2010 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines
|
|
|
- Garey Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section I, Part A Question Answer C D A 4 B 5 D 6 B 7 D 8 C 9 C 0 D D B D 4 C 5 B 6 A 7 D 8 C 9 B 0 B
2 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section I, Part B Question Sketches in general terms TWO consequences of the angle not being optimal and for each, relates it explicitly to the angle States ONE consequence of the angle not being optimal and relates it explicitly to the angle Identifies TWO consequences, but does not relate them explicitly to the angle Question (a) Substitutes correct values into the equation for the uniform horizontal velocity of the projectile Question (b) Substitutes the correct values, including +/- to indicate directions, into correct equation, relating initial vertical velocity to the other known variables Substitutes the magnitudes of the correct variables into correct equation relating initial vertical velocity to the other known variables Question (c) Provides sketch showing path with shorter range and lower maximum height Provides sketch showing path with shorter range or lower maximum height to the angle
3 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question (a) Provides ONE or more correct explanations including direction of acceleration Correctly identifies cause of mass not hanging vertically but gives incorrect direction Question (b) Draws a path from the position of the mass on the diagram along the line of the string Identifies the vertical component of the acceleration Identifies the horizontal component of the acceleration Provides any TWO of the above Provides any ONE of the above Question 4 States that both the Sun and the Earth exert a gravitational force on the JWST Reasons that the resultant force is consistent with a greater orbital speed of the JWST than would be the case if the Sun's gravitational force alone were acting on the JWST Indicates that their analysis is related to Kepler s law of periods States Kepler s law of periods Makes a correct deduction about the motion of the JWST States Kepler s law of periods Makes a correct deduction about the motion of the JWST
4 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 5 (a) States that the momentum of the burnt fuel and the momentum of the rocket must be equal but in opposite directions for total momentum to be conserved Reasons that the change in momentum of the fuel and the rocket is produced by equal and opposite forces acting on the fuel and rocket States that the momentum of the burnt fuel and the momentum of the rocket are in opposite directions Describes the force pair in opposite directions associated with the fuel and rocket States the law of conservation of momentum Question 5 (b) Relates the decrease in mass to an increase in acceleration Relates a change in mass to acceleration Question 6 (a) Correctly relates the rate of flux change, and hence potential difference, to the speed of the falling magnet. States that the magnet is moving faster at Y than it is at X. States that the rate of flux change is greater at Y than X. 4
5 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 6 (b) Shows on the graph that compared to the original graph: the induced potential difference is initially negative, and then positive the potential difference has a greater magnitude at positions corresponding to X and Y it takes less time for both the negative and positive changes in potential difference to take place Correctly shows TWO changes to the graph that result from the described experiment Correctly shows ONE change to the graph that results from the described experiment Question 7 States TWO applications of superconductors that are not related to MRI Provides a point for each application to show how these applications affect society AND/ the environment Provide a clear judgement as to the impact on society and the environment of ONE or TWO applications States TWO applications of superconductors that are not related to MRI Provides a point for each application to show how the applications affect society AND/ the environment States TWO applications of superconductors that are not related to MRI Provides a point for ONE application to show how ONE application affects society AND/ the environment Mentions valid applications but does not discuss their impact on society AND/ the environment
6 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 8 States the direction of the field unambiguously and correctly calculates strength Calculates strength correctly Calculates strength incorrectly by failing to convert kilograms to Newtons AND correctly states the direction of the field Calculates strength incorrectly by failing to convert kilograms to Newtons States the direction of the field unambiguously Provides a similar relevant formula 4 Question 9 Correctly identifies the number of plates and how signals applied to them result in the observed pattern Identifies that there are two pairs of plates which deflect the beam horizontally and vertically States that the plates deflect the beam or that they produce an electric field Question 0 (a) Identifies the semiconductor as p-type and relates this to a comparison of the number of outer electrons in boron and germanium Identifies the semi conductor as a p-type and relates this to the electron structure of boron Question 0 (b) States that the addition of boron increases the conductivity and relates this to the greater number of charge carriers resulting from hole formation, in comparison to electron-hole pair formation in pure germanium Associates increased conductivity with the formation of holes Identifies the conductivity of boron-doped germanium is better than pure germanium 6
7 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question (a) Selects correct formulae and correctly substitutes Correctly links relevant formulae Correctly uses ONE of the formulae Question (b) Shows a good understanding of the photoelectric effect and relates it to the production of a current Shows understanding that longer wavelengths mean lower energy photons Shows a basic understanding of the photoelectric effect Mentions the connection between cut-off frequency and some threshold in response Shows understanding that longer wavelengths mean lower energy photons Provides a relevant statement about the photoelectric effect States a connection between wavelength and photon energy 7
8 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question Demonstrates thorough knowledge and understanding of the physics related to the problems affecting a manned spaceflight to Mars Identifies the components of each problem Draws out or shows the relationship between the physics and the problem Demonstrates coherence and logical progression and includes correct use of scientific principles and ideas Demonstrates sound knowledge and understanding of the physics related to the problems affecting a manned spaceflight to Mars Describes the issues related to the problems Communicates some scientific principles and ideas in a clear manner Demonstrates a basic knowledge of the physics related to either problem identified Outlines the problems or the implications of these Communicates ideas in a basic form using general scientific terms Demonstrates a limited knowledge of the physics related to either problem identified States an aspect of the problems or an implication Communicates simple ideas
9 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section II Question (a) (i) Identifies THREE properties studied in geophysics Question (a) (ii) Correctly outlines the shape of Earth Shows how the period at sea level varies with latitude States that the period varies inversely with the value of g and that g increases if closer to the centre Any TWO of the above Any ONE of the above Question (a) (iii) Correct substitution into the TWO formulae to determine ratio Correct substitution in the formula Question (b) Provides a coherent, extensive and detailed discussion, explaining steps in going from initial measurement to final result. Discussion may mention gravimetric surveys, steps included in data reduction, Earth properties, satellite paths, structure and function of gravimeter Provides satisfactory but not extensive discussion of how gravity data obtained and the uses to which it is put Shows limited understanding of how gravity data obtained and uses to which it is put
10 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question (c) (i) Provides features or characteristics of the properties of S AND P waves Provides a correct statement about ONE type of wave Question (c) (ii) Identifies the THREE properties that can be deduced from the equations Identifies TWO of the properties Identifies ONE of the properties Question (c) (iii) Indicates why the path of the P-wave is incorrect Indicates why the path of the S-wave is incorrect Indicates why the path of the P-wave is incorrect Indicates why the path of the S-wave is incorrect Question (d) Demonstrates thorough knowledge and understanding of the plate tectonics theory Describes thoroughly the evidence supporting plate tectonics Shows how this overcame the initial reluctance to accept the notion of continental movement Demonstrates coherence and logical progression and includes correct use of scientific principles and ideas Demonstrates sound knowledge and understanding of the plate tectonics theory Describes some evidence supporting plate tectonics theory Communicates some scientific principles and ideas in a clear manner Demonstrates a basic knowledge of the plate tectonic theory Outlines a supporting piece of evidence of the plate tectonic theory Communicates ideas in a basic form using general scientific terms
11 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 4 (a) Relates the detection of different X-ray intensities after the X-rays pass from one side of the hand to the other with greater absorption of X-rays by bone than by soft tissues Describes the passage of X-rays through the hand and either the absorption by bone or the detection by film or detector Identifies ONE part of the process by which X-rays produce an image Question 4 (b) (i) States ONE advantage AND ONE disadvantage States ONE advantage ONE disadvantage Question 4 (b) (ii) Plots points accurately Draws a smooth curved line showing a half-life of 6 hours Draws a smooth curved line indicative of an exponential decay, however, points are not correct Question 4 (c) (i) States reasons why hydrogen is the main element targeted in the MR imaging process. States a reason why hydrogen is the main element targeted in the MR imaging process.
