Kepler Data Release 23 Notes Q17. KSCI Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Susan E. Thompson (Editor)
|
|
|
- Brent Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kepler Data Release 23 Notes Q17 KSCI Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Susan E. Thompson (Editor)
2 KSCI : Kepler Data Release 23 Kotes Prepared by:,~-(~ n.te Izj;Z/13 Susan E. Thompson,eplerSCiEmce Office, for t he DAWG (page 4) Approved by: ~!::==:==--- > Date: \'d.,j I \ /13 r-in-chief Approved by: -~----.il---+~== I JSU;~.L - l I)I (3 or Da.ta Analysis & DAWG Lead A pproved by: ~ "-.~ Date: Michael R. Haas, Kepler Science Office Director 2
3 Document Control Ownership This document is part of the Kepler Project Documentation that is controlled by the Kepler Project Office, NASA/Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California. Control Level This document will be controlled under Ames Configuration Management system. Changes to this document shall be controlled. Physical Location The physical location of this document will be in the Ames Data Center. Distribution Requests To be place on the distribution list for additional revisions of this document, please address your request to the Kepler Science Office: Michael R. Haas Kepler Science Office Director MS NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA Michael.R.Haas@nasa.gov 3
4 The Data Characteristics Handbook and accompanying Data Release Notes are the collective effort of the Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG), composed of Science Office (SO), Science Operations Center (SOC), and Guest Observer (GO) Office members as listed below: Jon Jenkins, Chair Doug Caldwell, Co-Chair Barclay, Thomas Bryson, Stephen T. Burke, Christopher J. Campbell, Jennifer Catanzarite, Joseph Clarke, Bruce D. Coughlin, Jeffrey L. Girouard, Forrest Haas, Michael R. Ibrahim, Khadeejah Klaus, Todd Kolodziejczak, Jeffery (MSFC) Li, Jie McCauliff, Sean D. Morris, Rob Mullally, Fergal Quintana, Elisa V. Rowe, Jason Sabale, Anima Seader, Shawn Smith, Jeffrey Claiborne Still, Martin D. Tenenbaum, Peter G. Thompson, Susan E. Twicken, Joseph D. Uddin, Akm Kamal The correct citation for this document is: S. E. Thompson, J. L. Christiansen, J. M. Jenkins, D. A. Caldwell, T. Barclay, S. T. Bryson, C. J. Burke, J. R. Campbell, J. Catanzarite, B. D. Clarke, J. L. Coughlin, F. Girouard, M. R. Haas, K. Ibrahim, T. C. Klaus, J. J. Kolodziejczak, J. Li, S. D. McCauliff, R. Morris, F. Mullally, E. V. Quintana, J. Rowe, A. Sabale, S. Seader, J. C. Smith, M. D. Still, P. G. Tenenbaum, J. D. Twicken, and A. K. Uddin, 2013, Kepler Data Release 23 Notes (KSCI ). 4
5 Contents 1 Introduction Dates and Cadence Numbers for Q The SOC Pipeline for Q Kepler Mission Timeline to Date Data Quality in Q Evaluation of CDPP Summary of Data Anomalies Notable Features of the Q17 Data Solar Flare PDC Uses Regular MAP for All Targets PDC Corrected Short Cadence Data Final Data Set Collected
6 1 Introduction These Data Release Notes provide information specific to the release of Q17 data, processed with SOC Pipeline 9.1. These Notes contain the summary figures and tables for this quarter. The Kepler Data Characteristics Handbook (Christiansen et al., 2013) discusses most of the known phenomena found in the Kepler data in more detail. 1.1 Dates and Cadence Numbers for Q17 Contents of Data Release 23 Cadence Data Q.m First Cadence Last Cadence First Cadence Last Cadence Num Start End MJD midtime MJD midtime UT midtime UT midtime CINs CIN CIN 17 LC Apr :26:44 11-May :01: SCM Apr :12:31 02-May :11: SCM May :15:26 11-May :15: Contents of Data Release 23 FFIs No Full Frame Images are available this quarter. 6
7 1.2 The SOC Pipeline for Q17 Data Release 23 was processed with the SOC Pipeline 9.1. For details on how Kepler processes the data through the front-end of the pipeline (modules CAL, PA, PDC), please see the Data Processing Handbook (Fanelli et al., 2011). Notable changes and improvements to the pipeline in 9.1 include the following: The algorithm used by the CAL module to propagate the errors on the flux for each pixel and cadence was changed to improve its performance for stars that are highly variable on timescales of less than 12 hours. Under the old approach, undersampling of the error estimates resulted from only calculating the full propagation of uncertainties every 24 cadences and interpolating the results beetween these cadences. See of the Data Characteristics Handbook (Christiansen et al., 2013) for more details. In SOC 9.1 the reported errors for each cadence are a sum of the minimal error calculation (shot noise plus read noise) and an offset term to account for the extra error from the full propagation of errors. This offset is calculated by taking the mean of the difference between the full and the minimal error calculation across all cadences for which both were calculated. See Figure 1 for an example comparing the new and old methods of calculating the error for one pixel of a rapidly variable target. PDC now protects known transits from incorrectly being identified as Sudden Pixel Sensitivity Dropouts (SPSDs) or other types of outlier. Cadences containing known transits and eclipses are computed using the known epoch, period and duration of the events. No SPSDs or outliers are flagged during the known transits. This helps preserve transit depths and shapes from corruption by the SPSD and outlier correction algorithms. Note that this only affects known transits. Identification of a transit as an outlier may still occur for transits not identified prior to the data processing. Figure 1: The error on the flux for one pixel plotted against relative, long cadence number for a target that is highly variable on rapid timescales. The error calculated by a previous version of the pipeline is plotted in blue and the error calculated by the current SOC Pipeline 9.1 is plotted in red. 7
8 1.3 Kepler Mission Timeline to Date Kepler Mission Timeline January February March April May June July August September October November December SM 6/15 SM 7/2 LOFP LOFP LOFP SM 11/ Commissioning Q1-Spr Q2-Summer Q3-Fall Launch Science 7/20 8/20 10/19 11/19 12/17 Mod 3 SM - 2/2 3/6/09 FSW patch 5/12/09 6/18 9/17 SM 12/22 LOFP 12/ Q4-Winter Q5-Spring Q6-Summer Q7-Fall 1/19 2/18 3/19 4/21 5/20 7/21 8/22 9/22 10/23 11/23 12/21 SM - 2/1 SM 3/14 SM 12/ Q8 Winter Q9-Spring Q10-Summer Q11-Fall 1/24 2/23 3/19 4/26 5/25 6/26 7/27 8/29 9/29 10/31 12/1 LOFP LOFP & SM RW Q12-Winter Q13-Spring Q14-Summer Q15-Fall 1/4 2/1 2/29 4/30 5/31 7/30 8/30 11/5 12/6 3/28 6/28 10/3 SM 2013 rest Q16-Winter Q17 - Spring 3/6 5/7 1/11 4/8 You are here Symbol Key Quarterly roll Safe Mode Event Loss of Fine-Point Monthly Module 3 anomaly Chart update date Coronal Mass Ejection Figure 2: Kepler Mission Timeline as of the end of Q17. 8
