The Dawn of Gravitational Wave Astronomy
|
|
|
- Fay Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Dawn of Gravitational Wave Astronomy KMI colloquium Apr. 26, 2017 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Seiji Kawamura (ICRR, UTokyo) 1 SXS
2 Outline: Gravitational wave and detector Existing detectors - LIGO, Virgo, KAGRA Future detectors - ET, LISA, DECIGO Summary 2
3 Outline: Gravitational wave and detector Existing detectors - LIGO, Virgo, KAGRA Future detectors - ET, LISA, DECIGO Summary 3
4 What is gravitational wave? Tidal distortion of space Propagating at the speed of light
5 Profile of gravitational wave Derived by A. Einstein in his general relativity Propagates at the speed of light Propagates in vacuum Penetrates anything Detected by LIGO recently 5
6 Gravitational wave sources Binary coalescence: Neutron star Black hole Burst: Supernovae Black hole ringdown: Continuous: Pulsar Binary Stochastic Background Early universe (i.e. Inflation) Cosmic string Unknown
7 strain amplitude Neutron star binary coalescence inspiral phase merger Black hole quasinormal mode time 7
8 1 sec (First atoms) Observation of the beginning of the Universe The beginning of the Universe sec (Planck epock) Gravitational wave Neutrino Electromagnetic wave 380,000 year (Recombination) 13.7B year (Now)
9 Gravitational wave detector Gravitational waves The mirrors and beam splitter are suspended. Mirror Mirror Beam splitter Lens Interfering light Laser Screen
10 Detectors in the world Ground-based 2nd-generation detectors Ground-based 3rd-generation detectors LIGO GEO ET Space detectors KAGRA LISA LIGO Virgo DECIGO
11 Outline: Gravitational wave and detector Existing detectors - LIGO, Virgo, KAGRA Future detectors - ET, LISA, DECIGO Summary 11
12 LIGO LIGO Laboratory: 180 staff located at Caltech, MIT, Hanford, Livingston Hanford, WA LIGO Livingston Observatory LIGO Scientific Collaboration: ~ 1000 scientists, ~80 institutions, 15 countries LIGO Hanford Observatory Livingston, LA LIGO-G v1
13 LIGO Livingston Observatory 4 km 4 km LIGO-G v1 LIGO Laboratory 13
14 LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO-G v1
15 Advanced LIGO Interferometer Pre-stabilized Laser 200W, 1064 nm Active Seismic Isolation 40 kg Test Mass Mirror Input Optics Output Mode Cleaner LIGO-G v1 Auxiliary Laser 15
16 RSE interferometer Power recycling mirror: Increase the effective power -> Improve the shot noise Fabry-Perot arm cavity: Increase the effective arm length -> Increase the GW signal Detuned for the best NS-NS inspiral range Signal extraction mirror: Extract GW signal before cancellation -> Optimize the quantum noise
17 The Advanced LIGO Detector Sensitivity During O1 LIGO-G v1 Abbott, et al.,ligo Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration, GW150914: The Advanced LIGO Detectors in the Era of First Discoveries, Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, (2016). 17
18 Abbott, et al.,ligo Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration, Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, (2016) 4 x m LIGO-G v1 18
19 Source of detected gravitational wave SXS
20 LIGO-G v1
21 LIGO-G v1
22 Extracting Astrophysical Parameters from Detections GW GW LVT GW GW LVT Hanford Livingston Abbott, et al., LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration, Binary Black Hole Mergers in the first Advanced LIGO Observing Run, accepted in Phys. Rev. X LIGO-G v1 22
23 Implications for Astrophysics and l l First direct observation of a binary black hole merger!» BBH systems can merge in a Hubble time» GWs may be the only way to detect BBH mergers First direct experimental evidence for heavy stellar mass black holes» Implication: assuming direct formation from core collapse of heavy star, favors low metallicity environment (z < ½)» Implication: kicks from core collapse supernova can t be very large l Binary black hole merger rates are in the range per Gpc 3 per year l l BBH mergers are Kerr black holes, consistent with general relativity First test of general relativity in the dynamical strong field limit:» Inspiral waveforms consistent with Post-Newtonian expansion» Limit on graviton mass General Relativity Compton Wavelength of the Graviton Abbott, et al., LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration, Astrophysical Implications of the Binary Black Hole Merger GW150914, Ap. J. Lett. 818, L22 (2016). Abbott, et al., LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration, Tests of General Relativity with GW Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, (2016) LIGO-G v1 23
24 LIGO l LIGO s first O1 observing run (Sept 12, 2015 Jan 19, 2016)» Produced first direct gravitational wave detections! l LIGO began O2 run on November 30, 2016; 6 month scheduled duration» LIGO Livingston interferometer operating at nearly 1/2 design sensitivity» LIGO Hanford interferometer operating at approximately 1/3 design sensitivity» Joint running with Advanced Virgo planned for the 2nd half of O2 Hanford, WA LIGO Hanford Observatory Livingston, LA LIGO Livingston Observatory Hanford and Livingston Strain Sensitivities for LIGO s Second O2 Observing Run Hanford, O2 Livingston, O km LIGO-G v LIGO Laboratory 24
25
26 LIGO s Plans for the Future l l l l l After O2 run completes, Advanced LIGO detectors will undergo a period of commissioning and detector improvements» Goal is to achieve design sensitivity by the end of the decade 200 Mpc average binary neutron star (BNS) detection range, 1.3 Gpc average binary black hole (BBH) detection range Longer duration O3 and O4 runs are planned in the next 5 year period Early next decade, a set of upgrades to Advanced LIGO is anticipated» Broadband squeezed light injection to reduce quantum noise (shot noise and radiation pressure)» Improved test mass mirror coatings to reduce thermal noise in the critical mid-frequency band region» Preliminary design sensitivity increase to 350/2200 Mpc BNS/BBH detection range LIGO-India has been approved and is underway; expected to begin operations in 2024» An international collaboration between the USA and India to construct an identical Advanced LIGO interferometer in India Longer term: plans for a new network of ground-based observatories with sensitivities capable of seeing back to the formation of the first stars LIGO-G v1 26
27 Participated by scientists from Italy and France (former founders of Virgo), The Netherlands, Poland, Hungary, and Spain Advanced Virgo Tot.~300 scientists
