Swinburne Research Bank
|
|
|
- Garry Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Swinburne Research Bank Forbes, Duncan A.; Michael A. Beasley; Carlton M. Baugh; Ray M. Sharples; Carlos S. Frenk. (2002). Forming Globular Cluster Systems in a Semi-analytic Scheme. ESO workshop "Extragalactic Globular Cluster Systems", August 2002, Garching, Germany. Berlin: Springer. Copyright Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg The original publication is available at HUwww.springerlink.comUH. This is the author s version of the work. It is posted here with the permission of the publisher for your personal use. No further distribution is permitted. If your Library has a subscription to these conference proceedings, you may also be able to access the published version via the library catalogue.
2 Forming Globular Cluster Systems in a Semi-analytic Scheme Michael A. Beasley 1, Carlton M. Baugh 2, Duncan A. Forbes 1, Ray M. Sharples 2, and Carlos S. Frenk 2 arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Oct Astrophysics & Supercomputing, Swinburne University, Hawthorn VIC 3122, Australia. 2 Department of Physics, University of Durham, Durham DH1 3LE, UK. Abstract. We apply the semi-analytical galaxy formation code of Cole et al. to investigate the formation of globular cluster (GC) systems in hierarchical clustering scenarios. The nature of the model allows us to investigate the properties of GC systems and their parent galaxies within a cosmological framework, over a wide dynamic range of mass and time resolution. Assuming GCs form during mergers of gaseous systems, the metal-rich peak of the classical bimodal metallicity distribution of GCs naturally falls out of our model, where such merging occurs over a wide range of redshifts. The physical origin of old, metal-poor GCs (the metal-poor peak) is harder to understand, since their formation must be decoupled from the ongoing star formation in these systems at high redshift (z 5). Within the context of semi-analytic models in general, a possible solution lies in a cut-off in the GC formation efficiency at a characteristic local star formation rate. 1 Introduction Globular cluster (GC) systems are generally regarded as probes of galaxy formation. They inhabit all luminous galaxies in the local Universe, and a number of their properties (e.g. total population, mean metallicity) scale with the mass of their host galaxy. However, the potential for GC systems in revealing insights into the formation of their hosts has been hampered by a lack of understanding of the origin of GCs, and how GC formation relates to galaxy formation in general. A number of models exist in the literature discussing the formation of GC systems and their associated galaxies (or vice versa, from a non-gc researcher viewpoint) through gaseous mergers (Ashman & Zepf 1992; Barnes 1998), singular collapse (e.g Forbes, Brodie & Grillmair 1997) or the dissipationless accretion of satellites (Forte, Martinez & Muzzio 1982; Cote, Marzke & West 1998). Whilst all these models have had important successes in explaining the observables (for example, the Ashman & Zepf model predicted the observed colour bimodality seen in many GC systems), the distinction between the processes of rapid collapse, merging and accretion is likely to be artificial in a Universe where we expect all these mechanisms to occur. A viable route to following the evolution of galaxies and their GC systems within a cosmological framework is through semi-analytic modelling (e.g. White & Rees 1978). We have applied the fiducial semi-analytic model of Cole et al. (2000) to such a purpose, which is described in Beasley et al. (2002).
3 2 Mike Beasley et al. 1.1 A Synopsis of the Model Fig.1. Redshift distribution of major-mergers for a high-luminosity (M B - 5 log h = 22.0, solid lines) and low-luminosity (M B - 5 log h = 19.0, dashed lines) elliptical galaxy in the SAM. Each merger induces a burst of star formation, creating both field stars and GCs Semi-analytic models (SAMs) deal with the evolution of both baryonic and non-baryonic matter using a number of analytical formulae and observed scaling relations. The evolution of dark matter is either dealt with using extended Press-Schechter formalism, or direct N-body numerical simulations. Gas, which is assumed to follow the distribution of dark matter, is shock-heated when dark matter haloes merge. Over time, and in the absence of further halo merging, this gas will cool and settle into a disc 1 at the centre of the halo. Star formation is then allowed to proceed in these discs in what is termed a quiescent mode. As dark matter haloes merge, they bring with them their own stellar systems, the most massive of which becomes the central galaxy and the others satellites of the new halo. If the dynamical timescales of these satellites are shorter than the timescale for halo merging, they will merge. If this is a major merger, it will lead to a burst of star formation. 1.2 Metal-rich Globular Clusters A key aspect of our model are galaxy major mergers, which not only govern the morphology of the final galaxy (e.g. Baugh et al. 1996), but are also responsible 1 The taxonomy of these objects is ill defined, since they exhibit a range of physical sizes, gas-fractions and stellar populations. In the CDM picture, they may be classified as Searle-Zinn fragments or galaxy building blocks.
