Chapter 18. The laws of nature oppose the evolutionary theory THE LAWS OF NATURE
|
|
|
- Peter Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 743 Chapter 18 THE LAWS OF NATURE The laws of nature oppose the evolutionary theory This chapter is based on pp of Other Evidence (Volume Three of our three-volume Evolution Disproved Series). Not included in this book chapter are at least 37 statements in the chapter of the larger book, plus 87 more in its appendix. You will find them, plus much more, on our website: evolution-facts.org. According to evolutionary theory, all matter came into existence by itself. At a later time on our planet, living creatures quite literally made themselves. Such views sound like Greek myths. But if these theories are true, where did the laws of nature come from? Too often these are overlooked. There are a variety of very complicated natural laws. How did these come into existence? People assume that they too just sprung up spontaneously. But they are assuming too much. INTRODUCTION This chapter is of such importance that after reading it, someone will say, Why did you not place it at the beginning of the book? Someone else might add, All you need is this chapter and you can omit the rest! The earlier portions of this volume met evolution on its own ground. When given a hearing, common sense combined with scientific facts will always tear the theory of evolution to pieces. Evolutionary theory is built on two foundational pillars. But there are two laws that crush those pillars to powder. Let us look at the two evolutionary pillars and the two laws that destroy them:
2 744 Science vs. Evolution (1) Evolution teaches that matter is not conservative but self-originating; it can arise from nothing and increase. The First Law of Thermodynamics annihilates this error. (2) Evolution teaches that matter and living things keep becoming more complex and continually evolve toward greater perfection. Just as inorganic matter becomes successively more ordered and perfect (via the Big Bang and stellar evolution), so living creatures are always evolving into higher planes of existence (via species evolution). The Second Law of Thermodynamics devastates this theory. 1 - LOOKING AT LAW DESIGNS AND LAWS In our civilizations, we find that it is highly intelligent people who design the machinery and make the laws that govern the nation. Because of our human limitations, much time needs to be spent in improving man-made mechanical designs and rewriting human laws. But in nature we find the perfection in design and laws which humans cannot achieve. Every bird and animal is perfectly designed; and fossil evidence indicates that each one has had the same design all the way back to its first appearance in the fossil record. The laws of nature are perfect also. If we need evidence about the perfection of natural laws, now and in the past, all we need do is gaze upon the planets, moons, stars, and galactic systems. The perfect balancing of their rotations on their axes and revolutions (orbits) around still larger spheres or star complexes is astounding. The laws are operating with total precision. Any aberration of those laws in the past would have brought the suns and stars and systems and our own world crashing in upon each other. The evidence is clear that, from the most distant past, the laws of nature have operated accurately. NO SELF-MADE LAWS Evolutionists work on three basic assumptions: (1) laws automatically sprang into existence out of designless confusion, (2) matter originated from nothing, and (3) living things came from non-living things. But just as matter and life did not make itself, so law did not make itself either.
3 Laws of Nature 745 The naive view implies that the universe suddenly came into existence and found a complete system of physical laws waiting to be obeyed. Actually it seems more natural to suppose that the physical universe and the laws of physics are inter-dependent. *W.H. McCrea, Cosmology after Half a Century, Science, Vol. 160, June 1968, p Even if one day we find our knowledge of the basic laws concerning inanimate nature to be complete, this would not mean that we had explained all of inanimate nature. All we should have done is to show that all the complex phenomena of our experience are derived from some simple basic laws. But how to explain the laws themselves? *R.E. Peieris, The Laws of Nature (1956), p THE LAW OF MANUFACTURE A law is a principle that is never, never violated. Let us for a moment postulate a couple candidates for new laws: A cardinal rule of existence would be this. We shall call it the Law of Manufacture. We could word the law something like this: The maker of a product has to be more complicated than the product. The equipment needed to make a bolt and nut had to be far more complex than the bolt and nut! Let us call that the First Law of Products. Here is another law to consider. We will call this one the Law of Originator, and describe it in this way: The designer of a product has to be more intelligent than the product. Let us return to the bolt and nut for our example of what we shall call our Second Law of Products. Neither the bolt nor the nut made themselves. But more: The person who made this bolt and nut had to be far more intelligent than the bolt and nut, and far more intelligent than the production methods used to make it. MANY LAWS There are many, many laws operating in the natural world. It is intriguing that there are also moral laws operating among human beings: laws of honesty, purity, etc. We get into trouble when we violate moral law the Ten Commandments, just as when we violate natural laws, such as the Law of Gravity. Facts are the air of science. Without them a man of science can
4 746 Science vs. Evolution never rise. Without them your theories are vain surmises. But while you are studying, observing, experimenting, do not remain content with the surface of things. Do not become a mere recorder of facts, but try to penetrate the mystery of their origin. Seek obstinately for the laws that govern them! *lvan Pavlov, quoted in *Isaac Asimov s Book of Science and Nature Quotations, p. 99. Let us now consider the two special laws that we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter: The two laws of thermodynamics. As with other laws, these two laws operate throughout the universe. The first is a law of conservation that works to preserve the basic categories of nature (matter, energy, etc.). The second is a law of decay that works to reduce the useful amount of matter, energy, etc., as the original organization of the cosmos tends to run down. Let us now closely examine each of these laws: 2 - THE TWO LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS The First Law of Thermodynamics (hereinafter called the First Law ) is also called the Law of Conservation of Mass/Energy. It says this: Energy cannot by itself be created nor destroyed. Energy may be changed from one form into another, but the total amount remains unchanged. Einstein showed that matter is but another form of energy, as expressed in the equation: E = MC 2 (E = Energy, m = mass, c 2 = velocity of light squared). A nuclear explosion (such as we find in an atomic bomb) suddenly changes a small amount of matter into energy. But, according to the First Law, the sum total of energy (or its sister, matter) will always remain the same. None of it will disappear by itself. (The corollary is that no new matter or energy will make itself.) The Law of Energy Conservation Energy can be converted from one form into another, but can neither be created nor destroyed, is the most important and best-proved law in science. This law is considered the most powerful and most fundamental generalization about the universe that scientists have ever been able to make. *Isaac Asimov, In the Game of Energy and Thermodynamics You Can t Even Break Even, Journal of Smithsonian Institute, June 1970, p. 6.