28 Larger central vacuum links Ad Virgo in a nutshell Large cryotraps WE heavier mirrors (42 kg) Input Mode Cleaner high finesse ( 1000) new IP tilt control WI Faraday Isolator POP BS CP NI larger beam waist NE PRM 2x100 W fiber rod amplifier SRM signal recycling 28 1W OMC new payload EOM high power SSL (200 W) B1 DC detection fused silica suspensions
29 Beam Splitter integrated hooked to the super attenuator (now in vacuum ) Payloads Input mirror payloads of the FP cavities assembled and integrated in the super attenuator vacuum chamber
30 MILESTONES 1 LOCK AT HALF FRINGE ACHIEVED DEC 30TH 2 LOCK AT DARK FRINGE First lock achieved 3 LOW NOISE STABLE CONFIGURATION Final alignment, OMC lock, lock on B1, low noise actuation. 1st noise budget 4 SCIENCE MODE Full automation, final calibration, more DET benches in vacuum (TBC) - Sensitivity target
31 O2 TIMELINE
32 Cryogenic Mirror KAGRA Underground Technologies crucial for the 3rd-generation detectors; KAGRA can be regarded as a 2.5-generation detector. 32
33 Location (Kamioka) Mozumi Entrance CLIO Super-Kamiokande Kamioka Tokyo Toyama airport 40min. by car Shin-Atotsu Entrance 33
34 Ground motion in Kamioka mine Kashiwa Kamioka 34
35 Vibration isolation system 2nd floor Inverted pendulum Geometrical antispring (GAS) filter Multi-stage pendulum (with GAS filter) GAS filter 1st floor Another pendulum (with GAS filter) Two-layer structure to avoid the resonances of the tall structure. Mirror suspension 35
36 Cryogenic system Platform (14 K) Upper mass (15 K) Mirror (20 K) Cryocooler Inner shield (8 K) Outer shield (80 K) Heat link Cryocooler Main beam Cryocooler Beam tube shield
37 Optical configuration Input mode cleaner 26 m Finesse: 500 Input Bench PRM ETM ITM BS Interferometer Resonant sideband extraction with detuning Power recycling gain: 11 Signal band gain: 15 DC readout ITM 400 kw ETM 80 W 825 W Laser Wavelength: 1064 nm Power: 180 W NPRO + Fiber amp. + laser module SEM 37 Output mode cleaner
38 Ultimate sensitivity limit of KAGRA Duty factor: > 80% Inspiral range: 176 Mpc
39 Expected event rate for NS-NS coalescence Inspiral range: 176 Mpc (the same definition as LIGO/Virgo) Assuming Inspiral rate per galaxy: 100 Myr -1 Expected event rate: 10 yr -1 39
40 Other GW sources BH-BH coalescence: e.g. 20 M at 2 Gpc (Binary black hole merger rates are in the range per Gpc 3 per year.) Quasi-normal mode of BH: e.g M at 3 Gpc Supernova: Hopefully 1 Mpc, 1 event per 30 years Pulsar: Crab and Vela, possibly other invisible pulsars Beginning of the Universe: non-standard model Unknown: Nature likes to surprise us.
41 KAGRA in network LIGO(H)+LIGO(L)+Virgo Coverage at 0.5 M.S.: 72% 3 detector duty factor: 51% L/H+L/L+V 50% LIGO(H)+LIGO(L)+Virgo+KAGRA Max sensitivity (M.S.): +13% Coverage at 0.5 M.S.: 100% 3 detector duty factor: 82% L/H+L/L+V+LCGT 50 B. F. Schutz
42 Schedule of KAGRA Project start Tunnel excavation ikagra bkagra Test run 3km cryogenic Michelson Cryogenic RSE Commissioning and observation
43 Shin-Atotsu entrance ( )
44 Central area ( )
45 Pre-stabilized laser ( )
46 input mode cleaner suspension system ( )
47 Cryostat for input test mass ( )
48 3km arm ( )
49 Control room ( )
50 Outline: Gravitational wave and detector Existing detectors - LIGO, Virgo, KAGRA Future detectors - ET, LISA, DECIGO Summary 50
51 Einstein Telescope (ET)
52 Central area
53 Sensitivity comparison(100 Mpc) Van Den Broeck and Sengupta (2007)
54 Physics of extreme Extreme matter: Neutron Stars (NS) are a natural laboratory of nuclear physics at densities unreachable in human laboratory We don t know the state of matter in NS, but the observation of several NS-NS coalescences at high SNR will allow the determination of the NS EOS Extreme gravity: GW are the only tool to observe the coalesce of BHs; but is the Kerr solution the right description of a BH? Measuring more than one quasi normal mode in the ringdown of a Bh-BH coalescence it will be possible to test the no-hair theorem Is GR the right gravity theory? Extreme Universe: What are the GRB progenitors? Long GRB are produced by BNS coalescence? Is the current cosmological model of the Universe the right one? Measuring simultaneously the GW signal and the GRB flash it will be possible to test the cosmological model
55 AdV+ R&D AdV AdV+ A+/Voyager R&D aligo A+ Voyager KAGRA LIGO India Mission definition Space system development elisa ESFRI Roadmap ET R&D ET Infrastructure Technical Design ET Detector Technical Design ET Observatory & Detector funding ET site construction - detector installation & commissioning Cosmic Explorer R&D CE site&detector installation R&D Installation Commissioning Data taking Other PAX Workshop
56 LISA: Opens the low-frequency gravitational universe 3 satellites 2.5 million km arms 50 million km behind Earth 56
57 LISA Sources 57
58 LISA Layout Laser transponder with 6 Links 2.5 Million km arms Watt sent pw received Michelson with third arm and Sagnac mode reference laser beams main transponded laser beams 58
59 Mission Profile and Orbit Three arms of 2.5 Million km 2W lasers 30 cm telescopes Breathing angles ± 1 deg Doppler shifts ± 5 MHz Launch on dedicated Ariane 6.4 Transfer time ~400 days Direct escape V = 260 m/s Propulsion module and S/C composite 59
60 NASA is back in LISA! 60
61 ESA L2 and L3 Missions Call for Mission Concepts fall 2016 Decision on Implementation 2020 Launch of L2 in 2028 Launch of L3 in 2034 LISA is ready for an early launch! 61
62 LISA Pathfinder Testing LISA technology in space! 62
63 LISA Pathfinder Take one LISA arm Squeeze it into ONE satellite Courtesy: Stefano Vitale 63
64 100 Years since GR Publication: Dec. 2,
65 What do we know? 65
66 Strain [Hz -1/2 ] DECIGO Deci-hertz Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory Bridges the gap between LISA and ground-based detectors Low confusion noise -> Extremely high sensitivity LISA Confusion Noise DECIGO Ground-based detectors Frequency [Hz]
67 Pre-conceptual design Differential FP interferometer Arm length: 1000 km Mirror diameter: 1 m Laser wavelength:0.532 m Finesse: 10 Laser power: 10 W Mirror mass: 100 kg S/C: drag free 3 interferometers Arm cavity Arm cavity Drag-free S/C Laser Photodetector Mirror
68 Target sensitivity and science PBH related Dark Matter Supermassive BH years 3 months Coalescence 1 cluster Saito, Yokoyama 2009 General relativity Yagi, Tanaka 2009 Inflation Correlation (3 years) Inflation ( GW ~ ) Coalescence Frequency [Hz] Acceleration of expansion of Universe Seto, Kawamura, Nakamura 2004
69 Strain Acceleration of Expansion of the Universe Expansion +Acceleration? DECIGO NS-NS (z~1) GW Output Template (No Acceleration) Real Signal? Phase Delay~1sec (10 years) Time Seto, Kawamura, Nakamura, PRL 87, (2001)
