Turbulence in Jupiter s Clouds
|
|
|
- Dwain Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Turbulence in Jupiter s Clouds N. Barrado-Izagirre, S. Pérez-Hoyos, and A. Sánchez-Lavega Abstract We have studied the spatial distribution of Jupiter s higher clouds in order to characterize the turbulent regime and the presence of waves in this planet s atmosphere. We have used images from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) 1995 s archive and from Cassini s ISS camera during its Jupiter fly-by in its way to Saturn in 2000 in three wavelengths: near infrared ( 940 nm), blue ( 430 nm) and ultraviolet ( 260 nm). These images were cylindrically projected and composed to obtain complete planispheres of Jupiter that cover the latitudinal range from 60 N to 60 S. When applying the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to each latitude reflectivity scan, we obtain brightness power spectra and periodograms that show the presence of wavy phenomena. From the spectra we study the decay of the slopes and their possible correlation with the underlying turbulent regime. We compare the turbulent structure of Jupiter s clouds with the dynamic structure characterized by the latitudinally alternating zonal wind regime (East-West) and with the meridional wind shear. 1 Wave Search Jupiter s atmosphere shows plenty of wavy and periodic features. Using a Lomb- Scargle technique we obtain a periodogram for each latitude s brightness scan that allows us to construct periodogram maps as those shown Fig. 1. Looking through the maps we found some periodic phenomena at different latitudes. We retrieve the latitudinal location and dominant wavenumber for the most strongly contributing periodic phenomena. Contrasting them in the planispheres we verify their existence avoiding possible artifacts on the image. Although there are waves in many latitudes, the strongest ones are located in the equatorial zone. N. Barrado-Izagirre, S. Pérez-Hoyos and A. Sánchez-Lavega Universidad del Pais Vasco, Alda. Urkijo s/n, Bilbao, naiara.barrado@ehu.es 1
2 2 N. Barrado-Izagirre, S. Pérez-Hoyos, and A. Sánchez-Lavega Fig. 1 Reflectivity NIR maps or planispheres in the left and periodogram maps on the right. Top figure constructed with HST images and bottom with Cassini ones. 2 Power Spectra Analysis The Fast Fourier Transform applied to a given brightness scan allows a one dimensional study of the power spectra. This can be performed either in the meridional and in the zonal directions. Meridional Analysis For the meridional analysis we take the zonal wind profile and the averaged North- South reflectivity profile and apply the FFT but from North to South. We compare the spectral decay obtained from both profiles in each wavelength. Obtained slopes are very similar in the near infrared and in the blue, but not in the case of the ultraviolet as shown in the Fig. 2. This figure uses Cassini s data it was also done for HST. All the results are summarized on Table 1. This analysis is in good agreement with previous theoretical models for terrestrial oceans and the atmospheres of the giant planets, as previously reported by [1], [2] and [3]. Zonal Analysis Most of the retrieved power spectra in the zonal analysis have two slope regimes, n 1 and n 2, separated at a turning point k I. We have selected three integration criteria
3 Turbulence in Jupiter s Clouds 3 Table 1 Power spectra slopes for meridional scans Profile Observations Near Infrared Blue Ultraviolet Zonal Wind HST -4.1±0.5 Cassini -4.6± ±0.4 Meridional Wind Shear HST -3.7±0.4 Cassini -4.2± ±0.5 Albedo HST -3.9± ± ±0.3 Cassini -4.1± ± ±0.2 Fig. 2 Top panels show the wind profiles and the averaged brightness profiles for the near infrared (NIR) and the ultraviolet (UV). Bottom ones show the power spectrum of each profile and the slope value. depending on wind direction (eastward or westward), local vorticity (cyclonic or anticyclonic) and brightness (dark belts or bright zones) to study the possible correlation of the spectral slopes with these physical factors as shown in Fig. 3 for the wind direction case. We obtain two slopes (n 1 and n 2 ) for each grey or white zone. This figure show results from NIR images but we have developed the same analysis for blue and ultraviolet wavelength images. It is noticeable that the value of the slopes is not correlated with these physical parameters; mean values of n 1 and n 2 are very similar following any criteria (n 1 = -1.3 ± 0.4 for wavenumbers between 10
4 4 N. Barrado-Izagirre, S. Pérez-Hoyos, and A. Sánchez-Lavega and 80 and n 2 = -2.5 ± 0.7 between 80 and 150 for near infrared and blue and n 1 = 1.9 ± 0.4 and n 2 = -0.7 ± 0.4 for ultraviolet) but they seem to be latitude dependent. Fig. 3 Left panel represents Jupiter s wind profile with the integration zones in grey and white. Center and right panel show the derived values of n 1 and n 2 for each zone. 3 Power Spectra Interpretation and Conclusions In the meridional direction resulting slopes are almost the same for both the zonal wind speeds and mean albedo and they are similar to those predicted by some previous theoretical models of turbulence. In the zonal direction, when comparing our results with previous works for kinetic energy [5] and for cloud opacity [6], [7] and with 2D and 3D turbulence theories (see Fig. 4) we find consistent results. We notice that our results are in good agreement with 2D turbulence in the longer wavelengths (NIR and BL), but not in the ultraviolet, where we observe that the results fit better with a passive tracers turbulence model. A first conclusion that immediately follows from this work is the anisotropy of the turbulent field in the zonal and meridional directions, being the spectral decay in stronger in the later than in the former. The link between the brightness power spectra and the kinetic energy spectrum remains unclear, although in this work we show new evidences that such a link may exist. Acknowledgements This work has been funded by Spanish MEC AYA with FEDER support and Grupos UPV 15946/2004 and Grupos GV IT N. Barrado-Izagirre acknowledges a fellowship from UPV/EHU. This research made use of the public Cassini images available
5 Turbulence in Jupiter s Clouds 5 Fig. 4 Schematic comparison between turbulence theories and this work experimental results. Upper grey lines show the 2D-turbulent regime: continuous line for the kinetic energy spectrum and dashed line for a passive tracer spectrum. Bottom grey line is the same but for the 3D-turbulent regime. The intermediate curves show our results for ultraviolet slopes (purple) and blue and nearinfrared slopes (blue). The shaded area depicts expected range of values for the Rhines and Rossby scales. at NASA Planetary Data System. We acknowledge the Cassini-ISS team for their dedication in planning the observations. References 1. Galperin, B., Nakano, H.,Huang, H.P., Sukoriansky, S.: The ubiquitous zonal jets in the atmosperes of giant planets and Earth oceans. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L13303 (2004) 2. Galperin, B., Sukoriansky, S., Huang, H.P.: Universal n-5 spectrum of zonal flows on giant planets. Phys. Fluids 13, (2001)
6 6 N. Barrado-Izagirre, S. Pérez-Hoyos, and A. Sánchez-Lavega 3. Sukoriansky, S., Galpering, B., Dikovskaya, N.: Universal Spectrum of Two-Dimensional Turbulence on a Rotating Sphere and Some Basic Features of Atmospheric Circulation On Giant Planets. Phis. Rev. Lett. 89, (2002) 4. Mitchell, J.L.: The nature of large-scale turbulence in the jovian atmosphere. Ph.D. Thesis. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology (1982) 5. Mitchell, J.L., Maxworthy, T.: Large-scale turbulence in the jovian atmosphere. In Turbulence Predictability in Geophisical Fluid Dynamics, pp Tipografia Compositori, Bologna, Italy (1985) 6. Harrington, J., Dowling, T.E., Baron, R.L.: Jupiter s Tropospheric Thermal Emission: I. Observations and Techniques, Icarus 124, (1996a) 7. Harrington, J., Dowling, T.E., Baron, R.L.: Jupiter s Tropospheric Thermal Emission: II. Power Analysis and Wave Search, Icarus 124, (1996b)
Power Spectral Analysis of Jupiter s Clouds and Kinetic Energy from Cassini
 1 2 3 4 Power Spectral Analysis of Jupiter s Clouds and Kinetic Energy from Cassini David S. Choi a, Adam P. Showman a a Department of Planetary Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 (U.S.A.)