5 Laws of Nature 747 Since matter/energy cannot make itself or eliminate itself, only an outside agency or power can make or destroy it. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that the total amount of energy in the universe, or in any isolated part of it, remains constant. It further states that although energy (or its mass equivalent) can change form, it is not now being created or destroyed. Countless experiments have verified this. A corollary of the First Law is that natural processes cannot create energy. Consequently, energy must have been created in the past by some agency or power outside of and independent of the natural universe. Furthermore, if natural processes cannot produce the relatively simple inorganic portion of the universe, then it is even less likely that natural processes can explain the much more complex organic (or living) portion of the universe. Walter T. Brown, In the Beginning (1989), p. 12. And now we come to the Second Law of Thermodynamics; and here we find an astounding proof that the entire evolutionary theory is totally incorrect: THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (*#1/16 Universality of the Second Law*) The Second Law of Thermodynamics is also called the Law of Increasing Entropy (or disorder). The First Law of Thermodynamics speaks of the quantitative conservation of energy. The Second Law of Thermodynamics (hereinafter called the Second Law ) refers to the qualitative degeneration of energy. That energy decay is also called entropy. Entropy increases as matter or energy becomes less useable. The Second Law may be expressed in several ways. It is a very broad and very general law, and because its applications are so varied it may be stated in a great variety of ways. *E.S. Greene, Principles of Physics (1962), p Here are the three most important applications of this law: 1. Classical Thermodynamics: The energy available for useful work in a functioning system tends to decrease, even though the total energy remains constant. 2. Statistical Thermodynamics: The organized complexity (order) of a structured system tends to become disorganized and random (disorder). 3. Informational Thermodynamics: The information conveyed by a communicating system tends to become distorted and incom-
6 748 Science vs. Evolution plete. Henry Morris and Gary Parker, What is Creation Science? (1987) p Basically, the Second Law states that all systems will tend toward the most mathematically probable state, and eventually become totally random and disorganized. To put it in the vernacular, apart from a Higher Power, everything left to itself will ultimately go to pieces. All science bows low before the Second Law. Genuine scientists do also. The exception would be (1) the evolutionists who, with no hesitation, ignore not only the First and Second Law, but also other principles and laws (such as those which govern matter, life, the DNA species wall, mutations, etc.), and (2) a number of scientists who did not receive an adequate education in basic laws in their university training, and therefore are favorable to deception by Darwinian errors. Such men have no clear conception of the fundamental laws governing nature. Evolution is an outlaw theory; and those who bow to it refuse to acknowledge the proper authority of law. To their credit, there are a few evolutionists (though apparently a few) who recognize the critical nature of this problem [of the Second Law] and who are trying to solve it. *Ilya Prigogine, Gregoire Nicolis & Agnes Babloyants, Thermodynamics of Evolution, Physics Today, Vol. 25, November 1972, pp [professor in the Faculty of Sciences at the University Libre de Belgique and one of the world s leading thermodynamicists]. Regardless of the excuses that evolutionists may offer, the Second Law rises above the foibles and errors of mankind, and will not be overthrown. The Entropy Principle will preside as the ruling paradigm over the next period of history. Albert Einstein said that it is the premier law of all science; Sir Arthur Eddington referred to it as the supreme metaphysical law of the entire universe. *Jeremy Rifkin, Entropy: A New World View (1980), p. 6. Only a power outside of all energy and matter could overrule the Second Law. *Blum of Princeton University has written: The second law of thermodynamics predicts that a system left to itself will, in the course of time, go toward greater disorder. *Harold Blum, Time s Arrow and Evolution (1968), p. 201 [emphasis ours].
7 Laws of Nature 749
8 750 Science vs. Evolution THE INEVITABLE ARROW (*#2/16 Entropy Is Always Increasing*) It was *Sir Arthur Eddington, a leading astronomer who coined the term Time s Arrow to succinctly describe this second law. He said the arrow points downward, never upward. Although evolution requires an upward arrow; the Second Law says, No, an upward arrow is not permissible. There is a general natural tendency of all observed systems to go from order to disorder, reflecting dissipation of energy available for future transformation the law of increasing entropy. *R.R. Kindsay, Physics: to What Extent Is it Deterministic? in American Scientist 56 (1968), p How difficult it is to maintain houses, and machinery, and our own bodies in perfect working order; how easy to let them deteriorate. In fact, all we have to do is nothing, and everything deteriorates, collapses, breaks down, wears out, all by itself and that is what the Second Law is all about. *Isaac Asimov, Smithsonian Institute Journal, June EVOLUTION SAYS NO (*#3/12 Evolution Claims to be above the Second Law*) Evolution teaches an upward arrow all the way from nothingness to the present and on into a glorious future when mankind will eventually evolve into godlike creatures with fantastic minds, engaged in intergalactic space trips while founding intergalactic space empires. You may recall a statement by a confirmed evolutionist, quoted earlier in this book, that the marvelous powers of evolution brought man out of dust, through microbes and monkeys to his present state and that, hereafter, we may next change into clouds. Here is that quotation again: In a billion years [from now], it seems, intelligent life might be as different from humans as humans are from insects.. To change from a human being to a cloud may seem a big order, but it s the kind of change you d expect over billions of years. *Freemen Dyson, 1988 statement, quoted in Asimov s Book of Science and Nature Quotations, p. 93 [American mathematician]. Although evolution is contrary to many physical laws, including the First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics, throughout the remainder of this chapter we will primarily concern ourselves with the Second Law. Evolutionary theory stands in obvious defiance of the Second Law, but evolutionists declare that this is no problem; for
9 Laws of Nature 751 they declare their theory to be above law! 3 - EVOLUTIONARY EXCUSES OPEN SYSTEMS ARGUMENT (*#5/5 The Second Law and Crystallization*) The evolutionist argument goes this way: Energy from the sun flows to our world and makes it an open system. As long as the sun sends this energy, it will fuel evolutionary development here. In contrast, a closed system is one that neither gains nor gives up energy to its surroundings. Therefore, sunshine negates the Second Law, in spite of what Einstein and all the other physicists say! It is obvious that their neat denial denies too much. Their argument effectively nullifies Second Law everywhere in the universe, except in the cold of outer space and on planets distant from stars. Evolution is apparently progressing even on our moon, for it is receiving as much energy from the sun as we are! In addition, there ought to be a lot of evolution going on inside stars, for they have the best open systems of all! ERROR IN OPEN SYSTEM (*#4/12 The Second Law and Open Systems*) Here is the answer to this naive argument: An influx of heat energy into a so-called open system (in this case, solar heat entering our planet) would not decrease entropy. The entropy continues apace, just as the scientists said it would. Reputable scientists discovered the working of the Second Law; yet sunshine was bathing the earth when they found it! If sunlight abrogated the Second Law, scientists could not have discovered the law. But there is more: Heat energy flowing into our world does not decrease entropy it increases it! The greater the outside heat energy that enters the system, the more will its entropy and disorder increase. Energy by itself increases entropy; therefore random energy or heat will increase entropy. Opening a system to random external heat energy will increase the entropy in that system even more rapidly than if it remained closed. Oxidation is increased, chemical actions speed up, and other patterns of degeneration quicken. TEMPORARILY SLOWING THE SECOND LAW Is there no
10 752 Science vs. Evolution way to temporarily curtail the effects of the Second Law? Yes, there is: Energy that is brought into a system from outside, AND which is intelligently controlled and directed, can temporarily interfere with the operation of the Second Law. It can for a time apparently stop entropy. But deliberate, ongoing effort has to be expended to accomplish this. To say it another way: The effects of the tearing down process of entropy have to be constantly repaired. Consider the following: There are many systems, especially artificial ones (buildings, machinery) and living systems (plants, animals) which appear to run counter to the Second Law. We walk down the street and stand in front of a house: A higher intelligence (intelligence higher than that which the building has) carefully constructed the building, keeps it heated, air conditioned, dehumidified, and in good repair. In spite of this, the building gradually ages. Eventually the higher intelligence steps back and stops repairing, replacing, and repainting and the building decays much more rapidly and finally falls to pieces. Ordered systems, such as a kept-up building or maintaining a human body, are working within the Second Law, not outside of it. Ordinarily the second law is stated for isolated systems, but the second law applies equally well to open systems. *John Ross, Chemical Engineering News, July 7, 1980, p. 4 [Harvard University researcher]. Consider a human body: We have to constantly feed, bathe, oxygenate, and maintain it, or it would immediately die. Yet, all the while, it keeps weakening. Eventually it dies anyway. But, before it did, the body produced offspring. But later the offspring die also. *Harold F. Blum, a biochemist at Princeton, wrote an entire book on the Second Law. He maintains that this law does indeed apply to our world and to everything in it including living creatures. No matter how carefully we examine the energetics of living systems, we find no evidence of defeat of thermodynamic principles [the First and Second Law], but we do encounter a degree of complexity not witnessed in the non-living world. *Harold Blum,
11 Laws of Nature 753 I m trying to invent some new laws. All the old ones disagree with evolutionary theory. How could the Second Law apply to everything, as Kelvin and Einstein said, when we evolutionists have decided that everything in our world is an open system and not subject to the Second Law at all? Let s get rid of the Second Law and all the other laws. Or pretty soon we ll have to begin keeping the moral law: the Ten Commandments! Tell the publishers to stop mentioning the Second Law in the textbooks they publish for the schools. It keeps embarrassing us. I m tring to find something that doesn t corrode, break down, rot, or fall to pieces. Then I can say the Second Law has been disproved. It s just a meeting of evolutionists.
