Dynamic Characteristic and Power Consumption on an Electro-Pneumatic Hybrid Positioning System
|
|
|
- Luke Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2B2-4 Proceedings of the 6th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TSUKUBA 2005 November 7-10, 2005 Dynamic Characteristic and Power Consumption on an Electro-Pneumatic Hybrid Positioning System Hiroshi HI GO*, Yasuo SAKURAI**, Takeshi NAKADA***, Kazuhiro TANAKA*, and Katsuya NAGAYAMA* * Department of Mechanical Information Science and Technology Kyushu Institute of Technology Kawatsu, Iizuka, Fukuoka, Japan ** Department of Mechanical Engineering, Ashikaga Institute of Technology Oomae, Ashikaga, Tochigi, Japan *** Department of Environment Integration and design, Tokyo Denki University Muzaigakuendai, Inzai, Chiba, Japan, ABSTRACT This paper deals with the dynamic characteristics of an electro-pneumatic hybrid positioning system. This system is composed of a pneumatic, an electric and a mechanical driving sub-system. The pneumatic driving system controls the pressure supporting the inertial mass, which means that the pressure is correspondent to the gravitational force acting on it. And the electric driving system with small capacity moves the inertial mass vertically through a ball screw as a mechanical driving sub-system. In the present study, in order to developing the electro-pneumatic hybrid positioning system, the mathematical model of this system has been refined by comparing calculation data with the experimental results, especially by measuring precisely frictional force of the ball screw. And the power consumption as well as the dynamic characteristics has been investigated numerically when the inertial mass is moved vertically upwards and downwards during one cycle by the electric driving system through the ball screw. The data on the power consumption during one cycle will be useful to select a suitable driving motor at the design stage. KEY WORDS Electro-pneumatic hybrid positioning system, Dynamic characteristics, Pressure control, Bondgraphs, Modeling NOMENCLATURE Ae: Effective area of the cylinder [m2] Ar: Area of rod side cylinder [m2] Ah: Area of head side cylinder [m2] C: Frictional loss coefficient [Ns/m] F: Force [N] k: Specific heat ratio [-] K: Rigidity of coupling [Nm/rad] Iz: Momentum of shaft [kgm2] 1: Lead of ball screw [m] m: Mass flow rate [kg/s] M: Inertial mass [kg] P: Pressure [Pa] Q: Flow rate R: Gas constant [m3/s] [J/(kgK)] T: Temperature [K] v: Velocity [m/s] co: Rotational speed [rad/s] r: Torque [Nm] INTRODUCTION A pneumatic system has some advantages such as safety, ease to maintenance, environment, and so on. Then the pneumatic system is used various automation machines. However, the pneumatic system is difficult to control velocity and positioning of an inertial mass precisely [1-2]. To improve these disadvantages, an electro-pneumatic hybrid system is proposed [3]. In this system, supplied air pressure supports an inertial mass and the positioning of the inertial mass is controlled by a servomotor. This mechanism can easily control the positioning of the inertial mass more precise than a
2 pneumatic system. However, when this actuator moves with suddenly large inertial mass, the servomotor faces unpredictably large torque and stops automatically. To avoid this stopping, it is important to predict the load of the servomotor precisely by analyzing the dynamic characteristics of the system. Bondgraph method is very convenient to predict the system dynamic characteristics and calculate power consumption. The method is available in various systems composed mechanical, electrical and hydraulic components because it is based on the viewpoint of power conservation. This method has been used for prediction of dynamic characteristics and designing real systems [4-6]. In order to establish a design method of an electro-pneumatic hybrid system, the Bondgraph method is surely useful. The objectives of this study are followings. 1. To investigate frictional loss of the electro-pneumatic actuator by experiment. 2. To construct a mathematical system model of the electro-pneumatic actuator. 3. To compare experimental results with calculated results when this actuator is operated and to verify the mathematical model of the system. ELECTRO-PNEUMATIC ACTUATOR gure 1 shows the electro-pneumatic hybrid actuator. The Electro-pneumatic actuator consists of a servomotor, a cylinder, a ball screw, a rod and a air supply system. The servomotor is combined with the ball screw. The rod is combined with the nut. The bottom part of ball screw is inside the rod, when the servomotor is driven, the ball screw rotates, the nut moves and the inertial mass also moves. The pressure of air supply system is correspondent gravitational force acting on an inertial mass. Therefore, even a servo motor with low-capacity can control a large inertial mass. EXPERIMENTAL EQUIPMENT Experimental equipment is shown in Fig.2. The pressure of the air supply unit is controlled by an electric-pneumatic regulator and is provided into the rod side of the cylinder. The pressure of another side chanber is atmospheric pressure. PC controls the electro-pneumatic regulator and angular velocity of the servomotor for precise positioning. In the experiment torque and rotational degree of the servomotor are measured. SIMULATION MODEL Generally, a physical system consists of electrical, mechanical, fluid, thermal system and so on. Because power flows between elements in physical systems, the systems can be expressed using power train. Bondgraph method is one of the system expression method based on power train. When power flows from a system to a sub-system, these two elements can be connected by a line, called bond, which indicates power flow, as shown in Fig.3. Power is the product of effort and flow variables in each system, shown in Table 1. Consequently, the power bond has two power variables, effort and flow. In Bondgraph method, an element indicates a physical quantity in each eld, shown as Table 2. fi Tablel Variables to Table2 Elements Fig.1 Schematic of Electro-pneumatic actuator
3 Fig. 2 Experimental apparatus (2) Fig. 3 Bond A system bondgraph model of the electro-pneumatic actuator is shown in Fig. 4. Output pressure of an air supply unit is assumed to be constant. Then an air supply unit is modeled by 'Se: Air supply unit' element. The following equation can be used for this element. Subscript indicates the number of bond. (1) An electric-pneumatic regulator is modeled by 'R: Valve' element and its constitutive equation is expressed as follows. Where Ae is effective area of the electric-pneumatic (3) regulator, Pi is pressure of air supply unit, T1 is temperature of air. C: Compressibility' ' element means compressibility of the air in the rod end chamber of the pneumatic cylinder. Its constitutive equation is expressed as follows. (4) Where Po is initial pressure of rod-end chamber, Vo is initial volume of rod-end chamber, Tt-1 is calculation
