The diagram shows a lens, the position of an object and the position of the image of the object.
|
|
|
- Oswald Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES PART II Q1. The diagram shows a lens, the position of an object and the position of the image of the object. What type of lens is shown? What is the name of the points, F, shown each side of the lens? (c) The image is real and can be put on a screen. How can you tell from the diagram that the image is real? Draw a ring around a word in the box which describes the image produced by the lens. inverted larger upright (d) A student investigates the relationship between the distance from the object to the lens and the magnification produced by the lens. The student s results are given in the table. The student did not repeat any measurements. Distance in millimetres Height of object in millimetres Height of image in millimetres Magnification produced
2 The student plots the points for a graph of magnification produced against distance. Draw a line of best fit for these points. Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct word in the box. A line graph has been drawn because both variables are categoric. described as being continuous. discrete. (iii) Describe the relationship between magnification produced and distance.
3 (Total 8 marks) Q2. At night, it is important that the lights of a car can be seen by other drivers but it is dangerous if these lights dazzle them. The diagram shows a rear light of a car. Name part A. Name the process which occurs at point B and at point C. A headlamp of a car contains a lens. The ray diagram shows the position and size of the image, I, of an object, O, formed by a lens similar to the one inside a car headlamp.
4 What type of lens is shown in the ray diagram? Draw a ring around your answer. converging diverging plane The ray diagram is drawn to scale. Use the equation in the box to calculate the magnification produced by the lens. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Magnification = (Total 5 marks) Q3. Glass reflects, absorbs and transmits both infra red radiation and visible light. /The diagram shows the percentages of visible light that are reflected and absorbed by one type of glass.
5 What percentage of visible light is transmitted by this type of glass? % The amounts of infra red radiation and visible light transmitted by glass depend on the type and thickness of glass. The data obtained from tests on two different types of glass is displayed in the graph below. To be able to compare the two types of glass, it was important to control one variable. What variable was controlled in the tests? A homeowner has a glass conservatory built on the back of the house. The
6 homeowner tells the builder that the inside of the conservatory should stay as cool as possible throughout the summer. Explain why the builder uses type B glass for the conservatory. (Total 4 marks) Q4. Electromagnetic waves have many uses. The diagram shows two ways of sending information using electromagnetic waves. What type of wave is used to send information to and from satellites? What property of this type of wave makes it suitable for satellite communications? Different frequency radio waves travel different distances through the atmosphere before being reflected.
7 Use the information in the diagram to describe the connection between the frequency of a radio wave and the distance the radio wave travels through the atmosphere before it is reflected. (c) Electromagnetic waves travel at a speed of m/s. A radio station transmits waves with a wavelength of 20 metres. Calculate the frequency, in kilohertz (khz), of these waves. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Frequency = khz (Total 5 marks) Q5. The table gives information about the frequencies in the hearing ranges of six different mammals. Name of mammal Frequencies in hearing range Bat 20 Hz 160 khz Dog 20 Hz 30 khz
8 Dolphin Elephant Human Tiger 40 Hz 110 khz 5 Hz 10 khz 20 Hz 20 khz 30 Hz 50 khz Which mammal in the table can hear the highest frequency? Which mammal in the table, apart from humans, cannot hear ultrasound? (iii) Give one example of a frequency which an elephant can hear but which a tiger cannot hear. Include the unit in your answer. Frequency The diagrams show six sound waves, A, B, C, D, E and F, represented on an oscilloscope screen. They are all drawn to the same scale. Which one of the waves has the greatest amplitude?
9 Wave Which one of the waves has the highest frequency? Wave (Total 5 marks) Q6. A student investigates how the magnification of an object changes at different distances from a converging lens. The diagram shows an object at distance d from a converging lens. The height of the object and the height of its image are drawn to scale. Use the equation in the box to calculate the magnification produced by the lens shown in the diagram. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Magnification = The points F are at equal distances on either side of the centre of the lens. State the name of these points. (iii) Explain how you can tell, from the diagram, that the image is virtual.
10 The student now uses a different converging lens. He places the object between the lens and point F on the left. The table shows the set of results that he gets for the distance d and for the magnification produced. Distance d measured in cm Magnification His friend looks at the table and observes that when the distance doubles from 10 cm to 20 cm, the magnification doubles from 1.5 to 3.0. His friend s conclusion is that: The magnification is directly proportional to the distance of the object from the lens. His friend s observation is correct but his friend s conclusion is not correct. Explain, with an example, why his friend s conclusion is not correct. Write a correct conclusion. (iii) The maximum range of measurements for d is from the centre of the lens to F on the left. The student cannot make a correct conclusion outside this range. Explain why.
11 (Total 8 marks) Q7. The diagram shows the seven types of wave that make up the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays X-rays Ultraviolet rays Visible light Infra red rays Microwaves Radio waves Microwaves and visible light can be used for communications. Name one more type of electromagnetic wave that can be used for communications. Name one type of electromagnetic wave that has a longer wavelength than microwaves. Wi-Fi is a system that joins a laptop computer to the internet without using wires. A 2400 megahertz microwave signal is used to link a computer to a device called a router. What quantity is measured in hertz? Draw a ring around your answer. frequency wavelength wave speed (c) A politician commented on the increasing use of Wi-Fi. He said: I believe that these systems may be harmful to children. Suggest one reason why more scientific research into the safety of Wi-Fi systems is needed. Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct line in the box. a fact. What the politician said was an opinion.
12 a prediction. (Total 5 marks) Q8. Microwaves and visible light are two types of electromagnetic wave. Both can be used for communications. Give two properties that are common to both visible light and microwaves Name two more types of electromagnetic wave that can be used for communications. and Wi-Fi is a system that joins computers to the internet without using wires. Microwaves, with a wavelength of 12.5 cm, are used to link a computer to a device called a router. Microwaves travel through the air at m/s. Calculate the frequency of the microwaves used to link the computer to the router. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Frequency = (3) (c) Wi-Fi is used widely in schools. However, not everyone thinks that this is a good idea. A politician commented on the increasing use of WiFi. He said: I believe that these systems may be harmful to children. However, one group of scientists said that there is no reason why Wi-Fi should not be used in schools. These scientists also suggested that there is a need for further research. Suggest what the politician could have done to persuade people that what he said was not just an opinion.
13 Why did the group of scientists suggest that there is a need for further research? (Total 8 marks) Q9. A student investigated how the nature of the image depends on the position of the object in front of a large converging lens. The diagram shows one position for the object. Use a ruler to complete a ray diagram to show how the image of the object is formed. (4) Describe the nature of this image relative to the object.
14 (Total 6 marks) Q10. The table shows the electromagnetic spectrum. Three types of wave have been missed out. Use words from the box to complete the table. infra red rays radio waves X-rays Which one of the following gives a use of gamma rays? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to your choice. to communicate with satellites to see objects to kill cancer cells (iii) Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct word in the box. energy All electromagnetic waves move gases from one place to another. particles (Total 4 marks) Q11. The picture shows a speed gun being used to measure how fast a tennis player hits the ball.
