M155 Exam 2 Concept Review
|
|
|
- Ashlee Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M155 Exam 2 Concept Review Mark Blumstein DERIVATIVES Product Rule Used to take the derivative of a product of two functions u and v. u v + uv Quotient Rule Used to take a derivative of the quotient of two functions u/v u v uv Chain Rule Used to take a derivative of the composition of two functions f (g(x)). v 2 g (x) f (g(x)) i.e. derivative of the inside function times derivative of the outside Since you have these derivative rules, you can take the derivative of any combination of the sum, difference, product, quotient, or composition of two functions. Example..1. Compute the derivatives of the functions f(x) = sin(x) (x 2 + 4x) g(x) = sin(x 2 + 4x). Both functions are a combination of the sine function and the function x 2 + 4x, but f(x) is a product of the two functions, and g(x) is a composition of the two functions (the function x 2 + 4x is inside of the sine function.) Therefore use the product rule on f(x) and the chain rule on g(x). You should get that f (x) = cos(x)(x 2 + 4x) + sin(x)(2x + 4) g (x) = (2x + 4) cos(x 2 + 4x) Example..2. Compute the derivative of f(x) = sin(3x + 4) (2x + 5) 6. The first thing you see is the product of two functions: sin(3x + 4) is multiplied by (2x + 5) 6, so use the product rule! u = sin(3x + 4) Composition use Chain Rule u = 3 cos(3x + 4) v = (2x + 5) 6 Composition use Chain Rule v = 2 6(2x + 5) 5 Therefore, f (x) = 3 cos(3x + 4) (2x + 5) 6 + sin(3x + 4) 12(2x + 5) 5. 1
2 Don t forget, the whole point of computing a derivative is to determine the rate of change (velocity) of some function! I like to draw the picture f(x) position deriv f (x) velocity deriv f (x) acceleration The following very simple observation allows us to solve optimization problems, and use the first and second derivative tests (covered below): Remark. As a function increases, its derivative is positive. As a function decreases, its derivative is negative. Example..3. I like the simple example of throwing a ball in the air. On its way up, as its position f(x) is increasing, its velocity f (x) is positive. Meanwhile, gravity is causing it to slow (the velocities are still positive, since the ball is moving up, but they are getting closer and closer to zero) eventually it reaches its maximum height, at which point the ball stops moving just for an instant so f (x) =. Then it begins to fall, so its position f(x) is decreasing, and its velocity f (x) is negative. Definition..4. A critical point of a function f(x) is where f (x) =, or f (x) is undefined. Intuitively, when f (x) =, the system has stopped moving. Think about the ball example above, when the ball reached its maximum height it stopped moving, in other words, it reached a critical point. For this reason, we will often be able to find maximums (or minimums) at critical points. Definition..5. An inflection point of a function f(x) is where f (x) =, and the concavity of the function changes. OPTIMIZATION For most of the examples, finding a max or a min is as easy as graphing the function and just looking where it is biggest and where it is smallest. In any question that asks you to find a max or a min, you will generally need to do the following three things: 1. Find the critical points. 2. Test each critical point to see if it is a local max, local min, or neither. This requires using either the first or second derivative test. 3. Check to see if there is a max or min at the endpoints. If a problem asks for the absolute maximum or absolute minimum, just check the values of the critical points and endpoints. For example, suppose there are critical points at (2, 49) and (5, 2), and the endpoints are ( 2, 5) and (1, 1). Clearly the biggest number on the board is ( 2, 5) so that is the absolute max, and the smallest number is (5, 2) so that is the absolute min. As always, graphing f(x) and just seeing what is biggest and smallest is an easy way to check your answer. Suppose I hand you a critical point at x = c where f (c) =. You want to know, is that critical point a maximum (like the ball example), a minimum, or neither a max nor a min. Use one of the following two tests. To get the ideas behind the tests, just draw the little pictures of what a max and min look like, and use the idea that as a function increases (resp. decreases) its derivative is positive (resp. negative). 2
3 The First Derivative Test: Start by computing the first derivative! 1. If f (x) goes from positive to negative, then f(x) goes from increasing to decreasing, so there is a local max at the critical point. 2. If f (x) goes from negative to positive, then f(x) goes from decreasing to increasing, so there is a local min at the critical point. 3. If f (x) goes from positive to positive, or negative to negative, then there is neither a max nor a min at the critical point. The Second Derivative Test: Start by computing the second derivative! The idea here is that a positive second derivative corresponds to a concave up (like a cup) graph, and there is a min. Why? As velocity increases, acceleration is positive. Similarly, a negative second derivative corresponds to concave down (like a frown), so there is a max. 1. If f (x) >, then concave up, then there is a local min at the critical point. 2. If f (x) <, then concave down, and there is a local max at the critical point. 3. If f (x) =, the test fails. In this case, try the first derivative test. This also might be an inflection point. Applied optimization problems: A couple problems from section 3.3 in the textbook. The fish harvest problem from Homework 8. In the same section, there is a problem about bee pollination. At the end of the day, both of these problems might seem very involved, but all you are required to do is write down a function and maximize it. Find critical points, test using first or second deriv test, and check the endpoints. That s it! STABILITY TEST Switch gears to discrete time dynamical systems. Suppose x t+1 = f(x t ) is an updating function modeling how some quantity x changes from one time to the next (let s say day to day). An equilibrium point x occurs when the amount stops changing from day to day, so in symbols x = f(x ). Question: When is an equilibrium point stable? Answer: If the updating function changes quickly at the equilibrium point, the system is not stable - there s too much day to day change for it to be stable. On the other hand, if the updating function is hardly changing at all, then the system is settling down towards stability. Now we just put this intuition into math symbols, and we get the stability test. 1. Slow case: If 1 < f (x ) < 1, then x is a stable equilibrium point. Why? f (x ) is the rate of change, and it s between 1 and 1, these are small velocities. 2. Fast case: If f (x ) > 1 or f (x ) < 1, then x is unstable. Why? Here the rate of change is large, lots of change, not stable. 3