12 754 Science vs. Evolution Time s Arrow and Evolution (1962), p. 14 [emphasis ours]. INFORMATION VS. THE LAW Theoreticians have decided that information is a partial disproof of the Second Law. The idea goes somewhat like this: If you were to write down all the sunspot data about a star for ages and ages, the star might be decaying, but your data would be increasing! This fact is thought to mean something, but it really proves nothing. It is just armchair theorizing. Nevertheless, it is a matter of deep concern to some. Here is the answer to this information theory puzzle in regard to entropy: The men gathering the sunspot data keep dying; and, if others do not take their place, the data is eventually lost or rots away. The gathering of data is much like continually repainting a house. As long as we keep working at it, the inevitable decay of entropy is masked over. But set the papers aside for a time; and the information becomes out-of-date and the paper it is on crumbles to dust. QUANTITY VS. CONVERSION Of all the arguments defending evolutionary theory against the Second Law, the open system argument is the most common. But the problem is that in using the open system defense, the evolutionists confuse quantity of energy (of which there certainly is enormous amounts sent us from the sun) with conversion of energy. NO EVOLUTION EVEN IN AN OPEN SYSTEM (*#5/5 The Second Law and Crystallization*) But even if open systems negated the Second Law, there could still be no evolution. The problem is how would the sun s energy begin and sustain evolutionary development? How can sunlight originate life? How can it produce a living cell or a living species? How could it change one species into another one? 4 - SOLIDITY OF THE SECOND LAW ACKNOWLEDGED BY LEADING SCIENTISTS (*#6/12 The Second Law Destroys Evolutionary Theory*) Dedicated evolutionists declare that evolution stands above the Second Law of Thermodynamics and is not subject to it. In contrast, many of the world s leading scientists maintain that everything is subject
13 Laws of Nature 755 to the Second Law. *Sir Arthur Eddington ( ) was a leading British astronomer of the first half of the 20th century. He said this: If your theory is found to be against the second law of thermodynamics, I can give you no hope; there is nothing for it [your theory] but to collapse in deepest humiliation. *Arthur S. Eddington, The Nature of the Physical World (1930), p. 74. *Albert Einstein ( ) is generally considered to have had one of the outstanding scientific minds of the 20th century. He made this highly significant statement regarding classical thermodynamics, which is the First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics: [A law] is more impressive the greater is the simplicity of its premises, the more different are the kinds of things it relates, and the more extended its range of applicability. Therefore, the deep impression which classical thermodynamics made on me. It is the only physical theory of universal content which I am convinced, that within the framework of applicability of its basic concepts will never be overthrown. *Albert Einstein, quoted in *M.J. Klein, Thermodynamics in Einstein s Universe, in Science, 157 (1967), p. 509; also in *Isaac Asimov s Book of Science and Nature Quotations, p. 76. Einstein said that the First and Second Laws were so inviolate because they applied to so many things. By the same rule, we could speak of another law, the Law of Creatorship, and declare that it is even more inviolate. Everything in the skies above and the earth beneath witnesses to the fact that God made it all! The Second Law has never failed to be substantiated: The second law of thermodynamics not only is a principle of wide reaching scope and application, but also is one which has never failed to satisfy the severest test of experiment. The numerous quantitative relations derived from this law have been subjected to more and more accurate experimental investigation without the detection of the slightest inaccuracy. *G.N. Lewis and *M. Randall, Thermodynamics (1961), p. 87. There is thus no justification for the view, often glibly repeated, that the Second Law of Thermodynamics is only statistically true, in the sense that microscopic violations repeatedly occur, but never violations of any serious magnitude. On the contrary, no evidence has ever been presented that the Second Law breaks down under any circumstances. *A.B. Pippard, Elements of Chemical Ther-
14 756 Science vs. Evolution modynamics for Advanced Students of Physics (1966), p THE SECOND LAW POINTS TO THE CREATOR (*#7/6 The Second Law Requires a Beginning / #8/7 The Laws and their Maker*) According to the First Law, matter can only be produced by an outside agency or power. According to the Second Law, its decay can only be postponed by activity of an outside agency or power. The second law of thermodynamics predicts that a system left to itself will, in the course of time, go toward greater disorder. *Harold Blum, Time s Arrow and Evolution (1968), pp. 201 [emphasis ours]. It is a striking fact that the Second Law of Thermodynamics points mankind to its Creator. The greatest scientists acknowledge the universality of this law. But if everything, everywhere is running down, Who got it started originally? If everything is moving toward an end, then it had to have a beginning! The Second Law testifies to the fact that there was a beginning to everything, and therefore a Beginner. The greatest puzzle is where all the order in the universe came from originally. How did the cosmos get wound up, if the second law of thermodynamics predicts asymmetric unwinding towards disorder? *Paul C.W. Davies (1979). All the stars and all of nature testify that there is a Creator. The perfect designs of nature and the precision of natural law point us to the One who prepared all these things. Look at a pansy or a rose; pet a rabbit; watch a hummingbird in action. Consider the awesome wonders of island universes with their complex inter-orbiting suns. There is One who stands above and beyond all of this. One who made it all, who is thoughtful of the needs of the universe and cares for His own. It seems to be one of the fundamental features of nature that fundamental physical laws are described in terms of a mathematical theory of great beauty and power, needing quite a high standard of mathematics for one to understand it.. One could perhaps describe the situation by saying that God is a mathematician of a very high order, and He used very advanced mathematics in constructing the universe. *P.A.M. Dirac, The Evolution of the Physicist s Picture of Nature, in Scientific American, May 1963, p. 53. The authors see the second law of thermodynamics as man s description of the prior and continuing work of a Creator, who also
15 Laws of Nature 757 holds the answer to the future destiny of man and the universe. Sonntag and Van Wylen, Fundamentals of Classical Thermodynamics, 2nd Ed., Vol. 1 (1973), p Very important: In order to round out your understanding of this topic, you will want to read the section, Six Strange Teachings of Evolution in chapter 10, Mutations. It presents several aspects of evolutionary theory which run remarkably opposite to the laws of thermodynamics, and also to common sense: (1) Evolution operates only upward, never downward; (2) evolution operates irreversibly; (3) evolution operates from smaller to bigger; (4) evolution only operates from less to more complex; (5) evolution only operates from less to more perfect; (6) evolution is not repeatable. Evolution is said to be totally random. Yet the evolutionists have fitted it into a mold of totally precisioned, carefully ordered and directed, and having intelligent complexity. Why do they fit their theoretical evolution into such a mold? Because that is what is in all of nature which evolution is supposed to have produced! EVOLUTION COULD NOT DO THIS Porpoises (bottle-nosed dolphins) never hurt humans, but crush vicious barracudas and kill deadly sharks. It is sonar (underwater radar) that enables them to successfully plan their attacks. With their high-pitched squeaks, they can identify the type of fish, and measure its distance and size. Porpoises have a special region in their head which contains a specialized type of fat. Scientists call it their melon, for that is its shape. Because the speed of sound in the fatty melon is different than that of the rest of the body, this melon is used as a sound lens to collect sonar signals and interpret them to the brain. It focuses sound, just as a glass lens focuses light. The focused sound produces a small sound picture in the porpoise s mind showing it the unseen things ahead in the dark, murky water. It has been discovered that the composition of this fatty lens can be altered by the porpoise in order to change the sound speed through the melon and thus change the focus of the lens to accord with variational factors in the surrounding water! There is also evidence that the composition of fat varies in different parts of the melon. This technique of doublet lens (two glass lenses glued together) is used in optical lenses in order to overcome chromatic aberrations and produce high-quality light lenses. The porpoise appears to be using a similar principle for its sound lens system!