12 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 4 (c) (ii) Provides features that include: RF energy at the Lamor frequency is directed into the body The RF energy is absorbed by the hydrogen nuclei RF energy is emitted from the body by the relaxing nuclei when the RF oscillator is turned off Provides features that include: RF energy at the Lamor frequency is directed into the body RF energy is emitted by the relaxing nuclei Any correct and relevant statement Question 4 (d) (i) Calculates z of muscle Substitutes acoustic impedance data into I r /I o formula Calculates z of muscle Selects I r /I o formula Calculates z of muscle Selects I r /I o formula Question 4 (d) (ii) Relates ultrasound frequency change to relative motion of source and detector States that the frequency change is caused by movement of blood and the rate of flow can be determined from the magnitude and direction of the Doppler shift Sketches in general terms a diagnostic use of Doppler ultrasound in the heart Describes a relationship between movement and frequency change and identifies a diagnostic use of Doppler ultrasound Identifies a feature of Doppler ultrasound and relevant diagnostic use Identifies a feature or use of Doppler ultrasound Defines the Doppler Effect in general terms 4
13 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 4 (e) Identifies the most appropriate technology to use Justifies their choice in terms of the nature of the technique and its ability to detect function Discounts the other techniques with valid reason(s) Demonstrates coherence and logical progression and includes correct use of scientific principles and ideas Identifies most appropriate technology and gives a valid reason Describes the techniques AND/ their diagnostic uses Communicates some scientific principles and ideas in a clear manner Identifies most appropriate technology and gives a reason Outlines the techniques or their diagnostic uses Communicates ideas in a basic form using general scientific terms Question 5 (a) (i) Recognises that interferometry is being used and relates the long baseline made possible by the space telescope and ground-based radio telescopes to improved resolution States that better resolution is possible using HALCA States that the use of HALCA allowed a greater distance between the ground-based radio telescope and HALCA than would be possible using ground-based radio telescopes alone Question 5 (a) (ii) Links the measurements taken at high altitude to TWO reasons for the improved validity of the data States ONE reason why measurements at high altitude are better than ground-based measurements Question 5 (b) (i) Identifies TWO properties of stars that can be deduced from their spectra Identifies a property of stars that can be deduced from their spectra
14 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 5 (b) (ii) Relates clearly both surface temperature and chemical composition to the corresponding features of stellar spectra Relates both surface temperature and composition to features of the spectrum, without clearly explaining the links Accounts for ONE of the identified properties only 4 5 Question 5 (c) (i) Identifies white dwarfs as the type of star Question 5 (c) (ii) Provides the features of the relationship by: -Stating that as mass increases, luminosity increases -Stating that as mass increases, lifetime decreases States ONE correct relationship between mass/luminosity, and mass/lifetime Question 5 (c) (iii) Shows the difference in the energy production by: -Identifying that stars at W produce energy through fusion -Identifying that stars at Z do not produce appreciable energy through fusion -Identifying that stars at Z produce energy through gravitational collapse Identifies that stars at W produce energy through fusion Identifies that stars at Z do not produce appreciable energy through fusion Identifies that stars at Z produce energy through gravitational collapse 4
15 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 5 (c) (iv) Indicates that the top left region of the diagram is free of stars Shows a linear region of stars with a clear bend to the right and up as it moves from bottom right towards the top left Indicates a region of stars with a clear bend in it Indicates a region of stars in the bottom right corner of the diagram Question 5 (d) Identifies THREE advances in measurement technologies and demonstrates thorough knowledge and understanding of how they improve our understanding of celestial objects Shows clearly the relationship between the advances and specific improvements in understanding that have resulted from them Demonstrates coherence and logical progression and includes correct use of scientific principles Identifies TWO advances in measurement technology and demonstrates sound knowledge and understanding of advances in measurement technology and how they improve our understanding of celestial objects Describes the measurement technology and attempts to link this to an advance in understanding Identifies the technology and clearly shows how the technology improved our understanding Communicates some scientific principles and ideas in a clear manner Demonstrates a basic knowledge of technology used to measure/observe celestial objects Outlines how our understanding has improved Communicates ideas in a basic form using general scientific terms Question 6 (a) Sketches in general terms the relationship between Bohr s atomic model and Planck s equation Outlines the emission or absorption of photons or the energy levels, and limited to Planck s equation Provides any relevant information 5
16 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 6 (b) Correctly substitutes into equation Uses correct equation but transposes n i and n f Question 6 (c) Shows clearly how de Broglie explained the stability of electron orbits in hydrogen atoms Outlines aspects of de Broglie s explanation Provides any relevant information Question 6 (d) Identifies clearly the neutrino and the law of conservation of energy Identifies either the neutrino or the law of conservation of energy or states a third particle carries away some of the energy Question 6 (e) (i) Clearly shows how Chadwick applied the conservation laws by outlining Chadwick s experiment Describes Chadwick s experiment and the conservation laws Outlines either Chadwick s experiment or conservation laws Question 6 (e) (ii) Sketches in general terms how the properties of neutrons make them useful in scattering experiments by identifying two properties Identifies ONE property 6