4 Fig. 4 System bondgraph model result of temperature, Pt-1 is calculation result of pressure. Each variable are calculational results before 1 time step. ' TF1:Cylinder head _side', 'TF1: Cylinder_rod_side' mean pressure area of piston, and its constitutive equation is expressed as follows Where Ar is area of rod side chamber, Ah is area of head side chamber. By these elements, pressure is changed mechanical force. SF: Servomotor' ' element represents angular velocity of a servomotor. The objective of present study is to establish a mathematical model of an electro-pneumatic hybrid positioning system. Therefore, the accurate mathematical model of the servomotor was not derived. (5) (6) (7) (8) Angular velocity w 9 is measured in experiment and used as an input to the system in simulation. C: Coupling' element means ' the torsion rigidity of the coupling, this equation is represented as follows. where K is rigidity of coupling. (9) I: Inertial _moment'' element means moment of ball screw. This equation is represented as follows (10) where Iz is the inertial momentum of shaft A ball screw is represented by 'TF: Ball screw' element for change from rotation motion to liner motion, and its constitutive equation is expressed as follows (11)
5 Relationship between the velocity and frictional coefficient is expressed as where l is lead of ball screw. R: Loss _Bscrew' ' and 'C: Elasticity_Bscrew' element mean the characteristic of a nut. 'I: Inertial mass' means an inertial mass. This constitutive equation is expressed as follows simulation. The frictional coefficient used here was taken from the experiment and was placed R element for the ' R: Loss' means frictional loss of cylinder. It is difficult to decide a frictional loss of a cylinder from using only parameters of equipment. Accordingly, this parameter is measured by experiment. Therefore this constitutive equation is expressed as 'Se: Gravity' indicates gravity force of an inertial mass. It is constant value. Fig. 5 Frictional Loss Table3 Experimental Parameters RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 1.Frictional loss Frictional force is measured by experiments. The pressure which is controlled by an electric-pneumatic regulator is set at the constant value correspondent to the gravitational force of an inertial mass. By rotating the servomotor, an inertial mass moves upwards or downwards. The relationship between force of the cylinder and moving velocity of the inertial mass is followings. F, force of the nut is calculated by pressure P, torque T and inertial mass M (Eq.(17)). Pressure and torque were measured. The coefficient of frictional force is calculated by Eq.(18). Fig. 5 shows the measured results of the frictional force. It can be seen from this figure that the frictional loss is affected by the velocity of inertial mass. 2. Dynamic characteristics and power consumption The experiment of dynamic characteristic of the
6 electro-pneumatic actuator is performed. Prior to the experiment, the position of the inertial mass was set at the lowest point and the control of the pressure acting on the inertial mass was started. The input signal to determine angular velocity of servomotor was added to the servomotor controller. And then, inertial mass moved upwards by 100 mm, then stopped, and moved downwards by 100 mm. These experiments were carried out at same angular velocities of the servomotor. Experimental results are inputted as the angular velocity in the simulation. Table 3 shows experimental parameters. Only parameters of friction loss coefficient and input angular velocity are the experimental data and the others are catalogue value. Simulation and experimental results are shown in Fig. 6. It can be seen from this figure that the experimental result and calculation result are agree well when inertial mass is moved. However, when inertial mass is stopping, calculation result is different from experimental ones. It might be thought that static friction at a moment when the servomotor stops is different in each case of experiments. When the mass moves downwards, the calculation data is stable compared with experimental data. This is because the capacity of the electro-pneumatic regulator is not suitably determined. If new regulator with more capacity is used, the both data will agree well. Any well, the data comes to a close match with an only minor discrepancy. Fig. 7 Power of servomotor Fig. 7 is comparison of calculation results with experimental ones on servomotor power. From this gure, calculation result and experimental one are agree fi well. Therefore, it is seemed that this model can predict the power of servomotor of electro-pneumatic hybrid actuator. CONCLUSION The mathematical model of the electro-pneumatic hybrid actuator was proposed to predict the system dynamic characteristics and power consumption. The frictional loss of the actuator, which is the most difficult parameter to be determined in the system, was measured precisely at moving upwards and downwards during the cycle. As a result, calculation result agrees well with experimental results. This proved that this mathematical model can predict dynamic behaviors of the system and the power of servomotor. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The authors would like to thank SMC Co, Ltd. for providing the experimental apparatus and helpful suggestions. REFERENCES 900[rpm] Fig. 6 Torque 1. SHIH, Ming chang and LUOR, Niarn-liarng. Self-tuning Neural Fuzzy Control the Position of a Pneumatic Cylinder Under Vertical Load. Proc of 6th FLUCOME, Sherbrooke CANADA, Cd-ROM, Baihai ZHANG, Bondgraph Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Characteristics of a Pneumatic System with an Air Cushion Cylinder, 5th JFPS International Symposium, , (2002). 3. Y. SAKURAI, K. TANAKA, T. NAKADA, Dynamic Characteristic On An Electro-Pneumatic Hybrid Positioning System, 7th Int. Symp. on Fluid Control, Measurement and Visualization, E. Benjamin Wylie, Victor L. Streeter, Fluid Transient in Systems, p.2-9, PRENTICE HALL Rosenberg R. C. and Kamopp D. C. Introduction to Physical System Dynamics, McGraw-Hill, Thoma J. Simulation by Bondgraphs, Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Load Prediction-based Energy-efficient Hydraulic Actuation. of a Robotic Arm. 1 Introduction
 oad rediction-based Energy-efficient Hydraulic ctuation of a Robotic rm Miss Can Du, rof ndrew lummer and Dr Nigel Johnston fixed displacement pump. This can reduce the weight of plant compared with the
oad rediction-based Energy-efficient Hydraulic ctuation of a Robotic rm Miss Can Du, rof ndrew lummer and Dr Nigel Johnston fixed displacement pump. This can reduce the weight of plant compared with the
POLE ASSIGNMENT CONTROL ON ROBOT ARM USING PNEUMATIC ACTUATORS. Osamu Oyama, Masakazu Harada. Faculty of Engineering Meiji University Kawasaki, Japan
 POLE ASSIGNMENT CONTROL ON ROBOT ARM USING PNEUMATIC ACTUATORS Osamu Oyama, Masakazu Harada Faculty of Engineering Meiji University Kawasaki, Japan ABSTRACT Pneumatic actuators are cheaper and lighter