4 3. Inconclusive case: If f (x ) = 1 or f (x ) = 1, then we don t know if the equilibrium is stable or unstable. If this happens, you could try cobwebbing to see the long term behavior. There are usually two types of questions you see for the stability test: one with parameters and one without. For example, if you get that f (x ) = 2, you know right away that x is unstable because the velocity is too fast. It s that easy, no inequalities or anything! On the other hand, for a problem with parameters, you might get that f (x ) = 1 1 r. Now say the question asks when x is stable. Now you set up the inequality 1 < 1 1 r < 1 and solve for r. Remember, that when you take a reciprocal everything flips (including the inequality signs). In this case 1 < 1 1 r < 1 1 > 1 r > > r > > r > 2 < r < Leading Behavior/L Hospital s Rule For leading behavior, the key is to identify which term has the fastest rate of change (incidentally, that s why this topic is in a section about derivatives). In order from slowest to fastest: ln(x), x ±n, e ±x, e ±x2. Observe that a negative in the exponent does not affect the rate of change of the function. For example, just as x 3 is faster than x 2, it s also true that x 3 is faster than x 2. There are two types of problems you are usually asked: (1) Identify the dominant term. (2) Compute a limit. The first step to either of those problems is to put arrows over every term so it s easier to pick out what is dominant. For example, a term approaching will always dominate a term approaching. Tip: When x, start by seeing if you can just plug in. One common mistake is to say that e x approaches or, but just plug in! You get that e = 1. When comparing the limiting behavior of a fraction of two functions you may end up with one of the following four cases: If the top is faster, the answer is since divided by whatever is. If the bottom is faster, then since dividing by small gives big, the answer is infinity. If the top is faster, the answer is. If the bottom is faster then the answer is, since dividing whatever by a large number is small. In this case you don t really need to compare the top to the bottom, the answer is. Why? The top says, since over anything is, but the bottom agrees with the top, since dividing by a large number is small. 4
5 4. 5. Again, you don t really need to compare the top to the bottom, the answer is. Why? The top says, and the bottom says dividing by a small number is big, so the bottom also says. Again, you don t really need to compare the top to the bottom, the answer is. Why? The top says, and the bottom says divide by a small number which is big, so the bottom also says. e x Example..6. lim x x 2 = The top and bottom both approach, like case 1 above. Now ask the golden question, which one is faster? The exponential function is faster than a power function, so the top wins, and the answer is. x 3 Example..7. lim x x 7 = The top and bottom approach like case 2 above. Now ask the golden question, which is faster? Since x 7 is faster than x 3, the bottom wins and the answer is. You could also rewrite x 3 x = x 4, which 7 goes to. Example..8. Compute x 3 + 4e x + x 2 lim x x 2 + e x. The terms on top approach, 4, and. So clearly x 3 is dominant. On bottom the terms approach and 1. So the bottom approaches + 1 = 1! Then, x 3 + 4e x + x 2 x 3 lim x x 2 + e x = lim x e x = 1 = L Hospitals Rule: This only applies to functions of the form ±. This rule says that all you need to do is compute the derivative of the top and bottom of a fraction, and then compute the limit. This should make sense, because the whole idea of this section is to compare which function is faster, and the derivative is exactly the rate of change of any function. Example..9. or ± lim x x 2 + x 5 sin(x) 2x + 1 = lim x 5 cos(x) = 2() cos() (has form /, so ok to use LH) (First rule of limits, just plug in!) = 1 5 OTHER d dx (2x ) = ln(2)2 x You can memorize that as a fact, or understand that to compute it, all I did was rewrite 2 x = e ln(2)x, and since I know the derivative of the exponential function is itself, I can apply the chain rule. 5
6 To compute the derivative of 5 (x+3) 2, you could use the quotient rule, but it might be easier to rewrite it as 5 (x + 3) 2. Since 5 is a constant multiplier it just sits out front and the answer is 5 ( 2(x + 3) 3 ) = 1(x + 3) 3. Derivatives of trig functions. You might be asked to compute the derivative of say csc(x). To do so, start with the definition, csc(x) = 1 sin(x). Now you can use the quotient rule (or alternatively 1 rewrite sin(x) = (sin(x)) 1 and use the chain rule). Doesn t matter which way. Here is a little table of the trig functions and their derivatives. You can compute them all just like I explained or you can just memorize. It s not too hard to memorize since there is a lot of parity: look at the derivatives of sin(x) and cos(x), see how it s very much like the derivative of sec(x) and csc(x), or tan(x) and cot(x). f(x) sin(x) cos(x) tan(x) cot(x) sec(x) csc(x) f (x) cos(x) sin(x) sec 2 (x) csc 2 (x) sec(x) tan(x) csc(x) cot(x) Sometimes a question will ask you to find the regions where f(x) increases and decreases. Remember f (x) is positive when f(x) increases and f (x) is negative when f(x) decreases. So to find the x-values for which f is increasing/decreasing, you need to find where f is positive and negative. So start by finding where f (x) =, as this will split up the positive and negative regions. For example, if f (x) = x + 2, then f (x) = when x = 2. Now check to the left of 2, plug in say x = 3. f ( 3) = 1 which is negative, so for values to the left of x = 2, f(x) is decreasing. Now check to the right: f ( 1) = 1 which is positive, so f(x) increases to the right. Therefore, if x < 2 we have that f(x) decreases, and when x > 2, f(x) increases. Just like the last problem, you may be asked to find intervals of concavity. Just start by finding where f (x) =, and test to the left and right. Remember that f (x) > means concave up, and f (x) < means concave down. 6
Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution
 Name: Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and that it
Name: Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and that it
Review Problems for Test 1
 Review Problems for Test Math 6-03/06 9 9/0 007 These problems are provided to help you study The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test And
Review Problems for Test Math 6-03/06 9 9/0 007 These problems are provided to help you study The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test And
14 Increasing and decreasing functions
 14 Increasing and decreasing functions 14.1 Sketching derivatives READING Read Section 3.2 of Rogawski Reading Recall, f (a) is the gradient of the tangent line of f(x) at x = a. We can use this fact to
14 Increasing and decreasing functions 14.1 Sketching derivatives READING Read Section 3.2 of Rogawski Reading Recall, f (a) is the gradient of the tangent line of f(x) at x = a. We can use this fact to
a x a y = a x+y a x a = y ax y (a x ) r = a rx and log a (xy) = log a (x) + log a (y) log a ( x y ) = log a(x) log a (y) log a (x r ) = r log a (x).
