An innovative OHL diagnosis procedure based on the pantograph dynamics measurements
|
|
|
- Rebecca Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An innovative OHL diagnosis procedure based on the pantograph dynamics measurements A. Collina*, F. Fossati**, F. Resta* * Dipartimento di Meccanica-Politecnico di Milano, Milano (Italy) **Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale e Meccanica - Facoltà di Ingegneria Università degli Studi di Catania, Catania (Italy) 1. Introduction High speed railways requires intensive investigation on different topics, such as vehicle dynamics, comfort, noise emission, and current collection quality. In particular the performance of the overhead line (OHL) - pantograph system, can be a limiting factor for the maximum train speed, since it affects the power collecting ([1], [2]). he variation of contact force, exchanged between pantograph and catenary and dependent on pantograph-ohl dynamic interaction, can cause excessive mechanical wear and contact wire uplift (for high values of contact forces), and to high percentage of loss of contact, arcing and electrically related wear if too low values of contact forces occur. Motivation for dynamic contact force variation are: - periodically varying stiffness of OHL along the span, related to its structure, (connection of the wires to the masts and the presence of the droppers between contact and messenger wires); - aerodynamic disturbances due to the turbulent flow incident on the pantograph; - pantograph and OHL dynamic behaviour; - irregularity of the contact wire. Overhead line conditions are very important for power collecting performance: due to this reason an effective maintenance of the OHL is required for an efficient operation of a high speed line. his is also important in view of interoperability, where pantographs optimised for a kind of OHL, are to interact with different kind of catenary. Since maintenance is related to the knowledge of the OHL condition, several procedures have been developed, to this purpose. Inspections of personnel along the line were used first to find catenary defects and their amount. More recently, railways network management use computerised systems for catenary conditions together with traditional methods [3]: these innovative methods ([4], [5], [6]) are based on specialised vehicles and enable to measure contact wire positioning, stagger, and in some cases also the contact line section reduction. hese modern techniques have high security levels for maintenance personnel and avoid traffic interruptions; on the other hand, very sophisticated devices are required. Aim of the present paper is to propose a technique of overhead diagnostics oriented to the maintenance, able to obtain some information relevant to overhead line conditions using only on board measurements of pantograph dynamics, by means of a set-up applicable on a train for normal service operation. he basic idea is to predict the presence of defect from the effect on the dynamic response of the pantograph. he contact force is the quantity most influenced by the OHL defects, but also the pantograph motion (displacement and velocity) can reveal some of them. Since the setup for the measurements of the contact force is quite complicated and sensitive to disturbances, it is not conceivable to apply it on an operating train, while the set-up necessary to measure pantograph motion is simpler, and can be mounted on a normal operating train.
2 In a previous paper [6] a contact force estimation procedure, based on the Extended Kalman Filter has been presented by the authors for the pantograph active control purposes: this approach leads to a great simplification of the measurement set-up with respect to a direct force measurement. A suitable reference model, able to obtain catenary dynamics information using only pantograph collector head and articulated frame displacement and velocity has been developed and Kalman Filtering estimation procedure has been set-up in order to estimate (instead of directly measure) the contact force. he estimated contact force enables to obtain some information useful to overhead line diagnostic: variation of contact line vertical positioning, level of wear of the contact wire, droppers failure, suspension set devices failure, contact line tension variation could be detected and examined by means of estimated contact force. As a first step of the research, in the present work the procedure has been tested numerically: different catenary defects have been modelled and included in a mathematical model of the catenary - pantograph system: several numerical simulation have been performed to generate the input data for the estimation procedure. In order to simulate the dynamic behaviour of the complete catenary - pantograph system, a mathematical model developed at Politecnico di Milano has been used ([7]). Using these results, the scenario corresponding to the considered defects can be compared with the "nominal" catenary status. In the following the modelled catenary defects and their effects on overall system dynamics will be described. hen some results in terms of system dynamics estimation will be presented: the results obtained from the simulations enable to give a preliminary check of the proposed diagnosis procedure which appears very attractive as a mean to estimate the presence of some of the possible catenary defects and their amount without specific overhead line inspection. Finally a critical analysis on the applicability of the proposed procedure on real measurements is also carried out, and the necessary improvements and developments are outlined. 2. EKF and the adopted reference model he proposed diagnostic procedure is based on contact force and catenary motion estimation, using only on-board pantograph displacement and velocity measurements. he procedure adopts the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) technique and an appropriate reference model (a simplified OHL schematisation and a pantograph), able to estimate the contact force, and to take into account the pantograph-ohl interaction. he simplified OHL, consisting of three consecutive spans (figure 1), is modelled by means of a tensioned beam, whose characteristics are the sum of the characteristics of the contact wires and the messenger wires of the real catenary. he vertical displacement w(,t) of the generic catenary point can be written in terms of vibration mode functions n and modal co-ordinates q n : w(,t ) ( ) q(t ) (1) where is the vibration mode vector, containing the modal shapes of the tensioned beam with length 3L (being L the length of each span), and q is the modal co-ordinate vector. he pantograph model is based on a two degrees of freedom system (one for the articulated frame and the other for the colelctor head): its parameters can be obtained from laboratory frequency response tests. he mass m h (representing the collector head) is supposed to be always in contact with the overhead line. herefore the collector head vertical displacement velocity and acceleration (figure 2) can be expressed as: 2 x h ( Vt) q( t) ; xh V '( Vt) q ( Vt) q ; xh V "( Vt) q 2V '( Vt) q ( Vt) q (2) where V is the train speed, and the prime denotes the spatial derivatives with respect to the abscissa. Following the Lagrangian approach, i.e. considering: the kinetic energy, the elastic energies (that includes also the contribution of the supporting spring k s ), and the dissipative function, the equations of motion of the overall system (pantograph+ohl) can be written as:
3 [ M(t )]x [R( t )]x [ K(t )]x Q (3) where x is the vector of the independent variables, i.e. the base frame displacement and modal coordinates of the overhead line: x x f q1 q2 q n (4) he vector Q represents the lagrangian component of the pre-load applied to the articulated frame of the pantograph. he matrices in (3) represent the catenary mass damping and stiffness matrices, which are time dependant due to the term = Vt, which represents the pantograph position along the contact wire. Figure 1 he simplified model for Pantograph- catenary interaction used as reference model for the EKF estimation procedure. For the purpose of the EKF use, the contact force F c has been included in the extended state vector z of the reference model: z [x f q 1 q 2.. q n x f q 1 q 2.. q n F c ] (5) he reference model equations are: z A z + B u (6) where u is the vector containing the static force P 0 applied at the pantograph articulated frame: u = [ P 0 0 ] (7) A is the system matrix, B is the input matrix and is modelled as additive white noise to the system. If only pantograph state variables are supposed available from the measurements set-up, the observation equation is: y C z (7) where y is the observed variables vector (collector head and articulated frame displacements and velocities), C is the observation matrix and is modelled as additive white noise. By means of a proper procedure, the pantograph travels only in the central span, switching the state of the system one span back, when pantograph reaches the end of the central span (Figure 2). he two lateral spans therefore are included to reproduce the boundary condition of the central span. In such a way, any desired number of consecutive spans, can be considered, using only few degrees of freedom
