Modern Problems of Nuclear Physics II.1. Physics of Compact Stars
|
|
|
- Josephine Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modern Problems of Nuclear Physics II.1. Physics of Compact Stars David Blaschke (University of Wroclaw & JINR Dubna & MEPhI) National Research Nuclear University (MEPhI), Summer Semester 2017
2 Lecture Overview... Modern Problems in Nuclear Physics II D. Blaschke (U Wroclaw, JINR, MEPhI) G. Röpke (U Rostock) A. Sedrakian (FIAS Frankfurt, Yerevan SU) 1. Physics of Neutron Stars I Phenomenology, EoS and Structure (3) 2. Statistical Model and HIC I NSE, Clusters in Nuclei, HIC & Femto-Nova (3) 3. Statistical Model and HIC II RHIC and CERN Experiments, Chemical Freeze-out (2) 4. Superfluidity in Nuclear Matter I BEC-BCS Crossover. NSR Theory (2) 5. Superfluidity in Nuclear Matter II Nuclear vs. Quark Matter and Atoms in Traps (3) 6. Physics of Neutron Stars II Cooling and Superfluidity, Nuclear vs. Quark Matter (2)
3 Physics of Compact Stars Contents: 1. Observations of compact star (CS) properties 2. Equation of state for the CS crust 3. Dense nuclear and quark matter in the CS interior 4. General relativistic CS structure 5. Neutrino processes and CS cooling 6. CS at birth: Supernovae and protoneutron stars 7. Gravitational wave signals and black hole formation Literature: Norman Glendenning: Compact Stars (Springer, 2000) Pawel Haensel et al.: Neutron Stars (Springer, 2007) Fridolin Weber: Pulsars as astrophysical laboratories... (IoP Publ., 1999) Stuart Shapiro & Saul Teukolsky: Black Holes, White Dwarfs & Neutron Stars (Wiley, 1983) David Blaschke et al. (Eds.): Physics of Neutron Star Interiors (Springer, 2001) D. Blaschke, J. Schaffner-Bielich, H.-J. Schulze (Eds.): Exotic Matter in Neutron Stars, EPJA (2016)
4 dn/dm Stars in the Galaxy Salpeter (1955) mass function: dn/dm ~ M-2.35 Long life time Short life time There are many modification (Miller-Scalo, Kroupa etc.). At high masses the slope is usually steeper. Note: it is initial mass function, not the present day! Mmin Mmax M It is possible to estimate the number of NS and BH progenitors. Then using there average lifetime we can estimate the birth rate and total numbers (with a given age of the Galaxy and assuming constant rate) taking into account SFR~3 solar mass per year. [see also Ch.1 in Shapiro, Teukolsky]
5 Prediction... Neutron stars have been predicted in 30s: L.D. Landau: Star-nuclei (1932) + anecdote Baade and Zwicky: neutron stars and supernovae (1934) (Landau) (Zwicky) (Baade)
6 (from lectures by D. Yakovlev) Shapiro,Teukolsky (1983) (see detailed description in the book by Haensel, Yakovlev, Potekhin and in the e-print arxiv: )
7 Landau paper BEFORE neutron discovery Physikalische Zeitschrift der Sowjetunion Vol. 1, No. 2, , 1932 Written: Feb. 1931, Zurich Received: Jan. 7, 1932 Published: Feb. 1932
8 This is correct! Disappered in reprints, so we have difficulties
9 Baade and Zwicky theoretical prediction W. Baade (Mt. Wilson Observatory) F. Zwicky (Caltech) The meeting of American Physical Society (Stanford, December 15-16, 1933) Published in Physical Review (January 15, 1934)
10 Phys. Rev. 46, 76, 1934 (July 1)
11 Good old classics For years two main types of NSs have been discussed: radio pulsars and accreting NSs in close binary systems The pulsar in the Crab nebula A binary system
12 The old zoo of neutron stars In 60s the first X-ray sources have been discovered. They were neutron stars in close binary systems, BUT they were «not recognized»... Now we know hundreds of X-ray binaries with neutron stars in the Milky Way and in other galaxies.
13 Rocket experiments Sco X-1 Giacconi, Gursky, Hendel 1962 In 2002 R. Giacconi was awarded with the Nobel prize.
14 UHURU The satellite was launched on December 12, The program was ended in March The other name SAS kev The first full sky survey. 339 sources.
15 Accretion in close binaries Accretion is the most powerful source of energy realized in Nature, which can give a huge energy output. When matter falls down onto the surface of a neutron star up to 10% of mc2 can be released.
16 Accretion disc The theory of accretion discs was developed in by N.I. Shakura and R.A. Sunyaev. Accretion is important not only in close binaries, but also in active galactic nuclei and many other types of astrophysical sources.
17 Close binary systems About ½ of massive stars Are members of close binary systems. Now we know many dozens of close binary systems with neutron stars. L=Mηc2 The accretion rate can be up to 1020 g/s; Accretion efficiency up to 10%; Luminosity thousands of hundreds of the solar.
