Supermassive black hole formation at high redshift
|
|
|
- Miranda Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supermassive black hole formation at high redshift Muhammad Latif Institut d'astrophysique de Paris, France Marta Volonteri, Dominik Schleicher, Melanie Habouzit,Tilman Hartwig, Kazu Omukai, Jens Niemeyer, Wolfram Schmidt, Marco Spaans, Caroline Van Borm, Stefano Bovino, Tommaso Grassi
2 High z Quasars Supermassive black holes of ~10 9 solar masses have been observed at z>6 (Venemans +15) The highest-redshift quasar at z=7.085 hosts a SMBH of 2x10 9 M (Mortlock et al. 2011) The most massive black hole has a mass of 1.3 x M at z=6.3 (Wu et al. Nature 2015) Wu et al. Nature 2015
3 Direct collapse scenario Provides massive seeds of M Key requirement is to have large inflow rate of > 0.1 M /yr Isothermal direct collapse with T~ 8000 K Primordial gas composition Requires strong LW flux to quench H 2 formation See recent review by Latif & Ferrara 2016 (arxiv: ) s Regan et al 2009
4 Supergiant protostar stellar+radius+: R * +(+R! ) TH+12 HIburning+starts HIburning+starts ZAMS stellar+mass +M * +(+M! ) " The+protostar+never+contracts+to+reach+the+ZAMS+stage,+but largely+expands+with+very+rapid+accredon,++>+0.01+m! /yr.+ " large+radius+ +low+effecdve+temperature+ +weak+uv+feedback+ Hoskawa et al. 2012, Schleicher, ML et al., A&A, 2013
5 Thermodynamics of primordial gas J>J crit H atomic cooling J<J crit H 2 molecular cooling Omukai 01, Also see Latif et. al 2014 MNRAS
6 Cosmological simulations Latif et al. 2013, 2014, 2015
7 Global properties of simulated halos Successes of Isothermal DC Latif et al 2013, MNRAS, 433, 1607L
8 Simulations exploring the direct collapse te of Simulations Collapse Latif et al 2013occurs MNRAS isothermally with T~ 8000 K L Provides large inflow rates of ~1M /yr Latif et al. 2013, MNRAS, 433, 1607L
9 Impact of H - cooling & Realistic opacities Latif, Schleicher & Hartwig, 2016, MNRAS, 458, 233L
10 Masses of protostars/sinks s s Employed sink particles and followed the evolution for 200,000 yrs Massive sinks of about 10 5 M are Latif et al. 2013, MNRAS, 436, 2989L formed
11 Fraction of metal free halos Latif et al ApJ L, See Habouzit, et al 2016
12 Estimates of J crit from 3D simulations Latif et al 2014 ArXiv: L Latif et al. MNRAS , Also see Agarwal et al. 2016
13 Number density of DCBHs Habouzit,Volonteri, ML et al. 2016, Also see Dijkstra et al. 2014
14 massive stars are favoured to reproduce the observations. 10 The Zcrit model yields larger masses of low-metallicity gas down to smaller redshifts and consequently allows primory CONSISTENT dial star formation at later times. Hence, more massive stars can also survive to contribute to the Heii luminosity at z = The Zcrit model produces the highest Heii luminosities, 10 Sobral et al 2015, Pallottini et al. 2015, Agarwal et al which are still more than 10 orders of magnitude below the observed value of erg s 1. Even for a higher t [Myr] halo mass, the final luminosities are too small. We note Figure 4. Mean cosmic Pop III SFR for all four models per that the corresponding Lyα luminosity for Pop III stars in a comoving volume. The primordial SFR peaks around redshift 20, 1012 M halo is of the order erg s 1, which is and decreases at z < 12. about 7 orders of magnitude below the observed value. -6 CR7: Potential host for a DCBH? What mostlyet limits the Heii luminosity is the mass of T. Hartwig al. Pop III stars that survive until z = 6.6. To show this effect, we plot the stellar mass distribution of primordial stars in 10 Figure 7. The more massive the stars, the shorter the lifefiducial times and the smaller the probability that they survive long 1->100 Zcrit enough to be present down to z = 6.6. For M < 2 M this merger plot represents the IMF, since the lifetimes of these stars are long enough for them to survive until z = 6.6. For higher masses we see that the Zcrit model is the most likely one to 108 also contain stars that are 10 M since it has the largest amount of gas available for star formation down to lower Prime target for JWST! redshifts. But even these stars are not massive enough to contribute significantly to the Heii luminosity, due to the steep dependence of the Heii luminosity on the stellar mass 107 (see also Table 1). We also test more extreme models for the Pop III IMF with a mass range from Mmin = 10 M to Mmax = 1000 M and find significantly fewer primordial stars at z = 6.6 and also a smaller Heii line luminosity than in the fiducial model. For Mmin " 50 M there are no Pop III starscomparison at all that might contribute to the Heii luminosity at Figure 17. of the three different models, regardin z = 6.6, such within a few the metallicity of because clump A at massive z = 6.6stars andexplode the mass of the stel Myr asor SNe. Hartwig, al MNRAS,The resubmitted t [Myr] lar population ofml theetbh, respectively. grey shaded are 9 Mprist [M ] z 10 9
15 Growth of a DCBH 3D RT+ hydro simulations Include both UV & X-ray feedback (0.1eV-1.1 KeV) from a BH Accretion Rate [M O /yr] M BH [10 4 M O ] Time [Myrs] Time [Myrs] Latif et al. in preparation
16 Summary Direct isothermal collapse provides massive seeds of about 10 5 M Large accretion rates of ~0.1 M /yr are found in numerical simulations Direct collapse model seems feasible Difficult to grow a DCBH 10 4 M in an atomic cooling halo Radiative feedback from active BH limits its growth