1 2 3 4 Power Spectral Analysis of Jupiter s Clouds and Kinetic Energy from Cassini David S. Choi a, Adam P. Showman a a Department of Planetary Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 (U.S.A.)
Icarus 216 (2011) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Icarus. journal homepage:
 Icarus 216 (2011) 597 609 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Power spectral analysis of Jupiter s clouds and kinetic energy from
Icarus 216 (2011) 597 609 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Power spectral analysis of Jupiter s clouds and kinetic energy from
Dynamics of the Venus atmosphere from a Fourier-transform analysis
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 16, 134 c SAIt 2011 Memorie della Supplementi Dynamics of the Venus atmosphere from a Fourier-transform analysis O. Lanciano 1, G. Piccioni 1, R. Hueso 2, A. Sánchez-Lavega 2,
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 16, 134 c SAIt 2011 Memorie della Supplementi Dynamics of the Venus atmosphere from a Fourier-transform analysis O. Lanciano 1, G. Piccioni 1, R. Hueso 2, A. Sánchez-Lavega 2,
The three-dimensional structure of Saturn s equatorial jet at cloud level
 Icarus 187 (2007) 510 519 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus The three-dimensional structure of Saturn s equatorial jet at cloud level A. Sánchez-Lavega, R. Hueso, S. Pérez-Hoyos Departamento de Física Aplicada
Icarus 187 (2007) 510 519 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus The three-dimensional structure of Saturn s equatorial jet at cloud level A. Sánchez-Lavega, R. Hueso, S. Pérez-Hoyos Departamento de Física Aplicada
Suppression of the Rhines effect and the location of vortices on Saturn
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009je003384, 2010 Suppression of the Rhines effect and the location of vortices on Saturn A. B. Penny, 1 A. P. Showman,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009je003384, 2010 Suppression of the Rhines effect and the location of vortices on Saturn A. B. Penny, 1 A. P. Showman,
High-resolution Global Climate Modeling of Saturn s and Jupiter s tropospheric and stratospheric circulations
 High-resolution Global Climate Modeling of Saturn s and Jupiter s tropospheric and stratospheric circulations Aymeric SPIGA, S. Guerlet, E. Millour, Y. Meurdesoif (LSCE/CEA), M. Indurain, S. Cabanes, M.
High-resolution Global Climate Modeling of Saturn s and Jupiter s tropospheric and stratospheric circulations Aymeric SPIGA, S. Guerlet, E. Millour, Y. Meurdesoif (LSCE/CEA), M. Indurain, S. Cabanes, M.
Dynamics of Saturn s South Polar Vortex
 Dynamics of Saturn s South Polar Vortex Ulyana A. Dyudina 1, Andrew P. Ingersoll 1,Shawn P. Ewald 1, Ashwin R. Vasavada 2, Robert A. West 2, Anthony D. Del Genio 3, John M. Barbara 3, Carolyn C. Porco
Dynamics of Saturn s South Polar Vortex Ulyana A. Dyudina 1, Andrew P. Ingersoll 1,Shawn P. Ewald 1, Ashwin R. Vasavada 2, Robert A. West 2, Anthony D. Del Genio 3, John M. Barbara 3, Carolyn C. Porco
STUDIES OF ATMOSPHERIC PHENOMENA IN THE GIANT PLANETS WITH GRANTECAN
 RevMexAA (Serie de Conferencias), 16, 98 102 (2003) STUDIES OF ATMOSPHERIC PHENOMENA IN THE GIANT PLANETS WITH GRANTECAN A. Sánchez-Lavega Escuela Superior de Ingenieros, UPV-EHU, Bilbao, Spain RESUMEN
RevMexAA (Serie de Conferencias), 16, 98 102 (2003) STUDIES OF ATMOSPHERIC PHENOMENA IN THE GIANT PLANETS WITH GRANTECAN A. Sánchez-Lavega Escuela Superior de Ingenieros, UPV-EHU, Bilbao, Spain RESUMEN
Icarus. Changes in Jupiter s zonal velocity between 1979 and 2008 q. Xylar S. Asay-Davis a,, Philip S. Marcus b, Michael H. Wong c, Imke de Pater c
 Icarus 211 (11) 1215 1232 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Changes in Jupiter s zonal velocity between 1979 and 8 q Xylar S. Asay-Davis
Icarus 211 (11) 1215 1232 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Changes in Jupiter s zonal velocity between 1979 and 8 q Xylar S. Asay-Davis
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Oct 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Oct 2016](/thumbs/89/97956588.jpg) 12 Saturn s Polar Atmosphere K.M. SAYANAGI 1, K.H. BAINES 2, U.A. DYUDINA 3, L.N. FLETCHER 4, A. SÁNCHEZ-LAVEGA5, R.A. WEST 2 arxiv:1609.09626v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Oct 2016 1 Department of Atmospheric and
12 Saturn s Polar Atmosphere K.M. SAYANAGI 1, K.H. BAINES 2, U.A. DYUDINA 3, L.N. FLETCHER 4, A. SÁNCHEZ-LAVEGA5, R.A. WEST 2 arxiv:1609.09626v2 [astro-ph.ep] 3 Oct 2016 1 Department of Atmospheric and
Strong jet and a new thermal wave in Saturn s equatorial stratosphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L23208, doi:10.1029/2008gl035515, 2008 Strong jet and a new thermal wave in Saturn s equatorial stratosphere Li Liming, 1 Peter J. Gierasch, 1 Richard K. Achterberg,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L23208, doi:10.1029/2008gl035515, 2008 Strong jet and a new thermal wave in Saturn s equatorial stratosphere Li Liming, 1 Peter J. Gierasch, 1 Richard K. Achterberg,
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. Vortices in Saturn s Northern Hemisphere ( ) observed by Cassini ISS
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Hemispheric maps (2008 2015) are processed to explore Saturn s vortices. Spatio-temporal variations of Saturn s vortices
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Hemispheric maps (2008 2015) are processed to explore Saturn s vortices. Spatio-temporal variations of Saturn s vortices
Dynamics of Giant Planet Atmospheres. Tapio Schneider (with Junjun Liu) California Institute of Technology
 Dynamics of Giant Planet Atmospheres Tapio Schneider (with Junjun Liu) California Institute of Technology Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000) Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000)
Dynamics of Giant Planet Atmospheres Tapio Schneider (with Junjun Liu) California Institute of Technology Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000) Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000)
Variable winds on Venus mapped in three dimensions
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13204, doi:10.1029/2008gl033817, 2008 Variable winds on Venus mapped in three dimensions A. Sánchez-Lavega, 1 R. Hueso, 1 G. Piccioni,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13204, doi:10.1029/2008gl033817, 2008 Variable winds on Venus mapped in three dimensions A. Sánchez-Lavega, 1 R. Hueso, 1 G. Piccioni,