4 GCs in semi-analytic models 3 for the formation the metal-rich peak of the GC systems. We know that this latter assumption, one which was made by Ashman & Zepf (1992), is at least partially correct. Young, massive clusters have been identified in many nearby merging/interacting systems (e.g. Whitmore & Schweizer 1995), some of which are expected to evolve into long-lived GCs (e.g Goudfrooij et al. 2001). In the SAM, each merger induces a burst of star formation, producing stars and GCs. The relative fraction of GCs formed in each burst is determined by the GC formation efficiency, ǫ GC (the mass of GCs/mass of stars). This efficiency is determined from counting the total populations of metal-rich GCs in presentday ellipticals, and typically corresponds to 0.5% efficiency. The redshift distributions of major mergers for two galaxies in the model are shown in Fig. 1. Each merger corresponds to the formation of field stars and GCs. The high-luminosity elliptical undergoes 80 mergers, the low-luminosity elliptical in the figure has undergone 10. In this hierarchical picture, significant age and metallicity sub-structure is present in this metal-rich peak. Such substructure has now been detected (e.g. Forbes et al. 2001; Kissler-patig et al., this volume), and the question is now perhaps not if GCs are formed in mergers, but what fraction and when. 1.3 Metal-poor Globular Clusters The source of metal-poor GCs (hereafter halo GCs) in the model are the star forming discs which grow from gas which has cooled out of the dark matter halo. Star formation proceeds as an accreting box model, fresh gas continually falls onto the discs, which is also expelled through feedback from supernovae. The star formation rate in these discs is governed by the mass of gas available divided by an efficiency τ. The fraction of these stars which become GCs are again governed by ǫ GC. However, the drawback of this picture, where the progenitors of halo GCs are gaseous galaxy building blocks is that in our model, these building blocks proceed to aggregate mass and form stars quiescently until they reach metallicities at or above solar. This leads to metallicity distributions for the GCs which are similar to that of the bulge stars. A key to forming halo GCs from these building blocks is to disconnect GC formation from the more general star formation occurring at early epochs, and in Beasley et al. (2002) it is was necessary to truncate their formation at z 5. A physically reasonable way of achieving this truncation is to tie ǫ GC to the local star formation rate (SFR) (e.g. Larsen & Richtler 2000). Hence, GCs are only allowed to form above a given SFR threshold, whereas field stars may form irrespective of this criterion. In the fiducial model of Cole et al., such a SFR criterion fails for the halo GCs because the SFR peaks rather late, yielding halo GCs which are too metal rich. We show the mean SFR in discs for three different assumptions about τ in Fig. 2. Nomenclature for the different star formation schemes comes from Somerville, Primack & Faber (2001), whose motivation was to explain the observed characteristics of Lyman-break galaxies at z 2. Star formation schemes such as the accelerated quiescent mode (see Kauffmann, White & Guideroni
5 4 Mike Beasley et al. Fig. 2. Mean instantaneous star formation rates for three different assumptions about τ. In the fiducial model of Cole et al. (2000), the star formation history follows the quiescent lines. The upper limits represent the observed maximal dust correction from Somerville, Primack & Faber (2001) 1993; Somerville, Primack & Faber 2001) which produce higher SFRs at early times do allow for a more natural truncation of the halo GC formation. This is illustrated in Fig. 3, where we show the metallicity distributions for halo GCs adopting three different thresholds for the SFR in the accelerated quiescent mode. This is compared to Gemini/GMOS data for the halo GCs in the Virgo elliptical NGC 4649 (Forte et al., in prep). For the SFRs shown Fig. 2, values of ṗ = 1.3 adequately reproduce the form of the halo GC metallicity distribution. The values in Fig. 3 are illustrative only, since both the exact form and normalisation of these SFRs are not strongly constrained observationally (e.g. Steidel et al. 1999). Although initially promising, how well such a scheme can be made to work in the broader context of galaxy formation and cosmology (e.g. M. Santos, these proceedings) remains to be seen. Importantly, the effects of other influences, such as the UV ionising background in SAMs (e.g. Benson et al. 2002), and its relation to GC formation (e.g. Cen 2001) must be accounted for. 1.4 The GC-Spheroid Connection In our model, the entire metal-rich peak of the GC systems is created during merger-induced star formation. The metal-poor peak reflects the mass spectrum and accretion history of the galaxy progenitors. Since reproducing the bimodal metallicity distribution function (MDF) is regarded as a key problem in GC
6 GCs in semi-analytic models 5 Fig. 3. Resultant metallicity distributions of metal-poor GCs for different star formation rate thresholds in the SAM (broken lines). The solid line corresponds to the observed halo GCs in the Virgo elliptical NGC 4649 (Forte et al., in preparation) research, we should ask the question how well does the SAM reproduce the MDF of the spheroid stars? Until recently, this question was unimportant since no MDFs of elliptical galaxies were observed. However, recent observations of individual stars in the nearby elliptical NGC 5128 (e.g. Harris & Harris 2002), have made this an important test. Such a comparison is shown in Fig. 4 for four model ellipticals compared to the stellar data of Harris & Harris (2002). The galaxies have been chosen to be similar to the luminosity and from similar environments to NGC 5128, but otherwise have been chosen arbitrarily. The agreement is surprisingly good, considering that the models were not intended for making such detailed comparisons. We argue that such results demonstrate the utility of semi-analytic models in understanding the formation and evolution of GC systems in a cosmological context. 1.5 Acknowledgements MB thanks the organisers for an excellent workshop, and T. Puzia in particular for the extracurricular activities. MB also thanks Daisuke Kawata and Kenji Bekki for useful discussions.