18 Discovery!!!! 1967: Jocelyn Bell. Radio pulsars. Seredipitous discovery.
19 The pulsar in the Crab nebula
20 The old Zoo: young pulsars & old accretors
21 The new zoo of young neutron stars During the last >10 years it became clear that neutron stars can be born very differently. In particular, absolutely non-similar to the Crab pulsar. o High-B PSRs o Compact central X-ray sources in supernova remnants. o Anomalous X-ray pulsars o Soft gamma repeaters o The Magnificent Seven o Transient radio sources (RRATs) Old and new zoos: Harding arxiv:
22 Compact central X-ray sources in supernova remnants Cas A Rapid cooling (Heinke et al ) RCW hour period (de Luca et al. 2006)
23 CCOs in SNRs J J J J J J Age [kyr] Cas A 0.32 G Pup A 1 3 G Kes 79 ~9 G ~10 Distance [kpc] ~10 ~6 Pavlov, Sanwal, Teter: astro-ph/ , de Luca: arxiv: For three sources there are strong indications for large (>~100 msec) initial spin periods and low magnetic fields: 1E in PKS /52 PSR J in Kesteven 79 PSR J in Puppis A see Halpern et al. [ ] and [ ]
24 CCOs High proper motion of CCO in Pup A. Velocity 672 +/- 115 km/s [ ] Puppis A [ ]
25 Anti-magnetars Star marks the CCO from New results Spins and derivative are measured for PSR J and PSR J
26 Magnetars de/dt > derot/dt By definition: The energy of the magnetic field is released Magnetic fields G
27 Magnetic field estimates Spin down Long spin periods Energy to support bursts Field to confine a fireball (tails) Duration of spikes (Alfven waves) Direct measurements of magnetic field (cyclotron lines) Ibrahim et al. 2002
28 Known magnetars AXPs SGRs (?) (?) (СТВ 109) CXO U E CXO J RXS J XTE J E AX J E E PSR J CXO J Catalogue:
29 Extragalactic SGRs It was suggested long ago (Mazets et al. 1982) that present-day detectors could already detect giant flares from extragalactic magnetars. However, all searches in, e.g., the BATSE database did not provide good candidates (Lazzati et al. 2006, Popov & Stern 2006, etc.). Finally, recently several good candidates have been proposed by different groups (Mazets et al., Frederiks et al., Golenetskii et al., Ofek et al, Crider..., see arxiv: and references therein, for example). Burst from M31 [D. Frederiks et al. astro-ph/ ]
30 Transient radio emission from AXP ROSAT and XMM images an X-ray outburst happened in AXP has spin period 5.54 s Radio emission was detected from XTE J during its active state. Clear pulsations have been detected. Large radio luminosity. Strong polarization. Precise Pdot measurement. Important to constrain models, for better distance and coordinates determinations, etc. (Camilo et al. astro-ph/ )
31 Another AXP detected in radio 1E P= 2 sec SNR G Pdot changed significantly on the scale of just ~few months Rotation and magnetic axis seem to be aligned Also this AXP demonstrated weak SGR-like bursts (Rea et al. 2008, GCN 8313) Radio [simultaneous] X-rays (see also arxiv: )
32 Transient radiopulsar PSR J However, no radio emission P=0.326 sec detected. B= G Due to beaming? Among all rotation powered PSRs it has the largest Edot. Smallest spindown age (884 yrs). The pulsar increased its luminosity in X-rays. Increase of pulsed X-ray flux. Magnetar-like X-ray bursts (RXTE). Timing noise. See additional info about this pulsar at the web-site ,
33 Bursts from the transient PSR Chandra: Oct 2000 Gavriil et al June 2006
34 Weak dipole field magnetar Spin period of a neutron star grows. The rate of deceleration is related to the dipole magnetic field. Measuring the spin-down rate we measure the field. The source is a soft gamma-ray repeater: SGR P=9.1 s The straight line in the plot corresponds to a constant spin periods: i.e. no spin-down B< G (arxiv: ) Old magnetar? ( ) 200 Spectral data suggests high field on the surface:
35 Another low field magnetar Swift J (SGR ) P=8.44 s B= G New data:
36 Quiescent magnetar Normally magnetars are detected via their strong activity: gamma-ray bursts or enhanced X-ray luminosity. This one was detected in radio observations The field is estimated to be B~ G Chandra It seems to be the first magnetar to be Detected in a quiescent state. PSR J was detected in a radio survey As a pulsar with P=4.3 s. ATCA Noisy behavior in radio (see a review on high-b PSRs in arxiv:
37 A transient magnetar? PSR J X-ray flux is decaying for several years. Probably, the source was active years before. G SNR? See also
38 A pulsar with growing field? PSR J n=0.9+/-0.2 Will it become a magnetar? Espinoza et al. arxiv:
39 ROSAT ROentgen SATellite German satellite (with participation of US and UK). Launched 01 June The program was successfully ended on 12 Feb 1999.
40 Close-by radioquiet NSs RX J Discovery: Walter et al. (1996) Proper motion and distance: Kaplan et al. No pulsations Thermal spectrum Later on: six brothers
41 Magnificent Seven (M7) Name Period, s RXJ RXJ RBS RBS ? RXJ RXJ RBS Radioquiet Close-by Thermal emission Absorption features Long periods
42 Spin properties and other parameters Kaplan arxiv: Updates: νdot= ( νdot < ) van Kerkwijk & Kaplan [ ] νdot= Kaplan & van Kerkwijk [ ] νdot < Kaplan and van Kerkwijk [ ]
43 Spectral properties Van Kerkwijk et al. (2004) Kaplan arxiv: Spectra are blackbody plus one or several wide absorption features. The origin of features is not understood, yet. New data: Kaplan et al. [ ]
44 Resolution of radius puzzle for RX J1856? Blackbody fits to the optical And X-ray spectra (Truemper et al., 2004) Two-component model or Model with continuous T-distribution (hot spots) Radius determination --> EoS --> matter at high densities
45 Double Neutron Stars and Millisecond Pulsars
46 Double Neutron Stars and Millisecond Pulsars
47 Neutron star mass measurements with binary radio pulsars MSP with period P=3.15 ms Pb = 8.68 d, e= (4) Inclination angle = 89.17(2) degrees! Precise masses derived from Shapiro delay only: Update [Fonseca et al. (2016)] PSR J Demorest et al., Nature (2010)
48 PSR J A precise AND large mass measurement Shapiro delay:
49 The big one: PSR J
50 PSR J
51 GR test / better mass measurement
52 NS Masses and Radii <--> EoS
53 Mystery of the NS core composition
54 The isolated neutron star candidate 2XMM J A new INS candidate. B >26, V >25.5, R >25 (at 2.5σ confidence level) log(fx/fv) >3.1 kt = 118 +/-15 ev unabsorbed X-ray flux: Fx ~ erg s 1 cm 2 in the kev band. At 2.3 kpc (Eta Carinae) the luminosity is LX ~ erg s 1 R ~ 5.7 km M7-like? Yes! Pires & Motch [ ]; Pires et al. [ ]
55 Radio observations Up to now the M7 are not detected for sure at radio wavelengths, however, there was a paper by Malofeev et al., in which the authors claim that they had detect two of the M7 at very low wavelength (<~100 MHz). At the moment the most strict limits are given by Kondratiev et al. Non-detection is still consistent with narrow beams. Kondratiev et al. arxiv:
56 M7 among other NSs Evolutionary links of M7 with other NSs are not clear, yet. M7-like NSs can be numerous. They can be descendants of magnetars. Can be related to RRATs. Or, can be a different population. Kaplan arxiv:
57 How to find new candidates? 1. Digging the data Many attempts failed. One of the latest used SDSS optical data together with ROSAT X-ray. Candidates have been observed by Chandra. Nothing was found (Agueros et al. arxiv: ). 2. erosita is coming! In 2014 spectrum-rg with erosita will be launched. It is expected that with this telescope tens of new M7-like NSs can be found (Boldin et al., Pires et al.)