4 Figure 2. Span transition of the pantograph Figure 3. Contact force estimation procedure: in the present work the real system is replaced by a numerical simulation 3. Complete modelling of overhead line and pantograph As previously said, the proposed approach (figure 3) has been up to now tested numerically, generating the measurements to be performed on the real system by means of a computer code able to simulate the dynamic behaviour of the complete catenary - pantograph system (figure 2). he OHL mathematical model for the simulation with the complete system, is based on a finite element schematisation, taking into account the real catenary configuration, the non-linear behaviour of the droppers and the overhead line irregularity. A lumped parameters model has been adopted for the pantograph dynamics. Details on this numerical model can be found in [1]. Different catenary defects have been modelled and included in this mathematical model of the system in such a way to understand their effects on the overall (OHL+pantograph) system dynamics: in particular the considered defects can be divided into two main categories: distributed defects such as geometrical variation of contact line due to creep phenomena or/and variation of contact line vertical position related to deviation of droppers length from the nominal value; localised defects like broken droppers or registration arm mounting errors. Some of the above mentioned defects are progressive, other are related to initial mounting errors, or to failure. In the following some results with reference to the "nominal" catenary status (i.e. without any defects) obtained from the simulation will be reported. hen the same quantities modifications due to the presence of each of the considered defect will be reported. 3.1 results with the catenary in nominal status and related estimation
5 First the results of the simulation with the complete model, and the results of the estimation obtained from the simulated data, are compared. Figure 4 reports the vertical absolute motion of the collector head as a function of position along the line: the typical shape of the trajectory and the effects of the droppers are noticeable. As said above, based on the collector head and the articulated frame motion, both the contact force and the catenary motion have been estimated. In figure 5 a comparison between central span catenary motion obtained by means of the estimation technique and to detailed FEM model is reported. As can be seen the adopted reference model shows good capabilities for catenary motion estimation too, even if only pantograph motion is available to the estimation procedurehe subsequent figure 6 shows the total contact force. he highest variations occur when the pantograph transits across the suspension s of the OHL. he spectral component relevant to pantograph span passage frequency (about 1.Hz) and relevant to pantograph droppers passage frequency (about 10-15Hz). Figure 4. Pantograph front collector head displacement versus train position comparison between simulated and estimated values Figure 5. Catenary motion: simulation and estimation. Figure 6. Contact force versus train position: simulated values Figure 7. Contact force versus train position: estimated values
6 4. Application to identification of catenary defects 4.1 Overhead line distributed defects In the following a brief description of the OHL distributed defects considered in the numerical model will be described, and the effects on the current collection will be simulated, testing the capabilities of the proposed procedure to detect the presence of the defect. It must be pointed out that in the estimation procedure, the reference model has always the nominal parameters, the difference in the estimated contact force and catenary motion, between the nominal condition, and the condition with the defect, is due to the input quantiti4s, i.e. pantograph motion, which in the presented cases obtained from simulation with the complete model, in the real condition obtained from the measurements Geometrical variation of contact line due to creep phenomena Catenary wires are tensioned by means of tensioning devices: conductors (and in particular contact wires) experience an increase of their length due to long term viscous creep effects. his produces a geometrical variation of the OHL, as shown in figure 8, more evident if a different level of creep takes place due to a different temperature conditions. In order to calculate the OHL displacements due to viscous effects, an equivalent traction load which produces the same effects are applied to conductor extremities, and a non linear static analysis is performed, taking into account the non linear effects due to the droppers, because of their non linear mechanical characteristics and to the variation of OHL geometry, also related to he inclined position assumed by the droppers. Several contact wires and suspension cable lengthening due to long term viscous effects have been considered and contact force estimation has been performed in each case: estimated results were very good in comparison with detailed FEM model ones, not shown here. In figure 9 the ratio between contact force span passage (1.17Hz) and droppers passage spectral components (10.5Hz) as a function of contact wires and suspension cable lengthening is reported. As can be seen a typical trend of these quantities can be put in evidence the viscous creep effect and using the proposed technique is able to identify this trend. Figure 8.OHL geometrical variation due to viscous effects: static calculation from FEM model. Figure 9. Identification: ratio between spectral components of contact force (span passage/droppers passage) for different lengthening of contact wires and messenger wire
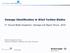
7 4.1.3 Contact line section reduction due to wear his effect is reproduced simply reducing the section of the contact wire in the FEM model properties. Uniform reduction of contact wire section has been considered and the estimation of the first frequency of the catenary motion has been evaluated in each case. Figure 10 shows the obtained results in comparison with those obtained by means of detailed FEM model. As can be seen, the identification procedure gives good results, with maximum differences less than 5%. he identified frequency is a parameter that can put in evidence the section reduction due to wear. 1,15 1,1 f [Hz] FE model EKF estimation 1,15 1,1 1,05 f [Hz] 1, m 0,95 0% 0,95 FE model 0,9 EKF estimation 0,85-40% -20% 0% 20% 40% -10% -20% -30% ***<147-figura10-10.jpg>*** Figure 12. Variation of first span frequency for contact wire mass variation: comparison between FEM simulation end EKF estimation. ***<147-figura11-11.jpg>*** Figure 11. Variation of first span frequency for contact wire tension variation: comparison between FEM simulation end EKF estimation Effects of friction on tensioning device of the wires Contact line tension variation may occur when changes of wires length due to temperature are not compensated by the pulleys of the tensioning devices. his fact, that has been reproduced changing wires tension in the OHL FEM model, produces effect both on frequencies of catenary free motion and maximum up-lift of contact wire in coincidence of pantograph passage. By means of the proposed procedure the first frequency of catenary free motion and maximum up-lift of contact wire in coincidence of pantograph passage have been estimated using only pantograph dynamics measurements for several tension changes. As an example figure 12 shows the comparison between estimated uplift of contact wire at suspension in nominal conditions and with a 30% decrease of contact wire tension: change of catenary motion frequency is detected. It can be observed that a tension increase gives the same indication as the mean wear of the contact wire (i.e. both increase catenary free motion frequencies). he two defects could, at least in principle, be distinguished considering also uplift variation of contact wire which is affected only by tension variations. Examining the statistical distribution of the contact force (figures 14-and 15), it can be observed the change of standard deviation and kurtosis, for increased and decreased values of wires tension, with respect to the nominal condition, shown in figure 13
8 ***<147-figura12-12.jpg>*** Figure 12. Comparison between catenary motion at midspan whit nominal condition and 30% in contact wire tension ***<147-figura13-13.jpg>*** Statistical distribution of estimated contact force: nominal condition Figure 14. Statistical distribution of estimated contact force: contact wire tension 30%. Figure 15. Statistical distribution of estimated contact force: contact wire tension +30% Error of droppers length Deviation of droppers length from the nominal value is a systematic cause of geometrical variation of contact line vertical position, which in turn increases contact wire irregularity and contact force dynamic variation. his defect has been introduced by means of an auxiliary FEM model which considers only the contact wire and a stochastic contribution of dropper length. he obtained irregularity is superimposed to the configuration, due to its own weight, that the contact wire assumes between two consecutive droppers. Since this defect produces an increase of contact wire irregularity, an increase of contact force standard deviation is expected. he estimation procedure allows to detect this effect as shown in table II, where the estimated value of standard deviation of contact force and the one obtained from the complete model are reported as a function of maximum tolerance of dropper length.