9 2 Data Quality in Q Evaluation of CDPP To understand the overall performance of the pipeline, we show the Temporal Median (TM) of the CDPP time series as calculated by the TPS module for different versions of the SOC pipeline (Figure 3). We also provide the CDPP statistics for Q17 binned by magnitude in Table 1. Figure 3: 6.5-h Temporal Median of the CDPP time series. The median (circles) and 10th percentile value (diamonds) for all dwarf stars between Kp= are given. The 6-h TMCDPPs have been divided by sqrt(13/12) = to approximate 6.5-h TMCDPPs. A detailed discussion of the CDPP values is given in the Kepler Data Characteristics Handbook. The 6.x, 8.x and 9.x labels given in the legend refer to the version of the SOC pipeline used. The reduction in CDPP starting in Q14 may be related to the new method used to calculate CDPP in Q14 (see DRN 19, 1.2.) Table 1: Aggregate statistics for the TMCDPPs by magnitude. Column Definitions: (1) Kepler Magnitude at the center of the bin. Bins are ± 0.25 mag, for a bin of width 0.5 mag centered on this value. (2) Number of dwarfs (log g > 4) in the bin. (3) 10th percentile TMCDPP for dwarfs in the bin. (4) Median TMCDPP for dwarfs in the bin. (5) Number of all stars in the bin. (6) 10th percentile TMCDPP of all observed stars in the bin. (7) Median TMCDPP for all stars in the bin. (8) Simplified noise model CDPP. Kp mag No. dwarfs 10th prctile Median No. stars 10th prctile Median Noise model
10 2.2 Summary of Data Anomalies Certain cadences are flagged to indicate a possible reduction of quality. See the QUALITY and SAP QUALITY columns of the target pixel and light curve files, respectively. Cadences with data anomalies that affect the entire focal plane are shown in Figure 4. The meaning of the flags are explained in the Data Characteristics Handbook (Christiansen et al., 2013) and Archive Manual (Thompson & Fraquelli, 2012). Two Safe Modes occurred during Q17. The first, spanning CIN , marks the end of the first month of data. The second, at CIN 72532, marks the end of month 2 and the end of data collection for Kepler (see 3.4). With no further data to report, the cadences of the second safe mode are not included as part of the archived data set. Figure 4: An overview of the location of the data anomalies flagged in Q17. NO DATA indicates those cadences with no data collected (e.g. during Earth-point or Safe Mode events). Clarifications on select flags in Figure 4 are listed here: ARGABRIGHTENING refers to cadences where the multiple-channel Argabrightening flag (flag 0x07, decimal value 64) was set. The single channel Argabrightening flag (0x0D, decimal value 4096) is not represented on this plot. COARSE POINT refers to cadences where the pointing of the telescope drifted by more than 0.5 millipixels from the nominal value (flag 0x16, decimal 32768). NOT FINE POINT refers to cadences where the telescope s fine guidance sensor reported that the telescope was not in fine point mode (flag 0x03, decimal value 4). LDE FLAG refers to flags set by the Spacecraft when a error was detected in the Local Detector Electronics (LDE) or the on-board memory (flag 0x15, decimal value 16385). The pipeline does not process these cadences and only raw pixels are available. 10
11 3 Notable Features of the Q17 Data In this section we discuss features of the data that occurred during collection or processing that are either new to Q17, significantly different than previous quarters, or not discussed in the Data Characteristics Handbook (Christiansen et al., 2013). A more complete listing of events that are known to affect the data are discussed in the Data Characteristics Handbook. 3.1 Solar Flare The sun emitted a series of X-ray flares on and around CIN in month 1 of Q17. Cadences to were gapped with the EXCLUDE flag to indicate that this data is of bad quality. However, the dark current remained elevated for several hours after the peak of the event, and users may notice degraded quality, especially for fainter stars. 3.2 PDC Uses Regular MAP for All Targets Because of the short duration of this quarter, the PDC (Pre-Search Data Conditioning) module of the pipeline did not perform the multi-scale MAP algorithm. As a result all PDC light curves were co-trended without band splitting, using the regular MAP algorithm. This information has also been reported in the headers of the light curve FITS files available at MAST, see the keyword PDCMTHD. 3.3 PDC Corrected Short Cadence Data As discussed in 5.15 of the Data Characteristics Handbook (Christiansen et al., 2013) (and 3.6 of DRN 19), PDC attenuates signals with timescales longer than approximately one third the quarter duration. For Q17, this timescale is shorter, 7-10 days, instead of the typical 20 days of other quarters. In short cadence, MAP is applied on a monthly basis. Since Q17M2 is only a week long, signals with timescales longer than a few days are removed. Short cadence data for this month should not be used to examine phenomena with timescales of days or longer. 3.4 Final Data Set Collected The second month of Q17 was interrupted by a safe mode event. After the spacecraft was commanded to return to science attitude, reaction wheel 4 failed and the spacecraft returned to safe mode. Extensive analysis concluded that neither of the two failed wheels could be recovered. With only two wheels, it is not possible to point at the Kepler field for the purpose of collecting high precision photometry. No futher data will be collected for the original Kepler Mission; however there are still plans to reprocess the entire Q0 Q17 data set with an improved SOC pipeline. 11
12 References Christiansen, J. L., Van Cleve, J. E., Jenkins, J. M., Caldwell, D. A., Barclay, T., Bryson, S., Burke, C. J., Twicken, J. D., & Uddin, A. K. (2013). Kepler Data Characteristics Handbook. KSCI Fanelli, M. N., Jenkins, J. M., Bryson, S. T., Quintana, E. V., Twicken, J. D., Wu, H. W., Tenenbaum, P., Allen, C. L., Caldwell, D. A., Chandrasekaran, H., Christansen, B. D., & Uddin, A. K. (2011). Kepler Data Processing Handbook. KSCI Smith, J. C., Stumpe, M. C., Van Cleve, J. E., Jenkins, J. M., Barclay, T. S., Fanelli, M. N., Girouard, F. R., Kolodziejczak, J. J., McCauliff, S. D., Morris, R. L., & Twicken, J. D. (2012). Kepler Presearch Data Conditioning II - A Bayesian Approach to Systematic Error Correction. PASP, 124, Stumpe, M. C., Smith, J. C., Van Cleve, J. E., Twicken, J. D., Barclay, T. S., Fanelli, M. N., Girouard, F. R., Jenkins, J. M., Kolodziejczak, J. J., McCauliff, S. D., & Morris, R. L. (2012). Kepler Presearch Data Conditioning I - Architecture and Algorithms for Error Correction in Kepler Light Curves. PASP, 124, Thompson, S. E., & Fraquelli, D. (2012). Kepler Archive Manual. KDMC
Kepler Data Release 24 Notes Q0 Q17. KSCI Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Susan E. Thompson (Editor) February 11, 2015
 Kepler Data Release 24 Notes Q0 Q17 KSCI-19064-001 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Susan E. Thompson (Editor) February 11, 2015 KS CI-19064-00l: Kepler Data Release 24 Notes Approved by: ----=~q~=h-~::==::::::~---
Kepler Data Release 24 Notes Q0 Q17 KSCI-19064-001 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Susan E. Thompson (Editor) February 11, 2015 KS CI-19064-00l: Kepler Data Release 24 Notes Approved by: ----=~q~=h-~::==::::::~---
Kepler Q1 Q12 TCE Release Notes. KSCI Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Jessie L. Christiansen (Editor)
 Kepler Q1 Q12 TCE Release Notes KSCI-1912-1 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Jessie L. Christiansen (Editor) KSCI-1912-l: Kepler QI-Q12 TCE Release Notes Prepared b...,::;ld:f~r44~~:::::::.::;;~== -
