The ANSWER Einstein looked for Issued: July 10th ANSWER in htm: - Quick version of.
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The ANSWER Einstein looked for Issued: July 10th ANSWER in htm: - Also ANSWER in Word: - And ANSWER in Adobe pdf: - Quick version of "Ampere's Laws" Ampere's 1824 Laws Abstract These relative motion laws greatly simply all of science: These laws are essentially Ampere's simple 1824 long, parallel wire laws with a frequency modification..these are universal laws that unify all the forces by seeing all forces as spacetime creations similar to the way it's done in general relativity.. These laws, though, visualize different spacetime intervals (different gauges) being created at various different spin/orbit frequencies. Despite the fact that quantum theory does not see our type of spin causing angular momentum in the microcosm, these laws show it is there nevertheless but with a different spacetime interval (different gauge = different spin/orbit frequency level = different spacetime realm). file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (1 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
2 The "A" Laws [The reason these "A" Laws work relates to the superposition principle that there is an attractive force between in phase entities snd a repulsive force between out of phase entities and (space) is always generated by the AVERAGE out of phase amount]. These laws pertain to all Scalar, Spherical, Standing Wave Resonances KEY is the relative motion between the closest sides of two SSSWRs. Remember, these "A" Laws (Ampere or Aufbau) have unified ALL the forces so these are now the NEW laws for everything, from the smallest spinning particle to the largest spinning super cluster of galaxies even where high relativistic speeds and mass are encountered. For simplicity, we must return to the Bohr concept of the electron and the concept of impedance matching. I have shown why in numerous other papers. * The 1 st. "A" Law shows us where all SSSWRs in relative motion produce the least spacetime between themselves: The space time interval is created the least between any two SSSWRs, the closest sides of which "see" themselves spinning or moving on parallel paths in the same direction at the same frequency (like gears meshing) or a close harmonic thereof. You can also say these two objects will attract each other. file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (2 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
3 * The motion produce the most spacetime between themselves: 2 nd. "A" Law shows us where all SSSWRs in relative Both space and time are created the most between any two SSSWRs, the closest sides of which "see" themselves spinning or moving on parallel paths in opposite directions at the same frequency (like gears clashing) or a close harmonic thereof. You can also say these two objects will repel each other. I use the quoted word "see" to emphasize the particular spacetime realm in which these entities actually find themselves although this will NOT be the way it is seen from our particular spacetime reference frame realm. Of great importance, in the two preceding laws, is that these laws are frequency laws and they work separately for each separate spin/orbit frequency level which means these individual wave-particles must "see" themselves doing these things from their viewpoint in their local gauge environment. It does not matter how some other spin/orbit frequency level views these things because space and time and indeed the average space time interval is entirely different for each different spin/orbit frequency level (gauge). These two laws look equal and opposite but they are not: The 1 st "A" law "locks on" while its opposite 2 nd sister law never does. This is because the total force is generally centralized and you can feel this 1 st "A" law "lock on" when two magnets come together. These two laws result in limits of aggregation being established all throughout file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (3 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
4 this universe: This is why there are limits to the size of atoms and limits to the size of stars as well. * The Aufbau or Ampere Corollary The aforementioned forces, or spacetime intervals, between two SSSWRs will vary proportionally with the cosine of the angle of their paths. And they will have a torque that will tend to make the paths parallel and to become oriented so that SSSWRs on both paths will be traveling in the same direction. Or All SSSWRs that "see" themselves traveling in the same direction on parallel paths at the same frequency will attract and/or space and time, at that frequency, between them is created the least. All SSSWRs that "see" themselves traveling in opposite directions on parallel paths at the same frequency will repel and/or space and time between them, at that frequency, increases or is created the most. And please don't forget this: Why electrons, stars & galaxies repel each other Remember, we have completely chucked out all those invisible forces you are familiar with and all we have now are these two "A" Laws. Please remember, in this new "big picture" of everything, ALL FORCES ARE NOW UNIFIED so there are no such things as gravity, magnetic lines of force or plus and minus charges or for that matter even the strong force. file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (4 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
5 Please pay particular attention to the following. Remember, it's motion between the closest sides that counts. Electrons can exhibit either an attraction or repulsion when they are "locked" spin up or spin down on orbitals such as like or unlike charges; like or unlike poles OR they may even display a gyroscopic type repulsive behavior when they are "free". Our "A" Laws show us why this is so and in the next 6 paragraphs you have the best explanation of why electrons and even stars & galaxies repel each other. Lets look at these free electrons first: They spin and hence they have inertial qualities and this includes gyroscopic inertia which always provides this force 90 degrees to any external force acting on such a spinning item. Completely forget about charge now and only look at our new "A" Laws and what they say. The 1 st "A" Law tells us that there is a possibility that two free electrons can attract each other providing that any portion of their closest sides are spinning in the same direction at the same frequency. This means either their sides can be spinning in the same directions or they can be lined up so that both of their poles can be spinning in the same directions: Any such two electrons will attract each other (magnetism also sigma and pi bonding). file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (5 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
6 Then we see that there is something else: This torque twisting force - on BOTH free items - depends on the cosine of the angle of their respective spin planes. As this force begins to act, it in turn causes this 90-degree gyroscopic torque to twist both of those totally free electrons away from this initial attracting position, doesn't it? So because of this gyro torque, two free electrons can never remain in a full attracting position and they will therefore be forced to stay more in a repelling position. Therefore free electrons will always end up repelling each other and this repelling is not explained by using this thing called charge: it is explained only by simply using global inertial qualities and our new global "A" Laws. The above 6 paragraphs explain not only why electrons repel each other but they also explain why any two perfectly free similar spinning SSSWRs of the same size must repel each other. So now you know why both electrons and galaxies stay well away from each other. This is Einstein's cosmological constant. Something somewhere has to be "locked" in place and synchronized in frequency (such as the electron's spin with another electron's spin) or a close subharmonic to get any kind of attracting force: Yes, the proton attracts an electron but instead of charge please see it as an in phase or relative motion type of binding. We can see phase sometimes better as relative motion, so use either. This is why aggregations (gravity) and larger aggregations come together and accumulate because as these things grow in size there are more things "locked" in place strengthening the attractive force file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (6 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