16 758 Science vs. Evolution CHAPTER 18 - STUDY AND REVIEW QUESTIONS THE LAWS OF NATURE GRADES 5 TO 12 ON A GRADUATED SCALE 1 - If everything is under law, where did those laws come from? Could they have made themselves? Do human laws make themselves? 2 - Explain the first and second laws of products. 3 - Are even the smallest and largest things under laws? Why? 4 - There are many types of physical laws. There are also moral laws and different health laws. Think about this and list about 12 different natural laws. 5 - Define and explain the First Law of Thermodynamics. 6 - In what way does evolution agree or disagree with the First Law. 7 - Define and explain the Second Law of Thermodynamics. 8 - In what way does evolution agree or disagree with the Second Law. 9 - Why do scientists speak of an arrow in describing the Second Law? 10 - Give three examples from practical life of the Second Law in operation Discuss the flaws in the open systems argument Some say that the Second Law only applies to closed systems, and that our solar system and everything in it is an open system, and therefore not subject to the Second Law. Explain why that idea is wrong. Everything in the universe is either a closed system (both laws apply to everything) or everything in the universe is an open system (both laws apply to nothing) Why do evolutionists claim that evolutionary theory is above all law? 14 - Write a brief paragraph or two, describing what scientists say about the importance and universality of the Second Law.
Entropy and Open Systems
 Evidence for Creation Entropy and Open Systems by Henry Morris, Ph.D. The most devastating and conclusive argument against evolution is the entropy principle. This principle (also known as the Second Law
Evidence for Creation Entropy and Open Systems by Henry Morris, Ph.D. The most devastating and conclusive argument against evolution is the entropy principle. This principle (also known as the Second Law
Debunking Misconceptions Regarding the Theory of Evolution
 Debunking Misconceptions Regarding the Theory of Evolution Myth 1 - Evolution has never been observed. Biologists define evolution as a change in the gene pool of a population over time. One example is
Debunking Misconceptions Regarding the Theory of Evolution Myth 1 - Evolution has never been observed. Biologists define evolution as a change in the gene pool of a population over time. One example is
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
Any particle in the universe attracts any other particle with a gravitational force whose magnitude is
 Print this page CHAPTER 13 Gravitation 13-1 NEWTON'S LAW OF GRAVITATION Learning Objectives After reading this module, you should be able to 13.01 Apply Newton's law of gravitation to relate the gravitational
Print this page CHAPTER 13 Gravitation 13-1 NEWTON'S LAW OF GRAVITATION Learning Objectives After reading this module, you should be able to 13.01 Apply Newton's law of gravitation to relate the gravitational
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang
 The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution
 Chapter 9: Evidence for Plant and Animal Evolution Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution Many questions about evolution arise in Christian circles. We ll discuss just a few that we frequently
Chapter 9: Evidence for Plant and Animal Evolution Questions Sometimes Asked About the Theory of Evolution Many questions about evolution arise in Christian circles. We ll discuss just a few that we frequently
Introduction. THE FORMATION OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM - Theories Old and New Imperial College Press
 Most scientists think that the work they do is very important. Well, they would wouldn t they? It is a human trait, an aspect of vanity, to consider that what one does is more significant than it really
Most scientists think that the work they do is very important. Well, they would wouldn t they? It is a human trait, an aspect of vanity, to consider that what one does is more significant than it really
Bell s spaceship paradox
 Bell s spaceship paradox If the two ships start accelerating at the same time, I always see them travelling at the same velocity, and keeping a constant distance... But I said the objects get shorter when
Bell s spaceship paradox If the two ships start accelerating at the same time, I always see them travelling at the same velocity, and keeping a constant distance... But I said the objects get shorter when
Leader Discussion Guide for Cosmos: A SpaceTime Odyssey
 Leader Discussion Guide for Cosmos: A SpaceTime Odyssey Episode 1: Standing Up in the Milky Way The creators of Cosmos: A SpaceTime Odyssey state that their aim is to promote scientific literacy. We know
Leader Discussion Guide for Cosmos: A SpaceTime Odyssey Episode 1: Standing Up in the Milky Way The creators of Cosmos: A SpaceTime Odyssey state that their aim is to promote scientific literacy. We know
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Physical Matter and Entropy Were Made
 T H E U LT I M AT E L A W O F T H E R M O DY N A M I C S Physical Matter and Entropy Were Made Read this carefully, because it s the KEY to everything else in Science. The first law of thermodynamics is
T H E U LT I M AT E L A W O F T H E R M O DY N A M I C S Physical Matter and Entropy Were Made Read this carefully, because it s the KEY to everything else in Science. The first law of thermodynamics is
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Grade 5. Practice Test. Telescopes: An Introduction Powerful Telescopes
 Name Date Grade 5 Telescopes: An Introduction Powerful Telescopes Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Excerpt from
Name Date Grade 5 Telescopes: An Introduction Powerful Telescopes Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Excerpt from
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 27 What s Next?
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
Reading Passage. Darwin's Theory of Evolution - The Premise
 Darwin's Theory of Evolution - The Premise Reading Passage Darwin's Theory of Evolution is the widely held notion that all life is related and has descended from a common ancestor: the birds and the bananas,
Darwin's Theory of Evolution - The Premise Reading Passage Darwin's Theory of Evolution is the widely held notion that all life is related and has descended from a common ancestor: the birds and the bananas,
Critical Notice: Bas van Fraassen, Scientific Representation: Paradoxes of Perspective Oxford University Press, 2008, xiv pages
 Critical Notice: Bas van Fraassen, Scientific Representation: Paradoxes of Perspective Oxford University Press, 2008, xiv + 408 pages by Bradley Monton June 24, 2009 It probably goes without saying that
Critical Notice: Bas van Fraassen, Scientific Representation: Paradoxes of Perspective Oxford University Press, 2008, xiv + 408 pages by Bradley Monton June 24, 2009 It probably goes without saying that
Can ANYTHING Happen in an Open System?