17 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 6 (f) Provides reasons for the existence of stable isotopes by: Identifying THREE fundamental forces and their relative sizes/nature of the forces exerted Identifies TWO forces, their relative sizes/nature and relates to stability of nucleus Describes TWO forces Identifies all of the forces and whether they are attractive or repulsive Any relevant information about the forces which operate in the atomic nucleus Question 6 (g) Demonstrates thorough knowledge and understanding of the contributions of Rutherford, Einstein and Fermi to the development of the atomic bomb Provides a judgement of the statement Describes the effect of the atomic bomb on society Demonstrates coherence and logical progression and includes correct use of scientific principles and ideas Demonstrates sound knowledge and understanding of the contributions of Rutherford, Einstein and Fermi to the development of the atomic bomb Provides either a judgement of the statement or outlines the effect of the atomic bomb on society Communicates some scientific principles and ideas in a clear manner Demonstrates a basic knowledge of the contribution of Rutherford AND/ Einstein AND/ Fermi to the development of the atomic bomb Communicates ideas in a basic form using general scientific terms Demonstrates a limited knowledge of Rutherford AND/ Einstein AND/ Fermi Communicates simple ideas Question 7 (a) (i) Identifies section A s function correctly 7
18 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 7 (a) (ii) Determines the resistance of the thermistor at 60ºC Calculates the voltage V t in the potential divider Determines the resistance of the thermistor at 60ºC but not V t Calculates the voltage V t in the potential divider but not using the correct resistance Question 7 (a) (iii) Identifies the overall function of the circuit Shows how the circuit output changes depending on the inputs 4 Identifies and explains the effect of R Identifies the overall function of the circuit Shows how the circuit output changes depending on the inputs Identifies and explains the effect of R Correct statement about the function of the circuit Question 7 (a) (iv) Identifies the output is 0 V for low temperatures Identifies the output is 5 V for high temperatures Determines the switching point is greater than 40ºC but less than 45ºC Identifies the output is 0 V for low temperatures Identifies the output is 5 V for high temperatures Determines the switching point is greater than 40ºC but less than 45ºC 8
19 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 7 (b) Identifies the components of a relay Outlines the operation of a relay Provides a diagram to support their answer Identifies the components of a relay Outlines the operation of a relay 4 Question 7 (c) Determines the truth table for the circuit with correct elements Draws a truth table with most elements correct Question 7 (d) (i) Identifies function Question 7 (d) (ii) Identifies type 9
20 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 7 (e) Demonstrates thorough knowledge and understanding of the effect of the rapid development of integrated circuits on society Provides an analysis that identifies that: integrated circuits have developed rapidly (what has changed and how fast/moore s Law) relates the rapid development of electronics in general to ICs shows that this development has enabled the development of new applications of electronics/ics Provides several examples of IC/electronics applications and clearly shows how their rapid advancement has had an impact on society Demonstrates coherence and logical progression and includes correct use of scientific principles and ideas Demonstrates sound knowledge and understanding of the effect of rapid development of integrated circuits on society Describes some aspects of IC AND/ electronics development Describes ONE application and its impact on society Communicates some scientific principles and ideas in a clear manner Demonstrates a basic knowledge of integrated circuits Provides statements related to IC development and applications in society Communicates ideas in a basic form using general scientific terms
21 Physics 00 HSC Examination Mapping Grid Question Content Syllabus outcomes Section I Part A H H6, H , , , 9 H6, H.4b , H.c, H6, H , H6, H.4b H8, H, H, H4.f H6, H.4b /6 H H7, H4.f , H7, H , H7, H9 9. H.c H, H H, H , , 9...8, H9, H.c, H.4b , H9, H.c H, H H, H8, H , , H , H9, H.c Section I Part B 9..., 9... H7, H9 (a) 9... H9, H, H4 (b) 9... H9, H, H4 (c) 9... H9, H, H4 (a) , H6, H9, H4 (b) H6, H9, H , 9...0, H9 5(a) H6 5(b) 9...7, H6, H4 6(a) 9..., H9, H4 6(b) 9...4, 9... H, H H , 9... H , H9
22 00 HSC Physics Mapping Grid Question Content Syllabus outcomes 0 (a) H7 0 (b) H7 (a) , H7, H8, H4, H0 (b) H7, H8, H , 9..., 9..., 9..., 9... H6, H7, H9 Section II Question Geophysics (a)(i) H9 (ii) H9 (iii) H9 (b) , , , , H9 (c) (i) H8 (ii) , H8 (iii) H8, H4 (d) , H, H Section II Question 4 Medical Physics (a) , H8 (b)(i) H7 (b)(ii) H7, H (c)(i) , H8 (ii) , H7 (d)(i) H8. H.c (ii) , H8 (e) , 9.6., 9.6. H4, H8, H0 Section II Question 5 Astrophysics (a)(i) H8 (ii) , H4, H8 (b)(i) H7, H0 (b)(ii) H7, H0 (c)(i) H4 (ii) , , , H7, H9 (iii) , H7, H9 (iv) , , H (d) , , H4 Section II Question 6 From Quanta to Quarks (a) , , H0 (b) H0 (c) , H8, H0
23 00 HSC Physics Mapping Grid Question Content Syllabus outcomes (d) H7 (e)(i) H6, H7, H0 (e)(ii) H7 (f) , H0 (g) , , , , H, H8 Section II Question 7 The Age of Silicon (a)(i) H9, H4 (ii) , H9, H4 (iii) , H9 (iv) H9, H4 (b) H9 (c) , , H9, H4 (d)(i) H9 (ii) , H9 (e) , , , H, H4
2001 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines
 00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 6 (a) ( mark) Outcomes assessed: H6 Time dilation Question 6 (b) ( marks) Outcomes assessed: H6 Calculates the correct answer (units necessary) Time dilation
00 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Question 6 (a) ( mark) Outcomes assessed: H6 Time dilation Question 6 (b) ( marks) Outcomes assessed: H6 Calculates the correct answer (units necessary) Time dilation
2001 HSC Notes from the Examination Centre Physics
 00 HSC Notes from the Examination Centre Physics 00 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared by the
00 HSC Notes from the Examination Centre Physics 00 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared by the
CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 76 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 76 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
Wednesday 23 January 2013 Afternoon
 Wednesday 23 January 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *G411600113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and
Wednesday 23 January 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *G411600113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and
Physics. General Instructions
 2017 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Physics General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black pen Draw diagrams using pencil NESA approved calculators may be used
2017 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Physics General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 3 hours Write using black pen Draw diagrams using pencil NESA approved calculators may be used
2005 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Physics
 005 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Physics 006 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared by the
005 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Physics 006 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared by the
Switching to OCR from AQA