7 of the 1 st "A" Law. We will soon know even more about the attractive quark strong force binding functions. Attraction is always a synchronized frequency attraction and it is not simply the old idea of plus and minus charges. All attractions in this theory must be synchronized frequency attractions. Both light and inertial mass are caused by these synchronized frequency attractions. As quantum theory shows us, the orbital of an electron on a distant star goes down a certain amount while the orbital of the electron receiving this quantum of energy---in your eye---goes up the exact same amount. But what quantum mechanics does not tell you is that these two energy-exchanging orbitals must be in the same exact plane. They must be a sigma bond whose strength does not vary with distance but entirely ceases at the Hubble limit because the "angle of lock on" becomes too acute for these two entities to bind. If two distant quarks are lined up so that their closest sides are in the same directions as the two aforementioned electrons - and their impedances match - then they too will bind with each other---even from a vast distance---and cause what we see as inertial mass. When you spin a flywheel and notice the gyroscopic inertia, you should also notice that the gyroscopic torque that is always 90 degrees to the axis of rotation can also be seen as a linkage with the rim of the rapidly spinning flywheel to a path projected in the sky (macrocosm surroundings). The rim tries to stay in this path. This is showing you that you do have an absolute reference frame, which is Mach's principle. Billions of quarks in BOTH the flywheel and in the macrocosm are both being pulled and extended more than normal, toward the outer edge of the neutron or proton, thus giving you this added gyroscopic inertia. So gyroscopic inertia is a quark to quark force that pulls AGAINST what we call the strong force. You might have to read the long TOE at file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (7 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
8 to get the full picture of what happens when you crank up a gyroscope or a flywheel or ride a bicycle and produce gyroscopic inertia. It's similar to the reason you need cyclic pitch on a helicopter. When a helicopter moves forward then the blades on one side travel through the air faster than the blades on the other side and this tries to tip the helicopter over. (Igor Sikorsky had to invent cyclic pitch to prevent this). The same thing happens to certain quarks whose rims line up with the rim of the gyroscope, flywheel or bicycle wheels. The speed that these items are turning---in respect to the macrocosm---now adds to portions of the quark rim speed which before was close to the speed of light and now gets even closer to the speed of light (becoming more massive hence at a higher frequency). So you are moving up an asymptotic curve close to that unsurpassable speed of c. And this---even with a miniscule number of quarks involved---gives us this gyroscopic inertia. It does this because the mass of these few quarks increase tremendously as portions of their rim speed approach the speed of light. As Einstein has shown us, mass increases with speed and especially increases when on that asymptotic portion of the curve. Of available electrons, only the smallest fraction impedance match and link with others a distance away to transfer light and heat. The same with the spinning quark that causes gyroscopic inertia. All spinning quarks link to cause inertial mass. Now let's go to the stars and you will see the same "A" Laws apply there as well and, as you can see, these too will always have to remain in a repelling position with each other. Close stars, especially close binary stars, will NEVER be spinning so that their closest sides are moving in the same direction at the same frequency. Recently Perlmutter discovered this acceleration and showed we must have Einstein's cosmological constant---a repulsive force---between all the stars and galaxies. file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (8 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
9 If you think Perlmutter is wrong then why do we have Einstein's Principle of Equivalence? Why is the earth's gravity the same as an acceleration? Present science doesn't answer that but the only possible answer, my friend, is that spacetime is being created MORE in the surroundings than it is between you and the earth thereby pushing you toward the earth. And if gravity can not be discerned from an accelerating contraction (Principle of Equivalence) then that repulsive force in all the surroundings can not be discerned from an accelerating expansion either. Scientists have been recently wracking their brains to figure out why we have Perlmutter's acceleration because nothing in our present science has even predicted such a thing. But read those preceding blue sentences again! Now I hope you can finally see that our "A" Laws tell you exactly why we have Einstein's "cosmological constant" not only in the sky but in the microcosm as well. And they tell you why we have gravity too. Your present science doesn't even do this. The reason these "A" Laws work is that this universe is built on an extraordinarily simple principle via an endless supply of vector wave resonances producing lower frequency spherical standing wave, scalar wave resonances that, in turn, produce spacetime by spinning, orbiting and precessing. A minimum of space (at that particular frequency) is produced between the closest sides of spinning entities that are in the same phase. Bindings must be in phase and impedanced matched: THIS is the reason energy cannot be created nor destroyed. file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (9 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
10 These "A" Laws show us the production of the most important vector forces between the closest sides of such spinning spherical resonances and in the direction of the axis of each spin. There are also vector forces via orbits and spin and orbital and spin precessions. This universe equalizes the energy vector force input to vector force output of these scalar wave resonances by balancing them on specific spin and orbital geodesics. Daniel P. Fitzpatrick Jr Very Latest in SCIENCE - Click one of the links below: Latest SCIENCE.htm Latest SCIENCE.pdf Latest SCIENCE.doc Over 4 Decades of Daniel P. Fitzpatrick's Books, Papers and Thoughts Over 4 Decades of Fitzpatrick's Books, Papers & Thoughts web page file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (10 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
11 file:///c /Users/d/Desktop/qamp.htm (11 of 11) [7/24/2018 6:45:31 PM]
This new hypothesis has "complementarity" because it shows us the sa...actly what space and time are plus it unifies the fundamental forces
 SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
an important Matter seen by "Michael Crichton"
 SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
SCIENCE CONCEPTS that will never change.