 Can ANYTHING Happen in an Open System? Granville Sewell Mathematics Dept. University of Texas El Paso The Mathematical Intelligencer 23 (2001), no. 4, 8-10 Copyright held by Springer Verlag, NY, LLC Critics
Can ANYTHING Happen in an Open System? Granville Sewell Mathematics Dept. University of Texas El Paso The Mathematical Intelligencer 23 (2001), no. 4, 8-10 Copyright held by Springer Verlag, NY, LLC Critics
On the Shoulders of Giants: Isaac Newton and Modern Science
 22 May 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com On the Shoulders of Giants: Isaac Newton and Modern Science SHIRLEY GRIFFITH: This is Shirley Griffith. STEVE EMBER: And this is Steve Ember with the VOA Special
22 May 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com On the Shoulders of Giants: Isaac Newton and Modern Science SHIRLEY GRIFFITH: This is Shirley Griffith. STEVE EMBER: And this is Steve Ember with the VOA Special
Entropy for Mathematicians or... The final Blaubeuren chapters
 Entropy for Mathematicians or... The final Blaubeuren chapters Who? Stephan Fackler When? December 16, 2016 Life, the Universe and Everything The general struggle for existence of animate beings is not
Entropy for Mathematicians or... The final Blaubeuren chapters Who? Stephan Fackler When? December 16, 2016 Life, the Universe and Everything The general struggle for existence of animate beings is not
226 My God, He Plays Dice! Entanglement. Chapter This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/entanglement
 226 My God, He Plays Dice! Entanglement Chapter 29 20 This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/entanglement Entanglement 227 Entanglement Entanglement is a mysterious quantum phenomenon
226 My God, He Plays Dice! Entanglement Chapter 29 20 This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/entanglement Entanglement 227 Entanglement Entanglement is a mysterious quantum phenomenon
Heat is often called a form of energy. Sunlight is heat energy. You can feel the energy from the sun as it warms your body.
 jonathanpark book2 9/22/04 6:02 PM Page 35 The Long Road Home The root word "thermo" means heat, and "dynamics" means power. So thermodynamics is the study of heat-power. Thermodynamics is all about how
jonathanpark book2 9/22/04 6:02 PM Page 35 The Long Road Home The root word "thermo" means heat, and "dynamics" means power. So thermodynamics is the study of heat-power. Thermodynamics is all about how
Atomic Theory. Introducing the Atomic Theory:
 Atomic Theory Chemistry is the science of matter. Matter is made up of things called atoms, elements, and molecules. But have you ever wondered if atoms and molecules are real? Would you be surprised to
Atomic Theory Chemistry is the science of matter. Matter is made up of things called atoms, elements, and molecules. But have you ever wondered if atoms and molecules are real? Would you be surprised to
Physics 10 Spring Final Exam: You are a Turtle. Name:
 Physics 10 Spring 2013 Final Exam: You are a Turtle. Name: (c) Randall Munroe, www.xkcd.com also (c) Randall Munroe, www.xkcd.com Part I: Short-Answer Questions. Answer all the questions in this section.
Physics 10 Spring 2013 Final Exam: You are a Turtle. Name: (c) Randall Munroe, www.xkcd.com also (c) Randall Munroe, www.xkcd.com Part I: Short-Answer Questions. Answer all the questions in this section.
Does the Big Bang Fit with the Bible?
 Does the Big Bang Fit with the Bible? The big bang is a story about how the universe came into existence. The big bang is a story about how the universe came into existence. It proposes that billions of
Does the Big Bang Fit with the Bible? The big bang is a story about how the universe came into existence. The big bang is a story about how the universe came into existence. It proposes that billions of
Do you know the man that dropped out of school and still was one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century? That is Albert Einstein.
 Do you know the man that dropped out of school and still was one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century? That is Albert Einstein. Albert was a man that thought for himself and changed the world
Do you know the man that dropped out of school and still was one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century? That is Albert Einstein. Albert was a man that thought for himself and changed the world
G 8243 Entropy and Information in Probability
 G 8243 Entropy and Information in Probability I. Kontoyiannis Columbia University Spring 2009 What is Information Theory? Born in 1948, it is the mathematical foundation of communication theory; it quantifies
G 8243 Entropy and Information in Probability I. Kontoyiannis Columbia University Spring 2009 What is Information Theory? Born in 1948, it is the mathematical foundation of communication theory; it quantifies
Superposition - World of Color and Hardness
 Superposition - World of Color and Hardness We start our formal discussion of quantum mechanics with a story about something that can happen to various particles in the microworld, which we generically
Superposition - World of Color and Hardness We start our formal discussion of quantum mechanics with a story about something that can happen to various particles in the microworld, which we generically
Quantum Entanglement. Chapter Introduction. 8.2 Entangled Two-Particle States
 Chapter 8 Quantum Entanglement 8.1 Introduction In our final chapter on quantum mechanics we introduce the concept of entanglement. This is a feature of two-particle states (or multi-particle states) in
Chapter 8 Quantum Entanglement 8.1 Introduction In our final chapter on quantum mechanics we introduce the concept of entanglement. This is a feature of two-particle states (or multi-particle states) in
Chapter One BASIC QUESTIONS
 Chapter One BASIC QUESTIONS In natural science, the observations in everyday life are of particular relevance. We normally base our analysis on those events and things which are spontaneous in front of
Chapter One BASIC QUESTIONS In natural science, the observations in everyday life are of particular relevance. We normally base our analysis on those events and things which are spontaneous in front of
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Using Reference Materials
 Using Reference Materials LA #3636 Have you ever had a project to complete, but were not sure where to find information about the topic or person? There is a great way to learn about famous people, events,
Using Reference Materials LA #3636 Have you ever had a project to complete, but were not sure where to find information about the topic or person? There is a great way to learn about famous people, events,
1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP?
 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP? UNIT 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? CONTENTS UNIT 1 BASICS 3 Unit 1 Overview 4 Unit 1 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 1 Lessons 7 Unit 1 Key
1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? WHY DO WE LOOK AT THINGS FROM FAR AWAY AND CLOSE UP? UNIT 1 WHAT IS BIG HISTORY? CONTENTS UNIT 1 BASICS 3 Unit 1 Overview 4 Unit 1 Learning Outcomes 5 Unit 1 Lessons 7 Unit 1 Key
Max Planck, Nobel Prize in Physics and inventor of Quantum Mechanics said:
 Max Planck, Nobel Prize in Physics and inventor of Quantum Mechanics said: As a man who has devoted his whole life to the most clear-headed science, to the study of matter, I can tell you as a result of
Max Planck, Nobel Prize in Physics and inventor of Quantum Mechanics said: As a man who has devoted his whole life to the most clear-headed science, to the study of matter, I can tell you as a result of
3 Newton s First Law of Motion Inertia. Forces cause changes in motion.
 Forces cause changes in motion. A ball at rest in the middle of a flat field is in equilibrium. No net force acts on it. If you saw it begin to move across the ground, you d look for forces that don t
Forces cause changes in motion. A ball at rest in the middle of a flat field is in equilibrium. No net force acts on it. If you saw it begin to move across the ground, you d look for forces that don t
PREAMBLE (Revised) Why Einstein was Mistaken About the Velocity of Light.
 PREAMBLE (Revised) Why Einstein was Mistaken About the Velocity of Light. Einstein s 1905 Special Theory of Relativity is primarily about the velocity of a ray of light after it is emitted from a material
PREAMBLE (Revised) Why Einstein was Mistaken About the Velocity of Light. Einstein s 1905 Special Theory of Relativity is primarily about the velocity of a ray of light after it is emitted from a material
Flat Geometry. Spherical Geometry
 The Geometry of the Universe What does the constant k in the Friedmann equation really mean? In this lecture we will follow Chapter 4 of Liddle to show that it has close connections with the geometry of
The Geometry of the Universe What does the constant k in the Friedmann equation really mean? In this lecture we will follow Chapter 4 of Liddle to show that it has close connections with the geometry of
1 MODERN SCIENTIFIC ORIGIN STORY 1070L
 1 MODERN SCIENTIFIC ORIGIN STORY 1070L MODERN SCIENTIFIC THE BIG BANG By Cynthia Stokes Brown From vast nothingness to a Universe of stars and galaxies and our own Earth. 2 3 This version of modern science
1 MODERN SCIENTIFIC ORIGIN STORY 1070L MODERN SCIENTIFIC THE BIG BANG By Cynthia Stokes Brown From vast nothingness to a Universe of stars and galaxies and our own Earth. 2 3 This version of modern science
The Myth of Dirac supposedly combining Special Relativity with Quantum Mechanics Roger J. Anderton
 The Myth of Dirac supposedly combining Special Relativity with Quantum Mechanics Roger J. Anderton R.J.Anderton@btinternet.com Many popular texts state that Dirac - combined Special Relativity (SR) with
The Myth of Dirac supposedly combining Special Relativity with Quantum Mechanics Roger J. Anderton R.J.Anderton@btinternet.com Many popular texts state that Dirac - combined Special Relativity (SR) with
Our Origins. Chapter 1
 Part 1 Origins What is there beyond everything? Have you ever stayed out late, just to look at the stars? Long enough to make your head spin Not because you re bent back, But because you looked so far
Part 1 Origins What is there beyond everything? Have you ever stayed out late, just to look at the stars? Long enough to make your head spin Not because you re bent back, But because you looked so far
Intensity of Light and Heat. The second reason that scientists prefer the word intensity is Well, see for yourself.