17 Thank you!
Massive black hole formation in cosmological simulations
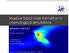 Institut d Astrophysique de Paris IAP - France Massive black hole formation in cosmological simulations Mélanie HABOUZIT Marta Volonteri In collaboration with Yohan Dubois Muhammed Latif Outline Project:
Institut d Astrophysique de Paris IAP - France Massive black hole formation in cosmological simulations Mélanie HABOUZIT Marta Volonteri In collaboration with Yohan Dubois Muhammed Latif Outline Project:
The Growth and Radiative Signatures of High Redshift Black Holes
 The Growth and Radiative Signatures of High Redshift Black Holes Jarrett Johnson (LANL) with Bhaskar Agarwal (Yale) Joe Smidt (LANL) Brandon Wiggins (LANL, BYU) Dan Whalen (Heidelberg, Portsmouth) Erik
The Growth and Radiative Signatures of High Redshift Black Holes Jarrett Johnson (LANL) with Bhaskar Agarwal (Yale) Joe Smidt (LANL) Brandon Wiggins (LANL, BYU) Dan Whalen (Heidelberg, Portsmouth) Erik
The Impact of Radiation on the Formation and Growth of Seed Black Holes
 The Impact of Radiation on the Formation and Growth of Seed Black Holes Jarrett Johnson Los Alamos National Laboratory with Joe Smidt (LANL) Aycin Aykutalp (LANL) Daniel Whalen (Portsmouth) Hui Li (LANL)
The Impact of Radiation on the Formation and Growth of Seed Black Holes Jarrett Johnson Los Alamos National Laboratory with Joe Smidt (LANL) Aycin Aykutalp (LANL) Daniel Whalen (Portsmouth) Hui Li (LANL)
The first black holes
 The first black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris M. Habouzit, Y. Dubois, M. Latif (IAP) A. Reines (NOAO) M. Tremmel (University of Washington) F. Pacucci (SNS) High-redshift quasars
The first black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris M. Habouzit, Y. Dubois, M. Latif (IAP) A. Reines (NOAO) M. Tremmel (University of Washington) F. Pacucci (SNS) High-redshift quasars
The Supermassive Seeds of Supermassive Black Holes
 The Supermassive Seeds of Supermassive Black Holes Jarrett Johnson (LANL) with Hui Li, Joe Smidt, Dan Whalen, Wes Even, Chris Fryer (LANL) Bhaskar Agarwal, Claudio Dalla Vecchia, Eyal Neistein (MPE) Ken
The Supermassive Seeds of Supermassive Black Holes Jarrett Johnson (LANL) with Hui Li, Joe Smidt, Dan Whalen, Wes Even, Chris Fryer (LANL) Bhaskar Agarwal, Claudio Dalla Vecchia, Eyal Neistein (MPE) Ken
The First Black Holes and. their Host Galaxies. John Wise
 The First Black Holes and John Wise Chao Shi (GT), Pengfei Chen (UCSD), Ayçin Aykutalp (GT), Tom Abel (Stanford), Peter Johansson (Helsinki), Michael Norman (UCSD), Brian O Shea (MSU), John Regan (Helsinki),
The First Black Holes and John Wise Chao Shi (GT), Pengfei Chen (UCSD), Ayçin Aykutalp (GT), Tom Abel (Stanford), Peter Johansson (Helsinki), Michael Norman (UCSD), Brian O Shea (MSU), John Regan (Helsinki),
Forma&on of supermassive black holes
 Forma&on of supermassive black holes Mélanie Habouzit Marta Volonteri Muhammad La&f Yohan Dubois Collaborators: Joe Silk, Gary Mamon, Sébas&en Peirani, Takahiro Nishimichi Two main scenarios to form supermassive
Forma&on of supermassive black holes Mélanie Habouzit Marta Volonteri Muhammad La&f Yohan Dubois Collaborators: Joe Silk, Gary Mamon, Sébas&en Peirani, Takahiro Nishimichi Two main scenarios to form supermassive
M. Dijkstra (UiO) Aspen, Mark Dijkstra. with: Shiv Sethi (RRI), Abraham Loeb (CfA), Max Gronke (UiO) & David Sobral (Lancaster)
 Mark Dijkstra with: Shiv Sethi (RRI), Abraham Loeb (CfA), Max Gronke (UiO) & David Sobral (Lancaster) arxiv:1601.04712 (ApJ accepted), Dijkstra, Sethi & Loeb arxiv:1602.07695 (resubmitted to ApJ), Dijkstra,
Mark Dijkstra with: Shiv Sethi (RRI), Abraham Loeb (CfA), Max Gronke (UiO) & David Sobral (Lancaster) arxiv:1601.04712 (ApJ accepted), Dijkstra, Sethi & Loeb arxiv:1602.07695 (resubmitted to ApJ), Dijkstra,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Jun 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Jun 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Jun 2014](/thumbs/85/91559799.jpg) The formation of massive primordial stars in the presence of moderate UV backgrounds arxiv:1406.1465v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Jun 2014 M. A. Latif 1, D. R. G. Schleicher 1, S. Bovino 1, T. Grassi 2,3, M. Spaans
The formation of massive primordial stars in the presence of moderate UV backgrounds arxiv:1406.1465v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Jun 2014 M. A. Latif 1, D. R. G. Schleicher 1, S. Bovino 1, T. Grassi 2,3, M. Spaans
DIRECT COLLAPSE BLACK HOLES AS SEEDS OF QUASARS AT REDSHIFT > 6. Bhaskar Agarwal TMoX Group Max Planck for Extraterrestrial Physics!!