 January, 28, 2019 Shedding a bit of light on the few absolutely TRUE SCIENCE CONCEPTS that will never change. Don't skip this paper if you are interested in theoretical physics. Kurt Gödel, mathematician
January, 28, 2019 Shedding a bit of light on the few absolutely TRUE SCIENCE CONCEPTS that will never change. Don't skip this paper if you are interested in theoretical physics. Kurt Gödel, mathematician
UNIVERSITIES ASLEEP AT THE SWITCH. Copyright Unlimited Publishing LLC, All Rights Reserved
 UNIVERSITIES ASLEEP AT THE SWITCH Copyright Unlimited Publishing LLC, All Rights Reserved UNIVERSITIES ASLEEP AT THE SWITCH: A FRESH LOOK AT QUANTUM PHYSICS DANIEL P. FITZPATRICK, JR. Unlimited Publishing
UNIVERSITIES ASLEEP AT THE SWITCH Copyright Unlimited Publishing LLC, All Rights Reserved UNIVERSITIES ASLEEP AT THE SWITCH: A FRESH LOOK AT QUANTUM PHYSICS DANIEL P. FITZPATRICK, JR. Unlimited Publishing
DEFIES GRAVITY. why a gyroscope. It really does defy gravity even though the present science establishment seems to want to convince us otherwise.
 SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
The LARGE POP TREMENDOUS EXPLOSION GIANT POW ENORMOUS WALLOP. BIG BANG(theory)!
 The LARGE POP TREMENDOUS EXPLOSION GIANT POW ENORMOUS WALLOP BIG BANG(theory)! What IS the Big Bang? One of many plausible theories that tries to answer the question: How did the universe get to be the
The LARGE POP TREMENDOUS EXPLOSION GIANT POW ENORMOUS WALLOP BIG BANG(theory)! What IS the Big Bang? One of many plausible theories that tries to answer the question: How did the universe get to be the
Please pick up your midterms from front of class
 Please pick up your midterms from front of class Average: 70 % Test % score distribution: Top grade: 92 % Make sure you go through your test and the solutions carefully to understand where you went wrong.
Please pick up your midterms from front of class Average: 70 % Test % score distribution: Top grade: 92 % Make sure you go through your test and the solutions carefully to understand where you went wrong.
Schrödinger's Universe
 VERY LATEST IN SCIENCE: Do Ampere's Laws give us the final answer to DARK MATTER? 7-7-2017.The final answer to the cause of Dark Matter.htm Final and SIMPLE answer to the DARK MATTER attractive force.
VERY LATEST IN SCIENCE: Do Ampere's Laws give us the final answer to DARK MATTER? 7-7-2017.The final answer to the cause of Dark Matter.htm Final and SIMPLE answer to the DARK MATTER attractive force.
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 27 What s Next?
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
Name Final Exam December 7, 2015
 Name Final Exam December 7, 015 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Name Final Exam December 7, 015 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Algebra Based Physics
 1 / 88 Algebra Based Physics Electric Charge and Force 20151130 www.njctl.org 2 / 88 Electric Charge and Force Click on the topic to go to that section Electric Charge Atomic Structure and Source of Charge
1 / 88 Algebra Based Physics Electric Charge and Force 20151130 www.njctl.org 2 / 88 Electric Charge and Force Click on the topic to go to that section Electric Charge Atomic Structure and Source of Charge
Fitz's 1966 book in PDF. This was the way the site --below-- looked many years ago. - - Dan Fitz. Shedding a bit of light. on the cause of.
 SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
SEE, HOW the complexities of FIELD THEORIES HID from us, the fact that relative motion (phase) between all these spinning entities, in the micro & macro universe, gives us all the attractive and repulsive
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 05 The Fundamental Forces of Nature In this lecture, we will discuss the
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 05 The Fundamental Forces of Nature In this lecture, we will discuss the
Electric Charge. Demo Lab. Return to Table of Contents. abp_electric charge force presentation_ notebook. March 21, 2017
 abp_electricchargeforcepresentation_20170207.notebook Electric Charge Demo Lab https://www.njctl.org/video/?v=xbmbaekusb4 Return to Table of Contents 1 abp_electricchargeforcepresentation_20170207.notebook
abp_electricchargeforcepresentation_20170207.notebook Electric Charge Demo Lab https://www.njctl.org/video/?v=xbmbaekusb4 Return to Table of Contents 1 abp_electricchargeforcepresentation_20170207.notebook
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
Lecture 01. Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics
 Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics Particle Astrophysics Particle physics Fundamental constituents of nature Most basic building blocks Describe all particles and interactions Shortest length
Introduction to Elementary Particle Physics Particle Astrophysics Particle physics Fundamental constituents of nature Most basic building blocks Describe all particles and interactions Shortest length
How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves example: speed of
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves example: speed of
Crossing the Event Horizon Presented by Nassim Haramein
 Crossing the Event Horizon Presented by Nassim Haramein Part 1: The Untold Physics Chapter 5: Concept of Black Holes In order to understand the concept of atoms, planets, galaxies and stars as all having
Crossing the Event Horizon Presented by Nassim Haramein Part 1: The Untold Physics Chapter 5: Concept of Black Holes In order to understand the concept of atoms, planets, galaxies and stars as all having
Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles
 Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles The basic Cosmological Principles The geometry of the Universe The scale factor R and curvature constant k Comoving coordinates Einstein s initial solutions 3/28/11
Lecture 14: Cosmological Principles The basic Cosmological Principles The geometry of the Universe The scale factor R and curvature constant k Comoving coordinates Einstein s initial solutions 3/28/11
Scott Hughes 12 May Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Spring 2005
 Scott Hughes 12 May 2005 24.1 Gravity? Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics 8.022 Spring 2005 Lecture 24: A (very) brief introduction to general relativity. The Coulomb interaction
Scott Hughes 12 May 2005 24.1 Gravity? Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics 8.022 Spring 2005 Lecture 24: A (very) brief introduction to general relativity. The Coulomb interaction
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
Select/ Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Select/ Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 06 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics Greetings, we will begin
Select/ Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 06 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics Greetings, we will begin
Dark Matter and Energy
 Dark Matter and Energy The gravitational force attracting the matter, causing concentration of the matter in a small space and leaving much space with low matter concentration: dark matter and energy.
Dark Matter and Energy The gravitational force attracting the matter, causing concentration of the matter in a small space and leaving much space with low matter concentration: dark matter and energy.
This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws.
 This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws. There are changes coming to our planet and solar system and after these
This is a brief overview of some of the very basic and classic laws of physics and how magnetic energy theory fits into those laws. There are changes coming to our planet and solar system and after these
Chapter 32 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 32 Lecture Notes Physics 2424 - Strauss Formulas: mc 2 hc/2πd 1. INTRODUCTION What are the most fundamental particles and what are the most fundamental forces that make up the universe? For a brick
Chapter 32 Lecture Notes Physics 2424 - Strauss Formulas: mc 2 hc/2πd 1. INTRODUCTION What are the most fundamental particles and what are the most fundamental forces that make up the universe? For a brick
The Magnetic field of the Electric current and the Magnetic induction
 The Magnetic field of the Electric current and the Magnetic induction This paper explains the magnetic effect of the electric current from the observed effects of the accelerating electrons, causing naturally
The Magnetic field of the Electric current and the Magnetic induction This paper explains the magnetic effect of the electric current from the observed effects of the accelerating electrons, causing naturally
Inertial Frame frame-dragging
 Frame Dragging Frame Dragging An Inertial Frame is a frame that is not accelerating (in the sense of proper acceleration that would be detected by an accelerometer). In Einstein s theory of General Relativity
Frame Dragging Frame Dragging An Inertial Frame is a frame that is not accelerating (in the sense of proper acceleration that would be detected by an accelerometer). In Einstein s theory of General Relativity
Today: Start Ch. 18: Cosmology. Homework # 5 due next Wed. (HW #6 is online)
 Today: Start Ch. 18: Cosmology Homework # 5 due next Wed. (HW #6 is online) Dark Matter! A rotation curve is a graph of how fast a something is rotating, as a function of distance from the center.! We
Today: Start Ch. 18: Cosmology Homework # 5 due next Wed. (HW #6 is online) Dark Matter! A rotation curve is a graph of how fast a something is rotating, as a function of distance from the center.! We