 IDS 102 Intensity of Light and Heat When talking about a light source, most people are more comfortable with the word brightness than they are with the word intensity. Scientists generally prefer the word
IDS 102 Intensity of Light and Heat When talking about a light source, most people are more comfortable with the word brightness than they are with the word intensity. Scientists generally prefer the word
3 Newton s First Law of Motion Inertia. Forces cause changes in motion.
 Forces cause changes in motion. A ball at rest in the middle of a flat field is in equilibrium. No net force acts on it. If you saw it begin to move across the ground, you d look for forces that don t
Forces cause changes in motion. A ball at rest in the middle of a flat field is in equilibrium. No net force acts on it. If you saw it begin to move across the ground, you d look for forces that don t
Elementary Linear Algebra, Second Edition, by Spence, Insel, and Friedberg. ISBN Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ.
 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. APPENDIX: Mathematical Proof There are many mathematical statements whose truth is not obvious. For example, the French mathematician
2008 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. APPENDIX: Mathematical Proof There are many mathematical statements whose truth is not obvious. For example, the French mathematician
Cosmology. What is Cosmology?
 Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
What s the longest single-shot exposure ever recorded of any object or area of space by Hubble?
 Hubblecast Episode 50: Q&A with Dr J 00:00 Have you ever wondered why Hubble can make detailed images of of galaxies, but stars appear as featureless blobs? What the most distant object ever observed is?
Hubblecast Episode 50: Q&A with Dr J 00:00 Have you ever wondered why Hubble can make detailed images of of galaxies, but stars appear as featureless blobs? What the most distant object ever observed is?
UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE LAWS OF NATURE: DARK MATTER, SUPERSYMMETRY, AND THE LHC. Gordon Kane, Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Warsaw, June 2009
 UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE LAWS OF NATURE: DARK MATTER, SUPERSYMMETRY, AND THE LHC Gordon Kane, Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Warsaw, June 2009 OUTLINE! Some things we ve learned about the physical
UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE LAWS OF NATURE: DARK MATTER, SUPERSYMMETRY, AND THE LHC Gordon Kane, Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Warsaw, June 2009 OUTLINE! Some things we ve learned about the physical
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
THE LAWS OF PHYSICS. DOSE THE S.E.G. AND I.G.V. BREAK THESE LAWS? PART 2.
 THE LAWS OF PHYSICS. DOSE THE S.E.G. AND I.G.V. BREAK THESE LAWS? PART 2. 1: I mainly presented just five key words that I often use and to what impression they create upon my brain. I also presented some
THE LAWS OF PHYSICS. DOSE THE S.E.G. AND I.G.V. BREAK THESE LAWS? PART 2. 1: I mainly presented just five key words that I often use and to what impression they create upon my brain. I also presented some
Special Theory of Relativity Prof. Dr. Shiva Prasad Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:36) Special Theory of Relativity Prof. Dr. Shiva Prasad Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 7 Examples of Length Contraction and Time Dilation Hello,
(Refer Slide Time: 00:36) Special Theory of Relativity Prof. Dr. Shiva Prasad Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 7 Examples of Length Contraction and Time Dilation Hello,
Chapter 2. Mathematical Reasoning. 2.1 Mathematical Models
 Contents Mathematical Reasoning 3.1 Mathematical Models........................... 3. Mathematical Proof............................ 4..1 Structure of Proofs........................ 4.. Direct Method..........................
Contents Mathematical Reasoning 3.1 Mathematical Models........................... 3. Mathematical Proof............................ 4..1 Structure of Proofs........................ 4.. Direct Method..........................
The Cycloid. and the Kinematic Circumference. by Miles Mathis
 return to updates The Cycloid and the Kinematic Circumference First published August 31, 2016 by Miles Mathis Those of you who have read my papers on π=4 will know I have explained that problem using many
return to updates The Cycloid and the Kinematic Circumference First published August 31, 2016 by Miles Mathis Those of you who have read my papers on π=4 will know I have explained that problem using many
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 1: The Puzzle of Motion. In American universities there are three main types of physics courses for nonspecialists.
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 1: The Puzzle of Motion About this course In American universities there are three main types of physics courses for nonspecialists. The first kind teaches about the physics of everyday
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 1: The Puzzle of Motion About this course In American universities there are three main types of physics courses for nonspecialists. The first kind teaches about the physics of everyday
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
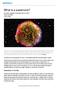 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran
 ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran Surprising as it may be to most non-scientists and even to some scientists, Albert Einstein concluded in his later years that the past, present,
ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran Surprising as it may be to most non-scientists and even to some scientists, Albert Einstein concluded in his later years that the past, present,
ACTIVITY 5. Figure 5-1: Simulated electron interference pattern with your prediction for the next electron s position.
 Name: WAVES of matter Class: Visual Quantum Mechanics ACTIVITY 5 Interpr preting Wave Functions Goal We will return to the two- slit experiment for electrons. Using this experiment we will see how matter
Name: WAVES of matter Class: Visual Quantum Mechanics ACTIVITY 5 Interpr preting Wave Functions Goal We will return to the two- slit experiment for electrons. Using this experiment we will see how matter
Evidence is Clear. Students consider observations and inferences about the Steady State and Big Bang theories.
 The Evidence is Clear! Summary Students consider observations and inferences about the Steady State and Big Bang theories. Objectives Distinguish between data collected from empirical observations and
The Evidence is Clear! Summary Students consider observations and inferences about the Steady State and Big Bang theories. Objectives Distinguish between data collected from empirical observations and
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
On GRB And The M&L Universe
 Rothwell Bronrowan physbron@t-online.de This paper contains some new ideas on the universe. The Background On 23rd April 2009 (090423 backwards) a 10-second gamma-ray burst (GRB) was recorded by the NASA
Rothwell Bronrowan physbron@t-online.de This paper contains some new ideas on the universe. The Background On 23rd April 2009 (090423 backwards) a 10-second gamma-ray burst (GRB) was recorded by the NASA
1PRELUDE: THE MYSTERY OF
 1PRELUDE: THE MYSTERY OF THE MISSING ANTIMATTER In the beginning what was the beginning? Every culture asks this question. Traditionally each finds some answer, a creation myth, a cosmology. These stories
1PRELUDE: THE MYSTERY OF THE MISSING ANTIMATTER In the beginning what was the beginning? Every culture asks this question. Traditionally each finds some answer, a creation myth, a cosmology. These stories
Lecture 2 - Length Contraction
 Lecture 2 - Length Contraction A Puzzle We are all aware that if you jump to the right, your reflection in the mirror will jump left. But if you raise your hand up, your reflection will also raise its
Lecture 2 - Length Contraction A Puzzle We are all aware that if you jump to the right, your reflection in the mirror will jump left. But if you raise your hand up, your reflection will also raise its
What If We Had No Moon?