 DIRECT COLLAPSE BLACK HOLES AS SEEDS OF QUASARS AT REDSHIFT > 6 Bhaskar Agarwal TMoX Group Max Planck for Extraterrestrial Physics!! OPINAS Seminar, 30 April 2014 PROBLEM Explain supermassive black holes
DIRECT COLLAPSE BLACK HOLES AS SEEDS OF QUASARS AT REDSHIFT > 6 Bhaskar Agarwal TMoX Group Max Planck for Extraterrestrial Physics!! OPINAS Seminar, 30 April 2014 PROBLEM Explain supermassive black holes
Michael Shull (University of Colorado)
 Early Galaxies, Stars, Metals, and the Epoch of Reionization Michael Shull (University of Colorado) Far-IR Workshop (Pasadena, CA) May 29, 2008 Submillimeter Galaxies: only the brightest? How long? [dust
Early Galaxies, Stars, Metals, and the Epoch of Reionization Michael Shull (University of Colorado) Far-IR Workshop (Pasadena, CA) May 29, 2008 Submillimeter Galaxies: only the brightest? How long? [dust
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Aug 2016
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Aug 2016 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Aug 2016](/thumbs/75/72418774.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 21 (2016) Printed 10 August 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Exploring the nature of the Lyman-α emitter CR7 arxiv:1512.01111v3 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Aug 2016 Tilman Hartwig 1,2,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 21 (2016) Printed 10 August 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Exploring the nature of the Lyman-α emitter CR7 arxiv:1512.01111v3 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Aug 2016 Tilman Hartwig 1,2,
Quasi-stars and the Cosmic Evolution of Massive Black Holes
 Quasi-stars and the Cosmic Evolution of Massive Black Holes Marta Volonteri and Mitchell C. Begelman 2010 MNRAS 409:1022 David Riethmiller January 26, 2011 Outline Two different methods for MBH formation:
Quasi-stars and the Cosmic Evolution of Massive Black Holes Marta Volonteri and Mitchell C. Begelman 2010 MNRAS 409:1022 David Riethmiller January 26, 2011 Outline Two different methods for MBH formation:
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Jan 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Jan 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Jan 2016](/thumbs/88/115400688.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000,?? 16 (2016) Printed 1 February 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) From the first stars to the first black holes Rosa Valiante 1, Raffaella Schneider 1, Marta Volonteri 2, Kazuyuki
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000,?? 16 (2016) Printed 1 February 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) From the first stars to the first black holes Rosa Valiante 1, Raffaella Schneider 1, Marta Volonteri 2, Kazuyuki
Current Paradigm of Direct Collapse BH formation
 Guillermo Haro Workshop, 2015 Current Paradigm of Direct Collapse BH formation Bhaskar Agarwal Yale University (prev: PhD at Max Planck for Extraterrestrial Physics) What is the Problem? SDSS Quasars at
Guillermo Haro Workshop, 2015 Current Paradigm of Direct Collapse BH formation Bhaskar Agarwal Yale University (prev: PhD at Max Planck for Extraterrestrial Physics) What is the Problem? SDSS Quasars at
Growing and merging massive black holes
 Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
The First Billion Years project: birthplaces of direct collapse black holes
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu1112 The First Billion Years project: birthplaces of direct collapse black holes Bhaskar Agarwal, 1 Claudio Dalla Vecchia, 1,2,3 Jarrett L. Johnson, 1,4 Sadegh Khochfar 1,5 and Jan-Pieter
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu1112 The First Billion Years project: birthplaces of direct collapse black holes Bhaskar Agarwal, 1 Claudio Dalla Vecchia, 1,2,3 Jarrett L. Johnson, 1,4 Sadegh Khochfar 1,5 and Jan-Pieter
Formation of primordial supermassive stars by burst accretion
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 15 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Formation of primordial supermassive stars by burst accretion An alternative model which circumvents these
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 15 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Formation of primordial supermassive stars by burst accretion An alternative model which circumvents these
The Origin of Supermassive Black Holes. Daniel Whalen. McWilliams Fellow Carnegie Mellon
 The Origin of Supermassive Black Holes Daniel Whalen McWilliams Fellow Carnegie Mellon Mergers Accretion The SMBH Conundrum SDSS quasars of ~ 10 9 Msun have been found at z ~ 6, a Gyr after the Big Bang
The Origin of Supermassive Black Holes Daniel Whalen McWilliams Fellow Carnegie Mellon Mergers Accretion The SMBH Conundrum SDSS quasars of ~ 10 9 Msun have been found at z ~ 6, a Gyr after the Big Bang
RADIATION HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE FIRST QUASARS
 Draft version September 25, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 RADIATION HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE FIRST QUASARS Joseph Smidt 1, Daniel J. Whalen 2, Jarrett L. Johnson
Draft version September 25, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 RADIATION HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE FIRST QUASARS Joseph Smidt 1, Daniel J. Whalen 2, Jarrett L. Johnson
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 May 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 May 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 May 2014](/thumbs/85/91745591.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2012) Printed 18 June 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1405.6743v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 May 2014 Feedback-regulated Super Massive Black Hole Seed Formation Mark Dijkstra
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2012) Printed 18 June 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1405.6743v1 [astro-ph.ga] 26 May 2014 Feedback-regulated Super Massive Black Hole Seed Formation Mark Dijkstra
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Effects of turbulence and rotation on protostar formation as a precursor of massive black holes
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201424658 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics Effects of turbulence and rotation on protostar formation as a precursor of massive black holes C. Van Borm 1,2, S. Bovino 1, M. A.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201424658 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics Effects of turbulence and rotation on protostar formation as a precursor of massive black holes C. Van Borm 1,2, S. Bovino 1, M. A.