POLE ASSIGNMENT CONTROL ON ROBOT ARM USING PNEUMATIC ACTUATORS Osamu Oyama, Masakazu Harada Faculty of Engineering Meiji University Kawasaki, Japan ABSTRACT Pneumatic actuators are cheaper and lighter
Master-Slave Control for a Tele-Operation System of Construction Robot
 2C13 Master-Slave Control for a Tele-Operation System of Construction Robot (Improved Method of Control Compared with a Variable-Gain Symmetric-Position) Hidetoshi KATO*, Hironao YAMADA** and Takayoshi
2C13 Master-Slave Control for a Tele-Operation System of Construction Robot (Improved Method of Control Compared with a Variable-Gain Symmetric-Position) Hidetoshi KATO*, Hironao YAMADA** and Takayoshi
SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY ACTUATOR PROTECTED BY ROLLED FILM TUBE FOR ARTIFICIAL MUSCLE
 P2-47 Proceedings of the 7th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TOYAMA 28 September 1-18, 28 SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY ACTUATOR PROTECTED BY ROLLED FILM TUBE FOR ARTIFICIAL MUSCLE Toshiya ISHIKAWA*
P2-47 Proceedings of the 7th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TOYAMA 28 September 1-18, 28 SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY ACTUATOR PROTECTED BY ROLLED FILM TUBE FOR ARTIFICIAL MUSCLE Toshiya ISHIKAWA*
Flywheels-Function need and Operation
 STUDY OF FLYWHEEL Flywheel definition A flywheel is an inertial energy-storage device. It absorbs mechanical energy and serves as a reservoir, storing energy during the period when the supply of energy
STUDY OF FLYWHEEL Flywheel definition A flywheel is an inertial energy-storage device. It absorbs mechanical energy and serves as a reservoir, storing energy during the period when the supply of energy
STICK-SLIP MOTION IN PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS DRIVEN BY METER-OUT CIRCUIT
 STICK-SLIP MOTION IN PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS DRIVEN BY METER-OUT CIRCUIT Toshinori FUJITA*, Luis R. TOKASHIKI*, Toshiharu KAGAWA* * Tokyo Institute of Technology Precision and Intelligence Laboratory 4259,
STICK-SLIP MOTION IN PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS DRIVEN BY METER-OUT CIRCUIT Toshinori FUJITA*, Luis R. TOKASHIKI*, Toshiharu KAGAWA* * Tokyo Institute of Technology Precision and Intelligence Laboratory 4259,
DYNAMICS OF PNEUMATIC CYLINDER SYSTEMS
 DYNAMICS OF PNEUMATIC CYLINDER SYSTEMS Toshinori FUJITA*, Jiseong JANG*, Toshiharu KAGAWA* and Masaaki TAKEUCHI** *Department of Control & Systems Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Tokyo Institute of
DYNAMICS OF PNEUMATIC CYLINDER SYSTEMS Toshinori FUJITA*, Jiseong JANG*, Toshiharu KAGAWA* and Masaaki TAKEUCHI** *Department of Control & Systems Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Tokyo Institute of
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
is acting on a body of mass m = 3.0 kg and changes its velocity from an initial
 PHYS 101 second major Exam Term 102 (Zero Version) Q1. A 15.0-kg block is pulled over a rough, horizontal surface by a constant force of 70.0 N acting at an angle of 20.0 above the horizontal. The block
PHYS 101 second major Exam Term 102 (Zero Version) Q1. A 15.0-kg block is pulled over a rough, horizontal surface by a constant force of 70.0 N acting at an angle of 20.0 above the horizontal. The block
Reduction of Mechanical Loss of Flywheel Energy Storage System with Spherical Spiral Groove Bearing
 Reduction of Mechanical Loss of Flywheel Energy Storage System with Spherical Spiral Groove Bearing Takeo Suuki, Takumi Masuda, Jun-ichi Itoh, Noboru Yamada Nagaoka University of Technology Nagaoka, Niigata,
Reduction of Mechanical Loss of Flywheel Energy Storage System with Spherical Spiral Groove Bearing Takeo Suuki, Takumi Masuda, Jun-ichi Itoh, Noboru Yamada Nagaoka University of Technology Nagaoka, Niigata,
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Precision Ball Screw/Spline
 58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
Vane Type Rotary Actuators Series Variations
 Vane Type Rotary Actuators Series Variations Vane Type Exterior CRB Series 0,, 0,, CRBU Series 0,, 0,, CRB Series, 6, 80, Has a compact body with exterior dimensions that do not change regardless of the
Vane Type Rotary Actuators Series Variations Vane Type Exterior CRB Series 0,, 0,, CRBU Series 0,, 0,, CRB Series, 6, 80, Has a compact body with exterior dimensions that do not change regardless of the
LECTURE 8. Hydraulic machines and systems II 2002 MIT PSDAM LAB
 LECTURE 8 Hydraulic machines and systems II Basic hydraulic machines & components Graphical Nomenclature Arrows show direction of flow Control Volume Pipe or hose with fluid flow Pipe or hose without fluid
LECTURE 8 Hydraulic machines and systems II Basic hydraulic machines & components Graphical Nomenclature Arrows show direction of flow Control Volume Pipe or hose with fluid flow Pipe or hose without fluid
Radial Turbine with Pitch-controlled Guide Vanes for Wave Energy Conversion
 Radial Turbine with Pitch-controlled Guide Vanes for Wave Energy Conversion M. Takao 1, M. Suzuki, T. Setoguchi 3, B. Pereiras and F. Castro 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Matsue College of Technology,
Radial Turbine with Pitch-controlled Guide Vanes for Wave Energy Conversion M. Takao 1, M. Suzuki, T. Setoguchi 3, B. Pereiras and F. Castro 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Matsue College of Technology,
FPMC PASSIVITY BASED BACKSTEPPING CONTROL FOR TRAJECTORY TRACKING USING A HYDRAULIC TRANSFORMER
 Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 25 Symposium on Fluid Power & Motion Control FPMC25 October 2-4, 25, Chicago, Illinois, United States FPMC25-968 PASSIVITY BASED BACKSTEPPING CONTROL FOR TRAJECTORY TRACKING
Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 25 Symposium on Fluid Power & Motion Control FPMC25 October 2-4, 25, Chicago, Illinois, United States FPMC25-968 PASSIVITY BASED BACKSTEPPING CONTROL FOR TRAJECTORY TRACKING
ME332 FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY (PART II)
 ME332 FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY (PART II) Mihir Sen Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Version: April 2, 2002 Contents Unit 5: Momentum transfer
ME332 FLUID MECHANICS LABORATORY (PART II) Mihir Sen Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Version: April 2, 2002 Contents Unit 5: Momentum transfer
Impact. m k. Natural Period of Vibration τ. Static load Gray area Impact load t > 3 τ. Absorbing energy. Carrying loads
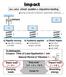 Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) APPLIED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) APPLIED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009 (6021024) 30 October (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used. This question
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) APPLIED ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY NQF LEVEL 4 NOVEMBER 2009 (6021024) 30 October (Y-Paper) 13:00 16:00 A non-programmable scientific calculator may be used. This question
A) 4.0 m/s B) 5.0 m/s C) 0 m/s D) 3.0 m/s E) 2.0 m/s. Ans: Q2.
 Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Supersonic air and wet steam jet using simplified de Laval nozzle
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Engineering-15 (ICOPE-15) November 30- December 4, 2015, Yokohama, Japan Paper ID: ICOPE-15-1158 Supersonic air and wet steam jet using simplified de
Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Engineering-15 (ICOPE-15) November 30- December 4, 2015, Yokohama, Japan Paper ID: ICOPE-15-1158 Supersonic air and wet steam jet using simplified de
Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
Linear guide drives. Synchronous shafts The use of synchronous shafts enables several linear axes to be operated with one drive.
 Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
MODELING WITH CURRENT DYNAMICS AND VIBRATION CONTROL OF TWO PHASE HYBRID STEPPING MOTOR IN INTERMITTENT DRIVE
 MODELING WITH CURRENT DYNAMICS AND VIBRATION CONTROL OF TWO PHASE HYBRID STEPPING MOTOR IN INTERMITTENT DRIVE Ryota Mori, Yoshiyuki Noda, Takanori Miyoshi, Kazuhiko Terashima Department of Production Systems
MODELING WITH CURRENT DYNAMICS AND VIBRATION CONTROL OF TWO PHASE HYBRID STEPPING MOTOR IN INTERMITTENT DRIVE Ryota Mori, Yoshiyuki Noda, Takanori Miyoshi, Kazuhiko Terashima Department of Production Systems
Investigation of a nonlinear dynamic hydraulic system model through the energy analysis approach
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 3 (009) 973~979 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-9x DOI.07/s6-009-081- Investigation of a nonlinear dynamic hydraulic
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 3 (009) 973~979 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-9x DOI.07/s6-009-081- Investigation of a nonlinear dynamic hydraulic
Joint Torque Control for Backlash Compensation in Two-Inertia System
 Joint Torque Control for Backlash Compensation in Two-Inertia System Shota Yamada*, Hiroshi Fujimoto** The University of Tokyo 5--5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba, 227-856 Japan Phone: +8-4-736-3873*, +8-4-736-43**
Joint Torque Control for Backlash Compensation in Two-Inertia System Shota Yamada*, Hiroshi Fujimoto** The University of Tokyo 5--5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba, 227-856 Japan Phone: +8-4-736-3873*, +8-4-736-43**
Pneumatic Universal. Actuator MOTORIZED VALVES USE TECHNICAL FEATURES OF THE ACTUATOR. Data sheet
 Data sheet. - 8 USE The motorized valve is specifically used for the interception and regulation of fluids in: systems using alternative energy industrial systems in general using hot and cold fluids automation
Data sheet. - 8 USE The motorized valve is specifically used for the interception and regulation of fluids in: systems using alternative energy industrial systems in general using hot and cold fluids automation
SOLUTION 8 7. To hold lever: a+ M O = 0; F B (0.15) - 5 = 0; F B = N. Require = N N B = N 0.3. Lever,
 8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
Study on Material Recognition of Artificial Finger for Pneumatic Robot Arm
 Study on Material Recognition of Artificial Finger for Pneumatic Robot Arm Mitsuru TOYAMA, Osamu OYAMA and Kazuya TAMURA Department of Mechanical Engineering Informatics Meiji University 1-1-1 Higashimita,
Study on Material Recognition of Artificial Finger for Pneumatic Robot Arm Mitsuru TOYAMA, Osamu OYAMA and Kazuya TAMURA Department of Mechanical Engineering Informatics Meiji University 1-1-1 Higashimita,
Vibration Suppression of a 2-Mass Drive System with Multiple Feedbacks
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 11, November 2015 168 Vibration Suppression of a 2-Mass Drive System with Multiple Feedbacks L. Vidyaratan Meetei, Benjamin
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 11, November 2015 168 Vibration Suppression of a 2-Mass Drive System with Multiple Feedbacks L. Vidyaratan Meetei, Benjamin
DEVELOPMENT OF A REAL-TIME HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL SYSTEM USING A SHAKING TABLE
 DEVELOPMENT OF A REAL-TIME HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL SYSTEM USING A SHAKING TABLE Toshihiko HORIUCHI, Masahiko INOUE And Takao KONNO 3 SUMMARY A hybrid experimental method, in which an actuator-excited vibration
DEVELOPMENT OF A REAL-TIME HYBRID EXPERIMENTAL SYSTEM USING A SHAKING TABLE Toshihiko HORIUCHI, Masahiko INOUE And Takao KONNO 3 SUMMARY A hybrid experimental method, in which an actuator-excited vibration
Simulation Study on Pressure Control using Nonlinear Input/Output Linearization Method and Classical PID Approach
 Simulation Study on Pressure Control using Nonlinear Input/Output Linearization Method and Classical PID Approach Ufuk Bakirdogen*, Matthias Liermann** *Institute for Fluid Power Drives and Controls (IFAS),
Simulation Study on Pressure Control using Nonlinear Input/Output Linearization Method and Classical PID Approach Ufuk Bakirdogen*, Matthias Liermann** *Institute for Fluid Power Drives and Controls (IFAS),
An Earth Auger as Excavator for Planetary Underground Explorer Robot. Using Peristaltic Crawling
 An Earth Auger as Excavator for Planetary Underground Explorer Robot Using Peristaltic Crawling H. Omori *, T. Murakami, H. Nagai, T. Nakamura **, and T. Kubota *** * Department of Precision Mechanics,
An Earth Auger as Excavator for Planetary Underground Explorer Robot Using Peristaltic Crawling H. Omori *, T. Murakami, H. Nagai, T. Nakamura **, and T. Kubota *** * Department of Precision Mechanics,
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling.
 SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
DESIGN OF A NOVEL HAND-HELD PNEUMATIC VACUUM PAD USING CFD
 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 18, No. 5, pp. 637-643 (21) 637 DESIGN OF A NOVEL HAND-HELD PNEUMATIC VACUUM PAD USING CFD Jyh-Chyang Renn*, Chin-Yi Cheng*, and Yong-Chao Yang* Key words:
Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 18, No. 5, pp. 637-643 (21) 637 DESIGN OF A NOVEL HAND-HELD PNEUMATIC VACUUM PAD USING CFD Jyh-Chyang Renn*, Chin-Yi Cheng*, and Yong-Chao Yang* Key words:
KNIFE EDGE FLAT ROLLER
 EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
Formulae and examples of calculation
 Shock absorber Formulae and examples of calculation A shock absorber decelerates linearly. Roughly 90% of shock absorber applications can be modelled if the following 4 factors are known: 1. Mass to slow
Shock absorber Formulae and examples of calculation A shock absorber decelerates linearly. Roughly 90% of shock absorber applications can be modelled if the following 4 factors are known: 1. Mass to slow
AGITATION/GAS-LIQUID DISPERSION. CHEM-E Fluid Flow in Process Units
 AGITATION/GAS-LIQUID DISPERSION CHEM-E7160 - Fluid Flow in Process Units 1. INTRODUCTION Agitation: Mixing: Blending: Suspension: Dispersion: Induced motion of a material in a specific way, usually in
AGITATION/GAS-LIQUID DISPERSION CHEM-E7160 - Fluid Flow in Process Units 1. INTRODUCTION Agitation: Mixing: Blending: Suspension: Dispersion: Induced motion of a material in a specific way, usually in
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 106 (2015 ) Dynamics and Vibroacoustics of Machines (DVM2014)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering (5 ) 49 57 Dynamics and Vibroacoustics of Machines (DVM4) Process simulation of energy behaviour of pneumatic drives Elvira
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering (5 ) 49 57 Dynamics and Vibroacoustics of Machines (DVM4) Process simulation of energy behaviour of pneumatic drives Elvira
Phys101 Second Major-173 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. M. Al-Kuhaili Thursday, August 02, 2018 Page: 1. = 159 kw
 Coordinator: Dr. M. Al-Kuhaili Thursday, August 2, 218 Page: 1 Q1. A car, of mass 23 kg, reaches a speed of 29. m/s in 6.1 s starting from rest. What is the average power used by the engine during the
Coordinator: Dr. M. Al-Kuhaili Thursday, August 2, 218 Page: 1 Q1. A car, of mass 23 kg, reaches a speed of 29. m/s in 6.1 s starting from rest. What is the average power used by the engine during the
Example of Calculating the Nominal Life
 Condition (Horizontal Installation) Assumed model number : KR 5520A LM Guide unit (C = 800N, C 0 = 6900N) Ball Screw unit (C a = 620N, C 0a = 9290N) Bearing unit(fixed Side) (C a = 7600N, P 0a = 990N)
Condition (Horizontal Installation) Assumed model number : KR 5520A LM Guide unit (C = 800N, C 0 = 6900N) Ball Screw unit (C a = 620N, C 0a = 9290N) Bearing unit(fixed Side) (C a = 7600N, P 0a = 990N)
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Momentum Methods
 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Momentum Methods Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Momentum Methods Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
To investigate the performance of the Pelton Wheel turbine with different range of flow rates and rotational speeds.
 Experiment No. 1 PELTON WHEEL TURBINE Objective To investigate the performance of the Pelton Wheel turbine with different range of flow rates and rotational speeds. Summary of theory Pelton Wheel turbine
Experiment No. 1 PELTON WHEEL TURBINE Objective To investigate the performance of the Pelton Wheel turbine with different range of flow rates and rotational speeds. Summary of theory Pelton Wheel turbine
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2012/2013 XE121. ENGINEERING CONCEPTS (Test)
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 202/203 XE2 ENGINEERING CONCEPTS (Test) Time allowed: TWO hours Answer: Attempt FOUR questions only, a maximum of TWO questions
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS 202/203 XE2 ENGINEERING CONCEPTS (Test) Time allowed: TWO hours Answer: Attempt FOUR questions only, a maximum of TWO questions
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Design of Torque Balancing Mechanisms. 1. Introduction. Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada
 Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (207) 32-320 doi: 0.7265/259-5275/207.06.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada Department of Engineering
Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (207) 32-320 doi: 0.7265/259-5275/207.06.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada Department of Engineering
PUMP MODE PREDICTION FOR FOUR-QUADRANT VELOCITY CONTROL OF VALUELESS HYDRAULIC ACTUATORS
 Proceedings of the 7th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TOYAMA 2008 September 15-18, 2008 P1-13 PUMP MODE PREDICTION FOR FOUR-QUADRANT VELOCITY CONTROL OF VALUELESS HYDRAULIC ACTUATORS Christopher
Proceedings of the 7th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TOYAMA 2008 September 15-18, 2008 P1-13 PUMP MODE PREDICTION FOR FOUR-QUADRANT VELOCITY CONTROL OF VALUELESS HYDRAULIC ACTUATORS Christopher
Simulation of Energy Consumption of Machine Tool Motion for 3-Axis Machining
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 11 (17) 37-43 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/17.01.005 D DAVID PUBISHING of Energy Consumption of Machine Tool Motion for 3-Axis Machining Akio Hayashi 1, Zen Kimura 2
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 11 (17) 37-43 doi: 10.17265/1934-8975/17.01.005 D DAVID PUBISHING of Energy Consumption of Machine Tool Motion for 3-Axis Machining Akio Hayashi 1, Zen Kimura 2
RESEARCH ON AIRBORNE INTELLIGENT HYDRAULIC PUMP SYSTEM
 8 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ON AIRBORNE INTELLIGENT HYDRAULIC PUMP SYSTEM Jungong Ma, Xiaoye Qi, Juan Chen BeiHang University,Beijing,China jgma@buaa.edu.cn;qixiaoye@buaa.edu.cn;sunchenjuan@hotmail.com
8 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ON AIRBORNE INTELLIGENT HYDRAULIC PUMP SYSTEM Jungong Ma, Xiaoye Qi, Juan Chen BeiHang University,Beijing,China jgma@buaa.edu.cn;qixiaoye@buaa.edu.cn;sunchenjuan@hotmail.com
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT
 Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive MKUVE15-KGT, MKUVE20-KGT Product overview Actuators with ball monorail guidance system and ball screw drive Actuators with ball monorail
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
Chapter Four fluid flow mass, energy, Bernoulli and momentum
 4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
Chapter 6. Hydraulic cylinders/rams (linear motors), and Lines/fittings. - Transforms the flow of a pressurized fluid into a push or pull of a rod.