The Bohr Magneton and Bohr's second and third biggest mistakes
 The Bohr Magneton and Bohr's second and third biggest mistakes by Miles Mathis Abstract: I will show several problems with the derivation of the Bohr Magneton. Using that analysis, I will look again at
The Bohr Magneton and Bohr's second and third biggest mistakes by Miles Mathis Abstract: I will show several problems with the derivation of the Bohr Magneton. Using that analysis, I will look again at
Agenda Announce: 4.1 Describing Motion. Tests. How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity Agenda Announce: Stony Brook talk this Friday on Precision Cosmology Project Part I due in one week before class: one paragraph
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity Agenda Announce: Stony Brook talk this Friday on Precision Cosmology Project Part I due in one week before class: one paragraph
Lesson 1: Forces. Fascinating Education Script Fascinating Intro to Chemistry Lessons. Slide 1: Introduction. Slide 2: Forces
 Fascinating Education Script Fascinating Intro to Chemistry Lessons Lesson 1: Forces Slide 1: Introduction Slide 2: Forces Hi. My name is Sheldon Margulies, and we re about to learn what things are made
Fascinating Education Script Fascinating Intro to Chemistry Lessons Lesson 1: Forces Slide 1: Introduction Slide 2: Forces Hi. My name is Sheldon Margulies, and we re about to learn what things are made
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley Lecture 38
 Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Dark Energy and Dark Matter
 Dark Energy and Dark Matter Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) The Dark Lord wants his ring back! Final Exam The final exam is Thursday, 6/8, from 11:30am to 1:30pm (2 hours),
Dark Energy and Dark Matter Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) The Dark Lord wants his ring back! Final Exam The final exam is Thursday, 6/8, from 11:30am to 1:30pm (2 hours),
Electric Fields -- Conceptual Solutions. 1.) What does an electric field actually tell you? That is:
 Electric Fields Electric Fields -- onceptual Solutions 1.) What does an electric field actually tell you? That is: a.) Is it a vector? If so, what does its direction signify? Solution: An electric field
Electric Fields Electric Fields -- onceptual Solutions 1.) What does an electric field actually tell you? That is: a.) Is it a vector? If so, what does its direction signify? Solution: An electric field
Chapter 13 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline Neutron Stars. Neutron Stars and Black Holes Neutron Stars. Units of Chapter
 13.1 Neutron Stars Lecture Outline Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and After a Type I supernova, little or nothing remains of the original star. After a Type II supernova, part of the core may survive. It is
13.1 Neutron Stars Lecture Outline Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and After a Type I supernova, little or nothing remains of the original star. After a Type II supernova, part of the core may survive. It is
Gravity Well Demo - 1 of 9. Gravity Well Demo
 Gravity Well Demo - 1 of 9 Gravity Well Demo Brief Summary This demo/activity in Space Odyssey will give visitors a hands-on feel for how gravity works. Specifically, how Newton interpreted the force of
Gravity Well Demo - 1 of 9 Gravity Well Demo Brief Summary This demo/activity in Space Odyssey will give visitors a hands-on feel for how gravity works. Specifically, how Newton interpreted the force of
On The Discrete Nature of The Gravitational Force. Dewey Lewis Boatmun.
 On The Discrete Nature of The Gravitational Force Dewey Lewis Boatmun BOATMUN@sbcglobal.net Abstract The standard model of particle physics has been extremely successful in unifying the strong, weak, and
On The Discrete Nature of The Gravitational Force Dewey Lewis Boatmun BOATMUN@sbcglobal.net Abstract The standard model of particle physics has been extremely successful in unifying the strong, weak, and
2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Daily Life Some of the topics we will explore: How do we describe motion? (Speed,
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Daily Life Some of the topics we will explore: How do we describe motion? (Speed,
Chapter S3 Spacetime and Gravity. Agenda. Distinguishing Crackpots
 Chapter S3 Spacetime and Gravity Agenda Announce: Online Quizzes Observations Extra Credit Lecture Distinguishing Crackpot/Genuine Science Review of Special Relativity General Relativity Distinguishing
Chapter S3 Spacetime and Gravity Agenda Announce: Online Quizzes Observations Extra Credit Lecture Distinguishing Crackpot/Genuine Science Review of Special Relativity General Relativity Distinguishing
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe
 Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different
How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves $ speed = distance!#"units
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves $ speed = distance!#"units
Limitations of Newtonian Physics
 Limitations of Newtonian Physics 18 th and 19 th Centuries Newtonian Physics was accepted as an ultimate truth Science is never absolute Hundreds of experiments can t prove my theory right but only one
Limitations of Newtonian Physics 18 th and 19 th Centuries Newtonian Physics was accepted as an ultimate truth Science is never absolute Hundreds of experiments can t prove my theory right but only one
Gravitation. Adrian Ferent. This is a new quantum gravity theory which breaks the wall of Planck scale. Abstract
 Gravitation Adrian Ferent This is a new quantum gravity theory which breaks the wall of Planck scale. My Nobel Prize Idea Abstract The Photon Graviton pair (coupled) has the same speed and frequency, and
Gravitation Adrian Ferent This is a new quantum gravity theory which breaks the wall of Planck scale. My Nobel Prize Idea Abstract The Photon Graviton pair (coupled) has the same speed and frequency, and
Cosmology. Chapter 18. Cosmology. Observations of the Universe. Observations of the Universe. Motion of Galaxies. Cosmology
 Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
IF A NUCLEUS IS FULL OF POSITIVELY CHARGED PROTONS, WHY DOESN T IT FLY APART?