 Switching to OCR from AQA The content within the OCR Physics A specification covers the Big Ideas of physics and will be very familiar. We ve laid it out in a logical progression to support co-teaching
Switching to OCR from AQA The content within the OCR Physics A specification covers the Big Ideas of physics and will be very familiar. We ve laid it out in a logical progression to support co-teaching
2015 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines
 015 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section I, Part A Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 C B B 4 D 5 A 6 B 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 A 11 D 1 D 1 C 14 C 15 A 16 C 17 A 18 A 19 D * 0 B * D was considered
015 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section I, Part A Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 C B B 4 D 5 A 6 B 7 C 8 C 9 B 10 A 11 D 1 D 1 C 14 C 15 A 16 C 17 A 18 A 19 D * 0 B * D was considered
Unified School District of De Pere Physics Benchmarks
 Content Standards: A. Students will understand that among the science disciplines, there are unifying themes: systems, order, organization, and interactions; evidence, models, and explanations; constancy,
Content Standards: A. Students will understand that among the science disciplines, there are unifying themes: systems, order, organization, and interactions; evidence, models, and explanations; constancy,
IB Physics SL Y2 Option B (Quantum and Nuclear Physics) Exam Study Guide Practice Problem Solutions
 IB Physics SL Y2 Option B (Quantum and Nuclear Physics) Exam Study Guide Practice Problem Solutions Objectives: 1. Describe the photoelectric effect. (B.1.1) 2. Describe the concept of the photon and use
IB Physics SL Y2 Option B (Quantum and Nuclear Physics) Exam Study Guide Practice Problem Solutions Objectives: 1. Describe the photoelectric effect. (B.1.1) 2. Describe the concept of the photon and use
Thursday 19 June 2014 Morning
 Thursday 19 June 2014 Morning A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *3270254576* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships
Thursday 19 June 2014 Morning A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *3270254576* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships
Selected "Phacts" for the Physics Regents Exam You Should Know
 Selected "Phacts" for the Physics Regents Exam You Should Know I. Mechanics Study Hard! 1. Mass and inertia are the same thing. (Mass actually measures inertia in kilograms Much as monetary resources measures
Selected "Phacts" for the Physics Regents Exam You Should Know I. Mechanics Study Hard! 1. Mass and inertia are the same thing. (Mass actually measures inertia in kilograms Much as monetary resources measures
Wave Motion and Sound
 Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Year 9 AQA GCSE Physics Revision Booklet
 Year 9 AQA GCSE Physics Revision Booklet Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain
Year 9 AQA GCSE Physics Revision Booklet Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain
Section I 20 marks (pages 3 6) Attempt Questions 1 20 Allow about 35 minutes for this section
 Sample Questions HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION This document shows the layout of the examination and provides some sample questions for each of the sections. Physics General Instructions Reading
Sample Questions HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION This document shows the layout of the examination and provides some sample questions for each of the sections. Physics General Instructions Reading
2017 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines
 017 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section I, Part A Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 A B 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 B 7 D 8 C 9 A 10 A 11 C 1 B 13 C 14 A 15 B 16 D 17 B 18 C 19 C 0 D 1 Section I, Part
017 HSC Physics Marking Guidelines Section I, Part A Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 A B 3 A 4 B 5 D 6 B 7 D 8 C 9 A 10 A 11 C 1 B 13 C 14 A 15 B 16 D 17 B 18 C 19 C 0 D 1 Section I, Part
An ion follows a circular path in a uniform magnetic field. Which single change decreases the radius of the path?
 T5-1 [237 marks] 1. A circuit is formed by connecting a resistor between the terminals of a battery of electromotive force (emf) 6 V. The battery has internal resistance. Which statement is correct when
T5-1 [237 marks] 1. A circuit is formed by connecting a resistor between the terminals of a battery of electromotive force (emf) 6 V. The battery has internal resistance. Which statement is correct when
G485. PHYSICS A Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics ADVANCED GCE. Wednesday 2 February 2011 Afternoon PMT INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES
 ADVANCED GCE PHYSICS A Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics G485 * OCE / 1 732 7 * Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet Other
ADVANCED GCE PHYSICS A Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics G485 * OCE / 1 732 7 * Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet Other
Topic 7 &13 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics
 Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
1 P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w. c i e n o t e s. c o m / Physics (A-level)
 1 P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w. c i e n o t e s. c o m / Physics (A-level) Electromagnetic induction (Chapter 23): For a straight wire, the induced current or e.m.f. depends on: The magnitude of the magnetic
1 P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w. c i e n o t e s. c o m / Physics (A-level) Electromagnetic induction (Chapter 23): For a straight wire, the induced current or e.m.f. depends on: The magnitude of the magnetic
CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 94 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 94 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
Tuesday 28 June 2016 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Tuesday 28 June 2016 Morning A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *1321073468* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data,
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Tuesday 28 June 2016 Morning A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *1321073468* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data,
Particle nature of light & Quantization
 Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 3204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Force, Motion and Energy From the first intellectual musings of the human species came questions which are answered in this unit.
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 3204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Force, Motion and Energy From the first intellectual musings of the human species came questions which are answered in this unit.
Optics Definitions. The apparent movement of one object relative to another due to the motion of the observer is called parallax.