 You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
Exam 3 Review. Lesson 19: Concavity, Inflection Points, and the Second Derivative Test. Lesson 20: Absolute Extrema on an Interval
 Exam 3 Review Lessons 17-18: Relative Extrema, Critical Numbers, an First Derivative Test (from exam 2 review neee for curve sketching) Critical Numbers: where the erivative of a function is zero or unefine.
Exam 3 Review Lessons 17-18: Relative Extrema, Critical Numbers, an First Derivative Test (from exam 2 review neee for curve sketching) Critical Numbers: where the erivative of a function is zero or unefine.
MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL
 05/05/2012 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Name: TA session: Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! (1) Calculate the following limits, using whatever tools are appropriate. State which results
05/05/2012 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Name: TA session: Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! (1) Calculate the following limits, using whatever tools are appropriate. State which results
Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017
 Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017 This review set gives a list of topics that we explored throughout this course, as well as a few practice problems at the end of the document. A complete
Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017 This review set gives a list of topics that we explored throughout this course, as well as a few practice problems at the end of the document. A complete
Finding local extrema and intervals of increase/decrease
 Finding local extrema and intervals of increase/decrease Example 1 Find the relative extrema of f(x) = increasing and decreasing. ln x x. Also, find where f(x) is STEP 1: Find the domain of the function
Finding local extrema and intervals of increase/decrease Example 1 Find the relative extrema of f(x) = increasing and decreasing. ln x x. Also, find where f(x) is STEP 1: Find the domain of the function
Math 230 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution
 Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
2.5 The Chain Rule Brian E. Veitch
 2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
Using this definition, it is possible to define an angle of any (positive or negative) measurement by recognizing how its terminal side is obtained.
 Angle in Standard Position With the Cartesian plane, we define an angle in Standard Position if it has its vertex on the origin and one of its sides ( called the initial side ) is always on the positive
Angle in Standard Position With the Cartesian plane, we define an angle in Standard Position if it has its vertex on the origin and one of its sides ( called the initial side ) is always on the positive
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued)
 Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
Calculus AB Topics Limits Continuity, Asymptotes
 Calculus AB Topics Limits Continuity, Asymptotes Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3 x 3 Is there a vertical asymptote at x = 3? Do not give a Precalculus answer on a Calculus exam. Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3
Calculus AB Topics Limits Continuity, Asymptotes Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3 x 3 Is there a vertical asymptote at x = 3? Do not give a Precalculus answer on a Calculus exam. Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3
One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the unit circle.
 2.24 Tanz and the Reciprocals Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the
2.24 Tanz and the Reciprocals Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the
Calculating the Derivative Using Derivative Rules Implicit Functions Higher-Order Derivatives
 Topic 4 Outline 1 Derivative Rules Calculating the Derivative Using Derivative Rules Implicit Functions Higher-Order Derivatives D. Kalajdzievska (University of Manitoba) Math 1500 Fall 2015 1 / 32 Topic
Topic 4 Outline 1 Derivative Rules Calculating the Derivative Using Derivative Rules Implicit Functions Higher-Order Derivatives D. Kalajdzievska (University of Manitoba) Math 1500 Fall 2015 1 / 32 Topic
Math 251, Spring 2005: Exam #2 Preview Problems
 Math 5, Spring 005: Exam # Preview Problems. Using the definition of derivative find the derivative of the following functions: a) fx) = e x e h. Use the following lim =, e x+h = e x e h.) h b) fx) = x
Math 5, Spring 005: Exam # Preview Problems. Using the definition of derivative find the derivative of the following functions: a) fx) = e x e h. Use the following lim =, e x+h = e x e h.) h b) fx) = x
8.7 Taylor s Inequality Math 2300 Section 005 Calculus II. f(x) = ln(1 + x) f(0) = 0
 8.7 Taylor s Inequality Math 00 Section 005 Calculus II Name: ANSWER KEY Taylor s Inequality: If f (n+) is continuous and f (n+) < M between the center a and some point x, then f(x) T n (x) M x a n+ (n
8.7 Taylor s Inequality Math 00 Section 005 Calculus II Name: ANSWER KEY Taylor s Inequality: If f (n+) is continuous and f (n+) < M between the center a and some point x, then f(x) T n (x) M x a n+ (n
Summary of Derivative Tests
 Summary of Derivative Tests Note that for all the tests given below it is assumed that the function f is continuous. Critical Numbers Definition. A critical number of a function f is a number c in the
Summary of Derivative Tests Note that for all the tests given below it is assumed that the function f is continuous. Critical Numbers Definition. A critical number of a function f is a number c in the
Investigation 2 (Calculator): f(x) = 2sin(0.5x)
 Section 3.3 Increasing/Decreasing & The 1 st Derivative Test Day 1 Investigation 1 (Calculator): f(x) = x 2 3x + 4 State all extremes on [0, 5]: Original graph: Global min(s): Global max(s): Local min(s):
Section 3.3 Increasing/Decreasing & The 1 st Derivative Test Day 1 Investigation 1 (Calculator): f(x) = x 2 3x + 4 State all extremes on [0, 5]: Original graph: Global min(s): Global max(s): Local min(s):
Calculus I Announcements
 Slie 1 Calculus I Announcements Office Hours: Amos Eaton 309, Monays 12:50-2:50 Exam 2 is Thursay, October 22n. The stuy guie is now on the course web page. Start stuying now, an make a plan to succee.
