DO SOLAR FLARES AFFECT TOTAL OZONE? DEGO MARIN. I.N.T.A., Atmospheric Sounding Station "ElArenosillo", Mazagon, Spain' JAN LASTOVICKA
|
|
|
- Jeffry McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DO SOLAR FLARES AFFECT TOTAL OZONE? DEGO MARIN I.N.T.A., Atmospheric Sounding Station "ElArenosillo", Mazagon, Spain' JAN LASTOVICKA Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Acad. Sci. Czech Rep., Prague 4, Czech Republic* Summary: An analysis of total ozone from Hradec Kralove (50,25"N, E) and of radio wave absorption in the lower ionosphere at 1539 khz (reflection point 50.3"N, ]J.8 E) shows that there is no detectable effect of strong solar flares in total ozone, no correlation between total ozone and absorption on a day-to-day time scale, and that strong solar flares do not affect this correlation. Thus the long-term correlation of monthly average values (Alberca et al, 1996) is not reproduced on a day-to-day time scale, and the effects of strong geomagnetic storms in total ozone (LaStovicka et al., 1992; Mich and LaStovicka, 1996) have no counterpart in effects of strong solar flares. Key words: total ozone, lower ionosphere, solar flares 1. INTRODUCTION Atmospheric ozone is affected primarily by internal atmospheric processes, namely by dynamics and to some extent by chemistry. However, there are also some effects of extraterrestrial origin on ozone. The variations of stratospheric and mesospheric ozone and total ozone with the 11 -year solar cycle and the 27-day solar rotation due to variations of solar UV irradiance are a well-known phenomenon. In total ozone, the solar cycle variation attains 1.5-2%, about 85% of this variation being from heights below 25 km (e.g. Hood, 1997}. The total ozone changes by less than 0.5% in the 27-day cycle (e.g. Brasseur, 1993). Among the solar wind and high energy particle-related effects on ozone layer, the best known effects are those of solar proton events (SPEs). SPEs reduce ozone concentration (e.g. Jackman et al., 1995) mainly in the mesosphere. For the SPEs of August 1972, the decrease in total ozone attained only 2% (Reagan et al., 1981), for the SPE of October 1981 only slightly more than 2% (Jackman et al., 1995). Shumilov et al. (1992) found, for ground level SPEs, a significant decrease of total ozone in the polar cap, but no detectable effect at auroral latitudes. Highly relativistic electrons (HRE) affect ozone, as well. Goldberg et al. (1995) found an ozone depletion of more than 25% near 75 km above Poker Flat, Alaska as a consequence of a HRE event. 1 Address: I.N.T.A., Space Sci. Div., Remote Sensing Aeron. Dept., Atmospheric Sounding Station "El Arenosillo", Mazagon (Moguer, Huelva), Spain; marinsd@inta.es 2 Address: Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Acad. Sci. Czech Rep., Bocni II, Prague 4, Czech Republic; jla@ufa.cas.cz Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998), StudiaGeo s.r.o., Prague 533
2 D. Marin andj. Lastovicka Another factor are strong geomagnetic storms. Lastovifka et al. (1992), Mich (1994) and Mich and LaStovicka (1995) analysed the total ozone along the three latitudinal circles, 40, 50 and 60"N. They found that the effect was developed best near 50 N, was much less systematic near 60 N, and was negligible near 40 N; it occurred in winter, was much weaker in equinoctial periods, and was absent in summer. The effect was well-developed and statistically significant only for strong geomagnetic storms under high solar activity and the east phase of QBO. The effect is qualitatively consistent with storm-related changes in dynamics. It consists in ozone redistribution. The possible effect of solar flares on total ozone have not yet been studied. It is impossible to study effects of flare-enhanced solar UV-irradiance. First, at UV wavelengths in question the flare effect is weak, if detectable. Second, continuous total ozone measurements during flares at one place with a time resolution of a few minutes are not available. Thus, we concentrate on longer-term effects of flares on total ozone, e.g. through changes of dynamics. Alberca etal. (1996) found positive correlations between monthly values of total ozone and radio wave absorption in the lower ionosphere. Therefore, we investigate the possible effect of solar flares on the relationship between them. We do not study effects of solar flares on absorption. These effects (SWFs) are well known. 2. DATA The central European data (analysed also by Alberca et al., 1996), are analyzed in this paper. The data from two other regions, used by Alberca et al. (1996) - Bulgaria and Spain - cannot be used to analyze daily values because too many data are missing on the day-to-day time scale. The period was investigated. Altogether 114 events with good quality data were selected. They were all analyzed individually as case studies from both points of view, solar flare effect on total ozone and solar flare effect on the correlation between total ozone and absorption variations. The preliminary results based on a limited data sample (de la Moreno et al., 1997) and confirmed by the analysis of the 114 events with absorption at 6090, 1539 and 243 khz, indicate that some effects can be expected only for strong flares associated with strong sudden ionospheric disturbances (SIDs) and apparently correlating absorption only occurs at 1539 khz (closest to the site of ozone measurements). Some ozone data from the winter of 1989/1990 were used in Fig. 4. The homogenized Dobson total ozone data from Hradec Kralove (50.25 N, E; Vanidek, 1991) are used to represent ozone in central Europe. The radio wave absorption at 1539kHz (reflection point <p = 50.3 N, A= 11.8 E) is used as measured by the A3 method (oblique incidence on the ionosphere) and reduced to % = 15. Solar flares were selected according to their effects in the lower ionosphere, SIDs (information on flare-related enhancement of UV flux is not available). Data were taken from Solar-Geophysical Data of ERL/NOAA, Boulder. Only flares with SIDs of importance 3- and higher, i.e. mighty flares with very profound ionospheric effects, were taken into account. We found only ten such events with good quality ozone and absorption data for the period Five other events were selected in winter 1989/ Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998)
3 Do Solar Flares Affect Total Ozone? 3. RESULTS The data have been analyzed by the linear cross-correlation technique, and using the Fisher criterion with a reliability of 95%, to obtain the significance levels of correlations for different time lags between the absorption and ozone series. First we will present the results obtained for the three solar flares that occurred on 28/01/81, 8/02/81 and 19/08/81, which were accompanied by SIDs of importance 3, 3 and 3+, respectively. Figure 1 shows the evolution of the total ozone from Hradec Kralove for all three events. The vertical dotted lines represent the days when solar flares occurred. Some events, as that of 28/01/81, perhaps seem to indicate an apparent slight flare-related decrease of total ozone. However, when we compare all three events shown in Fig. 1, no evident and persistent flare effect on total ozone is found. Short-term changes of total ozone are substantially affected by meteorological changes. In the periods of 26/01-07/02 (event 28/01) and 03/02-16/02 (event 08/02), Hradec KrSlove was first located in the anticyclonic area both at the surface and at 500 hpa with a relatively weak circulation changing between coming from west (W) to coming from northeast (NE), i.e. with no southern component (27/01-02/02). Then it changed to a regime with everyday frontal passages and prevailingly cyclonic circulation from W to NW (04/02-11/2). This was followed by a period (12/02-16/02) of weaker circulation from W to NE in a less Fig. 1. Response of total ozone at Hradec Kralov6 to strong solar flares of 28 January, 8 February and 19 August 1981 (marked by dotted vertical lines). Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998) 535