70 Roadmap Mission Objectives R&D Fabrication SWIM Ground test + piggyback Test of key technologies R&D Fabrication B-DECIGO Detection of GW Test FP cavity between S/C R&D Fabrication DECIGO Direct observation of the inflation Scope 1 S/C 1 arm 3 S/C 3 interferometer 3 S/C, 3 interferometer 3 or 4 units
71 Outline: Gravitational wave and detector Existing detectors - LIGO, Virgo, KAGRA Future detectors - ET, LISA, DECIGO Summary 71
72 Summary Gravitational waves have been detected for the first time. Gravitational wave astronomy has been established. Gravitational wave astronomy will be developed with the addition of Virgo and KAGRA. ET, LISA, and DECIGO will produce amazing science in the future. 72
Status of LIGO. David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 LIGO-G M
 Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Gravitational Wave Detectors: Back to the Future
 Gravitational Wave Detectors: Back to the Future Raffaele Flaminio National Astronomical Observatory of Japan University of Tokyo, March 12th, 2017 1 Summary Short introduction to gravitational waves (GW)
Gravitational Wave Detectors: Back to the Future Raffaele Flaminio National Astronomical Observatory of Japan University of Tokyo, March 12th, 2017 1 Summary Short introduction to gravitational waves (GW)
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era
 The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
Takaaki Kajita, JGRG 22(2012) Status of KAGRA RESCEU SYMPOSIUM ON GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION JGRG 22. November
 Takaaki Kajita, JGRG 22(2012)111402 Status of KAGRA RESCEU SYMPOSIUM ON GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION JGRG 22 November 12-16 2012 Koshiba Hall, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Tokyo, Japan RESCEU
Takaaki Kajita, JGRG 22(2012)111402 Status of KAGRA RESCEU SYMPOSIUM ON GENERAL RELATIVITY AND GRAVITATION JGRG 22 November 12-16 2012 Koshiba Hall, The University of Tokyo, Hongo, Tokyo, Japan RESCEU
Overview of future interferometric GW detectors
 Overview of future interferometric GW detectors Giovanni Andrea Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, many credits to Michele Punturo, INFN Perugia New perspectives on Neutron Star Interiors Oct.9-13 2017,
Overview of future interferometric GW detectors Giovanni Andrea Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, many credits to Michele Punturo, INFN Perugia New perspectives on Neutron Star Interiors Oct.9-13 2017,
The Status of KAGRA Underground Cryogenic Gravitational Wave Telescope
 TAUP2017 @ Laurentian University Jul 26, 2017 The Status of KAGRA Underground Cryogenic Gravitational Wave Telescope Yuta Michimura Department of Physics, University of Tokyo on behalf of the KAGRA Collaboration
TAUP2017 @ Laurentian University Jul 26, 2017 The Status of KAGRA Underground Cryogenic Gravitational Wave Telescope Yuta Michimura Department of Physics, University of Tokyo on behalf of the KAGRA Collaboration
Development of ground based laser interferometers for the detection of gravitational waves
 Development of ground based laser interferometers for the detection of gravitational waves Rahul Kumar ICRR, The University of Tokyo, 7 th March 2014 1 Outline 1. Gravitational waves, nature & their sources
Development of ground based laser interferometers for the detection of gravitational waves Rahul Kumar ICRR, The University of Tokyo, 7 th March 2014 1 Outline 1. Gravitational waves, nature & their sources
Gravitational Wave Astronomy
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy Giles Hammond SUPA, University of Glasgow, UK on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 14 th Lomonosov conference on Elementary Particle Physics
Gravitational Wave Astronomy Giles Hammond SUPA, University of Glasgow, UK on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 14 th Lomonosov conference on Elementary Particle Physics
Status and Plans for Future Generations of Ground-based Interferometric Gravitational-Wave Antennas
 Status and Plans for Future Generations of Ground-based Interferometric Gravitational-Wave Antennas 4 th international LISA Symposium July 22, 2002 @ Penn State University Seiji Kawamura National Astronomical
Status and Plans for Future Generations of Ground-based Interferometric Gravitational-Wave Antennas 4 th international LISA Symposium July 22, 2002 @ Penn State University Seiji Kawamura National Astronomical
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up
 Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
LIGOʼs first detection of gravitational waves and the development of KAGRA
 LIGOʼs first detection of gravitational waves and the development of KAGRA KMI2017 Jan. 2017 Tokyo Institute of Technology Kentaro Somiya Self Introduction Applied Physics (U Tokyo) NAOJ 2000-04 Albert-Einstein
LIGOʼs first detection of gravitational waves and the development of KAGRA KMI2017 Jan. 2017 Tokyo Institute of Technology Kentaro Somiya Self Introduction Applied Physics (U Tokyo) NAOJ 2000-04 Albert-Einstein
Advanced LIGO, Advanced VIRGO and KAGRA: Precision Measurement for Astronomy. Stefan Ballmer For the LVC Miami 2012 Dec 18, 2012 LIGO-G
 Advanced LIGO, Advanced VIRGO and KAGRA: Precision Measurement for Astronomy Stefan Ballmer For the LVC Miami 2012 Dec 18, 2012 LIGO-G1201293 Outline Introduction: What are Gravitational Waves? The brief
Advanced LIGO, Advanced VIRGO and KAGRA: Precision Measurement for Astronomy Stefan Ballmer For the LVC Miami 2012 Dec 18, 2012 LIGO-G1201293 Outline Introduction: What are Gravitational Waves? The brief
Status and Prospects for LIGO
 Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
LIGO: On the Threshold of Gravitational-wave Astronomy
 LIGO: On the Threshold of Gravitational-wave Astronomy Stan Whitcomb LIGO/Caltech IIT, Kanpur 18 December 2011 Outline of Talk Quick Review of GW Physics and Astrophysics LIGO Overview» Initial Detectors»
LIGO: On the Threshold of Gravitational-wave Astronomy Stan Whitcomb LIGO/Caltech IIT, Kanpur 18 December 2011 Outline of Talk Quick Review of GW Physics and Astrophysics LIGO Overview» Initial Detectors»
Advanced Virgo: Status and Perspectives. A.Chiummo on behalf of the VIRGO collaboration
 Advanced Virgo: Status and Perspectives A.Chiummo on behalf of the VIRGO collaboration Advanced Virgo 2 Advanced Virgo What s that? 3 Advanced Virgo Advanced Virgo (AdV): upgrade of the Virgo interferometric
Advanced Virgo: Status and Perspectives A.Chiummo on behalf of the VIRGO collaboration Advanced Virgo 2 Advanced Virgo What s that? 3 Advanced Virgo Advanced Virgo (AdV): upgrade of the Virgo interferometric
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2. Daniel Holz The University of Chicago
 Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Squeezed Light Techniques for Gravitational Wave Detection
 Squeezed Light Techniques for Gravitational Wave Detection July 6, 2012 Daniel Sigg LIGO Hanford Observatory Seminar at TIFR, Mumbai, India G1200688-v1 Squeezed Light Interferometry 1 Abstract Several
Squeezed Light Techniques for Gravitational Wave Detection July 6, 2012 Daniel Sigg LIGO Hanford Observatory Seminar at TIFR, Mumbai, India G1200688-v1 Squeezed Light Interferometry 1 Abstract Several
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring
 The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
The GW research in Japan - Current Status of KAGRA -
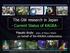 GW RSS Amplitude and Detector Noise Level [1/Hz 1/2 ] 10 18 10 20 10 22 10 24 100pc events 10kpc events 10 2 10 3 Frequency [Hz] TAMA noise level (DT9) LCGT design sensitivity The GW research in Japan
GW RSS Amplitude and Detector Noise Level [1/Hz 1/2 ] 10 18 10 20 10 22 10 24 100pc events 10kpc events 10 2 10 3 Frequency [Hz] TAMA noise level (DT9) LCGT design sensitivity The GW research in Japan
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans. Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04
 LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
Discovery of Gravita/onal Waves
 Discovery of Gravita/onal Waves Avto Kharchilava QuarkNet Workshop, August 2016 https://www.ligo.caltech.edu/news/ligo20160211 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity: Gravity is a manifestation
Discovery of Gravita/onal Waves Avto Kharchilava QuarkNet Workshop, August 2016 https://www.ligo.caltech.edu/news/ligo20160211 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity: Gravity is a manifestation
Status of the KAGRA Project
 Status of the KAGRA Project Takaaki Kajita, for the KAGRA collaboration (~230 members) ICRR, Univ. of Tokyo Kajita_at_icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp GWPAW2015 June, 2015, Osaka Outline Introduction: Overview of KAGRA
Status of the KAGRA Project Takaaki Kajita, for the KAGRA collaboration (~230 members) ICRR, Univ. of Tokyo Kajita_at_icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp GWPAW2015 June, 2015, Osaka Outline Introduction: Overview of KAGRA
How to measure a distance of one thousandth of the proton diameter? The detection of gravitational waves
 How to measure a distance of one thousandth of the proton diameter? The detection of gravitational waves M. Tacca Laboratoire AstroParticule et Cosmologie (APC) - Paris Journée GPhys - 2016 July 6th General
How to measure a distance of one thousandth of the proton diameter? The detection of gravitational waves M. Tacca Laboratoire AstroParticule et Cosmologie (APC) - Paris Journée GPhys - 2016 July 6th General
Searching for gravitational waves
 Searching for gravitational waves Matteo Barsuglia (barsuglia@apc.univ-paris7.fr) CNRS - Laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie 1 The gravitational waves (GW) Perturbations of the space-time metrics
Searching for gravitational waves Matteo Barsuglia (barsuglia@apc.univ-paris7.fr) CNRS - Laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie 1 The gravitational waves (GW) Perturbations of the space-time metrics
Gravitational Waves and LIGO
 Gravitational Waves and LIGO Ray Frey, University of Oregon 1. GW Physics and Astrophysics 2. How to detect GWs The experimental challenge 3. Prospects June 16, 2004 R. Frey QNet 1 General Relativity Some
Gravitational Waves and LIGO Ray Frey, University of Oregon 1. GW Physics and Astrophysics 2. How to detect GWs The experimental challenge 3. Prospects June 16, 2004 R. Frey QNet 1 General Relativity Some
Ground-based GW detectors: status of experiments and collaborations
 Ground-based GW detectors: status of experiments and collaborations C.N.Man Univ. Nice-Sophia-Antipolis, CNRS, Observatoire de Cote d Azur A short history GW & how to detect them with interferometry What
Ground-based GW detectors: status of experiments and collaborations C.N.Man Univ. Nice-Sophia-Antipolis, CNRS, Observatoire de Cote d Azur A short history GW & how to detect them with interferometry What
Advanced Virgo and LIGO: today and tomorrow
 Advanced Virgo and LIGO: today and tomorrow Michał Was for the LIGO and Virgo collaborations Michał Was (SFP Gravitation) 2017 Nov 22 1 / 21 d Basics of interferometric gravitational wave detections Need
Advanced Virgo and LIGO: today and tomorrow Michał Was for the LIGO and Virgo collaborations Michał Was (SFP Gravitation) 2017 Nov 22 1 / 21 d Basics of interferometric gravitational wave detections Need
Long-term strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups
 Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Status of the International Second-generation Gravitational-wave Detector Network
 Status of the International Second-generation Gravitational-wave Detector Network Albert Lazzarini Deputy Director, LIGO Laboratory California Institute of Technology On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
Status of the International Second-generation Gravitational-wave Detector Network Albert Lazzarini Deputy Director, LIGO Laboratory California Institute of Technology On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
Gravitational Waves & Precision Measurements
 Gravitational Waves & Precision Measurements Mike Smith 1 -20 2 HOW SMALL IS THAT? Einstein 1 meter 1/1,000,000 3 1,000,000 smaller Wavelength of light 10-6 meters 1/10,000 4 10,000 smaller Atom 10-10
Gravitational Waves & Precision Measurements Mike Smith 1 -20 2 HOW SMALL IS THAT? Einstein 1 meter 1/1,000,000 3 1,000,000 smaller Wavelength of light 10-6 meters 1/10,000 4 10,000 smaller Atom 10-10
Synergy with Gravitational Waves
 Synergy with Gravitational Waves Alexandre Le Tiec and Jérôme Novak Laboratoire Univers et Théories Observatoire de Paris / CNRS LIGO, Virgo, ( elisa, ET,... ( What is a gravitational wave? A gravitational
Synergy with Gravitational Waves Alexandre Le Tiec and Jérôme Novak Laboratoire Univers et Théories Observatoire de Paris / CNRS LIGO, Virgo, ( elisa, ET,... ( What is a gravitational wave? A gravitational
Next Generation Interferometers
 Next Generation Interferometers TeV 06 Madison Rana Adhikari Caltech 1 Advanced LIGO LIGO mission: detect gravitational waves and initiate GW astronomy Next detector» Should have assured detectability
Next Generation Interferometers TeV 06 Madison Rana Adhikari Caltech 1 Advanced LIGO LIGO mission: detect gravitational waves and initiate GW astronomy Next detector» Should have assured detectability
The Status of Enhanced LIGO.