9 Nevertheless this symptom cannot be separated from other defects which give analogous effects. Only it can be observed that the shape of statistical distribution is nearer to a gaussian, as indicated by the value of the kurtosis, approaching a value of Overhead line localised defects In the following a brief description of the OHL localised defects considered in the numerical model and their consequences on overall system dynamics will be described Dropper failure he occurrence of broken droppers causes a local variation of contact wire stiffness and as a consequence a variation of pantograph motion and contact force. he inclusion of this effect in the FEM is obtained omitting the considered droppers for what concerns stiffness and damping, and considering it for what concerns the mass: the effect on contact force is shown in fig.16, where the rear collector contact force is show, obtained from the simulation with the complete model. he total estimated contact force, is not able to detect clearly the considered defect, probably due to a limitation of the reference model, which does not take into account the two collectors separately. Figure 16. Contact force simulated with the complete model on the rear collector: dropper failure Figure 17. Estimated total contact force: registration arm error Registration arm mounting errors A typical defect is the incorrect positioning of the registration arm, which causes a sudden deviation of the contact wire from its natural position. A singularity in the contact force is found, this information indicates some troubles with the registration arm (figure 17) 5. Conclusions he possibility to correlate OHL defects and contact force has been investigated, and a procedure for the estimation of the contact force, (instead of a direct measurements, has been proposed. Obtained results show that as far as OHL distributed defects are concerned, it is possible to put in evidence correlation between causes and effects: the contact force and catenary motion estimation procedure allows in several cases defect detection using only pantograph dynamics measurements. As far as the concentrated OHL defects are concerned, pantograph motions analysis reveals useful for defect location recognition but not its feature: in particular dropper lacking defect is not
10 reproduced in the reference model, so it is not possible to detect this problem which, on the other hand, can be revealed by a direct observation of collector and articulated frame relative motion. In any case power collecting performance degradation can be detected by means of the contact force estimation, statistical analysis of contact force may give some help from a diagnostic point of view. Some topics requires further investigations and development: - improvement of the reference model in order to better recognise also the concentrated defect; - investigation of the capability of the proposed procedure with respect to measurement noise and disturbances, and in presence of a defect superimposed to a generic irregularity; - strategy for the diagnosis storage and/or on-board elaboration of the data and their usage for diagnosis. his last aspect is crucial, because of the great amount of data to be managed. Acnowledgemnents Dr. Alessandro Raggi is gratefully acknowledged for having performed most of the simulations. References [1]. K. Becker, A. Konig, U. Resch, B-W Zweig, Systematic development of a high speed Overhead Contact Line, RR, No3-4/1995G. [2]. K. Becker, U. Resch, B-W Zweig, Optimising High-Speed Overhead Contact Lines, AEG report, ABF 14.7/ [3]. P. Meiattini, Manutenzione delle linee di alimentazione: dati storici, azioni preventive ed interventi correttivi, Atti del convegno: Problemi dell interazione pantografo-catenaria, Firenze, 12 Dicembre 1996 [4]. A. Fumi, Computerised systems for catenary geometry assesment, Proceedings of Comprail 98, Lisboa, 2-4 September 1998, in Computer in Railways VI, Wit Press, pp [5]. H. Höfler, N. Dimopoulos, B. Metzeger, F. Eglseer, Fast and precise position measurements of contact wires by a laser scanning system, WCRR 97, November 1997, Florence, Italy [6]. R. Müller, Contact wire wear measurements devices. A system comparison,, WCRR 97, November 1997, Florence, Italy [7]. Diana, A. Collina, F. Fossati, F. Resta, Active control of High speed pantograph III Int. Conf. On Motion adn Vibration Control, Chiba, 1-6 settembre 1996, Giappone, [8]. G. Diana, S. Bruni, A. Collina, F. Fossati, & F. Resta: High speed railways: pantograph and overhead line modelling and simulation, Proceedings of Comprail 98, Lisboa, 2-4 September 1998, in Computer in Railways VI, Wit Press, pp
Pantograph-catenary Dynamic Interaction for a Overhead Line Supported by Noise Barrier
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 5, No. 2 / June 2012, pp. 55-64 The Korean Society for Railway Pantograph-catenary Dynamic Interaction for a Overhead Line Supported by Noise Barrier Marco Belloli*,
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 5, No. 2 / June 2012, pp. 55-64 The Korean Society for Railway Pantograph-catenary Dynamic Interaction for a Overhead Line Supported by Noise Barrier Marco Belloli*,
Prediction of Contact Wire Wear in High-speed Railways
 Prediction of Contact Wire Wear in High-speed Railways 1 T. USUDA M. IKEDA Y. YAMASHITA 1 Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, JAPAN Abstract Although wear of contact wire has been one of the most
Prediction of Contact Wire Wear in High-speed Railways 1 T. USUDA M. IKEDA Y. YAMASHITA 1 Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, JAPAN Abstract Although wear of contact wire has been one of the most
Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II The Influence of the Impedance Matrix Terms on the Energy Dissipated
 1470 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II The Influence of the Impedance Matrix Terms on the Energy Dissipated Giorgio
1470 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Stockbridge-Type Damper Effectiveness Evaluation: Part II The Influence of the Impedance Matrix Terms on the Energy Dissipated Giorgio
Diagnosis of Overhead Contact Line based on Contact Force. Takahiro FUKUTANI Current Collection Laboratory, Power Supply Division
 PAPER Diagnosis of Overhead Contact Line based on Contact Force Shunichi KUSUMI Contact Line Structures Laboratory, Takahiro FUKUTANI Current Collection Laboratory, Power Supply Division Kazuyoshi NEZU
PAPER Diagnosis of Overhead Contact Line based on Contact Force Shunichi KUSUMI Contact Line Structures Laboratory, Takahiro FUKUTANI Current Collection Laboratory, Power Supply Division Kazuyoshi NEZU
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Tribology International Manuscript Draft
 Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Tribology International Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: TRIBINT-D-14-00933 Title: ELECTROMECHANICAL INTERACTION BETWEEN CARBON BASED PANTOGRAPH STRIP AND COPPER CONTACT
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Tribology International Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: TRIBINT-D-14-00933 Title: ELECTROMECHANICAL INTERACTION BETWEEN CARBON BASED PANTOGRAPH STRIP AND COPPER CONTACT
Estimation of the characteristic of contact line uplift and strain in the neighborhood of a tunnel inlet by computer simulation
 Computers in Railways XIII 147 Estimation of the characteristic of contact line uplift and strain in the neighborhood of a tunnel inlet by computer simulation Y. Sugama1, K. Shimizu1 & S. Amari 1 Railway
Computers in Railways XIII 147 Estimation of the characteristic of contact line uplift and strain in the neighborhood of a tunnel inlet by computer simulation Y. Sugama1, K. Shimizu1 & S. Amari 1 Railway
Overhead catenary system-pantograph coupled system dynamics modelling and analysis
 Acta Technica 62 (2017), No. 6A, 109 118 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Overhead catenary system-pantograph coupled system dynamics modelling and analysis Luo Jianguo 2, Liu Hang 2, 4,
Acta Technica 62 (2017), No. 6A, 109 118 c 2017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Overhead catenary system-pantograph coupled system dynamics modelling and analysis Luo Jianguo 2, Liu Hang 2, 4,
Modeling of Pantograph-Catenary dynamic stability
 Technical Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences Available online at www.tjeas.com 2013 TJEAS Journal-2013-3-14/1486-1491 ISSN 2051-0853 2013 TJEAS Modeling of Pantograph-Catenary dynamic stability
Technical Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences Available online at www.tjeas.com 2013 TJEAS Journal-2013-3-14/1486-1491 ISSN 2051-0853 2013 TJEAS Modeling of Pantograph-Catenary dynamic stability
VIBRATION OF A DISCRETE-CONTINUOUS STRUCTURE UNDER MOVINGLOADWITHONEORTWOCONTACTPOINTS
 JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED MECHANICS 53, 4, pp. 935-945, Warsaw 2015 DOI: 10.15632/jtam-pl.53.4.935 VIBRATION OF A DISCRETE-CONTINUOUS STRUCTURE UNDER MOVINGLOADWITHONEORTWOCONTACTPOINTS Anna Kumaniecka
JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED MECHANICS 53, 4, pp. 935-945, Warsaw 2015 DOI: 10.15632/jtam-pl.53.4.935 VIBRATION OF A DISCRETE-CONTINUOUS STRUCTURE UNDER MOVINGLOADWITHONEORTWOCONTACTPOINTS Anna Kumaniecka
DESIGN OF A HIGH SPEED TRAIN USING A MULTIPHYSICAL APPROACH
 DESIGN OF A HIGH SPEED TRAIN USING A MULTIPHYSICAL APPROACH Aitor Berasarte Technologies Management Area Technology Division CAF WHAT DO WE ANALYSE? AERODYNAMICS STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS DYNAMICS NOISE & VIBRATIONS
DESIGN OF A HIGH SPEED TRAIN USING A MULTIPHYSICAL APPROACH Aitor Berasarte Technologies Management Area Technology Division CAF WHAT DO WE ANALYSE? AERODYNAMICS STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS DYNAMICS NOISE & VIBRATIONS
2031. Using new analytical algorithm to study the effect of temperature variations on static shape of contact wire of OCS
 2031. Using new analytical algorithm to study the effect of temperature variations on static shape of contact wire of OCS Farzad Vesali 1, Habibollah Molatefi 2, Mohammad Ali Rezvani 3 Iran University
2031. Using new analytical algorithm to study the effect of temperature variations on static shape of contact wire of OCS Farzad Vesali 1, Habibollah Molatefi 2, Mohammad Ali Rezvani 3 Iran University
