BIOMEDICAL ADMISSIONS TEST (BMAT Leiden) Specimen paper. Section 2 explained answers
|
|
|
- Allen Harris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOMEDICAL ADMISSIONS TEST (BMAT Leiden) Specimen paper Section explained answers
2 1 Process 1 is nitrogen fixation which is the process of turning nitrogen gas from the air into nitrogen compounds in the soil Process is denitrification which is the release of nitrogen back into the air Process is the breakdown of nitrogen-rich dead plant material such as plant protein Therefore the correct answer is H Addition polymerisation takes place between unsaturated molecules, such as those containing the C = C double bond (alkenes) which can join with another C = C bond to form a C C linkage in a polymer Fully saturated molecules, such as alkanes, cannot undergo addition polymerisation Alkenes have the general formula C n H n whilst alkanes have the general formula C n H n+ Both formulae can have other atoms in them replacing one or more H atoms eg Cl, Br, I In this question compound 1 is fully saturated, it is an alkane; there are no double (or triple) bonds present Compound is an alkene as is compound 4 (with Cl atoms) Compound matches the general formula of an alkane (with 1 Br atom) and therefore is fully saturated Compound 5 matches the general formula of an alkene (with 4 Cl atoms) Therefore the correct answer is E (, 4 and 5 only) Statement 1: Aluminium is a good conductor of heat and would increase, not decrease, the rate of heat loss by conduction Statement 1 is therefore not correct Statement : The aluminium sheet does trap air and the fact that air is trapped reduces heat loss by convection Statement is therefore correct Statement : Aluminium is shiny and therefore a poor emitter of thermal radiation It therefore does reduce heat loss by radiation Statement is correct The correct option is that statements and only are correct Therefore the correct answer is F 1 4 The area of a triangle is given by base height The height is the vertical height which is given as In this case the area is 6 Because then this simplifies to Therefore the correct answer is C 5 The SAN pacemaker is found within the wall of the right atrium which leaves the answers of B or F Whilst the left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body, the right pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs Therefore the correct answer F UCLES 015
3 6 This type of question relies on studying the equation and the numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation In this question the Na atoms give the starting point as on the right there are c 5 and on the left are a 1 and b The first effort would be would be to make c = 1, a = 1 and b = in order to balance the Na atoms and then use them to find the value of d Using the original values (c, a and b ) the P atoms are also balanced so it is then a matter of adding up the O and H atoms on the leftthis gives d = as a value to balance them Therefore the correct answer is D (1,, 1, ) 7 The mass of the two cars is the same which means that kinetic energy is proportional to speed squared Therefore, as car Q has twice the speed of car P, it will have four times the kinetic energy Gravitational potential energy is proportional to height, and so the car which rises 50 m will have double the potential energy of the car that has only risen 5 m The correct answer is therefore that car Q will have twice as much potential energy but four times as much kinetic energy as car P Therefore the correct answer is C 8 In the expression every term inside the bracket has to be squared The easiest way is to consider each term separately 4 x x Remember that when raising one power to another, you multiply them, so: x x In the same way we have to square which leaves us with z The square of y is y 6 The expression simplifies to 4x y z Therefore the correct answer is B, 6 4x y z 6 None of the other expressions are equivalent to this 9 As the genotypes of P and Q are given, the genotype of S will be a combination of one allele from each of P and Q which makes S heterozygous There is a 50% chance that U will inherit the recessive allele from S If T is homozygous recessive then individual U will have a 100% chance of inheriting a recessive allele from T So the chance of individual U, inheriting both recessive alleles is 50% (answers A and C) However, if T is heterozygous, then individual U will have a 50% chance of inheriting the recessive allele from T Therefore the chance of individual U inheriting both recessive alleles from heterozygous parents will be 5% Therefore the correct answer is C UCLES 015
4 4 10 Bond breaking is an endothermic process whilst bond making is an exothermic process The equation is exothermic overall, which means that more energy is released when bonds are made than is needed for bonds being broken The bonds to be broken are on the left (N and H ) and made on the right ( N H) of the equation This means that the 6 N H bond energies must be greater than the N and H bond energies in total Looking at the number of bonds from the mole ratios in the equation (1 : : ) the correct answer is D: 6z x y 11 When travelling at terminal velocity, the force of air resistance (drag) on the parachutist will be equal and opposite to his weight This is true when travelling at a high terminal velocity before opening the parachute and when travelling at a lower terminal velocity after opening the parachute Terminal velocity means zero acceleration which means zero resultant force During the act of opening the parachute there is a rapid deceleration which means that momentarily there must be a resultant upwards force acting on the parachutist During that instant there must therefore be air resistance which is much greater than the weight The correct graph is therefore one that shows the same air resistance force, in the same direction throughout, apart from during the moment of opening the parachute And during that moment there must be a much larger air resistance force, again all in the same direction The only graph that shows all this is graph A B and D are incorrect because they show the air resistance force changing direction, which it cannot do It will always be upwards C and D are incorrect because they show different air resistance forces at terminal velocity before and after opening the parachute Therefore the correct answer is A 1 The probability of an event, if all events are equally likely, is the number of ways for something to happen divided by the total number of possible results The balls are identical except for colour, and are well mixed, so picking any of the colours is equally likely x The probability that the first ball taken out was red is x y z The chosen ball is now replaced, irrespective of colour There are still the bag y The probability that the second ball taken out was blue is x y z Therefore the correct answer is E x y z balls in 1 The transfer between one neuron and the next is via a transmitter substance that diffuses across the synaptic gap hence statement 4 is correct The arrival of the signal at the end of the neuron next to the synapse stimulates the release of the transmitter, hence statement is also correct Therefore the correct answer is E UCLES 015