Slie 1 Calculus I Announcements Office Hours: Amos Eaton 309, Monays 12:50-2:50 Exam 2 is Thursay, October 22n. The stuy guie is now on the course web page. Start stuying now, an make a plan to succee.
MA1021 Calculus I B Term, Sign:
 MA1021 Calculus I B Term, 2014 Final Exam Print Name: Sign: Write up your solutions neatly and show all your work. 1. (28 pts) Compute each of the following derivatives: You do not have to simplify your
MA1021 Calculus I B Term, 2014 Final Exam Print Name: Sign: Write up your solutions neatly and show all your work. 1. (28 pts) Compute each of the following derivatives: You do not have to simplify your
(e) 2 (f) 2. (c) + (d). Limits at Infinity. 2.5) 9-14,25-34,41-43,46-47,56-57, (c) (d) 2
 Math 150A. Final Review Answers, Spring 2018. Limits. 2.2) 7-10, 21-24, 28-1, 6-8, 4-44. 1. Find the values, or state they do not exist. (a) (b) 1 (c) DNE (d) 1 (e) 2 (f) 2 (g) 2 (h) 4 2. lim f(x) = 2,
Math 150A. Final Review Answers, Spring 2018. Limits. 2.2) 7-10, 21-24, 28-1, 6-8, 4-44. 1. Find the values, or state they do not exist. (a) (b) 1 (c) DNE (d) 1 (e) 2 (f) 2 (g) 2 (h) 4 2. lim f(x) = 2,
You are being asked to create your own AP CALCULUS Survival kit. For the survival kit you will need:
 You are being asked to create your own AP CALCULUS Survival kit. For the survival kit you will need: Index cards Ring (so that you can put all of your flash cards together) Hole punch (to punch holes in
You are being asked to create your own AP CALCULUS Survival kit. For the survival kit you will need: Index cards Ring (so that you can put all of your flash cards together) Hole punch (to punch holes in
Blue Pelican Calculus First Semester
 Blue Pelican Calculus First Semester Student Version 1.01 Copyright 2011-2013 by Charles E. Cook; Refugio, Tx Edited by Jacob Cobb (All rights reserved) Calculus AP Syllabus (First Semester) Unit 1: Function
Blue Pelican Calculus First Semester Student Version 1.01 Copyright 2011-2013 by Charles E. Cook; Refugio, Tx Edited by Jacob Cobb (All rights reserved) Calculus AP Syllabus (First Semester) Unit 1: Function
Math 180, Final Exam, Fall 2012 Problem 1 Solution
 Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
Mathematic 108, Fall 2015: Solutions to assignment #7
 Mathematic 08, Fall 05: Solutions to assignment #7 Problem # Suppose f is a function with f continuous on the open interval I and so that f has a local maximum at both x = a and x = b for a, b I with a
Mathematic 08, Fall 05: Solutions to assignment #7 Problem # Suppose f is a function with f continuous on the open interval I and so that f has a local maximum at both x = a and x = b for a, b I with a
In general, if we start with a function f and want to reverse the differentiation process, then we are finding an antiderivative of f.
 Math 1410 Worksheet #27: Section 4.9 Name: Our final application of derivatives is a prelude to what will come in later chapters. In many situations, it will be necessary to find a way to reverse the differentiation
Math 1410 Worksheet #27: Section 4.9 Name: Our final application of derivatives is a prelude to what will come in later chapters. In many situations, it will be necessary to find a way to reverse the differentiation
Chapter 2 Derivatives
 Contents Chapter 2 Derivatives Motivation to Chapter 2 2 1 Derivatives and Rates of Change 3 1.1 VIDEO - Definitions................................................... 3 1.2 VIDEO - Examples and Applications
Contents Chapter 2 Derivatives Motivation to Chapter 2 2 1 Derivatives and Rates of Change 3 1.1 VIDEO - Definitions................................................... 3 1.2 VIDEO - Examples and Applications
M152: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review
 M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
Rolle s Theorem. The theorem states that if f (a) = f (b), then there is at least one number c between a and b at which f ' (c) = 0.