The ubiquitous zonal jets in the atmospheres of giant planets and Earth s oceans
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L13303, doi:10.1029/2004gl019691, 2004 The ubiquitous zonal jets in the atmospheres of giant planets and Earth s oceans Boris Galperin, 1 Hideyuki Nakano, 2 Huei-Ping
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L13303, doi:10.1029/2004gl019691, 2004 The ubiquitous zonal jets in the atmospheres of giant planets and Earth s oceans Boris Galperin, 1 Hideyuki Nakano, 2 Huei-Ping
Modeling the atmosphere of Jupiter
 Modeling the atmosphere of Jupiter Bruce Turkington UMass Amherst Collaborators: Richard S. Ellis (UMass Professor) Andrew Majda (NYU Professor) Mark DiBattista (NYU Postdoc) Kyle Haven (UMass PhD Student)
Modeling the atmosphere of Jupiter Bruce Turkington UMass Amherst Collaborators: Richard S. Ellis (UMass Professor) Andrew Majda (NYU Professor) Mark DiBattista (NYU Postdoc) Kyle Haven (UMass PhD Student)
What is the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)?
 What is the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)? Planetary scale, 30 90 day oscillation in zonal wind, precipitation, surface pressure, humidity, etc., that propagates slowly eastward Wavelength = 12,000 20,000
What is the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)? Planetary scale, 30 90 day oscillation in zonal wind, precipitation, surface pressure, humidity, etc., that propagates slowly eastward Wavelength = 12,000 20,000
Part-8c Circulation (Cont)
 Part-8c Circulation (Cont) Global Circulation Means of Transfering Heat Easterlies /Westerlies Polar Front Planetary Waves Gravity Waves Mars Circulation Giant Planet Atmospheres Zones and Belts Global
Part-8c Circulation (Cont) Global Circulation Means of Transfering Heat Easterlies /Westerlies Polar Front Planetary Waves Gravity Waves Mars Circulation Giant Planet Atmospheres Zones and Belts Global
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0187 Stationary waves and slowly moving features in the night upper clouds of Venus J. Peralta 1*,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0187 Stationary waves and slowly moving features in the night upper clouds of Venus J. Peralta 1*,
Weather in the Solar System
 Weather in the Solar System Sanjay S. Limaye Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison 8 February 2002 What is Weather? Webster s New Collegiate Dictionary: state of the atmosphere
Weather in the Solar System Sanjay S. Limaye Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison 8 February 2002 What is Weather? Webster s New Collegiate Dictionary: state of the atmosphere
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
The Saturn s Atmosphere
 The Saturn s Atmosphere Ben Wei Peng Lew May 2, 2017 1 Introduction Saturn is 9.5 AU away from the Sun. Given a radius of 58000 km (0.84 R Jup ) and mass of 5.68 10 26 kg (0.28M Jup ), the surface gravity
The Saturn s Atmosphere Ben Wei Peng Lew May 2, 2017 1 Introduction Saturn is 9.5 AU away from the Sun. Given a radius of 58000 km (0.84 R Jup ) and mass of 5.68 10 26 kg (0.28M Jup ), the surface gravity
Equatorial superrotation in shallow atmospheres
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24202, doi:10.1029/2008gl036060, 2008 Equatorial superrotation in shallow atmospheres R. K. Scott 1 and L. M. Polvani 2 Received 18 September
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24202, doi:10.1029/2008gl036060, 2008 Equatorial superrotation in shallow atmospheres R. K. Scott 1 and L. M. Polvani 2 Received 18 September
Chapter 6 Saturn Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics
 Chapter 6 Saturn Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics AnthonyD.DelGenio,RichardK.Achterberg,KevinH.Baines,F.MichaelFlasar,PeterL.Read, Agustín Sánchez-Lavega, and Adam P. Showman Abstract Saturn inhabits
Chapter 6 Saturn Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics AnthonyD.DelGenio,RichardK.Achterberg,KevinH.Baines,F.MichaelFlasar,PeterL.Read, Agustín Sánchez-Lavega, and Adam P. Showman Abstract Saturn inhabits
Zonal jets in rotating shallow water turbulence
 Earth Science 2013; 2(2) : 23-30 Published online April 2, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/earth) doi: 10.11648/j. earth.20130202.11 Zonal jets in rotating shallow water turbulence G. Di
Earth Science 2013; 2(2) : 23-30 Published online April 2, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/earth) doi: 10.11648/j. earth.20130202.11 Zonal jets in rotating shallow water turbulence G. Di
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature149 1 Observation information This study examines 2 hours of data obtained between :33:42 and 12:46:28 Universal Time (UT) on April 17 11 using the -metre Keck telescope. This dataset was
doi:.38/nature149 1 Observation information This study examines 2 hours of data obtained between :33:42 and 12:46:28 Universal Time (UT) on April 17 11 using the -metre Keck telescope. This dataset was
Numerical Simulations of Forced Shallow-Water Turbulence: Effects of Moist Convection on the Large-Scale Circulation of Jupiter and Saturn
 313 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 Numerical Simulations of Forced Shallow-Water Turbulence: Effects of Moist Convection on the Large-Scale Circulation of Jupiter
313 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 64 Numerical Simulations of Forced Shallow-Water Turbulence: Effects of Moist Convection on the Large-Scale Circulation of Jupiter
Effects of a large convective storm on Saturn s equatorial jet
 Icarus 187 (2007) 520 539 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Effects of a large convective storm on Saturn s equatorial jet Kunio M. Sayanagi a,, Adam P. Showman b a Department of Physics, Lunar and Planetary
Icarus 187 (2007) 520 539 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Effects of a large convective storm on Saturn s equatorial jet Kunio M. Sayanagi a,, Adam P. Showman b a Department of Physics, Lunar and Planetary
Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics
 Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH Zurich, Caltech (Source: CLAUS, http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/claus/) Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH
Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH Zurich, Caltech (Source: CLAUS, http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/claus/) Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH
Equatorial Superrotation on Tidally Locked Exoplanets
 Equatorial Superrotation on Tidally Locked Exoplanets Adam P. Showman University of Arizona Lorenzo M. Polvani Columbia University Synopsis Most 3D atmospheric circulation models of tidally locked exoplanets
Equatorial Superrotation on Tidally Locked Exoplanets Adam P. Showman University of Arizona Lorenzo M. Polvani Columbia University Synopsis Most 3D atmospheric circulation models of tidally locked exoplanets
Climate Change on Jupiter. Philip Marcus University of California at Berkeley
 Climate Change on Jupiter Philip Marcus University of California at Berkeley 1998 2007 Climate Change on Jupiter? Starting in 2001 we began publishing claims that Jupiter would have a significant climate
Climate Change on Jupiter Philip Marcus University of California at Berkeley 1998 2007 Climate Change on Jupiter? Starting in 2001 we began publishing claims that Jupiter would have a significant climate
Meridional Transport in the Stratosphere of Jupiter
 Submitted to Astrophysical Journal Letters Meridional Transport in the Stratosphere of Jupiter Mao-Chang Liang 1, Run-Lie Shia 1, Anthony Y.-T. Lee 1, Mark Allen 1,2,A.James Friedson 2, and Yuk L. Yung
Submitted to Astrophysical Journal Letters Meridional Transport in the Stratosphere of Jupiter Mao-Chang Liang 1, Run-Lie Shia 1, Anthony Y.-T. Lee 1, Mark Allen 1,2,A.James Friedson 2, and Yuk L. Yung
Modeling of Jupiter s stratosphere: new radiation code and impacts on the dynamics
 Symposium on Planetary Science 2015, 2015/02/16, Tohoku Univ. Modeling of Jupiter s stratosphere: new radiation code and impacts on the dynamics Takeshi Kuroda Tohoku University A.S. Medvedev, J. Sethunadh,
Symposium on Planetary Science 2015, 2015/02/16, Tohoku Univ. Modeling of Jupiter s stratosphere: new radiation code and impacts on the dynamics Takeshi Kuroda Tohoku University A.S. Medvedev, J. Sethunadh,
Today. Next time. Emission & Absorption lines measuring elemental abundances. Doppler Effect. Telescopes technology to measure with
 Today Emission & Absorption lines measuring elemental abundances Doppler Effect measuring motion Telescopes technology to measure with Solar System Overview what s out there? Next time Homework 3 Due Chemical
Today Emission & Absorption lines measuring elemental abundances Doppler Effect measuring motion Telescopes technology to measure with Solar System Overview what s out there? Next time Homework 3 Due Chemical
Widespread Morning Drizzle on Titan
 Widespread Morning Drizzle on Titan Máté Ádámkovics, 1,2 Michael H. Wong, 1 Conor Laver, 1 Imke de Pater 1,2 1 Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94611, USA. 2 Center for Integrative
Widespread Morning Drizzle on Titan Máté Ádámkovics, 1,2 Michael H. Wong, 1 Conor Laver, 1 Imke de Pater 1,2 1 Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94611, USA. 2 Center for Integrative
Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport
 Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport is which can also be written as (14.1) i.e., #Q x,y
Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport is which can also be written as (14.1) i.e., #Q x,y
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Chapter 7 Clouds and Aerosols in Saturn s Atmosphere
 Chapter 7 Clouds and Aerosols in Saturn s Atmosphere R.A. West, K.H. Baines, E. Karkoschka, and A. Sánchez-Lavega Abstract In this chapter we review the photochemical and thermochemical equilibrium theories
Chapter 7 Clouds and Aerosols in Saturn s Atmosphere R.A. West, K.H. Baines, E. Karkoschka, and A. Sánchez-Lavega Abstract In this chapter we review the photochemical and thermochemical equilibrium theories
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
Icarus 223 (2013) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Icarus. journal homepage:
 Icarus 223 (2013) 460 478 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Dynamics of Saturn s great storm of 2010 2011 from Cassini ISS and RPWS
Icarus 223 (2013) 460 478 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Icarus journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Dynamics of Saturn s great storm of 2010 2011 from Cassini ISS and RPWS
Behavioral Changes of Jupiter s Little and Great Red Spot: a Survey
 Behavioral Changes of Jupiter s Little and Great Red Spot: a Survey Asit Baran Bhattacharya, Mintu Debnath and Bipasa Raha Department of Physics, University of Kalyani, Kalyani 741235, West Bengal, India
Behavioral Changes of Jupiter s Little and Great Red Spot: a Survey Asit Baran Bhattacharya, Mintu Debnath and Bipasa Raha Department of Physics, University of Kalyani, Kalyani 741235, West Bengal, India
The Turbulent Wake of the Jupiter's Great Red Spot observed with MAD
 The Turbulent Wake of the Jupiter's Great Red Spot observed with MAD F. Marchis (UC-Berkeley), M. Wong (UC-Berkeley), E. Marchetti (ESO), J. Kolb (ESO) ABSTRACT The turbulent wake of Jupiter's Great Red
The Turbulent Wake of the Jupiter's Great Red Spot observed with MAD F. Marchis (UC-Berkeley), M. Wong (UC-Berkeley), E. Marchetti (ESO), J. Kolb (ESO) ABSTRACT The turbulent wake of Jupiter's Great Red
TIME-AVERAGES OF FAST OSCILLATORY SYSTEMS. Bin Cheng and Alex Mahalov. (Communicated by the associate editor name)
 Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number X, XX 2X Website: http://aimsciences.org pp. X XX TIME-AVERAGES OF FAST OSCILLATORY SYSTEMS Bin Cheng and Alex Mahalov School of Mathematical and
Manuscript submitted to AIMS Journals Volume X, Number X, XX 2X Website: http://aimsciences.org pp. X XX TIME-AVERAGES OF FAST OSCILLATORY SYSTEMS Bin Cheng and Alex Mahalov School of Mathematical and
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF ATMOSPHERIC DYNAMICS ON THE GIANT PLANETS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF ATMOSPHERIC DYNAMICS ON THE GIANT PLANETS Item Type text; Electronic Dissertation Authors Lian, Yuan Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author.