58 Pulsars invisible in radio? EGRET data Many unidentified sources (Nolan et al. astro-ph/ ) (Grenier astro-ph/ )
59 Fermi pulsars In the 2nd catalogue there are 117 pulsars. 1/3 mpsr The rest are young: 1/3 radio-loud 1/3 radio-quiet See also ; ; ;
60 Discovery of radio transients McLaughlin et al. (2006) discovered a new type of sources RRATs (Rotating Radio Transients). For most of the sources periods about few seconds were discovered. The result was obtained during the Parkes survey of the Galactic plane. Burst duration 2-30 ms, interval 4 min-3 hr Periods in the range s Thermal X-rays were observed from one of the RRATs (Reynolds et al. 2006). This one seems to me the youngest. Recent review: Catalogue:
61 RRATs. X-ray + radio data X-ray pulses overlaped on radio data of RRAT J (arxiv: )
62 RRATs properties 19 with P-Pdot RRATs seem to be similar to PSRs
63 Calvera et al. In 2008 Rutledge et al. reported the discovery of an enigmatic NS candidate dubbed Calvera. It is high above the galactic plane. [ ] Shevchuk et al. [ ]
64 More data on Calvera XMM-Newton observations. Zane et al. [ ] Thermal emission (two blackbody or two hydrogen atmospheric: T_1~55/150 ev and T_2~80/250 ev) P=0.06 sec now doubt Pdot < (B< G) No radio emission Probably detected also by Fermi [ ]
65 Some LIGO results Beating the spin-down limit on gravitational wave emission from the Crab pulsar h095% < ε< (single template) All-sky search for periodic grav. waves in LIGO S4 data HZ No evidence. Upper limits on isolated NSs GW emission. 3. gr-qc/ Upper limits on gravitational wave emission from 78 PSRs ε< 10-6 for PSR J h< for PSR J A search for grav waves associated with glitch of the Vela pulsar h< Search for Gravitational Wave Bursts from Six Magnetars Limits on the energy emitted in GW during bursts See a review on gravitational waves from NSs in
66 Pulsars, positrons, PAMELA Geminga, PSR B , and all PSRs [O. Adriani et al.] arxiv: [Dan Hooper et al arxiv: ]
67 Pulsars, positrons, PAMELA, AMS First Result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station: Precision Measurement of the Positron Fraction in Primary Cosmic Rays of GeV [M. Aguilar et al. (AMS Collaboration), PRL 110 (2013)
68 NS birth rate [Keane, Kramer 2008, arxiv: ]
69 Too many NSs??? It seems, that the total birth rate is larger than the rate of CCSN. e- - capture SN cannot save the situation, as they are <~20%. Note, that the authors do not include CCOs. So, either some estimates are wrong, or some sources evolve into others. See also astro-ph/ GRAND UNIFICATION: [Keane, Kramer 2008, arxiv: ]
70 Conclusion There are several types of sources: CCOs, M7, SGRs, AXPs, RRATs... Magnetars Significant fraction of all newborn NSs Unsolved problems: 1. Are there links? 2. Reasons for diversity
71 Some reviews on isolated neutron stars NS basics: physics/ astro-ph/ X-rays from INS arxiv: SGRs & AXPs: arxiv: arxiv: CCOs: astro-ph/ arxiv: Quark stars: arxiv: The Magnificent Seven: astro-ph/ arxiv: RRATs: arxiv: Cooling of NSs: arxiv: astro-ph/ NS structure arxiv: EoS arxiv: arxiv: NS atmospheres astro-ph/ NS magnetic fields arxiv: arxiv: Different types arxiv: arxiv: Read the OVERVIEW in the book by Haensel, Yakovlev, Potekhin
Physics of Compact Stars. David Blaschke (University of Wroclaw & JINR Dubna)
 Physics of Compact Stars David Blaschke (University of Wroclaw & JINR Dubna) University of Bielefeld, Summer Semester 2013 Physics of Compact Stars Contents: 1. Observations of compact star (CS) properties
Physics of Compact Stars David Blaschke (University of Wroclaw & JINR Dubna) University of Bielefeld, Summer Semester 2013 Physics of Compact Stars Contents: 1. Observations of compact star (CS) properties
The Neutron Star Zoo. Stephen C.-Y. Ng ( 吳志勇 ) HKU
 The Neutron Star Zoo Stephen C.-Y. Ng ( 吳志勇 ) HKU Overview Introduction to neutron stars Different classes of neutron stars: Radio Pulsars MSPs Magnetars DINS CCOs Unification 6/12/2017 NAOC Stephen Ng
The Neutron Star Zoo Stephen C.-Y. Ng ( 吳志勇 ) HKU Overview Introduction to neutron stars Different classes of neutron stars: Radio Pulsars MSPs Magnetars DINS CCOs Unification 6/12/2017 NAOC Stephen Ng
X-ray Properties of Rotation Powered Pulsars and Thermally Emitting Neutron Stars
 X-ray Properties of Rotation Powered Pulsars and Thermally Emitting Neutron Stars George Pavlov (Penn State; Polytech.Univ SPb) Collaborators: Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Bettina Posselt
X-ray Properties of Rotation Powered Pulsars and Thermally Emitting Neutron Stars George Pavlov (Penn State; Polytech.Univ SPb) Collaborators: Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Bettina Posselt
(Anomalous) X-Ray Pulsars. Vicky Kaspi. Montreal, Canada. Stanford December 16, 2004
 (Anomalous) X-Ray Pulsars Vicky Kaspi Montreal, Canada Texas @ Stanford December 16, 2004 Summary Introduction to AXPs Evidence that AXPs are magnetars Open Issues and Recent Results: IR emission Transient
(Anomalous) X-Ray Pulsars Vicky Kaspi Montreal, Canada Texas @ Stanford December 16, 2004 Summary Introduction to AXPs Evidence that AXPs are magnetars Open Issues and Recent Results: IR emission Transient
Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal, Canada)
 Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal, Canada) C. Espinoza M. Gonzalez M. Kramer M. Livingstone A. Lyne M. McLaughlin S. Olausen C.Y. Ng G. Pavlov W. Zhu Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal,
Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal, Canada) C. Espinoza M. Gonzalez M. Kramer M. Livingstone A. Lyne M. McLaughlin S. Olausen C.Y. Ng G. Pavlov W. Zhu Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal,
Evolution with decaying and re-emerging magnetic field
 Evolution with decaying and re-emerging magnetic field Diversity of young neutron stars Young isolated neutron stars can appear in many flavors: o Radio pulsars o Compact central X-ray sources in supernova
Evolution with decaying and re-emerging magnetic field Diversity of young neutron stars Young isolated neutron stars can appear in many flavors: o Radio pulsars o Compact central X-ray sources in supernova
X-ray Observations of Rotation Powered Pulsars
 X-ray Observations of Rotation Powered Pulsars George Pavlov (Penn State) Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Martin Durant (Univ. of Toronto) Bettina Posselt (Penn State) Isolated neutron stars
X-ray Observations of Rotation Powered Pulsars George Pavlov (Penn State) Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Martin Durant (Univ. of Toronto) Bettina Posselt (Penn State) Isolated neutron stars
Cooling Limits for the
 Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
The Magnificent Seven: Nearby, Thermally Emitting, Isolated Neutron Stars
 The Magnificent Seven: Nearby, Thermally Emitting, Isolated Neutron Stars Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching A legacy of ROSAT Proper motions and distances Observations
The Magnificent Seven: Nearby, Thermally Emitting, Isolated Neutron Stars Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching A legacy of ROSAT Proper motions and distances Observations
Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) ApJ, 2006, 646, L139 Nature, 2006, 439, 817 Astro-ph/
 Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) ApJ, 2006, 646, L139 Nature, 2006, 439, 817 Astro-ph/0608311 Introduction 11 Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) (Mclaughlin et al 2006) Repeated, irregular radio bursts
Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) ApJ, 2006, 646, L139 Nature, 2006, 439, 817 Astro-ph/0608311 Introduction 11 Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) (Mclaughlin et al 2006) Repeated, irregular radio bursts
Neutron Stars. Melissa Louie
 Neutron Stars Melissa Louie 11-08-10 Outline History, Formation, Properties Detection Pulsars Crab Nebula Pulsar Pulsar Timing Pulsars in Binary Systems Isolated Neutron Stars J185635-3754 Summary 2 The
Neutron Stars Melissa Louie 11-08-10 Outline History, Formation, Properties Detection Pulsars Crab Nebula Pulsar Pulsar Timing Pulsars in Binary Systems Isolated Neutron Stars J185635-3754 Summary 2 The
Astronomy 421. Lecture 23: End states of stars - Neutron stars
 Astronomy 421 Lecture 23: End states of stars - Neutron stars 1 Outline Neutron stars Pulsars properties distribution emission mechanism evolution 2 Neutron stars Typical values: M ~ 1.4M R ~ 10 km ρ ~
Astronomy 421 Lecture 23: End states of stars - Neutron stars 1 Outline Neutron stars Pulsars properties distribution emission mechanism evolution 2 Neutron stars Typical values: M ~ 1.4M R ~ 10 km ρ ~
Neutron Stars. We now know that SN 1054 was a Type II supernova that ended the life of a massive star and left behind a neutron star.