 Optics Definitions Reflection is the bouncing of light off an object Laws of Reflection of Light: 1. The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Optics Definitions Reflection is the bouncing of light off an object Laws of Reflection of Light: 1. The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 4 of 35
 field 64 If a dielectric is inserted b/w the plates of a charged capacitor, its Remains Becomes infinite capacitance constant decreases increases 65 Selenium is an insulator in the dark but when exposed
field 64 If a dielectric is inserted b/w the plates of a charged capacitor, its Remains Becomes infinite capacitance constant decreases increases 65 Selenium is an insulator in the dark but when exposed
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Subject: PHYSICS Level: ADVANCED Time: 3 hrs
 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Annual Exam 2013 Subject: PHYSICS Level: ADVANCED Time: 3 hrs Take the acceleration due to gravity g = 10m/s 2 Section A Answer all questions
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Annual Exam 2013 Subject: PHYSICS Level: ADVANCED Time: 3 hrs Take the acceleration due to gravity g = 10m/s 2 Section A Answer all questions
Chapter 6 Electronic structure of atoms
 Chapter 6 Electronic structure of atoms light photons spectra Heisenberg s uncertainty principle atomic orbitals electron configurations the periodic table 6.1 The wave nature of light Visible light is
Chapter 6 Electronic structure of atoms light photons spectra Heisenberg s uncertainty principle atomic orbitals electron configurations the periodic table 6.1 The wave nature of light Visible light is
EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (6)
 1. What is a beta-particle? A a helium nucleus B a high-energy electron C four protons D two neutrons EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (6) 2. The diagram shows part of a circuit used to switch street lamps on and
1. What is a beta-particle? A a helium nucleus B a high-energy electron C four protons D two neutrons EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (6) 2. The diagram shows part of a circuit used to switch street lamps on and
is the minimum stopping potential for which the current between the plates reduces to zero.
 Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
PHYSICS (Theory) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
 Sample Paper (CBSE) Series PHY/SP/1D Code No. SP/1-D PHYSICS (Theory) Time Allowed: hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This question paper
Sample Paper (CBSE) Series PHY/SP/1D Code No. SP/1-D PHYSICS (Theory) Time Allowed: hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This question paper
MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS
 No. of Pages: 6 No. of Questions: 10 MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 Subject PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS Title of Paper MODULE PA266
No. of Pages: 6 No. of Questions: 10 MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 Subject PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS Title of Paper MODULE PA266
AQA Physics Checklist
 Topic 1. Energy Video: Energy changes in a system To understand the ways in which energy can be stored in a system and can be transferred from one energy store to another within a system To understand
Topic 1. Energy Video: Energy changes in a system To understand the ways in which energy can be stored in a system and can be transferred from one energy store to another within a system To understand
Wednesday 21 June 2017 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Wednesday 21 June 2017 Morning A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *6808554474* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Wednesday 21 June 2017 Morning A2 GCE PHYSICS A G485/01 Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics *6808554474* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials:
Norton City Schools Standards-Based Science Course of Study 2003
 HIGH SCHOOL ELECTIVE PHYSICS (USED AS A YEAR-LONG OR BLOCK-SCHEDULED COURSE) Physical Sciences Standard (PS) 11-12 Benchmarks By the end of the 11-12 program, the student will, Physical Sciences Recognize
HIGH SCHOOL ELECTIVE PHYSICS (USED AS A YEAR-LONG OR BLOCK-SCHEDULED COURSE) Physical Sciences Standard (PS) 11-12 Benchmarks By the end of the 11-12 program, the student will, Physical Sciences Recognize
G485. PHYSICS A Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics ADVANCED GCE. Wednesday 2 February 2011 Afternoon INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES
 ADVANCED GCE PHYSICS A Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics G485 * OCE / 1 732 7 * Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet Other
ADVANCED GCE PHYSICS A Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics G485 * OCE / 1 732 7 * Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet Other
Name: Multiple choice questions. 1 mark each.
 Name: Multiple choice questions. 1 mark each. 1. A spaceship moves towards you at 1/3c, where c is the speed of light. The spaceship emits a beam of light in your direction. As measured in your frame of
Name: Multiple choice questions. 1 mark each. 1. A spaceship moves towards you at 1/3c, where c is the speed of light. The spaceship emits a beam of light in your direction. As measured in your frame of
hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Physics A Changes to Content
 hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Physics A Changes to Content Copyright 2008 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee
hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Physics A Changes to Content Copyright 2008 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee
Pre-Leaving Certi cate Examination, 2017 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2017
 *B16* Pre-Leaving Certi cate Examination, 2017 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2017 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from Section A and ve questions from Section B. Relevant
*B16* Pre-Leaving Certi cate Examination, 2017 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2017 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from Section A and ve questions from Section B. Relevant
Sample Question Paper (PHYSICS) CLASS-XII ( ) Time Allowed: 3Hours Maximum Marks: 70
 Sample Question Paper (PHYSICS) CLASS-XII (2017-18) Time Allowed: 3Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all. 2. This question paper has
Sample Question Paper (PHYSICS) CLASS-XII (2017-18) Time Allowed: 3Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all. 2. This question paper has
Sample Examination Questions
 Sample Examination Questions Contents NB. Material covered by the AS papers may also appear in A2 papers. Question Question type Question focus number (section A or B) 1 A Ideal transformer 2 A Induced
Sample Examination Questions Contents NB. Material covered by the AS papers may also appear in A2 papers. Question Question type Question focus number (section A or B) 1 A Ideal transformer 2 A Induced
(d) None 11. The unit for moment of inertia is (a) kg m 2 (b) kg m (c) kg m 2 (d) kg m The unit for pressure is
 1. A man is standing between two parallel cliffs and fires a gun. If he hears first and second echos after 1.5s and 3.5s respectively, the distance between the cliffs is (velocity of sound in air = 340ms
1. A man is standing between two parallel cliffs and fires a gun. If he hears first and second echos after 1.5s and 3.5s respectively, the distance between the cliffs is (velocity of sound in air = 340ms
Topics Covered in Chapter. Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation. A Subatomic Interlude II. A Subatomic Interlude. A Subatomic Interlude III
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 M 36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2004 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL MONDAY, 21 JUNE MORNING 9.30 TO 12.30 Answer three questions from section A and
M 36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2004 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL MONDAY, 21 JUNE MORNING 9.30 TO 12.30 Answer three questions from section A and
T10 [186 marks] y 2. w 2
![T10 [186 marks] y 2. w 2 T10 [186 marks] y 2. w 2](/thumbs/90/103453547.jpg) T10 [186 marks] 1. A particle of charge q is at point S in a uniform electric field of strength E. The particle moves a distance w parallel to the field lines and then a distance y perpendicular to the
T10 [186 marks] 1. A particle of charge q is at point S in a uniform electric field of strength E. The particle moves a distance w parallel to the field lines and then a distance y perpendicular to the
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST
 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
Special Relativity. Principles of Special Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same for all inertial observers.