 The Status of Enhanced LIGO. Aidan Brooks. December 2008 AIP Congress 2008, Adelaide, Australia 1 Outline Gravitational Waves» Potential sources» Initial LIGO interferometer Enhanced LIGO upgrades» Increased
The Status of Enhanced LIGO. Aidan Brooks. December 2008 AIP Congress 2008, Adelaide, Australia 1 Outline Gravitational Waves» Potential sources» Initial LIGO interferometer Enhanced LIGO upgrades» Increased
Present and Future. Nergis Mavalvala October 09, 2002
 Gravitational-wave Detection with Interferometers Present and Future Nergis Mavalvala October 09, 2002 1 Interferometric Detectors Worldwide LIGO TAMA LISA LIGO VIRGO GEO 2 Global network of detectors
Gravitational-wave Detection with Interferometers Present and Future Nergis Mavalvala October 09, 2002 1 Interferometric Detectors Worldwide LIGO TAMA LISA LIGO VIRGO GEO 2 Global network of detectors
The gravitational wave detector VIRGO
 The gravitational wave detector VIRGO for the VIRGO collaboration Raffaele Flaminio Laboratoire d Annecy-le-Vieux de Physique des Particules (LAPP) IN2P3 - CNRS Summary I. A bit of gravitational wave physics
The gravitational wave detector VIRGO for the VIRGO collaboration Raffaele Flaminio Laboratoire d Annecy-le-Vieux de Physique des Particules (LAPP) IN2P3 - CNRS Summary I. A bit of gravitational wave physics
Large-scale Cryogenic Gravitational wave Telescope (LCGT) TAMA/CLIO/LCGT Collaboration Kazuaki KURODA
 29-March, 2009 JPS Meeting@Rikkyo Univ Large-scale Cryogenic Gravitational wave Telescope (LCGT) TAMA/CLIO/LCGT Collaboration Kazuaki KURODA Overview of This talk Science goal of LCGT First detection of
29-March, 2009 JPS Meeting@Rikkyo Univ Large-scale Cryogenic Gravitational wave Telescope (LCGT) TAMA/CLIO/LCGT Collaboration Kazuaki KURODA Overview of This talk Science goal of LCGT First detection of
The Quest to Detect Gravitational Waves
 The Quest to Detect Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan California Institute of Technology / LIGO Laboratory What Physicists Do lecture Sonoma State University March 8, 2004 LIGO-G040055-00-E Outline Different
The Quest to Detect Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan California Institute of Technology / LIGO Laboratory What Physicists Do lecture Sonoma State University March 8, 2004 LIGO-G040055-00-E Outline Different
Advanced LIGO Status Report
 Advanced LIGO Status Report Gregory Harry LIGO/MIT On behalf of the LIGO Science Collaboration 22 September 2005 ESF PESC Exploratory Workshop Perugia Italy LIGO-G050477 G050477-00-R Advanced LIGO Overview
Advanced LIGO Status Report Gregory Harry LIGO/MIT On behalf of the LIGO Science Collaboration 22 September 2005 ESF PESC Exploratory Workshop Perugia Italy LIGO-G050477 G050477-00-R Advanced LIGO Overview
Future underground gravitational wave observatories. Michele Punturo INFN Perugia
 Future underground gravitational wave observatories Michele Punturo INFN Perugia Terrestrial Detectors Advanced detectors 2015-2025 GEO, Hannover, 600 m aligo Hanford, 4 km 2015 2016 AdV, Cascina, 3 km
Future underground gravitational wave observatories Michele Punturo INFN Perugia Terrestrial Detectors Advanced detectors 2015-2025 GEO, Hannover, 600 m aligo Hanford, 4 km 2015 2016 AdV, Cascina, 3 km
Progress in Gravitational Wave Detection: Interferometers
 1 Progress in Gravitational Wave Detection: Interferometers Kazuaki Kuroda a and LCGT Collaboration b a Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8582,
1 Progress in Gravitational Wave Detection: Interferometers Kazuaki Kuroda a and LCGT Collaboration b a Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8582,
Gravitational Waves: From Einstein to a New Science
 Gravitational Waves: From Einstein to a New Science LIGO-G1602199 Barry C Barish Caltech - LIGO 1.3 Billion Years Ago 2 Black Holes Regions of space created by super dense matter from where nothing can
Gravitational Waves: From Einstein to a New Science LIGO-G1602199 Barry C Barish Caltech - LIGO 1.3 Billion Years Ago 2 Black Holes Regions of space created by super dense matter from where nothing can
The LIGO Project: a Status Report
 The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
ET: Einstein Telescope
 ET: Einstein Telescope Michele Punturo INFN Perugia On behalf of the ET design study team ILIAS General meeting, Jaca Feb 2008 1 Evolution of the current GW detectors Current Gravitational Wave interferometric
ET: Einstein Telescope Michele Punturo INFN Perugia On behalf of the ET design study team ILIAS General meeting, Jaca Feb 2008 1 Evolution of the current GW detectors Current Gravitational Wave interferometric
Searching for Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background with LIGO
 Searching for Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background with LIGO Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 09/21/07 Outline LIGO Experiment:» Overview» Status» Future upgrades Stochastic background of gravitational
Searching for Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background with LIGO Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 09/21/07 Outline LIGO Experiment:» Overview» Status» Future upgrades Stochastic background of gravitational
LIGO s Detection of Gravitational Waves from Two Black Holes
 LIGO s Detection of Gravitational Waves from Two Black Holes Gregory Harry Department of Physics, American University February 17,2016 LIGO-G1600274 GW150914 Early History of Gravity Aristotle Kepler Laplace
LIGO s Detection of Gravitational Waves from Two Black Holes Gregory Harry Department of Physics, American University February 17,2016 LIGO-G1600274 GW150914 Early History of Gravity Aristotle Kepler Laplace
Fulvio Ricci Università di Roma La Sapienza INFN Roma on behalf of the design study team
 Fulvio Ricci Università di Roma La Sapienza INFN Roma on behalf of the design study team TAUP 2009 - Roma 1 !The ET project: organization and the road map! The ET scientific targets!conclusion TAUP 2009
Fulvio Ricci Università di Roma La Sapienza INFN Roma on behalf of the design study team TAUP 2009 - Roma 1 !The ET project: organization and the road map! The ET scientific targets!conclusion TAUP 2009
LISA mission design. Guido Mueller. APS April Meeting, Jan 30th, 2017, Washington DC
 LISA mission design Guido Mueller University of Florida APS April Meeting, Jan 30th, 2017, Washington DC 1 L3 from ESA s perspective 2013: Selection of L3 Science Theme by ESA The Gravitational Universe
LISA mission design Guido Mueller University of Florida APS April Meeting, Jan 30th, 2017, Washington DC 1 L3 from ESA s perspective 2013: Selection of L3 Science Theme by ESA The Gravitational Universe
Gravity -- Studying the Fabric of the Universe
 Gravity -- Studying the Fabric of the Universe Barry C. Barish Caltech "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) AAAS Annual Meeting Denver, Colorado 17-Feb-03
Gravity -- Studying the Fabric of the Universe Barry C. Barish Caltech "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) AAAS Annual Meeting Denver, Colorado 17-Feb-03
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer. Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1 In 2001 we considered what we can do using 0.1 hertz laser interferometer ( Seto, Kawamura
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1 In 2001 we considered what we can do using 0.1 hertz laser interferometer ( Seto, Kawamura
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves. Dr. Stephen Ng
 LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
Advanced VIRGO EXPERIMENT
