Bias in parallax measurements
|
|
|
- Kory Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bias in parallax measurements When we measure some physical quantity experimentally, we usually incur some error in the measurement process, leading to an uncertainty in the result. Parallax is no exception: there are a number of sources of error in the measurement of very small angles between blobs of light from different stars. The topic for today is the sad, but true, fact that random errors in the measurements of parallax angles will NOT lead to "random" errors in the derived distances. We can expect to see a systematic errorin distances measured via parallax. Example of an unbiased error Let's start off with a simple experiment which does not lead to any bias in the result. I have a series of lead balls: I want to know the mass of each ball. My method: 1. Place each ball on a scale 2. Read the weight (in Newtons) from the scale 3. Divide the weight by g to find the mass (in kg) Now, in step 2, reading the scale, I can't do a perfect job. My scale has markings for every 0.1 Newton, so I can't make readings any more precisely than that. However, my scale is well calibrated. I decide that there's an uncertainty of +/ Newton in each measurement. Let's look at the results: both the mass I derive, based on my measurement, and the average ACTUAL mass of a large set of weights which give the same reading. I'll assume for the moment that g = 10 m/s^2 for simplicity. I'll also assume that the errors in measurement are uniformly distributed between and Newtons. Ball measured derived range of poss range of poss average
2 weight (N) mass(kg) weight(n) mass (kg) mass (kg) A B C D E Compare the mass I derive for each ball to the average mass of a whole bunch of similar balls which give identical readings. That is, in the first row, the "derived mass" column is my estimate of the mass of ball A: kg. Now, if I find a box full of balls roughly the same size and shape as A, put them on the scale, and pick out all those which give a reading of "5.20 N", I'll have some which are just a bit more massive, and some just a bit less massive. If I weigh all these balls on a much more precise scale, and find their true masses, then average them all together... I'll find the same value of kg. So there's no difference between a single calculated mass (0.520 kg) and the average value of a whole bunch of TRUE masses, all of which yield the same measurement (5.20 N). The difference is zero: (average of true masses) - (mass derived from one reading) = 0 In other words, an error in the measurement of weight doesn't cause any bias in the derived calculation of mass. Example of a biased error Now, let's look at a slightly different experiment, in which random errors in the measured quantity DO lead to a bias in the result. I'm again interested in finding the mass of a bunch of balls:
3 This time, however, I don't use a scale. Instead, I measure mass by pushing each ball gently with a standard force (10 Newtons), and measuring the balls subsequent acceleration: My measured accelerations have an error of +/- 5.0 m/s^2, which I assume again to be uniformly distributed. Here are my measured accelerations, and the masses I derive from each one. Ball measured derived range of poss range of poss average accel(m/s^2) mass(kg) accel(m/s^2) mass (kg) mass (kg) A B C D E Compare the "derived mass" column in this table to the "average mass" column: they are NOT the same. The average of all possible masses which are consistent with the measured acceleration is LARGER than the mass derived from a single measurement. (average of true masses) - (mass derived from one reading) >= 0 The size of this systematic bias depends on the mass of the ball. For very massive balls, the bias is large; for less massive balls, the bias is smaller. A very lightweight ball might have no perceptible bias at all.
4 Q: Why does the size of the bias depend on the mass of the ball? Symmetric errors and asymmetric results The root of the difference between the two examples above is in the connection between the measured quantity (which has some uncertainty in it) and the derived result. In the first case, we have: mass = weight / g In this direct linear relationship, an error of +10 0n weight leads to an error of +10 0n mass; and an error of -10 0n weight leads to an error of -10 0n mass. Symmetric errors in the measurement cause matching symmetric errors in the result. But in the second case, the equation is mass = F / accel In this inverse linear relationship, an error in the positive direction does NOT have the same effect on the result as an error in the negative direction. Well, let's qualify that claim just a bit: the errors in the result are actually pretty symmetric when the fractional error in the measurement is very small; it's only when the fractional error in the measurement becomes large that the asymmetric mistake in result becomes obvious. See for yourself. Given a force of F = 10 N, and the relationship mass = F / accel Measured if wrong yields true accel true mass error in accel (m/s^2) by (kg) (m/s^2) (kg) result (kg) %
5 10 + 1% % % % % % % % % % We can show this effect graphically: symmetric error bars on the measured acceleration lead to asymmetric error bars on the derived mass. And it's even worse for parallax... In general, an inverse relationship between measurement and derived quantity leads to asymmetric errors and a bias in the final result. That's not good. But in the particular case of parallax, there's an additional factor which accentuates the bias, making the problem even worse.