Detecting direct collapse black holes: making the case for CR7
 Advance Access publication 2016 May 19 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1173 Detecting direct collapse black holes: making the case for CR7 Bhaskar Agarwal, 1 Jarrett L. Johnson, 2 Erik Zackrisson, 3 Ivo Labbe, 4
Advance Access publication 2016 May 19 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1173 Detecting direct collapse black holes: making the case for CR7 Bhaskar Agarwal, 1 Jarrett L. Johnson, 2 Erik Zackrisson, 3 Ivo Labbe, 4
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird. University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester)
 Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
The Illustris simulation: a new look at galaxy black hole co-evolution. Debora Sijacki IoA & KICC Cambridge
 The Illustris simulation: a new look at galaxy black hole co-evolution Debora Sijacki IoA & KICC Cambridge LSS conference July 23 2015 Cosmological simulations of galaxy and structure formation Hierarchical
The Illustris simulation: a new look at galaxy black hole co-evolution Debora Sijacki IoA & KICC Cambridge LSS conference July 23 2015 Cosmological simulations of galaxy and structure formation Hierarchical
The Interplay Between Galaxies and Black Holes A Theoretical Overview. Massimo Ricotti (U of Maryland)
 The Interplay Between Galaxies and Black Holes A Theoretical Overview Massimo Ricotti (U of Maryland) ..a tale of many sleepless nights Maya and Noemi Ricotti Cosmological Context Outline Formation of
The Interplay Between Galaxies and Black Holes A Theoretical Overview Massimo Ricotti (U of Maryland) ..a tale of many sleepless nights Maya and Noemi Ricotti Cosmological Context Outline Formation of
The First Stars and their Impact on Cosmology
 The First Stars and their Impact on Cosmology V. Bromm University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712, USA Within variants of the cold dark matter model of cosmological structure formation, the first sources of
The First Stars and their Impact on Cosmology V. Bromm University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712, USA Within variants of the cold dark matter model of cosmological structure formation, the first sources of
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Oct 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Oct 2014](/thumbs/73/68830827.jpg) Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. paper01_aanda_final_publish_arxiv c ESO 2017 December 11, 2017 Effects of turbulence and rotation on protostar formation as a precursor of massive black holes C.
Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. paper01_aanda_final_publish_arxiv c ESO 2017 December 11, 2017 Effects of turbulence and rotation on protostar formation as a precursor of massive black holes C.
The First Galaxies. Erik Zackrisson. Department of Astronomy Stockholm University
 The First Galaxies Erik Zackrisson Department of Astronomy Stockholm University Outline The first galaxies what, when, why? What s so special about them? Why are they important for cosmology? How can we
The First Galaxies Erik Zackrisson Department of Astronomy Stockholm University Outline The first galaxies what, when, why? What s so special about them? Why are they important for cosmology? How can we
WFIRST and JWST synergies in the study of First Light. M. Stiavelli STScI, Baltimore
 WFIRST and JWST synergies in the study of First Light M. Stiavelli STScI, Baltimore 1 WFIRST and JWST synergies in the study of First Light Plan: - Detecting the First Stars WFIRST-AFTA as an object finder
WFIRST and JWST synergies in the study of First Light M. Stiavelli STScI, Baltimore 1 WFIRST and JWST synergies in the study of First Light Plan: - Detecting the First Stars WFIRST-AFTA as an object finder
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Apr 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Apr 2017](/thumbs/92/110800629.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (0000) Printed 21 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Effects of binary stellar populations on direct collapse black hole formation arxiv:1609.08605v2 [astro-ph.ga]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 6 (0000) Printed 21 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Effects of binary stellar populations on direct collapse black hole formation arxiv:1609.08605v2 [astro-ph.ga]
Formation and cosmic evolution of supermassive black holes. Debora Sijacki
 Formation and cosmic evolution of supermassive black holes Debora Sijacki Summer school: Black Holes at all scales Ioannina, Greece, Sept 16-19, 2013 Lecture 1: - formation of black hole seeds - low mass
Formation and cosmic evolution of supermassive black holes Debora Sijacki Summer school: Black Holes at all scales Ioannina, Greece, Sept 16-19, 2013 Lecture 1: - formation of black hole seeds - low mass
Unveiling the nature of bright z ~ 7 galaxies with HST and JWST
 Unveiling the nature of bright z ~ 7 galaxies with HST and JWST Rebecca Bowler Hintze Fellow, University of Oxford Nicholas Kurti Junior Fellow, Brasenose College with Jim Dunlop, Ross McLure, Derek McLeod,
Unveiling the nature of bright z ~ 7 galaxies with HST and JWST Rebecca Bowler Hintze Fellow, University of Oxford Nicholas Kurti Junior Fellow, Brasenose College with Jim Dunlop, Ross McLure, Derek McLeod,
ON THE ROTATION OF SUPERMASSIVE STARS. Submitted to ApJL
 Draft version October 13, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX61 ON THE ROTATION OF SUPERMASSIVE STARS Lionel Haemmerlé, 1 Tyrone E. Woods, 2 Ralf S. Klessen, 3, 4 Alexander Heger, 5 and
Draft version October 13, 2018 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX61 ON THE ROTATION OF SUPERMASSIVE STARS Lionel Haemmerlé, 1 Tyrone E. Woods, 2 Ralf S. Klessen, 3, 4 Alexander Heger, 5 and
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model
 Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers
 Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy
 AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy Feng Yuan Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS Collaborators: Zhaoming Gan (SHAO) Jerry Ostriker (Princeton) Luca Ciotti (Bologna) Greg Novak (Paris) 2014.9.10;
AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy Feng Yuan Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS Collaborators: Zhaoming Gan (SHAO) Jerry Ostriker (Princeton) Luca Ciotti (Bologna) Greg Novak (Paris) 2014.9.10;
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Mar 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 11 Mar 2014](/thumbs/88/114710567.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2009) Printed 26 June 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Impact of baryonic streaming velocities on the formation of supermassive black holes via direct collapse arxiv:1311.5866v2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2009) Printed 26 June 2018 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Impact of baryonic streaming velocities on the formation of supermassive black holes via direct collapse arxiv:1311.5866v2