7 6 Mike Beasley et al. Fig. 4. Metallicity distribution functions for four model ellipticals (open histograms) compared to the NGC 5128 distributions from Harris & Harris (2002). In each panel, M B refers to the B-band absolute magnitude of the model galaxy, and σ refers to its halo velocity dispersion References 1. Ashman, K., Zepf, S.E., 1992, ApJ, 384, Barnes, J.E., 1998, in The Evolution of Galaxies on Cosmological Timescales, eds. Beckmen, J.E. & Mahoney, T.J., ASP Conference Series, v. 187, pp Baugh, C.M., Cole, S., Frenk, C.S., 1996, MNRAS, 283, Beasley, M.A., Baugh, C.M., Forbes, D.A., Sharples, R.M., Frenk, C.S., 2002, MN- RAS, 333, Benson, A.J., Lacey, C.G., Baugh, C.M., Cole, S., Frenk, C.S., 2002, MNRAS, 333, Cen, R., 2001, ApJ, 560, Cole, S., Lacey, C.G., Baugh, C.M., Frenk, C.S., 2000, MNRAS, 319, Cote, P., Marzke, R.O., West, M.J., 1998, ApJ, 501, Forbes, D.A., Brodie, J.P., Grillmair, C.J., AJ, 1997, 113, Forte, J.C., Martinez, R.E., Muzzio, J.C., 1982, AJ, 87, Goudfrooij, P., Mack, J., Kissler-Patig, M., Meylan, G, Minniti, D., 2001, MNRAS, 322, Harris, W.E., Harris, G.L.H., 2002, AJ, 123, Kauffmann, G., White, S.D.M., Guiderdoni, B., 1993, MNRAS, 264, Larsen, S.S., Richtler, T., 2000, A&A, 354, Somerville, R.S., Primack, J.R., Faber, S.M., 2001, MNRAS, 320, Steidel, C.C., Adelberger, K.L., Giavalisco, M., Dickinson, M., Pettini, M., 1999, ApJ, 519, White, S.M., Rees, M.J., 1978, MNRAS, 183, Whitmore, B.C., Schweizer, P., 1995, AJ, 109, 960
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Aug 2001
 HOW DID GLOBULAR CLUSTERS FORM? Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National arxiv:astro-ph/0108298v1 17 Aug 2001 Research Council of Canada, 5071
HOW DID GLOBULAR CLUSTERS FORM? Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National arxiv:astro-ph/0108298v1 17 Aug 2001 Research Council of Canada, 5071
The formation and evolution of globular cluster systems. Joel Pfeffer, Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU)
 The formation and evolution of globular cluster systems Joel Pfeffer, Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU) Introduction to stellar clusters Open clusters: few - 10 4 M few Myr - few Gyr solar metallicity disk
The formation and evolution of globular cluster systems Joel Pfeffer, Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU) Introduction to stellar clusters Open clusters: few - 10 4 M few Myr - few Gyr solar metallicity disk
The dark matter crisis
 The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
Environment and the Formation of Globular Cluster Systems
 Environment and the Formation of Globular Cluster Systems Eric Peng Peking University, Dept of Astronomy Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics Peking University (PKU) in Beijing, China China s
Environment and the Formation of Globular Cluster Systems Eric Peng Peking University, Dept of Astronomy Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics Peking University (PKU) in Beijing, China China s
Origin of Bi-modality
 Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
The Formation and Evolution of Star Cluster Systems An Astro2010 Science White Paper
 The Formation and Evolution of Star Cluster Systems An Astro2010 Science White Paper Primary Science Panel : The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Lead Co-Authors: Katherine Rhode Department of Astronomy Indiana
The Formation and Evolution of Star Cluster Systems An Astro2010 Science White Paper Primary Science Panel : The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Lead Co-Authors: Katherine Rhode Department of Astronomy Indiana
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Nov 2002
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (0000) Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LaT E X style file v1.4) Simultaneous Modelling of the Stellar Halo and Globular Cluster System of NGC 5128 arxiv:astro-ph/0211586v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (0000) Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LaT E X style file v1.4) Simultaneous Modelling of the Stellar Halo and Globular Cluster System of NGC 5128 arxiv:astro-ph/0211586v1
Spectroscopy of Extra-galactic Globular Clusters
 Spectroscopy of Extra-galactic Globular Clusters Michael J. Pierce, BSc(Hons) A dissertation presented in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Faculty of ICT Swinburne
Spectroscopy of Extra-galactic Globular Clusters Michael J. Pierce, BSc(Hons) A dissertation presented in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Faculty of ICT Swinburne
Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea
 Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmology and Structure Formation (The 4 th KIAS workshop), Nov 4-6, 2010, KIAS, Korea 1 M.G. Lee, Sungsoon Lim (SNU)
Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmology and Structure Formation (The 4 th KIAS workshop), Nov 4-6, 2010, KIAS, Korea 1 M.G. Lee, Sungsoon Lim (SNU)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 May 2000
 The Detection Rate of Molecular Gas in Elliptical Galaxies: Constraints on Galaxy Formation Theories arxiv:astro-ph/0005304v1 15 May 2000 Yutaka Fujita, and Masahiro Nagashima Department of Earth and Space
The Detection Rate of Molecular Gas in Elliptical Galaxies: Constraints on Galaxy Formation Theories arxiv:astro-ph/0005304v1 15 May 2000 Yutaka Fujita, and Masahiro Nagashima Department of Earth and Space
Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies
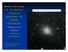 Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies Katherine Rhode Indiana University 38 x 38 R image of Virgo elliptical NGC 4472 KITP Conference January 2009 Observations of Globular Cluster
Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies Katherine Rhode Indiana University 38 x 38 R image of Virgo elliptical NGC 4472 KITP Conference January 2009 Observations of Globular Cluster
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 Sep 2005
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2005) Printed 5 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Formation of intracluster globular clusters Hideki Yahagi 1 and Kenji Bekki 2 1 Department of Astronomy, University
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2005) Printed 5 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Formation of intracluster globular clusters Hideki Yahagi 1 and Kenji Bekki 2 1 Department of Astronomy, University
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 27 Feb 2006
 Extragalactic Globular Clusters 1 Extragalactic Globular Clusters and Galaxy Formation arxiv:astro-ph/0602601v1 27 Feb 2006 Jean P. Brodie and Jay Strader UCO/Lick Observatory Key Words globular clusters,
Extragalactic Globular Clusters 1 Extragalactic Globular Clusters and Galaxy Formation arxiv:astro-ph/0602601v1 27 Feb 2006 Jean P. Brodie and Jay Strader UCO/Lick Observatory Key Words globular clusters,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
Supplements to A Critical Supermassive Black Hole Mass Regulating Galaxy Evolution
 Supplements to A Critical Supermassive Black Hole Mass Regulating Galaxy Evolution 1 Galaxy Formation Modelling The main strategy behind the modelling approach we follow is to first calculate the collapse
Supplements to A Critical Supermassive Black Hole Mass Regulating Galaxy Evolution 1 Galaxy Formation Modelling The main strategy behind the modelling approach we follow is to first calculate the collapse
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Nov 2015](/thumbs/96/127300274.jpg) Formation, evolution, and survival of massive star clusters Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 316, 2015 C. Charbonnel & A. Nota, eds. c 2015 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
Formation, evolution, and survival of massive star clusters Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 316, 2015 C. Charbonnel & A. Nota, eds. c 2015 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 Jul 1998
 Cosmic Star Formation from the Milky Way and its Satellites arxiv:astro-ph/973v1 31 Jul 199 F.D.A. Hartwick Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, VW 3P Abstract.