 IF A NUCLEUS IS FULL OF POSITIVELY CHARGED PROTONS, WHY DOESN T IT FLY APART? An introduction to the fundamental forces that control our world. Remembering that like charges repel each other, you may have
IF A NUCLEUS IS FULL OF POSITIVELY CHARGED PROTONS, WHY DOESN T IT FLY APART? An introduction to the fundamental forces that control our world. Remembering that like charges repel each other, you may have
Potential-energy of the photon emitted by an atom: And the cosmological red-shift
 1 Potential-energy of the photon emitted by an atom: And the cosmological red-shift Hasmukh K. Tank Indian Space Research Organization, 22/693 Krishna Dham-2 Ahmedabad 380015 India Abstract When an electron
1 Potential-energy of the photon emitted by an atom: And the cosmological red-shift Hasmukh K. Tank Indian Space Research Organization, 22/693 Krishna Dham-2 Ahmedabad 380015 India Abstract When an electron
The Cycloid. and the Kinematic Circumference. by Miles Mathis
 return to updates The Cycloid and the Kinematic Circumference First published August 31, 2016 by Miles Mathis Those of you who have read my papers on π=4 will know I have explained that problem using many
return to updates The Cycloid and the Kinematic Circumference First published August 31, 2016 by Miles Mathis Those of you who have read my papers on π=4 will know I have explained that problem using many
Wallace Hall Academy
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Universe Notes Name 1 Newton and Gravity Newton s Thought Experiment Satellite s orbit as an Application of Projectiles Isaac Newton, as well as giving
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 1 - Universe Notes Name 1 Newton and Gravity Newton s Thought Experiment Satellite s orbit as an Application of Projectiles Isaac Newton, as well as giving
4.1 Describing Motion
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
What is a supernova? They Outshine Their Entire Galaxy. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 675 Level 840L
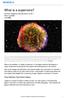 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 675 Level 840L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 675 Level 840L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
8. The Expanding Universe, Revisited
 8. The Expanding Universe, Revisited A1143: History of the Universe, Autumn 2012 Now that we have learned something about Einstein s theory of gravity, we are ready to revisit what we have learned about
8. The Expanding Universe, Revisited A1143: History of the Universe, Autumn 2012 Now that we have learned something about Einstein s theory of gravity, we are ready to revisit what we have learned about
The Magnetic field of the Electric current and the Magnetic induction
 The Magnetic field of the Electric current and the Magnetic induction This paper explains the magnetic effect of the electric current from the observed effects of the accelerating electrons, causing naturally
The Magnetic field of the Electric current and the Magnetic induction This paper explains the magnetic effect of the electric current from the observed effects of the accelerating electrons, causing naturally
Review of Lecture 15 3/17/10. Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath
 Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
Gravity as the cause for nuclear force and cosmological acceleration
 Gravity as the cause for nuclear force and cosmological acceleration Henok Tadesse, Electrical Engineer, BSc. Ethiopia, Debrezeit, P.O Box 12 Mobile: +251 910 751339; email entkidmt@yahoo.com or wchmar@gmail.com
Gravity as the cause for nuclear force and cosmological acceleration Henok Tadesse, Electrical Engineer, BSc. Ethiopia, Debrezeit, P.O Box 12 Mobile: +251 910 751339; email entkidmt@yahoo.com or wchmar@gmail.com
Basic Physical Chemistry Lecture 2. Keisuke Goda Summer Semester 2015
 Basic Physical Chemistry Lecture 2 Keisuke Goda Summer Semester 2015 Lecture schedule Since we only have three lectures, let s focus on a few important topics of quantum chemistry and structural chemistry
Basic Physical Chemistry Lecture 2 Keisuke Goda Summer Semester 2015 Lecture schedule Since we only have three lectures, let s focus on a few important topics of quantum chemistry and structural chemistry
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Chapter 18. Cosmology. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 18 Cosmology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole
Chapter 18 Cosmology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole
Bell s spaceship paradox
 Bell s spaceship paradox If the two ships start accelerating at the same time, I always see them travelling at the same velocity, and keeping a constant distance... But I said the objects get shorter when
Bell s spaceship paradox If the two ships start accelerating at the same time, I always see them travelling at the same velocity, and keeping a constant distance... But I said the objects get shorter when
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013
 Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
Please pick up your midterms from front of class
 Please pick up your midterms from front of class Average: 70 % Test % score distribution: Top grade: 92 % Make sure you go through your test and the solutions carefully to understand where you went wrong.
Please pick up your midterms from front of class Average: 70 % Test % score distribution: Top grade: 92 % Make sure you go through your test and the solutions carefully to understand where you went wrong.
4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy
 4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy Our goals for learning: Why do objects move at constant velocity if no force acts on them? What keeps a planet rotating and orbiting the Sun? Where do objects get their
4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy Our goals for learning: Why do objects move at constant velocity if no force acts on them? What keeps a planet rotating and orbiting the Sun? Where do objects get their
First some Introductory Stuff => On The Web.