 Neutron Stars Neutron Stars The emission from the supernova that produced the crab nebula was observed in 1054 AD by Chinese, Japanese, Native Americans, and Persian/Arab astronomers as being bright enough
Neutron Stars Neutron Stars The emission from the supernova that produced the crab nebula was observed in 1054 AD by Chinese, Japanese, Native Americans, and Persian/Arab astronomers as being bright enough
Thermal Radiation from Isolated Neutron Stars
 Thermal Radiation from Isolated Neutron Stars George Pavlov Penn State Slava Zavlin MSFC (Huntsville) Divas Sanwal Penn State Oleg Kargaltsev Penn State Roger Romani Stanford Thermal emission: Why important?
Thermal Radiation from Isolated Neutron Stars George Pavlov Penn State Slava Zavlin MSFC (Huntsville) Divas Sanwal Penn State Oleg Kargaltsev Penn State Roger Romani Stanford Thermal emission: Why important?
The Magnificent Seven Similarities and Differences
 The Magnificent Seven Similarities and Differences Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching The discovery of thermal, radio quiet isolated neutron stars New XMM-Newton
The Magnificent Seven Similarities and Differences Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching The discovery of thermal, radio quiet isolated neutron stars New XMM-Newton
Young Neutron Stars and the Role of Magnetic Fields in their Evolution
 Young Neutron Stars and the Role of Magnetic Fields in their Evolution Eric Gotthelf (Columbia University) The X-ray Universe 2011 28 June 2011, Berlin Germany Talk Outline Recent Highlights of Young Isolated
Young Neutron Stars and the Role of Magnetic Fields in their Evolution Eric Gotthelf (Columbia University) The X-ray Universe 2011 28 June 2011, Berlin Germany Talk Outline Recent Highlights of Young Isolated
Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin. Crab Pulsar in X-rays
 Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin Crab Pulsar in X-rays Test #2 Monday, November 13, 11-11:50 am Ruffner G006 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin Crab Pulsar in X-rays Test #2 Monday, November 13, 11-11:50 am Ruffner G006 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Monday, October 21, 2013 Third exam this Friday, October 25. Third Sky Watch watch the weather! Review sheet posted today. Review Thursday, 5 6 PM,
 Monday, October 21, 2013 Third exam this Friday, October 25. Third Sky Watch watch the weather! Review sheet posted today. Review Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 2.256 Lecture 19 posted today Reading: Chapter
Monday, October 21, 2013 Third exam this Friday, October 25. Third Sky Watch watch the weather! Review sheet posted today. Review Thursday, 5 6 PM, Room WEL 2.256 Lecture 19 posted today Reading: Chapter
Compact stars as laboratories to test matter at extreme conditions. Alessandro Drago Otranto, June 2009
 Compact stars as laboratories to test matter at extreme conditions Alessandro Drago Otranto, June 2009 Plan of the lectures Introduction: the discovery of neutron stars and pulsars; main facts about their
Compact stars as laboratories to test matter at extreme conditions Alessandro Drago Otranto, June 2009 Plan of the lectures Introduction: the discovery of neutron stars and pulsars; main facts about their
Measuring MNS, RNS, MNS/RNS or R
 Measuring MNS, RNS, MNS/RNS or R Sebastien Guillot Advisor: Robert Rutledge Galileo Galilei Institute, Firenze March 2014 Some Reviews Lattimer and Prakash, 2007 Miller C., 2013 Heinke et al., 2013 Reminder
Measuring MNS, RNS, MNS/RNS or R Sebastien Guillot Advisor: Robert Rutledge Galileo Galilei Institute, Firenze March 2014 Some Reviews Lattimer and Prakash, 2007 Miller C., 2013 Heinke et al., 2013 Reminder
Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars. Observations and model applications
 Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars Theoretical aspects Observations and model applications Slava Zavlin (MPE, Garching) A Short History Chi & Salpeter (1964) and Tsuruta (1964): thermal radiation
Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars Theoretical aspects Observations and model applications Slava Zavlin (MPE, Garching) A Short History Chi & Salpeter (1964) and Tsuruta (1964): thermal radiation
Probing Extreme Physics with Compact Objects
 Probing Extreme Physics with Compact Objects Dong Lai Department of Astronomy Cornell University Extremes in Astrophysics: Most energetic particles: 10 20 ev Most energetic photons: 10 14 ev Highest temperature:
Probing Extreme Physics with Compact Objects Dong Lai Department of Astronomy Cornell University Extremes in Astrophysics: Most energetic particles: 10 20 ev Most energetic photons: 10 14 ev Highest temperature:
21. Neutron Stars. The Crab Pulsar: On & Off. Intensity Variations of a Pulsar
 21. Neutron Stars Neutron stars were proposed in the 1930 s Pulsars were discovered in the 1960 s Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars Pulsars slow down as they age Neutron stars are superfluid &
21. Neutron Stars Neutron stars were proposed in the 1930 s Pulsars were discovered in the 1960 s Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars Pulsars slow down as they age Neutron stars are superfluid &
Isolated Neutron Stars: Calvera and Beyond
 Isolated Neutron Stars: Calvera and Beyond Bob Rutledge McGill University Collaborators: Derek Fox and Andrew Shevchuk (PSU) Monica Turner (McGill) Jason Hessels, Ben Stappers X-ray Observations of Isolated
Isolated Neutron Stars: Calvera and Beyond Bob Rutledge McGill University Collaborators: Derek Fox and Andrew Shevchuk (PSU) Monica Turner (McGill) Jason Hessels, Ben Stappers X-ray Observations of Isolated
Editorial comment: research and teaching at UT
 Wednesday, March 23, 2017 Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), Background: Sections 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.8, 3.10,
Wednesday, March 23, 2017 Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), Background: Sections 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.8, 3.10,
Fermi Large Area Telescope:
 Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae
 Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae Pulsars Characteristic parameters Pulsar wind nebulae Properties Evolution Exotic central compact objects - Magnetars The Crab Pulsar http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/education/sounds/sounds.html
Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae Pulsars Characteristic parameters Pulsar wind nebulae Properties Evolution Exotic central compact objects - Magnetars The Crab Pulsar http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/education/sounds/sounds.html
Chapter 0 Introduction X-RAY BINARIES
 X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
X-RAY BINARIES 1 Structure of this course 0. Introduction 1. Compact stars: formation and observational appearance. Mass transfer in binaries 3. Observational properties of XRBs 4. Formation and evolution
Compact Stars. Lecture 4
 Compact Stars Lecture 4 X-ray binaries We have talked about the basic structure of accretion disks in X-ray binaries and evolutionary scenarios of low mass and high mass XRBs I will now present the observational
Compact Stars Lecture 4 X-ray binaries We have talked about the basic structure of accretion disks in X-ray binaries and evolutionary scenarios of low mass and high mass XRBs I will now present the observational
Neutron Stars. J.M. Lattimer. Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University. 25 July 2011
 Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University 25 July 2011 Computational Explosive Astrophysics Summer School LBL Outline Observed Properties of Structure of Formation and Evolution of Mass
Department of Physics & Astronomy Stony Brook University 25 July 2011 Computational Explosive Astrophysics Summer School LBL Outline Observed Properties of Structure of Formation and Evolution of Mass
Neutron Stars: Observations
 Neutron Stars: Observations Ian Jones School of Mathematics, University of Southampton, UK Neutron star observations: overview From the observational point of view, neutron stars come in many different
Neutron Stars: Observations Ian Jones School of Mathematics, University of Southampton, UK Neutron star observations: overview From the observational point of view, neutron stars come in many different
MILLISECOND PULSARS. Merve Çolak
 MILLISECOND PULSARS Merve Çolak OUTLINE Corbet Diagram (again) P-P(dot) Diagram MSPs and Their History Properties of MSPs Spin-up of Neutron Stars Spin-down of MSPs MSP Evolution Recent MSP Evolution Model
MILLISECOND PULSARS Merve Çolak OUTLINE Corbet Diagram (again) P-P(dot) Diagram MSPs and Their History Properties of MSPs Spin-up of Neutron Stars Spin-down of MSPs MSP Evolution Recent MSP Evolution Model
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants
 Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Anomalous X-ray Pulsars
 Anomalous X-ray Pulsars GRBs: The Brightest Explosions in the Universe Harvard University, May 23, 2002 Vicky Kaspi Montreal, Canada What are Anomalous X-ray Pulsars? exotic class of objects 1st discovered
Anomalous X-ray Pulsars GRBs: The Brightest Explosions in the Universe Harvard University, May 23, 2002 Vicky Kaspi Montreal, Canada What are Anomalous X-ray Pulsars? exotic class of objects 1st discovered
FERMI. YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars. 25 novembre 2008 Damien Parent. Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
 FERMI Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars 25 novembre 2008 1 Topics 1. Young pulsars, our best candidates 2 examples : J0205+6449 and
FERMI Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars 25 novembre 2008 1 Topics 1. Young pulsars, our best candidates 2 examples : J0205+6449 and
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results
 Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Pulsar Astronomy with GLAST Steve Thorsett UC Santa Cruz GLAST
 Pulsar Astronomy with Steve Thorsett UC Santa Cruz Discovery of Neutron Stars: Pulsars In 1967, Jocelyn Bell discovered a strange, pulsating radio source (dubbed LGM 1) http://www.ggw.org/asras/ snimages/
Pulsar Astronomy with Steve Thorsett UC Santa Cruz Discovery of Neutron Stars: Pulsars In 1967, Jocelyn Bell discovered a strange, pulsating radio source (dubbed LGM 1) http://www.ggw.org/asras/ snimages/
Distribution of X-ray binary stars in the Galaxy (RXTE) High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 8: Accretion and jets in binary stars
 High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 8: Accretion and jets in binary stars Distribution of X-ray binary stars in the Galaxy (RXTE) Robert Laing Primary Compact accreting binary systems Compact star WD NS BH
High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 8: Accretion and jets in binary stars Distribution of X-ray binary stars in the Galaxy (RXTE) Robert Laing Primary Compact accreting binary systems Compact star WD NS BH
Chapter 14. Outline. Neutron Stars and Black Holes. Note that the following lectures include. animations and PowerPoint effects such as
 Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 14 Neutron
Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 14 Neutron
The Secret Life of Neutron Stars. Jeremy Heyl Harvard-Smithsonian CfA
 The Secret Life of Neutron Stars Jeremy Heyl Harvard-Smithsonian CfA The Life of a 10 M Star PNS 10 5 yr 10 6 yr 10 7 yr 10 8 yr 10 9 yr 10 10 yr PMS MS Radio Pulsars Thermal Accretion-, Nuclear-, GWpowered
The Secret Life of Neutron Stars Jeremy Heyl Harvard-Smithsonian CfA The Life of a 10 M Star PNS 10 5 yr 10 6 yr 10 7 yr 10 8 yr 10 9 yr 10 10 yr PMS MS Radio Pulsars Thermal Accretion-, Nuclear-, GWpowered
INTEGRAL & Magnetars: a high energy approach to extreme neutron stars
 INTEGRAL & Magnetars: a high energy approach to extreme neutron stars Diego Götz CEA - Saclay - Irfu/Service d Astrophysique N. Rea (UvA), S. Zane (MSSL), R. Turolla (Uni Padova), M. Lyutikov (Purdue Univ.)
INTEGRAL & Magnetars: a high energy approach to extreme neutron stars Diego Götz CEA - Saclay - Irfu/Service d Astrophysique N. Rea (UvA), S. Zane (MSSL), R. Turolla (Uni Padova), M. Lyutikov (Purdue Univ.)