Curve squeal in the presence of two wheel/rail contact points
 Curve squeal in the presence of two wheel/rail contact points G. Squicciarini 1, S. Usberti 2, D.J. hompson 1, R. Corradi 2 and A. Barbera 2 1 Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton
Curve squeal in the presence of two wheel/rail contact points G. Squicciarini 1, S. Usberti 2, D.J. hompson 1, R. Corradi 2 and A. Barbera 2 1 Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton
EXPERIMENTAL MODAL ANALYSIS OF A SCALED CAR BODY FOR METRO VEHICLES
 EXPERIMENTAL MODAL ANALYSIS OF A SCALED CAR BODY FOR METRO VEHICLES S. Popprath 1, C. Benatzky 2, C. Bilik 2, M. Kozek 2, A. Stribersky 3 and J. Wassermann 1 1 Institute of Mechanics and Mechatronics,
EXPERIMENTAL MODAL ANALYSIS OF A SCALED CAR BODY FOR METRO VEHICLES S. Popprath 1, C. Benatzky 2, C. Bilik 2, M. Kozek 2, A. Stribersky 3 and J. Wassermann 1 1 Institute of Mechanics and Mechatronics,
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
Non-hertzian contact model in wheel/rail or vehicle/track system
 XXV Symposium Vibrations in Physical Systems, Poznan Bedlewo, May 15-19, 212 Non-hertzian contact model in wheel/rail or vehicle/track system Bartłomiej DYNIEWICZ Institute of Fundamental Technological
XXV Symposium Vibrations in Physical Systems, Poznan Bedlewo, May 15-19, 212 Non-hertzian contact model in wheel/rail or vehicle/track system Bartłomiej DYNIEWICZ Institute of Fundamental Technological
Development of a Computational Tool for the Dynamic Analysis of the Pantograph-Catenary Interaction for High-Speed Trains
 Paper 129 Civil-Comp Press, 212 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, B.H.V. Topping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, Scotland Development
Paper 129 Civil-Comp Press, 212 Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Computational Structures Technology, B.H.V. Topping, (Editor), Civil-Comp Press, Stirlingshire, Scotland Development
Wire rope springs for passive vibration control of a light steel structure
 Wire rope springs for passive vibration control of a light steel structure STEFANO PAGANO, SALVATORE STRANO Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II Via Claudio
Wire rope springs for passive vibration control of a light steel structure STEFANO PAGANO, SALVATORE STRANO Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II Via Claudio
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
Optimization of high-speed railway pantographs for improving pantograph-catenary contact
 THEORETICAL & APPLIED MECHANICS LETTERS 3, 136 (213) Optimization of high-speed railway pantographs for improving pantograph-catenary contact Jorge Ambrósio, a) João Pombo, b) and Manuel Pereira c) IDMEC-IST
THEORETICAL & APPLIED MECHANICS LETTERS 3, 136 (213) Optimization of high-speed railway pantographs for improving pantograph-catenary contact Jorge Ambrósio, a) João Pombo, b) and Manuel Pereira c) IDMEC-IST
Hybrid active and semi-active control for pantograph-catenary system of high-speed train
 Hybrid active and semi-active control for pantograph-catenary system of high-speed train I.U. Khan 1, D. Wagg 1, N.D. Sims 1 1 University of Sheffield, Department of Mechanical Engineering, S1 3JD, Sheffield,
Hybrid active and semi-active control for pantograph-catenary system of high-speed train I.U. Khan 1, D. Wagg 1, N.D. Sims 1 1 University of Sheffield, Department of Mechanical Engineering, S1 3JD, Sheffield,
SHORT CIRCUITS IN 3kV DC SYSTEM: STRESSES ON VEHICLES AND INFRASTRUCTURE ELECTRIC EQUIPMENT
 SHORT CIRCUITS IN 3kV DC SYSTEM: STRESSES ON VEHICLES AND INFRASTRUCTURE ELECTRIC EQUIPMENT 1 Gabriele Alessandro ANTONACCI, 2 Paolo MEIATTINI 1 Trenitalia S.p.A., Unità Tecnologie Materiale Rotabile,
SHORT CIRCUITS IN 3kV DC SYSTEM: STRESSES ON VEHICLES AND INFRASTRUCTURE ELECTRIC EQUIPMENT 1 Gabriele Alessandro ANTONACCI, 2 Paolo MEIATTINI 1 Trenitalia S.p.A., Unità Tecnologie Materiale Rotabile,
Structural Dynamics Lecture 7. Outline of Lecture 7. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) System Reduction. Vibration due to Movable Supports.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) System Reduction. Truncated Modal Expansion with Quasi-Static Correction. Guyan Reduction. Vibration due to Movable Supports. Earthquake Excitations.
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) System Reduction. Truncated Modal Expansion with Quasi-Static Correction. Guyan Reduction. Vibration due to Movable Supports. Earthquake Excitations.
Sensitivity analysis and its application for dynamic improvement
 SaÅdhanaÅ, Vol. 25, Part 3, June 2000, pp. 291±303. # Printed in India Sensitivity analysis and its application for dynamic improvement NOBUYUKI OKUBO and TAKESHI TOI Department of Precision Mechanics,
SaÅdhanaÅ, Vol. 25, Part 3, June 2000, pp. 291±303. # Printed in India Sensitivity analysis and its application for dynamic improvement NOBUYUKI OKUBO and TAKESHI TOI Department of Precision Mechanics,
On the Dynamics of Suspension Bridge Decks with Wind-induced Second-order Effects
 MMPS 015 Convegno Modelli Matematici per Ponti Sospesi Politecnico di Torino Dipartimento di Scienze Matematiche 17-18 Settembre 015 On the Dynamics of Suspension Bridge Decks with Wind-induced Second-order
MMPS 015 Convegno Modelli Matematici per Ponti Sospesi Politecnico di Torino Dipartimento di Scienze Matematiche 17-18 Settembre 015 On the Dynamics of Suspension Bridge Decks with Wind-induced Second-order
DYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BRIDGES
 2 nd Int. PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 1998 Budapest DYNMIC INVESTIGTIONS ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BRIDGES Tamás Kovács 1 Technical University of Budapest, Department of Reinforced Concrete Structures
2 nd Int. PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 1998 Budapest DYNMIC INVESTIGTIONS ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BRIDGES Tamás Kovács 1 Technical University of Budapest, Department of Reinforced Concrete Structures
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
 Watanabe, N., & Stoten, D. P. (214). Actuator control for a rapid prototyping railway bogie, using a dynamically substructured systems approach. In Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Motion
Watanabe, N., & Stoten, D. P. (214). Actuator control for a rapid prototyping railway bogie, using a dynamically substructured systems approach. In Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Motion
Dynamic analysis of railway bridges by means of the spectral method
 Dynamic analysis of railway bridges by means of the spectral method Giuseppe Catania, Silvio Sorrentino DIEM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Bologna, Viale del Risorgimento, 436 Bologna,
Dynamic analysis of railway bridges by means of the spectral method Giuseppe Catania, Silvio Sorrentino DIEM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Bologna, Viale del Risorgimento, 436 Bologna,
Transition Structures between Rigid Conductor Line and Catenary Overhead Contact Line
 Transition Structures between Rigid Conductor Line and Catenary Overhead Contact Line T.Kobayashi 1,M.Shimizu 1,A.Oya 2 1 Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan; 2 Former Railway Technical
Transition Structures between Rigid Conductor Line and Catenary Overhead Contact Line T.Kobayashi 1,M.Shimizu 1,A.Oya 2 1 Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan; 2 Former Railway Technical
INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR LONG-SPAN SUSPENSION BRIDGES
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 28 INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR LONG-SPAN SUSPENSION BRIDGES Gianni Bartoli, Piero D Asdia, Sofia Febo,
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 2-24 28 INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR LONG-SPAN SUSPENSION BRIDGES Gianni Bartoli, Piero D Asdia, Sofia Febo,
Attenuation of rail vibration: Analysis of experimental data
 Attenuation of rail vibration: Analysis of experimental data A. Bracciali, F. Piccioli Dipartimento di Meccanica e Tecnologie Industriali Università di Firenze v. Santa Marta, 3 50139 Firenze e-mail: bracciali@ing.unifi.it
Attenuation of rail vibration: Analysis of experimental data A. Bracciali, F. Piccioli Dipartimento di Meccanica e Tecnologie Industriali Università di Firenze v. Santa Marta, 3 50139 Firenze e-mail: bracciali@ing.unifi.it
Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator
 , July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator R. Brancati, G. Di Massa, S. Pagano, E. Rocca and S. Strano Abstract This paper describes an
, July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Experimental Investigation of the Performances of a WRS-BTU Seismic Isolator R. Brancati, G. Di Massa, S. Pagano, E. Rocca and S. Strano Abstract This paper describes an
L13 Structural Engineering Laboratory
 LABORATORY PLANNING GUIDE L13 Structural Engineering Laboratory Content Covered subjects according to the curriculum of Structural Engineering... 2 Main concept... 4 Initial training provided for laboratory
LABORATORY PLANNING GUIDE L13 Structural Engineering Laboratory Content Covered subjects according to the curriculum of Structural Engineering... 2 Main concept... 4 Initial training provided for laboratory
CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE PROPAGATION ON THE SOFT GROUND WITH NON-FLAT BASE -FROM THE VIEW POINT OF RAILWAY VEHICLE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR-
 October 2-7, 28, Beijing, China CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE PROPAGATION ON THE SOFT GROUND WITH NON-FLAT BASE -FROM THE VIEW POINT OF RAILWAY VEHICLE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR- T. Kawanishi, Y. Murono 2, T. Miyamoto
October 2-7, 28, Beijing, China CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE PROPAGATION ON THE SOFT GROUND WITH NON-FLAT BASE -FROM THE VIEW POINT OF RAILWAY VEHICLE DYNAMIC BEHAVIOR- T. Kawanishi, Y. Murono 2, T. Miyamoto
Efficient simulation of railway pantograph/ catenary interaction using pantograph-fixed coordinates
 Efficient simulation of railway pantograph/ catenary interaction using pantograph-fixed coordinates Daniel Ritzberger Emir Talic Alexander Schirrer Vienna University of Technology, Austria, (e-mail: daniel.ritzberger@gmail.com).