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF ATMOSPHERIC DYNAMICS ON THE GIANT PLANETS Item Type text; Electronic Dissertation Authors Lian, Yuan Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author.
THE ENIGMA OF SATURN S NORTH-POLAR HEXAGON
 THE ENIGMA OF SATURN S NORTH-POLAR HEXAGON Gerald E. Marsh Argonne National Laboratory (Ret) gemarsh@uchicago.edu ABSTRACT It has been suggested that the north-polar hexagon found on Saturn is an unusual
THE ENIGMA OF SATURN S NORTH-POLAR HEXAGON Gerald E. Marsh Argonne National Laboratory (Ret) gemarsh@uchicago.edu ABSTRACT It has been suggested that the north-polar hexagon found on Saturn is an unusual
Exoplanets Atmospheres. Characterization of planetary atmospheres. Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging
 Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Influence of Jupiter s South Equatorial Disturbance on
 Influence of Jupiter s South Equatorial Disturbance on jetstream eam speed John H. Rogers & Hans Jörg Mettig A report of the Jupiter Section (Director: John H. Rogers) The eastward jets on Jupiter are,
Influence of Jupiter s South Equatorial Disturbance on jetstream eam speed John H. Rogers & Hans Jörg Mettig A report of the Jupiter Section (Director: John H. Rogers) The eastward jets on Jupiter are,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Macroturbulent cascades of energy and enstrophy in models and observations of planetary atmospheres
 Macroturbulent cascades of energy and enstrophy in models and observations of planetary atmospheres Peter Read + Roland Young + Fachreddin Tabataba-Vakili + Yixiong Wang [Dept. of Physics, University of
Macroturbulent cascades of energy and enstrophy in models and observations of planetary atmospheres Peter Read + Roland Young + Fachreddin Tabataba-Vakili + Yixiong Wang [Dept. of Physics, University of
Jupiter. Jupiter, its atmosphere, and its magnetic field 10/19/17 PROBLEM SET #5 DUE TUESDAY AT THE BEGINNING OF LECTURE
 Jupiter PROBLEM SET #5 DUE TUESDAY AT THE BEGINNING OF LECTURE 19 October 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Jupiter and Io as seen from Cassini as it flew by (JPL/NASA) Jupiter, its atmosphere, and its magnetic
Jupiter PROBLEM SET #5 DUE TUESDAY AT THE BEGINNING OF LECTURE 19 October 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Jupiter and Io as seen from Cassini as it flew by (JPL/NASA) Jupiter, its atmosphere, and its magnetic
Kandis Lea Jessup 1 Franklin Mills 2 Emmanuel Marcq 3 Jean-Loup Bertaux 3 Tony Roman 4 Yuk Yung 5. Southwest Research Institute (Boulder CO) 2
 "Coordinated HST, Venus Express, and Venus Climate Orbiter Observations of Venus", NASA program 12433. Kandis Lea Jessup 1 Franklin Mills 2 Emmanuel Marcq 3 Jean-Loup Bertaux 3 Tony Roman 4 Yuk Yung 5
"Coordinated HST, Venus Express, and Venus Climate Orbiter Observations of Venus", NASA program 12433. Kandis Lea Jessup 1 Franklin Mills 2 Emmanuel Marcq 3 Jean-Loup Bertaux 3 Tony Roman 4 Yuk Yung 5
1/27/2010. With this method, all filed variables are separated into. from the basic state: Assumptions 1: : the basic state variables must
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Dust in the Atmosphere of Mars 2017 (LPI Contrib. No. 1966)
 Dust in the Atmosphere of Mars 2017 (LPI Contrib. No. 1966) MARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (MCS) OBSERVATIONS OF MARTIAN DUST A DECADE-LONG RECORD. D. M. Kass1, D. J. McCleese1, A. Kleinböhl1, J. T. Schofield1 and
Dust in the Atmosphere of Mars 2017 (LPI Contrib. No. 1966) MARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (MCS) OBSERVATIONS OF MARTIAN DUST A DECADE-LONG RECORD. D. M. Kass1, D. J. McCleese1, A. Kleinböhl1, J. T. Schofield1 and
Dynamics and Interaction between a Large-Scale Vortex and the Great Red Spot in Jupiter
 ICARUS 136, 14 26 (1998) ARTICLE NO. IS986006 Dynamics and Interaction between a Large-Scale Vortex and the Great Red Spot in Jupiter A. Sanchez-Lavega and R. Hueso Departamento Física Aplicada I, E.T.S.
ICARUS 136, 14 26 (1998) ARTICLE NO. IS986006 Dynamics and Interaction between a Large-Scale Vortex and the Great Red Spot in Jupiter A. Sanchez-Lavega and R. Hueso Departamento Física Aplicada I, E.T.S.
Solar radiation - the major source of energy for almost all environmental flows
 Solar radiation - the major source of energy for almost all environmental flows Radiation = electromagnetic waves Different types of heat transfer: Heat conduction by molecular diffusion (no large-scale
Solar radiation - the major source of energy for almost all environmental flows Radiation = electromagnetic waves Different types of heat transfer: Heat conduction by molecular diffusion (no large-scale
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability
 GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
Turbulent convection in rapidly rotating spherical shells: A model for equatorial and high latitude jets on Jupiter and Saturn
 Icarus 187 (2007) 540 557 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Turbulent convection in rapidly rotating spherical shells: A model for equatorial and high latitude jets on Jupiter and Saturn Moritz Heimpel a,,
Icarus 187 (2007) 540 557 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Turbulent convection in rapidly rotating spherical shells: A model for equatorial and high latitude jets on Jupiter and Saturn Moritz Heimpel a,,
HST Observations of Planetary Atmospheres
 HST Observations of Planetary Atmospheres John T. Clarke Boston University Hubble Science Legacy 3 April 2002 Venus - Near-UV images reveal cloud motions and winds - UV spectra track SO 2 composition,
HST Observations of Planetary Atmospheres John T. Clarke Boston University Hubble Science Legacy 3 April 2002 Venus - Near-UV images reveal cloud motions and winds - UV spectra track SO 2 composition,
Waves in Jupiter s atmosphere observed by the Cassini ISS and CIRS instruments
 Icarus 185 (2006) 416 429 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Waves in Jupiter s atmosphere observed by the Cassini ISS and CIRS instruments Liming Li a,, Andrew P. Ingersoll a, Ashwin R. Vasavada b, Amy A.