Kepler Q1 Q12 TCE Release Notes KSCI-1912-1 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Jessie L. Christiansen (Editor) KSCI-1912-l: Kepler QI-Q12 TCE Release Notes Prepared b...,::;ld:f~r44~~:::::::.::;;~== -
Kepler Data Release 12 Notes
 Kepler Data Release 12 Notes KSCI-19052-001 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Thomas Barclay (Editor) Jessie Christiansen (Editor) Data Release 12 for Quarter Q9 Q.m First Cadence Last Cadence First Cadence
Kepler Data Release 12 Notes KSCI-19052-001 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Thomas Barclay (Editor) Jessie Christiansen (Editor) Data Release 12 for Quarter Q9 Q.m First Cadence Last Cadence First Cadence
Planet Detection Metrics:
 Planet Detection Metrics: Window and One-Sigma Depth Functions KSCI-19085-001 Christopher J. Burke and Shawn E. Seader 20 March 2015 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date
Planet Detection Metrics: Window and One-Sigma Depth Functions KSCI-19085-001 Christopher J. Burke and Shawn E. Seader 20 March 2015 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date
Kepler Data Release 7 Notes
 Kepler Data Release 7 Notes KSCI-19047-001 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Jessie Christiansen (Editor) Pavel Machalek (Editor) Data Release 7 for Quarter Q2 Q.m First Cadence MJD midtime Last Cadence
Kepler Data Release 7 Notes KSCI-19047-001 Data Analysis Working Group (DAWG) Jessie Christiansen (Editor) Pavel Machalek (Editor) Data Release 7 for Quarter Q2 Q.m First Cadence MJD midtime Last Cadence
Planet Detection Metrics:
 Planet Detection Metrics: Pipeline Detection Efficiency KSCI-19094-001 Jessie L. Christiansen 31 August 2015 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date 8/31/15 Jessie L. Christiansen,
Planet Detection Metrics: Pipeline Detection Efficiency KSCI-19094-001 Jessie L. Christiansen 31 August 2015 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date 8/31/15 Jessie L. Christiansen,
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Kepler Data Processing Handbook 1 April 2011 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA. 94035 Prologue Prepared by: Date 'YJ (J~ ")01/ Michael N. Fanelli, Kepler
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Kepler Data Processing Handbook 1 April 2011 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA. 94035 Prologue Prepared by: Date 'YJ (J~ ")01/ Michael N. Fanelli, Kepler
Planet Detection Metrics:
 Planet Detection Metrics: Window and One-Sigma Depth Functions for Data Release 25 KSCI-19101-002 Christopher J. Burke and Joseph Catanzarite 03 May 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035
Planet Detection Metrics: Window and One-Sigma Depth Functions for Data Release 25 KSCI-19101-002 Christopher J. Burke and Joseph Catanzarite 03 May 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jan 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jan 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jan 2010](/thumbs/93/113749179.jpg) Received 2009 November 14; accepted 2009 December 21 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/10/09 arxiv:1001.0258v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jan 2010 OVERVIEW OF THE KEPLER SCIENCE PROCESSING PIPELINE
Received 2009 November 14; accepted 2009 December 21 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/10/09 arxiv:1001.0258v1 [astro-ph.ep] 1 Jan 2010 OVERVIEW OF THE KEPLER SCIENCE PROCESSING PIPELINE
Fine Guidance Sensor Data
 Fine Guidance Sensor Data KSCI-19112-001 Jeffrey Van Cleve & Jennifer Campbell 19 Apr 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 19 Document Control Ownership This document is part of
Fine Guidance Sensor Data KSCI-19112-001 Jeffrey Van Cleve & Jennifer Campbell 19 Apr 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 19 Document Control Ownership This document is part of
Planet Detection Metrics: Per-Target Flux-Level Transit Injection Tests of TPS for Data Release 25
 Planet Detection Metrics: Per-Target Flux-Level Transit Injection Tests of TPS for Data Release 25 KSCI-19109-002 Christopher J. Burke & Joseph Catanzarite June 13, 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Mo ett
Planet Detection Metrics: Per-Target Flux-Level Transit Injection Tests of TPS for Data Release 25 KSCI-19109-002 Christopher J. Burke & Joseph Catanzarite June 13, 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Mo ett
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 22 Aug 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 22 Aug 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 22 Aug 2012](/thumbs/87/95735299.jpg) Identification and Removal of Noise Modes in Kepler Photometry Erik A. Petigura Astronomy Department, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 arxiv:1208.4554v1 [astro-ph.im] 22 Aug 2012 epetigura@berkeley.edu
Identification and Removal of Noise Modes in Kepler Photometry Erik A. Petigura Astronomy Department, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 arxiv:1208.4554v1 [astro-ph.im] 22 Aug 2012 epetigura@berkeley.edu
Planet Detection Metrics: Automatic Detection of Background Objects Using the Centroid Robovetter
 Planet Detection Metrics: Automatic Detection of Background Objects Using the Centroid Robovetter KSCI-19115-001 Fergal Mullally May 22, 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 Document
Planet Detection Metrics: Automatic Detection of Background Objects Using the Centroid Robovetter KSCI-19115-001 Fergal Mullally May 22, 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 Document
Calculating the Occurrence Rate of Earth-Like Planets from the NASA Kepler Mission
 Calculating the Occurrence Rate of Earth-Like Planets from the NASA Kepler Mission Jessie Christiansen Kepler Participating Scientist NASA Exoplanet Science Institute/Caltech jessie.christiansen@caltech.edu
Calculating the Occurrence Rate of Earth-Like Planets from the NASA Kepler Mission Jessie Christiansen Kepler Participating Scientist NASA Exoplanet Science Institute/Caltech jessie.christiansen@caltech.edu
Uniform Modeling of KOIs:
 ! Uniform Modeling of KOIs: MCMC Notes for Data Release 25 KSCI-19113-001 Kelsey L. Hoffman and Jason F. Rowe 4 April 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 16 Document Control Ownership
! Uniform Modeling of KOIs: MCMC Notes for Data Release 25 KSCI-19113-001 Kelsey L. Hoffman and Jason F. Rowe 4 April 2017 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 16 Document Control Ownership
Kepler Stellar Properties Catalog Update for Q1-Q17 Transit Search
 Kepler Stellar Properties Catalog Update for Q1-Q17 Transit Search KSCI-19083 Stellar Properties Working Group 05 February 2014 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date: 2/6/14
Kepler Stellar Properties Catalog Update for Q1-Q17 Transit Search KSCI-19083 Stellar Properties Working Group 05 February 2014 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date: 2/6/14
Demystifying Kepler Data: A Primer for Systematic Artifact Mitigation
 PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 124:963 984, 2012 September 2012. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Demystifying Kepler Data: A Primer
PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 124:963 984, 2012 September 2012. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Demystifying Kepler Data: A Primer