Efficient simulation of railway pantograph/ catenary interaction using pantograph-fixed coordinates Daniel Ritzberger Emir Talic Alexander Schirrer Vienna University of Technology, Austria, (e-mail: daniel.ritzberger@gmail.com).
Pantograph wear assesment in overhead conductor rail systems P. Rodríguez, B. Suarez, J.A. Chover, J. Terrón andj.d. Sanz
 Pantograph wear assesment in overhead conductor rail systems P. Rodríguez, B. Suarez, J.. Chover, J. Terrón andj.d. Sanz Wear is the phenomenon that determines the Hfetime of the collector strips. Since
Pantograph wear assesment in overhead conductor rail systems P. Rodríguez, B. Suarez, J.. Chover, J. Terrón andj.d. Sanz Wear is the phenomenon that determines the Hfetime of the collector strips. Since
Giacomo Boffi. Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano
 http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 21, 2017 Outline of Structural Members Elastic-plastic Idealization
http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 21, 2017 Outline of Structural Members Elastic-plastic Idealization
Yang Song, 1,2 Zhigang Liu, 1,2 Huajiang Ouyang, 3 Hongrui Wang, 1,2 and Xiaobing Lu 1,2. 1. Introduction
 Hindawi Shock and Vibration Volume 217, Article ID 4895321, 16 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/217/4895321 Research Article Sliding Mode Control with PD Sliding Surface for High-Speed Railway Pantograph-Catenary
Hindawi Shock and Vibration Volume 217, Article ID 4895321, 16 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/217/4895321 Research Article Sliding Mode Control with PD Sliding Surface for High-Speed Railway Pantograph-Catenary
Analysis of Local Vibration for High-Speed Railway Bridge Based on Finite Element Method
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 91 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 214, 8, 91-915 Open Access Analysis of Local Vibration for High-Speed Railway Bridge Based on Finite Element
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 91 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 214, 8, 91-915 Open Access Analysis of Local Vibration for High-Speed Railway Bridge Based on Finite Element
A NEW ANALYSIS APPROACH FOR MOTORCYCLE BRAKE SQUEAL NOISE AND ITS ADAPTATION
 SETC001 01 1850 A NEW ANALYSIS APPROACH FOR MOTORCYCLE BRAKE SQUEAL NOISE AND ITS ADAPTATION Hiroyuki Nakata, Kiyoshi Kobayashi, Masashi Kajita - Honda R&D Co., Ltd. - JAPAN C.H.Jerry CHUNG - MTS Systems
SETC001 01 1850 A NEW ANALYSIS APPROACH FOR MOTORCYCLE BRAKE SQUEAL NOISE AND ITS ADAPTATION Hiroyuki Nakata, Kiyoshi Kobayashi, Masashi Kajita - Honda R&D Co., Ltd. - JAPAN C.H.Jerry CHUNG - MTS Systems
A Sample Durability Study of a Circuit Board under Random Vibration and Design Optimization
 A Sample Durability Study of a Circuit Board under Random Vibration and Design Optimization By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Ahmad.Abbas@AdvancedCAE.com www.advancedcae.com Sunday, March 07, 2010 Advanced CAE
A Sample Durability Study of a Circuit Board under Random Vibration and Design Optimization By: MS.ME Ahmad A. Abbas Ahmad.Abbas@AdvancedCAE.com www.advancedcae.com Sunday, March 07, 2010 Advanced CAE
TENSIONING SECTION. PFISTERER provides a full range of products for tensioning applications TENSIONING SECTION TENSOREX PHANTOM TENSOREX C+
 TENSIONING SECTION PFISTERER provides a full range of products for tensioning applications TENSIONING SECTION Midpoint Automatic Tensioning Devices TENSOREX PHANTOM TENSOREX C+ COMPENSATING EQUIPMENT TENSOREX
TENSIONING SECTION PFISTERER provides a full range of products for tensioning applications TENSIONING SECTION Midpoint Automatic Tensioning Devices TENSOREX PHANTOM TENSOREX C+ COMPENSATING EQUIPMENT TENSOREX
This is an author-deposited version published in: Handle ID:.
 Science Arts & Métiers (SAM) is an open access repository that collects the work of Arts et Métiers ParisTech researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Science Arts & Métiers (SAM) is an open access repository that collects the work of Arts et Métiers ParisTech researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Nonlinear buffeting response of bridge deck using the Band Superposition approach: comparison between rheological models and convolution integrals.
 Nonlinear buffeting response of bridge deck using the Band Superposition approach: comparison between rheological models and convolution integrals. Argentini, T. ), Diana, G. ), Portentoso, M. * ), Rocchi,
Nonlinear buffeting response of bridge deck using the Band Superposition approach: comparison between rheological models and convolution integrals. Argentini, T. ), Diana, G. ), Portentoso, M. * ), Rocchi,
CWR track vibration characteristics varying with the change of supporting condition
 Computers in Railways XIII 745 CWR track vibration characteristics varying with the change of supporting condition L. Li & Y. Luo Railway and Urban Mass Transit Research Institute, Tongji University, China
Computers in Railways XIII 745 CWR track vibration characteristics varying with the change of supporting condition L. Li & Y. Luo Railway and Urban Mass Transit Research Institute, Tongji University, China