Cosmic Star Formation from the Milky Way and its Satellites arxiv:astro-ph/973v1 31 Jul 199 F.D.A. Hartwick Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, VW 3P Abstract.
Reconstructing galaxy histories from globular clusters
 Review Article published in Nature, Vol. 427, p. 31 (January 1, 2004) Reconstructing galaxy histories from globular clusters Michael J. West 1, Patrick Côté 2, Ronald O. Marzke 3 & Andrés Jordán 2 1 Department
Review Article published in Nature, Vol. 427, p. 31 (January 1, 2004) Reconstructing galaxy histories from globular clusters Michael J. West 1, Patrick Côté 2, Ronald O. Marzke 3 & Andrés Jordán 2 1 Department
RECONSTRUCTION OF THE EVOLUTION OF GALAXIES USING THE EXTENDED-PRESS-SCHECHTER MODEL WITH GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 RECONSTRUCTION OF THE EVOLUTION OF GALAXIES USING THE EXTENDED-PRESS-SCHECHTER MODEL WITH GLOBULAR CLUSTERS Eli Bressert Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Hawaii at Hilo Hilo, HI 96720
RECONSTRUCTION OF THE EVOLUTION OF GALAXIES USING THE EXTENDED-PRESS-SCHECHTER MODEL WITH GLOBULAR CLUSTERS Eli Bressert Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Hawaii at Hilo Hilo, HI 96720
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
AGN feedback and its influence on massive galaxy evolution
 AGN feedback and its influence on massive galaxy evolution Darren Croton (University of California Berkeley) Simon White, Volker Springel, et al. (MPA) DEEP2 & AEGIS collaborations (Berkeley & everywhere
AGN feedback and its influence on massive galaxy evolution Darren Croton (University of California Berkeley) Simon White, Volker Springel, et al. (MPA) DEEP2 & AEGIS collaborations (Berkeley & everywhere
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Some remarks on extragalactic globular clusters
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2006) 34, 83 97 Some remarks on extragalactic globular clusters Tom Richtler Departamento de Física, Universidad de Concepción, Concepción, Chile Abstract. I comment (in a review
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2006) 34, 83 97 Some remarks on extragalactic globular clusters Tom Richtler Departamento de Física, Universidad de Concepción, Concepción, Chile Abstract. I comment (in a review
Evolving Disks in Cold Dark Matter Cosmology
 Evolving Disks in Cold Dark Matter Cosmology C. B. Brook 1, H. Martel 1 1 Université Laval, Québec, Qc, G1K-7P4 Canada B. K. Gibson 2.3, D. Kawata 2 2 Swinburne University, Vic., Australia and 3 School
Evolving Disks in Cold Dark Matter Cosmology C. B. Brook 1, H. Martel 1 1 Université Laval, Québec, Qc, G1K-7P4 Canada B. K. Gibson 2.3, D. Kawata 2 2 Swinburne University, Vic., Australia and 3 School
Faint galaxy counts as a function of morphological type in a hierarchical merger model
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (1996) Faint galaxy counts as a function of morphological type in a hierarchical merger model C.M. Baugh, S. Cole & C.S. Frenk University of Durham, Department of
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (1996) Faint galaxy counts as a function of morphological type in a hierarchical merger model C.M. Baugh, S. Cole & C.S. Frenk University of Durham, Department of
AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models
 AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models Nikos Fanidakis and C.M. Baugh, R.G. Bower, S. Cole, C. Done, C. S. Frenk Physics of Galactic Nuclei, Ringberg Castle, June 18, 2009 Outline Brief introduction
AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models Nikos Fanidakis and C.M. Baugh, R.G. Bower, S. Cole, C. Done, C. S. Frenk Physics of Galactic Nuclei, Ringberg Castle, June 18, 2009 Outline Brief introduction
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Nov 1999
 Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007](/thumbs/81/84026065.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (1994) Printed 1 February 8 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Origin of lower velocity dispersions of ultra-compact dwarf galaxy populations in clusters of galaxies K. Bekki
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (1994) Printed 1 February 8 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Origin of lower velocity dispersions of ultra-compact dwarf galaxy populations in clusters of galaxies K. Bekki
The Globular Clusters-Field Stars Connection (in early type galaxies)
 The Globular Clusters-Field Stars Connection (in early type galaxies) Juan Carlos Forte Universidad Nacional de La Plata and CONICET, Argentina forte@fcaglp.unlp.edu.ar A frequent statement: Globular clusters
The Globular Clusters-Field Stars Connection (in early type galaxies) Juan Carlos Forte Universidad Nacional de La Plata and CONICET, Argentina forte@fcaglp.unlp.edu.ar A frequent statement: Globular clusters
The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data
 Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Studying Galaxy Formation with Hubble s Successor
 Hubble s Science Legacy: Future Optical-Ultraviolet Astronomy from Space ASP Conference Series, Vol. 000, 2002 K.R. Sembach, J.C. Blades, G.D. Illingworth, R.C. Kennicutt Studying Galaxy Formation with
Hubble s Science Legacy: Future Optical-Ultraviolet Astronomy from Space ASP Conference Series, Vol. 000, 2002 K.R. Sembach, J.C. Blades, G.D. Illingworth, R.C. Kennicutt Studying Galaxy Formation with
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model
 Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Major Review: A very dense article" Dawes Review 4: Spiral Structures in Disc Galaxies; C. Dobbs and J Baba arxiv "
 The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
The structures of distant galaxies IV. A new empirical measurement of the time-scale for galaxy mergers implications for the merger history