Kepler photometric accuracy with degraded attitude control
 Kepler photometric accuracy with degraded attitude control Hans Kjeldsen, Torben Arentoft and Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard KASOC, Stellar Astrophysics Centre, Aarhus University, Denmark - 25 July 2013
Kepler photometric accuracy with degraded attitude control Hans Kjeldsen, Torben Arentoft and Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard KASOC, Stellar Astrophysics Centre, Aarhus University, Denmark - 25 July 2013
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 4 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 4 Dec 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 4 Dec 2014](/thumbs/84/89105815.jpg) Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 0 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., Cambridge,
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 0 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., Cambridge,
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q16 Catalog Using SOC 9.1 KSCI-19103 November 19, 2014 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q16 Catalog Using SOC 9.1 KSCI-19103 November 19, 2014 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared
Angelika Dehn Rob Koopman 10 Years GOME on ERS-2 Workshop
 Angelika Dehn (ADehn@serco.it), Rob Koopman (Rob.Koopman@esa.int), Overview I. ERS-2 Mission History 1. Mission Plan Highlights 2. GOME Special Operations II. GOME-1 Engineering Performance 1. Routine
Angelika Dehn (ADehn@serco.it), Rob Koopman (Rob.Koopman@esa.int), Overview I. ERS-2 Mission History 1. Mission Plan Highlights 2. GOME Special Operations II. GOME-1 Engineering Performance 1. Routine
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q17 DR24 Catalog KSCI-19104 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date: Jeffrey L.
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Products for the Q1-Q17 DR24 Catalog KSCI-19104 NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 Prepared by: Date: Jeffrey L.
1. Go the Kepler and K2 Science Center:
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING THE KEPLER FITS v2.0 FILE VStar PLUG IN This contains instructions for first time use. After that you can skip directly to the URL for the Kepler (or K2) Data Search and Retrieval
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING THE KEPLER FITS v2.0 FILE VStar PLUG IN This contains instructions for first time use. After that you can skip directly to the URL for the Kepler (or K2) Data Search and Retrieval
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 12 Jul 2012](/thumbs/72/66668086.jpg) Draft version July 16, 2012 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 DEMYSTIFYING KEPLER DATA: A PRIMER FOR SYSTEMATIC ARTIFACT MITIGATION K. Kinemuchi Bay Area Environmental Research
Draft version July 16, 2012 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 DEMYSTIFYING KEPLER DATA: A PRIMER FOR SYSTEMATIC ARTIFACT MITIGATION K. Kinemuchi Bay Area Environmental Research
PACS Wavelength Switching AOT release note
 PACS Wavelength Switching AOT release note 1 Prepared by the PACS ICC 20 January 2010 Wavelength switching release note version of 03-dec-2009 updated with full dynamic range saturation limits. Differences
PACS Wavelength Switching AOT release note 1 Prepared by the PACS ICC 20 January 2010 Wavelength switching release note version of 03-dec-2009 updated with full dynamic range saturation limits. Differences
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 18 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 18 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 18 Dec 2015](/thumbs/92/109052466.jpg) Submitted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal on October 27, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 PLANETARY CANDIDATES OBSERVED BY KEPLER. VII. THE FIRST FULLY UNIFORM
Submitted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal on October 27, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 PLANETARY CANDIDATES OBSERVED BY KEPLER. VII. THE FIRST FULLY UNIFORM
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Reports for Data Release 25 KSCI-19105-002 Jeffrey L. Coughlin NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 2 of 42 Table of
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Description of the TCERT Vetting Reports for Data Release 25 KSCI-19105-002 Jeffrey L. Coughlin NASA Ames Research Center Moffet Field, CA 94035 2 of 42 Table of
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Stellar Classification Program Plan NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA. 94035 Warning! This printed copy may not be the latest released version. It is
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Stellar Classification Program Plan NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA. 94035 Warning! This printed copy may not be the latest released version. It is
Astrophysics Advisory Committee
 Astrophysics Advisory Committee K2 End of Mission Science Planning Charlie Sobeck July 20, 2017 K2 Mission Genesis K2 is a follow-on to the original Kepler mission, driven by the loss of two reaction wheels.
Astrophysics Advisory Committee K2 End of Mission Science Planning Charlie Sobeck July 20, 2017 K2 Mission Genesis K2 is a follow-on to the original Kepler mission, driven by the loss of two reaction wheels.
MEMORANDUM. Focal-Point: Point on the focal plane where the sharpest PSF is located.
 CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: October 16, 2017 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis and Aimpoint File: oxap memo 2017.tex Version:
CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: October 16, 2017 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis and Aimpoint File: oxap memo 2017.tex Version:
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements
 ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
ASTRONOMY Merit Badge Requirements 1) Do the following: A) Sketch the face of the moon, indicating on it the locations of at least five seas and five craters. B) Within a single week, sketch the position
PLANETARY CANDIDATES OBSERVED BY KEPLER. VII. THE FIRST FULLY UNIFORM CATALOG BASED ON THE ENTIRE 48 MONTH DATASET (Q1 Q17 DR24)
 Accepted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal on February 15, 2015 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 PLANETARY CANDIDATES OBSERVED BY KEPLER. VII. THE FIRST FULLY UNIFORM
Accepted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal on February 15, 2015 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 PLANETARY CANDIDATES OBSERVED BY KEPLER. VII. THE FIRST FULLY UNIFORM
Campaign 9 of K2: News from the K2 team
 Campaign 9 of K2: News from the K2 team A talk by Geert Barentsen & Tom Barclay for the 20th Microlensing workshop in Paris on 14 January 2016. K2 Guest Observer Office (NASA Ames) http://keplerscience.arc.nasa.gov
Campaign 9 of K2: News from the K2 team A talk by Geert Barentsen & Tom Barclay for the 20th Microlensing workshop in Paris on 14 January 2016. K2 Guest Observer Office (NASA Ames) http://keplerscience.arc.nasa.gov
MEMORANDUM. Focal-Point: Point on the focal plane where the sharpest PSF is located.
 CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: November 1, 2014 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis, Aimpoint and Their Drifts File: oxap memo.tex
CHANDRA X-ray Center 60 Garden St., Cambridge Massachusetts 02138 USA MEMORANDUM Date: November 1, 2014 From: Ping Zhao To: CXC Subject: Chandra Optical Axis, Aimpoint and Their Drifts File: oxap memo.tex
REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 1 OF THE K2 MISSION
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 1 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 6 Garden St., Cambridge,
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 REDUCED LIGHT CURVES FROM CAMPAIGN 1 OF THE K2 MISSION Andrew Vanderburg 1,2 Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 6 Garden St., Cambridge,
Sumi-NPP OMPS Calibration and Characterization from Early Orbit Images
 Sumi-NPP OMPS Calibration and Characterization from Early Orbit Images *C. Pan 1, F. Weng 2, X. Wu 2, L. Flynn 2, G. Jaross 3 and S. Janz 4 * 1 ESSIC, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20740 2 NOAA
Sumi-NPP OMPS Calibration and Characterization from Early Orbit Images *C. Pan 1, F. Weng 2, X. Wu 2, L. Flynn 2, G. Jaross 3 and S. Janz 4 * 1 ESSIC, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20740 2 NOAA
The Behaviour of the XMM-Newton Background: From the beginning of the mission until May XMM-SOC-GEN-TN-0014 issue 3.10
 The Behaviour of the XMM-Newton Background: From the beginning of the mission until May 2017 XMM-SOC-GEN-TN-0014 issue 3.10 R. González-Riestra and P.M. Rodríguez-Pascual XMM-SOC User Support Group June
The Behaviour of the XMM-Newton Background: From the beginning of the mission until May 2017 XMM-SOC-GEN-TN-0014 issue 3.10 R. González-Riestra and P.M. Rodríguez-Pascual XMM-SOC User Support Group June
Automatic Classification of Transiting Planet Candidates with Deep Learning
 Automatic Classification of Transiting Planet Candidates with Deep Learning Megan Ansdell 1 Hugh Osborn, 2 Yani Ioannou, 3 Michele Sasdelli, 4 Jeff Smith, 5,6 Doug Caldwell, 5,6 Chedy Raissi, 7 Daniel
Automatic Classification of Transiting Planet Candidates with Deep Learning Megan Ansdell 1 Hugh Osborn, 2 Yani Ioannou, 3 Michele Sasdelli, 4 Jeff Smith, 5,6 Doug Caldwell, 5,6 Chedy Raissi, 7 Daniel
The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results
 The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results Thomas N. Gautier, Kepler Project Scientist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 3 July 2012 SAO STScI 2012
The Kepler Exoplanet Survey: Instrumentation, Performance and Results Thomas N. Gautier, Kepler Project Scientist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 3 July 2012 SAO STScI 2012
WFC3 IR Blobs, IR Sky Flats and the measured IR background levels
 The 2010 STScI Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2010 Susana Deustua and Cristina Oliveira, eds. WFC3 IR Blobs, IR Sky Flats and the measured IR background levels N. Pirzkal 1 Space
The 2010 STScI Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2010 Susana Deustua and Cristina Oliveira, eds. WFC3 IR Blobs, IR Sky Flats and the measured IR background levels N. Pirzkal 1 Space
Dark Rate of the STIS NUV Detector
 SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report STIS 2011-03 Dark Rate of the STIS NUV Detector Wei Zheng 1, Charles Proffitt 2, and David Sahnow 1 1 Department of
SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report STIS 2011-03 Dark Rate of the STIS NUV Detector Wei Zheng 1, Charles Proffitt 2, and David Sahnow 1 1 Department of
VIIRS SDR Cal/Val: S-NPP Update and JPSS-1 Preparations
 VIIRS SDR Cal/Val: S-NPP Update and JPSS-1 Preparations VIIRS SDR Cal/Val Posters: Xi Shao Zhuo Wang Slawomir Blonski ESSIC/CICS, University of Maryland, College Park NOAA/NESDIS/STAR Affiliate Spectral
VIIRS SDR Cal/Val: S-NPP Update and JPSS-1 Preparations VIIRS SDR Cal/Val Posters: Xi Shao Zhuo Wang Slawomir Blonski ESSIC/CICS, University of Maryland, College Park NOAA/NESDIS/STAR Affiliate Spectral
Practice Seasons Moon Quiz
 1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
1. Which diagram represents the tilt of Earth's axis relative to the Sun's rays on December 15? A) B) C) D) 2. The diagram below represents Earth in space on the first day of a season. 5. Base your answer
Breathing, Position Drift, and PSF Variations on the UVIS Detector
 SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report WFC3 1-1 Breathing, Position Drift, and PSF Variations on the UVIS Detector L. Dressel July 13, 1 ABSTRACT This study
SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report WFC3 1-1 Breathing, Position Drift, and PSF Variations on the UVIS Detector L. Dressel July 13, 1 ABSTRACT This study
A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC
 National Snow and Ice Data Center ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH'S FROZEN REGIONS Special Report #18 06 July 2016 A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC W. Meier NASA GSFC i 2 Contents List of Figures... 4 List of
National Snow and Ice Data Center ADVANCING KNOWLEDGE OF EARTH'S FROZEN REGIONS Special Report #18 06 July 2016 A. Windnagel M. Savoie NSIDC W. Meier NASA GSFC i 2 Contents List of Figures... 4 List of
Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2013 01 Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss Leonardo Úbeda and Jay Anderson Space Telescope Science Institute January 28, 2013 ABSTRACT We present a study
Instrument Science Report ACS 2013 01 Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss Leonardo Úbeda and Jay Anderson Space Telescope Science Institute January 28, 2013 ABSTRACT We present a study
Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks
 Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks Pierre Waller, Francisco Gonzalez, Stefano Binda, ESA/ESTEC Ilaria Sesia, Patrizia Tavella, INRiM Irene Hidalgo, Guillermo Tobias, GMV Abstract The Galileo
Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks Pierre Waller, Francisco Gonzalez, Stefano Binda, ESA/ESTEC Ilaria Sesia, Patrizia Tavella, INRiM Irene Hidalgo, Guillermo Tobias, GMV Abstract The Galileo
Solar Flare Durations
 Solar Flare Durations Whitham D. Reeve 1. Introduction Scientific investigation of solar flares is an ongoing pursuit by researchers around the world. Flares are described by their intensity, duration
Solar Flare Durations Whitham D. Reeve 1. Introduction Scientific investigation of solar flares is an ongoing pursuit by researchers around the world. Flares are described by their intensity, duration
TESS and Galactic Science
 TESS and Galactic Science! Keivan Stassun!! WFIRST Meeting! 18 November 2014! 1! Preliminary TESS Mission Schedule! Activity! Date! Status! Systems Requirement Review! 12-13 Feb 2014! Completed! Preliminary