 Black Holes Special Relativity Principles of Special Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same for all inertial observers. 2. The speed of light is the same for all inertial observers regardless
Black Holes Special Relativity Principles of Special Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same for all inertial observers. 2. The speed of light is the same for all inertial observers regardless
DEFINITIONS. Linear Motion. Conservation of Momentum. Vectors and Scalars. Circular Motion. Newton s Laws of Motion
 DEFINITIONS Linear Motion Mass: The mass of a body is the amount of matter in it. Displacement: The displacement of a body from a point is its distance from a point in a given direction. Velocity: The
DEFINITIONS Linear Motion Mass: The mass of a body is the amount of matter in it. Displacement: The displacement of a body from a point is its distance from a point in a given direction. Velocity: The
Chapter 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 7 P a g e 1 Chapter 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Homework: Read Chapter 7. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 7 P a g e 1 Chapter 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Homework: Read Chapter 7. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
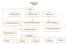 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level *2900417311* PHYSICS 9702/42 Paper 4 A2 Structured Questions October/November 2010 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level *2900417311* PHYSICS 9702/42 Paper 4 A2 Structured Questions October/November 2010 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
PHYSICS. Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter
 PHYSICS Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time). -------------------------------------------------------------------
PHYSICS Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time). -------------------------------------------------------------------
and another with a peak frequency ω 2
 Physics Qualifying Examination Part I 7-Minute Questions September 13, 2014 1. A sealed container is divided into two volumes by a moveable piston. There are N A molecules on one side and N B molecules
Physics Qualifying Examination Part I 7-Minute Questions September 13, 2014 1. A sealed container is divided into two volumes by a moveable piston. There are N A molecules on one side and N B molecules
Potentially useful formulas: F = G m 1m 2 r 2 F = k q 1q 2 F = ma Distance = Speed Time
 PHY100 May 4, 2010 Final Exam Name: Aran Garcia-Bellido Please read the problems carefully and answer them in the space provided. Write on the back of the page, if necessary. Show your work where requested
PHY100 May 4, 2010 Final Exam Name: Aran Garcia-Bellido Please read the problems carefully and answer them in the space provided. Write on the back of the page, if necessary. Show your work where requested
THE EDUCARE (SIROHI CLASSES) TEST SERIES 2018
 THE EDUCARE (SIROHI CLASSES) TEST SERIES 2018 XII PHYSICS TEST MODERN PHYSICS NAME-... DATE-.. MM- 25 TIME-1 HR 1) Write one equation representing nuclear fusion reaction. (1) 2) Arrange radioactive radiations
THE EDUCARE (SIROHI CLASSES) TEST SERIES 2018 XII PHYSICS TEST MODERN PHYSICS NAME-... DATE-.. MM- 25 TIME-1 HR 1) Write one equation representing nuclear fusion reaction. (1) 2) Arrange radioactive radiations
M05/4/PHYSI/HP2/ENG/TZ1/XX+ PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL PAPER 2. Candidate session number 0 0. Thursday 19 May 2005 (afternoon) 2 hours 15 minutes
 IB PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL PAPER 2 DIPLOMA PROGRAMME PROGRAMME DU DIPLÔME DU BI PROGRAMA DEL DIPLOMA DEL BI Thursday 19 May 2005 (afternoon) 2 hours 15 minutes M05/4/PHYSI/HP2/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 22056508 Candidate
IB PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL PAPER 2 DIPLOMA PROGRAMME PROGRAMME DU DIPLÔME DU BI PROGRAMA DEL DIPLOMA DEL BI Thursday 19 May 2005 (afternoon) 2 hours 15 minutes M05/4/PHYSI/HP2/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 22056508 Candidate
Saint Lucie County Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Honors Physics 1 Course Code: 2003390 UNIT 9 TOPIC of STUDY: Electricity STANDARDS: 10: Energy ~The electric force between two charged particles depends upon the size of the charge and the distance
Course: Honors Physics 1 Course Code: 2003390 UNIT 9 TOPIC of STUDY: Electricity STANDARDS: 10: Energy ~The electric force between two charged particles depends upon the size of the charge and the distance
CBSE XII Physics 2016
 Time: 3 hours; Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all. 2. This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section, Section D
Time: 3 hours; Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all. 2. This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section, Section D
Bannerman High School Physics Department. Making Accurate Statements. Higher Physics. Quanta and Waves
 Bannerman High School Physics Department Making Accurate Statements Higher Physics Quanta and Waves Mandatory Key Area: Particle Physics 1. Use your knowledge of physics to estimate the ratio of the smallest
Bannerman High School Physics Department Making Accurate Statements Higher Physics Quanta and Waves Mandatory Key Area: Particle Physics 1. Use your knowledge of physics to estimate the ratio of the smallest
Advanced Higher Physics
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Astrophysics Problems Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration g 9.8 m s -2 Radius of Earth R E 6.4
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Astrophysics Problems Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration g 9.8 m s -2 Radius of Earth R E 6.4
tip conducting surface
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. The diagram shows the tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) above a conducting surface. The tip is at a potential of 1.0 V relative to the surface. If the tip is sufficiently
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. The diagram shows the tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) above a conducting surface. The tip is at a potential of 1.0 V relative to the surface. If the tip is sufficiently
Study Guide for Physics 1100 Final Exam
 Study Guide for Physics 1100 Final Exam Dr. Fazzini s Physics 1100 Final Exam will take place on Wednesday, May 16 th, 2018 from 9:00AM-10:50AM in Room BIC-3535. Click on the Detailed Class Information
Study Guide for Physics 1100 Final Exam Dr. Fazzini s Physics 1100 Final Exam will take place on Wednesday, May 16 th, 2018 from 9:00AM-10:50AM in Room BIC-3535. Click on the Detailed Class Information
10/27/2017 [pgs ]
![10/27/2017 [pgs ] 10/27/2017 [pgs ]](/thumbs/82/85139288.jpg) Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Particles and Waves Final Revision Exam Questions Part 1
 Particles and Waves Final Revision Exam Questions Part 1 Cover image: cutaway diagram of CERN, CERN Version 2013 P&W: Exam Questions Part 1 Version 2013 Contents Section 1: The Standard Model 1 Section
Particles and Waves Final Revision Exam Questions Part 1 Cover image: cutaway diagram of CERN, CERN Version 2013 P&W: Exam Questions Part 1 Version 2013 Contents Section 1: The Standard Model 1 Section
CCE PF KARNATAKA SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD, MALLESWARAM, BANGALORE S. S. L. C. EXAMINATION, MARCH/APRIL, 2015 MODEL ANSWERS
 CCE PF 560 003 KARNATAKA SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD, MALLESWARAM, BANGALE 560 003 05 S. S. L. C. EXAMINATION, MARCH/APRIL, 05 MODEL ANSWERS : 0. 04. 05 ] : 83-E (Phy) Date : 0. 04. 05 ] CODE
CCE PF 560 003 KARNATAKA SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD, MALLESWARAM, BANGALE 560 003 05 S. S. L. C. EXAMINATION, MARCH/APRIL, 05 MODEL ANSWERS : 0. 04. 05 ] : 83-E (Phy) Date : 0. 04. 05 ] CODE