15 Some of the microwaves from the speed gun are absorbed by the ball and some are reflected by the ball. Complete the following sentence by choosing one of the phrases from the box. longer than the same as shorter than The wavelength of the microwaves reflected from the ball are the wavelength of the microwaves from the speed gun. Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct line in the box. decrease slightly When the ball absorbs microwaves, its temperature will not change increase slightly The microwaves reflected from the ball have a higher frequency than the microwaves from the speed gun. The graph shows how the difference between the two frequencies depends on the speed of the ball.
16 Describe the pattern that links the difference between the two frequencies and the speed of the ball. The speed gun measures the difference between the two frequencies as 3200 Hz. Use the graph to find the speed of the tennis ball. Show clearly on the graph how you obtain your answer. Speed of the tennis ball = m/s (iii) Which one of the following gives the reason why the data has been shown as a line graph and not as a bar chart? Put a tick ( ) in the box next to your choice. Frequency and speed are both categoric variables. Frequency and speed are both continuous variables. Speed is a continuous variable and frequency is a categoric variable. (Total 6 marks) Q12. Microwaves are one type of electromagnetic wave. Which type of electromagnetic wave has a lower frequency than microwaves? What do all types of electromagnetic wave transfer from one place to another? The picture shows a tennis coach using a speed gun to measure how fast the player serves the ball.
17 The microwaves transmitted by the speed gun have a frequency of Hz and travel through the air at m/s. Calculate the wavelength of the microwaves emitted from the speed gun. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Wavelength = m Some of the microwaves transmitted by the speed gun are absorbed by the ball. What effect will the absorbed microwaves have on the ball? (Total 5 marks) Q13. A microphone and a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) can be used to show the pattern of a sound wave. Four sound wave patterns, A, B, C and D, are shown. They are all drawn to the same scale. Which one of the patterns has the smallest amplitude? Which one of the patterns has the lowest frequency?
18 (Total 2 marks) Q14. A puppy can see an image of himself in a plane mirror. The diagram shows how the puppy can see his disc. On the diagram, use a ruler to draw a ray to show how the puppy can see the top of his ear, which is marked as T. What is a plane mirror? (3) (Total 4 marks) Q15. Some scientists think that there is a link between using a mobile phone and some types of illness. Other scientists disagree. They say that the evidence is limited and unreliable. Suggest what scientists could do to show a link between using a mobile phone and illness.
19 How could scientists improve the reliability of the evidence? (iii) Complete the following passage by drawing a ring around the word in the box that is correct. There has been little or no experimental research into the health of children who use mobile phones. economic This is partly because of the environmental ethical issues involved in using children in scientific research. Before being sold, new mobile phones must be tested and given a SAR value. The SAR value is a measure of the energy absorbed by the head while a mobile phone is being used. The table gives the SAR value for three mobile phones made by different companies. To be sold in the UK, a mobile phone must have a SAR value lower than 2.0 W/kg. Mobile phone SAR value in W/kg J 0.18 K 0.86 L 1.40 All companies use the same test to measure a SAR value. Why is using the same test important? Would the companies that make the mobile phones, J, K and L, be correct to claim that these three phones are totally safe to use? Answer yes or no. Give a reason for your answer.
20 (c) Devices designed to protect a mobile phone user from microwave radiation are now available. Why is it important that these devices are tested by scientists who are not working for the company that makes the devices? (Total 6 marks) Q16. In the diagram below, a frog sits on a rock in a pond. Complete the following sentences by drawing a ring around the correct line in the box. The frog can see its image in the pond because the surface of the pond acts like a concave convex plane mirror. Draw a ring around each of two words from the box below to describe the image in the pond. bigger inverted real smaller upright virtual There is an insect underneath the rock. Use a ruler to draw rays of light on the diagram to show how the frog uses reflection to see the insect. Mark the direction of the rays.
21 (3) (Total 6 marks) Q17. A student uses a ray box and a semicircular glass block to investigate refraction. What is the vertical dashed line called? Which angle, v, w, x, y or z, is the angle of refraction? (c) Why has refraction taken place?
22 (d) In an investigation, a student always aims the light from the ray box at point P. She moves the ray box to give different values of angle v. She records angle y for each of these values. The table shows her results. Angle v measured in degrees Angle y measured in degrees The student studies the data and comes to the following conclusion. Angle y is directly proportional to angle v. Her friend says that this conclusion is not correct. Use data from the table to explain why the conclusion is not correct. Write a correct conclusion for the experiment. (iii) Why is your conclusion only valid when angle v is between 30 and 80? (Total 7 marks) Q18. Infra red radiation can be reflected, absorbed and transmitted by glass.
23 What percentage of infra red is absorbed by the glass? Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct word or phrase. Theabsorbed infra red increases does not change decreases the temperature of the glass. Two of the following statements are true. One of the statements is false. Tick ( ) the boxes next to the two true statements. All objectsabsorb infra red radiation. Blacksurfaces are poor emitters of infra red radiation. A hot objectemits more infra red than a cooler object. (c) The following statement is false. Blacksurfaces are good reflectors of infra red radiation. Change one word in this statement to make it true. Write down your new statement. (Total 4 marks) Q19.
24 The wavelengths of four different types of electromagnetic wave, including visible light waves, are given in the table. Type of wave Visible light A B C Wavelength mm 1.1 km 100 mm 0.18 mm Which of the waves, A, B or C, is an infra red wave? A TV station broadcasts at khz. The waves travel through the air at m/s. Calculate the wavelength of the waves broadcast by this station. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Wavelength = m (c) What happens when a metal aerial absorbs radio waves? (d) Stars emit all types of electromagnetic waves. Telescopes that monitor X-rays are mounted on satellites in space. Why would an X-ray telescope based on Earth not be able to detect X-rays emitted from distant stars? (Total 6 marks) Q20. The ray diagram shows the position and size of the image, I, of an object, O, formed by a lens, L.
25 What type of lens is shown in the ray diagram? Name the point labelled P. (c) The ray diagram has been drawn to scale. Use the equation to calculate the magnification. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Magnification = (d) How can you tell from this ray diagram that the image is a real image? (Total 5 marks) Q21. A student investigated the refraction of light as it passes out of a transparent plastic block. She aimed a ray of light at point X. She marked the position of the ray as it passed through the transparent plastic block and into the air.
26 The angle i is the angle of incidence. What is the name of angle r? What is the name of the dashed line? A camera uses a lens to produce an image which falls on a light detector. Name a light detecting device which may be used in a camera. (c) The diagram shows the position of an image formed in a camera.
27 What type of lens is shown in the diagram? Use the equation in the box to calculate the magnification. magnification = Show clearly how you work out your answer. Magnification = (d) Why does the image formed in a camera have to be a real image? (Total 7 marks) Q22. The diagram shows a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum divided into seven sections. The different properties of the waves in each section make them useful in different ways.