 What If We Had No Moon? By Bob Gard Hollister Missouri church of Christ www.hollisterchurchofchrist.org Notes For Sermon, What If We Had No Moon? Slide 1 What are we talking about?... Slide 2 Moons! Let
What If We Had No Moon? By Bob Gard Hollister Missouri church of Christ www.hollisterchurchofchrist.org Notes For Sermon, What If We Had No Moon? Slide 1 What are we talking about?... Slide 2 Moons! Let
Killer Skies. HW 10/Moon Report due Dec 2nd Solar Obs due now. Last time: Galaxies Today: Galaxies Collide. Music: The Universe Song Animaniacs
 Killer Skies HW 10/Moon Report due Dec 2nd Solar Obs due now Last time: Galaxies Today: Galaxies Collide Music: The Universe Song Animaniacs 1 The Andromeda Galaxy 2.5 million light years away About the
Killer Skies HW 10/Moon Report due Dec 2nd Solar Obs due now Last time: Galaxies Today: Galaxies Collide Music: The Universe Song Animaniacs 1 The Andromeda Galaxy 2.5 million light years away About the
No Math. ASTR/PHYS 109 at. Texas A&M University November Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math ASTR/PHYS 109 at Texas A&M 1
 Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math ASTR/PHYS 109 at Texas A&M David Toback Texas A&M University November 2009 ASTR/PHYS 109 at Texas A&M 1 Talk Outline Motivation, Intended Audience and Class Goals Course
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math ASTR/PHYS 109 at Texas A&M David Toback Texas A&M University November 2009 ASTR/PHYS 109 at Texas A&M 1 Talk Outline Motivation, Intended Audience and Class Goals Course
empowertm STUDENT SAMPLE ITEM BOOKLET Reading Grade 7
 empowertm ME STUDENT SAMPLE ITEM BOOKLET Grade 7 Developed and published by Measured Progress, 100 Education Way, Dover, NH 03820. Copyright 2016. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
empowertm ME STUDENT SAMPLE ITEM BOOKLET Grade 7 Developed and published by Measured Progress, 100 Education Way, Dover, NH 03820. Copyright 2016. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction A typical Modern Geometry course will focus on some variation of a set of axioms for Euclidean geometry due to Hilbert. At the end of such a course, non-euclidean geometries (always
CHAPTER 1 Introduction A typical Modern Geometry course will focus on some variation of a set of axioms for Euclidean geometry due to Hilbert. At the end of such a course, non-euclidean geometries (always
Wednesday 21 June 2017 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Wednesday 21 June 2017 Afternoon GCSE HUMANITIES B032/01 Application of Knowledge *5986624494* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Wednesday 21 June 2017 Afternoon GCSE HUMANITIES B032/01 Application of Knowledge *5986624494* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws.
 This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws. There are changes coming to our planet and solar system and after these
This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws. There are changes coming to our planet and solar system and after these
ELEMENTS OF PHYSICS ENERGY: WORK and POWER
 1 Pre-Test Directions: This will help you discover what you know about the subject of energy before you begin this lesson. Answer the following true or false. 1. To a physicist, energy is work or the capacity
1 Pre-Test Directions: This will help you discover what you know about the subject of energy before you begin this lesson. Answer the following true or false. 1. To a physicist, energy is work or the capacity
The phenomenon of gravitational lenses
 The phenomenon of gravitational lenses The phenomenon of gravitational lenses If we look carefully at the image taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, of the Galaxy Cluster Abell 2218 in the constellation
The phenomenon of gravitational lenses The phenomenon of gravitational lenses If we look carefully at the image taken with the Hubble Space Telescope, of the Galaxy Cluster Abell 2218 in the constellation
The Challenge of Light
 Thomas Alva Edison The Challenge of Light We have been studying light for years Do we know everything about it? Absolutely not! Greeks & Chinese have been using light for years with no real concept of
Thomas Alva Edison The Challenge of Light We have been studying light for years Do we know everything about it? Absolutely not! Greeks & Chinese have been using light for years with no real concept of
Lesson 12 Relativity
 Lesson 12 Relativity Introduction: Connecting Your Learning Relative motion was studied at the beginning of the course when the simple notion of adding or subtracting velocities made perfect sense. If
Lesson 12 Relativity Introduction: Connecting Your Learning Relative motion was studied at the beginning of the course when the simple notion of adding or subtracting velocities made perfect sense. If
Chapter 3. Estimation of p. 3.1 Point and Interval Estimates of p
 Chapter 3 Estimation of p 3.1 Point and Interval Estimates of p Suppose that we have Bernoulli Trials (BT). So far, in every example I have told you the (numerical) value of p. In science, usually the
Chapter 3 Estimation of p 3.1 Point and Interval Estimates of p Suppose that we have Bernoulli Trials (BT). So far, in every example I have told you the (numerical) value of p. In science, usually the
UNIT 2 The Particulate Nature of Matter
 UNIT 2 The Particulate Nature of Matter Take a moment to think about all of the different properties which can be exhibited by matter. The list seems endless. Matter can be found in a variety of forms,
UNIT 2 The Particulate Nature of Matter Take a moment to think about all of the different properties which can be exhibited by matter. The list seems endless. Matter can be found in a variety of forms,
Introduction to Algebra: The First Week
 Introduction to Algebra: The First Week Background: According to the thermostat on the wall, the temperature in the classroom right now is 72 degrees Fahrenheit. I want to write to my friend in Europe,
Introduction to Algebra: The First Week Background: According to the thermostat on the wall, the temperature in the classroom right now is 72 degrees Fahrenheit. I want to write to my friend in Europe,
Beyond the Book. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book Scientists and engineers use models to plan investigations and to describe results. Create a scale model that represents part or all of Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 s journey so far. Your model can
FOCUS Book Scientists and engineers use models to plan investigations and to describe results. Create a scale model that represents part or all of Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 s journey so far. Your model can
9/28/2017 A New Theory of How the Moon Formed - Scientific American Blog Network. Observations. A New Theory of How the Moon Formed
 Observations A New Theory of How the Moon Formed Contrary to what we now think, it could be that it came from a violent impact that temporarily turned Earth into a "synestia" By Simon Lock on June 9, 2017
Observations A New Theory of How the Moon Formed Contrary to what we now think, it could be that it came from a violent impact that temporarily turned Earth into a "synestia" By Simon Lock on June 9, 2017
Isaac Newton & Gravity
 Isaac Newton & Gravity Isaac Newton was born in England in 1642 the year that Galileo died. Newton would extend Galileo s study on the motion of bodies, correctly deduce the form of the gravitational force,
Isaac Newton & Gravity Isaac Newton was born in England in 1642 the year that Galileo died. Newton would extend Galileo s study on the motion of bodies, correctly deduce the form of the gravitational force,
CHAPTER 9 THE ARROW OF TIME
 CHAPTER 9 THE ARROW OF TIME In previous chapters we have seen how our views of the nature of time have changed over the years. Up to the beginning of this century people believed in an absolute time. That
CHAPTER 9 THE ARROW OF TIME In previous chapters we have seen how our views of the nature of time have changed over the years. Up to the beginning of this century people believed in an absolute time. That
Statistical Mechanics
 42 My God, He Plays Dice! Statistical Mechanics Statistical Mechanics 43 Statistical Mechanics Statistical mechanics and thermodynamics are nineteenthcentury classical physics, but they contain the seeds
42 My God, He Plays Dice! Statistical Mechanics Statistical Mechanics 43 Statistical Mechanics Statistical mechanics and thermodynamics are nineteenthcentury classical physics, but they contain the seeds