The Stellar Graveyard
 Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. Announcements MIDTERM #2
Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. Announcements MIDTERM #2
The magnetic properties of Main Sequence Stars, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
 The magnetic properties of Main Sequence Stars, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars Lilia Ferrario Mathematical Sciences Institute Australian National University Properties of MWDs High Field MWDs ~ 10 6-10
The magnetic properties of Main Sequence Stars, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars Lilia Ferrario Mathematical Sciences Institute Australian National University Properties of MWDs High Field MWDs ~ 10 6-10
Millisecond X-ray pulsars: 10 years of progress. Maurizio Falanga
 Millisecond X-ray pulsars: 10 years of progress Maurizio Falanga History I Radio Astronomy in the 30 s-60 s Karl Jansky 1933 3C273 Discovery (1961-63) Quasi-Stellar Radio Sources as the most energetic
Millisecond X-ray pulsars: 10 years of progress Maurizio Falanga History I Radio Astronomy in the 30 s-60 s Karl Jansky 1933 3C273 Discovery (1961-63) Quasi-Stellar Radio Sources as the most energetic
Systematic study of magnetar outbursts
 Systematic study of magnetar outbursts Francesco Coti Zelati Institute for Space Sciences, CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona In collaboration with N. Rea (CSIC-IEEC, U. Amsterdam), J. A. Pons (U. Alicante), S. Campana
Systematic study of magnetar outbursts Francesco Coti Zelati Institute for Space Sciences, CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona In collaboration with N. Rea (CSIC-IEEC, U. Amsterdam), J. A. Pons (U. Alicante), S. Campana
Surface emission of neutron stars
 Surface emission of neutron stars NS Radii A NS with homogeneous surface temperature and local blackbody emission L 4 R 2 T 4 From dispersion measure F 4 L D 2 2 R / D T 4 From X-ray spectroscopy NS Radii
Surface emission of neutron stars NS Radii A NS with homogeneous surface temperature and local blackbody emission L 4 R 2 T 4 From dispersion measure F 4 L D 2 2 R / D T 4 From X-ray spectroscopy NS Radii
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 30 Dec 2001
 Evolution of Isolated Neutron Stars Sergei Popov Sternberg Astronomical Institute November 10, 2000 arxiv:astro-ph/0101031v2 30 Dec 2001 Abstract. In this paper we briefly review our recent results on
Evolution of Isolated Neutron Stars Sergei Popov Sternberg Astronomical Institute November 10, 2000 arxiv:astro-ph/0101031v2 30 Dec 2001 Abstract. In this paper we briefly review our recent results on
Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT. Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn. NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12.
 Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Fermi = Large Area Telescope
Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Fermi = Large Area Telescope
Neutron star mass and radius constraints from millisecond X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursters
 Neutron star mass and radius constraints from millisecond X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursters Juri Poutanen (University of Turku, Finland) Collaborators:! Valery Suleimanov (Univ. Tübingen, Germany), Joonas
Neutron star mass and radius constraints from millisecond X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursters Juri Poutanen (University of Turku, Finland) Collaborators:! Valery Suleimanov (Univ. Tübingen, Germany), Joonas
Death of Stars Part II Neutron Stars
 Death of Stars Part II Neutron Stars 1 REMEMBER THIS!? 2 Guiding Questions 1. What led scientists to the idea of a neutron star? 2. What are pulsars, and how were they discovered? 3. How did astronomers
Death of Stars Part II Neutron Stars 1 REMEMBER THIS!? 2 Guiding Questions 1. What led scientists to the idea of a neutron star? 2. What are pulsars, and how were they discovered? 3. How did astronomers
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 23 Nov 2003
 Young Neutron Stars and Their Environments IAU Symposium, Vol. 218, 2004 F. Camilo and B. M. Gaensler, eds. Central Compact Objects in Supernova Remnants arxiv:astro-ph/0311526v1 23 Nov 2003 George G.
Young Neutron Stars and Their Environments IAU Symposium, Vol. 218, 2004 F. Camilo and B. M. Gaensler, eds. Central Compact Objects in Supernova Remnants arxiv:astro-ph/0311526v1 23 Nov 2003 George G.
Probing the physics of magnetars
 Probing the physics of magnetars GianLuca Israel (INAF - RomA ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY)...and many many many others Why Magnetars? Loss of rotational energy is orders of magnitudes too small (1030erg/s)
Probing the physics of magnetars GianLuca Israel (INAF - RomA ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY)...and many many many others Why Magnetars? Loss of rotational energy is orders of magnitudes too small (1030erg/s)
Pulsars and Radio Transients. Scott Ransom National Radio Astronomy Observatory / University of Virginia
 Pulsars and Radio Transients Scott Ransom National Radio Astronomy Observatory / University of Virginia TIARA Summer School on Radio Astronomy 2016 Radio Transients Non-thermal emission Emission types
Pulsars and Radio Transients Scott Ransom National Radio Astronomy Observatory / University of Virginia TIARA Summer School on Radio Astronomy 2016 Radio Transients Non-thermal emission Emission types
EXTREME NEUTRON STARS
 EXTREME NEUTRON STARS Christopher Thompson Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics University of Toronto SLAC Summer Institute 2005 Extreme Magnetism: B ~ 10 8-9 G (Low-mass X-ray binaries, millisecond
EXTREME NEUTRON STARS Christopher Thompson Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics University of Toronto SLAC Summer Institute 2005 Extreme Magnetism: B ~ 10 8-9 G (Low-mass X-ray binaries, millisecond
Compact Binaries - 3 ASTR2110 Sarazin
 Compact Binaries - 3 ASTR2110 Sarazin Zoology of Binary Stars X-ray Binary Pulsar Spin-Up Accreted material has high angular momentum Spins up neutron star (true of ~all X-ray binary pulsars) Millisecond
Compact Binaries - 3 ASTR2110 Sarazin Zoology of Binary Stars X-ray Binary Pulsar Spin-Up Accreted material has high angular momentum Spins up neutron star (true of ~all X-ray binary pulsars) Millisecond
Gamma-ray Astrophysics
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
Gamma-ray Astrophysics AGN Pulsar SNR GRB Radio Galaxy The very high energy -ray sky NEPPSR 25 Aug. 2004 Many thanks to Rene Ong at UCLA Guy Blaylock U. of Massachusetts Why gamma rays? Extragalactic Background
Thomas Tauris Bonn Uni. / MPIfR
 Thomas Tauris Bonn Uni. / MPIfR Heidelberg XXXI, Oct. 2013 1: Introduction Degenerate Fermi Gases Non-relativistic and extreme relativistic electron / (n,p,e - ) gases 2: White Dwarfs Structure, cooling
Thomas Tauris Bonn Uni. / MPIfR Heidelberg XXXI, Oct. 2013 1: Introduction Degenerate Fermi Gases Non-relativistic and extreme relativistic electron / (n,p,e - ) gases 2: White Dwarfs Structure, cooling
Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Astro 129: Chapter 1a
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Magnetars, the most extreme Neutron Stars. Multiwavelenght emission
 Magnetars, the most extreme Neutron Stars. Multiwavelenght emission Silvia Zane, MSSL, UCL Black Holes, jets and outflows Kathmandu, Nepal 14-18 Oct 2013 o SGRs/AXPs as magnetars, the most extreme compact
Magnetars, the most extreme Neutron Stars. Multiwavelenght emission Silvia Zane, MSSL, UCL Black Holes, jets and outflows Kathmandu, Nepal 14-18 Oct 2013 o SGRs/AXPs as magnetars, the most extreme compact
Neutron Stars. Neutron Stars Mass ~ 2.0 M sun! Radius ~ R sun! isolated neutron stars first seen only recently (1997)
 Neutron Stars 1 2 M core > 1.4 M - collapse past WD! sun nuclei packed tightly together! protons absorb electrons; only neutrons left! collapse halted by neutron degeneracy pressure How do you find something
Neutron Stars 1 2 M core > 1.4 M - collapse past WD! sun nuclei packed tightly together! protons absorb electrons; only neutrons left! collapse halted by neutron degeneracy pressure How do you find something