 Rolle s Theorem Rolle's Theorem guarantees that there will be at least one extreme value in the interior of a closed interval, given that certain conditions are satisfied. As with most of the theorems
Rolle s Theorem Rolle's Theorem guarantees that there will be at least one extreme value in the interior of a closed interval, given that certain conditions are satisfied. As with most of the theorems
Solutions to Math 41 First Exam October 18, 2012
 Solutions to Math 4 First Exam October 8, 202. (2 points) Find each of the following its, with justification. If the it does not exist, explain why. If there is an infinite it, then explain whether it
Solutions to Math 4 First Exam October 8, 202. (2 points) Find each of the following its, with justification. If the it does not exist, explain why. If there is an infinite it, then explain whether it
MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives
 MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives 1 Formal Definition of the Derivative We have seen plenty of limits so far, but very few applications. In particular, we have seen very few functions for which
MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives 1 Formal Definition of the Derivative We have seen plenty of limits so far, but very few applications. In particular, we have seen very few functions for which
Learning Objectives for Math 165
 Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
Algebra Exam. Solutions and Grading Guide
 Algebra Exam Solutions and Grading Guide You should use this grading guide to carefully grade your own exam, trying to be as objective as possible about what score the TAs would give your responses. Full
Algebra Exam Solutions and Grading Guide You should use this grading guide to carefully grade your own exam, trying to be as objective as possible about what score the TAs would give your responses. Full
Main topics for the First Midterm
 Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.2. This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I
Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.2. This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I
L Hopital s Rule. We will use our knowledge of derivatives in order to evaluate limits that produce indeterminate forms.
 L Hopital s Rule We will use our knowledge of derivatives in order to evaluate its that produce indeterminate forms. Main Idea x c f x g x If, when taking the it as x c, you get an INDETERMINATE FORM..
L Hopital s Rule We will use our knowledge of derivatives in order to evaluate its that produce indeterminate forms. Main Idea x c f x g x If, when taking the it as x c, you get an INDETERMINATE FORM..
Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications
 Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications Summary: The main purpose of this chapter is to use the derivative as a tool to assist in the graphing of functions and for solving optimization problems.
Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications Summary: The main purpose of this chapter is to use the derivative as a tool to assist in the graphing of functions and for solving optimization problems.
MAT 1320 Study Sheet for the final exam. Format. Topics
 MAT 1320 Study Sheet for the final exam August 2015 Format The exam consists of 10 Multiple Choice questions worth 1 point each, and 5 Long Answer questions worth 30 points in total. Please make sure that
MAT 1320 Study Sheet for the final exam August 2015 Format The exam consists of 10 Multiple Choice questions worth 1 point each, and 5 Long Answer questions worth 30 points in total. Please make sure that
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
Calculus I Review Solutions
 Calculus I Review Solutions. Compare and contrast the three Value Theorems of the course. When you would typically use each. The three value theorems are the Intermediate, Mean and Extreme value theorems.
Calculus I Review Solutions. Compare and contrast the three Value Theorems of the course. When you would typically use each. The three value theorems are the Intermediate, Mean and Extreme value theorems.
3. Go over old quizzes (there are blank copies on my website try timing yourself!)
 final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
Welcome to AP Calculus!!!
 Welcome to AP Calculus!!! In preparation for next year, you need to complete this summer packet. This packet reviews & expands upon the concepts you studied in Algebra II and Pre-calculus. Make sure you
Welcome to AP Calculus!!! In preparation for next year, you need to complete this summer packet. This packet reviews & expands upon the concepts you studied in Algebra II and Pre-calculus. Make sure you
Aim: How do we prepare for AP Problems on limits, continuity and differentiability? f (x)
 Name AP Calculus Date Supplemental Review 1 Aim: How do we prepare for AP Problems on limits, continuity and differentiability? Do Now: Use the graph of f(x) to evaluate each of the following: 1. lim x
Name AP Calculus Date Supplemental Review 1 Aim: How do we prepare for AP Problems on limits, continuity and differentiability? Do Now: Use the graph of f(x) to evaluate each of the following: 1. lim x
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections
 Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet
 Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
MATH 124. Midterm 2 Topics
 MATH 124 Midterm 2 Topics Anything you ve learned in class (from lecture and homework) so far is fair game, but here s a list of some main topics since the first midterm that you should be familiar with:
MATH 124 Midterm 2 Topics Anything you ve learned in class (from lecture and homework) so far is fair game, but here s a list of some main topics since the first midterm that you should be familiar with:
Review for Final Exam, MATH , Fall 2010
 Review for Final Exam, MATH 170-002, Fall 2010 The test will be on Wednesday December 15 in ILC 404 (usual class room), 8:00 a.m - 10:00 a.m. Please bring a non-graphing calculator for the test. No other
Review for Final Exam, MATH 170-002, Fall 2010 The test will be on Wednesday December 15 in ILC 404 (usual class room), 8:00 a.m - 10:00 a.m. Please bring a non-graphing calculator for the test. No other