 Chapter 6. Hydraulic cylinders/rams (linear motors), and Lines/fittings - Transforms the flow of a pressurized fluid into a push or pull of a rod. 6. Single cting Rams Gravity, spring, etc. can force piston
Chapter 6. Hydraulic cylinders/rams (linear motors), and Lines/fittings - Transforms the flow of a pressurized fluid into a push or pull of a rod. 6. Single cting Rams Gravity, spring, etc. can force piston
Real-Time Implementation of a LQR-Based Controller for the Stabilization of a Double Inverted Pendulum
 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 017 Vol I,, March 15-17, 017, Hong Kong Real-Time Implementation of a LQR-Based Controller for the Stabilization of
Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 017 Vol I,, March 15-17, 017, Hong Kong Real-Time Implementation of a LQR-Based Controller for the Stabilization of
Technical Guide for Servo Motor Selection
 Technical Guide for Servo otor Selection CS_Servo Selection_TG_E_3_1 Servo otor Selection Software Use your PC to select a Servo otor "otor Selection Program for Windows" o you always feel "Calculation
Technical Guide for Servo otor Selection CS_Servo Selection_TG_E_3_1 Servo otor Selection Software Use your PC to select a Servo otor "otor Selection Program for Windows" o you always feel "Calculation
Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral. mechanism under the vibration environment
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
Initial Stress Calculations
 Initial Stress Calculations The following are the initial hand stress calculations conducted during the early stages of the design process. Therefore, some of the material properties as well as dimensions
Initial Stress Calculations The following are the initial hand stress calculations conducted during the early stages of the design process. Therefore, some of the material properties as well as dimensions
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 113 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 113 (015 ) 186 191 International Conference on Oil and Gas Engineering, OGE-015 The theoretical and experimental studies comparison
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 113 (015 ) 186 191 International Conference on Oil and Gas Engineering, OGE-015 The theoretical and experimental studies comparison
Backlash Estimation of a Seeker Gimbal with Two-Stage Gear Reducers
 Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:604 611 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Backlash Estimation of a Seeker Gimbal with Two-Stage Gear Reducers J. H. Baek, Y. K. Kwak and S. H.
Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:604 611 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Backlash Estimation of a Seeker Gimbal with Two-Stage Gear Reducers J. H. Baek, Y. K. Kwak and S. H.
Lecture 5. Labs this week: Please review ME3281 Systems materials! Viscosity and pressure drop analysis Fluid Bulk modulus Fluid Inertance
 Labs this week: Lab 10: Sequencing circuit Lecture 5 Lab 11/12: Asynchronous/Synchronous and Parallel/Tandem Operations Please review ME3281 Systems materials! 132 Viscosity and pressure drop analysis
Labs this week: Lab 10: Sequencing circuit Lecture 5 Lab 11/12: Asynchronous/Synchronous and Parallel/Tandem Operations Please review ME3281 Systems materials! 132 Viscosity and pressure drop analysis
The problem of transmitting a torque or rotary motion from one plane to another is frequently encountered in machine design.
 CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
Selection Calculations For Motorized Actuators
 Selection Calculations/ Selection Calculations For Linear Slides and Cylinders Select from the EZS Series, EZS Series for Cleanroom Use, EZC Series First determine your series, then select your model.
Selection Calculations/ Selection Calculations For Linear Slides and Cylinders Select from the EZS Series, EZS Series for Cleanroom Use, EZC Series First determine your series, then select your model.
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM
 First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 December 20, 2004 Physics 201 FINAL EXAM Print your name and section clearly on all nine pages. (If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name.) Show all
Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications
 Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications Prof. P.B. Kadam 1, Prof. M.R. Todkar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, T.K.I.E.T.Warananagar,
Improvement in the Design & Manufacturing of Twin Worm Self Locking Technique and applications Prof. P.B. Kadam 1, Prof. M.R. Todkar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Department, T.K.I.E.T.Warananagar,
A 954 C HD. Technical Description Hydraulic Excavator. Machine for Industrial Applications
 Technical Description Hydraulic Excavator A 95 C HD litronic` Machine for Industrial Applications Operating Weight 165,800 170,0 lb Engine Output 36 hp (0 kw) Technical Data Engine Rating per ISO 99 0
Technical Description Hydraulic Excavator A 95 C HD litronic` Machine for Industrial Applications Operating Weight 165,800 170,0 lb Engine Output 36 hp (0 kw) Technical Data Engine Rating per ISO 99 0
WORK SHEET FOR MEP311
 EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
*Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units
 INTRODUCTION *Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under
INTRODUCTION *Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under
The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel.
 TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
TOM Fly Wheel Mechanical Engineering Department The principle of the flywheel is found before the many centuries ago in spindle and the potter's wheel. A heavy-rimmed rotating wheel used to minimize variations
for Articulated Robot Arms and Its Applications
 141 Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Automation, December 15-18, 25, Colombo, Sri Lanka. 1 Forcefree Control with Independent Compensation for Articulated Robot Arms and Its
141 Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Automation, December 15-18, 25, Colombo, Sri Lanka. 1 Forcefree Control with Independent Compensation for Articulated Robot Arms and Its
COILER CONTROL IN ENDLESS HOT STRIP ROLLING. T. Motomura, K. Ueda, T. Imazeki, Y. Fukui, K. Yahiro
 COILER CONTROL IN ENDLESS HOT STRIP ROLLING T. otomura, K. Ueda, T. Imazeki, Y. Fukui, K. Yahiro East Japan Works, JFE steel corporation,, Kawasaki-cho, Chuo-ku, Chiba 6-835, Japan Abstract: JFE Steel
COILER CONTROL IN ENDLESS HOT STRIP ROLLING T. otomura, K. Ueda, T. Imazeki, Y. Fukui, K. Yahiro East Japan Works, JFE steel corporation,, Kawasaki-cho, Chuo-ku, Chiba 6-835, Japan Abstract: JFE Steel
DYNAMICS MOMENT OF INERTIA
 DYNAMICS MOMENT OF INERTIA S TO SELF ASSESSMENT EXERCISE No.1 1. A cylinder has a mass of 1 kg, outer radius of 0.05 m and radius of gyration 0.03 m. It is allowed to roll down an inclined plane until
DYNAMICS MOMENT OF INERTIA S TO SELF ASSESSMENT EXERCISE No.1 1. A cylinder has a mass of 1 kg, outer radius of 0.05 m and radius of gyration 0.03 m. It is allowed to roll down an inclined plane until
All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (1:30 PM 4:30 PM) Page 1 of 6 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
(1:30 PM 4:30 PM) Page 1 of 6 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
Lecture Note 8-1 Hydraulic Systems. System Analysis Spring
 Lecture Note 8-1 Hydraulic Systems 1 Vehicle Model - Brake Model Brake Model Font Wheel Brake Pedal Vacuum Booster Master Cylinder Proportionnig Valve Vacuum Booster Rear Wheel Master Cylinder Proportioning
Lecture Note 8-1 Hydraulic Systems 1 Vehicle Model - Brake Model Brake Model Font Wheel Brake Pedal Vacuum Booster Master Cylinder Proportionnig Valve Vacuum Booster Rear Wheel Master Cylinder Proportioning
Servo Motor Selection Flow Chart
 Servo otor Selection Flow Chart START Selection Has the machine Been Selected? YES NO Explanation etermine the size, mass, coefficient of References friction, and external forces of all the moving part
Servo otor Selection Flow Chart START Selection Has the machine Been Selected? YES NO Explanation etermine the size, mass, coefficient of References friction, and external forces of all the moving part
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION ABOUT A FIXED AXIS (Section 17.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION ABOUT A FIXED AXIS (Section 17.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing rotational motion. APPLICATIONS The crank
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION ABOUT A FIXED AXIS (Section 17.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing rotational motion. APPLICATIONS The crank
APEX DYNAMICS, INC. Staianless
 APEX DYNAMICS, INC. HIGH PRECISION PLANETARY GEARBOXES AE / AER Series Staianless High precision high speed planetary gearboxes AE / AER series Apex Dynamics, Inc. is the world s most productive manufacturer
APEX DYNAMICS, INC. HIGH PRECISION PLANETARY GEARBOXES AE / AER Series Staianless High precision high speed planetary gearboxes AE / AER series Apex Dynamics, Inc. is the world s most productive manufacturer
Rotary modules.
 Rotary modules www.comoso.com www.comoso.com Rotary modules ROTARY MODULES Series Size Page Rotary modules RM swivel unit 156 RM 08 160 RM 10 162 RM 12 164 RM 15 168 RM 21 172 RM rotor 176 RM 50 180 RM
Rotary modules www.comoso.com www.comoso.com Rotary modules ROTARY MODULES Series Size Page Rotary modules RM swivel unit 156 RM 08 160 RM 10 162 RM 12 164 RM 15 168 RM 21 172 RM rotor 176 RM 50 180 RM
Robust Speed Controller Design for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Based on Sliding Mode Control
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 88 (2016 ) 867 873 CUE2015-Applied Energy Symposium and Summit 2015: ow carbon cities and urban energy systems Robust Speed Controller
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 88 (2016 ) 867 873 CUE2015-Applied Energy Symposium and Summit 2015: ow carbon cities and urban energy systems Robust Speed Controller
Welcome to where precision is. Large Ball Screws Diameter mm
 Welcome to where precision is. Large Ball Screws Diameter mm Large Ball Screws Diameter mm This section includes nuts with standard dimensions per ISO 8 / DIN 1. In most cases, there is a choice of three
Welcome to where precision is. Large Ball Screws Diameter mm Large Ball Screws Diameter mm This section includes nuts with standard dimensions per ISO 8 / DIN 1. In most cases, there is a choice of three
Thermal analysis of hydraulic system of landing gear
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Thermal analysis of hydraulic system of landing gear To cite this article: S Badrinarayanan et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Thermal analysis of hydraulic system of landing gear To cite this article: S Badrinarayanan et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater.