H. Tong, W. Wang
 Central compact objects, superslow X-ray pulsars, gamma-ray bursts: do they have anything to do with magnetars? arxiv:1406.6458v1 [astro-ph.he] 25 Jun 2014 H. Tong, W. Wang 2014.6 Abstract Magnetars and
Central compact objects, superslow X-ray pulsars, gamma-ray bursts: do they have anything to do with magnetars? arxiv:1406.6458v1 [astro-ph.he] 25 Jun 2014 H. Tong, W. Wang 2014.6 Abstract Magnetars and
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008](/thumbs/72/66863435.jpg) Astronomy and Astrophysics Review manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:0804.0250v1 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008 Sandro Mereghetti The strongest cosmic magnets: Soft Gamma-ray Repeaters and Anomalous
Astronomy and Astrophysics Review manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:0804.0250v1 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008 Sandro Mereghetti The strongest cosmic magnets: Soft Gamma-ray Repeaters and Anomalous
The Stellar Graveyard Neutron Stars & White Dwarfs
 The Stellar Graveyard Neutron Stars & White Dwarfs White Dwarfs White dwarfs are the remaining cores of low-mass (M < 8M sun ) stars Electron degeneracy pressure supports them against gravity Density ~
The Stellar Graveyard Neutron Stars & White Dwarfs White Dwarfs White dwarfs are the remaining cores of low-mass (M < 8M sun ) stars Electron degeneracy pressure supports them against gravity Density ~
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope
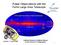 Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Final States of a Star
 Pulsars Final States of a Star 1. White Dwarf If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun, radius is about that of the Earth) 2. Neutron Star If initial mass > 8 MSun
Pulsars Final States of a Star 1. White Dwarf If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun, radius is about that of the Earth) 2. Neutron Star If initial mass > 8 MSun
The pulsar population and PSR/FRB searches with MeerKAT Slow boring pulsars
 The pulsar population and PSR/FRB searches with MeerKAT Slow boring pulsars Aris Karastergiou with contributions from Simon Johnston, Ben Stappers and the TRAPUM team P and Pdot are the observables. Lines
The pulsar population and PSR/FRB searches with MeerKAT Slow boring pulsars Aris Karastergiou with contributions from Simon Johnston, Ben Stappers and the TRAPUM team P and Pdot are the observables. Lines
discovers a radio-quiet gamma-ray millisecond Journal Group
 Einstein@Home discovers a radio-quiet gamma-ray millisecond pulsar @CHEA Journal Group Contribution of the paper Contribution of the paper Millisecond Pulsars (MSPs) Ver y rapid rotating neutron star
Einstein@Home discovers a radio-quiet gamma-ray millisecond pulsar @CHEA Journal Group Contribution of the paper Contribution of the paper Millisecond Pulsars (MSPs) Ver y rapid rotating neutron star
Science with Radio Pulsar Astrometry
 Science with Radio Pulsar Astrometry Shami Chatterjee Cornell University August 2012 Astrometry is a force multiplier Precise astrometry improves the science return from new discoveries. Astrometry is
Science with Radio Pulsar Astrometry Shami Chatterjee Cornell University August 2012 Astrometry is a force multiplier Precise astrometry improves the science return from new discoveries. Astrometry is
Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays
 The XXVII Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays Wei Wang National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing China Dec 8 13 2013, Dallas TX, USA Contents
The XXVII Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays Wei Wang National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing China Dec 8 13 2013, Dallas TX, USA Contents
Extreme Astrophysics with Neutron Stars
 Extreme Astrophysics with Neutron Stars A Whitepaper Submitted to the Astro 2010 Decadal Survey Committee Dong Lai (Cornell University) 1 Marten van Kerkwijk (University of Toronto) Jon Arons (UC Berkeley)
Extreme Astrophysics with Neutron Stars A Whitepaper Submitted to the Astro 2010 Decadal Survey Committee Dong Lai (Cornell University) 1 Marten van Kerkwijk (University of Toronto) Jon Arons (UC Berkeley)
Recent Radio Observations of Pulsars
 Recent Radio Observations of Pulsars R. N. Manchester Australia Telescope National Facility, CSIRO Sydney Australia Summary A pulsar census Recent pulsar surveys Pulse modulation and drifting subpulses
Recent Radio Observations of Pulsars R. N. Manchester Australia Telescope National Facility, CSIRO Sydney Australia Summary A pulsar census Recent pulsar surveys Pulse modulation and drifting subpulses
Early works. Dynamics of accretion, the role of turbulence, the role of magnetic fields in the ISM, spectrum. Victorij Shvartsman
 Isolated BHs Early works «Halos around black holes» Soviet Astronomy Astronom. Zhurn (1971) In this paper accretion onto isolated BHs from the ISM was studied for different BH masses (including intermediate).
Isolated BHs Early works «Halos around black holes» Soviet Astronomy Astronom. Zhurn (1971) In this paper accretion onto isolated BHs from the ISM was studied for different BH masses (including intermediate).
Crustal cooling in accretion heated neutron stars
 Crustal cooling in accretion heated neutron stars Ed Cackett ecackett@umich.edu University of Michigan Collaborators: Rudy Wijnands, Jon Miller, Jeroen Homan, Walter Lewin, Manuel Linares Outline X-ray
Crustal cooling in accretion heated neutron stars Ed Cackett ecackett@umich.edu University of Michigan Collaborators: Rudy Wijnands, Jon Miller, Jeroen Homan, Walter Lewin, Manuel Linares Outline X-ray
Radio counterparts of gamma-ray pulsars
 Radio counterparts of gamma-ray pulsars Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de on behalf of the Fermi LAT Collaboration IAU Symposium 2012, Beijing 20/08/12 117 gamma-ray pulsars! 41 young
Radio counterparts of gamma-ray pulsars Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de on behalf of the Fermi LAT Collaboration IAU Symposium 2012, Beijing 20/08/12 117 gamma-ray pulsars! 41 young
continuous waves from rotating neutron stars
 continuous waves from rotating neutron stars Matthew Pitkin - University of Glasgow DAWN Workshop 7 May 2015 LIGO G1500603 0 continuous wave sources Rotating neutron stars with a non-axisymmetric deformation
continuous waves from rotating neutron stars Matthew Pitkin - University of Glasgow DAWN Workshop 7 May 2015 LIGO G1500603 0 continuous wave sources Rotating neutron stars with a non-axisymmetric deformation
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy. HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric
 Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
Lecture 20 High-Energy Astronomy HEA intro X-ray astrophysics a very brief run through. Swift & GRBs 6.4 kev Fe line and the Kerr metric Tut 5 remarks Generally much better. However: Beam area. T inst
ASTR 200 : Lecture 20. Neutron stars
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 20 Neutron stars 1 Equation of state: Degenerate matter We saw that electrons exert a `quantum mechanical' pressure. This is because they are 'fermions' and are not allowed to occupy
ASTR 200 : Lecture 20 Neutron stars 1 Equation of state: Degenerate matter We saw that electrons exert a `quantum mechanical' pressure. This is because they are 'fermions' and are not allowed to occupy
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY. Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006
 PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
Physics of Compact Stars
 Physics of Compact Stars Crab nebula: Supernova 1054 Pulsars: rotating neutron stars Death of a massive star Pulsars: lab s of many-particle physics Equation of state and star structure Phase diagram of
Physics of Compact Stars Crab nebula: Supernova 1054 Pulsars: rotating neutron stars Death of a massive star Pulsars: lab s of many-particle physics Equation of state and star structure Phase diagram of
MIDTERM #2. ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. Can we detect BLACK HOLES? Black Holes in Binaries to the rescue. Black spot in the sky?