Math 210 Midterm #1 Review
 Math 20 Miterm # Review This ocument is intene to be a rough outline of what you are expecte to have learne an retaine from this course to be prepare for the first miterm. : Functions Definition: A function
Math 20 Miterm # Review This ocument is intene to be a rough outline of what you are expecte to have learne an retaine from this course to be prepare for the first miterm. : Functions Definition: A function
Core Mathematics 3 Differentiation
 http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
Math 180, Exam 2, Practice Fall 2009 Problem 1 Solution. f(x) = arcsin(2x + 1) = sin 1 (3x + 1), lnx
 Math 80, Exam, Practice Fall 009 Problem Solution. Differentiate the functions: (do not simplify) f(x) = x ln(x + ), f(x) = xe x f(x) = arcsin(x + ) = sin (3x + ), f(x) = e3x lnx Solution: For the first
Math 80, Exam, Practice Fall 009 Problem Solution. Differentiate the functions: (do not simplify) f(x) = x ln(x + ), f(x) = xe x f(x) = arcsin(x + ) = sin (3x + ), f(x) = e3x lnx Solution: For the first
GENERAL TIPS WHEN TAKING THE AP CALC EXAM. Multiple Choice Portion
 GENERAL TIPS WHEN TAKING THE AP CALC EXAM. Multiple Choice Portion 1. You are hunting for apples, aka easy questions. Do not go in numerical order; that is a trap! 2. Do all Level 1s first. Then 2. Then
GENERAL TIPS WHEN TAKING THE AP CALC EXAM. Multiple Choice Portion 1. You are hunting for apples, aka easy questions. Do not go in numerical order; that is a trap! 2. Do all Level 1s first. Then 2. Then
MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL
 2/03/20 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! () Let f(x) = ex e x. (a) [5 pts] State the domain and range of f(x). Name: TA session: Since e x is defined
2/03/20 Bormashenko MATH 408N PRACTICE FINAL Show your work for all the problems. Good luck! () Let f(x) = ex e x. (a) [5 pts] State the domain and range of f(x). Name: TA session: Since e x is defined
f(x 0 + h) f(x 0 ) h slope of secant line = m sec
 Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
Review for the First Midterm Exam
 Review for the First Midterm Exam Thomas Morrell 5 pm, Sunday, 4 April 9 B9 Van Vleck Hall For the purpose of creating questions for this review session, I did not make an effort to make any of the numbers
Review for the First Midterm Exam Thomas Morrell 5 pm, Sunday, 4 April 9 B9 Van Vleck Hall For the purpose of creating questions for this review session, I did not make an effort to make any of the numbers
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
MATH 1241 FINAL EXAM FALL 2012 Part I, No Calculators Allowed
 MATH 11 FINAL EXAM FALL 01 Part I, No Calculators Allowed 1. Evaluate the limit: lim x x x + x 1. (a) 0 (b) 0.5 0.5 1 Does not exist. Which of the following is the derivative of g(x) = x cos(3x + 1)? (a)
MATH 11 FINAL EXAM FALL 01 Part I, No Calculators Allowed 1. Evaluate the limit: lim x x x + x 1. (a) 0 (b) 0.5 0.5 1 Does not exist. Which of the following is the derivative of g(x) = x cos(3x + 1)? (a)
What makes f '(x) undefined? (set the denominator = 0)
 Chapter 3A Review 1. Find all critical numbers for the function ** Critical numbers find the first derivative and then find what makes f '(x) = 0 or undefined Q: What is the domain of this function (especially
Chapter 3A Review 1. Find all critical numbers for the function ** Critical numbers find the first derivative and then find what makes f '(x) = 0 or undefined Q: What is the domain of this function (especially
Answers for Calculus Review (Extrema and Concavity)
 Answers for Calculus Review 4.1-4.4 (Extrema and Concavity) 1. A critical number is a value of the independent variable (a/k/a x) in the domain of the function at which the derivative is zero or undefined.
Answers for Calculus Review 4.1-4.4 (Extrema and Concavity) 1. A critical number is a value of the independent variable (a/k/a x) in the domain of the function at which the derivative is zero or undefined.
Math 111, Introduction to the Calculus, Fall 2011 Midterm I Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Math 111, Introduction to the Calculus, Fall 2011 Midterm I Practice Exam 1 Solutions For each question, there is a model solution (showing you the level of detail I expect on the exam) and then below
Math 111, Introduction to the Calculus, Fall 2011 Midterm I Practice Exam 1 Solutions For each question, there is a model solution (showing you the level of detail I expect on the exam) and then below
Supplementary Trig Material
 Supplementary Trig Material Math U See Table of Contents Lesson A: Solving Equations with Radicals and Absolute Value Lesson Practice Worksheet A - 1 Lesson Practice Worksheet A - 2 Lesson B: Solving Inequalities
Supplementary Trig Material Math U See Table of Contents Lesson A: Solving Equations with Radicals and Absolute Value Lesson Practice Worksheet A - 1 Lesson Practice Worksheet A - 2 Lesson B: Solving Inequalities
Math 250 Skills Assessment Test
 Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Spring 2015, MA 252, Calculus II, Final Exam Preview Solutions
 Spring 5, MA 5, Calculus II, Final Exam Preview Solutions I will put the following formulas on the front of the final exam, to speed up certain problems. You do not need to put them on your index card,
Spring 5, MA 5, Calculus II, Final Exam Preview Solutions I will put the following formulas on the front of the final exam, to speed up certain problems. You do not need to put them on your index card,
10.7 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities
 0.7 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities 857 0.7 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities In Sections 0. 0. and most recently 0. we solved some basic equations involving the trigonometric functions.
0.7 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities 857 0.7 Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities In Sections 0. 0. and most recently 0. we solved some basic equations involving the trigonometric functions.
L Hopital s Rule. We will use our knowledge of derivatives in order to evaluate limits that produce indeterminate forms.