5.5 Exercises for This Chapter Two-Axle Vehicle on Cosine Track Two-Axle Vehicle on Generally Periodic Track...
 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Basic Function of the Wheel/rail System.... 1 1.2 Significance of Dynamics on the Operation of Rail Vehicles... 2 1.3 On the History of Research in the Field of Railway
Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Basic Function of the Wheel/rail System.... 1 1.2 Significance of Dynamics on the Operation of Rail Vehicles... 2 1.3 On the History of Research in the Field of Railway
The Effect of Distribution for a Moving Force
 Paper Number 66, Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2011 2-4 November 2011, Gold Coast, Australia The Effect of Distribution for a Moving Force Ahmed M. Reda (1,2), Gareth L. Forbes (2) (1) Atkins, Perth, Australia
Paper Number 66, Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2011 2-4 November 2011, Gold Coast, Australia The Effect of Distribution for a Moving Force Ahmed M. Reda (1,2), Gareth L. Forbes (2) (1) Atkins, Perth, Australia
Damage Identification in Wind Turbine Blades
 Damage Identification in Wind Turbine Blades 2 nd Annual Blade Inspection, Damage and Repair Forum, 2014 Martin Dalgaard Ulriksen Research Assistant, Aalborg University, Denmark Presentation outline Research
Damage Identification in Wind Turbine Blades 2 nd Annual Blade Inspection, Damage and Repair Forum, 2014 Martin Dalgaard Ulriksen Research Assistant, Aalborg University, Denmark Presentation outline Research
AC&ST AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND SYSTEM THEORY SYSTEMS AND MODELS. Claudio Melchiorri
 C. Melchiorri (DEI) Automatic Control & System Theory 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND SYSTEM THEORY SYSTEMS AND MODELS Claudio Melchiorri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Energia Elettrica e dell Informazione (DEI)
C. Melchiorri (DEI) Automatic Control & System Theory 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND SYSTEM THEORY SYSTEMS AND MODELS Claudio Melchiorri Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Energia Elettrica e dell Informazione (DEI)
Chaotic Vibration and Design Criteria for Machine Systems with Clearance Connections
 Proceeding of the Ninth World Congress of the heory of Machines and Mechanism, Sept. 1-3, 1995, Milan, Italy. Chaotic Vibration and Design Criteria for Machine Systems with Clearance Connections Pengyun
Proceeding of the Ninth World Congress of the heory of Machines and Mechanism, Sept. 1-3, 1995, Milan, Italy. Chaotic Vibration and Design Criteria for Machine Systems with Clearance Connections Pengyun
Advanced Vibrations. Elements of Analytical Dynamics. By: H. Ahmadian Lecture One
 Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Stochastic Dynamics of SDOF Systems (cont.).
 Outline of Stochastic Dynamics of SDOF Systems (cont.). Weakly Stationary Response Processes. Equivalent White Noise Approximations. Gaussian Response Processes as Conditional Normal Distributions. Stochastic
Outline of Stochastic Dynamics of SDOF Systems (cont.). Weakly Stationary Response Processes. Equivalent White Noise Approximations. Gaussian Response Processes as Conditional Normal Distributions. Stochastic
1.1 OBJECTIVE AND CONTENTS OF THE BOOK
 1 Introduction 1.1 OBJECTIVE AND CONTENTS OF THE BOOK Hysteresis is a nonlinear phenomenon exhibited by systems stemming from various science and engineering areas: under a low-frequency periodic excitation,
1 Introduction 1.1 OBJECTIVE AND CONTENTS OF THE BOOK Hysteresis is a nonlinear phenomenon exhibited by systems stemming from various science and engineering areas: under a low-frequency periodic excitation,
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations
 Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
A Complex Power Approach to Characterise Joints in Experimental Dynamic Substructuring
 A Complex Power Approach to Characterise Joints in Experimental Dynamic Substructuring Emiel Barten 20-12-2013 1 A Complex Power Approach to Characterise Joints in Experimental Dynamic Substructuring Experimental
A Complex Power Approach to Characterise Joints in Experimental Dynamic Substructuring Emiel Barten 20-12-2013 1 A Complex Power Approach to Characterise Joints in Experimental Dynamic Substructuring Experimental
Facing the winter challenges for railways in Europe - Winter & Railways Fact Sheet Root Causes Rolling Stock and Infrastructure UIC Survey Evaluation
 RAIL SYSTEM FORUM SECTOR «ROLLING STOCK» SECTOR «INFRASTRUCTURE» Facing the winter challenges for railways in Europe - Winter & Railways Fact Sheet Root Causes Rolling Stock and Infrastructure UIC Survey
RAIL SYSTEM FORUM SECTOR «ROLLING STOCK» SECTOR «INFRASTRUCTURE» Facing the winter challenges for railways in Europe - Winter & Railways Fact Sheet Root Causes Rolling Stock and Infrastructure UIC Survey
Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System
 Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System Uday M. Jamdade 1, Sandip H. Deshmukh 2, Sanjay S. Deshpande 3 1 Sinhgad college of engineering, pune. 2 Sinhgad college of engineering, Pune 3 Asian academy
Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System Uday M. Jamdade 1, Sandip H. Deshmukh 2, Sanjay S. Deshpande 3 1 Sinhgad college of engineering, pune. 2 Sinhgad college of engineering, Pune 3 Asian academy
VIBRATION ENERGY FLOW IN WELDED CONNECTION OF PLATES. 1. Introduction
 ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 31, 4 (Supplement), 53 58 (2006) VIBRATION ENERGY FLOW IN WELDED CONNECTION OF PLATES J. CIEŚLIK, W. BOCHNIAK AGH University of Science and Technology Department of Robotics and Mechatronics
ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 31, 4 (Supplement), 53 58 (2006) VIBRATION ENERGY FLOW IN WELDED CONNECTION OF PLATES J. CIEŚLIK, W. BOCHNIAK AGH University of Science and Technology Department of Robotics and Mechatronics
A CONTINUOUS MODEL FOR THE VERTICAL VIBRATION OF THE HUMAN BODY IN A STANDING POSITION
 ABSTRACT A CONTINUOUS MODEL FOR THE VERTICAL VIBRATION OF THE HUMAN BODY IN A STANDING POSITION Tianjian Ji Building Research Establishment, Watford, UK This paper is concerned with modelling the vertical
ABSTRACT A CONTINUOUS MODEL FOR THE VERTICAL VIBRATION OF THE HUMAN BODY IN A STANDING POSITION Tianjian Ji Building Research Establishment, Watford, UK This paper is concerned with modelling the vertical
18. FAST NONLINEAR ANALYSIS. The Dynamic Analysis of a Structure with a Small Number of Nonlinear Elements is Almost as Fast as a Linear Analysis
 18. FAS NONLINEAR ANALYSIS he Dynamic Analysis of a Structure with a Small Number of Nonlinear Elements is Almost as Fast as a Linear Analysis 18.1 INRODUCION he response of real structures when subjected
18. FAS NONLINEAR ANALYSIS he Dynamic Analysis of a Structure with a Small Number of Nonlinear Elements is Almost as Fast as a Linear Analysis 18.1 INRODUCION he response of real structures when subjected
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Seismic Retrofitting, Base Isolation, Dynamical Testing and System Identification: A Case Study in Sicily
 ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΉΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΏΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΏΝ - ΕΓΚΑΤΑΣΤΆΣΕΙΣ 19 ΜΆΙΟΣ 29 Seismic Retrofitting, Base Isolation, Dynamical Testing and : A Case Study in Sicily Giuseppe Oliveto, Department
ΑΡΙΣΤΟΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΘΕΣΣΑΛΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΤΜΉΜΑ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΏΝ ΜΗΧΑΝΙΚΏΝ - ΕΓΚΑΤΑΣΤΆΣΕΙΣ 19 ΜΆΙΟΣ 29 Seismic Retrofitting, Base Isolation, Dynamical Testing and : A Case Study in Sicily Giuseppe Oliveto, Department
Wind tunnel sectional tests for the identification of flutter derivatives and vortex shedding in long span bridges
 Fluid Structure Interaction VII 51 Wind tunnel sectional tests for the identification of flutter derivatives and vortex shedding in long span bridges J. Á. Jurado, R. Sánchez & S. Hernández School of Civil
Fluid Structure Interaction VII 51 Wind tunnel sectional tests for the identification of flutter derivatives and vortex shedding in long span bridges J. Á. Jurado, R. Sánchez & S. Hernández School of Civil
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber
 Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Analysis of shock force measurements for the model based dynamic calibration
 8 th Worshop on Analysis of Dynamic Measurements May 5-6, 4 Turin Analysis of shoc force measurements for the model based dynamic calibration Michael Kobusch, Sascha Eichstädt, Leonard Klaus, and Thomas
8 th Worshop on Analysis of Dynamic Measurements May 5-6, 4 Turin Analysis of shoc force measurements for the model based dynamic calibration Michael Kobusch, Sascha Eichstädt, Leonard Klaus, and Thomas
A mathematical study of the pantograph/catenary dynamic interaction on transition spans
 A mathematical study of the pantograph/catenary dynamic interaction on transition spans Jesús Benet, Angelines Alberto, Enrique Arias, Tomás Rojo Abstract This paper presents the work carried out by CALPE
A mathematical study of the pantograph/catenary dynamic interaction on transition spans Jesús Benet, Angelines Alberto, Enrique Arias, Tomás Rojo Abstract This paper presents the work carried out by CALPE
Ellis Cumberbatch, Mathematics Department Claremont Graduate School, Claremont, CA 91711, USA
 Aportaciones Matematicas Comunicaciones 17 (1996) 57-64. Ellis Cumberbatch, Mathematics Department Claremont Graduate School, Claremont, CA 91711, USA Markus Schichtel, Dipartimento di Matematica Universita
Aportaciones Matematicas Comunicaciones 17 (1996) 57-64. Ellis Cumberbatch, Mathematics Department Claremont Graduate School, Claremont, CA 91711, USA Markus Schichtel, Dipartimento di Matematica Universita
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS AND DYNAMICS
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS AND DYNAMICS Dr. A.K. Tayal ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATICS AND DYNAMICS A.K. Tayal Ph. D. Formerly Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Delhi College of Engineering
ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS AND DYNAMICS Dr. A.K. Tayal ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATICS AND DYNAMICS A.K. Tayal Ph. D. Formerly Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Delhi College of Engineering
A non-destructive technique for the health monitoring of tie-rods in ancient buildings
 Proceedings of the IMAC-XXVIII February 4, 00, Jacksonville, Florida USA 00 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc. A non-destructive technique for the health monitoring of tie-rods in ancient buildings
Proceedings of the IMAC-XXVIII February 4, 00, Jacksonville, Florida USA 00 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc. A non-destructive technique for the health monitoring of tie-rods in ancient buildings
REGULATION OF THE DYNAMIC LIVE LOAD FAC- TOR FOR CALCULATION OF BRIDGE STRUCTURES ON HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY MAINLINES
 Vol. 13, Issue 1/2017, 12-19, DOI: 10.1515/cee-2017-0002 REGULATION OF THE DYNAMIC LIVE LOAD FAC- TOR FOR CALCULATION OF BRIDGE STRUCTURES ON HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY MAINLINES Leonid K. DYACHENKO 1,*, Andrey
Vol. 13, Issue 1/2017, 12-19, DOI: 10.1515/cee-2017-0002 REGULATION OF THE DYNAMIC LIVE LOAD FAC- TOR FOR CALCULATION OF BRIDGE STRUCTURES ON HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY MAINLINES Leonid K. DYACHENKO 1,*, Andrey
Sub-structuring of mechanical systems based on the path concept
 Sub-structuring of mechanical systems based on the path concept Francesc Xavier MAGRANS 1 ; Jordi POBLET-PUIG 2 ; Antonio RODRÍGUEZ-FERRAN 3 1 Ingeniería para el Control del Ruido S.L., Spain 1,2,3 Universitat
Sub-structuring of mechanical systems based on the path concept Francesc Xavier MAGRANS 1 ; Jordi POBLET-PUIG 2 ; Antonio RODRÍGUEZ-FERRAN 3 1 Ingeniería para el Control del Ruido S.L., Spain 1,2,3 Universitat
Buffeting research of suspension steel frame for ±500 kv converter station DC filter
 Buffeting research of suspension steel frame for ±5 kv converter station DC filter Long-Yi Ou 1, Yang-Ke Jian 2 State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation Research Institute, Changsha 417, China 2 Corresponding
Buffeting research of suspension steel frame for ±5 kv converter station DC filter Long-Yi Ou 1, Yang-Ke Jian 2 State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation Research Institute, Changsha 417, China 2 Corresponding
Minimization Solutions for Vibrations Induced by Underground Train Circulation
 Minimization Solutions for Vibrations Induced by Underground Train Circulation Carlos Dinis da Gama 1, Gustavo Paneiro 2 1 Professor and Head, Geotechnical Center of IST, Technical University of Lisbon,
Minimization Solutions for Vibrations Induced by Underground Train Circulation Carlos Dinis da Gama 1, Gustavo Paneiro 2 1 Professor and Head, Geotechnical Center of IST, Technical University of Lisbon,
University of Huddersfield Repository
 University of Huddersfield Repository Pislaru, Crinela Modelling and Simulation of the Dynamic Behaviour of Wheel-Rail Interface Original Citation Pislaru, Crinela (2012) Modelling and Simulation of the
University of Huddersfield Repository Pislaru, Crinela Modelling and Simulation of the Dynamic Behaviour of Wheel-Rail Interface Original Citation Pislaru, Crinela (2012) Modelling and Simulation of the
STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF A MATERIAL EXHIBITING NEGATIVE STIFFNESS
 International Conference on Engineering Vibration Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7-0 September 05 STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF A MATERIAL EXHIBITING NEGATIVE STIFFNESS Zuzana Dimitrovová*, Jan Heczo, Helder C. Rodrigues
International Conference on Engineering Vibration Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7-0 September 05 STRUCTURAL OPTIMIZATION OF A MATERIAL EXHIBITING NEGATIVE STIFFNESS Zuzana Dimitrovová*, Jan Heczo, Helder C. Rodrigues
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp. 1167 1173, Article ID: IJMET_08_05_122 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=5
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp. 1167 1173, Article ID: IJMET_08_05_122 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=5
Viscoelastic vibration damping identification methods. Application to laminated glass.