6 Space is big, really big, and it's full of stars. To a decent approximation, stars in the local neighborhood are scattered at random in all directions. Let's consider an "ideal" universe, which is full of identical stars, uniformly spaced at intervals of 1 parsec. Suppose that we measure the parallax to one particular star, Abelix: π = / arcsec. Our best guess for the distance to Abelix is simply D = 1 / = 100 pc. Fine. But now let's think carefully about the possibilities produced by the error in our measurement. A. The true distance might be LESS than 100 pc. For example, the true distance could be 90 pc, with a true parallax of arcsec; that's consistent with our measurement. B. The true distance might be MORE than 100 pc. For example, the true distance could be 105 pc, with a true parallax of arcsec; that's consistent with our measurement, too. We can get a bit more quantitative. Exactly how many stars might turn out to have measured parallaxes within the range of < π < arcseconds? That corresponds to a range of distances from 125 pc < D < 83.3 pc. A. Inner shell, between 83.3 pc and 100 pc. The total volume within this shell is B. C. V = 4/3 π [ (100 pc)^3 - (83.3 pc)^3 ] D. E. ~ 1,765,000 pc^3 which means that the total number of stars which might APPEAR to have a parallax of arcsec -- but are actually closer -- is about 1,765,000. F. Outer shell, between 100 pc and 125 pc. The total volume within this shell is G. H. V = 4/3 π [ (125 pc)^3 - (100 pc)^3 ] I. J. ~ 3,992,000 pc^3 which means that the total number of stars which might APPEAR to have a parallax of arcsec -- but are actually farther away -- is about 3,992,000.
7 There are more than twice the number of stars in the outer shell as in the inner shell. So, if we just pick one star at random which has a measured parallax of π = / arcsec, the chances are about 70 percent that the ACTUAL parallax is less than arcsec, and the ACTUAL distance is larger than 100 pc. In other words, when the uncertainty in a measured parallax becomes a significant fraction of the measurement itself, the chances are that the ACTUAL distance to the star is larger than the calculated distance. This effect was pointed out by Trumpler and Weaver in 1953 (and possibly by others even earlier), but received a very detailed treatment by Lutz and Kelker in It is now often called the Lutz-Kelker bias as a result. Q: Hipparcos measurements have a typical uncertainty of +/ arcsec. Estimate the bias in the distance to a star with measured parallax of arcsec. (Yes, to do this right involves an integral. If you want to make simple approximations in class, go ahead) Source:
MITOCW ocw f99-lec09_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec09_300k OK, this is linear algebra lecture nine. And this is a key lecture, this is where we get these ideas of linear independence, when a bunch of vectors are independent -- or
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec09_300k OK, this is linear algebra lecture nine. And this is a key lecture, this is where we get these ideas of linear independence, when a bunch of vectors are independent -- or
MITOCW ocw f99-lec01_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec01_300k Hi. This is the first lecture in MIT's course 18.06, linear algebra, and I'm Gilbert Strang. The text for the course is this book, Introduction to Linear Algebra. And the
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec01_300k Hi. This is the first lecture in MIT's course 18.06, linear algebra, and I'm Gilbert Strang. The text for the course is this book, Introduction to Linear Algebra. And the
MITOCW ocw f99-lec30_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec30_300k OK, this is the lecture on linear transformations. Actually, linear algebra courses used to begin with this lecture, so you could say I'm beginning this course again by
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec30_300k OK, this is the lecture on linear transformations. Actually, linear algebra courses used to begin with this lecture, so you could say I'm beginning this course again by
The Inductive Proof Template
 CS103 Handout 24 Winter 2016 February 5, 2016 Guide to Inductive Proofs Induction gives a new way to prove results about natural numbers and discrete structures like games, puzzles, and graphs. All of
CS103 Handout 24 Winter 2016 February 5, 2016 Guide to Inductive Proofs Induction gives a new way to prove results about natural numbers and discrete structures like games, puzzles, and graphs. All of
MITOCW R11. Double Pendulum System
 MITOCW R11. Double Pendulum System The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
MITOCW R11. Double Pendulum System The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for
Force and motion practice questions
 Force and motion practice questions Put another way: 1. A cart with very low friction wheels (pretend that there is no friction) has a mass of 750 grams (this is the mass of the cart and the fan combined).
Force and motion practice questions Put another way: 1. A cart with very low friction wheels (pretend that there is no friction) has a mass of 750 grams (this is the mass of the cart and the fan combined).