10/27/2012. Chapter 18: The law of increasing disorder. The arrow of time. Irreversible processes are all around us
 Chapter 18: The law of increasing disorder Did you read chapter 18 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No The arrow of time Irreversible processes are all around us An irreversible process is one that occurs
Chapter 18: The law of increasing disorder Did you read chapter 18 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No The arrow of time Irreversible processes are all around us An irreversible process is one that occurs
Life on a New Planet
 Life on a New Planet Your Assignment: A national magazine is sponsoring a short story contest. Your teacher has assigned your class the task of entering this contest. The first, second, and third place
Life on a New Planet Your Assignment: A national magazine is sponsoring a short story contest. Your teacher has assigned your class the task of entering this contest. The first, second, and third place
Chapter 26: Comparing Counts (Chi Square)
 Chapter 6: Comparing Counts (Chi Square) We ve seen that you can turn a qualitative variable into a quantitative one (by counting the number of successes and failures), but that s a compromise it forces
Chapter 6: Comparing Counts (Chi Square) We ve seen that you can turn a qualitative variable into a quantitative one (by counting the number of successes and failures), but that s a compromise it forces
The cause and development of cosmic background radiation
 Background Radiation 1 The cause and development of cosmic background radiation A paper by: Dipl. Ing. Matthias Krause, (CID) Cosmological Independent Department, Germany, 2009 Objective The objective
Background Radiation 1 The cause and development of cosmic background radiation A paper by: Dipl. Ing. Matthias Krause, (CID) Cosmological Independent Department, Germany, 2009 Objective The objective
Topic 7 - Evolution. "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." Theodosius Dobzhansky,1973
 Topic 7 - Evolution "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." Theodosius Dobzhansky,1973 Before Darwin (1859) Scientific Understanding: Earth/nature static creation of God/Gods
Topic 7 - Evolution "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." Theodosius Dobzhansky,1973 Before Darwin (1859) Scientific Understanding: Earth/nature static creation of God/Gods
Is evolution the great lie part 4?
 Is evolution the great lie part 4? Organic evolution Organic evolution is the origin of life (evolution of non-living material) How did life get started? Here are some texts The history of life on earth
Is evolution the great lie part 4? Organic evolution Organic evolution is the origin of life (evolution of non-living material) How did life get started? Here are some texts The history of life on earth
Modern Physics notes Spring 2007 Paul Fendley Lecture 27
 Modern Physics notes Spring 2007 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 27 Angular momentum and positronium decay The EPR paradox Feynman, 8.3,.4 Blanton, http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/quantum/bells
Modern Physics notes Spring 2007 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 27 Angular momentum and positronium decay The EPR paradox Feynman, 8.3,.4 Blanton, http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/quantum/bells
Physics. Chapter 9 Gravity
 Physics Chapter 9 Gravity The Newtonian Synthesis Gravity is a Universal Force The Newtonian Synthesis According to legend, Newton discovered gravity while sitting under an apple tree. The Falling Moon
Physics Chapter 9 Gravity The Newtonian Synthesis Gravity is a Universal Force The Newtonian Synthesis According to legend, Newton discovered gravity while sitting under an apple tree. The Falling Moon
Introduction to Physics. Motion & Energy. Lecture 4
 Introduction to Physics Motion & Energy Lecture 4 Part I: the study of matter and energy, forces and motion (ideas central to all of the sciences) Classical physics: Mechanics Modern physics: Quantum mechanics
Introduction to Physics Motion & Energy Lecture 4 Part I: the study of matter and energy, forces and motion (ideas central to all of the sciences) Classical physics: Mechanics Modern physics: Quantum mechanics
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html NASA
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html NASA
An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos
 An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos What is Astronomy? 50 years ago, astronomy was the study of everything outside Earth s atmosphere: the planets, the Sun, stars, galaxies, the
An Introduction to AST 112 Stars, Galaxies, and the Cosmos What is Astronomy? 50 years ago, astronomy was the study of everything outside Earth s atmosphere: the planets, the Sun, stars, galaxies, the
AST 301: Topics for today!
 AST 301: Topics for today! 1.! Syllabus. You should have read the syllabus in detail. So only brief questions about course, grading, etc. today.!!!go to the course web site and bookmark it as soon as possible.!
AST 301: Topics for today! 1.! Syllabus. You should have read the syllabus in detail. So only brief questions about course, grading, etc. today.!!!go to the course web site and bookmark it as soon as possible.!
COPYRIGHT. Universis. Big Bangs and Universal Beings
 Universis Big Bangs and Universal Beings COPYRIGHT The untold history of the universe with new knowledge that will change the world 1st edition 2013 Text by Patrick Cusick eisbn 978-616-222-262-7 print
Universis Big Bangs and Universal Beings COPYRIGHT The untold history of the universe with new knowledge that will change the world 1st edition 2013 Text by Patrick Cusick eisbn 978-616-222-262-7 print
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Big Bang, Black Holes, No Math
 ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 5 1 Prep For Today (is now due) L5 Reading: No new reading Unit 2 reading assigned at the end of class Pre-Lecture Reading Questions: Unit 1: Grades have been posted
ASTR/PHYS 109 Dr. David Toback Lecture 5 1 Prep For Today (is now due) L5 Reading: No new reading Unit 2 reading assigned at the end of class Pre-Lecture Reading Questions: Unit 1: Grades have been posted
Grade 7/8 Math Circles. Mathematical Thinking
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 22 & 23 2016 Mathematical Thinking Today we will take a look at some of the
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles March 22 & 23 2016 Mathematical Thinking Today we will take a look at some of the
These are my slides and notes introducing the Red Queen Game to the National Association of Biology Teachers meeting in Denver in 2016.
 These are my slides and notes introducing the Red Queen Game to the National Association of Biology Teachers meeting in Denver in 2016. Thank you SSE and the Huxley Award for sending me to NABT 2016! I
These are my slides and notes introducing the Red Queen Game to the National Association of Biology Teachers meeting in Denver in 2016. Thank you SSE and the Huxley Award for sending me to NABT 2016! I
THEORY A. The life forms presently on the planet are the ones that have always existed.
 THEORY A Life has always existed. The life forms presently on the planet are the ones that have always existed. There is an immutability to life (life does not change). All biological types remain the
THEORY A Life has always existed. The life forms presently on the planet are the ones that have always existed. There is an immutability to life (life does not change). All biological types remain the
35 Chapter CHAPTER 4: Mathematical Proof
 35 Chapter 4 35 CHAPTER 4: Mathematical Proof Faith is different from proof; the one is human, the other is a gift of God. Justus ex fide vivit. It is this faith that God Himself puts into the heart. 21
35 Chapter 4 35 CHAPTER 4: Mathematical Proof Faith is different from proof; the one is human, the other is a gift of God. Justus ex fide vivit. It is this faith that God Himself puts into the heart. 21
( )( b + c) = ab + ac, but it can also be ( )( a) = ba + ca. Let s use the distributive property on a couple of
 Factoring Review for Algebra II The saddest thing about not doing well in Algebra II is that almost any math teacher can tell you going into it what s going to trip you up. One of the first things they
Factoring Review for Algebra II The saddest thing about not doing well in Algebra II is that almost any math teacher can tell you going into it what s going to trip you up. One of the first things they