UNIT 5 GOVERNORS 5.1 INTRODUCTION. Structure. 5.1 Introduction. 5.2 Classification of Governors 5.3 Gravity Controlled Centrifugal Governors
 UNIT 5 GVERNRS Governors Structure 5. Introduction bjectives 5. lassification of Governors 5.3 Gravity ontrolled entrifugal Governors 5.3. Watt Governor 5.3. Porter Governor 5.4 Spring ontrolled entrifugal
UNIT 5 GVERNRS Governors Structure 5. Introduction bjectives 5. lassification of Governors 5.3 Gravity ontrolled entrifugal Governors 5.3. Watt Governor 5.3. Porter Governor 5.4 Spring ontrolled entrifugal
Hydraulic Fundamentals Hydraulics Definition Advent of Oil Hydraulics Pascal s Law Pressure
 Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Mechanics. Moment of inertia / Steiner s theorem Dynamics. What you need:
 Dynamics Mechanics Moment of inertia / teiner s theorem What you can learn about Rigid body Moment of inertia Centre of gravity Axis of rota tion Torsional vibration pring constant Angular restoring force
Dynamics Mechanics Moment of inertia / teiner s theorem What you can learn about Rigid body Moment of inertia Centre of gravity Axis of rota tion Torsional vibration pring constant Angular restoring force
PASSIVE CONTROL OF FLUID POWERED HUMAN POWER AMPLIFIERS
 OS9-3 Proceedings of the 7th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TOYAMA 28 September 5-8, 28 PASSIVE CONTROL OF FLUID POWERED HUMAN POWER AMPLIFIERS Perry Y. Li and Venkat Durbha Center for Compact
OS9-3 Proceedings of the 7th JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, TOYAMA 28 September 5-8, 28 PASSIVE CONTROL OF FLUID POWERED HUMAN POWER AMPLIFIERS Perry Y. Li and Venkat Durbha Center for Compact
Manufacturing Equipment Control
 QUESTION 1 An electric drive spindle has the following parameters: J m = 2 1 3 kg m 2, R a = 8 Ω, K t =.5 N m/a, K v =.5 V/(rad/s), K a = 2, J s = 4 1 2 kg m 2, and K s =.3. Ignore electrical dynamics
QUESTION 1 An electric drive spindle has the following parameters: J m = 2 1 3 kg m 2, R a = 8 Ω, K t =.5 N m/a, K v =.5 V/(rad/s), K a = 2, J s = 4 1 2 kg m 2, and K s =.3. Ignore electrical dynamics
Grade XI. Physics Mock Test. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Mock Test #GrowWithGreen Mock Test Physics Questions General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) The question paper comprises 4 Sections, A, B, C and D. You are to attempt
Grade XI Physics Mock Test #GrowWithGreen Mock Test Physics Questions General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) The question paper comprises 4 Sections, A, B, C and D. You are to attempt
A Design Method of A Robust Controller for Hydraulic Actuation with Disturbance Observers
 A Design Method of A Robust Controller for Hydraulic Actuation with Disturbance Observers Hiroaki Kuwahara, Fujio Terai Corporate Manufacturing Engineering Center, TOSHIBA Corporation, Yokohama, Japan
A Design Method of A Robust Controller for Hydraulic Actuation with Disturbance Observers Hiroaki Kuwahara, Fujio Terai Corporate Manufacturing Engineering Center, TOSHIBA Corporation, Yokohama, Japan
Final Examination Thursday May Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Final Examination Thursday May 0 010 Division of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is permitted on this examination. You may
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Final Examination Thursday May 0 010 Division of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is permitted on this examination. You may
Modeling and Identification of Pouring Flow Process With Tilting-Type Ladle for an Innovative Press Casting Method Using Greensand Mold
 Modeling and Identification of Pouring Flow Process With Tilting-Type Ladle for an Innovative Press Casting Method Using Greensand Mold Yusuke Matsuo*, Yoshiyuki Noda*, azuhiko Terashima*, unihiro Hashimoto**,
Modeling and Identification of Pouring Flow Process With Tilting-Type Ladle for an Innovative Press Casting Method Using Greensand Mold Yusuke Matsuo*, Yoshiyuki Noda*, azuhiko Terashima*, unihiro Hashimoto**,
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Rotational Motion. Rotational Motion. Rotational Motion
 I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics (Netwton s Law for Rotation) III. Angular Momentum Conservation 1. Remember how Newton s Laws for translational motion were studied: 1. Kinematics (x =
I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics (Netwton s Law for Rotation) III. Angular Momentum Conservation 1. Remember how Newton s Laws for translational motion were studied: 1. Kinematics (x =
Technical Reference Selection calculations Motors Motorized Actuators Cooling Fans Technical Service Life Reference Standard AC Motors
 calculations... H-2 H-2 H Technical Reference H-8 H-28... H-29 AC... H-33... H-0 AC... H-6... H-55... H-58... H-66... H-68... H-77 H- / For Selecting a motor that satisfies the specifications required
calculations... H-2 H-2 H Technical Reference H-8 H-28... H-29 AC... H-33... H-0 AC... H-6... H-55... H-58... H-66... H-68... H-77 H- / For Selecting a motor that satisfies the specifications required
Identification system for short product names. Changes/amendments at a glance. 2 Bosch Rexroth AG OBB omega modules R ( )
 Omega Modules OBB 2 OBB omega modules R9990079 (206-05) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example: O B B - 085 - N N - System = Omega module Guideway = Ball Rail System Drive
Omega Modules OBB 2 OBB omega modules R9990079 (206-05) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example: O B B - 085 - N N - System = Omega module Guideway = Ball Rail System Drive
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Experimental Verification of Fault Predictions in High Pressure Hydraulic Systems
 Modern Mechanical Engineering, 204, 4, 67-8 Published Online May 204 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/mme http://dx.doi.org/0.426/mme.204.42008 Experimental Verification of Fault Predictions in
Modern Mechanical Engineering, 204, 4, 67-8 Published Online May 204 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/mme http://dx.doi.org/0.426/mme.204.42008 Experimental Verification of Fault Predictions in
Performance evaluation of first stage support system of launcher
 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 64, December 005, pp. 949-956 Performance evaluation of first stage support system of launcher A C Pankaj 1, *, Jhankar Basu 1, S N Shome 1, P K Mehta and
Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 64, December 005, pp. 949-956 Performance evaluation of first stage support system of launcher A C Pankaj 1, *, Jhankar Basu 1, S N Shome 1, P K Mehta and
First Name: Last Name: Section: 22 December, :25 2:25 PM Physics 207 FINAL EXAM
 1 First Name: Last Name: Section: 22 December, 2009 12:25 2:25 PM Physics 207 FINAL EXAM Please print your name and section number (or TA s name) clearly on the first page. Show all your work in the space
1 First Name: Last Name: Section: 22 December, 2009 12:25 2:25 PM Physics 207 FINAL EXAM Please print your name and section number (or TA s name) clearly on the first page. Show all your work in the space
Modeling of Hydraulic Turbine and Governor for Dynamic Studies of HPP
 Modeling of Hydraulic Turbine and Governor for Dynamic Studies of HPP Nanaware R. A. Department of Electronics, Shivaji University, Kolhapur Sawant S. R. Department of Technology, Shivaji University, Kolhapur
Modeling of Hydraulic Turbine and Governor for Dynamic Studies of HPP Nanaware R. A. Department of Electronics, Shivaji University, Kolhapur Sawant S. R. Department of Technology, Shivaji University, Kolhapur