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399, L16 L20 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00708.x The structures of distant galaxies IV. A new empirical measurement of the time-scale for galaxy mergers implications for
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 399, L16 L20 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00708.x The structures of distant galaxies IV. A new empirical measurement of the time-scale for galaxy mergers implications for
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Nov 2004
 Probing Halos with PNe: Mass and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxies Aaron J. Romanowsky arxiv:astro-ph/0411797v1 30 Nov 2004 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nottingham, University Park,
Probing Halos with PNe: Mass and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxies Aaron J. Romanowsky arxiv:astro-ph/0411797v1 30 Nov 2004 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nottingham, University Park,
Hierarchical Galaxy Formation
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Shaun Cole 1,4, Cedric G. Lacey 1,2,3,5, Carlton M. Baugh 1,6 and Carlos S.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Shaun Cole 1,4, Cedric G. Lacey 1,2,3,5, Carlton M. Baugh 1,6 and Carlos S.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Mar 2006
 A search for ultra-compact dwarf galaxies in the NGC 1023 group of galaxies Steffen Mieske 1, Michael J. West 2, and Claudia Mendes de Oliveira 3 arxiv:astro-ph/0603524v1 20 Mar 2006 1 ESO, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.
A search for ultra-compact dwarf galaxies in the NGC 1023 group of galaxies Steffen Mieske 1, Michael J. West 2, and Claudia Mendes de Oliveira 3 arxiv:astro-ph/0603524v1 20 Mar 2006 1 ESO, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 2 Dec 1998
 FORMATION OF BULGES arxiv:astro-ph/981257v1 2 Dec 1998 JOSEPH SILK AND RYCHARD BOUWENS Departments of Astronomy and Physics, and Center for Particle Astrophysics, University of California, Berkeley, CA
FORMATION OF BULGES arxiv:astro-ph/981257v1 2 Dec 1998 JOSEPH SILK AND RYCHARD BOUWENS Departments of Astronomy and Physics, and Center for Particle Astrophysics, University of California, Berkeley, CA
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem. Presented by: Michael Solway
 Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 Jan 2004
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 73, 23 c SAIt 2002 Memorie della Ì ÑÓ¹ ÝÒ Ñ Ð ÚÓÐÙØ ÓÒ Ó ÐÐ ÔØ Ð Ð Ü ÈÖ ¹ Ø Ò Ò Æ Ø Ò Daisuke Kawata, and Brad K. Gibson, arxiv:astro-ph/0401232v1 13 Jan 2004 Centre for Astrophysics
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 73, 23 c SAIt 2002 Memorie della Ì ÑÓ¹ ÝÒ Ñ Ð ÚÓÐÙØ ÓÒ Ó ÐÐ ÔØ Ð Ð Ü ÈÖ ¹ Ø Ò Ò Æ Ø Ò Daisuke Kawata, and Brad K. Gibson, arxiv:astro-ph/0401232v1 13 Jan 2004 Centre for Astrophysics
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Jan 2003
 Galactic Halo Stars in Phase Space :A Hint of Satellite Accretion? Chris B. Brook 1, Daisuke Kawata 1, Brad K. Gibson 1 and Chris Flynn 1,2 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0301596v1 30 Jan 2003 The present day
Galactic Halo Stars in Phase Space :A Hint of Satellite Accretion? Chris B. Brook 1, Daisuke Kawata 1, Brad K. Gibson 1 and Chris Flynn 1,2 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0301596v1 30 Jan 2003 The present day
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Dec 2002
 New Horizons in Globular Cluster Astronomy ASP Conference Series, Vol.???, 2002 Giampaolo Piotto, Georges Meylan, George Djorgovski and Marco Riello, eds. Formation of Globular Clusters in Merging Galaxies
New Horizons in Globular Cluster Astronomy ASP Conference Series, Vol.???, 2002 Giampaolo Piotto, Georges Meylan, George Djorgovski and Marco Riello, eds. Formation of Globular Clusters in Merging Galaxies
Luminosity Functions of Planetary Nebulae & Globular Clusters. By Azmain Nisak ASTR 8400
 Luminosity Functions of Planetary Nebulae & Globular Clusters By Azmain Nisak ASTR 8400 Calculating Distance! m = apparent magnitude! M = absolute magnitude! r = distance in pc GLOBULAR CLUSTERS AS DISTANCE
Luminosity Functions of Planetary Nebulae & Globular Clusters By Azmain Nisak ASTR 8400 Calculating Distance! m = apparent magnitude! M = absolute magnitude! r = distance in pc GLOBULAR CLUSTERS AS DISTANCE
Feedback and Galaxy Formation
 Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 1 Feb 2000
 Compact Stellar Systems in the Fornax Cluster: Super-massive Star Clusters or Extremely Compact Dwarf Galaxies? M. J. Drinkwater 1 J. B. Jones 2 M. D. Gregg 3 S. Phillipps 4 to appear in Publications of
Compact Stellar Systems in the Fornax Cluster: Super-massive Star Clusters or Extremely Compact Dwarf Galaxies? M. J. Drinkwater 1 J. B. Jones 2 M. D. Gregg 3 S. Phillipps 4 to appear in Publications of
Globular Cluster Systems in Giant Ellipticals
 Globular Cluster Systems in Giant Ellipticals Karla Adriana Alamo Martínez CRyA - UNAM (México) ESO Chile Rosa Amelia González - CRyA-UNAM Michael West - ESO Chile John Blakeslee - Herzberg Institute for
Globular Cluster Systems in Giant Ellipticals Karla Adriana Alamo Martínez CRyA - UNAM (México) ESO Chile Rosa Amelia González - CRyA-UNAM Michael West - ESO Chile John Blakeslee - Herzberg Institute for
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Hubble Sequence. Environment! Globular Clusters in Milky Way. kpc
 Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Globular Cluster Systems as Tracers of Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Globular Cluster Systems as Tracers of Galaxy Formation and Evolution Clues from MOS Surveys Mihos+2005 Rubén Sánchez-Janssen Plaskett Fellow NRC Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics S/C de la Palma 2015-03-03