5 5 14 From the information provided it is clear that the compound is ionically bonded Remember that the overall charge of any compound is zero, so the total sum of the charges of the individual ions in the compounds A F must equal 0 if the compound exists The method is to work out for each compound the amount of positive (+) charges (Mg and H) and the amount of negative ( ) charges (PO 4 ) Only Mg(H PO 4 ) correctly balances the + and charges Therefore the correct answer is B: Mg(H PO 4 ) 15 Source X: 4 hours is 5 half-lives So in that time the activity of source X will halve 5 times 0 to 160 to 80 to 40 to 0 to 10 So after 4 hours the activity of X will have fallen to 10 counts per minute Source Y: 8 hours is half-lives So in that time the activity of Y will halve times 480 to 40 to 10 to 60 So after 4 hours the activity of Y will have fallen to 60 counts per minute The combined count rate after 4 hours is therefore = 70 counts per minute Therefore the correct answer is D 16 To rearrange a formula the subject has to be isolated In the formula 6 d r 1 the n n 1 d term has to be isolated There are several different ways of doing this but these all include the same steps In the first instance add 6 d n n 1 to both sides of the equation This gives 6 d r 1 n n 1 Then subtract r from both sides of the equation This gives 6 d r n n 1 1 Now divide both sides of the equation by 6 to give Finally multiply both sides of the equation by ( n 1) d 1 r n n r n to give nn 1 d 6 This is not exactly the same as any of the given answers but nn n n answer arrived at is equivalent to response E (1 r) Therefore the correct answer is E: d n n 6 1 and so the UCLES 015
6 6 17 During breathing out, the diaphragm muscles relax so statement is incorrect The ribcage moves down and in during breathing out, which is statement 1 This causes a decrease in the volume of the thorax leading to an increase in pressure within the lungs, which is statement As 1 and are right, the correct answer is E 18 Different methods can be used to calculate the answer and one is shown below: Maximum mass of PbS from the ore = kg Relative formula mass of PbS = 07 + = 9 Number of moles of PbS = = 7 10 = 14 Number of moles of Pb = 14 07, so the correct option must be more than 07 (= 1 07), and less than 414 (= 07) There is only one option that matches Therefore the correct answer is D, 8980 kg 19 The trough to peak height is = 6 m But amplitude is defined as the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position, ie from the middle to the trough or peak Amplitude is therefore 6 = m The period of the wave is 1 hours (from the graph) 1 hours = 1 60 minutes = seconds Frequency = 1 period = Hz Therefore the correct answer is A (amplitude = m, frequency = Hz UCLES 015
7 7 0 One way to approach this is to think about which quadrants of the graph the equations cover, the and intercepts, and any symmetrical shapes Quick sketches will help y x and y 1 x are quadratic functions they have a symmetrical U shape For y 1 x the sign means it is upside down, and the 1 means at 0, 1, so the top of the upside-down U is above the axis, at 1 So, and could intersect is a straight line, with a gradient of +, a intercept at and an intercept at It is in the same quadrants as either y x or y 1 x, or both of them, and so could intersect 6 is a straight line, with a gradient of +1 a intercept at 6 and an intercept at 6 For 6 it is in the same quadrants as y x, so these graphs could intersect 6 intersects the axis 6, and the graph of y 1 x intersects the axis 1, so these two graphs may not intersect 6 intersects the axis at 6, and y 1 x intersects the axis at 1, so these two lines do not intersect This is option E It is clear from the plots that y x 6 and y 1 x do not intersect An alternative approach is to solve each pair of equations The correct answer is E ( and 4) UCLES 015
8 8 1 Oxygen is required for aerobic respiration which releases energy The energy released is used for active transport which moves substances up the concentration gradient The only answer that shows movement against the concentration gradient is C Therefore the correct answer is C The Periodic Table is structured so that: the number of the group shows the number of electrons in the outer shell of the atom; the number of the period shows the total number of shells of the atom In this example Y has gained a charge ie electrons have been added to the atom to make the configuration of a noble gas of, 8, 8 The atom Y must have the electron configuration,8,5 This means it is in Group 15 and Period Therefore the correct answer is C (Group is 15, Period is ) Output power = 050 kw = 500 W Therefore output voltage = P I = = 50 V Number of turns on the secondary is therefore Therefore the correct answer is B = = 00 turns (Note the fact that the transformer is 100% efficient is not information that you need to answer this question, as you are already given the output power) UCLES 015
9 9 4 The volume of a cylinder (a circular prism) is the base area times the height, r h As the cylinder s height and internal diameter are the same as the diameter of the sphere then both of these are equal to r This means that the volume of the cylinder is r r The volume of the cylinder is r r r The volume of the sphere is 4 r The fraction of space inside the cylinder taken up by the sphere is 4 r r Simplify by cancelling the terms to leave 4 1 Therefore the correct answer is D, 5 The process of genetically engineering this bacterium requires a restriction enzyme to cut out the fluorescent gene from jellyfish DNA (answer B) This gene needs to be put into an appropriate vector (answer A) which uses a ligase (answer D) However, it is the gene that is being added, not the protein that it codes for, so answer C is correct because it is not needed 6 There are several methods that will give the correct answer and one is shown below: No of moles of I = = 1 = 05 No of moles of O = = 5 4 = 15 Ratio of I : O is 05 : 15 ie :5 Therefore the correct answer is E (I O 5 ) UCLES 015