 L Hopital s Rule We will use our knowledge of derivatives in order to evaluate its that produce indeterminate forms. Indeterminate Limits Main Idea x c f x g x If, when taking the it as x c, you get an
L Hopital s Rule We will use our knowledge of derivatives in order to evaluate its that produce indeterminate forms. Indeterminate Limits Main Idea x c f x g x If, when taking the it as x c, you get an
2t t dt.. So the distance is (t2 +6) 3/2
 Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Final Exam. Math 3 Daugherty March 13, 2012
 Final Exam Math 3 Daugherty March 3, 22 Name (Print): Last First On this, the Final Math 3 exams in Winter 22, I will work individually, neither giving nor receiving help, guided by the Dartmouth Academic
Final Exam Math 3 Daugherty March 3, 22 Name (Print): Last First On this, the Final Math 3 exams in Winter 22, I will work individually, neither giving nor receiving help, guided by the Dartmouth Academic
Sin, Cos and All That
 Sin, Cos and All That James K Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 9, 2014 Outline Sin, Cos and all that! A New Power Rule Derivatives
Sin, Cos and All That James K Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 9, 2014 Outline Sin, Cos and all that! A New Power Rule Derivatives
DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION PART 1. Mr C s IB Standard Notes
 DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION PART 1 Mr C s IB Standard Notes In this PDF you can find the following: 1. Notation 2. Keywords Make sure you read through everything and the try examples for yourself before
DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION PART 1 Mr C s IB Standard Notes In this PDF you can find the following: 1. Notation 2. Keywords Make sure you read through everything and the try examples for yourself before
+ i sin. + i sin. = 2 cos
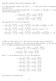 Math 11 Lesieutre); Exam review I; December 4, 017 1. a) Find all complex numbers z for which z = 8. Write your answers in rectangular non-polar) form. We are going to use de Moivre s theorem. For 1, r
Math 11 Lesieutre); Exam review I; December 4, 017 1. a) Find all complex numbers z for which z = 8. Write your answers in rectangular non-polar) form. We are going to use de Moivre s theorem. For 1, r
The Relation between the Integral and the Derivative Graphs. Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Suppose that f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then
![Suppose that f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then Suppose that f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then](/thumbs/74/71325034.jpg) Lectures 1/18 Derivatives and Graphs When we have a picture of the graph of a function f(x), we can make a picture of the derivative f (x) using the slopes of the tangents to the graph of f. In this section
Lectures 1/18 Derivatives and Graphs When we have a picture of the graph of a function f(x), we can make a picture of the derivative f (x) using the slopes of the tangents to the graph of f. In this section
Final Exam. Math 3 December 7, 2010
 Final Exam Math 3 December 7, 200 Name: On this final examination for Math 3 in Fall 200, I will work individually, neither giving nor receiving help, guided by the Dartmouth Academic Honor Principle.
Final Exam Math 3 December 7, 200 Name: On this final examination for Math 3 in Fall 200, I will work individually, neither giving nor receiving help, guided by the Dartmouth Academic Honor Principle.
LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES
 2 LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES 2.2 The Limit of a Function In this section, we will learn: About limits in general and about numerical and graphical methods for computing them. THE LIMIT
2 LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES 2.2 The Limit of a Function In this section, we will learn: About limits in general and about numerical and graphical methods for computing them. THE LIMIT
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals
 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives; Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F(x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
MATH 250 TOPIC 13 INTEGRATION. 13B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules
 Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
The Chain Rule. Composition Review. Intuition. = 2(1.5) = 3 times faster than (X)avier.
 The Chain Rule In the previous section we ha to use a trig ientity to etermine the erivative of. h(x) = sin(2x). We can view h(x) as the composition of two functions. Let g(x) = 2x an f (x) = sin x. Then
The Chain Rule In the previous section we ha to use a trig ientity to etermine the erivative of. h(x) = sin(2x). We can view h(x) as the composition of two functions. Let g(x) = 2x an f (x) = sin x. Then
Chapter Usual types of questions Tips What can go ugly. and, common denominator will be
 C3 Cheat Sheet Chapter Usual types of questions Tips What can go ugly 1 Algebraic Almost always adding or subtracting Factorise everything in each fraction first. e.g. If denominators Blindly multiplying
C3 Cheat Sheet Chapter Usual types of questions Tips What can go ugly 1 Algebraic Almost always adding or subtracting Factorise everything in each fraction first. e.g. If denominators Blindly multiplying
Solutions to Practice Problems Tuesday, October 28, 2008
 Solutions to Practice Problems Tuesay, October 28, 2008 1. The graph of the function f is shown below. Figure 1: The graph of f(x) What is x 1 + f(x)? What is x 1 f(x)? An oes x 1 f(x) exist? If so, what
Solutions to Practice Problems Tuesay, October 28, 2008 1. The graph of the function f is shown below. Figure 1: The graph of f(x) What is x 1 + f(x)? What is x 1 f(x)? An oes x 1 f(x) exist? If so, what
Sequences and Series
 Sequences and Series What do you think of when you read the title of our next unit? In case your answers are leading us off track, let's review the following IB problems. 1 November 2013 HL 2 3 November
Sequences and Series What do you think of when you read the title of our next unit? In case your answers are leading us off track, let's review the following IB problems. 1 November 2013 HL 2 3 November
Calculus II Lecture Notes
 Calculus II Lecture Notes David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 206 edition Contents Contents 2 Review of Calculus I 5. Limits..................................... 7.2 Derivatives...................................3
Calculus II Lecture Notes David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 206 edition Contents Contents 2 Review of Calculus I 5. Limits..................................... 7.2 Derivatives...................................3
5 Integrals reviewed Basic facts U-substitution... 4
 Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 4 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 4 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Test 3 Review. y f(a) = f (a)(x a) y = f (a)(x a) + f(a) L(x) = f (a)(x a) + f(a)
 MATH 2250 Calculus I Eric Perkerson Test 3 Review Sections Covered: 3.11, 4.1 4.6. Topics Covered: Linearization, Extreme Values, The Mean Value Theorem, Consequences of the Mean Value Theorem, Concavity
MATH 2250 Calculus I Eric Perkerson Test 3 Review Sections Covered: 3.11, 4.1 4.6. Topics Covered: Linearization, Extreme Values, The Mean Value Theorem, Consequences of the Mean Value Theorem, Concavity
Limit. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 9 Limit Limit is the foundation of calculus that it is so useful to understand more complicating chapters of calculus. Besides, Mathematics has black hole scenarios (dividing by zero, going to
Chapter 9 Limit Limit is the foundation of calculus that it is so useful to understand more complicating chapters of calculus. Besides, Mathematics has black hole scenarios (dividing by zero, going to
Sin, Cos and All That
 Sin, Cos and All That James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 9, 2017 Outline 1 Sin, Cos and all that! 2 A New Power Rule 3
Sin, Cos and All That James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 9, 2017 Outline 1 Sin, Cos and all that! 2 A New Power Rule 3
Math 121: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 11: Final Exam Review Sheet The Final Exam will be given on Thursday, March 1 from 10:30 am 1:30 pm. The exam is cumulative and will cover chapters 1.1-1.3, 1.5, 1.6,.1-.6, 3.1-3.6,
Exam Information Math 11: Final Exam Review Sheet The Final Exam will be given on Thursday, March 1 from 10:30 am 1:30 pm. The exam is cumulative and will cover chapters 1.1-1.3, 1.5, 1.6,.1-.6, 3.1-3.6,
We can see that f(2) is undefined. (Plugging x = 2 into the function results in a 0 in the denominator)
 In order to be successful in AP Calculus, you are expected to KNOW everything that came before. All topics from Algebra I, II, Geometry and of course Precalculus are expected to be mastered before you
In order to be successful in AP Calculus, you are expected to KNOW everything that came before. All topics from Algebra I, II, Geometry and of course Precalculus are expected to be mastered before you
Unit #3 : Differentiability, Computing Derivatives
 Unit #3 : Differentiability, Computing Derivatives Goals: Determine when a function is differentiable at a point Relate the derivative graph to the the graph of an original function Compute derivative
Unit #3 : Differentiability, Computing Derivatives Goals: Determine when a function is differentiable at a point Relate the derivative graph to the the graph of an original function Compute derivative
CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear Prospective Calculus Students, Welcome to AP Calculus. This is a rigorous, yet rewarding, math course. Most of the students who have taken Calculus in the past are amazed
CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear Prospective Calculus Students, Welcome to AP Calculus. This is a rigorous, yet rewarding, math course. Most of the students who have taken Calculus in the past are amazed
MATH 1004E Get out of your seat and mingle until you find someone with a name that either has:
 Monday 11:35-1:5 CORE CONCEPTS: Pre-calc review (key terms, exponents, factoring, rationalizing) Basic functions (absolute, trigonometric) Intro to limits (one-sided) OPENER (10min): Mingling Name Game
Monday 11:35-1:5 CORE CONCEPTS: Pre-calc review (key terms, exponents, factoring, rationalizing) Basic functions (absolute, trigonometric) Intro to limits (one-sided) OPENER (10min): Mingling Name Game
1.1 Definition of a Limit. 1.2 Computing Basic Limits. 1.3 Continuity. 1.4 Squeeze Theorem
 1. Limits 1.1 Definition of a Limit 1.2 Computing Basic Limits 1.3 Continuity 1.4 Squeeze Theorem 1.1 Definition of a Limit The limit is the central object of calculus. It is a tool from which other fundamental
1. Limits 1.1 Definition of a Limit 1.2 Computing Basic Limits 1.3 Continuity 1.4 Squeeze Theorem 1.1 Definition of a Limit The limit is the central object of calculus. It is a tool from which other fundamental
f(g(x)) g (x) dx = f(u) du.
 1. Techniques of Integration Section 8-IT 1.1. Basic integration formulas. Integration is more difficult than derivation. The derivative of every rational function or trigonometric function is another
1. Techniques of Integration Section 8-IT 1.1. Basic integration formulas. Integration is more difficult than derivation. The derivative of every rational function or trigonometric function is another
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
2015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution
 015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
015 Math Camp Calculus Exam Solution Problem 1: x = x x +5 4+5 = 9 = 3 1. lim We also accepted ±3, even though it is not according to the prevailing convention 1. x x 4 x+4 =. lim 4 4+4 = 4 0 = 4 0 = We
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student,
 Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Albertson AP Calculus AB AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school.
 Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2015 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2015 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
AP Calculus Chapter 9: Infinite Series
 AP Calculus Chapter 9: Infinite Series 9. Sequences a, a 2, a 3, a 4, a 5,... Sequence: A function whose domain is the set of positive integers n = 2 3 4 a n = a a 2 a 3 a 4 terms of the sequence Begin
AP Calculus Chapter 9: Infinite Series 9. Sequences a, a 2, a 3, a 4, a 5,... Sequence: A function whose domain is the set of positive integers n = 2 3 4 a n = a a 2 a 3 a 4 terms of the sequence Begin
Unit #3 : Differentiability, Computing Derivatives, Trig Review
 Unit #3 : Differentiability, Computing Derivatives, Trig Review Goals: Determine when a function is differentiable at a point Relate the derivative graph to the the graph of an original function Compute
Unit #3 : Differentiability, Computing Derivatives, Trig Review Goals: Determine when a function is differentiable at a point Relate the derivative graph to the the graph of an original function Compute
Calculus 221 worksheet
 Calculus 221 worksheet Graphing A function has a global maximum at some a in its domain if f(x) f(a) for all other x in the domain of f. Global maxima are sometimes also called absolute maxima. A function
Calculus 221 worksheet Graphing A function has a global maximum at some a in its domain if f(x) f(a) for all other x in the domain of f. Global maxima are sometimes also called absolute maxima. A function