MITOCW watch?v=t6tqhnxy5wg
 MITOCW watch?v=t6tqhnxy5wg PROFESSOR: So what are we trying to do? We're going to try to write a matter wave. We have a particle with energy e and momentum p. e is equal to h bar omega. So you can get
MITOCW watch?v=t6tqhnxy5wg PROFESSOR: So what are we trying to do? We're going to try to write a matter wave. We have a particle with energy e and momentum p. e is equal to h bar omega. So you can get
Characterizing Stars
 Characterizing Stars The stars Every star you see in the sky is a large hot ball of gas like our star the Sun. Each one possibly making up a solar system with planets and debris orbiting around them. Stellar
Characterizing Stars The stars Every star you see in the sky is a large hot ball of gas like our star the Sun. Each one possibly making up a solar system with planets and debris orbiting around them. Stellar
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.06 Linear Algebra, Spring 2005 Please use the following citation format: Gilbert Strang, 18.06 Linear Algebra, Spring 2005. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.06 Linear Algebra, Spring 2005 Please use the following citation format: Gilbert Strang, 18.06 Linear Algebra, Spring 2005. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology:
MITOCW free_body_diagrams
 MITOCW free_body_diagrams This is a bungee jumper at the bottom of his trajectory. This is a pack of dogs pulling a sled. And this is a golf ball about to be struck. All of these scenarios can be represented
MITOCW free_body_diagrams This is a bungee jumper at the bottom of his trajectory. This is a pack of dogs pulling a sled. And this is a golf ball about to be struck. All of these scenarios can be represented
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec25_220k
 MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec25_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec25_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW watch?v=vu_of9tcjaa
 MITOCW watch?v=vu_of9tcjaa The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=vu_of9tcjaa The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=ed_xr1bzuqs
 MITOCW watch?v=ed_xr1bzuqs The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=ed_xr1bzuqs The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW MITRES18_006F10_26_0602_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES18_006F10_26_0602_300k-mp4 FEMALE VOICE: The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational
MITOCW MITRES18_006F10_26_0602_300k-mp4 FEMALE VOICE: The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational
MITOCW ocw feb k
 MITOCW ocw-18-086-13feb2006-220k INTRODUCTION: The following content is provided by MIT OpenCourseWare under a Creative Commons license. Additional information about our license and MIT OpenCourseWare
MITOCW ocw-18-086-13feb2006-220k INTRODUCTION: The following content is provided by MIT OpenCourseWare under a Creative Commons license. Additional information about our license and MIT OpenCourseWare
MITOCW watch?v=0usje5vtiks
 MITOCW watch?v=0usje5vtiks PROFESSOR: Mach-Zehnder-- interferometers. And we have a beam splitter. And the beam coming in, it splits into 2. A mirror-- another mirror. The beams are recombined into another
MITOCW watch?v=0usje5vtiks PROFESSOR: Mach-Zehnder-- interferometers. And we have a beam splitter. And the beam coming in, it splits into 2. A mirror-- another mirror. The beams are recombined into another
MITOCW 18. Quiz Review From Optional Problem Set 8
 MITOCW 18. Quiz Review From Optional Problem Set 8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational
MITOCW 18. Quiz Review From Optional Problem Set 8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational
MITOCW watch?v=vjzv6wjttnc
 MITOCW watch?v=vjzv6wjttnc PROFESSOR: We just saw some random variables come up in the bigger number game. And we're going to be talking now about random variables, just formally what they are and their
MITOCW watch?v=vjzv6wjttnc PROFESSOR: We just saw some random variables come up in the bigger number game. And we're going to be talking now about random variables, just formally what they are and their
MITOCW ocw f99-lec05_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec05_300k This is lecture five in linear algebra. And, it will complete this chapter of the book. So the last section of this chapter is two point seven that talks about permutations,
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec05_300k This is lecture five in linear algebra. And, it will complete this chapter of the book. So the last section of this chapter is two point seven that talks about permutations,
The Cycloid. and the Kinematic Circumference. by Miles Mathis
 return to updates The Cycloid and the Kinematic Circumference First published August 31, 2016 by Miles Mathis Those of you who have read my papers on π=4 will know I have explained that problem using many
return to updates The Cycloid and the Kinematic Circumference First published August 31, 2016 by Miles Mathis Those of you who have read my papers on π=4 will know I have explained that problem using many
MITOCW R9. Generalized Forces
 MITOCW R9. Generalized Forces The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW R9. Generalized Forces The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DerivOfSinXCosX_300k_512kb-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DerivOfSinXCosX_300k_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, this lecture is about the slopes, the derivatives, of two of the great functions of mathematics: sine x and cosine x. Why do I say great
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DerivOfSinXCosX_300k_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, this lecture is about the slopes, the derivatives, of two of the great functions of mathematics: sine x and cosine x. Why do I say great
Note: Please use the actual date you accessed this material in your citation.
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2007 Please use the following citation format: Denis Auroux. 18.02 Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2007. (Massachusetts Institute of
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2007 Please use the following citation format: Denis Auroux. 18.02 Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2007. (Massachusetts Institute of
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k
 MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 3 Numbers and Units
 Numbers in Physics PHYSICS 107 Lecture 3 Numbers and Units We've seen already that even 2500 years ago Aristotle recognized that lengths and times are magnitudes, meaning that any length or time can be
Numbers in Physics PHYSICS 107 Lecture 3 Numbers and Units We've seen already that even 2500 years ago Aristotle recognized that lengths and times are magnitudes, meaning that any length or time can be
MITOCW MIT18_02SCF10Rec_61_300k
 MITOCW MIT18_02SCF10Rec_61_300k JOEL LEWIS: Hi. Welcome back to recitation. In lecture, you've been learning about the divergence theorem, also known as Gauss's theorem, and flux, and all that good stuff.
MITOCW MIT18_02SCF10Rec_61_300k JOEL LEWIS: Hi. Welcome back to recitation. In lecture, you've been learning about the divergence theorem, also known as Gauss's theorem, and flux, and all that good stuff.