10 10 7 First, consider these microwaves travelling in air We are told they have a wavelength of 1 cm (= 01 m) and a speed of m/s This means we can work out their frequency, from speed = frequency wavelength, v = f λ f = v = = = = = Hz Now consider the microwaves passing through the plastic We know the plastic will slow the waves down, therefore reducing the wavelength, but that the frequency remains unchanged We are therefore looking for a frequency of Hz but a wavelength shorter than 1 cm by a factor of / (ie 80 cm) Therefore the correct answer is B UCLES 015
BioMedical Admissions Test. Specimen Section 2 answers
 BioMedical Admissions Test Specimen Section answers UCLES 017 1 The correct answer is option H. The removal of nitrogen gas from the air, process 1, into the soil is nitrogen fixation. The release of nitrogen
BioMedical Admissions Test Specimen Section answers UCLES 017 1 The correct answer is option H. The removal of nitrogen gas from the air, process 1, into the soil is nitrogen fixation. The release of nitrogen
BioMedical Admissions Test BMAT LEIDEN 4500/12
 iomedical dmissions Test MT LEIEN 4500/1 Updated Specimen 40 minutes SETION Scientific Knowledge and pplications Instructions to andidates Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question
iomedical dmissions Test MT LEIEN 4500/1 Updated Specimen 40 minutes SETION Scientific Knowledge and pplications Instructions to andidates Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question
Scientific Knowledge and Applications
 iomedical dmissions Test Specimen 0 minutes SETION Scientific Knowledge and pplications Instructions to andidates Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question paper until you are told
iomedical dmissions Test Specimen 0 minutes SETION Scientific Knowledge and pplications Instructions to andidates Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question paper until you are told
BioMedical Admissions Test 4500/12
 iomedical dmissions Test 4500/12 *1811945425* Wednesday 4 th November 2009 30 minutes STION 2 Instructions to andidates Scientific Knowledge and pplications Please read this page carefully, but do not
iomedical dmissions Test 4500/12 *1811945425* Wednesday 4 th November 2009 30 minutes STION 2 Instructions to andidates Scientific Knowledge and pplications Please read this page carefully, but do not
Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips
 Chapter (a) There is a much greater gap between the mean values of x B for the 0.00 and 0.200 kg masses than there is between the 0.200 and 0.300 kg masses. Measurements for two more values of m between
Chapter (a) There is a much greater gap between the mean values of x B for the 0.00 and 0.200 kg masses than there is between the 0.200 and 0.300 kg masses. Measurements for two more values of m between
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-DINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-DINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe. You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of:
 OCR B Physics H557 Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 5.2: Matter Particle model: A gas consists of many very small, rapidly
OCR B Physics H557 Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 5.2: Matter Particle model: A gas consists of many very small, rapidly
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) 07 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 0 Published
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) 07 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 0 Published
Yarışma Sınavı. 4 2 litre of gas at a temperature of 27 o C and A ) 8/3 B ) 3/2 C ) 2/3 D ) 3/8 E ) 254/27
 1 Which pair of physical quantities consist of two vectors? ) speed and acceleration B ) power and momentum C ) force and displacement D ) mass and kinetic energy E ) momentum and speed 4 2 litre of gas
1 Which pair of physical quantities consist of two vectors? ) speed and acceleration B ) power and momentum C ) force and displacement D ) mass and kinetic energy E ) momentum and speed 4 2 litre of gas
Atoms, Elements, Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures. Compounds and Mixtures. Atoms and the Periodic Table. Atoms and the.
 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Motion Graphs Refer to the following information for the next four questions.
 Motion Graphs Refer to the following information for the next four questions. 1. Match the description provided about the behavior of a cart along a linear track to its best graphical representation. Remember
Motion Graphs Refer to the following information for the next four questions. 1. Match the description provided about the behavior of a cart along a linear track to its best graphical representation. Remember
Chapter 18 Solutions Set Up: (a) The proton has charge and mass Let point a be at the negative plate and
 Chapter 18 Solutions *18.1. Set Up: Since the charge is positive the force on it is in the same direction as the electric field. Since the field is uniform the force is constant is upward is to the right,
Chapter 18 Solutions *18.1. Set Up: Since the charge is positive the force on it is in the same direction as the electric field. Since the field is uniform the force is constant is upward is to the right,
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 H2 PHYSICS 9749/01. Paper 1 SEP 2018
 PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 H2 PHYSICS 9749/01 Paper 1 SEP 2018 Additional Materials: Multiple Choice Answer Sheet Duration: 1 hour DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2018 H2 PHYSICS 9749/01 Paper 1 SEP 2018 Additional Materials: Multiple Choice Answer Sheet Duration: 1 hour DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS
g E. An object whose weight on 6 Earth is 5.0 N is dropped from rest above the Moon s surface. What is its momentum after falling for 3.0s?