4 D. Marin and J. Lastovicka developed pressure field. Thus the meteorological regime at surface, as well as at 500 hpa was relatively stable, and its effect on total ozone was less than is typical for winter. For the event of 19/08 (14/08-26/08), the tropospheric pressure field was rather undeveloped, circulation was from W-N, weak to medium; the 500 hpa level displayed almost permanently a medium wind from W, usually in the external part of a relatively weak low. Figure 2 presents the coefficients of absorption-ozone correlation with their significance bands, calculated for time-lags from -6 to +6 days, for all three events. No statistically significant relation between absorption and ozone variations can be found for any event and any time-lag,. Moreover, flares do not seem to reveal any detectable and persistent influence on cross-correlation coefficients. The above case studies indicate rather no longer-time effect of solar flares on total ozone and its relation to ionospheric radio wave absorption. Figure 3 shows the average effect of strong solar flares on total ozone and ozone-absorption cross correlations, obtained for the ten events studied by the overlapping epoch method. There is no detectable effect of strong solar flares in total ozone at Hradec Kra"love", particularly in comparison with the magnitude of the effects of strong geomagnetic storms (LaStovidka et al., 1992). There is evidently no significant cross-correlation between day-to-day values of the 1539 khz absorption and total ozone with any time-lag. Long-term correlation between absorption and total ozone, found by Alberca et al. (1996), seems to be developed best with a time-lag of 1-2 months, thus absence of day-to-day correlations does not contradict to the existence of delayed long-term correlation. Fig. 2. Cross correlations between the 1539 khz radio wave absorption and total ozone from Hradec Kralove; lag -6 to +6 days; band of 95% significance level is shown. 536 Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998)
5 Do Solar Flares Affect Total Ozone? Fig. 3. The ten-event average effect of strong solar flares in total ozone (upper panel) and the tenevent average cross correlation of the 1539 khz absorption with total ozone (lower panel). Effects of geomagnetic storms on total ozone in central Europe occur and are distinct only for strong storms in winter under high solar activity and the E-phase of QBO (E-QBO) (Lastovidka et al., 1992). Under these conditions all events reveal a similar effect in total ozone in central Europe. Consequently, it is necessary to check the possible influence of QBO on the effect of solar flares on total ozone. All the examined effects occurred under high solar activity conditions - the period of was the period of maximum of solar cycle 21. Two of the three events shown in Figs. 1 and 2 occurred in winter. However, they both occurred under W-QBO conditions, i.e. under conditions when according to LaStovidka et at. (1992) a significant effect of strong geomagnetic storms cannot occur. Figure 3 consists almost exclusively of events under W-QBO conditions due to much more data gaps for events under E-QBO conditions. Due to the missing data in the winter of 1979/1980, we had to select several events from another high solar activity/e-qbo winter, that of 1989/1990. Figure 4 shows the average effect of strong solar flares of 8 February 1980, 26 November 1989, 29 December 1989,20 January 1990,23 February 1990 and 28 February Again we do not see any effect, which can be attributed to flares, particularly when we consider the standard deviations of the data points shown. For instance, for key day (day 0) <r= 44 D.U., which is twice as much as the difference between the local peak values on days 0 and 2. Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998) 537
6 D. MarinandJ. LaStovic'ka Fig. 4. The six-event average effect of strong solar flares in total ozone under high solar activity/e-qbo conditions. Moreover, individual events provide quite a different pattern. Consequently, even under high solar activity/e-qbo conditions we do not find a detectable total ozone response to strong solar flares, contrary to the existence of such a response to strong geomagnetic storms. 4. CONCLUSION An analysis of the response of total ozone from Hradec Kra'love' (central Europe) to strong solar flares with profound ionospheric effects shows that there is no detectable effect of strong solar flares in total ozone. Such an effect has not been observed even under conditions when a remarkable response to strong geomagnetic storms has occurred (LaStovicka et al., 1992; Mich and LaStovidka, 1995). A similar analysis of correlation of total ozone with radio wave absorption in the lower ionosphere reveals no correlation on a day-to-day time scale and no effect of strong solar flares on such correlation. The existence of the long-term correlation of monthly average values (Alberca et al., 1996) does not contradict the absence of short-term correlation, because the former is expressed best with a time lag of 1-2 months, which is out of the time scale of day-to-day variations. Acknowledgement: The work of J.L. was supported by grant of the Grant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic No. A /1998. Manuscript received: 23 March 1998; Revisions accepted: 19 May Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998)
7 Do Solar Flares Affect Total Ozone? References Alberca L.F., Apostolov E., Gil M, Kazimirovsky E.S., LaStoviCka J., de la Morena B.A. and Pancheva D., 1996: The possible coupling of the stratosphere and lower ionosphere at middle latitudes. Adv. Space Res., 18, Brasseur G., 1993: The response of the middle atmosphere to long-term and short-term solar variability: a two-dimensional model. J. Geophys. Res., 98, Goldberg R.A., Baker D.N., Herrero F.A., Jackman C.H., Kanekal S. and Twigg P.A., 1995: Mesospheric heating during highly relativistic electron precipitation events. J. Geomagn. Geoelectf., 47, Hood L.L., 1997: The solar cycle variation of total ozone: dynamical forcing in the lower stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 102, Jackman C.H., Cerniglia M.C., Nielsen I.E., Allen D.J., Zawodny J.M., McPeters R.D., Douglas A.R., Rosenfield J.E. and Rood R.B., 1995: Two-dimensional and three-dimensional model simulations, measurements, and interpretation of the influence of the October 1989 solar proton events on the middle atmosphere. /. Geophys. Res., 100, LaStoviCka J., Bremer J. and Gil M., 1992: Ozone response to major geomagnetic storms. Ann. Geophysicae, 10, Mich P., 1994: Total ozone response to major geomagnetic storms during non-winter period. Studio geoph. et geod., 38, Mich P. and Lastovidka J., 1995: Total ozone response to major geomagnetic storms and changes in meteorological situations. Studia geoph. et geod., 39, de la Morena B.A., LaStoviCka J., Alberca L.F., Sole G., Marin D., Miro G., Vilaplana J.M., 1997: Effects of strong solar flares on the middle atmosphere at middle latitudes. Sec. Workshop IAGA/ICMA "Solar Activity Forcing of the Middle Atmosphere", Prague. Reagan J.B., Meyerott R.E., Nightingale R.W., Gunton R.C., Johnson R.G., Imhoff W.L., Heath D.F. and Krueger A.J., 1981: Effects of the August 1972 solar particle events on stratospheric ozone. J. Geophys. Res., 86, Shumilov O.I., Henriksen K., Raspopov O.M. and Kasatkina E.A., 1992: Arctic ozone abundance and solar proton events. Geoph. Res. Lett., 19, VanfCek K., 1991: Recalculated Total Ozone Data, Hradec Kralove, Czech Hydromet. Inst., Prague. Studia geoph. et geod. 42 (1998) 539