28 The waves in which section, A, B, C, D, E, F or G, are: used to send a signal to a satellite in space used to communicate with a submarine under the water (c) used by a radio station to broadcast programmes around the world (d) the waves with the shortest wavelength? (Total 4 marks) Q23. Mobile phones send digital signals using electromagnetic waves. Which one of the following types of electromagnetic wave is used to carry information between masts in a mobile phone network? Draw a ring around your answer. light microwave radio Some people worry that using a mobile phone may be bad for their health. Look at this information taken from a recent newspaper article.
29 Scientists in Sweden found that the regular use of a mobile phone increases the risk of a cancerous growth between the ear and the brain. Some people who use mobile phones for a long time complain of headaches and tiredness. The same effect has not been noticed in laboratory tests. There is no reliable evidence to link using mobile phones with ill health. The waves from a mobile phone are not strong enough to cause long-term heat damage to cells in the body. Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the word in the box that is correct. The evidence from different scientists doing the same investigation is reliable if different all the scientists get identical random results. What information in the article supports the idea that mobile phones are bad for your health? (iii) Some scientists say that using a mobile phone is totally safe. What information in the article supports this view? (Total 6 marks) Q24. The diagram represents part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
30 Visible light travels through air at m/s. Why can we assume that radio waves travel through air at the same speed as light? A radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 200 khz. Calculate the wavelength of the waves broadcast by this radio station. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Wavelength = m (iii) Draw a vertical line on the diagram above to show the position of this radio wave in the electromagnetic spectrum. (Total 4 marks) Q25. Satellites fitted with various telescopes orbit the Earth. These telescopes detect different types of electromagnetic radiation. Why are telescopes that detect different types of electromagnetic waves used to observe the Universe? In 2005 a space telescope detected a star that exploded 13 billion years ago. The light from the star shows the biggest red-shift ever measured. What is red-shift? What does the measurement of its red-shift tell scientists about this star?
31 (c) Red-shift provides evidence for the big bang theory. Describe the big bang theory. Suggest what scientists should do if new evidence were found that did not support the big bang theory. (Total 6 marks) Q26. The new Tetra communications system to be used by the police transmits signals using microwaves of wavelength 75 cm. Calculate the frequency of the microwaves used by the Tetra system. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Frequency = hertz Read the following extract from a newspaper and then answer the questions that follow. Residents ofstag Hill Court, a luxuryblock of flats, are shocked at the plans to site a mobile phone mast on theroof of the flats. They oppose the mast on health grounds, quoting researchin Germany that has found apossible increase in cases of cancer around mobile phone masts. Aspokesperson for the telecoms company said, The residents should not worry.the research carried out by our own scientists has found no link between illhealth and mobile phone masts. This has notreassured the residents, who argue that new independent research is urgentlyneeded.
32 Explain why living near a mobile phone mast could cause ill health. (3) Suggest two reasons why the residents have not been reassured by the research carried out by the telecoms company (Total 7 marks) Q27. The diagram shows four oscilloscope wave traces. The controls of the oscilloscope were the same for each wave trace.
33 Which one of the waves traces, A, B, C or D, has: the largest amplitude, the lowest frequency? (Total 2 marks) Q28. The diagram shows how parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens. Mark the position of the focus. Is this a converging lens, a diverging lens, both or neither? The diagram shows how parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens. Mark the position of the focus. Is this a converging lens, a diverging lens, both or neither? (c) Complete these sentences by crossing out the two lines in each box that are wrong. In a camera, a lens is used to produce an image of an object on a.
34 The image is the object. The image is object from the lens. the lens, compared to the distance of the (4) (d) In a cinema projector, a convex lens is used to produce a magnified, real image. What does magnified mean? What is a real image? (e) You are in a dark room. You have a box containing some lenses. Only one of them is a converging lens. Describe how, by just feeling the lenses, you can pick out the converging lens. (Total 12 marks) Q29.
35 The drawing shows someone ironing a shirt. The top of the ironing board is covered in a shiny silver-coloured material. Explain why the shiny silver-coloured material helps to make ironing easier. (Total 2 marks) Q30. The diagram shows a lens used as a magnifying glass. The position of the eye is shown and the size and position of an object standing at point O. What type of lens is shown in the diagram? Two points are marked as F. What are these points? (iii) What is the name of the straight line which goes through the point F, through the point L at the centre of the lens, and through the point F on the other side? (iv) On the diagram, use a ruler to construct accurately the position of the image. You should show how you construct your ray diagram and how light appears to come from this image to enter the eye.
36 (5) (v) The image is virtual. What is a virtual image? The lens shown in the diagram in part (iv) can be used in a camera to produce a real image. Explain why a real image must be produced in a camera and how the object and the lens are positioned to produce a real image which is smaller than the object. Do not draw a ray diagram as part of your answer. (3) (Total 12 marks) Q31. The picture shows a horse being prepared for an X-ray.
37 The person who will take the X-ray and the person holding the horse are wearing special aprons. These aprons have a lead lining. Explain why the lead lining is important. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. (Total 3 marks) Q32. The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be used to describe this type of lens?
38 The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Which point A, B, C, D or E shows the focal point for this diagram? Point Explain your answer to part. (iii) What word can be used to describe this type of lens? (c) Complete the following three sentences by crossing out the two lines in each box which are wrong film In a camera a converging lens is used to produce an image on a lens screen The image is larger than smaller than the same size as the object. Compared to the distance of the image from the lens, the object is further away from nearer to the lens. the same distance from (3) (d) Explain the difference between a real image and a virtual image.
39 (3) (Total 13 marks) Q33. The diagram shows a wave pattern. Which letter, L, M or N shows: the wavelength? the amplitude? (c) Describe how you could show that visible light travels in straight lines. You may wish to draw a diagram to help explain your answer.
40 (Total 4 marks) Q34. All radio waves travel at m/s in air. Give the equation that links the frequency, speed and wavelength of a wave. Calculate the wavelength, in metres, of a radio wave which is broadcast at a frequency of 909 khz. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Wavelength = metres (Total 3 marks) Q35. The diagram represents the electromagnetic spectrum. Four of the waves have not been named. Draw lines to join each of the waves to its correct position in the electromagnetic spectrum. One has been done for you. Complete the following sentence by choosing the correct answer and crossing out in the box the two lines which are wrong. The speed of radio waves through a vacuum is the speed of light through a vacuum.
41 (c) The diagram shows an X-ray photograph of a broken leg. Bones show up white on the photographic film. Explain why. (Total 5 marks) Q36. A swimming pool has a wave making machine. The diagram shows the water wave pattern for 3 seconds. How many water waves are shown in the diagram? What is the frequency of the water waves? (iii) Which one of the units below is used to measure frequency? Underline your answer. hertz joule watt The diagram shows the direction of the waves across the pool. The waves reflect off the side of the pool.