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Take the acceleration due to gravity, g E, as 10 m s on the surface of the Earth. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is g E. n object whose weight on
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Take the acceleration due to gravity, g E, as 10 m s on the surface of the Earth. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is g E. n object whose weight on
Comment: Unlike distance, displacement takes into consideration the direction of motion from the point of origin (where the object starts to move).
 Chapter 3 Kinematics (A) Distance Vs Displacement 1. Compare distance and displacement in terms of: (a) definition Distance is the total length of travel, irrespective of direction. Displacement is the
Chapter 3 Kinematics (A) Distance Vs Displacement 1. Compare distance and displacement in terms of: (a) definition Distance is the total length of travel, irrespective of direction. Displacement is the
2.1. KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. 34 Reinforcement Unit 1 Resource Book
 2.1 ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. All matter, whether living or nonliving, is made of the same tiny building blocks, called atoms.
2.1 ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. All matter, whether living or nonliving, is made of the same tiny building blocks, called atoms.
Practice exam-style paper
 Practice exam-style paper Paper 4 Core and Supplement [1 hour 15 min] Write your answers on the question paper. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question.
Practice exam-style paper Paper 4 Core and Supplement [1 hour 15 min] Write your answers on the question paper. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question.
Sample questions: maths in science
 Sample questions: maths in science These sample questions show how the five mathematical skills areas could be assessed in GCSE Combined Science. You can use them to understand the types of maths questions
Sample questions: maths in science These sample questions show how the five mathematical skills areas could be assessed in GCSE Combined Science. You can use them to understand the types of maths questions
End-of-unit 2. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips
 (a) Arrowed lines drawn to show: two components at right angles vertical component in line with weight (b) (i) Horizontal component of T is T cos 60 = 25 0.5 = 2.5 N or 3 N to 2 significant figures. (ii)
(a) Arrowed lines drawn to show: two components at right angles vertical component in line with weight (b) (i) Horizontal component of T is T cos 60 = 25 0.5 = 2.5 N or 3 N to 2 significant figures. (ii)
Semester Question and Answer Booklet
 YEAR 10 SCIENCE EXAMINATION Semester 1 2016 Question and Answer Booklet STUDENT NAME: TEACHER: DATE: Time allowed for this paper: 1 hour and 30 minutes Materials required: Pens, pencils, eraser, ruler,
YEAR 10 SCIENCE EXAMINATION Semester 1 2016 Question and Answer Booklet STUDENT NAME: TEACHER: DATE: Time allowed for this paper: 1 hour and 30 minutes Materials required: Pens, pencils, eraser, ruler,
Maths tutorial booklet for. M2: Algebra. Name: Target grade: Quiz scores: M2.1 Understand and use symbols =,,,,, α, ~ =
 Maths tutorial booklet for M2: Algebra Name: Target grade: Quiz scores: M2.1 Understand and use symbols =,,,,, α, ~ = M2.2 = Change the subject of an equation M2.3 Substitute numerical values into algebraic
Maths tutorial booklet for M2: Algebra Name: Target grade: Quiz scores: M2.1 Understand and use symbols =,,,,, α, ~ = M2.2 = Change the subject of an equation M2.3 Substitute numerical values into algebraic
Chemical Kinetics. Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions:
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions: reactant concentration temperature action of catalysts surface
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions: reactant concentration temperature action of catalysts surface
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/33 Paper 3 Extended Theory May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/33 Paper 3 Extended Theory May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published
This unit will help you define health, learn about some pathogens and the diseases they cause, medicines and about the immune system.
 YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
Elements and Chemical Bonds. Chapter 11
 Elements and Chemical Bonds Chapter 11 Essential Question How does understanding periodic trends allow us to predict properties of different elements? Vocabulary Ionic bond Covalent bond Compounds, Chemical
Elements and Chemical Bonds Chapter 11 Essential Question How does understanding periodic trends allow us to predict properties of different elements? Vocabulary Ionic bond Covalent bond Compounds, Chemical
PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST Thursday, 2 November Time allowed: 2 hours
 PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST Thursday, 2 November 2017 Time allowed: 2 hours For candidates applying to Physics, Physics and Philosophy, Engineering, or Materials Total 23 questions [100 Marks] Answers should
PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST Thursday, 2 November 2017 Time allowed: 2 hours For candidates applying to Physics, Physics and Philosophy, Engineering, or Materials Total 23 questions [100 Marks] Answers should
Number 1 What is a chemical reaction?
 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Number 1 What is a chemical reaction? A process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another by changing the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds.
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Number 1 What is a chemical reaction? A process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another by changing the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds.