Total ozone decrease in the Arctic after REP events
 Ann. Geophysicae 18, 332±336 (2000) Ó EGS ± Springer-Verlag 2000 Total ozone decrease in the Arctic after REP events V. C. Roldugin 1, M. I. Beloglazov 1, G. F. Remenets 2 1 Polar Geophysical Institute,
Ann. Geophysicae 18, 332±336 (2000) Ó EGS ± Springer-Verlag 2000 Total ozone decrease in the Arctic after REP events V. C. Roldugin 1, M. I. Beloglazov 1, G. F. Remenets 2 1 Polar Geophysical Institute,
Long-term trends in the relation between daytime and nighttime values of fof2
 Ann. Geophys., 6, 1199 16, 8 www.ann-geophys.net/6/1199/8/ European Geosciences Union 8 Annales Geophysicae Long-term trends in the relation between daytime and nighttime values of fof A. D. Danilov Institute
Ann. Geophys., 6, 1199 16, 8 www.ann-geophys.net/6/1199/8/ European Geosciences Union 8 Annales Geophysicae Long-term trends in the relation between daytime and nighttime values of fof A. D. Danilov Institute
An Overview of the Impact. on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere
 An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation it ti on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere Charles Jackman NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD Aspen GCI Workshop 2010 Colorado June
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation it ti on the Stratosphere and Mesosphere Charles Jackman NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD Aspen GCI Workshop 2010 Colorado June
Examination of the solar cycle variation of fof2 for cycles 22 and 23
 Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics 70 (2008) 268 276 www.elsevier.com/locate/jastp Examination of the solar cycle variation of fof2 for cycles 22 and 23 A. O zgu c-, T. Atac-, R. Pektas-
Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics 70 (2008) 268 276 www.elsevier.com/locate/jastp Examination of the solar cycle variation of fof2 for cycles 22 and 23 A. O zgu c-, T. Atac-, R. Pektas-
Veretenenko S., Ogurtsov M.
 First VarSITI General Symposium Albena, Bulgaria 6-10 June 2016 Veretenenko S., Ogurtsov M. Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute Saint-Petersburg, Russia Correlation coefficient between globally averaged
First VarSITI General Symposium Albena, Bulgaria 6-10 June 2016 Veretenenko S., Ogurtsov M. Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute Saint-Petersburg, Russia Correlation coefficient between globally averaged
Differences in mid-latitude stratospheric winds between reanalysis data and versus radiosonde observations at Prague
 doi:10.5194/angeo-32-353-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Open Access Differences in mid-latitude stratospheric winds between reanalysis data and versus radiosonde observations
doi:10.5194/angeo-32-353-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Open Access Differences in mid-latitude stratospheric winds between reanalysis data and versus radiosonde observations
Ionization Rates for from Solar Proton Events
 Ionization Rates for 1963-2005 from Solar Proton Events Charles H. Jackman E-mail: Charles.H.Jackman@nasa.gov Phone: 301-614-6053 Code 613.3 Laboratory for Atmospheres NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Ionization Rates for 1963-2005 from Solar Proton Events Charles H. Jackman E-mail: Charles.H.Jackman@nasa.gov Phone: 301-614-6053 Code 613.3 Laboratory for Atmospheres NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure
 Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Mesospheric dynamical changes induced by the solar proton events in October November 2003
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L04812, doi:10.1029/2006gl028328, 2007 Mesospheric dynamical changes induced by the solar proton events in October November 2003 Charles
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L04812, doi:10.1029/2006gl028328, 2007 Mesospheric dynamical changes induced by the solar proton events in October November 2003 Charles
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF SOLAR PROTON FLUX INFLUENCE ON THERMODYNAMICS OF MIDDLE ATMOSPHERE IN THE NORTH HEMISPHERE
 Доклади на Българската академия на науките Comptes rendus de l Académie bulgare des Sciences Tome 67, No 1, 2014 EXPLORATIONS COSMIQUES STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF SOLAR PROTON FLUX INFLUENCE ON THERMODYNAMICS
Доклади на Българската академия на науките Comptes rendus de l Académie bulgare des Sciences Tome 67, No 1, 2014 EXPLORATIONS COSMIQUES STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF SOLAR PROTON FLUX INFLUENCE ON THERMODYNAMICS
P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES
 P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES Taehyoun Shim 1, Gyu-Ho Lim* 1 and Dong-In Lee 2 1 School of Earth and Environmental Sciences,
P4.2 THE THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND TIME EVOLUTION OF THE DECADAL VARIABILITY REVEALED IN ECMWF REANALYSES Taehyoun Shim 1, Gyu-Ho Lim* 1 and Dong-In Lee 2 1 School of Earth and Environmental Sciences,
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier
 Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
Meridional structure of the downwelling branch of the BDC Susann Tegtmeier Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel (GEOMAR), Germany SPARC Brewer-Dobson Circulation Workshop, Grindelwald, June 2012 no
DO STRATWARMS AFFECT 160M PROPAGATION? A Look at the North America to Europe Path
 DO STRATWARMS AFFECT 160M PROPAGATION? A Look at the North America to Europe Path by Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA (this article appeared in the January 1998 issue of The Low Band Monitor) Stratwarms (stratospheric
DO STRATWARMS AFFECT 160M PROPAGATION? A Look at the North America to Europe Path by Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA (this article appeared in the January 1998 issue of The Low Band Monitor) Stratwarms (stratospheric
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations. Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland
 EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
EPP contribution to (stratospheric and) tropospheric variations Annika Seppälä Finnish Meteorological Institute Academy of Finland A. Seppälä, HEPPA-SOLARIS Workshop, Boulder, Oct 0 So far... Energetic