 Advanced VIRGO EXPERIMENT Advanced VIRGO Interferometer: a second generation detector for Gravitational Waves observation F. Frasconi for the VIRGO Collaboration 16 th Lomonosov Conference Moscow State
Advanced VIRGO EXPERIMENT Advanced VIRGO Interferometer: a second generation detector for Gravitational Waves observation F. Frasconi for the VIRGO Collaboration 16 th Lomonosov Conference Moscow State
LIGO workshop What Comes Next for LIGO May 7-8, 2015, Silver Spring, MD KAGRA KAGRA. Takaaki Kajita, ICRR, Univ. of Tokyo for the KAGRA collaboration
 LIGO workshop What Comes Next for LIGO May 7-8, 2015, Silver Spring, MD KAGRA KAGRA Takaaki Kajita, ICRR, Univ. of Tokyo for the KAGRA collaboration Outline Introduction: Overview of KAGRA Status of the
LIGO workshop What Comes Next for LIGO May 7-8, 2015, Silver Spring, MD KAGRA KAGRA Takaaki Kajita, ICRR, Univ. of Tokyo for the KAGRA collaboration Outline Introduction: Overview of KAGRA Status of the
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
LISA: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves. Tom Prince Caltech/JPL. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna LISA
 : Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
Probing for Gravitational Waves
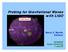 Probing for Gravitational Waves LIGO Reach with LIGO AdLIGO Initial LIGO Barry C. Barish Caltech YKIS2005 Kyoto University 1-July-05 Einstein s Theory of Gravitation a necessary consequence of Special
Probing for Gravitational Waves LIGO Reach with LIGO AdLIGO Initial LIGO Barry C. Barish Caltech YKIS2005 Kyoto University 1-July-05 Einstein s Theory of Gravitation a necessary consequence of Special
Advanced LIGO, LIGO-Australia and the International Network
 Advanced LIGO, LIGO-Australia and the International Network Stan Whitcomb LIGO/Caltech IndIGO - ACIGA meeting on LIGO-Australia 8 February 2011 Gravitational Waves Einstein in 1916 and 1918 recognized
Advanced LIGO, LIGO-Australia and the International Network Stan Whitcomb LIGO/Caltech IndIGO - ACIGA meeting on LIGO-Australia 8 February 2011 Gravitational Waves Einstein in 1916 and 1918 recognized
Searching for gravitational waves. with LIGO detectors
 Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Advanced Virgo: status and gravitational waves detection. Flavio Travasso on behalf of Virgo Collaboration INFN Perugia - University of Perugia - EGO
 Advanced Virgo: status and gravitational waves detection Flavio Travasso on behalf of Virgo Collaboration INFN Perugia - University of Perugia - EGO Minkowski vs general metric dx dx ds 2 1 1 1 1 Flat
Advanced Virgo: status and gravitational waves detection Flavio Travasso on behalf of Virgo Collaboration INFN Perugia - University of Perugia - EGO Minkowski vs general metric dx dx ds 2 1 1 1 1 Flat
Overview of Gravitational Wave Observations by LIGO and Virgo
 Overview of Gravitational Wave Observations by LIGO and Virgo Giovanni Andrea Prodi Virgo Group at Padova-Trento, LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration Vulcano Workshop 2016, May 23 Published
Overview of Gravitational Wave Observations by LIGO and Virgo Giovanni Andrea Prodi Virgo Group at Padova-Trento, LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration Vulcano Workshop 2016, May 23 Published
LIGO Present and Future. Barry Barish Directory of the LIGO Laboratory
 LIGO Present and Future Barry Barish Directory of the LIGO Laboratory LIGO I Schedule and Plan LIGO I has been built by LIGO Lab (Caltech & MIT) 1996 Construction Underway (mostly civil) 1997 Facility
LIGO Present and Future Barry Barish Directory of the LIGO Laboratory LIGO I Schedule and Plan LIGO I has been built by LIGO Lab (Caltech & MIT) 1996 Construction Underway (mostly civil) 1997 Facility
KAGAYA studio. Status of DECIGO. Shuichi Sato Hosei University. For the DECIGO and the DPF collaboration
 KAGAYA studio Status of DECIGO Shuichi Sato Hosei University For the DECIGO and the DPF collaboration Title Outline v DECIGO v DECIGO pathfinder v Mission status Idea of DECIGO v DECi-hertz Interferometer
KAGAYA studio Status of DECIGO Shuichi Sato Hosei University For the DECIGO and the DPF collaboration Title Outline v DECIGO v DECIGO pathfinder v Mission status Idea of DECIGO v DECi-hertz Interferometer
Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves
 Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves July 25, 2017 Bonn Seoul National University Outline What are the gravitational waves? Generation of
Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves July 25, 2017 Bonn Seoul National University Outline What are the gravitational waves? Generation of
Squeezed Light for Gravitational Wave Interferometers
 Squeezed Light for Gravitational Wave Interferometers R. Schnabel, S. Chelkowski, H. Vahlbruch, B. Hage, A. Franzen, and K. Danzmann. Institut für Atom- und Molekülphysik, Universität Hannover Max-Planck-Institut
Squeezed Light for Gravitational Wave Interferometers R. Schnabel, S. Chelkowski, H. Vahlbruch, B. Hage, A. Franzen, and K. Danzmann. Institut für Atom- und Molekülphysik, Universität Hannover Max-Planck-Institut
Gravitational wave detection. K.A. Strain
 Gravitational wave detection K.A. Strain Contents gravitational waves: introduction sources of waves, amplitudes and rates basics of GW detection current projects future plans and hopes Gravitational Waves:
Gravitational wave detection K.A. Strain Contents gravitational waves: introduction sources of waves, amplitudes and rates basics of GW detection current projects future plans and hopes Gravitational Waves:
Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance General Relativity information carried by gravitational radiation at the speed of light
 Modern View of Gravitation Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance G µ = 8 µ # General Relativity information carried by gravitational radiation at the speed of light Gravitational Waves GR predicts
Modern View of Gravitation Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance G µ = 8 µ # General Relativity information carried by gravitational radiation at the speed of light Gravitational Waves GR predicts
Gearing up for Gravitational Waves: the Status of Building LIGO
 Gearing up for Gravitational Waves: the Status of Building LIGO Frederick J. Raab, LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO s Mission is to Open a New Portal on the Universe In 1609 Galileo viewed the sky through
Gearing up for Gravitational Waves: the Status of Building LIGO Frederick J. Raab, LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO s Mission is to Open a New Portal on the Universe In 1609 Galileo viewed the sky through
Laser Interferometer Gravitationalwave Observatory LIGO Industrial Physics Forum. Barry Barish 7 November 2000 LIGO-G9900XX-00-M
 Laser Interferometer Gravitationalwave Observatory LIGO 2000 Industrial Physics Forum Barry Barish 7 November 2000 Sir Isaac Newton Perhaps the most important scientist of all time! Invented the scientific
Laser Interferometer Gravitationalwave Observatory LIGO 2000 Industrial Physics Forum Barry Barish 7 November 2000 Sir Isaac Newton Perhaps the most important scientist of all time! Invented the scientific
LIGO I status and advanced LIGO proposal
 LIGO I status and advanced LIGO proposal Hiro Yamamoto LIGO Lab / Caltech LIGO I» basic design» current status advanced LIGO» outline of the proposal» technical issues GW signals and data analysis ICRR
LIGO I status and advanced LIGO proposal Hiro Yamamoto LIGO Lab / Caltech LIGO I» basic design» current status advanced LIGO» outline of the proposal» technical issues GW signals and data analysis ICRR
Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection
 Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection M. Tacca Nikhef - Amsterdam Nikhef- 2017 July 14th Born in Novara (Italy) Introducing Myself PostDoc Fellow @ Nikhef (since July 2017) Laurea & PhD @
Optical Techniques for Gravitational-Wave Detection M. Tacca Nikhef - Amsterdam Nikhef- 2017 July 14th Born in Novara (Italy) Introducing Myself PostDoc Fellow @ Nikhef (since July 2017) Laurea & PhD @
Gravity. Newtonian gravity: F = G M1 M2/r 2
 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Gravitational waves from the early Universe
 Gravitational waves from the early Universe Part 1 Sachiko Kuroyanagi (Nagoya University) 26 Aug 2017 Summer Institute 2017 What is a Gravitational Wave? What is a Gravitational Wave? 11 Feb 2016 We have
Gravitational waves from the early Universe Part 1 Sachiko Kuroyanagi (Nagoya University) 26 Aug 2017 Summer Institute 2017 What is a Gravitational Wave? What is a Gravitational Wave? 11 Feb 2016 We have
Review of LIGO Upgrade Plans
 Ando Lab Seminar April 13, 2017 Review of LIGO Upgrade Plans Yuta Michimura Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Contents Introduction A+ Voyager Cosmic Explorer Other issues on ISC Summary KAGRA+
Ando Lab Seminar April 13, 2017 Review of LIGO Upgrade Plans Yuta Michimura Department of Physics, University of Tokyo Contents Introduction A+ Voyager Cosmic Explorer Other issues on ISC Summary KAGRA+
Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna.
 Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna. 1) LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) Why? 2)How? 1 Frequency Limitation Seismic noise cannot be cancelled at low-frequency
Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna. 1) LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) Why? 2)How? 1 Frequency Limitation Seismic noise cannot be cancelled at low-frequency
Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1
 1 Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1 Joan Centrella Chief, Gravitational Astrophysics Laboratory NASA/GSFC Summer School on Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics: Connecting
1 Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1 Joan Centrella Chief, Gravitational Astrophysics Laboratory NASA/GSFC Summer School on Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics: Connecting
LIGO: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory
 LIGO: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory Credit: Werner Benger/ZIB/AEI/CCT-LSU Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory/Caltech for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) http://www.ligo.org
LIGO: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory Credit: Werner Benger/ZIB/AEI/CCT-LSU Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory/Caltech for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) http://www.ligo.org
The LIGO Experiment Present and Future
 The LIGO Experiment Present and Future Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting Denver May 1 4, 2004 LIGO-G040239-00-Z What are Gravitational Waves? Gravitational
The LIGO Experiment Present and Future Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting Denver May 1 4, 2004 LIGO-G040239-00-Z What are Gravitational Waves? Gravitational
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort
 The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
LIGO Observational Results
 LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
Plan of Lectures. Lecture (I) Ground-based detector : LCGT. Lecture (II) Space-borne detector : DECIGO. Lecture (III) Novel type detector : TOBA
 Plan of Lectures Lecture (I) Ground-based detector : LCGT Lecture (II) Space-borne detector : DECIGO Lecture (III) Novel type detector : TOBA Space-borne detector : DECIGO Original Picture : Sora Masaki
Plan of Lectures Lecture (I) Ground-based detector : LCGT Lecture (II) Space-borne detector : DECIGO Lecture (III) Novel type detector : TOBA Space-borne detector : DECIGO Original Picture : Sora Masaki
Exploring the Warped Side of the Universe
 Exploring the Warped Side of the Universe Nergis Mavalvala Department of Physics Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Alumni Club, Washington DC October 2014 Einstein s legacies A story about our
Exploring the Warped Side of the Universe Nergis Mavalvala Department of Physics Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Alumni Club, Washington DC October 2014 Einstein s legacies A story about our
Overview Ground-based Interferometers. Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05
 Overview Ground-based Interferometers Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05 TAMA Japan 300m Interferometer Detectors LIGO Louisiana 4000m Virgo Italy 3000m AIGO Australia future GEO Germany 600m LIGO
Overview Ground-based Interferometers Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05 TAMA Japan 300m Interferometer Detectors LIGO Louisiana 4000m Virgo Italy 3000m AIGO Australia future GEO Germany 600m LIGO
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Space Gravitational-Wave Antenna DECIGO
 Space Gravitational-Wave Antenna DECIGO Original Picture : Sora Masaki Ando (Department of Physics, Kyoto University) Wataru Kokuyama (Department of Physics, University of Tokyo) On behalf of DECIGO working
Space Gravitational-Wave Antenna DECIGO Original Picture : Sora Masaki Ando (Department of Physics, Kyoto University) Wataru Kokuyama (Department of Physics, University of Tokyo) On behalf of DECIGO working
The Search for Gravitational Waves
 The Search for Gravitational Waves Fred Raab, LIGO Hanford Observatory, on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 21 October 2008 Outline What are gravitational waves? What do generic detectors look
The Search for Gravitational Waves Fred Raab, LIGO Hanford Observatory, on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 21 October 2008 Outline What are gravitational waves? What do generic detectors look
TOBA: Torsion-Bar Antenna
 TOBA: Torsion-Bar Antenna Small-scale TOBA at Tokyo Small-scale TOBA at Kyoto SWIM on SDS-1 satellite Masaki Ando (National Astronomical Observatory) K.Ishidoshiro, A.Shoda, K.Okada, W.Kokuyama, K.Yagi,
TOBA: Torsion-Bar Antenna Small-scale TOBA at Tokyo Small-scale TOBA at Kyoto SWIM on SDS-1 satellite Masaki Ando (National Astronomical Observatory) K.Ishidoshiro, A.Shoda, K.Okada, W.Kokuyama, K.Yagi,
EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd. 3 generation GW detector
 EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd 3 generation GW detector http://www.et-gw.eu/ Dorota Gondek-Rosińska University of Zielona Góra w imieniu polskiego ET konsorcjum (UW, UZG, UwB, PW, CAMK, IMPAN ) Gravitational wave
EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd 3 generation GW detector http://www.et-gw.eu/ Dorota Gondek-Rosińska University of Zielona Góra w imieniu polskiego ET konsorcjum (UW, UZG, UwB, PW, CAMK, IMPAN ) Gravitational wave
Current Experimental Limits on Gravitational Waves. Nelson Christensen Artemis, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Nice
 Current Experimental Limits on Gravitational Waves Nelson Christensen Artemis, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Nice September 28, 2017. DESY Theory Workshop General Relativity 1915: Einstein s Theory of
Current Experimental Limits on Gravitational Waves Nelson Christensen Artemis, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Nice September 28, 2017. DESY Theory Workshop General Relativity 1915: Einstein s Theory of
Figure 1: An example of the stretching and contracting of space-time caused by a gravitational wave.