Icarus 185 (2006) 416 429 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus Waves in Jupiter s atmosphere observed by the Cassini ISS and CIRS instruments Liming Li a,, Andrew P. Ingersoll a, Ashwin R. Vasavada b, Amy A.
Geostrophic turbulence: How Jupiter got its stripes? D. Gurarie Math. Department CWRU Cleveland, Ohio
 STOCHASTIC MODELS IN ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE October 10-11, 2008 Geostrophic turbulence: How Jupiter got its stripes? D. Gurarie Math. Department CWRU Cleveland, Ohio Applied Math projecyts at Case in
STOCHASTIC MODELS IN ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE October 10-11, 2008 Geostrophic turbulence: How Jupiter got its stripes? D. Gurarie Math. Department CWRU Cleveland, Ohio Applied Math projecyts at Case in
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Feb 2013](/thumbs/92/110458419.jpg) accepted for publication in Icarus Meteorology of Jupiter s Equatorial Hot Spots and Plumes from Cassini arxiv:1302.0277v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Feb 2013 David S. Choi ORAU / NASA Goddard Space Flight Center,
accepted for publication in Icarus Meteorology of Jupiter s Equatorial Hot Spots and Plumes from Cassini arxiv:1302.0277v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Feb 2013 David S. Choi ORAU / NASA Goddard Space Flight Center,
12a. Jupiter. Jupiter Data (Table 12-1) Jupiter Data: Numbers
 12a. Jupiter Jupiter & Saturn data Jupiter & Saturn seen from the Earth Jupiter & Saturn rotation & structure Jupiter & Saturn clouds Jupiter & Saturn atmospheric motions Jupiter & Saturn rocky cores Jupiter
12a. Jupiter Jupiter & Saturn data Jupiter & Saturn seen from the Earth Jupiter & Saturn rotation & structure Jupiter & Saturn clouds Jupiter & Saturn atmospheric motions Jupiter & Saturn rocky cores Jupiter
SATURN EDDY MOMENTUM FLUXES AND CONVECTION: FIRST ESTIMATES FROM CASSINI IMAGES
 SATURN EDDY MOMENTUM FLUXES AND CONVECTION: FIRST ESTIMATES FROM CASSINI IMAGES Anthony D. Del Genio 1, John M. Barbara 2, Joseph Ferrier 2, Andrew P. Ingersoll 3, Robert A. West 4, Ashwin R. Vasavada
SATURN EDDY MOMENTUM FLUXES AND CONVECTION: FIRST ESTIMATES FROM CASSINI IMAGES Anthony D. Del Genio 1, John M. Barbara 2, Joseph Ferrier 2, Andrew P. Ingersoll 3, Robert A. West 4, Ashwin R. Vasavada
Jupiter. Notes compiled by Paul Woodward Department of Astronomy
 Jupiter Notes compiled by Paul Woodward Department of Astronomy We will spend about one week on the outer, gaseous planets, focusing first on Jupiter, then on Saturn. We will not spend time on Uranus and
Jupiter Notes compiled by Paul Woodward Department of Astronomy We will spend about one week on the outer, gaseous planets, focusing first on Jupiter, then on Saturn. We will not spend time on Uranus and
VIRTIS-Venus Express
 VIRTIS-Venus Express - G. Piccioni, P. Drossart and the VIRTIS-VenusX Team Scientific Team Members by Countries I (1) (PI) Total 14 F (2) PO ES RU NL US D UK P Total (PI) 10 1 2 2 1 2 5 2 1 (1) G. Piccioni,
VIRTIS-Venus Express - G. Piccioni, P. Drossart and the VIRTIS-VenusX Team Scientific Team Members by Countries I (1) (PI) Total 14 F (2) PO ES RU NL US D UK P Total (PI) 10 1 2 2 1 2 5 2 1 (1) G. Piccioni,
The Great Saturn Storm of
 1 13 The Great Saturn Storm of 2010-2011 Agustín Sánchez-Lavega 1 Georg Fischer 2 Leigh N. Fletcher 3 Enrique García-Melendo 1, 4 Brigette Hesman 5 Santiago Pérez-Hoyos 1 Kunio M. Sayanagi 6 Lawrence A.
1 13 The Great Saturn Storm of 2010-2011 Agustín Sánchez-Lavega 1 Georg Fischer 2 Leigh N. Fletcher 3 Enrique García-Melendo 1, 4 Brigette Hesman 5 Santiago Pérez-Hoyos 1 Kunio M. Sayanagi 6 Lawrence A.
Lecture #27: Saturn. The Main Point. The Jovian Planets. Basic Properties of Saturn. Saturn:
 Lecture #27: Saturn Saturn: General properties. Atmosphere. Interior. Origin and evolution. Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Saturn) and 11.1. The Main Point Saturn is a large Jovian-class planet with a composition
Lecture #27: Saturn Saturn: General properties. Atmosphere. Interior. Origin and evolution. Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Saturn) and 11.1. The Main Point Saturn is a large Jovian-class planet with a composition
Modeling the Effects of Anisotropic Turbulence and Dispersive Waves on Oceanic Circulation and their Incorporation in Navy Ocean Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Modeling the Effects of Anisotropic Turbulence and Dispersive Waves on Oceanic Circulation and their Incorporation in Navy
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Modeling the Effects of Anisotropic Turbulence and Dispersive Waves on Oceanic Circulation and their Incorporation in Navy
The effects of vigorous mixing in a convective model of zonal flow on the ice giants
 Icarus 190 (2007) 110 126 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus The effects of vigorous mixing in a convective model of zonal flow on the ice giants Jonathan Aurnou a,, Moritz Heimpel b, Johannes Wicht c a Earth
Icarus 190 (2007) 110 126 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus The effects of vigorous mixing in a convective model of zonal flow on the ice giants Jonathan Aurnou a,, Moritz Heimpel b, Johannes Wicht c a Earth
Simultaneous Cassini, HST, and ground-based observations of Saturn s aurorae during the 2013 auroral campaign
 Simultaneous Cassini, HST, and ground-based observations of Saturn s aurorae during the 2013 auroral campaign Henrik Melin! S. V. Badman, T. S. Stallard, K. H. Baines, J. Nichols, W. R. Pryor, U. Dyudina,
Simultaneous Cassini, HST, and ground-based observations of Saturn s aurorae during the 2013 auroral campaign Henrik Melin! S. V. Badman, T. S. Stallard, K. H. Baines, J. Nichols, W. R. Pryor, U. Dyudina,
Nightside Winds at the Lower Clouds of Venus with Akatsuki/IR2 Javier Peralta
 (c)jaxa / ISAS / DARTS / Damia Bouic Nightside Winds at the Lower Clouds of Venus with Akatsuki/IR2 Javier Peralta International Top Young Fellow (ITYF), ISAS 1 Venus and its atmospheric super-rotation.