Physical Model of Solar Activity Influence on Climate Characteristics of Troposphere
 Sun and Geosphere, 2009; 4(1): 25-30 ISSN 1819-0839 Physical Model of Solar Activity Influence on Climate Characteristics of Troposphere S.I. Molodykh, G.A. Zherebtsov, V.A. Kovalenko Institute of Solar-Terrestrial
Sun and Geosphere, 2009; 4(1): 25-30 ISSN 1819-0839 Physical Model of Solar Activity Influence on Climate Characteristics of Troposphere S.I. Molodykh, G.A. Zherebtsov, V.A. Kovalenko Institute of Solar-Terrestrial
Direct effects of particle precipitation and ion chemistry in the middle atmosphere
 Direct effects of particle precipitation and ion chemistry in the middle atmosphere P. T. Verronen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Earth Observation Helsinki, Finland Contents of presentation 1. Middle
Direct effects of particle precipitation and ion chemistry in the middle atmosphere P. T. Verronen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Earth Observation Helsinki, Finland Contents of presentation 1. Middle
2 Preliminary Results Achieved by the Meridian Project
 Space Science Activities in China cycle peak year ( ), magnetic storm activities increased significantly, the Meridian Project has repeatedly observed the responses of the space environment to solar storms
Space Science Activities in China cycle peak year ( ), magnetic storm activities increased significantly, the Meridian Project has repeatedly observed the responses of the space environment to solar storms
SOLAR ACTIVITY DEPENDENCE OF EFFECTIVE WINDS DERIVED FROM IONOSPHERIC DATAAT WUHAN
 Pergamon wwwelseviercom/locate/asi doi: 1,116/SO27-1177()678-l Available online at wwwsciencedirectcom SClENCE DIRECT SOLAR ACTIVITY DEPENDENCE OF EFFECTIVE WINDS DERIVED FROM IONOSPHERIC DATAAT WUHAN
Pergamon wwwelseviercom/locate/asi doi: 1,116/SO27-1177()678-l Available online at wwwsciencedirectcom SClENCE DIRECT SOLAR ACTIVITY DEPENDENCE OF EFFECTIVE WINDS DERIVED FROM IONOSPHERIC DATAAT WUHAN
EQUATORIAL ELECTROJET STRENGTH IN THE AFRICAN SECTOR DURING HIGH AND LOW SOLAR ACTIVITY YEARS
 SINET: ETHIOP. J. SCI., 26(1):77 81, 2003 Faculty of Science, Addis Ababa University, 2003 ISSN: 0379 2897 Short communication EQUATORIAL ELECTROJET STRENGTH IN THE AFRICAN SECTOR DURING HIGH AND LOW SOLAR
SINET: ETHIOP. J. SCI., 26(1):77 81, 2003 Faculty of Science, Addis Ababa University, 2003 ISSN: 0379 2897 Short communication EQUATORIAL ELECTROJET STRENGTH IN THE AFRICAN SECTOR DURING HIGH AND LOW SOLAR
SEASONAL AND ANNUAL TRENDS OF AUSTRALIAN MINIMUM/MAXIMUM DAILY TEMPERATURES DURING
 SEASONAL AND ANNUAL TRENDS OF AUSTRALIAN MINIMUM/MAXIMUM DAILY TEMPERATURES DURING 1856-2014 W. A. van Wijngaarden* and A. Mouraviev Physics Department, York University, Toronto, Ontario, Canada 1. INTRODUCTION
SEASONAL AND ANNUAL TRENDS OF AUSTRALIAN MINIMUM/MAXIMUM DAILY TEMPERATURES DURING 1856-2014 W. A. van Wijngaarden* and A. Mouraviev Physics Department, York University, Toronto, Ontario, Canada 1. INTRODUCTION
On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012273, 2009 On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009 K. Labitzke 1 and M. Kunze 1 Received 17 April 2009; revised 11 June 2009; accepted
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd012273, 2009 On the remarkable Arctic winter in 2008/2009 K. Labitzke 1 and M. Kunze 1 Received 17 April 2009; revised 11 June 2009; accepted
An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997
 San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Eugene C. Cordero April, 2002 An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997 Eugene C. Cordero, San
San Jose State University From the SelectedWorks of Eugene C. Cordero April, 2002 An Examination of Anomalously Low Column Ozone in the Southern Hemisphere Midlatitudes During 1997 Eugene C. Cordero, San
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere
 An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere Charles Jackman & Dean Pesnell NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD International Workshop
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere Charles Jackman & Dean Pesnell NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD International Workshop
INVESTIGATIONS OF THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIURNAL VARIATIONS OF GEOMAGNETIC FIELD
 Geologica Macedonica, Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 37 51 (2012) GEOME 2 ISSN 0352 1206 Manuscript received: May 6, 2012 UDC: 556.385 Accepted: October 10, 2012 Original scientific paper INVESTIGATIONS OF THE STRUCTURE
Geologica Macedonica, Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 37 51 (2012) GEOME 2 ISSN 0352 1206 Manuscript received: May 6, 2012 UDC: 556.385 Accepted: October 10, 2012 Original scientific paper INVESTIGATIONS OF THE STRUCTURE
The Atmosphere. Importance of our. 4 Layers of the Atmosphere. Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate. What makes up the atmosphere?
 The Atmosphere Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate Where is the atmosphere? Everywhere! Completely surrounds Earth February 20, 2010 What makes up the atmosphere? Argon Inert gas 1% Variable
The Atmosphere Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate Where is the atmosphere? Everywhere! Completely surrounds Earth February 20, 2010 What makes up the atmosphere? Argon Inert gas 1% Variable
GPC Exeter forecast for winter Crown copyright Met Office
 GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
GPC Exeter forecast for winter 2015-2016 Global Seasonal Forecast System version 5 (GloSea5) ensemble prediction system the source for Met Office monthly and seasonal forecasts uses a coupled model (atmosphere
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE. V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva
 HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
HEIGHT-LATITUDE STRUCTURE OF PLANETARY WAVES IN THE STRATOSPHERE AND TROPOSPHERE INTRODUCTION V. Guryanov, A. Fahrutdinova, S. Yurtaeva Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia When constructing empirical
Day-to-day variations of migrating semidiurnal tide in the mesosphere and thermosphere
 Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, /3, +33,*1,,**0,**0 National Institute of Polar Research Scientific paper Day-to-day variations of migrating semidiurnal tide in the mesosphere and thermosphere
Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, /3, +33,*1,,**0,**0 National Institute of Polar Research Scientific paper Day-to-day variations of migrating semidiurnal tide in the mesosphere and thermosphere
TOTAL COLUMN OZONE AND SOLAR UV-B ERYTHEMAL IRRADIANCE OVER KISHINEV, MOLDOVA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 8, No 3, pp 204-209, 2006 Copyright 2006 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved TOTAL COLUMN OZONE AND SOLAR UV-B ERYTHEMAL IRRADIANCE OVER KISHINEV, MOLDOVA A.A. ACULININ
Global NEST Journal, Vol 8, No 3, pp 204-209, 2006 Copyright 2006 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved TOTAL COLUMN OZONE AND SOLAR UV-B ERYTHEMAL IRRADIANCE OVER KISHINEV, MOLDOVA A.A. ACULININ
The role of teleconnections in extreme (high and low) precipitation events: The case of the Mediterranean region