Globular Cluster Systems as Tracers of Galaxy Formation and Evolution Clues from MOS Surveys Mihos+2005 Rubén Sánchez-Janssen Plaskett Fellow NRC Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics S/C de la Palma 2015-03-03
Theoretical models of the halo occupation distribution: Separating central and satellite galaxies
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Astronomy Department Faculty Publication Series Astronomy 2005 Theoretical models of the halo occupation distribution: Separating central
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Astronomy Department Faculty Publication Series Astronomy 2005 Theoretical models of the halo occupation distribution: Separating central
(i) All relevant physics included shaping galaxy evolution. (ii) Model gas content/star formation in a self-consistent scenario.
 Useful theoretical tool to predict galaxy evolution in CDM structures: Semi-analytic models (i) All relevant physics included shaping galaxy evolution. (ii) Model gas content/star formation in a self-consistent
Useful theoretical tool to predict galaxy evolution in CDM structures: Semi-analytic models (i) All relevant physics included shaping galaxy evolution. (ii) Model gas content/star formation in a self-consistent
UNder CLose Examination: Semi Analytical Models
 UNder CLose Examination: Semi Analytical Models Jerusalem Winter School 2003-2004 Frank van den Bosch (ETH Zürich) Outline Semi-Analytical Models: Ingredients Merger Trees; the skeleton of hierarchical
UNder CLose Examination: Semi Analytical Models Jerusalem Winter School 2003-2004 Frank van den Bosch (ETH Zürich) Outline Semi-Analytical Models: Ingredients Merger Trees; the skeleton of hierarchical
On The Formation of Giant Elliptical Galaxies and Globular Clusters
 Journal of The Korean Astronomical Society 35: 1 99, 2002 On The Formation of Giant Elliptical Galaxies and Globular Clusters Myung Gyoon Lee Astronomy Program, SEES, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742,
Journal of The Korean Astronomical Society 35: 1 99, 2002 On The Formation of Giant Elliptical Galaxies and Globular Clusters Myung Gyoon Lee Astronomy Program, SEES, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742,
The growth and structure of dark matter haloes
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, 12 24 (2003) The growth and structure of dark matter haloes D. H. Zhao, 1,2 H. J. Mo, 2 Y. P. Jing 1,2 and G. Börner 2 1 Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, The Partner Group
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, 12 24 (2003) The growth and structure of dark matter haloes D. H. Zhao, 1,2 H. J. Mo, 2 Y. P. Jing 1,2 and G. Börner 2 1 Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, The Partner Group
The separate formation of different galaxy components
 The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
 ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
Structure of Merger Remnants:
 Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 10 Apr 2001
 Astrophysical Ages and Time Scales ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 T. von Hippel, N. Manset, C. Simpson Age Estimation of Extragalactic Globular Cluster Systems Using Hβ Index arxiv:astro-ph/0104129v2
Astrophysical Ages and Time Scales ASP Conference Series, Vol. TBD, 2001 T. von Hippel, N. Manset, C. Simpson Age Estimation of Extragalactic Globular Cluster Systems Using Hβ Index arxiv:astro-ph/0104129v2
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies
 Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies Patrick Durrell (Youngstown State University) + Pat Côté, John Blakeslee, Laura Ferrarese (Herzberg-Victoria), Eric Peng (Peking Univ) Chris Mihos (CWRU) + NGVS Team
Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies Patrick Durrell (Youngstown State University) + Pat Côté, John Blakeslee, Laura Ferrarese (Herzberg-Victoria), Eric Peng (Peking Univ) Chris Mihos (CWRU) + NGVS Team
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd. Longair, chapter 3 + literature. Monday 18th Feb
 Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd. Longair, chapter 3 + literature Monday 18th Feb 1 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram magnitude colour LOW MASS STARS LIVE A VERY VERY LONG TIME! 2 The
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd. Longair, chapter 3 + literature Monday 18th Feb 1 The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram magnitude colour LOW MASS STARS LIVE A VERY VERY LONG TIME! 2 The
SURVEYS: THE MASS ASSEMBLY AND STAR FORMATION HISTORY
 Lecture #4 SURVEYS: THE MASS ASSEMBLY AND STAR FORMATION HISTORY Observational facts Olivier Le Fèvre ON Rio de Janeiro School 2014 Putting it all together Clear survey strategies Instrumentation and observing
Lecture #4 SURVEYS: THE MASS ASSEMBLY AND STAR FORMATION HISTORY Observational facts Olivier Le Fèvre ON Rio de Janeiro School 2014 Putting it all together Clear survey strategies Instrumentation and observing
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 8 Oct 2002
 Blue Horizontal-Branch Stars and Simple Stellar Populations Hyun-chul Lee 1,2, Young-Wook Lee 2, and Brad K. Gibson 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0210178 v1 8 Oct 2002 1 Centre for Astrophysics & Supercomputing, Swinburne
Blue Horizontal-Branch Stars and Simple Stellar Populations Hyun-chul Lee 1,2, Young-Wook Lee 2, and Brad K. Gibson 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0210178 v1 8 Oct 2002 1 Centre for Astrophysics & Supercomputing, Swinburne
Luminous red galaxies in hierarchical cosmologies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 386, 2145 2160 (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13179.x Luminous red galaxies in hierarchical cosmologies C. Almeida, 1 C. M. Baugh, 1 D. A. Wake, 1 C. G. Lacey, 1 A. J. Benson,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 386, 2145 2160 (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13179.x Luminous red galaxies in hierarchical cosmologies C. Almeida, 1 C. M. Baugh, 1 D. A. Wake, 1 C. G. Lacey, 1 A. J. Benson,