Lecture 12: Distances to stars. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 12: Distances to stars Astronomy 111 Why are distances important? Distances are necessary for estimating: Total energy released by an object (Luminosity) Masses of objects from orbital motions
Lecture 12: Distances to stars Astronomy 111 Why are distances important? Distances are necessary for estimating: Total energy released by an object (Luminosity) Masses of objects from orbital motions
MITOCW watch?v=wr88_vzfcx4
 MITOCW watch?v=wr88_vzfcx4 PROFESSOR: So we're building this story. We had the photoelectric effect. But at this moment, Einstein, in the same year that he was talking about general relativity, he came
MITOCW watch?v=wr88_vzfcx4 PROFESSOR: So we're building this story. We had the photoelectric effect. But at this moment, Einstein, in the same year that he was talking about general relativity, he came
Measuring the Stars. Chapter 10. Chapters 17, 19, 18
 Measuring the Stars Chapter 10 Chapters 17, 19, 18 1 2 3 Bessel Hipparcos 4 Lecture-Tutorial on Parallax and the Parsec p 37 6) Consider two stars (C and D) that both exhibit parallax. If C appears to
Measuring the Stars Chapter 10 Chapters 17, 19, 18 1 2 3 Bessel Hipparcos 4 Lecture-Tutorial on Parallax and the Parsec p 37 6) Consider two stars (C and D) that both exhibit parallax. If C appears to
MITOCW ocw f99-lec17_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec17_300k OK, here's the last lecture in the chapter on orthogonality. So we met orthogonal vectors, two vectors, we met orthogonal subspaces, like the row space and null space. Now
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec17_300k OK, here's the last lecture in the chapter on orthogonality. So we met orthogonal vectors, two vectors, we met orthogonal subspaces, like the row space and null space. Now
MITOCW MIT8_01F16_w02s05v06_360p
 MITOCW MIT8_01F16_w02s05v06_360p One of our classic problems to analyze using Newton's second law is the motion of two blocks with a rope that's wrapped around a pulley. So imagine we have a pulley, P,
MITOCW MIT8_01F16_w02s05v06_360p One of our classic problems to analyze using Newton's second law is the motion of two blocks with a rope that's wrapped around a pulley. So imagine we have a pulley, P,
MITOCW watch?v=pqkyqu11eta
 MITOCW watch?v=pqkyqu11eta The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=pqkyqu11eta The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013
 Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
= v = 2πr. = mv2 r. = v2 r. F g. a c. F c. Text: Chapter 12 Chapter 13. Chapter 13. Think and Explain: Think and Solve:
 NAME: Chapters 12, 13 & 14: Universal Gravitation Text: Chapter 12 Chapter 13 Think and Explain: Think and Explain: Think and Solve: Think and Solve: Chapter 13 Think and Explain: Think and Solve: Vocabulary:
NAME: Chapters 12, 13 & 14: Universal Gravitation Text: Chapter 12 Chapter 13 Think and Explain: Think and Explain: Think and Solve: Think and Solve: Chapter 13 Think and Explain: Think and Solve: Vocabulary:
MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec19_300k
 MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec19_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec19_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
PROFESSOR: WELCOME BACK TO THE LAST LECTURE OF THE SEMESTER. PLANNING TO DO TODAY WAS FINISH THE BOOK. FINISH SECTION 6.5
 1 MATH 16A LECTURE. DECEMBER 9, 2008. PROFESSOR: WELCOME BACK TO THE LAST LECTURE OF THE SEMESTER. I HOPE YOU ALL WILL MISS IT AS MUCH AS I DO. SO WHAT I WAS PLANNING TO DO TODAY WAS FINISH THE BOOK. FINISH
1 MATH 16A LECTURE. DECEMBER 9, 2008. PROFESSOR: WELCOME BACK TO THE LAST LECTURE OF THE SEMESTER. I HOPE YOU ALL WILL MISS IT AS MUCH AS I DO. SO WHAT I WAS PLANNING TO DO TODAY WAS FINISH THE BOOK. FINISH
MITOCW MIT8_01F16_w02s07v03_1_360p
 MITOCW MIT8_01F16_w02s07v03_1_360p Let's consider what we call the window washer problem. What we have is suspended from some ceiling. We have a pulley. And the pulley is suspended by a rope, which we're
MITOCW MIT8_01F16_w02s07v03_1_360p Let's consider what we call the window washer problem. What we have is suspended from some ceiling. We have a pulley. And the pulley is suspended by a rope, which we're
ASTRO 1050 LAB #9: Parallax and Angular Size-Distance relations
 ASTRO 1050 LAB #9: Parallax and Angular Size-Distance relations ABSTRACT Parallax is the name given to the technique astronomers use to find distances to the nearby stars. You will calibrate their own
ASTRO 1050 LAB #9: Parallax and Angular Size-Distance relations ABSTRACT Parallax is the name given to the technique astronomers use to find distances to the nearby stars. You will calibrate their own
MITOCW watch?v=ztnnigvy5iq
 MITOCW watch?v=ztnnigvy5iq GILBERT STRANG: OK. So this is a "prepare the way" video about symmetric matrices and complex matrices. We'll see symmetric matrices in second order systems of differential equations.
MITOCW watch?v=ztnnigvy5iq GILBERT STRANG: OK. So this is a "prepare the way" video about symmetric matrices and complex matrices. We'll see symmetric matrices in second order systems of differential equations.