 European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2013 Vienna, Austria, 7 12 April 2013 Session HS7.5/NP8.4: Hydroclimatic Stochastics The role of teleconnections in extreme (high and low) events: The case of
European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2013 Vienna, Austria, 7 12 April 2013 Session HS7.5/NP8.4: Hydroclimatic Stochastics The role of teleconnections in extreme (high and low) events: The case of
The Effect of Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Middle Atmosphere: a study using the Canadian Middle Atmosphere Model
 The Effect of Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Middle Atmosphere: a study using the Canadian Middle Atmosphere Model A web of theory has been spun around the Sun's climate influence BBC News, Nov 14, 2007 Robert
The Effect of Galactic Cosmic Rays on the Middle Atmosphere: a study using the Canadian Middle Atmosphere Model A web of theory has been spun around the Sun's climate influence BBC News, Nov 14, 2007 Robert
Enhancement of stratospheric aerosols after solar proton event
 Ann. Geophysicae 14, 1119 1123 (1996) EGS Springer-Verlag 1996 Enhancement of stratospheric aerosols after solar proton event O. I. Shumilov, E. A. Kasatkina, K. Henriksen *, E. V. Vashenyuk High-Latitude
Ann. Geophysicae 14, 1119 1123 (1996) EGS Springer-Verlag 1996 Enhancement of stratospheric aerosols after solar proton event O. I. Shumilov, E. A. Kasatkina, K. Henriksen *, E. V. Vashenyuk High-Latitude
The Atmospheric Circulation
 The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
The Atmospheric Circulation Vertical structure of the Atmosphere http://www.uwsp.edu/geo/faculty/ritter/geog101/textbook/atmosphere/atmospheric_structure.html The global heat engine [courtesy Kevin Trenberth,
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole
 SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
SC-WACCM! and! Problems with Specifying the Ozone Hole R. Neely III, K. Smith2, D. Marsh,L. Polvani2 NCAR, 2Columbia Thanks to: Mike Mills, Francis Vitt and Sean Santos Motivation To design a stratosphere-resolving
The influence of geomagnetic activity on the subauroral mesopause temperature over Yakutia
 on the subauroral mesopause temperature over Yakutia Ammosova Anastasiia 1 E-mail: ammosovaam@mail.ru Gavrilyeva Galina E-mail: gagavrilyeva@ikfia.ysn.ru Ammosov Petr E-mail: ammosov@ikfia.ysn.ru Koltovskoi
on the subauroral mesopause temperature over Yakutia Ammosova Anastasiia 1 E-mail: ammosovaam@mail.ru Gavrilyeva Galina E-mail: gagavrilyeva@ikfia.ysn.ru Ammosov Petr E-mail: ammosov@ikfia.ysn.ru Koltovskoi
Signatures of Geomagnetic Storms and Coronal Mass Ejections on Electron and Ion Temperatures At Low Latitude Upper Ionosphere
 International Journal of Physics and Applications. ISSN 0974-3103 Volume 7, Number 1 (2015), pp. 43-48 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Signatures of Geomagnetic Storms
International Journal of Physics and Applications. ISSN 0974-3103 Volume 7, Number 1 (2015), pp. 43-48 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Signatures of Geomagnetic Storms
CTU Presents. The Fitful Rise of Solar Cycle 24 What it Means in the Coming Year. Frank Donovan W3LPL
 CTU Presents The Fitful Rise of Solar Cycle 24 What it Means in the Coming Year Frank Donovan W3LPL Introduction This presentation focuses on: The four major fall and winter DX contests: CQ WW SSB and
CTU Presents The Fitful Rise of Solar Cycle 24 What it Means in the Coming Year Frank Donovan W3LPL Introduction This presentation focuses on: The four major fall and winter DX contests: CQ WW SSB and
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming?
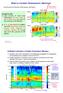 What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
What is a Sudden Stratospheric Warming? rapid increase of T at h~32 km from Evelyn De Wachter (PhD thesis, IAP-Bern):!"#$%&'()*+,-*../0** DA /%:,'$,&?/.%0.$ 34$ N3&%8$ 9.%&$ 1.9:./%1/.$ 34$ 93/.$ 17%&$
THERMOSPHERIC TIDES DURING THERMOSPHERE MAPPING STUDY PERIODS
 Adv. Space Res. Vot. 7, No. 10, pp. (10)277 (10)283, 1987 0273 1177/87 $0.t~+.50 Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved. Copyright 1987 COSPAR THERMOSPHERIC TIDES DURING THERMOSPHERE MAPPING STUDY
Adv. Space Res. Vot. 7, No. 10, pp. (10)277 (10)283, 1987 0273 1177/87 $0.t~+.50 Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved. Copyright 1987 COSPAR THERMOSPHERIC TIDES DURING THERMOSPHERE MAPPING STUDY
Lecture 8. Monsoons and the seasonal variation of tropical circulation and rainfall
 Lecture 8 Monsoons and the seasonal variation of tropical circulation and rainfall According to the second hypothesis, the monsoon is a manifestation of the seasonal variation of the tropical circulation
Lecture 8 Monsoons and the seasonal variation of tropical circulation and rainfall According to the second hypothesis, the monsoon is a manifestation of the seasonal variation of the tropical circulation
State of polar boreal winter stratosphere ( ) The middle and upper regions of the atmosphere are now recognized as important and
 CHAPTER 3 State of polar boreal winter stratosphere (1993-2009) 3.1 Introduction The middle and upper regions of the atmosphere are now recognized as important and sensitive indicators of the polar middle
CHAPTER 3 State of polar boreal winter stratosphere (1993-2009) 3.1 Introduction The middle and upper regions of the atmosphere are now recognized as important and sensitive indicators of the polar middle
TRANSPORT STUDIES IN THE SUMMER STRATOSPHERE 2003 USING MIPAS OBSERVATIONS
 TRANSPORT STUDIES IN THE SUMMER STRATOSPHERE 2003 USING MIPAS OBSERVATIONS Y.J. Orsolini (2), W.A. Lahoz (1), A.J. Geer (1) (1) Data Assimilation Research Centre, DARC, University of Reading, UK (2) Norwegian
TRANSPORT STUDIES IN THE SUMMER STRATOSPHERE 2003 USING MIPAS OBSERVATIONS Y.J. Orsolini (2), W.A. Lahoz (1), A.J. Geer (1) (1) Data Assimilation Research Centre, DARC, University of Reading, UK (2) Norwegian
DETECTION OF THE WAVE-LIKE STRUCTURES IN THE F-REGION ELECTRON DENSITY: TWO STATION MEASUREMENTS ABSTRACT
 DETECTION OF THE WAVE-LIKE STRUCTURES IN THE F-REGION ELECTRON DENSITY: TWO STATION MEASUREMENTS P. ŠAULI 1, P. ABRY 2, D. ALTADILL 3, J. BOŠKA 1 1 Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Acad. Sci. Czech Republic,
DETECTION OF THE WAVE-LIKE STRUCTURES IN THE F-REGION ELECTRON DENSITY: TWO STATION MEASUREMENTS P. ŠAULI 1, P. ABRY 2, D. ALTADILL 3, J. BOŠKA 1 1 Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Acad. Sci. Czech Republic,
D-region electron density and effective recombination coefficients during twilight experimental data and modelling during solar proton events
 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae D-region electron density and effective recombination coefficients during twilight experimental
Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae D-region electron density and effective recombination coefficients during twilight experimental
Analysis of gross alpha, gross beta activities and beryllium-7 concentrations in surface air: their variation and statistical prediction model
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2006; 4 (3): 155-159 Analysis of gross alpha, gross beta activities and beryllium-7 concentrations in surface air: their variation and statistical prediction model F.Arkian 1*, M.