(c)jaxa / ISAS / DARTS / Damia Bouic Nightside Winds at the Lower Clouds of Venus with Akatsuki/IR2 Javier Peralta International Top Young Fellow (ITYF), ISAS 1 Venus and its atmospheric super-rotation.
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere
 DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere Lodovica Illari 1 Introduction What is responsible for stormy weather? What causes relatively warm temperatures one day and
DEAPS Activity 3 Weather systems and the general circulation of the atmosphere Lodovica Illari 1 Introduction What is responsible for stormy weather? What causes relatively warm temperatures one day and
Waves in Jupiter s Atmosphere Observed by the Cassini ISS and CIRS Instruments
 Waves in Jupiter s Atmosphere Observed by the Cassini ISS and CIRS Instruments Liming Li a,*, Andrew P. Ingersoll a, Ashwin R. Vasavada b, Amy A. Simon-Miller c, Richard K. Achterberg d, Shawn P. Ewald
Waves in Jupiter s Atmosphere Observed by the Cassini ISS and CIRS Instruments Liming Li a,*, Andrew P. Ingersoll a, Ashwin R. Vasavada b, Amy A. Simon-Miller c, Richard K. Achterberg d, Shawn P. Ewald
AN OBJECTIVE CLASSIFICATION OF SATURN CLOUD FEATURES
 1 AN OBJECTIVE CLASSIFICATION OF SATURN CLOUD FEATURES FROM CASSINI ISS IMAGES Anthony D. Del Genio a* and John M. Barbara b a NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, New York, NY 10025 USA b Trinnovim
1 AN OBJECTIVE CLASSIFICATION OF SATURN CLOUD FEATURES FROM CASSINI ISS IMAGES Anthony D. Del Genio a* and John M. Barbara b a NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, New York, NY 10025 USA b Trinnovim
Radiative Heat Balances in Jupiter s Stratosphere: Development of a Radiation Code for the Implementation to a GCM
 Radiative Heat Balances in Jupiter s Stratosphere: Development of a Radiation Code for the Implementation to a GCM T. Kuroda Tohoku University A.S. Medvedev, P. Hartogh Max Planck Institute for Solar System
Radiative Heat Balances in Jupiter s Stratosphere: Development of a Radiation Code for the Implementation to a GCM T. Kuroda Tohoku University A.S. Medvedev, P. Hartogh Max Planck Institute for Solar System
Disruption of Saturn s Quasi-Periodic Equatorial Oscillation by the Great Northern Storm
 Disruption of Saturn s Quasi-Periodic Equatorial Oscillation by the Great Northern Storm Leigh N. Fletcher 1*, Sandrine Guerlet 2, Glenn S. Orton 3, Richard G. Cosentino 4, Thierry Fouchet 5, Patrick G.J.
Disruption of Saturn s Quasi-Periodic Equatorial Oscillation by the Great Northern Storm Leigh N. Fletcher 1*, Sandrine Guerlet 2, Glenn S. Orton 3, Richard G. Cosentino 4, Thierry Fouchet 5, Patrick G.J.
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework. 5-7 May 2015
 Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
Synoptic Meteorology II: Self-Development in the IPV Framework 5-7 May 2015 Readings: Section 5.3.6 of Midlatitude Synoptic Meteorology. Introduction In this and other recent lectures, we have developed
PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES 4. Global Climate Modeling Sébastien LEBONNOIS CNRS Researcher Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, Paris PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Global Climate Modeling Virtual planets Different
PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES 4. Global Climate Modeling Sébastien LEBONNOIS CNRS Researcher Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique, Paris PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Global Climate Modeling Virtual planets Different
Polar vortex formation in giant planet atmospheres under moist convection
 TITLE: Polar vortex formation in giant planet atmospheres under moist convection AUTHORS: Morgan E O Neill* morgan.oneill@weizmann.ac.il Kerry A. Emanuel Emanuel@mit.edu Glenn R. Flierl Glenn@lake.mit.edu
TITLE: Polar vortex formation in giant planet atmospheres under moist convection AUTHORS: Morgan E O Neill* morgan.oneill@weizmann.ac.il Kerry A. Emanuel Emanuel@mit.edu Glenn R. Flierl Glenn@lake.mit.edu
The 6 9 day wave and rainfall modulation in northern Africa during summer 1981
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D17, 4535, doi:10.1029/2002jd003215, 2003 The 6 9 day wave and rainfall modulation in northern Africa during summer 1981 David Monkam Département de Physique,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. D17, 4535, doi:10.1029/2002jd003215, 2003 The 6 9 day wave and rainfall modulation in northern Africa during summer 1981 David Monkam Département de Physique,
Jupiter Science and Capabilities on the Europa Jupiter System Mission
 Jupiter Science and Capabilities on the Europa Jupiter System Mission Leigh N. Fletcher(*), Amy Simon-Miller, P. Drossart, A. Showman, G. Orton, K. Baines and the EJSM Joint Science Definition Team *Jet
Jupiter Science and Capabilities on the Europa Jupiter System Mission Leigh N. Fletcher(*), Amy Simon-Miller, P. Drossart, A. Showman, G. Orton, K. Baines and the EJSM Joint Science Definition Team *Jet
Mechanisms of Jet Formation on the Giant Planets
 3652 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 67 Mechanisms of Jet Formation on the Giant Planets JUNJUN LIU AND TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
3652 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 67 Mechanisms of Jet Formation on the Giant Planets JUNJUN LIU AND TAPIO SCHNEIDER California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Wind-driven Western Boundary Ocean Currents in Terran and Superterran Exoplanets
 Wind-driven Western Boundary Ocean Currents in Terran and Superterran Exoplanets By Edwin Alfonso-Sosa, Ph.D. Ocean Physics Education, Inc. 10-Jul-2014 Introduction Simple models of oceanic general circulation
Wind-driven Western Boundary Ocean Currents in Terran and Superterran Exoplanets By Edwin Alfonso-Sosa, Ph.D. Ocean Physics Education, Inc. 10-Jul-2014 Introduction Simple models of oceanic general circulation
[1]{Izaña Atmospheric Research Centre (AEMET), Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain}
![[1]{Izaña Atmospheric Research Centre (AEMET), Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain} [1]{Izaña Atmospheric Research Centre (AEMET), Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain}](/thumbs/72/66953681.jpg) Supplement of Pivotal role of the North African Dipole Intensity (NAFDI) on alternate Saharan dust export over the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean, and relationship with the Saharan Heat Low and mid-latitude
Supplement of Pivotal role of the North African Dipole Intensity (NAFDI) on alternate Saharan dust export over the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean, and relationship with the Saharan Heat Low and mid-latitude