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS. The globular cluster system around the low-luminosity S0 galaxy NGC 7457
 Astron. Astrophys. 346, 721 730 (1999) The globular cluster system around the low-luminosity S0 galaxy NGC 7457 ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS S. Chapelon 1, V. Buat 1,2, D. Burgarella 1, and M. Kissler-Patig
Astron. Astrophys. 346, 721 730 (1999) The globular cluster system around the low-luminosity S0 galaxy NGC 7457 ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS S. Chapelon 1, V. Buat 1,2, D. Burgarella 1, and M. Kissler-Patig
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Diffuse Extragalactic Background Radiation and Gamma-Ray Attenuation
 Diffuse Extragalactic Background Radiation and Gamma-Ray Attenuation Joel Primack, Rudy Gilmore, Piero Madau & Rachel Somerville UCSC & STScI The EBL is very difficult to observe directly because of foregrounds,
Diffuse Extragalactic Background Radiation and Gamma-Ray Attenuation Joel Primack, Rudy Gilmore, Piero Madau & Rachel Somerville UCSC & STScI The EBL is very difficult to observe directly because of foregrounds,
Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies
 Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies Benjamin Moster (IoA/KICC)! Simon White, Thorsten Naab (MPA), Rachel Somerville (Rutgers), Frank van den Bosch (Yale),
Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies Benjamin Moster (IoA/KICC)! Simon White, Thorsten Naab (MPA), Rachel Somerville (Rutgers), Frank van den Bosch (Yale),
Age-redshift relation. The time since the big bang depends on the cosmological parameters.
 Age-redshift relation The time since the big bang depends on the cosmological parameters. Lyman Break Galaxies High redshift galaxies are red or absent in blue filters because of attenuation from the neutral
Age-redshift relation The time since the big bang depends on the cosmological parameters. Lyman Break Galaxies High redshift galaxies are red or absent in blue filters because of attenuation from the neutral
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation. Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan)
 Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
The Spin of M87 as measured from the Rotation of its Globular Clusters
 The Spin of M87 as measured from the Rotation of its Globular Clusters Markus Kissler-Patig 1 and Karl Gebhardt 2 University of California Observatories / Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
The Spin of M87 as measured from the Rotation of its Globular Clusters Markus Kissler-Patig 1 and Karl Gebhardt 2 University of California Observatories / Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models. Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11
 Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
The Different Physical Mechanisms that Drive the Star-formation Histories of Giant and Dwarf Galaxies
 The Different Physical Mechanisms that Drive the Star-formation Histories of Giant and Dwarf Galaxies Chris Haines (University of Birmingham) Adriana Gargiulo, Gianni Busarello, Francesco La Barbera, Amata
The Different Physical Mechanisms that Drive the Star-formation Histories of Giant and Dwarf Galaxies Chris Haines (University of Birmingham) Adriana Gargiulo, Gianni Busarello, Francesco La Barbera, Amata
Galaxy Formation. Physics 463, Spring 07
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 9 Galaxy Formation We see that scattered through space! out to in"nite distances! there exist similar systems of stars! and that all of creation! in the whole extent of its
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 9 Galaxy Formation We see that scattered through space! out to in"nite distances! there exist similar systems of stars! and that all of creation! in the whole extent of its
Probing the evolution of massive galaxies with the K20 survey
 Probing the evolution of massive galaxies with the K20 survey Andrea Cimatti Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, I-50125, Firenze, Italy Abstract. The motivations and the status of the
Probing the evolution of massive galaxies with the K20 survey Andrea Cimatti Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, I-50125, Firenze, Italy Abstract. The motivations and the status of the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 23 Dec 2004
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The metal enrichment of the intracluster medium in hierarchical galaxy formation models arxiv:astro-ph/0408529v2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The metal enrichment of the intracluster medium in hierarchical galaxy formation models arxiv:astro-ph/0408529v2
Astro-2: History of the Universe
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 13; May 30 2013 Previously on astro-2 Energy and mass are equivalent through Einstein s equation and can be converted into each other (pair production and annihilations)
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 13; May 30 2013 Previously on astro-2 Energy and mass are equivalent through Einstein s equation and can be converted into each other (pair production and annihilations)
The Role Of Globular Clusters During Reionization
 The Role Of Globular Clusters During Reionization MKI Level 5, Room 582K Collaboration University of Queensland University of Sussex University of Stockholm Michael Drinkwater Ilian Iliev Peter Thomas
The Role Of Globular Clusters During Reionization MKI Level 5, Room 582K Collaboration University of Queensland University of Sussex University of Stockholm Michael Drinkwater Ilian Iliev Peter Thomas