 First some Introductory Stuff => On The Web http://hep.physics.utoronto.ca/~orr/wwwroot/phy357/phy357s.htm PHY357 = What is the Universe Made Of? Is the Universe Made of These? Proton = (u u d) held
First some Introductory Stuff => On The Web http://hep.physics.utoronto.ca/~orr/wwwroot/phy357/phy357s.htm PHY357 = What is the Universe Made Of? Is the Universe Made of These? Proton = (u u d) held
carroll/notes/ has a lot of good notes on GR and links to other pages. General Relativity Philosophy of general
 http://pancake.uchicago.edu/ carroll/notes/ has a lot of good notes on GR and links to other pages. General Relativity Philosophy of general relativity. As with any major theory in physics, GR has been
http://pancake.uchicago.edu/ carroll/notes/ has a lot of good notes on GR and links to other pages. General Relativity Philosophy of general relativity. As with any major theory in physics, GR has been
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
CHAPTER 9 THE ARROW OF TIME
 CHAPTER 9 THE ARROW OF TIME In previous chapters we have seen how our views of the nature of time have changed over the years. Up to the beginning of this century people believed in an absolute time. That
CHAPTER 9 THE ARROW OF TIME In previous chapters we have seen how our views of the nature of time have changed over the years. Up to the beginning of this century people believed in an absolute time. That
Chapter 3 - Gravity and Motion. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 3 - Gravity and Motion Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. In 1687 Isaac Newton published the Principia in which he set out his concept
Chapter 3 - Gravity and Motion Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. In 1687 Isaac Newton published the Principia in which he set out his concept
Lab 5: Rotational Motion II
 Lab 5: Rotational Motion II Written October-November 1986 by Nancy Bronder '86, Tom Budka '89, Bob Hamwey GS, D. Mook revised by Mook, K. Muenchinger '93 and E. Pleger '94 July-November 1991 and by Melissa
Lab 5: Rotational Motion II Written October-November 1986 by Nancy Bronder '86, Tom Budka '89, Bob Hamwey GS, D. Mook revised by Mook, K. Muenchinger '93 and E. Pleger '94 July-November 1991 and by Melissa
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 22. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Units of Chapter 22 22.1 Neutron Stars 22.2 Pulsars 22.3 Neutron-Star Binaries 22.4 Gamma-Ray
Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Units of Chapter 22 22.1 Neutron Stars 22.2 Pulsars 22.3 Neutron-Star Binaries 22.4 Gamma-Ray
4.1 Describing Motion. How do we describe motion? Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
Review Special Relativity. February 3, Absolutes of Relativity. Key Ideas of Special Relativity. Path of Ball in a Moving Train
 February 3, 2009 Review Special Relativity General Relativity Key Ideas of Special Relativity No material object can travel faster than light If you observe something moving near light speed: Its time
February 3, 2009 Review Special Relativity General Relativity Key Ideas of Special Relativity No material object can travel faster than light If you observe something moving near light speed: Its time
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Forces and Nuclear Processes
 Forces and Nuclear Processes To understand how stars generate the enormous amounts of light they produce will require us to delve into a wee bit of physics. First we will examine the forces that act at
Forces and Nuclear Processes To understand how stars generate the enormous amounts of light they produce will require us to delve into a wee bit of physics. First we will examine the forces that act at
FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E
 FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page 675-683 T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E COSMOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE Is the Universe isotropic or homogeneous? There is no place in the Universe that would be considered
FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page 675-683 T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E COSMOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE Is the Universe isotropic or homogeneous? There is no place in the Universe that would be considered
The interpretation is that gravity bends spacetime and that light follows the curvature of space.
 7/8 General Theory of Relativity GR Two Postulates of the General Theory of Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same in all frames of reference. 2. The principle of equivalence. Three statements
7/8 General Theory of Relativity GR Two Postulates of the General Theory of Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same in all frames of reference. 2. The principle of equivalence. Three statements
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley Lecture 37
 Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 37 The red shift The Hubble constant Critical density Weinberg, chapters I and II cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 37 The red shift The Hubble constant Critical density Weinberg, chapters I and II cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Mr Green sees the shorter, straight, green path and Mr. Red sees the longer, curved, red path.
 Mr Green sees the shorter, straight, green path and Mr. Red sees the longer, curved, red path. In an accelerated frame, time runs slow compared to a non-accelerated frame. The Equivalence Principle tells
Mr Green sees the shorter, straight, green path and Mr. Red sees the longer, curved, red path. In an accelerated frame, time runs slow compared to a non-accelerated frame. The Equivalence Principle tells
Announcement. Station #2 Stars. The Laws of Physics for Elementary Particles. Lecture 9 Basic Physics
 Announcement Pick up your quiz after this lecture as you leave the lecture hall. Homework#2 due on Thursday No hand-written homework! Please staple them! Put it in the box before the lecture begins! Station
Announcement Pick up your quiz after this lecture as you leave the lecture hall. Homework#2 due on Thursday No hand-written homework! Please staple them! Put it in the box before the lecture begins! Station
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
 AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy John Lacy RLM 16.332 471-1469 lacy@astro.as.utexas.edu Myoungwon Jeon RLM 16.216 471-0445 myjeon@astro.as.utexas.edu Bohua Li RLM 16.212 471-8443 bohuali@astro.as.utexas.edu
Chapter 33 The History of a Star. Introduction. Radio telescopes allow us to look into the center of the galaxy. The milky way
 Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Central Potential and Central Force Ready now to take up the idea
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Central Potential and Central Force Ready now to take up the idea
Higgs Field and Quantum Gravity