42 Draw a line on the diagram to show the direction of the waves after they hit the side of the pool. (c) The swimming pool is used to test a model of an electricity generator. The waves make the floating generator move up and down. This energy is transferred to electricity. In the following sentence, cross out the two lines that are wrong in the box. The diagram shoes that the amplitude of the waves waves pass the generator. as the What type of energy does the generator transfer to electricity? (iii) Energy from ocean waves could be used to generate electricity. Would this be a renewable or non-renewable energy resource? (Total 7 marks) Q37. Microwaves are used to transmit signals to the satellite. The microwaves have a wavelength of 0.6 metres (m) and travel through space at a speed of metres per second (m/s). Write down the equation which links frequency, wavelength and wave speed. Calculate the frequency of the microwaves. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Frequency = (3) (Total 4 marks)
43 Q38. The vibration caused by a P wave travelling at 7.6 km/s has been recorded on a seismic chart. How many waves are produced in one second? Write down the equation which links frequency, wavelength and wave speed. (iii) Calculate the wavelength of the P wave. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Wavelength = (Total 4 marks) Q39. After a person is injured a doctor will sometimes ask for a photograph to be taken of the patient s bone structure, e.g. in the case of a suspected broken arm. Which type of electromagnetic radiation would be used to take the photograph? Describe the properties of this radiation which enable it to be used to photograph bone structure.
44 (Total 3 marks) Q40. The diagrams below show rays of light striking a mirror and a perspex block. Complete the paths of the three rays of light on the diagrams to show the rays leaving the mirror and the perspex block. (4) The diagram below shows a beam of light striking a perspex block. (iii) Continue the paths of the rays AB and CD inside the perspex block. Draw the wavefronts of the beam of light in the perspex. Explain why the beam behaves in the way you have shown. (7) (c) The diagram below shows a ray of light striking a perspex-air surface from inside the perspex. The critical angle is 45º.
45 Draw the path of the ray after it reaches the perspex-air boundary. (Total 13 marks) Q41. The diagram shows the image IC formed by a lens, of an object OB a long way from it. The points F mark the focal points of the lens. Describe, either by writing below or drawing on the diagram, how the size and position of the image changes: when the object OB is moved towards the focal point F. when the object OB is moved past F to a point nearer the lens than the focal point. (4) Explain how a converging lens in a camera is used to produce sharp images on the film when the object is a long distance away from the camera, and when it is close to the camera.
46 (3) (Total 7 marks) Q42. The diagrams show rays of light. Each ray strikes a surface of a glass block. On the diagram draw the path of each ray through the glass block and out into the air again. Label another angle on the diagram which is equal to the angle marked X. Label this angle Y. (4) The diagrams show two beakers. Both beakers have a drawing pin inside as shown. The first beaker is empty. The eye cannot see the drawing pin. The second beaker is full of water and the eye can see the drawing pin. Explain how the eye is able to see the drawing pin in the second beaker. You may add to the diagram if it helps your answer. (3) (Total 7 marks) Q43.
47 Lenses are used in many optical devices. Complete the table below about the images formed by some optical devices. OPTICAL DEVICE NATURE OF IMAGE SIZE OF IMAGE POSITION OF IMAGE Eye real Projector Magnified camera Closer to lens than the object (Total 6 marks) Q44. Radio waves, ultra-violet, visible light and X-rays are all types of electromagnetic radiation. Choose wavelengths from the list below to complete the table m m m 1500 m TYPE OF RADIATION WAVELENGTH (m) Radio waves Ultra-violet Visible light X-rays (4) Microwaves are another type of electromagnetic radiation. Calculate the frequency of microwaves of wavelength 3 cm. (The velocity of electromagnetic waves is m/s.) (4) (Total 8 marks) Q45. An aquarium contains only one fish. But if you look at the comer of the aquarium, there seem to be two fish.
48 The diagram below shows the top of the aquarium. Two light waves have been drawn from the fish. Complete the diagram to show how the light waves reach the eye. Complete each sentence by using the correct words from the box. colour diffraction longitudinal reflection refraction speed transverse When the light waves pass from glass into the air they change This causes a change in direction called Light waves are waves. (3) (Total 5 marks) Q46. The diagram shows a wave travelling along a rope.
49 On the diagram: show the wavelength and label it W; show the amplitude and label it A. The wavelength of the wave is 0. I m. Its frequency is 2 Hz. Calculate the speed of the wave. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. Speed of wave (3) (Total 5 marks) Q47. The diagram shows how ultrasonic waves can be used to clean a watch. Suggest how this method cleans the watch.
50 (Total 2 marks) Q48. Glass prisms are used in many optical devices. The diagram shows what happens to a ray of light as it travels through a glass prism. To gain full marks for this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and use the correct scientific words. Use the words in the box to help you to explain why the ray behaves in this way. angle critical normal (3) Periscopes can be used to look over the heads of other people. A periscope contains two glass prisms. Complete the diagram to show the ray of light reaching the person s eye.
51 (3) (Total 6 marks) Q49. Microwave ovens can be used to heat many types of food. Describe, in as much detail as you can, how microwaves heat food. Microwaves have a frequency of million Hz. Their wavelength is 0.03 m. Calculate the speed of microwaves. Show clearly how you work out your answer.
52 Speed of microwaves m/s (Total 4 marks) Q50. The diagram shows oscilloscope traces of four waves, A, B, C and D. All four waves are drawn to the same scale. Which wave has: (c) the longest wavelength; the greatest amplitude; the highest frequency? (Total 3 marks) Q51. The diagram shows two mirrors at right angles to each other. A ray of light shines onto one mirror as shown. Carefully draw the path of the ray which is reflected from both mirrors. Draw an arrow on the ray to show the direction of the light.
53 (3) Light can also be made to change direction as it passes into and out from a block of glass. Complete the ray diagram below. (Total 5 marks) Q52. Some students made a small hand-turned a.c. generator, similar to a bicycle dynamo. They connected it to the Y plates of a cathode ray oscilloscope, CRO, and turned the generator slowly. The trace on the CRO looked like this: They then turned the generator faster and the trace looked like this:
54 Why did the trace on the CRO show: an increase in frequency; a decrease in wavelength; (iii) an increase in amplitude? One way to alter the output from the generator is to change the speed of turning. State two other ways to adapt parts of the generator to increase its output. (Total 5 marks) Q53. On the wave drawn below, mark the amplitude and wavelength. A wave is said to have a frequency of 25 Hz. Explain what the term frequency means. (c) From the electromagnetic spectrum, give the name and use of a radiation of lower frequency than light. Name Use _
55 (Total 5 marks) Q54. The diagram shows a glass prism. Explain why refraction has not occurred at point X. (A) Give the full name for the process which has occurred at point Y. (B) Explain why this process has occurred. (Total 4 marks) Q55. Use the words frequency, wavelength and wave speed to write an equation which shows the relationship between them. Calculate the speed of a sound wave with a frequency of 250 Hz and a wavelength of 1.3 m. Show how you get to your answer and give the unit.
56 Speed = (Total 3 marks) Q56. The diagrams show how the same two lenses can be used to make a microscope or a telescope. The microscope and the telescope made from the two lenses are similar in some ways but different in others. Complete the table to show these similarities and differences.