MITOCW MITRES_18-007_Part5_lec3_300k.mp4
 MITOCW MITRES_18-007_Part5_lec3_300k.mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES_18-007_Part5_lec3_300k.mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources
University of Maryland Department of Physics
 Spring 2002 University of Maryland Department of Physics Laura Lising Physics 122 April 24, 2003 Exam #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions. Just the answer counts for these. (8 points each) 1) Suppose
Spring 2002 University of Maryland Department of Physics Laura Lising Physics 122 April 24, 2003 Exam #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions. Just the answer counts for these. (8 points each) 1) Suppose
PHY 123 Lab 1 - Error and Uncertainty and the Simple Pendulum
 To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel. PHY 13 Lab 1 - Error and Uncertainty and the Simple Pendulum Important: You need to print
To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel. PHY 13 Lab 1 - Error and Uncertainty and the Simple Pendulum Important: You need to print
Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars
 Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars Luminosity Luminosity: Rate of energy emitted by star every second. Apparent brightness (flux): Amount of energy passing through every second per unit area. Luninosity =
Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars Luminosity Luminosity: Rate of energy emitted by star every second. Apparent brightness (flux): Amount of energy passing through every second per unit area. Luninosity =
Instructor (Brad Osgood)
 TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture26 Instructor (Brad Osgood): Relax, but no, no, no, the TV is on. It's time to hit the road. Time to rock and roll. We're going to now turn to our last topic
TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture26 Instructor (Brad Osgood): Relax, but no, no, no, the TV is on. It's time to hit the road. Time to rock and roll. We're going to now turn to our last topic
Experiment 0 ~ Introduction to Statistics and Excel Tutorial. Introduction to Statistics, Error and Measurement
 Experiment 0 ~ Introduction to Statistics and Excel Tutorial Many of you already went through the introduction to laboratory practice and excel tutorial in Physics 1011. For that reason, we aren t going
Experiment 0 ~ Introduction to Statistics and Excel Tutorial Many of you already went through the introduction to laboratory practice and excel tutorial in Physics 1011. For that reason, we aren t going
MITOCW Investigation 3, Part 1
 MITOCW Investigation 3, Part 1 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW Investigation 3, Part 1 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Instructor (Brad Osgood)
 TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture21 Instructor (Brad Osgood): Here we go. All right. The exams, you remember the exams, I think they've all been graded, and the scores have all been entered.
TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture21 Instructor (Brad Osgood): Here we go. All right. The exams, you remember the exams, I think they've all been graded, and the scores have all been entered.
MITOCW watch?v=ko0vmalkgj8
 MITOCW watch?v=ko0vmalkgj8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=ko0vmalkgj8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW ocw f08-lec19_300k
 MITOCW ocw-5-111-f08-lec19_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-5-111-f08-lec19_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam]
![Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam]](/thumbs/85/91935248.jpg) Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Although we can be certain that other stars are as complex as the Sun, we will try to
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Although we can be certain that other stars are as complex as the Sun, we will try to
Astronomy 141 Life in the Universe Professor Gaudi Homework #4 Solutions
 Astronomy 141 Life in the Universe Autumn Quarter 008 Prof Gaudi Homework #4 Solutions These questions concern the concept of targets for searches for extrasolar planets specifically (a) the number of
Astronomy 141 Life in the Universe Autumn Quarter 008 Prof Gaudi Homework #4 Solutions These questions concern the concept of targets for searches for extrasolar planets specifically (a) the number of
MITOCW Investigation 4, Part 3
 MITOCW Investigation 4, Part 3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW Investigation 4, Part 3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
CS 124 Math Review Section January 29, 2018
 CS 124 Math Review Section CS 124 is more math intensive than most of the introductory courses in the department. You re going to need to be able to do two things: 1. Perform some clever calculations to
CS 124 Math Review Section CS 124 is more math intensive than most of the introductory courses in the department. You re going to need to be able to do two things: 1. Perform some clever calculations to
MITOCW watch?v=rwzg8ieoc8s
 MITOCW watch?v=rwzg8ieoc8s PROFESSOR: ih bar d psi dt equal E psi where E hat is equal to p squared over 2m, the operator. That is the Schrodinger equation. The free particle Schrodinger equation-- you
MITOCW watch?v=rwzg8ieoc8s PROFESSOR: ih bar d psi dt equal E psi where E hat is equal to p squared over 2m, the operator. That is the Schrodinger equation. The free particle Schrodinger equation-- you
Lab 1: Measurement, Uncertainty, and Uncertainty Propagation
 Lab 1: Measurement, Uncertainty, and Uncertainty Propagation 17 ame Date Partners TA Section Lab 1: Measurement, Uncertainty, and Uncertainty Propagation The first principle is that you must not fool yourself
Lab 1: Measurement, Uncertainty, and Uncertainty Propagation 17 ame Date Partners TA Section Lab 1: Measurement, Uncertainty, and Uncertainty Propagation The first principle is that you must not fool yourself
Ted Pedersen. University of Minnesota, Duluth
 Ted Pedersen University of Minnesota, Duluth http://www.d.umn.edu/~tpederse tpederse@d.umn.edu The road from good software engineering to good science ...is a two way street... Three Themes : Philosophy
Ted Pedersen University of Minnesota, Duluth http://www.d.umn.edu/~tpederse tpederse@d.umn.edu The road from good software engineering to good science ...is a two way street... Three Themes : Philosophy
Properties of Stars. 1.1 Brightnesses of Stars
 Properties of Stars 1.1 Brightnesses of Stars I m sure you have noticed that some stars are very bright, others less bright, and some are quite dim. There is a true brightness of a star and an apparent
Properties of Stars 1.1 Brightnesses of Stars I m sure you have noticed that some stars are very bright, others less bright, and some are quite dim. There is a true brightness of a star and an apparent
Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis
 Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis Advance Study Assignment Please contact Dr. Reuven at yreuven@mhrd.org if you have any questions Read the Theory part of the experiment (pages 2-14) and
Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis Advance Study Assignment Please contact Dr. Reuven at yreuven@mhrd.org if you have any questions Read the Theory part of the experiment (pages 2-14) and
MITOCW MIT18_01SCF10Rec_24_300k
 MITOCW MIT18_01SCF10Rec_24_300k JOEL LEWIS: Hi. Welcome back to recitation. In lecture, you've been doing related rates problems. I've got another example for you, here. So this one's a really tricky one.