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2006; 4 (3): 155-159 Analysis of gross alpha, gross beta activities and beryllium-7 concentrations in surface air: their variation and statistical prediction model F.Arkian 1*, M.
Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change
 Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change Project Representative Tatsushi
Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Development of a Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Land General Circulation Model (GCM) at the Frontier Research Center for Global Change Project Representative Tatsushi
Enhancement of High Energy Electron Fluxes and Variation of Atmospheric Electric Field in the Antarctic Region
 0254-6124/2016/36(1)-040 09 Chin. J. Space Sci. Ξ ΛΠΠ LI Renkang, CHEN Tao, LUO Jing, ZHOU Limin, HE Zhaohai, WANG Chunqin, SUN Yueqiang. Enhancement of high energy electron fluxes and variation of atmospheric
0254-6124/2016/36(1)-040 09 Chin. J. Space Sci. Ξ ΛΠΠ LI Renkang, CHEN Tao, LUO Jing, ZHOU Limin, HE Zhaohai, WANG Chunqin, SUN Yueqiang. Enhancement of high energy electron fluxes and variation of atmospheric
Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere Coupling and Their Potential Use in Seasonal to Decadal Climate Predictions
 US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Test Bed Joint Seminar Series NCEP, Camp Springs, Maryland, 22 June 2011 Eurasian Snow Cover Variability and Links with Stratosphere-Troposphere
THE EFFECTS OF THERMAL AND WIND FIELDS IN THE PROPAGATION OF INFRASONIC WAVES IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 THE EFFECTS OF THERMAL AND WIND FIELDS IN THE PROPAGATION OF INFRASONIC WAVES IN THE ATMOSPHERE Omar Marcillo Sound waves traveling at frequencies between 0.05 and 20 Hertz are called infrasound waves.
THE EFFECTS OF THERMAL AND WIND FIELDS IN THE PROPAGATION OF INFRASONIC WAVES IN THE ATMOSPHERE Omar Marcillo Sound waves traveling at frequencies between 0.05 and 20 Hertz are called infrasound waves.
Solar Flare Durations
 Solar Flare Durations Whitham D. Reeve 1. Introduction Scientific investigation of solar flares is an ongoing pursuit by researchers around the world. Flares are described by their intensity, duration
Solar Flare Durations Whitham D. Reeve 1. Introduction Scientific investigation of solar flares is an ongoing pursuit by researchers around the world. Flares are described by their intensity, duration
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
Characteristics of the storm-induced big bubbles (SIBBs)
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006ja011743, 2006 Characteristics of the storm-induced big bubbles (SIBBs) Hyosub Kil, 1 Larry J. Paxton, 1 Shin-Yi Su, 2 Yongliang Zhang, 1 and
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2006ja011743, 2006 Characteristics of the storm-induced big bubbles (SIBBs) Hyosub Kil, 1 Larry J. Paxton, 1 Shin-Yi Su, 2 Yongliang Zhang, 1 and
AGU Chapman Conference on The Role of the Stratosphere in Climate and Climate Change in Santorini, Greece, on 28th September, 2007
 AGU Chapman Conference on The Role of the Stratosphere in Climate and Climate Change in Santorini, Greece, on 28th September, 2007 Parameter Sweep Experiments on the Remote Influences of the Equatorial
AGU Chapman Conference on The Role of the Stratosphere in Climate and Climate Change in Santorini, Greece, on 28th September, 2007 Parameter Sweep Experiments on the Remote Influences of the Equatorial
Introduction to Space Weather and Propagation
 Introduction to Space Weather and Propagation Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA ARRL Vice Director, Central Division k9la@arrl.net https://k9la.us K9LA 1 What Is Space Weather? Space weather is the quiet Sun Electromagnetic
Introduction to Space Weather and Propagation Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA ARRL Vice Director, Central Division k9la@arrl.net https://k9la.us K9LA 1 What Is Space Weather? Space weather is the quiet Sun Electromagnetic
UV RADIATION IN THE SOUTHERN SEAS IN SUMMER 2000 Gerd Wendler and Brian Hartmann Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska 99775
 P3.2 UV RADIATION IN THE SOUTHERN SEAS IN SUMMER 2000 Gerd Wendler and Brian Hartmann Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska 99775 Abstract During a cruise on the USCGC POLAR SEA
P3.2 UV RADIATION IN THE SOUTHERN SEAS IN SUMMER 2000 Gerd Wendler and Brian Hartmann Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska 99775 Abstract During a cruise on the USCGC POLAR SEA
TIME SERIES COMPARISONS OF MIPAS LEVEL 2 NEAR REAL TIME PRODUCTS WITH CLIMATOLOGY
 TIME SERIES COMPARISONS OF MIPAS LEVEL 2 NEAR REAL TIME PRODUCTS WITH CLIMATOLOGY Vivienne Payne, Anu Dudhia, and Chiara Piccolo Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Department of Physics, University
TIME SERIES COMPARISONS OF MIPAS LEVEL 2 NEAR REAL TIME PRODUCTS WITH CLIMATOLOGY Vivienne Payne, Anu Dudhia, and Chiara Piccolo Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics, Department of Physics, University
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 21 Dec 2006
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Modeling atmospheric effects of the September 1859 Solar Flare B. C. Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy, Washburn University, Topeka,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Modeling atmospheric effects of the September 1859 Solar Flare B. C. Thomas Department of Physics and Astronomy, Washburn University, Topeka,
Stratospheric vacillations, QBO, and solar activity
 Summary Stratospheric vacillations, QBO, and solar activity Kanukhina A., Jacobi C., Pogoreltsev A. The aim of the study is to compare planetary wave characteristics derived from NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data
Summary Stratospheric vacillations, QBO, and solar activity Kanukhina A., Jacobi C., Pogoreltsev A. The aim of the study is to compare planetary wave characteristics derived from NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Homogenization of the total ozone amount series derived from NOAA/TOVS data
 Homogenization of the total ozone amount series derived from NOAA/TOVS data B.Lapeta 1, I.Dyras 1, Z.Ustrnul 2 1 Institute of Meteorology and Water Management, ul. Borowego 14, 30-215 Krakow, Poland e-mail:
Homogenization of the total ozone amount series derived from NOAA/TOVS data B.Lapeta 1, I.Dyras 1, Z.Ustrnul 2 1 Institute of Meteorology and Water Management, ul. Borowego 14, 30-215 Krakow, Poland e-mail:
Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of
 Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
Article Atmospheric Science September 2013 Vol.58 No.25: 3155 3160 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5945-5 Extremely cold and persistent stratospheric Arctic vortex in the winter of 2010 2011 HU YongYun 1* & XIA
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
New average divisional daily temperature normals, shown in Table 2, range. Lawrence A. Schaal
 The New Decade and Changing Normals of Temperature and Precipitation in Indiana Lawrence A. Schaal Department of Agronomy Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907 Introduction "Normals" of temperature
The New Decade and Changing Normals of Temperature and Precipitation in Indiana Lawrence A. Schaal Department of Agronomy Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907 Introduction "Normals" of temperature
Comparative Analysis of Total Ozone Data from Satellite EPTOMS and Ground-Based Dobson Instrument at Lagos-Nigeria (pp )
 Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Science 2(3), May, 2011. ISSN : 2141-8225 Global Research Publishing, 2011. Comparative Analysis of Total Ozone Data from Satellite EPTOMS and Ground-Based
Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Science 2(3), May, 2011. ISSN : 2141-8225 Global Research Publishing, 2011. Comparative Analysis of Total Ozone Data from Satellite EPTOMS and Ground-Based
Bugs in JRA-55 snow depth analysis
 14 December 2015 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency Bugs in JRA-55 snow depth analysis Bugs were recently found in the snow depth analysis (i.e., the snow depth data generation process)
14 December 2015 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency Bugs in JRA-55 snow depth analysis Bugs were recently found in the snow depth analysis (i.e., the snow depth data generation process)
Simulated Radiances for OMI
 Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Simulated Radiances for OMI document: KNMI-OMI-2000-004 version: 1.0 date: 11 February 2000 author: J.P. Veefkind approved: G.H.J. van den Oord checked: J. de Haan Index 0. Abstract 1. Introduction 2.