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Can we detect BLACK HOLES? NEXT Friday 04/03: MIDTERM #2 [Image by A. Hamilton] Black spot in the sky? Black Holes in Binaries to the rescue Black Holes in
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Can we detect BLACK HOLES? NEXT Friday 04/03: MIDTERM #2 [Image by A. Hamilton] Black spot in the sky? Black Holes in Binaries to the rescue Black Holes in
ASTR Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
RX J and RX J : recent results and status
 RX J0806+15 and RX J1914+24: recent results and status Gavin Ramsay (Armagh Observatory) Overview of talk Remind you what they are! Recent observational work since Nijmegen Meeting. Modelling and theoretical
RX J0806+15 and RX J1914+24: recent results and status Gavin Ramsay (Armagh Observatory) Overview of talk Remind you what they are! Recent observational work since Nijmegen Meeting. Modelling and theoretical
Tests of nuclear properties with astronomical observations of neutron stars
 Institute for Nuclear Theory 17 July 2014 Tests of nuclear properties with astronomical observations of neutron stars Wynn Ho University of Southampton, UK Nils Andersson University of Southampton, UK
Institute for Nuclear Theory 17 July 2014 Tests of nuclear properties with astronomical observations of neutron stars Wynn Ho University of Southampton, UK Nils Andersson University of Southampton, UK
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Mass loss from stars
 Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes
 Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes Massive stars and Type II supernovae Massive stars (greater than 8 solar masses) can create core temperatures high enough to burn carbon and heavier
Cooling Neutron Stars. What we actually see.
 Cooling Neutron Stars What we actually see. The Equilibrium We discussed the equilibrium in neutron star cores through this reaction (direct Urca). nëp + e à + ö e ö n = ö p + ö e + ö öe Does the reaction
Cooling Neutron Stars What we actually see. The Equilibrium We discussed the equilibrium in neutron star cores through this reaction (direct Urca). nëp + e à + ö e ö n = ö p + ö e + ö öe Does the reaction
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 4 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 4 Feb 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 4 Feb 2013](/thumbs/74/71345611.jpg) The Neutron Star Zoo Alice K. Harding Astrophysics Science Division NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD 20771 (Dated: February 6, 2013) Neutron stars are a very diverse population, both in their
The Neutron Star Zoo Alice K. Harding Astrophysics Science Division NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD 20771 (Dated: February 6, 2013) Neutron stars are a very diverse population, both in their
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J
 H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
A RADIO SEARCH FOR BLACK HOLES IN THE MILKY WAY GLOBULAR CLUSTER M10
 (nrao/aui) LAURA SHISHKOVSKY, J. STRADER, L. CHOMIUK, L. TREMOU (MSU), J. MILLER-JONES, V. TUDOR (CURTIN), T. MACCARONE (TEXAS TECH), G. SIVAKOFF, C. HEINKE (U. ALBERTA) A RADIO SEARCH FOR BLACK HOLES
(nrao/aui) LAURA SHISHKOVSKY, J. STRADER, L. CHOMIUK, L. TREMOU (MSU), J. MILLER-JONES, V. TUDOR (CURTIN), T. MACCARONE (TEXAS TECH), G. SIVAKOFF, C. HEINKE (U. ALBERTA) A RADIO SEARCH FOR BLACK HOLES
Object Index. Einstein, 118, 177, 347 EXO , 312, 318 EXO , 264, 268, 273 EXOSAT, 118, 299
 Object Index 1E 1048.1-5937, 270, 330, 332, 336 1E 1207.4-5209, 51, 185 1E 2259+586, 336 1E 2259+589, 332 1E 2259+59, 270, 330 1RXS J130848.6+212708, 122 1RXS J1708-4009, 332 1RXS J214303.7+065419, 122
Object Index 1E 1048.1-5937, 270, 330, 332, 336 1E 1207.4-5209, 51, 185 1E 2259+586, 336 1E 2259+589, 332 1E 2259+59, 270, 330 1RXS J130848.6+212708, 122 1RXS J1708-4009, 332 1RXS J214303.7+065419, 122
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J / RBS 1774
 XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)
 This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White dwarfs
The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White dwarfs
X-ray Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity
 X-ray Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity The Magnificent Seven R Turolla Department of Physics University of Padova, Italy M Cropper, CP De Vries, JJ Drake, F Haberl, A Treves J Vink,
X-ray Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity The Magnificent Seven R Turolla Department of Physics University of Padova, Italy M Cropper, CP De Vries, JJ Drake, F Haberl, A Treves J Vink,
Polarized (Surface) X-Rays from Highly Magnetized Neutron Stars
 Polarized (Surface) X-Rays from Highly Magnetized Neutron Stars Dong Lai Cornell University The Coming Age of X-Ray Polarimetry, April 29, 2009, Rome, Italy Thermal (Surface) Radiation from Neutron Stars
Polarized (Surface) X-Rays from Highly Magnetized Neutron Stars Dong Lai Cornell University The Coming Age of X-Ray Polarimetry, April 29, 2009, Rome, Italy Thermal (Surface) Radiation from Neutron Stars
X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age. Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs)
 X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) Cooling neutron stars ( ~10 5-10 6 yrs)
X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) Cooling neutron stars ( ~10 5-10 6 yrs)
Neutron Stars: Introduction. Stephen Eikenberry 16 Jan 2018
 Neutron Stars: Introduction Stephen Eikenberry 16 Jan 2018 Original Ideas - I May 1932: James Chadwick discovers the neutron People knew that nuclei were not protons only (nuclear mass >> mass of protons)
Neutron Stars: Introduction Stephen Eikenberry 16 Jan 2018 Original Ideas - I May 1932: James Chadwick discovers the neutron People knew that nuclei were not protons only (nuclear mass >> mass of protons)