MITOCW MIT18_01SCF10Rec_24_300k JOEL LEWIS: Hi. Welcome back to recitation. In lecture, you've been doing related rates problems. I've got another example for you, here. So this one's a really tricky one.
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Demonstrating Rotational Inertia (or Moment of Inertia)
 Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Demonstrating Rotational Inertia (or Moment of Inertia) Have you ever struggled to describe Rotational Inertia to your students? Even worse, have you ever struggled to understand
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Demonstrating Rotational Inertia (or Moment of Inertia) Have you ever struggled to describe Rotational Inertia to your students? Even worse, have you ever struggled to understand
California State Science Fair
 California State Science Fair How to Estimate the Experimental Uncertainty in Your Science Fair Project Part 2 -- The Gaussian Distribution: What the Heck is it Good For Anyway? Edward Ruth drruth6617@aol.com
California State Science Fair How to Estimate the Experimental Uncertainty in Your Science Fair Project Part 2 -- The Gaussian Distribution: What the Heck is it Good For Anyway? Edward Ruth drruth6617@aol.com
Achilles: Now I know how powerful computers are going to become!
 A Sigmoid Dialogue By Anders Sandberg Achilles: Now I know how powerful computers are going to become! Tortoise: How? Achilles: I did curve fitting to Moore s law. I know you are going to object that technological
A Sigmoid Dialogue By Anders Sandberg Achilles: Now I know how powerful computers are going to become! Tortoise: How? Achilles: I did curve fitting to Moore s law. I know you are going to object that technological
Lab 8: Measuring Distances Using Parallax
 Lab 8: Measuring Distances Using Parallax Names: 8.1.1 Parallax in the classroom Measure each object s shift THREE TIMES, and then take the average. Try to measure to the nearest fraction of a tick mark.
Lab 8: Measuring Distances Using Parallax Names: 8.1.1 Parallax in the classroom Measure each object s shift THREE TIMES, and then take the average. Try to measure to the nearest fraction of a tick mark.
Instructor (Brad Osgood)
 TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture14 Instructor (Brad Osgood):Okay. Let me circulate, starting over this side of the room this time, the sign-up sheet for the midterm exams. So remember, next
TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture14 Instructor (Brad Osgood):Okay. Let me circulate, starting over this side of the room this time, the sign-up sheet for the midterm exams. So remember, next
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3
 October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
This is particularly true if you see long tails in your data. What are you testing? That the two distributions are the same!
 Two sample tests (part II): What to do if your data are not distributed normally: Option 1: if your sample size is large enough, don't worry - go ahead and use a t-test (the CLT will take care of non-normal
Two sample tests (part II): What to do if your data are not distributed normally: Option 1: if your sample size is large enough, don't worry - go ahead and use a t-test (the CLT will take care of non-normal
How big is the Universe and where are we in it?
 Announcements Results of clicker questions from Monday are on ICON. First homework is graded on ICON. Next homework due one minute before midnight on Tuesday, September 6. Labs start this week. All lab
Announcements Results of clicker questions from Monday are on ICON. First homework is graded on ICON. Next homework due one minute before midnight on Tuesday, September 6. Labs start this week. All lab
Lecture 1 Notes: 06 / 27. The first part of this class will primarily cover oscillating systems (harmonic oscillators and waves).
 Lecture 1 Notes: 06 / 27 The first part of this class will primarily cover oscillating systems (harmonic oscillators and waves). These systems are very common in nature - a system displaced from equilibrium
Lecture 1 Notes: 06 / 27 The first part of this class will primarily cover oscillating systems (harmonic oscillators and waves). These systems are very common in nature - a system displaced from equilibrium
Solving and Graphing a Linear Inequality of a Single Variable
 Chapter 3 Graphing Fundamentals Section 3.1 Solving and Graphing a Linear Inequality of a Single Variable TERMINOLOGY 3.1 Previously Used: Isolate a Variable Simplifying Expressions Prerequisite Terms:
Chapter 3 Graphing Fundamentals Section 3.1 Solving and Graphing a Linear Inequality of a Single Variable TERMINOLOGY 3.1 Previously Used: Isolate a Variable Simplifying Expressions Prerequisite Terms:
MITOCW watch?v=nxgobnabn7u
 MITOCW watch?v=nxgobnabn7u The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=nxgobnabn7u The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec17_300k
 MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec17_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec17_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Where Is Newton Taking Us? And How Fast?