57 (Total 7 marks) Q57. Explain fully why pregnant women should not normally have X-rays of the lower body. (Total 4 marks) Q58. The diagram below shows the range of wavelengths and frequencies for all the types of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum. X rays, which have frequencies in the range Hz are already marked on the diagram.
58 Complete the diagram by adding the following: (c) (d) (e) gamma radiation, which has shorter wavelengths than X rays; radio waves which have wavelengths longer than 0.1m; the visible spectrum which has wavelengths from 400 nm (violet) to 700 nm (red); ultraviolet radiation (i.e. radiation with a higher frequency than violet light); microwaves which have a shorter wavelength than radio waves and infrared radiation which has a higher frequency than microwaves; (f) an FM radio programme on 92MHz. (Show this with an arrow ) (Total 7 marks) Q59. A man is walking along the bank of a river. He sees a fish which seems to be at X. Show, on the diagram, where the fish really is. Complete the ray of light which goes from the fish into the man s eye. Complete the sentence. The ray of light is as it passes from the water into the air. (Total 3 marks) Q60. The diagram shows the oscilloscope traces of two different sounds P and Q. The oscilloscope setting is exactly the same in both cases.
59 P and Q sound different. Write down two differences in the way they sound. Explain your answers as fully as you can (Total 5 marks)
60
National 3 Waves and Radiation
 What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
0.4 s 0.8 s 1.5 s. 2.5 s. 2. A beam of light from a ray box spreads out as shown in the diagram and strikes a plane mirror.
 1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Waves Atoms & Space
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Waves Atoms & Space Moulsham High School 1 1. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown below. gamma rays X-rays A visible light infra-red
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Waves Atoms & Space Moulsham High School 1 1. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown below. gamma rays X-rays A visible light infra-red
Q1. A person uses a stairlift to go upstairs. The stairlift is powered by an electric motor.
 Q. A person uses a stairlift to go upstairs. The stairlift is powered by an electric mot. The Sankey diagram shows the energy transfers f the electric mot. (a) Complete the following sentence. The electric
Q. A person uses a stairlift to go upstairs. The stairlift is powered by an electric mot. The Sankey diagram shows the energy transfers f the electric mot. (a) Complete the following sentence. The electric
Name Class Date. What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How can electromagnetic waves be used?
 CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
PHY1H (JUN09PHY1H01) General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June Unit Physics P1. PHYSICS Unit Physics P1. Higher Tier
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2009 SCIENCE B Unit Physics P1 PHYSICS Unit Physics P1 PHY1H H
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2009 SCIENCE B Unit Physics P1 PHYSICS Unit Physics P1 PHY1H H
Name Date Class _. Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light.
 Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
WAVES AND RADIATION. 1 Measuring the focal length of a lens. Topic 7 Physics. The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens.
 1 Measuring the focal length of a lens The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens. Which of these is the correct distance for the focal length? A from the window to the lens B from the
1 Measuring the focal length of a lens The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens. Which of these is the correct distance for the focal length? A from the window to the lens B from the
Grade 10 First Term Examination (Revision) Physics. 1. A part of travel graph of John's journey from his house to the shops and back is shown below.
 Grade 10 First Term Examination (Revision) Physics SP1 & SP2: Motion & Forces 1. A part of travel graph of John's journey from his house to the shops and back is shown below. a) Find out John's speed for
Grade 10 First Term Examination (Revision) Physics SP1 & SP2: Motion & Forces 1. A part of travel graph of John's journey from his house to the shops and back is shown below. a) Find out John's speed for
The figure below shows an incomplete electromagnetic spectrum. A microwaves B C ultraviolet D gamma
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Q1. The figure below shows an incomplete electromagnetic spectrum. A microwaves B C ultraviolet D gamma (a) What name is given to the group of waves at the position labelled A in
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Q1. The figure below shows an incomplete electromagnetic spectrum. A microwaves B C ultraviolet D gamma (a) What name is given to the group of waves at the position labelled A in
Properties of Waves. Before You Read. What are the features of a wave?
 Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 9 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 9 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
Being a Physicist Unit 5. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES
 Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
Physics Unit Physics P1
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science B Unit Physics P1 Physics Unit Physics P1 Thursday 24 June 2010 General Certificate
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science B Unit Physics P1 Physics Unit Physics P1 Thursday 24 June 2010 General Certificate
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
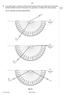 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
Figure 1 shows white light passing through a triangular glass prism. The white light splits up into different colours. Two of the colours are shown.
 Name Q9.Visible white light consists of several different colours. Figure 1 shows white light passing through a triangular glass prism. The white light splits up into different colours. Two of the colours
Name Q9.Visible white light consists of several different colours. Figure 1 shows white light passing through a triangular glass prism. The white light splits up into different colours. Two of the colours
Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. diffraction reflection refraction
 Q1. Light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. (a) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. diffraction reflection refraction The change of direction when light
Q1. Light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. (a) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. diffraction reflection refraction The change of direction when light
Physics Unit Physics P1b (Radiation and the Universe)
 Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier June 2010 Science A Unit Physics P1b (Radiation and the
Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier June 2010 Science A Unit Physics P1b (Radiation and the
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER
 SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
GOZO COLLEGE. Half Yearly Examinations for Secondary Schools FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min
 GOZO COLLEGE Track 3 Half Yearly Examinations for Secondary Schools 2011 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator is allowed.
GOZO COLLEGE Track 3 Half Yearly Examinations for Secondary Schools 2011 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator is allowed.
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light
 Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
Grade 8 Science: Unit 3-Optics Chapter 4: Properties of Light Key Terms: Microscope, telescope, amplitude, crest, energy, force, frequency, hertz, medium, transverse wave, trough, wave, wavelength, reflection,
3 Properties of Waves:
 3 Properties of Waves: Including Light and Sound 1. General wave properties 2. Light 3. Sound 1. Which of the following is an example of transverse and a longitudinal wave? 4. A boy stands beside a girl
3 Properties of Waves: Including Light and Sound 1. General wave properties 2. Light 3. Sound 1. Which of the following is an example of transverse and a longitudinal wave? 4. A boy stands beside a girl
Gr 10 Physics Worksheet paper 1. Sound and hearing
 Gr 10 Physics Worksheet paper 1 Sound and hearing 1 (a)which row of the table is correct for both infrasound radiation and infrared radiation? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. [1] (b) Describe
Gr 10 Physics Worksheet paper 1 Sound and hearing 1 (a)which row of the table is correct for both infrasound radiation and infrared radiation? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. [1] (b) Describe
Physics/Science *P41958A0120* Edexcel GCSE P41958A. Unit P1: Universal Physics. Foundation Tier. Thursday 7 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Thursday 7 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Thursday 7 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate Number
PHY1F (JAN08PHY1F01) General Certifi cate of Secondary Education January Unit Physics P1. PHYSICS Unit Physics P1.