Unit 6 Kinetics and Equilibrium.docx
 6-1 Unit 6 Kinetics and Equilibrium At the end of this unit, you ll be familiar with the following: Kinetics: Reaction Rate Collision Theory Reaction Mechanism Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction: o Nature
6-1 Unit 6 Kinetics and Equilibrium At the end of this unit, you ll be familiar with the following: Kinetics: Reaction Rate Collision Theory Reaction Mechanism Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction: o Nature
Math 105 Exit Exam Review
 Math 105 Exit Exam Review The review below refers to sections in the main textbook Modeling the Dynamics of Life, 2 nd edition by Frederick F. Adler. (This will also be the textbook for the subsequent
Math 105 Exit Exam Review The review below refers to sections in the main textbook Modeling the Dynamics of Life, 2 nd edition by Frederick F. Adler. (This will also be the textbook for the subsequent
Definition: An Ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer.
 3 Bonding Definition An Ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer. Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. on-metal atoms gain
3 Bonding Definition An Ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer. Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. on-metal atoms gain
In your answer, you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly [1]
![In your answer, you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly [1] In your answer, you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly [1]](/thumbs/79/79102420.jpg) 1 (a) Define moment of a force. In your answer, you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly.... [1] (b) State the two conditions that apply when an object is in equilibrium. 1.... 2....
1 (a) Define moment of a force. In your answer, you should use appropriate technical terms, spelled correctly.... [1] (b) State the two conditions that apply when an object is in equilibrium. 1.... 2....
Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy
 Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy AEROBIC RESPIRATION All cells in the body need energy - this energy is released in a process known as respiration Cells that are more active need more energy - e.g during
Topic 2 notes Organisms and energy AEROBIC RESPIRATION All cells in the body need energy - this energy is released in a process known as respiration Cells that are more active need more energy - e.g during
BioMedical Admissions Test 4500/12
 iomedical dmissions Test 4500/12 Wednesday 4 th November 2015 30 minutes STION 2 Instructions to andidates Scientific Knowledge and pplications Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question
iomedical dmissions Test 4500/12 Wednesday 4 th November 2015 30 minutes STION 2 Instructions to andidates Scientific Knowledge and pplications Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question
2016 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET
 2016 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN CHAPTER TOPIC # OF QUESTIONS 6 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY 22 7 MOMENTUM/COLLISIONS 17 5 CIRCULAR MOTION GRAVITY/SATELLITE MOTION 30 11 WAVES 24 - ELECTROMAGNETISM/MISC./LABS
2016 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN CHAPTER TOPIC # OF QUESTIONS 6 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY 22 7 MOMENTUM/COLLISIONS 17 5 CIRCULAR MOTION GRAVITY/SATELLITE MOTION 30 11 WAVES 24 - ELECTROMAGNETISM/MISC./LABS
The Periodic Table. run vertically on the periodic table (up and down).
 Lesson Objective: The Periodic Table Science 8.5B Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements 8.2E Analyze data
Lesson Objective: The Periodic Table Science 8.5B Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements 8.2E Analyze data
4-4 Bioenergetics Biology
 4-4 Bioenergetics Biology.0 Figure shows a plant cell. Figure. Draw one line from each part of the cell to its function. [3 marks] Part of the cell Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondria Function Where most
4-4 Bioenergetics Biology.0 Figure shows a plant cell. Figure. Draw one line from each part of the cell to its function. [3 marks] Part of the cell Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondria Function Where most
SECONDARY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT UNIT- EDUCATION DIVISION. FORM 3 PHYSICS Time: 1h 30min
 SECONDARY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT UNIT- EDUCATION DIVISION FORM 3 PHYSICS Time: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator
SECONDARY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 EDUCATIONAL ASSESSMENT UNIT- EDUCATION DIVISION FORM 3 PHYSICS Time: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator
5.1 Module 1: Rates, Equilibrium and ph
 5.1 Module 1: Rates, Equilibrium and ph 5.1.1 How Fast? The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm 3 s 1 When a graph of concentration
5.1 Module 1: Rates, Equilibrium and ph 5.1.1 How Fast? The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm 3 s 1 When a graph of concentration
Paget High School. Preparing for A level Biology
 Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
COSMIC CHALLENGING EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level. MARK SCHEME for the challenging Set 1 question paper 5058 PHYSICS
 COSMIC CHALLENGING EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level 01 MARK SCHEME for the challenging Set 1 question paper 5058 PHYSICS 5058/01 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 40 This mark scheme
COSMIC CHALLENGING EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level 01 MARK SCHEME for the challenging Set 1 question paper 5058 PHYSICS 5058/01 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 40 This mark scheme
Time (s) Velocity (m/s)
 29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* PHYSICS 0625/04 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* PHYSICS 0625/04 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1
BioMedical Admissions Test 4500/12
 BioMedical Admissions Test 4500/12 Wednesday 7 th November 2012 30 minutes SECTION 2 Instructions to Candidates Scientific Knowledge and Applications Please read this page carefully, but do not open the
BioMedical Admissions Test 4500/12 Wednesday 7 th November 2012 30 minutes SECTION 2 Instructions to Candidates Scientific Knowledge and Applications Please read this page carefully, but do not open the
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
8. More about calculus in physics
 8. More about calculus in physics This section is about physical quantities that change with time or change when a different quantity changes. Calculus is about the mathematics of rates of change (differentiation)
8. More about calculus in physics This section is about physical quantities that change with time or change when a different quantity changes. Calculus is about the mathematics of rates of change (differentiation)
Cells the Building Blocks of Life. Cells the Building Blocks of Life. Cells the Building Blocks of Life. Cells the Building Blocks of Life
 1 What is gestation? 2 Give three ways in which alveoli are adapted for gas exchange. 3 Describe what happens to someone when they suffer from an asthma attack. 4 What is meant by the term antagonistic
1 What is gestation? 2 Give three ways in which alveoli are adapted for gas exchange. 3 Describe what happens to someone when they suffer from an asthma attack. 4 What is meant by the term antagonistic