Is Antarctic climate most sensitive to ozone depletion in the middle or lower stratosphere?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L22812, doi:10.1029/2007gl031238, 2007 Is Antarctic climate most sensitive to ozone depletion in the middle or lower stratosphere? S.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L22812, doi:10.1029/2007gl031238, 2007 Is Antarctic climate most sensitive to ozone depletion in the middle or lower stratosphere? S.
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere
 ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
Influences of the 11-year sunspot cycle on the stratosphere and the importance of the QBO
 Influences of the 11-year sunspot cycle on the stratosphere and the importance of the QBO Karin Labitzke, Institute for Meteorology, F.U. Berlin Germany (Labitzke and van Loon, numerous papers, 1987 2006)
Influences of the 11-year sunspot cycle on the stratosphere and the importance of the QBO Karin Labitzke, Institute for Meteorology, F.U. Berlin Germany (Labitzke and van Loon, numerous papers, 1987 2006)
P2.14 CLOUD TO GROUND FLASHES IN MEXICO AND ADJACENT OCEANIC AREAS: A PRELIMINARY STUDY USING DATA FROM THE WWLL NETWORK
 P2.14 CLOUD TO GROUND FLASHES IN MEXICO AND ADJACENT OCEANIC AREAS: A PRELIMINARY STUDY USING DATA FROM THE WWLL NETWORK G.B. Raga and Olivia Rodríguez* Centro de Ciencias de la Atmósfera, UNAM 1. INTRODUCTION
P2.14 CLOUD TO GROUND FLASHES IN MEXICO AND ADJACENT OCEANIC AREAS: A PRELIMINARY STUDY USING DATA FROM THE WWLL NETWORK G.B. Raga and Olivia Rodríguez* Centro de Ciencias de la Atmósfera, UNAM 1. INTRODUCTION
ISSI Meeting - Bern, Switzerland, March Laboratory for Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamiics
 ISSI Meeting - Bern, Switzerland, 23-28 March 214 3D simulations of atmospheric response caused by precipitating electrons and solar protons at both polar regions induced by geomagnetic storms Alexei Krivolutsky
ISSI Meeting - Bern, Switzerland, 23-28 March 214 3D simulations of atmospheric response caused by precipitating electrons and solar protons at both polar regions induced by geomagnetic storms Alexei Krivolutsky
Influence of solar activity on the occurrence of weather types over Europe from 1763 to 2009
 Influence of solar activity on the occurrence of weather types over Europe from 1763 to 2009 05.10.2016 SCOSTEP Workshop Mikhaël Schwander & Stefan Brönnimann Oeschger Centre for Climate Change Research
Influence of solar activity on the occurrence of weather types over Europe from 1763 to 2009 05.10.2016 SCOSTEP Workshop Mikhaël Schwander & Stefan Brönnimann Oeschger Centre for Climate Change Research
General Circulation of Basic Atmospheric Parameters over a Low Latitude Station (Hyderabad)
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 7, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. - Jun. 2015), PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org General Circulation of Basic Atmospheric Parameters over a Low
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 7, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. - Jun. 2015), PP 01-05 www.iosrjournals.org General Circulation of Basic Atmospheric Parameters over a Low
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate
 The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate The Stratospheric Link Between the Sun and Climate Mark P. Baldwin Northwest Research Associates, USA SORCE, 27 October 2004 Overview Climatology of the
Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring
 Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring U. Langematz and M. Kunze Abstract Short- and long-term changes in the intensity and persistence of the Arctic and Antarctic stratospheric
Dynamical Changes in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere During Spring U. Langematz and M. Kunze Abstract Short- and long-term changes in the intensity and persistence of the Arctic and Antarctic stratospheric
Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models
 Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models Alexey Karpechko Finnish Meteorological Institute with contributions from A. Charlton-Perez, N. Tyrrell, M. Balmaseda, F.
Predictability of Sudden Stratospheric Warmings in sub-seasonal forecast models Alexey Karpechko Finnish Meteorological Institute with contributions from A. Charlton-Perez, N. Tyrrell, M. Balmaseda, F.
Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and Production Association "Typhoon" 4 Pobedy Street, , Obninsk, Kaluga Region, Russia.
 DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
Influences of the 11-year sunspot cycle on the stratosphere and the importance of the QBO
 (Solar Variability, Earth s Climate and the Space Environment; Bozeman, Montana, June 2008) Influences of the 11-year sunspot cycle on the stratosphere and the importance of the QBO Karin Labitzke, Institute
(Solar Variability, Earth s Climate and the Space Environment; Bozeman, Montana, June 2008) Influences of the 11-year sunspot cycle on the stratosphere and the importance of the QBO Karin Labitzke, Institute
Verification of Short-Term Predictions of Solar Soft X-ray Bursts for the Maximum Phase ( ) of Solar Cycle 23
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 3 (2003), No. 6, 563 568 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Verification of Short-Term Predictions of Solar
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 3 (2003), No. 6, 563 568 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Verification of Short-Term Predictions of Solar
Understanding Solar Indices
 Understanding Solar Indices By Ken Larson KJ6RZ Long distance HF radio communications is made possible by a region of charged particles in the Earth s upper atmosphere, 30 to 200 miles above the Earth
Understanding Solar Indices By Ken Larson KJ6RZ Long distance HF radio communications is made possible by a region of charged particles in the Earth s upper atmosphere, 30 to 200 miles above the Earth
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed
 Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051977, 2012 The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle Harry van Loon 1,2 and Gerald A. Meehl 1 Received 9 April 2012;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051977, 2012 The Indian summer monsoon during peaks in the 11 year sunspot cycle Harry van Loon 1,2 and Gerald A. Meehl 1 Received 9 April 2012;
Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling -
 Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling - Yvan J. Orsolini NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research and Birkeland
Coupling of the polar stratosphere and mesosphere during stratospheric sudden warmings - Relevance for solar-terrestrial coupling - Yvan J. Orsolini NILU - Norwegian Institute for Air Research and Birkeland
In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. as waves. thermosphere
 Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. layers of the atmosphere 2. radiation 3. conduction 4. convection 5.
Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. layers of the atmosphere 2. radiation 3. conduction 4. convection 5.
11-year solar cycle Mechanisms and Modelling in the Stratosphere and Troposphere
 11-year solar cycle Mechanisms and Modelling in the Stratosphere and Troposphere Lesley Gray University of Reading U.K. 1. Overview of Gray et al. 2010, Solar Influence on Climate, Rev. Geophys. (in press).
11-year solar cycle Mechanisms and Modelling in the Stratosphere and Troposphere Lesley Gray University of Reading U.K. 1. Overview of Gray et al. 2010, Solar Influence on Climate, Rev. Geophys. (in press).
Researcher. Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences. University of Wisconsin-Madison W. Dayton Street, Madison, WI 53706
 Researcher Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin-Madison 1225 W. Dayton Street, Madison, WI 53706 http://www.aos.wisc.edu/~meteor75 rowe1@wisc.edu PUBLICATIONS Rowe, S.
Researcher Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences University of Wisconsin-Madison 1225 W. Dayton Street, Madison, WI 53706 http://www.aos.wisc.edu/~meteor75 rowe1@wisc.edu PUBLICATIONS Rowe, S.
Dynamical. regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event)
 Dynamical Coupling between high and low latitude regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event) Vinay Kumar 1,S. K. Dhaka 1,R. K. Choudhary 2,Shu-Peng Ho 3,M. Takahashi
Dynamical Coupling between high and low latitude regions during sudden stratospheric warming event (Case study of 2009 and 2013 event) Vinay Kumar 1,S. K. Dhaka 1,R. K. Choudhary 2,Shu-Peng Ho 3,M. Takahashi
Atmospheric impact of the Carrington event solar protons
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010702, 2008 Atmospheric impact of the Carrington event solar protons Craig J. Rodger, 1 Pekka T. Verronen, 2 Mark A. Clilverd, 3 Annika Seppälä,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010702, 2008 Atmospheric impact of the Carrington event solar protons Craig J. Rodger, 1 Pekka T. Verronen, 2 Mark A. Clilverd, 3 Annika Seppälä,
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007
 The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The feature of atmospheric circulation in the extremely warm winter 2006/2007 Hiroshi Hasegawa 1, Yayoi Harada 1, Hiroshi Nakamigawa 1, Atsushi Goto 1 1 Climate Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological
The Climate of Texas County
 The Climate of Texas County Texas County is part of the Western High Plains in the north and west and the Southwestern Tablelands in the east. The Western High Plains are characterized by abundant cropland
The Climate of Texas County Texas County is part of the Western High Plains in the north and west and the Southwestern Tablelands in the east. The Western High Plains are characterized by abundant cropland
Research Institute of Atmospherics, Nagoya University, Toyokawa, Aichi 442, Japan. (Received August 20, 1982; Revised February 2, 1983)
 J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 35, 29-38, 1983 Recent Measurements of Electrical Conductivity and Ion Pair Production Rate, and the Ion-Ion Recombination Coefficient Derived from Them in the Lower Stratosphere
J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 35, 29-38, 1983 Recent Measurements of Electrical Conductivity and Ion Pair Production Rate, and the Ion-Ion Recombination Coefficient Derived from Them in the Lower Stratosphere
V.L.F. Emissions and Geomagnetic Disturbances at the Auroral Zone
 V.L.F. Emissions and Geomagnetic Disturbances at the Auroral Zone By Hachiroe ToKUDA Geophysical Institute, Kyoto University (Read, November 22, 1961; Received Feb. 28, 1962) Abstract Some studies of the
V.L.F. Emissions and Geomagnetic Disturbances at the Auroral Zone By Hachiroe ToKUDA Geophysical Institute, Kyoto University (Read, November 22, 1961; Received Feb. 28, 1962) Abstract Some studies of the
The Climate of Seminole County
 The Climate of Seminole County Seminole County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
The Climate of Seminole County Seminole County is part of the Crosstimbers. This region is a transition region from the Central Great Plains to the more irregular terrain of southeastern Oklahoma. Average
The Meteorological Observatory from Neumayer Gert König-Langlo, Bernd Loose Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Bremerhaven, Germany
 The Meteorological Observatory from Neumayer Gert König-Langlo, Bernd Loose Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Bremerhaven, Germany History of Neumayer In March 1981, the Georg von Neumayer Station (70 37 S, 8 22
The Meteorological Observatory from Neumayer Gert König-Langlo, Bernd Loose Alfred-Wegener-Institut, Bremerhaven, Germany History of Neumayer In March 1981, the Georg von Neumayer Station (70 37 S, 8 22
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere?
 What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
What kind of stratospheric sudden warming propagates to the troposphere? Ken I. Nakagawa 1, and Koji Yamazaki 2 1 Sapporo District Meteorological Observatory, Japan Meteorological Agency Kita-2, Nishi-18,
Effect of Solar Activity on the Polar-night Jet Oscillation in the Northern and Southern Hemisphere Winter
 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 80, No. 4B, pp. 973--984, 2002 973 Effect of Solar Activity on the Polar-night Jet Oscillation in the Northern and Southern Hemisphere Winter Yuhji
Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Vol. 80, No. 4B, pp. 973--984, 2002 973 Effect of Solar Activity on the Polar-night Jet Oscillation in the Northern and Southern Hemisphere Winter Yuhji
Study of Solar Proton Event Observed using Riometers
 Proceedings of the National Symposium on Current trends in Atmospheric Research including Communication And Navigation aspects (CARCAN-), Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, A.P. December
Proceedings of the National Symposium on Current trends in Atmospheric Research including Communication And Navigation aspects (CARCAN-), Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, A.P. December
IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS. D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea SYNOPSIS
 IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea Emeritus at AFRL (RVBXS), Bedford, MA, 01731, USA SYNOPSIS The endothermic chemical reaction
IMPULSIVE NITRATE DEPOSITION EVENTS IN POLAR ICE THE RESULT OF SOLAR PROTON EVENTS D. F. Smart and M. A. Shea Emeritus at AFRL (RVBXS), Bedford, MA, 01731, USA SYNOPSIS The endothermic chemical reaction