AST Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy. Lecture 20. Black Holes Part II
 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 20 Black Holes Part II 1 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Outline: Black Holes Part II Gas accretion disks around black holes, and
AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 20 Black Holes Part II 1 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Outline: Black Holes Part II Gas accretion disks around black holes, and
The first stars and primordial IMBHs
 The first stars and primordial IMBHs Ab initio predictions of black hole merger rates by the time LISA flies? Tom Abel Penn State Initial Conditions Time Evolution z=100 z=24 z=20.4 10 comoving kpc Cosmological
The first stars and primordial IMBHs Ab initio predictions of black hole merger rates by the time LISA flies? Tom Abel Penn State Initial Conditions Time Evolution z=100 z=24 z=20.4 10 comoving kpc Cosmological
The First Stars. Simone Ferraro Princeton University. Sept 25, 2012
 The First Stars Simone Ferraro Princeton University Sept 25, 2012 Outline Star forming minihalos at high z Cooling physics and chemistry Gravitational Collapse and formation of protostar Magnetic fields
The First Stars Simone Ferraro Princeton University Sept 25, 2012 Outline Star forming minihalos at high z Cooling physics and chemistry Gravitational Collapse and formation of protostar Magnetic fields
Growing massive black holes via super-critical accretion on to stellar-mass seeds
 Growing massive black holes via super-critical accretion on to stellar-mass seeds Alessandro Lupi IAP (Paris) DARK ERC-2010 AdG_20100224 in collaboration with: F. Haardt, M. Dotti, M. Colpi, D. Fiacconi,
Growing massive black holes via super-critical accretion on to stellar-mass seeds Alessandro Lupi IAP (Paris) DARK ERC-2010 AdG_20100224 in collaboration with: F. Haardt, M. Dotti, M. Colpi, D. Fiacconi,
The improvement of START
 The improvement of START Kenji Hasegawa (U. Tsukuba, CCS Kobe branch) Takashi Okamoto (U. Tsukuba, CCS Kobe branch) Cosmological Radiative Transfer Comparison Project Workshop IV @ Austin, Texas, Dec 11-14,
The improvement of START Kenji Hasegawa (U. Tsukuba, CCS Kobe branch) Takashi Okamoto (U. Tsukuba, CCS Kobe branch) Cosmological Radiative Transfer Comparison Project Workshop IV @ Austin, Texas, Dec 11-14,
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved
 Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
The formation of direct collapse black holes under the influence of streaming velocities
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 1 8 (22) Printed 12 January 218 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The formation of direct collapse black holes under the influence of streaming velocities Anna T. P. Schauer 1, John
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 1 8 (22) Printed 12 January 218 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The formation of direct collapse black holes under the influence of streaming velocities Anna T. P. Schauer 1, John
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Jul 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Jul 2018](/thumbs/94/120286531.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2016) Printed 2 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Growth of Black Holes from Population III Remnants in the Renaissance Simulations arxiv:1804.06477v2 [astro-ph.ga]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 12 (2016) Printed 2 August 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Growth of Black Holes from Population III Remnants in the Renaissance Simulations arxiv:1804.06477v2 [astro-ph.ga]
The Pop III/II Transition
 The First Stars and Galaxies: Challenges for the Next Decade March 8-11, 2010 Austin, Texas The Pop III/II Transition Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri What are the minimal conditions
The First Stars and Galaxies: Challenges for the Next Decade March 8-11, 2010 Austin, Texas The Pop III/II Transition Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri What are the minimal conditions
Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation. Debora Sijacki
 Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation Debora Sijacki Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture Planck data, 2013 (new results 2015) Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture CMB black body spectrum
Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation Debora Sijacki Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture Planck data, 2013 (new results 2015) Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture CMB black body spectrum
The farthest GRBs similar to the closest
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 319 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della The farthest GRBs similar to the closest R. Salvaterra Dipartimento di Fisica e Matematica, Università dell Insubria, via Valleggio 7, 22100 Como, Italy
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 319 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della The farthest GRBs similar to the closest R. Salvaterra Dipartimento di Fisica e Matematica, Università dell Insubria, via Valleggio 7, 22100 Como, Italy
Black hole formation and growth with non-gaussian primordial density perturbations
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed November 5, 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Black hole formation and growth with non-gaussian primordial density perturbations Primordial perturbations
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed November 5, 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Black hole formation and growth with non-gaussian primordial density perturbations Primordial perturbations
Methodology. Friday, August 17, 12
 Methodology Conditions for the formation of massive seed black holes 1. Major merger (1:3) of gas-rich late-type galaxies (B/T < 0.2) 2. Host halo Mh > 10 11 MSun 3. No a pre-existing black hole of MBH
Methodology Conditions for the formation of massive seed black holes 1. Major merger (1:3) of gas-rich late-type galaxies (B/T < 0.2) 2. Host halo Mh > 10 11 MSun 3. No a pre-existing black hole of MBH
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx
 X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
FORMATION OF PRIMORDIAL STARS
 Talk@INT, UW, July 5, 2006 FORMATION OF PRIMORDIAL STARS Naoki Yoshida Department of Physics Nagoya University Outline Thermal evolution of a primordial gas - Physics at high densities (cooling, chem.