 Higgs Field and Quantum Gravity The magnetic induction creates a negative electric field, causing an electromagnetic inertia responsible for the relativistic mass change; it is the mysterious Higgs Field
Higgs Field and Quantum Gravity The magnetic induction creates a negative electric field, causing an electromagnetic inertia responsible for the relativistic mass change; it is the mysterious Higgs Field
Atom Model and Relativity
 Atom Model and Relativity Kimmo Rouvari March, 204 Abstract What is the theoretical explanation for fine structure? What is the mechanism behind relativity? These questions have bothered numerous physicists
Atom Model and Relativity Kimmo Rouvari March, 204 Abstract What is the theoretical explanation for fine structure? What is the mechanism behind relativity? These questions have bothered numerous physicists
How the Magnetic Field Works
 1 How the Magnetic Field Works Franklin T. Hu 19166 130 th Ct. NE, Bothell, WA 98011 Email: franklinhu@yahoo.com The existence of the magnetic field and the force it creates has been known for a long time,
1 How the Magnetic Field Works Franklin T. Hu 19166 130 th Ct. NE, Bothell, WA 98011 Email: franklinhu@yahoo.com The existence of the magnetic field and the force it creates has been known for a long time,
REALIZING EINSTEIN S DREAM. Exploring Our Mysterious Universe
 REALIZING EINSTEIN S DREAM Exploring Our Mysterious Universe Mysteries of the Universe Quarks Leptons Higgs Bosons Supersymmetric Particles SuperString Theory Dark Matter Dark Energy and the cosmological
REALIZING EINSTEIN S DREAM Exploring Our Mysterious Universe Mysteries of the Universe Quarks Leptons Higgs Bosons Supersymmetric Particles SuperString Theory Dark Matter Dark Energy and the cosmological
Rutherford s Gold Foil Experiment. Quantum Theory Max Planck (1910)
 Neils Bohr Niels Bohr (1913) developed the planetary model of the atom based upon the following: Rutherford s Gold Foil Experiment E = mc 2 Albert Einstein (1905) Quantum Theory Max Planck (1910) He postulated
Neils Bohr Niels Bohr (1913) developed the planetary model of the atom based upon the following: Rutherford s Gold Foil Experiment E = mc 2 Albert Einstein (1905) Quantum Theory Max Planck (1910) He postulated
Atomic Structure. Chapter 8
 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Overview To understand atomic structure requires understanding a special aspect of the electron - spin and its related magnetism - and properties of a collection of identical
Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Overview To understand atomic structure requires understanding a special aspect of the electron - spin and its related magnetism - and properties of a collection of identical
Chapter 9 Lecture. Pearson Physics. Gravity and Circular Motion. Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Lecture Pearson Physics Gravity and Circular Motion Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Newton's Law of Universal Gravity Applications of Gravity Circular Motion Planetary Motion and
Chapter 9 Lecture Pearson Physics Gravity and Circular Motion Prepared by Chris Chiaverina Chapter Contents Newton's Law of Universal Gravity Applications of Gravity Circular Motion Planetary Motion and
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
Outer space: A matter of gravity
 1997 2009, Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge. Permission is granted to print and copy this page on paper for non commercial use. For other uses, including electronic redistribution,
1997 2009, Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge. Permission is granted to print and copy this page on paper for non commercial use. For other uses, including electronic redistribution,
Cosmology. What is Cosmology?
 Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Cosmology Lecture 7 Mr. Kiledjian
 Cosmology Lecture 7 Mr. Kiledjian Lecture 7: The Age, Shape, Makeup, and Fate of our Brane Universe 1) In this final lecture, we will trace the history and development of our understanding of the Universe
Cosmology Lecture 7 Mr. Kiledjian Lecture 7: The Age, Shape, Makeup, and Fate of our Brane Universe 1) In this final lecture, we will trace the history and development of our understanding of the Universe
PHY326/426:Lecture 19
 PHY326/426:Lecture 19 Dark Energy Finish WIMP signals Evidence for Dark Energy Type Ia Supernovae What is Dark Energy The fate of the Universe The Distance-Redshift relation Recall from lecture 2: The
PHY326/426:Lecture 19 Dark Energy Finish WIMP signals Evidence for Dark Energy Type Ia Supernovae What is Dark Energy The fate of the Universe The Distance-Redshift relation Recall from lecture 2: The
Questioning the Foundations of Physics to Achieve Interstellar Travel. By Benjamin T Solomon
 Questioning the Foundations of Physics to Achieve Interstellar Travel By Benjamin T Solomon iseti LLC PO Box 8532 Denver, CO 80201 Tel: 303-618-2800 Email: benjamin.t.solomon@iseti.us Abstract: This essay
Questioning the Foundations of Physics to Achieve Interstellar Travel By Benjamin T Solomon iseti LLC PO Box 8532 Denver, CO 80201 Tel: 303-618-2800 Email: benjamin.t.solomon@iseti.us Abstract: This essay
Name Final Exam December 14, 2016
 Name Final Exam December 14, 016 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
Name Final Exam December 14, 016 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Part I: Multiple Choice (mixed new and review questions)
7/5. Consequences of the principle of equivalence (#3) 1. Gravity is a manifestation of the curvature of space.
 7/5 Consequences of the principle of equivalence (#3) 1. Gravity is a manifestation of the curvature of space. Follow the path of a light pulse in an elevator accelerating in gravityfree space. The dashed
7/5 Consequences of the principle of equivalence (#3) 1. Gravity is a manifestation of the curvature of space. Follow the path of a light pulse in an elevator accelerating in gravityfree space. The dashed
Type Ia Supernova Observations. Supernova Results:The Context. Supernova Results. Physics 121 December 4, fainter. brighter
 Physics 11 December 4, 009 Today Supernovae revisited Galaxy Rotation Curves Dark Matter & Dark Energy Scaling Factor a(t) Course Evaluations Type Ia Supernova Observations Distant supernovae are than
Physics 11 December 4, 009 Today Supernovae revisited Galaxy Rotation Curves Dark Matter & Dark Energy Scaling Factor a(t) Course Evaluations Type Ia Supernova Observations Distant supernovae are than
Chapter 18 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to
Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to
SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION.
 MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Lecture Outline Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 14.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf?
Lecture Outline Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 14.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf?