TESS and Galactic Science! Keivan Stassun!! WFIRST Meeting! 18 November 2014! 1! Preliminary TESS Mission Schedule! Activity! Date! Status! Systems Requirement Review! 12-13 Feb 2014! Completed! Preliminary
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 22 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 22 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 22 Jan 2019](/thumbs/88/115736855.jpg) Accepted for publication in the Astronomical Journal Discovery and Vetting of Exoplanets I: Benchmarking K2 Vetting Tools arxiv:1901.07459v1 [astro-ph.ep] 22 Jan 2019 Veselin B. Kostov 1,2, Susan E. Mullally
Accepted for publication in the Astronomical Journal Discovery and Vetting of Exoplanets I: Benchmarking K2 Vetting Tools arxiv:1901.07459v1 [astro-ph.ep] 22 Jan 2019 Veselin B. Kostov 1,2, Susan E. Mullally
Kepler s Multiple Planet Systems
 Kepler s Multiple Planet Systems TITech & Kobe Univ. February 2018 Jack J. Lissauer NASA Ames Outline Solar System & Exoplanets Kepler Mission Kepler planets and planetery systems Principal Kepler findings
Kepler s Multiple Planet Systems TITech & Kobe Univ. February 2018 Jack J. Lissauer NASA Ames Outline Solar System & Exoplanets Kepler Mission Kepler planets and planetery systems Principal Kepler findings
PACS Spectroscopy performance and calibration PACS Spectroscopy performance and calibration
 1 of 18 PACS Spectroscopy performance and PICC-KL-TN-041 Prepared by With inputs by Bart Vandenbussche Joris Blommaert Alessandra Contursi Helmut Feuchtgruber Christophe Jean Albrecht Poglitsch Pierre
1 of 18 PACS Spectroscopy performance and PICC-KL-TN-041 Prepared by With inputs by Bart Vandenbussche Joris Blommaert Alessandra Contursi Helmut Feuchtgruber Christophe Jean Albrecht Poglitsch Pierre
WFC3 TV2 Testing: IR Channel Read Noise
 Instrument Science Report WFC3 2008-04 WFC3 TV2 Testing: IR Channel Read B. Hilbert 12 Feb 2008 ABSTRACT Using data taken during WFC3's Thermal Vacuum 2 (TV2) testing campaign, we have characterized the
Instrument Science Report WFC3 2008-04 WFC3 TV2 Testing: IR Channel Read B. Hilbert 12 Feb 2008 ABSTRACT Using data taken during WFC3's Thermal Vacuum 2 (TV2) testing campaign, we have characterized the
Revision No Date Prepared By CNE CNE Checked By SM SM Approved By SM SM
 Supplier Document No. SM-100/002/TE Document Title Product WIND SENSOR SM-100 (Gill 1360) Revision No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Date 05.06.03 17.02.04 Prepared By CNE CNE Checked By SM SM Approved By SM SM Abstract
Supplier Document No. SM-100/002/TE Document Title Product WIND SENSOR SM-100 (Gill 1360) Revision No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Date 05.06.03 17.02.04 Prepared By CNE CNE Checked By SM SM Approved By SM SM Abstract
Spitzer Space Telescope Calibration Strategy: The Use of Asteroids
 Spitzer Space Telescope Calibration Strategy: The Use of Asteroids 1, J. Stansberry 2, C. Engelbracht 2, M. Blaylock 2, A. Noriega-Crespo 1 2004 December 3 Herschel Calibration Workshop, Leiden, The Netherlands
Spitzer Space Telescope Calibration Strategy: The Use of Asteroids 1, J. Stansberry 2, C. Engelbracht 2, M. Blaylock 2, A. Noriega-Crespo 1 2004 December 3 Herschel Calibration Workshop, Leiden, The Netherlands
Validation of GOMOS version 6.01 ozone profiles using ground-based lidar observations. October 2012
 Validation of GOMOS version 6.01 ozone profiles using ground-based lidar observations October 2012 Anne.van.Gijsel@knmi.nl Introduction In this study we have compared GOMOS IPF version 6.01 ozone profiles
Validation of GOMOS version 6.01 ozone profiles using ground-based lidar observations October 2012 Anne.van.Gijsel@knmi.nl Introduction In this study we have compared GOMOS IPF version 6.01 ozone profiles
Time and Frequency Activities at the JHU Applied Physics Laboratory
 Time and Frequency Activities at the JHU Applied Physics Laboratory Mihran Miranian, Gregory L. Weaver, Jeffrey F. Garstecki, and Richard A. Dragonette Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory,
Time and Frequency Activities at the JHU Applied Physics Laboratory Mihran Miranian, Gregory L. Weaver, Jeffrey F. Garstecki, and Richard A. Dragonette Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory,
Opportunities with the James Webb Space Telescope
 Opportunities with the James Webb Space Telescope Nancy A. Levenson Space Telescope Science Institute image credit: J.Dore JWST NASA, ESA, and CSA 6.5m mirror cooled instruments cover nearthrough mid-infrared
Opportunities with the James Webb Space Telescope Nancy A. Levenson Space Telescope Science Institute image credit: J.Dore JWST NASA, ESA, and CSA 6.5m mirror cooled instruments cover nearthrough mid-infrared
Asteroseismic Analysis of NASA s Kepler Space Telescope K2 Mission Data of Compact Stars
 Asteroseismic Analysis of NASA s Kepler Space Telescope K2 Mission Data of Compact Stars Matt Yeager Department of Physics, Astronomy, and Materials Science Missouri State University Advisor: Dr. Mike
Asteroseismic Analysis of NASA s Kepler Space Telescope K2 Mission Data of Compact Stars Matt Yeager Department of Physics, Astronomy, and Materials Science Missouri State University Advisor: Dr. Mike
Uncertainty analysis of heliostat alignment at the Sandia solar field
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 00 (2013) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia SolarPACES 2013 Uncertainty analysis of heliostat alignment at the Sandia solar field Rachel
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 00 (2013) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia SolarPACES 2013 Uncertainty analysis of heliostat alignment at the Sandia solar field Rachel
Charged Particle Measurements in Mars Orbit from 2002 to 2006
 Charged Particle Measurements in Mars Orbit from 2002 to 2006 Cary Zeitlin, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Kerry T. Lee, Lockheed Martin Aerospace Co. MARIE & MRME MRME The Mars Radiation Monitoring
Charged Particle Measurements in Mars Orbit from 2002 to 2006 Cary Zeitlin, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Kerry T. Lee, Lockheed Martin Aerospace Co. MARIE & MRME MRME The Mars Radiation Monitoring
Updated Measurements of ACS/SBC Dark Rates
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2017-04 Updated Measurements of ACS/SBC Dark Rates R.J. Avila May 3, 2017 Abstract The results of dark rate monitoring programs for the ACS/SBC are presented here. The dark
Instrument Science Report ACS 2017-04 Updated Measurements of ACS/SBC Dark Rates R.J. Avila May 3, 2017 Abstract The results of dark rate monitoring programs for the ACS/SBC are presented here. The dark
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 28 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 28 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 28 Sep 2018](/thumbs/87/96529533.jpg) Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol. (2xx) No., http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa (L A TEX: document.tex; printed on October 1, 218; 2:19) Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics
Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol. (2xx) No., http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa (L A TEX: document.tex; printed on October 1, 218; 2:19) Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
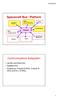 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014](/thumbs/86/94907870.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 15 (2014) Printed 25 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Precise time-series photometry for the Kepler-2.0 mission arxiv:1412.6304v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014 S. Aigrain
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 15 (2014) Printed 25 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Precise time-series photometry for the Kepler-2.0 mission arxiv:1412.6304v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Dec 2014 S. Aigrain
The Swift GRB MIDEX. Neil Gehrels May 20, 2002
 The Swift GRB MIDEX Neil Gehrels May 20, 2002 GSFC Swift Instruments Instruments Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) New CdZnTe detectors Detect >100 GRBs per year depending on logn-logs Most sensitive gamma-ray
The Swift GRB MIDEX Neil Gehrels May 20, 2002 GSFC Swift Instruments Instruments Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) New CdZnTe detectors Detect >100 GRBs per year depending on logn-logs Most sensitive gamma-ray
DARE Mission and Spacecraft Overview
 DARE Mission and Spacecraft Overview October 6, 2010 Lisa Hardaway, PhD Mike Weiss, Scott Mitchell, Susan Borutzki, John Iacometti, Grant Helling The information contained herein is the private property
DARE Mission and Spacecraft Overview October 6, 2010 Lisa Hardaway, PhD Mike Weiss, Scott Mitchell, Susan Borutzki, John Iacometti, Grant Helling The information contained herein is the private property
FIBER OPTIC GYRO-BASED ATTITUDE DETERMINATION FOR HIGH- PERFORMANCE TARGET TRACKING
 FIBER OPTIC GYRO-BASED ATTITUDE DETERMINATION FOR HIGH- PERFORMANCE TARGET TRACKING Elias F. Solorzano University of Toronto (Space Flight Laboratory) Toronto, ON (Canada) August 10 th, 2016 30 th AIAA/USU
FIBER OPTIC GYRO-BASED ATTITUDE DETERMINATION FOR HIGH- PERFORMANCE TARGET TRACKING Elias F. Solorzano University of Toronto (Space Flight Laboratory) Toronto, ON (Canada) August 10 th, 2016 30 th AIAA/USU
Early Results from the NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2)
 Early Results from the NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) David Crisp, OCO-2 Science Team Leader for the OCO-2 Science Team California Institute of Technology, Jet Propulsion Laboratory 08 June
Early Results from the NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) David Crisp, OCO-2 Science Team Leader for the OCO-2 Science Team California Institute of Technology, Jet Propulsion Laboratory 08 June
Pan-Planets. A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars. J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team
 Pan-Planets A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team Pan-STARRS 1: 1.8m prototype telescope operated on Haleakala/Hawaii consortium of few
Pan-Planets A Search for Transiting Planets Around Cool stars J. Koppenhoefer, Th. Henning and the Pan-PlanetS Team Pan-STARRS 1: 1.8m prototype telescope operated on Haleakala/Hawaii consortium of few
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/112423970.jpg) Draft version January 4, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 RE-EVALUATING SMALL LONG-PERIOD CONFIRMED PLANETS FROM KEPLER Christopher J. Burke, 1 F. Mullally, 2 Susan E. Thompson, 3 Jeffrey
Draft version January 4, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 RE-EVALUATING SMALL LONG-PERIOD CONFIRMED PLANETS FROM KEPLER Christopher J. Burke, 1 F. Mullally, 2 Susan E. Thompson, 3 Jeffrey
THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe
 THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe Rodrigo Leonardi Planck Science Office ESTEC/ESA OVERVIEW Planck observational objective & science.
THE PLANCK MISSION The most accurate measurement of the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the Universe Rodrigo Leonardi Planck Science Office ESTEC/ESA OVERVIEW Planck observational objective & science.
NICMOS Status and Plans
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
K2: Extending Kepler s Power to the Ecliptic
 K2: Extending Kepler s Power to the Ecliptic Ecliptic Plane Input Catalog KSCI-19082-020 Daniel Huber and Stephen T. Bryson 4 September 2018 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 32 Document
K2: Extending Kepler s Power to the Ecliptic Ecliptic Plane Input Catalog KSCI-19082-020 Daniel Huber and Stephen T. Bryson 4 September 2018 NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA 94035 2 of 32 Document
The AE9/AP9 Radiation and Plasma Environment Models
 Air Force Research Laboratory The AE9/AP9 Radiation and Plasma Environment Models 4 May 2017 Integrity Service Excellence Bob Johnston Air Force Research Laboratory Space Vehicles Directorate, Kirtland
Air Force Research Laboratory The AE9/AP9 Radiation and Plasma Environment Models 4 May 2017 Integrity Service Excellence Bob Johnston Air Force Research Laboratory Space Vehicles Directorate, Kirtland
ExoplanetSat: A Nanosatellite Space Telescope for Detecting Transiting Exoplanets
 1 2 ExoplanetSat: A Nanosatellite Space Telescope for Detecting Transiting Exoplanets Matthew W. Smith 1 (m_smith@mit.edu), Sara Seager 1, Christopher M. Pong 1, Sungyung Lim 2, Matthew W. Knutson 1, Timothy
1 2 ExoplanetSat: A Nanosatellite Space Telescope for Detecting Transiting Exoplanets Matthew W. Smith 1 (m_smith@mit.edu), Sara Seager 1, Christopher M. Pong 1, Sungyung Lim 2, Matthew W. Knutson 1, Timothy
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Aug 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 22 Aug 2014](/thumbs/79/79091908.jpg) 18th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun Proceedings of Lowell Observatory (9-13 June 2014) Edited by G. van Belle & H. Harris Using Transiting Planets to Model Starspot Evolution
18th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the Sun Proceedings of Lowell Observatory (9-13 June 2014) Edited by G. van Belle & H. Harris Using Transiting Planets to Model Starspot Evolution
BRITE One Year in Orbit
 BRITE One Year in Orbit O. Koudelka, M.Unterberger, P.Romano Graz University of Technology W.Weiss, R.Kuschnig University of Vienna 1 Contents Scientific Goals Mission Description Commissioning Science
BRITE One Year in Orbit O. Koudelka, M.Unterberger, P.Romano Graz University of Technology W.Weiss, R.Kuschnig University of Vienna 1 Contents Scientific Goals Mission Description Commissioning Science
PROBA 1. F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL
 PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
Why Study Magnetic Reconnection?