Talk@INT, UW, July 5, 2006 FORMATION OF PRIMORDIAL STARS Naoki Yoshida Department of Physics Nagoya University Outline Thermal evolution of a primordial gas - Physics at high densities (cooling, chem.
Massive Stellar Black Hole Binaries and Gravitational Waves
 BH-BH binaries: modeling Massive Stellar Black Hole Binaries and Gravitational Waves Chris Belczynski1 Tomek Bulik1 Daniel Holz Richard O Shaughnessy Wojciech Gladysz1 and Grzegorz Wiktorowicz1 1 Astronomical
BH-BH binaries: modeling Massive Stellar Black Hole Binaries and Gravitational Waves Chris Belczynski1 Tomek Bulik1 Daniel Holz Richard O Shaughnessy Wojciech Gladysz1 and Grzegorz Wiktorowicz1 1 Astronomical
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing Supermassive Black Hole Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model
 Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing Supermassive Black Hole Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro Enoki 1, Kaiki T. Inoue 2, Masahiro Nagashima 3 and Naoshi Sugiyama 1 1 National
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing Supermassive Black Hole Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro Enoki 1, Kaiki T. Inoue 2, Masahiro Nagashima 3 and Naoshi Sugiyama 1 1 National
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Jul 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Jul 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 28 Jul 2016](/thumbs/75/71947217.jpg) DRAFT VERSION FEBRUARY 15, 2018 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 AB INITIO COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OF CR7 AS AN ACTIVE BLACK HOLE JOSEPH SMIDT 1, BRANDON K. WIGGINS 1,2, JARRETT
DRAFT VERSION FEBRUARY 15, 2018 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 AB INITIO COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OF CR7 AS AN ACTIVE BLACK HOLE JOSEPH SMIDT 1, BRANDON K. WIGGINS 1,2, JARRETT
Supermassive Black Hole Formation in Galactic Nuclei
 Supermassive Black Hole Formation in Galactic Nuclei Melvyn B. Davies Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics Lund University Ross Church (Lund), Cole Miller (Maryland), Serge Nzoke (Lund), Jillian
Supermassive Black Hole Formation in Galactic Nuclei Melvyn B. Davies Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics Lund University Ross Church (Lund), Cole Miller (Maryland), Serge Nzoke (Lund), Jillian
Dual and Binary MBHs and AGN: Connecting Dynamics and Accretion
 Dual and Binary MBHs and AGN: Connecting Dynamics and Accretion Sandor Van Wassenhove Marta Volonteri Lucio Mayer Jillian Bellovary Massimo Dotti Simone Callegari BH-Galaxy Coevolution Black holes found
Dual and Binary MBHs and AGN: Connecting Dynamics and Accretion Sandor Van Wassenhove Marta Volonteri Lucio Mayer Jillian Bellovary Massimo Dotti Simone Callegari BH-Galaxy Coevolution Black holes found
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Feb 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Feb 2016](/thumbs/93/111653642.jpg) Draft version April 3, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 LYα SIGNATURES FROM DIRECT COLLAPSE BLACK HOLES arxiv:1602.07695v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Feb 2016 Mark Dijkstra 1, Max
Draft version April 3, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 01/23/15 LYα SIGNATURES FROM DIRECT COLLAPSE BLACK HOLES arxiv:1602.07695v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Feb 2016 Mark Dijkstra 1, Max
Supermassive Black Holes
 Supermassive Black Holes Leiden, Modern Research: Galaxy Formation and Evolution Tom van Leth & Maarten van Dijk November 25, 2005 1 Introduction Introduction Black hole theory Characteristics of SMBH
Supermassive Black Holes Leiden, Modern Research: Galaxy Formation and Evolution Tom van Leth & Maarten van Dijk November 25, 2005 1 Introduction Introduction Black hole theory Characteristics of SMBH
stelle e galassie primordiali
 stelle e galassie primordiali Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma Matteo de Bennassuti, PhD INAF/OAR Stefania Marassi, Pdoc INAF/OAR Luca Graziani, Pdoc INAF/OAR Rosa Valiante, Pdoc
stelle e galassie primordiali Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma Matteo de Bennassuti, PhD INAF/OAR Stefania Marassi, Pdoc INAF/OAR Luca Graziani, Pdoc INAF/OAR Rosa Valiante, Pdoc
Supermassive Black Holes in Galactic Nuclei and their Models of Formation
 Supermassive Black Holes in Galactic Nuclei and their Models of Formation Clemence Yun Chan Lee Abstract Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are black holes with masses larger than 10 5 solar mass, and they
Supermassive Black Holes in Galactic Nuclei and their Models of Formation Clemence Yun Chan Lee Abstract Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are black holes with masses larger than 10 5 solar mass, and they
Outline. Walls, Filaments, Voids. Cosmic epochs. Jeans length I. Jeans length II. Cosmology AS7009, 2008 Lecture 10. λ =
 Cosmology AS7009, 2008 Lecture 10 Outline Structure formation Jeans length, Jeans mass Structure formation with and without dark matter Cold versus hot dark matter Dissipation The matter power spectrum
Cosmology AS7009, 2008 Lecture 10 Outline Structure formation Jeans length, Jeans mass Structure formation with and without dark matter Cold versus hot dark matter Dissipation The matter power spectrum
Simulations of First Star Formation
 Simulations of First Star Formation Michael L. Norman (UCSD) Brian O Shea (LANL) 1 Formation of the first stars: current paradigm (Abel et al. 2002, Bromm et al. 2002,Yoshida et al. 2006) DM halos of M~10
Simulations of First Star Formation Michael L. Norman (UCSD) Brian O Shea (LANL) 1 Formation of the first stars: current paradigm (Abel et al. 2002, Bromm et al. 2002,Yoshida et al. 2006) DM halos of M~10
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ M gas / dyn. Log SFR. Kennicutt Log. gas / dyn
 Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS)
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 16 May 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 16 May 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 16 May 2013](/thumbs/71/66071169.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2009) Printed 17 May 2013 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Black hole formation in the early universe arxiv:1304.0962v2 [astro-ph.co] 16 May 2013 M. A. Latif, 1 D. R. G.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (2009) Printed 17 May 2013 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Black hole formation in the early universe arxiv:1304.0962v2 [astro-ph.co] 16 May 2013 M. A. Latif, 1 D. R. G.
Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies. Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville
 Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville Motivation: The origin of supermassive BH seeds Motivation: The origin of
Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville Motivation: The origin of supermassive BH seeds Motivation: The origin of
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Mar 2019](/thumbs/94/121759119.jpg) Supermassive and Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Growth at Galaxy Centers and Resulting Feedback using Cosmological Simulations arxiv:1903.04632v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Mar 2019 Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica
Supermassive and Intermediate-Mass Black Hole Growth at Galaxy Centers and Resulting Feedback using Cosmological Simulations arxiv:1903.04632v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Mar 2019 Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica
Black Hole Formation in the Early Universe
 1 Black Hole Formation in the Early Universe Luo Yang (Osaka University) XC30 2 1. Introduction Observations of high-redshift quasars reveal that some supermassive black holes (SMBH) with masses exceeding
1 Black Hole Formation in the Early Universe Luo Yang (Osaka University) XC30 2 1. Introduction Observations of high-redshift quasars reveal that some supermassive black holes (SMBH) with masses exceeding
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2016](/thumbs/75/72418766.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 00 Printed 16 December 016 MN LATEX style file v. Upper limits on the mass and luminosity of Population III-dominated galaxies arxiv:1610.044v [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 016
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 00 Printed 16 December 016 MN LATEX style file v. Upper limits on the mass and luminosity of Population III-dominated galaxies arxiv:1610.044v [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 016
from dust to galaxies: testing the evolution of the stellar IMF
 First Galaxies Ringberg, 26 June 1 July 2011 from dust to galaxies: testing the evolution of the stellar IMF Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma http://www.arcetri.astro.it/david
First Galaxies Ringberg, 26 June 1 July 2011 from dust to galaxies: testing the evolution of the stellar IMF Raffaella Schneider INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma http://www.arcetri.astro.it/david
Vivienne Wild. Timing the starburst AGN connection
 Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback
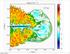 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback Geoff Bicknell & Alex Wagner Australian National University 1 1 High redshift radio
1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback Geoff Bicknell & Alex Wagner Australian National University 1 1 High redshift radio
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 2 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 2 Sep 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 2 Sep 2017](/thumbs/94/118286596.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 September 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Warm dark matter constraints from high-z Direct Collapse Black Holes using the JWST arxiv:1705.00632v2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 September 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Warm dark matter constraints from high-z Direct Collapse Black Holes using the JWST arxiv:1705.00632v2
The Early Generations of Low-metallicity Stars
 Stellar Evolution at low Metallicity: Mass Loss, Eplosions, Cosmology ASP Conference Series, Vol. 353, 2006 Henny J.G.L.M. Lamers, Norbert Langer, Tiit Nugis, Kalju Annuk The Early Generations of Low-metallicity
Stellar Evolution at low Metallicity: Mass Loss, Eplosions, Cosmology ASP Conference Series, Vol. 353, 2006 Henny J.G.L.M. Lamers, Norbert Langer, Tiit Nugis, Kalju Annuk The Early Generations of Low-metallicity
Feedback and Galaxy Formation
 Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera
 FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera In this presentation the different theories that can explain the formation of Supermassive Black Holes (SMBH) are presented. Before focus on
FORMATION OF SUPERMASSIVE BLACK HOLES Nestor M. Lasso Cabrera In this presentation the different theories that can explain the formation of Supermassive Black Holes (SMBH) are presented. Before focus on
The Very First Stars: Formation and Reionization of the Universe
 Chemical Abundances in the Universe: Connecting First Stars to Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 265, 2009 K. Cunha, M. Spite & B. Barbuy, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921310000116
Chemical Abundances in the Universe: Connecting First Stars to Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 265, 2009 K. Cunha, M. Spite & B. Barbuy, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921310000116
The Pop III IMF: A Progress Report. Michael L. Norman University of California, San Diego & San Diego Supercomputer Center
 The Pop III IMF: A Progress Report Michael L. Norman University of California, San Diego & San Diego Supercomputer Center Disclaimer Notion of Pop III IMF is not well-defined We don t observe Pop III stars
The Pop III IMF: A Progress Report Michael L. Norman University of California, San Diego & San Diego Supercomputer Center Disclaimer Notion of Pop III IMF is not well-defined We don t observe Pop III stars
Solving. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics
 Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
GALAXIES. Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak
 GALAXIES Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak Galaxy Science with AXIS How does gas get into and out of galaxies? How important is hot accretion for L* or larger galaxies? How does star formation/black hole
GALAXIES Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak Galaxy Science with AXIS How does gas get into and out of galaxies? How important is hot accretion for L* or larger galaxies? How does star formation/black hole
Optical/IR Counterparts of GW Signals (NS-NS and BH-NS mergers)
 Optical/IR Counterparts of GW Signals (NS-NS and BH-NS mergers) Chris Belczynski 1,2 1 Warsaw University Observatory 2 University of Texas, Brownsville Theoretical Rate Estimates (MOSTLY NS-NS MERGERS:
Optical/IR Counterparts of GW Signals (NS-NS and BH-NS mergers) Chris Belczynski 1,2 1 Warsaw University Observatory 2 University of Texas, Brownsville Theoretical Rate Estimates (MOSTLY NS-NS MERGERS:
The Impact of Quasar Feedback on the Formation & Evolution of Red Galaxies
 The Impact of Quasar Feedback on the Formation & Evolution of Red Galaxies Philip Hopkins 07/17/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, Gordon Richards, T. J. Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing
The Impact of Quasar Feedback on the Formation & Evolution of Red Galaxies Philip Hopkins 07/17/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, Gordon Richards, T. J. Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12 Outline of review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation Outline of (biased) review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12 Outline of review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation Outline of (biased) review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation
Research Collection. How will we determine the reionization history of the universe?: introduction to session 2. Other Conference Item.