 Name: Where Is Newton Taking Us? And How Fast? In this activity, you ll use a computer applet to investigate patterns in the way the approximations of Newton s Methods settle down to a solution of the
Name: Where Is Newton Taking Us? And How Fast? In this activity, you ll use a computer applet to investigate patterns in the way the approximations of Newton s Methods settle down to a solution of the
MITOCW Investigation 6, Part 6
 MITOCW Investigation 6, Part 6 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW Investigation 6, Part 6 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Post Activity/ Homework Questions: 1. Before a star forms A. Where do you think the gas and dust originally came from?
 Critical Thinking Questions: (work on these with a partner) 1. During the formation of a Red Giant Star, the core of a star pushes the outer shell back only enough to make the star larger. However, during
Critical Thinking Questions: (work on these with a partner) 1. During the formation of a Red Giant Star, the core of a star pushes the outer shell back only enough to make the star larger. However, during
6.041SC Probabilistic Systems Analysis and Applied Probability, Fall 2013 Transcript Tutorial:A Random Number of Coin Flips
 6.041SC Probabilistic Systems Analysis and Applied Probability, Fall 2013 Transcript Tutorial:A Random Number of Coin Flips Hey, everyone. Welcome back. Today, we're going to do another fun problem that
6.041SC Probabilistic Systems Analysis and Applied Probability, Fall 2013 Transcript Tutorial:A Random Number of Coin Flips Hey, everyone. Welcome back. Today, we're going to do another fun problem that
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsMotion_300k_512kb-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsMotion_300k_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, this lecture, this day, is differential equations day. I just feel even though these are not on the BC exams, that we've got everything
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsMotion_300k_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, this lecture, this day, is differential equations day. I just feel even though these are not on the BC exams, that we've got everything
LECTURE 26 GRAVITY. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 26 GRAVITY Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 26 2 Reading chapter 12-1 to 12-2 Newton s law of universal gravitation Gravitational attraction of spherical bodies Newton s universal law of gravitation
LECTURE 26 GRAVITY Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 26 2 Reading chapter 12-1 to 12-2 Newton s law of universal gravitation Gravitational attraction of spherical bodies Newton s universal law of gravitation
Laboratory 3: Acceleration due to gravity
 Physics 1020 NAME Laboratory 3: Acceleration due to gravity Prelab: Please do this prelab before you read the lab writeup. In Laboratory 1 you made use of the value of g, the acceleration due to gravity
Physics 1020 NAME Laboratory 3: Acceleration due to gravity Prelab: Please do this prelab before you read the lab writeup. In Laboratory 1 you made use of the value of g, the acceleration due to gravity
MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTIES
 MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTIES What distinguishes science rom philosophy is that it is grounded in experimental observations. These observations are most striking when they take the orm o a quantitative measurement.
MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTIES What distinguishes science rom philosophy is that it is grounded in experimental observations. These observations are most striking when they take the orm o a quantitative measurement.
MITOCW ocw f07-lec39_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18-01-f07-lec39_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18-01-f07-lec39_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw f07-lec36_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18-01-f07-lec36_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18-01-f07-lec36_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Lecture 2. ASTR 111 Section 002 Introductory Astronomy: Solar System. Dr. Weigel
 Lecture 2 ASTR 111 Section 002 Introductory Astronomy: Solar System Dr. Weigel Reading for this week The reading for this week is Chapter 1 (all) and Chapter 2 (sections 2.1 2.2 only) The quiz will cover
Lecture 2 ASTR 111 Section 002 Introductory Astronomy: Solar System Dr. Weigel Reading for this week The reading for this week is Chapter 1 (all) and Chapter 2 (sections 2.1 2.2 only) The quiz will cover
5. A particular star has an angle of parallax of 0.2 arcsecond. What is the distance to this star? A) 50 pc B) 2 pc C) 5 pc D) 0.
 Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
MITOCW MIT6_262S11_lec18_300k.mp4
 MITOCW MIT6_262S11_lec18_300k.mp4 NARRATOR: The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MIT6_262S11_lec18_300k.mp4 NARRATOR: The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MIT20_020S09_06_inverter
 MITOCW MIT20_020S09_06_inverter >> Izzy: Dude, I like what you built there. What's it do? >> Dude: Oh...hi Iz. This is a cool bug. I made it using an electronics building kit that Sally got me. She wanted
MITOCW MIT20_020S09_06_inverter >> Izzy: Dude, I like what you built there. What's it do? >> Dude: Oh...hi Iz. This is a cool bug. I made it using an electronics building kit that Sally got me. She wanted
MITOCW watch?v=fkfsmwatddy
 MITOCW watch?v=fkfsmwatddy PROFESSOR: We've seen a lot of functions in introductory calculus-- trig functions, rational functions, exponentials, logs and so on. I don't know whether your calculus course
MITOCW watch?v=fkfsmwatddy PROFESSOR: We've seen a lot of functions in introductory calculus-- trig functions, rational functions, exponentials, logs and so on. I don't know whether your calculus course
EXPERIMENT : Work and Energy. Topics of investigation: The relation between force and acceleration
 EXPERIMENT 2000031: Work and Energy Topics of investigation: The relation between force and acceleration Read about this topic in: Serway, Ch 7, 8; C&J Ch 6 Toolkit: Computer Laboratory interface & software
EXPERIMENT 2000031: Work and Energy Topics of investigation: The relation between force and acceleration Read about this topic in: Serway, Ch 7, 8; C&J Ch 6 Toolkit: Computer Laboratory interface & software
MITOCW Lec 11 MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Fall 2010
 MITOCW Lec 11 MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Fall 2010 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high
MITOCW Lec 11 MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Fall 2010 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high
MITOCW watch?v=wupemfon9lg
 MITOCW watch?v=wupemfon9lg The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=wupemfon9lg The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Averaging, Errors and Uncertainty
 Averaging, Errors and Uncertainty Types of Error There are three types of limitations to measurements: 1) Instrumental limitations Any measuring device can only be used to measure to with a certain degree
Averaging, Errors and Uncertainty Types of Error There are three types of limitations to measurements: 1) Instrumental limitations Any measuring device can only be used to measure to with a certain degree
MITOCW big_picture_derivatives_512kb-mp4
 MITOCW big_picture_derivatives_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, hi. This is the second in my videos about the main ideas, the big picture of calculus. And this is an important one, because I want to introduce
MITOCW big_picture_derivatives_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, hi. This is the second in my videos about the main ideas, the big picture of calculus. And this is an important one, because I want to introduce
For those of you who are taking Calculus AB concurrently with AP Physics, I have developed a
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Greetings, For those of you who are taking Calculus AB concurrently with AP Physics, I have developed a brief introduction to Calculus that gives you an operational knowledge of
AP Physics C: Mechanics Greetings, For those of you who are taking Calculus AB concurrently with AP Physics, I have developed a brief introduction to Calculus that gives you an operational knowledge of
MITOCW ocw f99-lec16_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec16_300k OK. Here's lecture sixteen and if you remember I ended up the last lecture with this formula for what I called a projection matrix. And maybe I could just recap for a minute
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec16_300k OK. Here's lecture sixteen and if you remember I ended up the last lecture with this formula for what I called a projection matrix. And maybe I could just recap for a minute
MITOCW watch?v=r2nmwesncts
 MITOCW watch?v=r2nmwesncts The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=r2nmwesncts The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties. Scott Oser Lecture #12
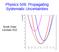 Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties Scott Oser Lecture #1 1 Additive offset model Suppose we take N measurements from a distribution, and wish to estimate the true mean of the underlying
Physics 509: Propagating Systematic Uncertainties Scott Oser Lecture #1 1 Additive offset model Suppose we take N measurements from a distribution, and wish to estimate the true mean of the underlying
MITOCW ocw f99-lec23_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec23_300k -- and lift-off on differential equations. So, this section is about how to solve a system of first order, first derivative, constant coefficient linear equations. And if
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec23_300k -- and lift-off on differential equations. So, this section is about how to solve a system of first order, first derivative, constant coefficient linear equations. And if
PHY 221 Lab 9 Work and Energy
 PHY 221 Lab 9 Work and Energy Name: Partners: Before coming to lab, please read this packet and do the prelab on page 13 of this handout. Goals: While F = ma may be one of the most important equations
PHY 221 Lab 9 Work and Energy Name: Partners: Before coming to lab, please read this packet and do the prelab on page 13 of this handout. Goals: While F = ma may be one of the most important equations
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsGrowth_300k_512kb-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsGrowth_300k_512kb-mp4 GILBERT STRANG: OK, today is about differential equations. That's where calculus really is applied. And these will be equations that describe growth.
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsGrowth_300k_512kb-mp4 GILBERT STRANG: OK, today is about differential equations. That's where calculus really is applied. And these will be equations that describe growth.
GALILEAN RELATIVITY. I defined inertial mass conceptually as a measure of how hard it is to change an
 GALILEAN RELATIVITY I defined inertial mass conceptually as a measure of how hard it is to change an object's state of motion, the implication being that if you don't interfere, the object's motion won't
GALILEAN RELATIVITY I defined inertial mass conceptually as a measure of how hard it is to change an object's state of motion, the implication being that if you don't interfere, the object's motion won't
MITOCW watch?v=7q32wnm4dew
 MITOCW watch?v=7q32wnm4dew BARTON ZWIEBACH: Hydrogen atom is the beginning of our analysis. It still won't solve differential equations, but we will now two particles, a proton, whose coordinates are going
MITOCW watch?v=7q32wnm4dew BARTON ZWIEBACH: Hydrogen atom is the beginning of our analysis. It still won't solve differential equations, but we will now two particles, a proton, whose coordinates are going