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education January 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Physics P1 PHYSICS Unit Physics P1 PHY1F
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education January 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Physics P1 PHYSICS Unit Physics P1 PHY1F
Being a Chemist. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Chemist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 State that the light year is a measure of astronomical distance State the speed at which light travels Give examples of the relative distance between
Being a Chemist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 State that the light year is a measure of astronomical distance State the speed at which light travels Give examples of the relative distance between
the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing;
 Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
) in the box next to your answer. (1) (b) Explain why it is difficult to predict when an earthquake will happen. (2)
 Earthquakes 1 (a) Seismic (earthquake) waves can be either P-waves or S-waves. Which row of the table is correct for P-waves? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) type of wave can they be
Earthquakes 1 (a) Seismic (earthquake) waves can be either P-waves or S-waves. Which row of the table is correct for P-waves? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) type of wave can they be
Introduction to Properties of Waves
 Introduction to Properties of Waves Waves travel through materials as vibrations and transmit energy. Though nearly all waves travel through matter, they never transmit matter. Waves are created when a
Introduction to Properties of Waves Waves travel through materials as vibrations and transmit energy. Though nearly all waves travel through matter, they never transmit matter. Waves are created when a
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4. Properties of Light
 Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 Properties of Light There are many types of light sources... Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion The Nature of Light Pythagoras A Greek
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 Properties of Light There are many types of light sources... Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion The Nature of Light Pythagoras A Greek
Revision checklist SP4 5. SP4 Waves. SP4a Describing waves. SP4b Wave speeds. SP4c Refraction
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
Fluorescence. Incandescence. Electric. Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence. Combustion
 Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion Pythagoras A Greek philosopher Believed light was beams of tiny particles The eyes could detect these particles and see
Fluorescence Incandescence Electric Bioluminescence Chemiluminescence Combustion Pythagoras A Greek philosopher Believed light was beams of tiny particles The eyes could detect these particles and see
AMERICAN NATIONAL SCHOOL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 AMERICAN NATIONAL SCHOOL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level PHYSICS 5054/02 Paper 2 Theory December 2009 Class Senior 2 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
AMERICAN NATIONAL SCHOOL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level PHYSICS 5054/02 Paper 2 Theory December 2009 Class Senior 2 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014. SUBJECT: PHYSICS Form 4 TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN
 KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 SUBJECT: PHYSICS Form 4 TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN NAME : CLASS : INDEX NO : Track 2 Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the
KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 SUBJECT: PHYSICS Form 4 TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN NAME : CLASS : INDEX NO : Track 2 Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the
Year 9- Physics First Term Revision
 Year 9- Physics First Term Revision All objects EMIT and ABSORB infrared radiation The hotter the obect, the more infrared radiation it emits (gives off) Dark/Matte surfaces are good absorbers of infrared
Year 9- Physics First Term Revision All objects EMIT and ABSORB infrared radiation The hotter the obect, the more infrared radiation it emits (gives off) Dark/Matte surfaces are good absorbers of infrared
P5 Revision Questions
 P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2010/2011
 KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2010/2011 SUBJECT: PHYSICS NAME : FORM : TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN INDEX NO : MARK: Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the Exam Paper.
KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2010/2011 SUBJECT: PHYSICS NAME : FORM : TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN INDEX NO : MARK: Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the Exam Paper.
Physics. Waves and Radiation. Homework Exercises. National 4 / 5
 Physics National 4 / 5 Waves and Radiation Summary Homework 1: Homework 2: Homework 3: Homework 4: Waves I -Wave definitions - Speed, distance, time calculations - Types of wave Waves II - Frequency calculations
Physics National 4 / 5 Waves and Radiation Summary Homework 1: Homework 2: Homework 3: Homework 4: Waves I -Wave definitions - Speed, distance, time calculations - Types of wave Waves II - Frequency calculations
High frequency photons have more energy than low frequency photons. Microwave radiation has the lowest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum.
 4 (a) Some of the statements below are true, and some are false. Put a tick ( ) in the correct box after each statement. High frequency photons have more energy than low frequency photons. Microwave radiation
4 (a) Some of the statements below are true, and some are false. Put a tick ( ) in the correct box after each statement. High frequency photons have more energy than low frequency photons. Microwave radiation
2. Light & Electromagne3c Spectrum
 2. Light & Electromagne3c Spectrum 2. Light/Electromagne3c Spectrum (10 lessons) EM spectrum (2 lessons) Essay (2 lessons) Light Basics (1 lesson) Reflec3on in Plane mirrors (2 lessons) Refrac3on (3 lessons)
2. Light & Electromagne3c Spectrum 2. Light/Electromagne3c Spectrum (10 lessons) EM spectrum (2 lessons) Essay (2 lessons) Light Basics (1 lesson) Reflec3on in Plane mirrors (2 lessons) Refrac3on (3 lessons)
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Friday 2 March 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Friday 2 March 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Candidate Number
Waves Junior Science. Easy to read Version
 Waves Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a Waves transfer energy Waves are a means of transferring energy from one place to another without also transferring matter. Some waves need a medium (matter)
Waves Junior Science Easy to read Version 1a Waves transfer energy Waves are a means of transferring energy from one place to another without also transferring matter. Some waves need a medium (matter)
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it! Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
LIGHT. A beam is made up of several rays. It maybe parallel, diverging (spreading out) or converging (getting narrower). Parallel Diverging Converging
 LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
PHY3F. (Jan11PHY3F01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January Unit Physics P3. Written Paper TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physics General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2011 PHY3F Question
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physics General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier January 2011 PHY3F Question
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/1F London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 1F Foundation Tier Monday 31 October 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Examiner
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/1F London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 1F Foundation Tier Monday 31 October 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Examiner
Motion. 1. Explain the difference between a scalar and vector quantity, including one example of each in your explanation.