 Why Study Magnetic Reconnection? Fundamental Process Sun: Solar flares, Flare loops, CMEs Interplanetary Space Planetary Magnetosphere: solar wind plasma entry, causes Aurora Ultimate goal of the project
Why Study Magnetic Reconnection? Fundamental Process Sun: Solar flares, Flare loops, CMEs Interplanetary Space Planetary Magnetosphere: solar wind plasma entry, causes Aurora Ultimate goal of the project
Overview of Hyperion On-Orbit Instrument Performance, Stability, and Artifacts
 Overview of Hyperion On-Orbit Instrument Performance, Stability, and Artifacts EO-1 Science Validation Team Meeting November 21, 2002 Debbie Beiso TRW Space and Electronics Redondo Beach, CA San Francisco
Overview of Hyperion On-Orbit Instrument Performance, Stability, and Artifacts EO-1 Science Validation Team Meeting November 21, 2002 Debbie Beiso TRW Space and Electronics Redondo Beach, CA San Francisco
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space
 The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
The Gravitational Microlensing Planet Search Technique from Space David Bennett & Sun Hong Rhie (University of Notre Dame) Abstract: Gravitational microlensing is the only known extra-solar planet search
Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra
 Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra S. Moehler (SDP) June 15, 2015 Executive Summary I investigated the causes for wavelength offsets seen in telluric lines and sky lines of extracted
Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra S. Moehler (SDP) June 15, 2015 Executive Summary I investigated the causes for wavelength offsets seen in telluric lines and sky lines of extracted
Solar Activity during the Rising Phase of Solar Cycle 24
 International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed
 Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
Changing Hydrology under a Changing Climate for a Coastal Plain Watershed David Bosch USDA-ARS, Tifton, GA Jeff Arnold ARS Temple, TX and Peter Allen Baylor University, TX SEWRU Objectives 1. Project changes
ASPIICS: a Giant Solar Coronagraph onboard the PROBA-3 Mission
 SOLI INVICTO ASPIICS: a Giant Solar Coronagraph onboard the PROBA-3 Mission Andrei Zhukov Principal Investigator of PROBA-3/ASPIICS Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium
SOLI INVICTO ASPIICS: a Giant Solar Coronagraph onboard the PROBA-3 Mission Andrei Zhukov Principal Investigator of PROBA-3/ASPIICS Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium
Instrument pointing issues on ENVISAT
 Institut für Umweltphysik/Fernerkundung Instrument pointing issues on ENVISAT Klaus Bramstedt 1, Gilbert Barrot 2, Gaetan Perron 3 1 IUP Bremen, 2 ACRI-ST, 3 ABB Inc. Page 1 Outline Envisat pointing history
Institut für Umweltphysik/Fernerkundung Instrument pointing issues on ENVISAT Klaus Bramstedt 1, Gilbert Barrot 2, Gaetan Perron 3 1 IUP Bremen, 2 ACRI-ST, 3 ABB Inc. Page 1 Outline Envisat pointing history
Spots and white light ares in an L dwarf
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 1147 c SAIt 213 Memorie della Spots and white light ares in an L dwarf J. E. Gizis 1, A. J. Burgasser 2, E. Berger 3, P. K. G. Williams 3, F. J. Vrba 4, K. L. Cruz 5,6, and S. Metchev
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 1147 c SAIt 213 Memorie della Spots and white light ares in an L dwarf J. E. Gizis 1, A. J. Burgasser 2, E. Berger 3, P. K. G. Williams 3, F. J. Vrba 4, K. L. Cruz 5,6, and S. Metchev
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/96/127816976.jpg) arxiv:87.69v [astro-ph.im] Jul 8 Emese Plachy, László Molnár, Attila Bódi, Marek Skarka, Áron L. Juhász, Ádam Sódor, Péter Klagyivik and Róbert Szabó. Konkoly Observatory, MTA CSFK, Budapest, Hungary.
arxiv:87.69v [astro-ph.im] Jul 8 Emese Plachy, László Molnár, Attila Bódi, Marek Skarka, Áron L. Juhász, Ádam Sódor, Péter Klagyivik and Róbert Szabó. Konkoly Observatory, MTA CSFK, Budapest, Hungary.
Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or November 19, 2008
 Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or 2018 2007 Solar Probe Study & Mission Requirements Trajectory study and mission design trades were conducted in the fall
Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or 2018 2007 Solar Probe Study & Mission Requirements Trajectory study and mission design trades were conducted in the fall
A Technique for Extracting Highly Precise Photometry for the Two-Wheeled Kepler Mission
 PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 126:948 958, 2014 October 2014. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A Technique for Extracting Highly
PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 126:948 958, 2014 October 2014. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A Technique for Extracting Highly
Update on asteroseismology with Plato
 M.J. Goupil and the WP120 team LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, France July 11, 2016 Outline Overview of the mission Photometric performances expected must be understood in the following! ;-) Scientific objectives
M.J. Goupil and the WP120 team LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, France July 11, 2016 Outline Overview of the mission Photometric performances expected must be understood in the following! ;-) Scientific objectives
The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3
 336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
Stellar Observations Network Group
 Stellar Observations Network Group Frank Grundahl, Jørgen Christensen Dalsgaard, Uffe Gråe Jørgensen, Hans Kjeldsen, Søren Frandsen, Per Kjærgaard Rasmussen + participation from IAC (Pere Pallé, Orlagh
Stellar Observations Network Group Frank Grundahl, Jørgen Christensen Dalsgaard, Uffe Gråe Jørgensen, Hans Kjeldsen, Søren Frandsen, Per Kjærgaard Rasmussen + participation from IAC (Pere Pallé, Orlagh
Sentinel-3A Product Notice STM L2 Marine ( Spring-2018 Reprocessing Campaign )
 Sentinel-3A Product Notice STM L2 Marine ( Spring-2018 Reprocessing Campaign ) Mission Sensor Product S3-A SRAL/MWR L2 NTC (Marine Reprocessed Dataset from Spring-2018 Reprocessing Campaign ) Product Notice
Sentinel-3A Product Notice STM L2 Marine ( Spring-2018 Reprocessing Campaign ) Mission Sensor Product S3-A SRAL/MWR L2 NTC (Marine Reprocessed Dataset from Spring-2018 Reprocessing Campaign ) Product Notice
A Plot of the Tracking Signals Calculated in Exhibit 3.9
 CHAPTER 3 FORECASTING 1 Measurement of Error We can get a better feel for what the MAD and tracking signal mean by plotting the points on a graph. Though this is not completely legitimate from a sample-size
CHAPTER 3 FORECASTING 1 Measurement of Error We can get a better feel for what the MAD and tracking signal mean by plotting the points on a graph. Though this is not completely legitimate from a sample-size
DETERMINATION OF SCIAMACHY LINE-OF-SIGHT MISALIGNMENTS
 DETERMINATION OF SCIAMACHY LINE-OF-SIGHT MISALIGNMENTS Manfred Gottwald (1), Eckhart Krieg (1), Sander Slijkhuis (1), Christian von Savigny (2), Stefan Noël (2), Heinrich Bovensmann (2), Klaus Bramstedt
DETERMINATION OF SCIAMACHY LINE-OF-SIGHT MISALIGNMENTS Manfred Gottwald (1), Eckhart Krieg (1), Sander Slijkhuis (1), Christian von Savigny (2), Stefan Noël (2), Heinrich Bovensmann (2), Klaus Bramstedt
The Transneptunian Automated Occultation Survey (TAOS II) Matthew Lehner ASIAA
 The Transneptunian Automated Occultation Survey (TAOS II) Matthew Lehner ASIAA Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Harvard-Smithsonian Center
The Transneptunian Automated Occultation Survey (TAOS II) Matthew Lehner ASIAA Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Harvard-Smithsonian Center