 Research Collection Other Conference Item How will we determine the reionization history of the universe?: introduction to session 2 Author(s): Haiman, Zoltàn Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004584667
Research Collection Other Conference Item How will we determine the reionization history of the universe?: introduction to session 2 Author(s): Haiman, Zoltàn Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004584667
Published in: LOW-METALLICITY STAR FORMATION: FROM THE FIRST STARS TO DWARF GALAXIES
 University of Groningen Interstellar Chemistry Spaans, Marco Published in: LOW-METALLICITY STAR FORMATION: FROM THE FIRST STARS TO DWARF GALAXIES DOI: 10.1017/S1743921308024885 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are
University of Groningen Interstellar Chemistry Spaans, Marco Published in: LOW-METALLICITY STAR FORMATION: FROM THE FIRST STARS TO DWARF GALAXIES DOI: 10.1017/S1743921308024885 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are
Lyman-alpha intensity mapping during the Epoch of Reionization
 Lyman-alpha intensity mapping during the Epoch of Reionization Mário G. Santos CENTRA IST (Austin, May 15, 2012) Marta Silva, Mario G. Santos, Yan Gong, Asantha Cooray (2012), arxiv:1205.1493 Intensity
Lyman-alpha intensity mapping during the Epoch of Reionization Mário G. Santos CENTRA IST (Austin, May 15, 2012) Marta Silva, Mario G. Santos, Yan Gong, Asantha Cooray (2012), arxiv:1205.1493 Intensity
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2012](/thumbs/74/69950125.jpg) The Formation of the First Massive Black Holes Zoltán Haiman arxiv:1203.6075v1 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2012 Abstract Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are common in local galactic nuclei, and SMBHs as massive
The Formation of the First Massive Black Holes Zoltán Haiman arxiv:1203.6075v1 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2012 Abstract Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are common in local galactic nuclei, and SMBHs as massive
STELLAR BLACK HOLES & HMXBs AT THE DAWN OF THE UNIVERSE
 STELLAR BLACK HOLES & HMXBs AT THE DAWN OF THE UNIVERSE Félix Mirabel CEA-Saclay (France) & CONICET (Argentina) At the crossroads of Stellar Evolution, High Energy Astrophysics & Cosmology FEEDBACK FROM
STELLAR BLACK HOLES & HMXBs AT THE DAWN OF THE UNIVERSE Félix Mirabel CEA-Saclay (France) & CONICET (Argentina) At the crossroads of Stellar Evolution, High Energy Astrophysics & Cosmology FEEDBACK FROM
Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically faint ellipticals. Part 3. After Chandra?
 Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/114328171.jpg) Draft version January 15, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 Following the Cosmic Evolution of Pristine Gas III: The Observational Consequences of the Unknown Properties of Population
Draft version January 15, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 Following the Cosmic Evolution of Pristine Gas III: The Observational Consequences of the Unknown Properties of Population
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters
 Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jun 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jun 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jun 2009](/thumbs/85/91855599.jpg) An idea for detecting capture dominated Dark Stars arxiv:0906.4106v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jun 2009 Fabio Iocco Institut de Physique Théorique, CNRS, URA 2306 & CEA/Saclay, F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France Institut
An idea for detecting capture dominated Dark Stars arxiv:0906.4106v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jun 2009 Fabio Iocco Institut de Physique Théorique, CNRS, URA 2306 & CEA/Saclay, F-91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France Institut
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation
 Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
High-redshift formation and evolution of central massive objects II. The census of BH seeds
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 421, 1465 1475 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.20406.x High-redshift formation and evolution of central massive objects II. The census of BH seeds B. Devecchi, 1 M. Volonteri,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 421, 1465 1475 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.20406.x High-redshift formation and evolution of central massive objects II. The census of BH seeds B. Devecchi, 1 M. Volonteri,
X-ray ionization of the intergalactic medium by quasars
 X-ray ionization of the intergalactic medium by quasars Luca Graziani In collaboration with: CRASH4 IGM reionisation by QSOs GAMESH, QSOs evolution & QSOs impact on SF B. Ciardi (MPA, Munich) A. Ferrara
X-ray ionization of the intergalactic medium by quasars Luca Graziani In collaboration with: CRASH4 IGM reionisation by QSOs GAMESH, QSOs evolution & QSOs impact on SF B. Ciardi (MPA, Munich) A. Ferrara
Simulations of quasar feedback
 Simulations of quasar feedback Volker Springel Main collaborators: Lars Hernquist Simon White Tiziana di Matteo Debora Sijacki Brant Robertson Darren Croton Phil Hopkins Yuexing Li Thomas Cox Modelling
Simulations of quasar feedback Volker Springel Main collaborators: Lars Hernquist Simon White Tiziana di Matteo Debora Sijacki Brant Robertson Darren Croton Phil Hopkins Yuexing Li Thomas Cox Modelling