GCE Physics A. Mark Scheme for June Unit G485: Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics. Advanced GCE. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Physics A Unit G485: Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 017 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
GCE Physics A Unit G485: Fields, Particles and Frontiers of Physics Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 017 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body,
M10/4/PHYSI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ Physics Standard level Paper 1. Monday 10 May 2010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M1/4/PHYSI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 221651 Physics Standard level Paper 1 Monday 1 May 21 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
M1/4/PHYSI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 221651 Physics Standard level Paper 1 Monday 1 May 21 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer all
CCE RF KARNATAKA SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD, MALLESWARAM, BANGALORE S. S. L. C. EXAMINATION, MARCH/APRIL, 2015 MODEL ANSWERS
 CCE RF 560 003 KARNATAKA SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD, MALLESWARAM, BANGALE 560 003 05 S. S. L. C. EXAMINATION, MARCH/APRIL, 05 MODEL ANSWERS : 0. 04. 05 ] : 83-E(Phy) Date : 0. 04. 05 ] CODE
CCE RF 560 003 KARNATAKA SECONDARY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD, MALLESWARAM, BANGALE 560 003 05 S. S. L. C. EXAMINATION, MARCH/APRIL, 05 MODEL ANSWERS : 0. 04. 05 ] : 83-E(Phy) Date : 0. 04. 05 ] CODE
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2009. M 35 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL MONDAY 15 JUNE MORNING 9:30 TO 12:30 Answer three questions from Section
2009. M 35 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL MONDAY 15 JUNE MORNING 9:30 TO 12:30 Answer three questions from Section
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2015. M36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL MONDAY, 15 JUNE MORNING, 9:30 TO 12:30 Answer three questions from Section
2015. M36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL MONDAY, 15 JUNE MORNING, 9:30 TO 12:30 Answer three questions from Section
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *7372632194* PHYSICS 9702/42 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions February/March 2017 2 hours Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *7372632194* PHYSICS 9702/42 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions February/March 2017 2 hours Candidates
Modern physics ideas are strange! L 36 Modern Physics [2] The Photon Concept. How are x-rays produced? The uncertainty principle
![Modern physics ideas are strange! L 36 Modern Physics [2] The Photon Concept. How are x-rays produced? The uncertainty principle Modern physics ideas are strange! L 36 Modern Physics [2] The Photon Concept. How are x-rays produced? The uncertainty principle](/thumbs/88/117098787.jpg) L 36 Modern Physics [2] X-rays & gamma rays How lasers work Medical applications of lasers Applications of high power lasers Medical imaging techniques CAT scans MRI s Modern physics ideas are strange!
L 36 Modern Physics [2] X-rays & gamma rays How lasers work Medical applications of lasers Applications of high power lasers Medical imaging techniques CAT scans MRI s Modern physics ideas are strange!
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2018. M36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2018 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL WEDNESDAY, 20 JUNE MORNING, 9:30 TO 12:30 Answer three questions from Section
2018. M36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2018 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL WEDNESDAY, 20 JUNE MORNING, 9:30 TO 12:30 Answer three questions from Section
Preview. Atomic Physics Section 1. Section 1 Quantization of Energy. Section 2 Models of the Atom. Section 3 Quantum Mechanics
 Atomic Physics Section 1 Preview Section 1 Quantization of Energy Section 2 Models of the Atom Section 3 Quantum Mechanics Atomic Physics Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 8A describe the photoelectric
Atomic Physics Section 1 Preview Section 1 Quantization of Energy Section 2 Models of the Atom Section 3 Quantum Mechanics Atomic Physics Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 8A describe the photoelectric
Chapter Modern Physics
 121 Chapter Modern Physics 1. Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3 mm. If speed of light in material of lens is 2 10 8 m/s, the focal length of the lens is [2013] 15
121 Chapter Modern Physics 1. Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3 mm. If speed of light in material of lens is 2 10 8 m/s, the focal length of the lens is [2013] 15
ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS PETER LANDSHOFF. University of Cambridge ALLEN METHERELL. University of Central Florida GARETH REES. University of Cambridge
 ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS PETER LANDSHOFF University of Cambridge ALLEN METHERELL University of Central Florida GARETH REES University of Cambridge CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Constants of quantum physics
ESSENTIAL QUANTUM PHYSICS PETER LANDSHOFF University of Cambridge ALLEN METHERELL University of Central Florida GARETH REES University of Cambridge CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Constants of quantum physics
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 M 36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2005 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL MONDAY, 20 JUNE MORNING 9.30 to 12.30 Answer three questions from section A and
M 36 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2005 PHYSICS HIGHER LEVEL MONDAY, 20 JUNE MORNING 9.30 to 12.30 Answer three questions from section A and
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 12-1A: INTERACTIONS OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers a range of phenomena,
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 12-1A: INTERACTIONS OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers a range of phenomena,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *3828804905* PHYSICS 9702/42 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions May/June 2017 2 hours Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *3828804905* PHYSICS 9702/42 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions May/June 2017 2 hours Candidates answer
PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PA10
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2004 Advanced Level Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 10 The Synoptic Unit
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2004 Advanced Level Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 10 The Synoptic Unit
CfE Higher Physics. Particles and Waves
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Particles and Waves Exam Questions Part 1 Cover image: cutaway diagram of CERN, CERN P&W: Exam Questions Part 1 Version 2013 Contents Section 1: The Standard Model
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Particles and Waves Exam Questions Part 1 Cover image: cutaway diagram of CERN, CERN P&W: Exam Questions Part 1 Version 2013 Contents Section 1: The Standard Model
SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
91525: Demonstrate understanding of Modern Physics
 91525: Demonstrate understanding of Modern Physics Modern Physics refers to discoveries since approximately 1890 that have caused paradigm shifts in physics theory. Note 3 has a list is for guidance only
91525: Demonstrate understanding of Modern Physics Modern Physics refers to discoveries since approximately 1890 that have caused paradigm shifts in physics theory. Note 3 has a list is for guidance only
Chemistry Terms. atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom.