1. Draw a graph showing what happens to water when we take ice in a beaker and heat it up until it boils.
 i Name: Date: Block: This is a basic guide and does not include everything that we covered; do not use this as your only study tool. Use your notebook, worksheets, tests, notes, and other materials to
i Name: Date: Block: This is a basic guide and does not include everything that we covered; do not use this as your only study tool. Use your notebook, worksheets, tests, notes, and other materials to
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1843469512* PHYSICS 0625/33 Paper 3 Extended October/November 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1843469512* PHYSICS 0625/33 Paper 3 Extended October/November 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
AS Unit G481: Mechanics
 Definitions: define scalar and vector quantities and give Scalar: Magnitude without direction examples; Examples: Length, area, volume, distance, speed, mass, density, pressure, temperature, energy, work,
Definitions: define scalar and vector quantities and give Scalar: Magnitude without direction examples; Examples: Length, area, volume, distance, speed, mass, density, pressure, temperature, energy, work,
GCSE 0241/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 0241/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 2 A.M. WEDNESDAY, 30 January 2013 45 minutes ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 0241/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 2 A.M. WEDNESDAY, 30 January 2013 45 minutes ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/23 Paper
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/23 Paper
exothermic reaction and that ΔH c will therefore be a negative value. Heat change, q = mcδt q = m(h 2
 Worked solutions hapter 5 Exercises 1 B If the temperature drops, the process must be endothermic. Δ for endothermic reactions is always positive. 2 B All exothermic reactions give out heat. While there
Worked solutions hapter 5 Exercises 1 B If the temperature drops, the process must be endothermic. Δ for endothermic reactions is always positive. 2 B All exothermic reactions give out heat. While there
Thermodynamics. Standard enthalpy change, H
 Standard enthalpy change, H Thermodynamics Enthalpy change, H, is defined as the heat energy change measured under conditions of constant pressure. The value of the enthalpy change for a particular reaction
Standard enthalpy change, H Thermodynamics Enthalpy change, H, is defined as the heat energy change measured under conditions of constant pressure. The value of the enthalpy change for a particular reaction
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration
 Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Bridging the Gap between GCSE and A level Chemistry
 Bridging the Gap between GCSE and A level Chemistry You should use your GCSE revision guide and your class notes to complete the following questions You can check your answers at the end of the power point,
Bridging the Gap between GCSE and A level Chemistry You should use your GCSE revision guide and your class notes to complete the following questions You can check your answers at the end of the power point,
BioMedical Admissions Test 4500/12
 iomedical dmissions Test 45/12 Wednesday 2 nd November 211 3 minutes STION 2 Instructions to andidates Scientific Knowledge and pplications Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question
iomedical dmissions Test 45/12 Wednesday 2 nd November 211 3 minutes STION 2 Instructions to andidates Scientific Knowledge and pplications Please read this page carefully, but do not open the question
P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January hour
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4473/02 W15-4473-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/PHYSICS PHYSICS 2 HIGHER TIER P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 15
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4473/02 W15-4473-02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE/PHYSICS PHYSICS 2 HIGHER TIER P.M. THURSDAY, 15 January 2015 1 hour For s use Question Maximum Mark 1. 15
0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCEME for the May/June 2014 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/33 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum raw
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCEME for the May/June 2014 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/33 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum raw
New GCSE 4473/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 New GCSE 4473/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 2 A.M. THURSDAY, 24 May 2012 1 hour ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may require
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 New GCSE 4473/02 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER PHYSICS 2 A.M. THURSDAY, 24 May 2012 1 hour ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this paper you may require
Mathematics and Physics (28 questions) Advanced Mathematics and Advanced Physics (26 questions)
 NGINRING MISSIONS SSSSMNT SPIMN PPR 80 minutes STION INSTRUTIONS TO NITS Please read these instructions carefully, but do not open this question paper until you are told that you may do so. This paper
NGINRING MISSIONS SSSSMNT SPIMN PPR 80 minutes STION INSTRUTIONS TO NITS Please read these instructions carefully, but do not open this question paper until you are told that you may do so. This paper
Physical Science Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Physical Science Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The electrons in a water molecule are gathered nearest
Name: Class: Date: Physical Science Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The electrons in a water molecule are gathered nearest
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/33 Paper 3 Extended Theory May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 120
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/33 Paper 3 Extended Theory May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 120
Unit 5 Test. Name: Score: 37 / 37 points (100%)
 Name: Score: 37 / 37 points (100%) Unit 5 Test Matching (1 point each) Match each item with the correct statement below a activity series j product b chemical equation k reactant c coefficient l reduction
Name: Score: 37 / 37 points (100%) Unit 5 Test Matching (1 point each) Match each item with the correct statement below a activity series j product b chemical equation k reactant c coefficient l reduction
YEAR 7. St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map New AQA Course Started November 2016
 YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
Additional Science. Important exam information and revision booklet
 Additional Science Important exam information and revision booklet CONTENTS PAGE Page Introduction 3 Section One When are my exams? What will they test 4 Useful places to help you to revise Additional
Additional Science Important exam information and revision booklet CONTENTS PAGE Page Introduction 3 Section One When are my exams? What will they test 4 Useful places to help you to revise Additional
1.9 Practice Problems
 1.9 Practice Problems 1. Solution: B It s not only chlorophyll a but a combination of pigments. 2. Solution: D See at what wavelength rate of photosynthesis is the highest. 3. Solution: D It s a fact.