 Viscoelastic vibration damping identification methods. Application to laminated glass. J. Barredo a *, M. Soriano b, M. S. Gómez b, L. Hermanns' 5 "Centre for Modelling in Mechanical Engineering (CEMIMF2I2),
Viscoelastic vibration damping identification methods. Application to laminated glass. J. Barredo a *, M. Soriano b, M. S. Gómez b, L. Hermanns' 5 "Centre for Modelling in Mechanical Engineering (CEMIMF2I2),
Maglev by a passive HT C superconducting short runner above the magnetic guideway
 Maglev by a passive HT C superconducting short runner above the magnetic guideway G. D Ovidio 1, F. Crisi 2, A. Navarra 2 & G. Lanzara 1 1 Transportation Department, University of L Aquila, Italy 2 Science
Maglev by a passive HT C superconducting short runner above the magnetic guideway G. D Ovidio 1, F. Crisi 2, A. Navarra 2 & G. Lanzara 1 1 Transportation Department, University of L Aquila, Italy 2 Science
Predictive Control of Gyroscopic-Force Actuators for Mechanical Vibration Damping
 ARC Centre of Excellence for Complex Dynamic Systems and Control, pp 1 15 Predictive Control of Gyroscopic-Force Actuators for Mechanical Vibration Damping Tristan Perez 1, 2 Joris B Termaat 3 1 School
ARC Centre of Excellence for Complex Dynamic Systems and Control, pp 1 15 Predictive Control of Gyroscopic-Force Actuators for Mechanical Vibration Damping Tristan Perez 1, 2 Joris B Termaat 3 1 School
Using SDM to Train Neural Networks for Solving Modal Sensitivity Problems
 Using SDM to Train Neural Networks for Solving Modal Sensitivity Problems Brian J. Schwarz, Patrick L. McHargue, & Mark H. Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. 18141 Main Street Jamestown, California 95327
Using SDM to Train Neural Networks for Solving Modal Sensitivity Problems Brian J. Schwarz, Patrick L. McHargue, & Mark H. Richardson Vibrant Technology, Inc. 18141 Main Street Jamestown, California 95327
Vibration Characteristics of the Platform in highspeed Railway Elevated Station
 TELKOMNIKA, Vol.11, No.3, March 2013, pp. 1383 ~ 1392 e-issn: 2087-278X 1383 Vibration Characteristics of the Platform in highspeed Railway Elevated Station Wang Tie*, Wei Qingchao School of Civil Engineering,
TELKOMNIKA, Vol.11, No.3, March 2013, pp. 1383 ~ 1392 e-issn: 2087-278X 1383 Vibration Characteristics of the Platform in highspeed Railway Elevated Station Wang Tie*, Wei Qingchao School of Civil Engineering,
Vibration Mechanics. Linear Discrete Systems SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V. M. Del Pedro and P. Pahud
 Vibration Mechanics Vibration Mechanics Linear Discrete Systems by M. Del Pedro and P. Pahud Swiss Federal Institute oftechnology, Lausanne, Switzerland SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V. ISBN 978-94-010-5554-3
Vibration Mechanics Vibration Mechanics Linear Discrete Systems by M. Del Pedro and P. Pahud Swiss Federal Institute oftechnology, Lausanne, Switzerland SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V. ISBN 978-94-010-5554-3
ROLLING STOCK BRAKING PERFORMANCE EVALUATION UNDER LOW ADHESION CONDITIONS
 11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-12 September 2013 ROLLING STOCK BRAKING PERFORMANCE EVALUATION UNDER LOW ADHESION CONDITIONS Marco
11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9-12 September 2013 ROLLING STOCK BRAKING PERFORMANCE EVALUATION UNDER LOW ADHESION CONDITIONS Marco
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Special edition paper
 Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES
 ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES A.1 Introduction Before discussing supplemental damping devices, this annex provides a brief review of the seismic analysis methods used in the optimization algorithms considered
ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES A.1 Introduction Before discussing supplemental damping devices, this annex provides a brief review of the seismic analysis methods used in the optimization algorithms considered
VIBRATION MEASUREMENT OF TSING MA BRIDGE DECK UNITS DURING ERECTION
 VIBRATION MEASUREMENT OF TSING MA BRIDGE DECK UNITS DURING ERECTION Tommy CHAN Assistant Professor The Polytechnic University Ching Kwong LAU Deputy Director Highways Dept., Government Jan Ming KO Chair
VIBRATION MEASUREMENT OF TSING MA BRIDGE DECK UNITS DURING ERECTION Tommy CHAN Assistant Professor The Polytechnic University Ching Kwong LAU Deputy Director Highways Dept., Government Jan Ming KO Chair
TASKQUARTERLY8No1(2004),79 87
 TASKQUARTERLY8No1(2004),79 87 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF VIBRATION SURVEILLANCE OF DISCRETELY IDEALISED MECHANICAL SYSTEMS. PART I: OPTIMAL CONTROL AT THE ENERGY PERFORMANCE INDEX FOR OPEN NON-STATIONARY SYSTEMS
TASKQUARTERLY8No1(2004),79 87 COMPUTER SIMULATION OF VIBRATION SURVEILLANCE OF DISCRETELY IDEALISED MECHANICAL SYSTEMS. PART I: OPTIMAL CONTROL AT THE ENERGY PERFORMANCE INDEX FOR OPEN NON-STATIONARY SYSTEMS
Monitoring based weak point determination of a steel bridge s torsional bracings with regard to fatigue threat
 Monitoring based weak point determination of a steel bridge s torsional bracings with regard to fatigue threat R. Veit-Egerer & H. Wenzel Vienna Consulting Engineers, Vienna, Austria ABSTRACT: Bridges
Monitoring based weak point determination of a steel bridge s torsional bracings with regard to fatigue threat R. Veit-Egerer & H. Wenzel Vienna Consulting Engineers, Vienna, Austria ABSTRACT: Bridges
Simulation of the Stick-Slip Friction between Steering Shafts Using ADAMS/PRE
 Simulation of the Stick-Slip Friction between Steering Shafts Using ADAMS/PRE Dexin Wang and Yuting Rui Research & Vehicle Technology Ford Motor Company ABSTRACT Cyclic stick-slip friction is a well-known
Simulation of the Stick-Slip Friction between Steering Shafts Using ADAMS/PRE Dexin Wang and Yuting Rui Research & Vehicle Technology Ford Motor Company ABSTRACT Cyclic stick-slip friction is a well-known
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A BODY STRUCTURE
 The 3rd International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2009 29 30 OCTOBER 2009, Brasov, Romania ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A
The 3rd International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2009 29 30 OCTOBER 2009, Brasov, Romania ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A
J. A. Jurado, S. Hernández, A. Baldomir, F. Nieto, School of Civil Engineering of the University of La Coruña.
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Aeroelastic Analysis of Miradoiros Bridge in La Coruña (Spain) J. A. Jurado, S. Hernández, A. Baldomir, F. Nieto,
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Aeroelastic Analysis of Miradoiros Bridge in La Coruña (Spain) J. A. Jurado, S. Hernández, A. Baldomir, F. Nieto,
The effect of unsteady crosswind forces on train dynamic behaviour
 EACWE 5 lorence, Italy 19 th 3 rd July 009 lying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The effect of unsteady crosswind forces on train dynamic behaviour C.J. Baker School of Civil Engineering, University
EACWE 5 lorence, Italy 19 th 3 rd July 009 lying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci The effect of unsteady crosswind forces on train dynamic behaviour C.J. Baker School of Civil Engineering, University
Development of a diagnosis technique for failures of V-belts by a cross-spectrum method and a discriminant function approach
 Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing (1996) 7, 85 93 Development of a diagnosis technique for failures of V-belts by a cross-spectrum method and a discriminant function approach HAJIME YAMASHINA, 1 SUSUMU
Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing (1996) 7, 85 93 Development of a diagnosis technique for failures of V-belts by a cross-spectrum method and a discriminant function approach HAJIME YAMASHINA, 1 SUSUMU
Composite Structures- Modeling, FEA, Optimization and Diagnostics
 Composite Structures- Modeling, FEA, Optimization and Diagnostics Ratan Jha Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering Clarkson University, Potsdam, NY Composite Laminate Modeling Refined Higher Order Displacement
Composite Structures- Modeling, FEA, Optimization and Diagnostics Ratan Jha Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering Clarkson University, Potsdam, NY Composite Laminate Modeling Refined Higher Order Displacement
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ADAPTIVE MAGNITUDE SPECTRUM ALGORITHM IDENTIFIED MODAL FREQUENCIES OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME STRUCTURES
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ADAPTIVE MAGNITUDE SPECTRUM ALGORITHM IDENTIFIED MODAL FREQUENCIES OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME STRUCTURES K. C. G. Ong*, National University of Singapore, Singapore M. Maalej,
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF ADAPTIVE MAGNITUDE SPECTRUM ALGORITHM IDENTIFIED MODAL FREQUENCIES OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAME STRUCTURES K. C. G. Ong*, National University of Singapore, Singapore M. Maalej,
A MECHANICAL MODEL FOR THE DYNAMICAL CONTACT OF ELASTIC ROUGH BODIES WITH VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES
 11 th International Conference on Engineering Vibration Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7 10 September 2015 A MECHANICAL MODEL FOR THE DYNAMICAL CONTACT OF ELASTIC ROUGH BODIES WITH VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES Frank
11 th International Conference on Engineering Vibration Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7 10 September 2015 A MECHANICAL MODEL FOR THE DYNAMICAL CONTACT OF ELASTIC ROUGH BODIES WITH VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES Frank
Damping from bearing hysteresis in railway bridges
 Porto, Portugal, 30 June - 2 July 2014 A. Cunha, E. Caetano, P. Ribeiro, G. Müller (eds.) ISSN: 2311-9020; ISBN: 978-972-752-165-4 Damping from bearing hysteresis in railway bridges Mahir Ülker-Kaustell
Porto, Portugal, 30 June - 2 July 2014 A. Cunha, E. Caetano, P. Ribeiro, G. Müller (eds.) ISSN: 2311-9020; ISBN: 978-972-752-165-4 Damping from bearing hysteresis in railway bridges Mahir Ülker-Kaustell