 Motion 1. Explain the difference between a scalar and vector quantity, including one example of each in your explanation. 2 Figure below shows graphs of velocity v against time t for two cars A and B travelling
Motion 1. Explain the difference between a scalar and vector quantity, including one example of each in your explanation. 2 Figure below shows graphs of velocity v against time t for two cars A and B travelling
Republic of Somaliland. Somaliland National Examination Board. Form Four. Physics Examination. June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS
 Name..... Total Score School... Roll No... Republic of Somaliland Form Four Physics Examination June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS Plus 10 minutes for reading through the paper Total time 2 Hours and 10 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS
Name..... Total Score School... Roll No... Republic of Somaliland Form Four Physics Examination June 2009 TIME 2 HOURS Plus 10 minutes for reading through the paper Total time 2 Hours and 10 Minutes INSTRUCTIONS
How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks)
 Q1. The diagram shows an atom. How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks) Page 1 of 53 Q2. The picture shows a man at work in a factory
Q1. The diagram shows an atom. How many protons are there in the nucleus of the atom?... What is the mass number of the atom?... (Total 2 marks) Page 1 of 53 Q2. The picture shows a man at work in a factory
Waves Problem Booklet
 Getting Started Success involves doing many different kinds of problems which help improve your knowledge and understanding of the ideas in the course and your ability to solve problems. In order to get
Getting Started Success involves doing many different kinds of problems which help improve your knowledge and understanding of the ideas in the course and your ability to solve problems. In order to get
Waves in air; fluids; solids
 Waves in air; fluids; solids Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Physics Exam Board AQA Topic 4.6 Waves Sub-Topic Waves in air; fluids; solids Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Question Paper
Waves in air; fluids; solids Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Physics Exam Board AQA Topic 4.6 Waves Sub-Topic Waves in air; fluids; solids Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Question Paper
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
Sri Lankan School Muscat
 Sri Lankan School Muscat Withdrawal Examination 2015/2016 Class : Subject : Paper : Duration: Year 11B/R Physics Name :... 1 2 Hours Q.No. Allocated 1 11 2 12 3 12 4 10 5 06 6 08 7 06 8 12 9 10 10 04 11
Sri Lankan School Muscat Withdrawal Examination 2015/2016 Class : Subject : Paper : Duration: Year 11B/R Physics Name :... 1 2 Hours Q.No. Allocated 1 11 2 12 3 12 4 10 5 06 6 08 7 06 8 12 9 10 10 04 11
P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating
 P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating Infrared Radiation What gives off infrared radiation? What is a vacuum? Surfaces & Radiation What surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation? What surfaces
P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating Infrared Radiation What gives off infrared radiation? What is a vacuum? Surfaces & Radiation What surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation? What surfaces
*GPH22* *28GPH2201* Science: Physics. Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] FRIDAY 24 JUNE, MORNING *GPH22* TIME 1 hour 45 minutes.
![*GPH22* *28GPH2201* Science: Physics. Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] FRIDAY 24 JUNE, MORNING *GPH22* TIME 1 hour 45 minutes. *GPH22* *28GPH2201* Science: Physics. Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] FRIDAY 24 JUNE, MORNING *GPH22* TIME 1 hour 45 minutes.](/thumbs/85/91929138.jpg) Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 Science: Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier *GPH22* [GPH22] *GPH22* FRIDAY 24 JUNE, MORNING TIME 1 hour 45 minutes. INSTRUCTIONS TO
Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 Science: Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier *GPH22* [GPH22] *GPH22* FRIDAY 24 JUNE, MORNING TIME 1 hour 45 minutes. INSTRUCTIONS TO
Physics: Waves, Sound/Light, Electromagnetic Waves, Magnetism, Mains Electricity and the National Grid
 6.7 Describe the method to measure the speed of sound in air and the speed of ripples on the water surface 7.5 Link the properties of EM waves to their practical application 7.6 Apply knowledge of reflection,
6.7 Describe the method to measure the speed of sound in air and the speed of ripples on the water surface 7.5 Link the properties of EM waves to their practical application 7.6 Apply knowledge of reflection,
Sunlight is a combination of light-waves of various frequencies. Some
 96 The Electromagnetic Spectrum r e a d i n g Sunlight is a combination of light-waves of various frequencies. Some of the frequencies can be seen and some cannot be seen by the human eye. The reading
96 The Electromagnetic Spectrum r e a d i n g Sunlight is a combination of light-waves of various frequencies. Some of the frequencies can be seen and some cannot be seen by the human eye. The reading
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
National 5. Waves and Radiation. Summary Notes. Name:
 National 5 Waves and Radiation Summary Notes Name: Wave Parameters and Behaviours Transverse Waves A water wave is a transverse wave. The direction of vibration is at right angles to the direction of wave
National 5 Waves and Radiation Summary Notes Name: Wave Parameters and Behaviours Transverse Waves A water wave is a transverse wave. The direction of vibration is at right angles to the direction of wave
wave speed (metre/second, m/s) = distance (metre, m) / time (second, s) v = x/t_ Universal physics
 Topic 1 Visible light and the Solar System 1.1 Describe how ideas about the structure of the Solar System have changed over time, including the change from the geocentric to the heliocentric models and
Topic 1 Visible light and the Solar System 1.1 Describe how ideas about the structure of the Solar System have changed over time, including the change from the geocentric to the heliocentric models and
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Foundation Tier Wednesday 5 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance
 Paper Reference(s) 5PH1F/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Foundation Tier Wednesday 5 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Paper Reference(s) 5PH1F/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Foundation Tier Wednesday 5 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Waves & Radiation exam questions
 National 5 Physics Waves & Radiation exam questions these questions have been collated from previous Standard Grade (Credit) and Intermediate 2 exams Thurso High School 1. A mountain climber carries a
National 5 Physics Waves & Radiation exam questions these questions have been collated from previous Standard Grade (Credit) and Intermediate 2 exams Thurso High School 1. A mountain climber carries a
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #2 Fall 2017 Version A I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. A blackbody emits all of its radiation
Year 10 End of Year Examination Revision Checklist
 St Olave s Physics Department Year 10 of Year Examination Revision Checklist The following checklists include all the topics that will be included in the Year 10 of Year exam. Students should use the tickboxes
St Olave s Physics Department Year 10 of Year Examination Revision Checklist The following checklists include all the topics that will be included in the Year 10 of Year exam. Students should use the tickboxes
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum
 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum 10 4 Hz 10 6 Hz 10 8 Hz 10 12 Hz 10 14 Hz 10 16 Hz 10 18 Hz 1 million 1 trillion
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM All waves travel the SAME speed (the speed of light) 300,000 km/sec (186,000 miles/sec) in a vacuum 10 4 Hz 10 6 Hz 10 8 Hz 10 12 Hz 10 14 Hz 10 16 Hz 10 18 Hz 1 million 1 trillion
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves. What is a wave?
 Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D.
 Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D. UV Rays Science Starter! 10.14-15.13! THE UNIVERSE AND ELECTROMAGNETIC
Which type of electromagnetic wave has a wavelength longer than that of yellow light? A. Infrared radiation C. X-rays B. Gamma Rays D. UV Rays Science Starter! 10.14-15.13! THE UNIVERSE AND ELECTROMAGNETIC
Pearson Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 24 May 2017 Afternoon Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 24 May 2017 Afternoon Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
School. Team Number. Optics
 School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6
 Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
*GPH22* *32GPH2201* GCSE Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] *GPH22* MONDAY 23 JUNE, MORNING. TIME 1 hour 45 minutes.