1.9 Practice Problems 1. Solution: B It s not only chlorophyll a but a combination of pigments. 2. Solution: D See at what wavelength rate of photosynthesis is the highest. 3. Solution: D It s a fact.
A particle travels at a constant speed around a circle of radius r with centripetal acceleration a. What is the time taken for ten complete rotations?
 1 particle travels at a constant speed around a circle of radius r with centripetal acceleration a. What is the time taken for ten complete rotations? 2 The frequency of a body moving with simple harmonic
1 particle travels at a constant speed around a circle of radius r with centripetal acceleration a. What is the time taken for ten complete rotations? 2 The frequency of a body moving with simple harmonic
Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things are made of what?
 All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
All living things are made of what? Do all living things grow, move, and breathe? All living things respond to external conditions. This is called what? Which of the 7 traits of life is defined as the
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/23 Paper 2 (Core
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/23 Paper 2 (Core
Physics *P43118A0128* Pearson Edexcel GCE P43118A. Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics on the Go. Tuesday 20 May 2014 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCE Physics Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics on the Go Centre Number Candidate Number Tuesday 20 May 2014 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCE Physics Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Physics on the Go Centre Number Candidate Number Tuesday 20 May 2014 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Review Chapter 1 and 2 [184 marks]
![Review Chapter 1 and 2 [184 marks] Review Chapter 1 and 2 [184 marks]](/thumbs/95/122506931.jpg) Review Chapter 1 and 2 [184 marks] This question is in two parts. Part 1 is about momentum. Part 2 is about electric point charges. Part 1 Momentum 1a. State the law of conservation of linear momentum.
Review Chapter 1 and 2 [184 marks] This question is in two parts. Part 1 is about momentum. Part 2 is about electric point charges. Part 1 Momentum 1a. State the law of conservation of linear momentum.
UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE CHEMISTRY Sample Assessment Materials 71 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE CHEMISTRY UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION
GCSE CHEMISTRY Sample Assessment Materials 71 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE CHEMISTRY UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION
Atomic Structure. The center of the Atom is called the Nucleus
 Basic Chemistry Review Atomic Structure The center of the Atom is called the Nucleus It is about 100,000 times smaller than the entire atom It makes up 99.9% of the mass of the atom In the Nucleus There
Basic Chemistry Review Atomic Structure The center of the Atom is called the Nucleus It is about 100,000 times smaller than the entire atom It makes up 99.9% of the mass of the atom In the Nucleus There
Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas HL
 Name: Chemical Bonding 5. Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forces Objectives -understand that compounds can be
Name: Chemical Bonding 5. Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forces Objectives -understand that compounds can be
Ponce de Leon 8thGrade Winter Science Package '13-'14
 Name: Teacher: Period: Date: Ponce de Leon 8thGrade Winter Science Package '13-'14 Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phrases
Name: Teacher: Period: Date: Ponce de Leon 8thGrade Winter Science Package '13-'14 Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phrases
Chapter 12. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips
 (a) v esc = gr = (.6 740 0 3 ) ½ = 400 m s (370 m s to 3 sig figs) (b) (i) Mean kinetic energy = 3_ kt =.5.38 0 3 400 = 8.3 0 J (ii) Mass of an oxygen molecule m= molar mass/n A 0.03 = kg 6.0 0 3 Rearranging
(a) v esc = gr = (.6 740 0 3 ) ½ = 400 m s (370 m s to 3 sig figs) (b) (i) Mean kinetic energy = 3_ kt =.5.38 0 3 400 = 8.3 0 J (ii) Mass of an oxygen molecule m= molar mass/n A 0.03 = kg 6.0 0 3 Rearranging
Waves Final Review. Name: Date: 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented?
 Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
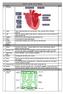 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Physics Standard level Paper 1
 Physics Standard level Paper 1 Friday 8 May 215 (morning) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates ydo not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. yanswer all the questions. yfor each question,
Physics Standard level Paper 1 Friday 8 May 215 (morning) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates ydo not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. yanswer all the questions. yfor each question,
Biology Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life. title 4 pictures, with color (black and white don t count!)