TEREZA JEŘÁBKOVÁ ESO GARCHING & UNIVERSITY OF BONN & CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE
 1 TEREZA JEŘÁBKOVÁ ESO GARCHING & UNIVERSITY OF BONN & CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE www: sirrah.troja.mff.cuni.cz/~tereza email: tjerabko@eso.org 17 MODEST UNDER PRAGUE S STARRY SKIES CZECH REPUBLIC 18-22
1 TEREZA JEŘÁBKOVÁ ESO GARCHING & UNIVERSITY OF BONN & CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE www: sirrah.troja.mff.cuni.cz/~tereza email: tjerabko@eso.org 17 MODEST UNDER PRAGUE S STARRY SKIES CZECH REPUBLIC 18-22
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Jun 1999
 to appear in AJ Globular Cluster Systems I: V I Color Distributions arxiv:astro-ph/9906499v1 30 Jun 1999 Karl Gebhardt 1,3 University of California Observatories / Lick Observatory, University of California,
to appear in AJ Globular Cluster Systems I: V I Color Distributions arxiv:astro-ph/9906499v1 30 Jun 1999 Karl Gebhardt 1,3 University of California Observatories / Lick Observatory, University of California,
Mock Surveys of the Sub-millimetre Sky
 Mock Surveys of the Sub-millimetre Sky William Cowley Supervisors: Carlton Baugh, Cedric Lacey, Shaun Cole DEX-X: Thurs 9th Jan Outline Sub-millimetre Galaxies Observational Motivation Angular resolution
Mock Surveys of the Sub-millimetre Sky William Cowley Supervisors: Carlton Baugh, Cedric Lacey, Shaun Cole DEX-X: Thurs 9th Jan Outline Sub-millimetre Galaxies Observational Motivation Angular resolution
Solving. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics
 Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation. Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology
 A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology M81 Angel Lopez Sanchez A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Lacey et al. 2015 arxiv:1509.08473
A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology M81 Angel Lopez Sanchez A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Lacey et al. 2015 arxiv:1509.08473
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Feb 2004
 **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Young Massive Clusters in Merging and Starburst Galaxies arxiv:astro-ph/0402377v1 16 Feb 2004 Richard
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Young Massive Clusters in Merging and Starburst Galaxies arxiv:astro-ph/0402377v1 16 Feb 2004 Richard
The formation history of elliptical galaxies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 366, 499 509 (2006) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09879.x The formation history of elliptical galaxies Gabriella De Lucia, Volker Springel, Simon D. M. White, Darren Croton and
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 366, 499 509 (2006) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09879.x The formation history of elliptical galaxies Gabriella De Lucia, Volker Springel, Simon D. M. White, Darren Croton and
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011](/thumbs/76/73863672.jpg) A Universe of Dwarf Galaxies, Lyon 2010 Editors : will be set by the publisher EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 2017 arxiv:1101.2232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011 HOW DOES FEEDBACK AFFECT MILKY WAY SATELLITE
A Universe of Dwarf Galaxies, Lyon 2010 Editors : will be set by the publisher EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 2017 arxiv:1101.2232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011 HOW DOES FEEDBACK AFFECT MILKY WAY SATELLITE
Difficulties of Star-forming Galaxies as the Source of IceCube Neutrinos. Takahiro Sudoh (UTokyo)
 Difficulties of Star-forming Galaxies as the Source of IceCube Neutrinos Takahiro Sudoh (UTokyo) IceCube Neutrino Astrophysical TeV - PeV neutrinos Isotropic arrival direction extragalactic origin? No
Difficulties of Star-forming Galaxies as the Source of IceCube Neutrinos Takahiro Sudoh (UTokyo) IceCube Neutrino Astrophysical TeV - PeV neutrinos Isotropic arrival direction extragalactic origin? No
Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation
 Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation Philip Hopkins, NoviCosmo 2007 Fundamental Planes = Scaling Laws Obeyed by Galaxies vs Origin of scaling laws: Ideally, we d understand every galaxy as an individual:
Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation Philip Hopkins, NoviCosmo 2007 Fundamental Planes = Scaling Laws Obeyed by Galaxies vs Origin of scaling laws: Ideally, we d understand every galaxy as an individual:
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Nov 2002
 Accepted for publication in ApJ Evidence for An Intermediate-age, Metal-rich Population of Globular Clusters in NGC 4365 1 Søren S. Larsen and Jean P. Brodie UCO / Lick Observatory, UC Santa Cruz, USA
Accepted for publication in ApJ Evidence for An Intermediate-age, Metal-rich Population of Globular Clusters in NGC 4365 1 Søren S. Larsen and Jean P. Brodie UCO / Lick Observatory, UC Santa Cruz, USA
Cosmological Merger Rates
 Cosmological Merger Rates C. Brook, F. Governato, P. Jonsson Not Phil Hopkins Kelly Holley-Bockelmann Vanderbilt University and Fisk University k.holley@vanderbilt.edu Why do we care so much about the
Cosmological Merger Rates C. Brook, F. Governato, P. Jonsson Not Phil Hopkins Kelly Holley-Bockelmann Vanderbilt University and Fisk University k.holley@vanderbilt.edu Why do we care so much about the
STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES
 STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES 23. Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen, the Netherlands www.astro.rug.nl/ vdkruit Beijing, September 2011 Outline The local Mass
STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES 23. Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen, the Netherlands www.astro.rug.nl/ vdkruit Beijing, September 2011 Outline The local Mass