Planetary atmospheric circulation
 Planetary atmospheric circulation Aurel Rusu Duma (rusuduma@yahoo.com) Translated from Romanian by Viorica Zamarcaru (zamarcaruv@yahoo.com) 1 Atmospheric motions The long-term global atmospheric circulation
Planetary atmospheric circulation Aurel Rusu Duma (rusuduma@yahoo.com) Translated from Romanian by Viorica Zamarcaru (zamarcaruv@yahoo.com) 1 Atmospheric motions The long-term global atmospheric circulation
Recovery of atmospheric flow statistics in a general circulation model without nonlinear eddy-eddy interactions
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L22801, doi:10.1029/2007gl031779, 2007 Recovery of atmospheric flow statistics in a general circulation model without nonlinear eddy-eddy
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L22801, doi:10.1029/2007gl031779, 2007 Recovery of atmospheric flow statistics in a general circulation model without nonlinear eddy-eddy
Radiation from planets
 Chapter 4 Radiation from planets We consider first basic, mostly photometric radiation parameters for solar system planets which can be easily compared with existing or future observations of extra-solar
Chapter 4 Radiation from planets We consider first basic, mostly photometric radiation parameters for solar system planets which can be easily compared with existing or future observations of extra-solar
Flux of impacts in Jupiter: From super bolides to larger scale collisions
 Flux of impacts in Jupiter: From super bolides to larger scale collisions R. Hueso 1, A. Sánchez-Lavega 1, S. Pérez-Hoyos 1, A. Wesley 2, C. Go 2, M. Tachikawa 2, K. Aoki 2, M. Ichimaru 2, M. Delcroix
Flux of impacts in Jupiter: From super bolides to larger scale collisions R. Hueso 1, A. Sánchez-Lavega 1, S. Pérez-Hoyos 1, A. Wesley 2, C. Go 2, M. Tachikawa 2, K. Aoki 2, M. Ichimaru 2, M. Delcroix
K32: The Structure of the Earth s Atmosphere
 K32: The Structure of the Earth s Atmosphere Chemical composition Vertical Layers Temperature structure Coriolis Force and horizontal structure Hadley Cells and Heat sources Current Molecular Composition
K32: The Structure of the Earth s Atmosphere Chemical composition Vertical Layers Temperature structure Coriolis Force and horizontal structure Hadley Cells and Heat sources Current Molecular Composition
AFRICAN EASTERLY WAVES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE CLIMATES
 AFRICAN EASTERLY WAVES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE CLIMATES Victoria Dollar RTG Seminar Research - Spring 2018 April 16, 2018 Victoria Dollar ASU April 16, 2018 1 / 26 Overview Introduction Rossby waves and
AFRICAN EASTERLY WAVES IN CURRENT AND FUTURE CLIMATES Victoria Dollar RTG Seminar Research - Spring 2018 April 16, 2018 Victoria Dollar ASU April 16, 2018 1 / 26 Overview Introduction Rossby waves and
Telescopes and the Atmosphere
 Telescopes and the Atmosphere Our goals for learning How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations? Why do we put telescopes into space? How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations?
Telescopes and the Atmosphere Our goals for learning How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations? Why do we put telescopes into space? How does Earth s atmosphere affect ground-based observations?
(after Stephens et al. 2012)
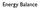 Energy Balance Incoming solar radiation 34 Reflected solar radiation Outgoing longwave radiation 1 24 TOA 75 Atmospheric absorption Atmospheric reflection 77 Atmospheric window 4 165 35 Clear Sky Cloud
Energy Balance Incoming solar radiation 34 Reflected solar radiation Outgoing longwave radiation 1 24 TOA 75 Atmospheric absorption Atmospheric reflection 77 Atmospheric window 4 165 35 Clear Sky Cloud
Dynamics of Convectively Driven Banded Jets in the Laboratory
 Dynamics of Convectively Driven Banded Jets in the Laboratory The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Read,
Dynamics of Convectively Driven Banded Jets in the Laboratory The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Read,
Spectral comparison and stability of red regions on Jupiter
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Red cyclones and belt regions are more spectrally red than the Great Red Spot The GRS shows significant spectral slope
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Red cyclones and belt regions are more spectrally red than the Great Red Spot The GRS shows significant spectral slope
Jupiter: Giant of the Solar System
 Jupiter: Giant of the Solar System Jupiter s Red spot : A huge storm that has raged for over 300 years that is ~2x size of the Earth. Gas Giant is really a Liquid Giant! Pictures over ~7 years from Hubble
Jupiter: Giant of the Solar System Jupiter s Red spot : A huge storm that has raged for over 300 years that is ~2x size of the Earth. Gas Giant is really a Liquid Giant! Pictures over ~7 years from Hubble
THE IMPACT OF SATELLITE-DERIVED WINDS ON GFDL HURRICANE MODEL FORECASTS
 THE IMPACT OF SATELLITE-DERIVED WINDS ON GFDL HURRICANE MODEL FORECASTS Brian J. Soden 1 and Christopher S. Velden 2 1) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
THE IMPACT OF SATELLITE-DERIVED WINDS ON GFDL HURRICANE MODEL FORECASTS Brian J. Soden 1 and Christopher S. Velden 2 1) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
S E C T I O N 7 P R O B E S C I E N C E R E S U L T S
 S E C T I O N 7 P R O B E S C I E N C E R E S U L T S Under surveillance by telescopes here on Earth as well as the Hubble Space Telescope, observations of Jupiter show that the probe apparently entered
S E C T I O N 7 P R O B E S C I E N C E R E S U L T S Under surveillance by telescopes here on Earth as well as the Hubble Space Telescope, observations of Jupiter show that the probe apparently entered
12. Jovian Planet Systems Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison Wesley
 12. Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive 2. are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen compounds 3. have
12. Jovian Planet Systems Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive 2. are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen compounds 3. have
Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets
 Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets 2-28-2018 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ASTR-101 Section 004 Bulk Properties of Terrestrial and Jovian Planets All Jovian planets have strong magnetic fields
Astro 101 Lecture 12 The Jovian Planets 2-28-2018 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ASTR-101 Section 004 Bulk Properties of Terrestrial and Jovian Planets All Jovian planets have strong magnetic fields
