordasini
 Theory of planet formation C. Mordasini Kiel, 26.5.2010 Y. Alibert, W. Benz, K. Dittkrist, H. Klahr Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Germany University of Berne, Switzerland Observatoire de Besancon,
Theory of planet formation C. Mordasini Kiel, 26.5.2010 Y. Alibert, W. Benz, K. Dittkrist, H. Klahr Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Germany University of Berne, Switzerland Observatoire de Besancon,
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets
 Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years
Dynamical Stability of Terrestrial and Giant Planets in the HD Planetary System
 Dynamical Stability of Terrestrial and Giant Planets in the HD 155358 Planetary System James Haynes Advisor: Nader Haghighipour ABSTRACT The results of a study of the dynamical evolution and the habitability
Dynamical Stability of Terrestrial and Giant Planets in the HD 155358 Planetary System James Haynes Advisor: Nader Haghighipour ABSTRACT The results of a study of the dynamical evolution and the habitability
Origins of Gas Giant Planets
 Origins of Gas Giant Planets Ruth Murray-Clay Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Image Credit: NASA Graduate Students Piso Tripathi Dawson Undergraduates Wolff Lau Alpert Mukherjee Wolansky Jackson
Origins of Gas Giant Planets Ruth Murray-Clay Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Image Credit: NASA Graduate Students Piso Tripathi Dawson Undergraduates Wolff Lau Alpert Mukherjee Wolansky Jackson
Observations of extrasolar planets
 Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Extrasolar Planets. By: Steve Strom 1
 Extrasolar Planets By: Steve Strom 1 NOTES: (a) JWST numbers appropriate to the assumptions in their updated Science Requirements Document must be calculated; (b) the GSMT sensitivity calculations must
Extrasolar Planets By: Steve Strom 1 NOTES: (a) JWST numbers appropriate to the assumptions in their updated Science Requirements Document must be calculated; (b) the GSMT sensitivity calculations must
Why Search for Extrasolar Planets?
 Why Search for Extrasolar Planets? What is the diversity of habitats for life in the universe? Are Earth-like planets common or rare in our region of the galaxy? We have an elaborate and self-consistent
Why Search for Extrasolar Planets? What is the diversity of habitats for life in the universe? Are Earth-like planets common or rare in our region of the galaxy? We have an elaborate and self-consistent
Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses
 Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses from ~3 M J to ~200 M J (0.2M ) Defining stars, brown dwarfs Stars and planets Objects formed by gravitational instability on a dynamical
Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses from ~3 M J to ~200 M J (0.2M ) Defining stars, brown dwarfs Stars and planets Objects formed by gravitational instability on a dynamical
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #6: Extrasolar Planets
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #6: Extrasolar Planets ABSTRACT This is an exciting time in astronomy. Over the past two decades we have begun to indirectly detect planets that orbit stars other than our sun.
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #6: Extrasolar Planets ABSTRACT This is an exciting time in astronomy. Over the past two decades we have begun to indirectly detect planets that orbit stars other than our sun.
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Oligarchic planetesimal accretion and giant planet formation. A. Fortier 1,2,,O.G.Benvenuto 1,2,, and A.
 A&A 473, 311 322 (27) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:266729 c ESO 27 Astronomy & Astrophysics Oligarchic planetesimal accretion and giant planet formation A. Fortier 1,2,,O.G.Benvenuto 1,2,, and A. Brunini 1,2, 1 Facultad
A&A 473, 311 322 (27) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:266729 c ESO 27 Astronomy & Astrophysics Oligarchic planetesimal accretion and giant planet formation A. Fortier 1,2,,O.G.Benvenuto 1,2,, and A. Brunini 1,2, 1 Facultad
Class 15 Formation of the Solar System
 Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
DATA LAB. Data Lab Page 1
 NOTE: This DataLab Activity Guide will be updated soon to reflect April 2015 changes DATA LAB PURPOSE. In this lab, students analyze and interpret quantitative features of their brightness graph to determine
NOTE: This DataLab Activity Guide will be updated soon to reflect April 2015 changes DATA LAB PURPOSE. In this lab, students analyze and interpret quantitative features of their brightness graph to determine
18 An Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet
 Name: Date: 18 An Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet 18.1 Introduction One of the more recent new fields in astronomy is the search for (and discovery of) planets orbiting around stars other than our Sun, or
Name: Date: 18 An Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet 18.1 Introduction One of the more recent new fields in astronomy is the search for (and discovery of) planets orbiting around stars other than our Sun, or
What is to expect from the transit method. M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France
 What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
What is to expect from the transit method M. Deleuil, Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Marseille Institut Universitaire de France Transit - method Occurrence: only if the planet orbital plane is close to
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 7 Aug 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 7 Aug 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 7 Aug 2009](/thumbs/75/72601293.jpg) DRAFT VERSION JANUARY 3, 28 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 DID FOMALHAUT, HR 8799, AND HL TAURI FORM PLANETS VIA THE GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? PLACING LIMITS ON THE REQUIRED DISK
DRAFT VERSION JANUARY 3, 28 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 DID FOMALHAUT, HR 8799, AND HL TAURI FORM PLANETS VIA THE GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? PLACING LIMITS ON THE REQUIRED DISK
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets. Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto
 Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Transiting Extrasolar Planets
 Transiting Extrasolar Planets Recent Progress, XO Survey, and the Future Christopher J. Burke Solar System Has Predominately Circular Orbits Top View Side View Planet Formation NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt
Transiting Extrasolar Planets Recent Progress, XO Survey, and the Future Christopher J. Burke Solar System Has Predominately Circular Orbits Top View Side View Planet Formation NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt
EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer. Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY
 EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY Kepler Mission The Kepler mission, launched in 2009, aims to explore the structure
EXONEST The Exoplanetary Explorer Kevin H. Knuth and Ben Placek Department of Physics University at Albany (SUNY) Albany NY Kepler Mission The Kepler mission, launched in 2009, aims to explore the structure
III The properties of extrasolar planets
 III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 18 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 25, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 18 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 25, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University. Results from Microlensing Searches for Planets.
 Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University Results from Microlensing Searches for Planets. Collaborative Efforts. Worldwide Collaborations: μfun MiNDSTEP MOA OGLE PLANET RoboNet Microlensing is a cult. -Dave
Scott Gaudi The Ohio State University Results from Microlensing Searches for Planets. Collaborative Efforts. Worldwide Collaborations: μfun MiNDSTEP MOA OGLE PLANET RoboNet Microlensing is a cult. -Dave
PLANETARY FORMATION THEORY EXPLORING EXOPLANETS
 PLANETARY FORMATION THEORY EXPLORING EXOPLANETS This is what we call planets around OTHER stars! PLANETARY FORMATION THEORY EXPLORING EXOPLANETS This is only as of June 2012. We ve found at least double
PLANETARY FORMATION THEORY EXPLORING EXOPLANETS This is what we call planets around OTHER stars! PLANETARY FORMATION THEORY EXPLORING EXOPLANETS This is only as of June 2012. We ve found at least double
PLANETARY FORMATION SCENARIOS REVISITED: CORE-ACCRETION VERSUS DISK INSTABILITY
 The Astrophysical Journal, 662:1282Y1292, 2007 June 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. PLANETARY FORATION SCENARIOS REVISITED: CORE-ACCRETION VERSUS DISK
The Astrophysical Journal, 662:1282Y1292, 2007 June 20 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. PLANETARY FORATION SCENARIOS REVISITED: CORE-ACCRETION VERSUS DISK
Eccentricity pumping of a planet on an inclined orbit by a disc
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 44, 49 414 21) doi:1.1111/j.1365-2966.21.16295.x Eccentricity pumping of a planet on an inclined orbit by a disc Caroline Terquem 1,2 and Aikel Ajmia 1 1 Institut d Astrophysique
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 44, 49 414 21) doi:1.1111/j.1365-2966.21.16295.x Eccentricity pumping of a planet on an inclined orbit by a disc Caroline Terquem 1,2 and Aikel Ajmia 1 1 Institut d Astrophysique
What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets candidates (http://exoplanets.
 Exoplanets. II What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets + 3787 candidates (http://exoplanets.org) Detected by radial velocity/astrometry: 621
Exoplanets. II What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets + 3787 candidates (http://exoplanets.org) Detected by radial velocity/astrometry: 621
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
THE SEPARATION/PERIOD GAP IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF EXTRASOLAR PLANETS AROUND STARS WITH MASSES M 1.2 M
 The Astrophysical Journal, 660:845Y849, 2007 ay 1 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE SEPARATION/PERIOD GAP IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF EXTRASOLAR PLANETS AROUND
The Astrophysical Journal, 660:845Y849, 2007 ay 1 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE SEPARATION/PERIOD GAP IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF EXTRASOLAR PLANETS AROUND
The Long-Term Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems
 The Long-Term Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems Melvyn B. Davies Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics Lund University Co-authors: Fred Adams, Philip Armitage, John Chambers, Eric Ford,
The Long-Term Dynamical Evolution of Planetary Systems Melvyn B. Davies Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics Lund University Co-authors: Fred Adams, Philip Armitage, John Chambers, Eric Ford,
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets. 4.1 Expected properties of extrasolar planets. Sizes of gas giants, brown dwarfs & low-mass stars
 4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
Accretion of Planets. Bill Hartmann. Star & Planet Formation Minicourse, U of T Astronomy Dept. Lecture 5 - Ed Thommes
 Accretion of Planets Bill Hartmann Star & Planet Formation Minicourse, U of T Astronomy Dept. Lecture 5 - Ed Thommes Overview Start with planetesimals: km-size bodies, interactions are gravitational (formation
Accretion of Planets Bill Hartmann Star & Planet Formation Minicourse, U of T Astronomy Dept. Lecture 5 - Ed Thommes Overview Start with planetesimals: km-size bodies, interactions are gravitational (formation
The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS. Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence
 The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence CHEOPS Characterizing Exoplanets Satellite Science Workshop
The obliquities of the planetary systems detected with CHEOPS Guillaume Hébrard Institut d astrophysique de Paris Observatoire de Haute-Provence CHEOPS Characterizing Exoplanets Satellite Science Workshop
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