 33 Biology Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life title 4 pictures, with color (black and white don t count!) 34 Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life Goals Highlight all unknown words 35-36 Chapter 2: The Chemistry
33 Biology Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life title 4 pictures, with color (black and white don t count!) 34 Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life Goals Highlight all unknown words 35-36 Chapter 2: The Chemistry
Part One: The Chemistry of Life
 Part One: The Chemistry of Life Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. Organisms obtain and use many chemicals The metabolism of organisms involves many chemical reactions To understand all
Part One: The Chemistry of Life Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. Organisms obtain and use many chemicals The metabolism of organisms involves many chemical reactions To understand all
Chapter 3. Accelerated Motion
 Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion In this chapter you will: Develop descriptions of accelerated motions. Use graphs and equations to solve problems involving moving objects. Describe
Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion In this chapter you will: Develop descriptions of accelerated motions. Use graphs and equations to solve problems involving moving objects. Describe
MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWER SHEET
 STUDENT NAME: MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWER SHEET Circle the letter indicating the best answer. 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C D 6 A B C D 7 A B C D 8 A B C D 9 A B C D 10 A B C D 11 A B C D
STUDENT NAME: MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWER SHEET Circle the letter indicating the best answer. 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C D 6 A B C D 7 A B C D 8 A B C D 9 A B C D 10 A B C D 11 A B C D
Chapter 8. Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Two Classes of Compounds Usually solids with high melting points Many are soluble in polar solvents such as water. Most are insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as hexane. Molten
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Two Classes of Compounds Usually solids with high melting points Many are soluble in polar solvents such as water. Most are insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as hexane. Molten
Mr. Jensen/Period: 1. The diagram below illustrates the distribution of fossils in undisturbed layers of silt at the bottom of the ocean.
 Name: 1. The diagram below illustrates the distribution of fossils in undisturbed layers of silt at the bottom of the ocean. Date: /Page#: Mr. Jensen/Period: 3. In the diagram below of undisturbed sedimentary
Name: 1. The diagram below illustrates the distribution of fossils in undisturbed layers of silt at the bottom of the ocean. Date: /Page#: Mr. Jensen/Period: 3. In the diagram below of undisturbed sedimentary
Study Guide Solutions
 Study Guide Solutions Table of Contents Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit... 3 Vocabulary Review... 3 Section 1.1: Mathematics and Physics... 3 Section 1.2: Measurement... 3 Section 1.3: Graphing Data... 4 Chapter
Study Guide Solutions Table of Contents Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit... 3 Vocabulary Review... 3 Section 1.1: Mathematics and Physics... 3 Section 1.2: Measurement... 3 Section 1.3: Graphing Data... 4 Chapter
PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST SAMPLE PAPER (2015 style, issued September 2015) Time allowed: 2 hours
 PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST SAMPLE PAPER (2015 style, issued September 2015) Time allowed: 2 hours For candidates applying to Physics, Physics and Philosophy, Engineering, or Materials There are two Sections
PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST SAMPLE PAPER (2015 style, issued September 2015) Time allowed: 2 hours For candidates applying to Physics, Physics and Philosophy, Engineering, or Materials There are two Sections
CHEM 110: CHAPTER 8 Basic Concepts of Chem Bonding. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
 1 CHEM 110: CHAPTER 8 Basic Concepts of Chem Bonding Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram Lewis Dot Diagrams (developed by chemist Gilbert Lewis) are used to indicate the number of valence
1 CHEM 110: CHAPTER 8 Basic Concepts of Chem Bonding Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram Lewis Dot Diagrams (developed by chemist Gilbert Lewis) are used to indicate the number of valence
PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 2 Mechanics and Molecular Kinetic Theory
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2002 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 2 Mechanics
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2002 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 2 Mechanics
Chemistry in Biology. Section 1. Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
 Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Atoms! Chemistry is the study of matter.! Atoms are the building blocks of matter.! Neutrons and protons are located at the center of the atom.! Protons are positively
Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Atoms! Chemistry is the study of matter.! Atoms are the building blocks of matter.! Neutrons and protons are located at the center of the atom.! Protons are positively
Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Guided Notes
 Name: Period: What is a Chemical Reaction and how do they occur? Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Guided Notes A chemical reaction is a process that involves of atoms Law of Conservation of : Mass is neither
Name: Period: What is a Chemical Reaction and how do they occur? Unit 13: Rates and Equilibrium- Guided Notes A chemical reaction is a process that involves of atoms Law of Conservation of : Mass is neither
How fast or slow will a reaction be? How can the reaction rate may be changed?
 Part I. 1.1 Introduction to Chemical Kinetics How fast or slow will a reaction be? How can the reaction rate may be changed? *In order to understand how these factors affect reaction rates, you will also
Part I. 1.1 Introduction to Chemical Kinetics How fast or slow will a reaction be? How can the reaction rate may be changed? *In order to understand how these factors affect reaction rates, you will also
Table of Contents. Chapter Preview. 5.1 Mendel s Work. 5.2 Probability and Heredity. 5.3 The Cell and Inheritance. 5.4 Genes, DNA, and Proteins
 Table of Contents Chapter Preview 5.1 Mendel s Work 5.2 Probability and Heredity 5.3 The Cell and Inheritance 5.4 Genes, DNA, and Proteins Chapter 5 Preview Questions 1. What carries the instructions that
Table of Contents Chapter Preview 5.1 Mendel s Work 5.2 Probability and Heredity 5.3 The Cell and Inheritance 5.4 Genes, DNA, and Proteins Chapter 5 Preview Questions 1. What carries the instructions that