 SEARCHING FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Nelson Christensen, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Physics and Astronomy, Carleton College, Northfield, Minnesota 55057 USA Abstract The search for gravitational
SEARCHING FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Nelson Christensen, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Physics and Astronomy, Carleton College, Northfield, Minnesota 55057 USA Abstract The search for gravitational
Advanced LIGO: Context and Overview
 Advanced LIGO Advanced LIGO: Context and Overview Gravitational waves offer a remarkable opportunity to see the universe from a new perspective, providing access to astrophysical insights that are available
Advanced LIGO Advanced LIGO: Context and Overview Gravitational waves offer a remarkable opportunity to see the universe from a new perspective, providing access to astrophysical insights that are available
Requirements for a 3G GW observatory
 Requirements for a 3G GW observatory SOME THOUGHTS FOR DISCUSSION HARALD LÜCK 3G Observatory & 3G Network Requirements = f(science, funding, politics, ) requirements for an individual observatory and the
Requirements for a 3G GW observatory SOME THOUGHTS FOR DISCUSSION HARALD LÜCK 3G Observatory & 3G Network Requirements = f(science, funding, politics, ) requirements for an individual observatory and the
Gravitational waves and fundamental physics
 Gravitational waves and fundamental physics Michele Maggiore Département de physique théorique Avignon, April 2008 Experimental situation Timeframe: present (LIGO, Virgo) ~2011-2014 advanced LIGO/Virgo
Gravitational waves and fundamental physics Michele Maggiore Département de physique théorique Avignon, April 2008 Experimental situation Timeframe: present (LIGO, Virgo) ~2011-2014 advanced LIGO/Virgo
DECIGO and DECIGO Pathfinder
 DECIGO and DECIGO Pathfinder Original Picture : Sora Masaki Ando (Department of Physics, Kyoto University) On behalf of DECIGO working group 1. DECIGO Overview and Science Pre-conceptual Design 2. DECIGO
DECIGO and DECIGO Pathfinder Original Picture : Sora Masaki Ando (Department of Physics, Kyoto University) On behalf of DECIGO working group 1. DECIGO Overview and Science Pre-conceptual Design 2. DECIGO
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO)! A Brief Overview!
 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Finding Black Holes with Lasers
 Finding Black Holes with Lasers Andreas Freise Royal Institute of Great Brtitain 18.02.2013 [Image shows guide laser at Allgäu Public Observatory in Ottobeuren, Germany. Credit: Martin Kornmesser] LIGO-G1300827
Finding Black Holes with Lasers Andreas Freise Royal Institute of Great Brtitain 18.02.2013 [Image shows guide laser at Allgäu Public Observatory in Ottobeuren, Germany. Credit: Martin Kornmesser] LIGO-G1300827
Prospects for joint transient searches with LOFAR and the LSC/Virgo gravitational wave interferometers
 Prospects for joint transient searches with LOFAR and the LSC/Virgo gravitational wave interferometers Ed Daw - University of Sheffield On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration
Prospects for joint transient searches with LOFAR and the LSC/Virgo gravitational wave interferometers Ed Daw - University of Sheffield On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration
Gravitational waves from the merger of two black holes
 Gravitational waves from the merger of two black holes Opening of the Academic Year by the Department of Physics and Astronomy (DPA) VU, Amsterdam, September 21 2016; Jo van den Brand; jo@nikhef.nl Event
Gravitational waves from the merger of two black holes Opening of the Academic Year by the Department of Physics and Astronomy (DPA) VU, Amsterdam, September 21 2016; Jo van den Brand; jo@nikhef.nl Event
Gravity s Standard Sirens. B.S. Sathyaprakash School of Physics and Astronomy
 Gravity s Standard Sirens B.S. Sathyaprakash School of Physics and Astronomy What this talk is about Introduction to Gravitational Waves What are gravitational waves Gravitational wave detectors: Current
Gravity s Standard Sirens B.S. Sathyaprakash School of Physics and Astronomy What this talk is about Introduction to Gravitational Waves What are gravitational waves Gravitational wave detectors: Current
How to listen to the Universe?
 How to listen to the Universe? Optimising future GW observatories for astrophysical sources Stefan Hild NIKHEF, May 2009 Overview Microphones to detect gravitational waves Why haven t we heard GW so far?
How to listen to the Universe? Optimising future GW observatories for astrophysical sources Stefan Hild NIKHEF, May 2009 Overview Microphones to detect gravitational waves Why haven t we heard GW so far?
Frequency dependent squeezing for quantum noise reduction in second generation Gravitational Wave detectors. Eleonora Capocasa
 Frequency dependent squeezing for quantum noise reduction in second generation Gravitational Wave detectors Eleonora Capocasa 10 novembre 2016 My thesis work is dived into two parts: Participation in the
Frequency dependent squeezing for quantum noise reduction in second generation Gravitational Wave detectors Eleonora Capocasa 10 novembre 2016 My thesis work is dived into two parts: Participation in the