![*GPH22* *32GPH2201* GCSE Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] *GPH22* MONDAY 23 JUNE, MORNING. TIME 1 hour 45 minutes. *GPH22* *32GPH2201* GCSE Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] *GPH22* MONDAY 23 JUNE, MORNING. TIME 1 hour 45 minutes.](/thumbs/95/123344565.jpg) Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 GCSE Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] MONDAY 23 JUNE, MORNING *GPH22* *GPH22* TIME 1 hour 45 minutes. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 GCSE Physics Unit 2 Higher Tier [GPH22] MONDAY 23 JUNE, MORNING *GPH22* *GPH22* TIME 1 hour 45 minutes. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing;
 Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Fluids density Pascal s principle (pressure vs. depth) Equation of continuity Buoyant force Bernoulli s (pressure, velocity, depth)
 Final Exam All Finals week in the testing center. 50 multiple choice questions. Equations on the back of the test. Calculators are allowed on the test. There is a practice test in the packet. Exam 1 Review
Final Exam All Finals week in the testing center. 50 multiple choice questions. Equations on the back of the test. Calculators are allowed on the test. There is a practice test in the packet. Exam 1 Review
PHYS 102 Exams. PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A)
 PHYS 102 Exams PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A) The next two questions pertain to the situation described below. A metal ring, in the page, is in a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page as
PHYS 102 Exams PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A) The next two questions pertain to the situation described below. A metal ring, in the page, is in a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page as
Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from
 Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from the one crest of a wave to the next. I. Electromagnetic
Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from the one crest of a wave to the next. I. Electromagnetic
Chapter 6: Waves. Student Book answers
 Chapter 6: Waves Lesson 6.1 Describing Waves 1 2 waves 2 As the amplitude increases, the amount of energy transferred by a wave increases. through the iron railing so Ann hears the sound wave that has
Chapter 6: Waves Lesson 6.1 Describing Waves 1 2 waves 2 As the amplitude increases, the amount of energy transferred by a wave increases. through the iron railing so Ann hears the sound wave that has
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Higher Tier Thursday 24 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance
 Paper Reference 5PH1H/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Higher Tier Thursday 24 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance Centre No. Candidate No. Surname
Paper Reference 5PH1H/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Higher Tier Thursday 24 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance Centre No. Candidate No. Surname
3. The dog ran 10m to the east, then 5m to the south,and another 10m to the west. What is the total distance?
 October 28, 2014 Refer to Module 1: Activity 1: Where is it? October 29, 2014 1. It refers to the length of the entire path that the object travelled. A. Displacement B. Velocity C. Speed D. Distance 2.
October 28, 2014 Refer to Module 1: Activity 1: Where is it? October 29, 2014 1. It refers to the length of the entire path that the object travelled. A. Displacement B. Velocity C. Speed D. Distance 2.
Physics Unit Physics P1
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science B Unit Physics P1 Physics Unit Physics P1 Friday 17 June 2011 General Certificate of
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science B Unit Physics P1 Physics Unit Physics P1 Friday 17 June 2011 General Certificate of
SCIENCE 8 CHAPTER 4 SECTION 1
 SCIENCE 8 CHAPTER 4 SECTION 1 The Nature of Light (pp. 132-137) What is light? (early ideas) One of the first people to attempt to explain how light made it possible to see was Pythagoras, a Greek philosopher
SCIENCE 8 CHAPTER 4 SECTION 1 The Nature of Light (pp. 132-137) What is light? (early ideas) One of the first people to attempt to explain how light made it possible to see was Pythagoras, a Greek philosopher
SNC2D PHYSICS 4/27/2013. LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P ) What Is Light? What Is Light?
 SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
SNC2D PHYSICS LIGHT & GEOMETRIC OPTICS L What Is Light? (P.380-391) What Is Light? For centuries, scientists have tried to understand the nature of light and its properties. Some of these properties are
Chapter 4 - Light. Name: Block:
 Chapter 4 Notes: Light Name: Block: Properties of Waves Waves are a repeating disturbance or movement that energy through matter or space without causing any displacement of material Features of a wave:
Chapter 4 Notes: Light Name: Block: Properties of Waves Waves are a repeating disturbance or movement that energy through matter or space without causing any displacement of material Features of a wave:
Had a go Nearly there Nailed it! Core. Key concepts. 2 Explain the difference between a base unit and a derived unit
 Out and about Core Key concepts 1 Complete the table for units of physical quantities and their abbreviations. ampere... joule... pascal Pa coulomb... mole... watt... newton... ohm... 2 Explain the difference
Out and about Core Key concepts 1 Complete the table for units of physical quantities and their abbreviations. ampere... joule... pascal Pa coulomb... mole... watt... newton... ohm... 2 Explain the difference
RADIATION and the EM Spectrum
 RADIATION and the EM Spectrum Radioactivity is the of high-energy particles and/or of energy from a substance as a result of of its atoms. There are several types of radiation. Radiation from the sun is
RADIATION and the EM Spectrum Radioactivity is the of high-energy particles and/or of energy from a substance as a result of of its atoms. There are several types of radiation. Radiation from the sun is
Waves ~ Learning Guide
 Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
ABOUT SPOTTINGSCOPES Background on Telescopes
 22 November 2010 ABOUT SPOTTINGSCOPES A spotting scope is a compact telescope designed primarily for terrestrial observing and is used in applications which require magnifications beyond the range of a
22 November 2010 ABOUT SPOTTINGSCOPES A spotting scope is a compact telescope designed primarily for terrestrial observing and is used in applications which require magnifications beyond the range of a
FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min
 DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management and elearning Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2013 Track 3 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME:
DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management and elearning Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2013 Track 3 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME:
Light is an electromagnetic wave (EM)
 What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
Space Physics Questions CfE
 Space Physics Questions CfE 1) Write down the definitions of the following: a) Moon b) Planet c) Sun d) Star e) Solar System f) Exoplanet g) Galaxy h) Universe. 2) What is cosmology the study of? 3) a)
Space Physics Questions CfE 1) Write down the definitions of the following: a) Moon b) Planet c) Sun d) Star e) Solar System f) Exoplanet g) Galaxy h) Universe. 2) What is cosmology the study of? 3) a)
Solution 3: A glass prism deviates the violet light most and the red light least.
 EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at January 2016
 Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
UNIT-5 EM WAVES UNIT-6 RAY OPTICS
 UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
Physics PH1FP. (Jun14PH1FP01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June Unit Physics P1. Unit Physics P1 TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Science A Unit Physics P1 Physics Unit Physics P1 Thursday 12 June 2014 General
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Science A Unit Physics P1 Physics Unit Physics P1 Thursday 12 June 2014 General
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/2H London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 2H Higher Tier Tuesday 2 May 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/2H London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 2H Higher Tier Tuesday 2 May 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination
Study Guide: Semester Two ( )
 Name Hour Study Guide: Semester Two (2017-2018) Unit 5 Chapter 9 Momentum and its Conservation Chapter 10 Energy, Work and Simple Machines Chapter 11 Energy and its Conservation Vocabulary (define the
Name Hour Study Guide: Semester Two (2017-2018) Unit 5 Chapter 9 Momentum and its Conservation Chapter 10 Energy, Work and Simple Machines Chapter 11 Energy and its Conservation Vocabulary (define the
Year 7 Physics Learning Cycle 4 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: How has our understanding of waves changed the life of the average English person?
 Year 7 Physics Learning Cycle 4 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: How has our understanding of waves changed the life of the average English person? Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: Hypothesis
Year 7 Physics Learning Cycle 4 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: How has our understanding of waves changed the life of the average English person? Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: Hypothesis
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Friday 2 March 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Friday 2 March 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Candidate Number