 Chemistry Terms atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. chemical reaction A process in which atoms and molecules interact, resulting in the alteration
Chemistry Terms atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. chemical reaction A process in which atoms and molecules interact, resulting in the alteration
UNIT 7 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 1 UNIT 7 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 33 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS (1) The physics that we have presented thus far in this course is classified as Classical Physics. Classical physics
1 UNIT 7 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS PHYS:1200 LECTURE 33 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS (1) The physics that we have presented thus far in this course is classified as Classical Physics. Classical physics
One student complains that this is impossible because the car would not be able to stop before hitting the cab of the lorry.
 Total 102 marks 1 hour and 45 minutes 31. Two students are watching an action film in which a car drives down a ramp onto the back of a moving lorry. Both are moving at high speed, the car slightly faster
Total 102 marks 1 hour and 45 minutes 31. Two students are watching an action film in which a car drives down a ramp onto the back of a moving lorry. Both are moving at high speed, the car slightly faster
Outline Chapter 9 The Atom Photons Photons The Photoelectron Effect Photons Photons
 Outline Chapter 9 The Atom 9-1. Photoelectric Effect 9-3. What Is Light? 9-4. X-rays 9-5. De Broglie Waves 9-6. Waves of What? 9-7. Uncertainty Principle 9-8. Atomic Spectra 9-9. The Bohr Model 9-10. Electron
Outline Chapter 9 The Atom 9-1. Photoelectric Effect 9-3. What Is Light? 9-4. X-rays 9-5. De Broglie Waves 9-6. Waves of What? 9-7. Uncertainty Principle 9-8. Atomic Spectra 9-9. The Bohr Model 9-10. Electron
Engage Education Foundation
 B Free Exam for 2013-16 VCE study design Engage Education Foundation Units 3 and 4 Physics Practice Exam Solutions Stop! Don t look at these solutions until you have attempted the exam. Any questions?
B Free Exam for 2013-16 VCE study design Engage Education Foundation Units 3 and 4 Physics Practice Exam Solutions Stop! Don t look at these solutions until you have attempted the exam. Any questions?
PSI AP Physics How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
MR. HOLL S PHYSICS FACTS MECHANICS. 1) Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
 MR. HOLL S PHYSICS FACTS MECHANICS 1) Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. 2) Speed is a scalar quantity that has ONLY magnitude. 3) Distance is a scalar and represents
MR. HOLL S PHYSICS FACTS MECHANICS 1) Velocity is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. 2) Speed is a scalar quantity that has ONLY magnitude. 3) Distance is a scalar and represents
GeV. Which graph best represents Y when it is the kinetic energy of an electron and X is its momentum?
 Unit 4: Physics on the Move 1 Which of the following is the same unit as the farad? C 1 An emf will only be induced across the wing tips of an aircraft if it is flying horizontally in D 1 3 A top quark
Unit 4: Physics on the Move 1 Which of the following is the same unit as the farad? C 1 An emf will only be induced across the wing tips of an aircraft if it is flying horizontally in D 1 3 A top quark
Today. Homework Due. Stars. Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions. proton-proton chain. CNO cycle. Stellar Lifetimes
 Today Stars Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions proton-proton chain CNO cycle Stellar Lifetimes Homework Due Stellar Properties Luminosity Surface Temperature Size Mass Composition Stellar Properties
Today Stars Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions proton-proton chain CNO cycle Stellar Lifetimes Homework Due Stellar Properties Luminosity Surface Temperature Size Mass Composition Stellar Properties
Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS. Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference
 Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference volt voltage Insulator Test body Gravitational field Field lines Solar wind
Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference volt voltage Insulator Test body Gravitational field Field lines Solar wind
U n 3 n Ba Kr (D) Br (C) Kr (B) Rb (E) 94 37
 1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
Physics for Poets. Gaurang Yodh, UC. (a) What does Physics study? Behavior of Matter, Radiation and their interaction.
 Physics for Poets Gaurang Yodh, UC (a) What does Physics study? Behavior of Matter, Radiation and their interaction. (b) What is method of study? Experiment - obtain hints about phenomena using imagination
Physics for Poets Gaurang Yodh, UC (a) What does Physics study? Behavior of Matter, Radiation and their interaction. (b) What is method of study? Experiment - obtain hints about phenomena using imagination
1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated. with: Millikan A B. Thomson. Townsend. Plank Compton
 1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated with: A B C D E Millikan Thomson Townsend Plank Compton 1 2 The electron charge was measured the first time in: A B C D E Cathode ray experiment Photoelectric
1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated with: A B C D E Millikan Thomson Townsend Plank Compton 1 2 The electron charge was measured the first time in: A B C D E Cathode ray experiment Photoelectric
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
MARKING SCHEME SET 55/1(Compartment) Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks
 MARKING SCHEME SET 55/(Compartment) Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks Set,Q Set2,Q5 Set3,Q4 Set,Q2 Set2,Q Set3,Q5 Set,Q3 Set2,Q2 Set3,Q Section A If it were not so, the presence of
MARKING SCHEME SET 55/(Compartment) Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks Set,Q Set2,Q5 Set3,Q4 Set,Q2 Set2,Q Set3,Q5 Set,Q3 Set2,Q2 Set3,Q Section A If it were not so, the presence of
