PHYSICS. Relative velocity
|
|
|
- Shanon Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AILY PRACTICE PROLEMS P4 Relative velocity Topics : Relative Velocity SECTION - I (Straight Objective Question) This section contains seven (7) multiple choice questions. Each question has four (4) options (a),, (c), (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.. A boat which rows with a speed of 5 kmh in still water crosses a river of width km along the shortest path in 5 min. The velocity of river water is (a) km h 3 km h (c) 4 km h (d) 5 km h - 9 R = resultant vel = 4km h = angle at which boat rows v sin tan u v cos cos u.u 5 R u v uv cos 4 u 5 u.u 6 = u + 5 u u = 9 u = 3 km h v 5 ms v = 5 4 km
2 . A train S, m long runs with a velocity 7 kmh ; while train T 3 m long is running in opposite direction with a velocity 8 kmh. The time taken by T to cross train S is (a) 5 sec sec (c) 5 sec (d) 5 sec (a) Velocity of S - train = ms Velocity of T - train = 3 ms Relative vel. of T w.r.t. s = 3 = 5 ms istance = l + l = 5 m time t 5 m 5 ms 5sec 3. A man swims in still water of a river of width with speed v. The river flows with velocity (v/). He swims making an angle with the upstream to cross the river in shortest distance. The time taken to cross the river is (a) /V vcos (c) vsin (d) v (c) v m = vel. of man = v v r = vel of river v v = v sin sin 3 time t v sin v v/ v m 4. A person aiming to reach the exactly opposite point on the bank of a strean is swimming with a speed of.5 ms at an angle of with teh direction of flow of the stream. The speed of the stream is (a) ms.5 ms (c).5 ms (d).433 ms (c) v = velocity of stream. Resultant of u and v must be R u =.5 ms, R = resultant velocity v = u sin ms river Relative Velocity
3 V u 3 R 5. A boat crosses a river from port A to port which are just on the opposite side. The speed of the water is V w and that of boat is V relative to still water. Assume V = V w. What is the time taken by the boat, if it has to cross the river directly on the A line (a) V 3 3 V (c) V (d) V (a) From figure, V sin V W Vw sin 3 V V V Time taken to cross the river, W t V cos V cos3 V 3 V V cos V sin Relative Velocity 3 A 6. A boat moves with a speed of 5 km/h relative to water in a river flowing with a speed of 3 km/h and having a width of km. The minium time taken around a round trip is (a) 5 min 6 min (c) min (d) 3 min (d) For the round trip he should cross perpendicular to the river Time for trip to that side km.5hr To come back, again he take.5 hr to cross the river. Total time is 3 min, he 4 km / hr goes to the other bank and come back at the same point. 7. Consider a collection of large number of particles each with speed v. The direction of velocity is randomly distributed in the collection. The magnitude of relative velocity between a pair of collection particles averaged over all the particles is (a) zero greater than v (c) less than v (d) v V W
4 Consider two particles with angle between their directions of velocities then V = V V. Hence magnitude of relative velocity V V V V V cos V V sin. V V V and average value of V r is or Vr. d V Vr sin sin V d d V V 4V cos cos8 cos SECTION-II (One or More than correct objective Question) This section contains three (3) multiple choice questions. Each question has four (4) options (a),, (c), (d) out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct. 8. A river flows at ms. The man can swim in still water with velocity of 4 ms. The angle at which man must swim with the banks so that he crosses the river in the shortest distance is (a) 3 up stream 3 down stream (c) 6 up stream (d) 6 down stream (d) 4 sin Sin 3 angle with downstream = (9 ) = 6 with downstream ms V. 4 ms River O ms 9. A boat crosses the river in short possible route. The speed of the boat in still water is 3 ms. The average speed of the boat while crossing the river comes out to be ms. The velocity of the river is (a) 5 ms 5 ms (c) ms (d) 4 ms (a) V b = velocity of boat = 3 ms V a = average speed = ms V r = velocity of river = 5 ms 3 4 Relative Velocity
5 . River is flowing with a velocity v 4iˆ m/s. A boat is moving with a volocity of v (4)() 5 m/s R relative to river. The width of the river is m along y-direction. Choose the correct alternative(s). (a) The boatman will cross the river in 5 s. Absolute velocity of boat man is 5 m/s. (c) rift of the boatman along current is 5 m (d) The boatman can never cross the river. (a, b, c) Absolute velocity of boatman is v v v v R R = ( iˆ 4)(4) ˆj iˆ = iˆ 4 ˆj 4 j V Time t = 5 s 4 rift x = () (5) = 5 m i v (4)() 5 m/s SECTION - III (Assertion & Reasoning Type Question) This section contains three (3) assertion & reasoning type questions. Each question has four (4) options (a),, (c), (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Statement based Questions : For the following question, choose the correct answer from the codes (a),, (c) and (d) defined as follows ; (a) Statement I is true, Statement II is true; Statement II is correct explanation for Statement I. Statement I is true, Statement I is true; Statement II is not correct explanation of Statement I (c) Statement I is true; Statement II is false. (d) Statement I is false; statement II is true.. STATEMENT- For an observer looking out through the windows of a fast moving train, the near by objects appear to move in opposite direction to the train. While distant appear to be stationary STATEMENT- If the observer and the object are moving with velocities V and V respectively with reference to a laboratory frame the velocities of the object with respect to the observer is V V oth statements are true but reason is not correct explanation of assertion. istant objects motion depends on the agle subtended at eye. It is illustrated in fig. O Relative Velocity 5
6 . STATEMENT The relative velocity between any two bodies moving in opposite direction is equal to the sum of the velocities of two bodies.() STATEMENT Some times relative velocity between two bodies is equal to the difference in velocities of the two bodies. When two bodies are moving in opposite direction relative velocity between then is equal to sum of the velocities of bodies (V = V (V ) =V + V ). ut if the bodies are moving in the same direction their relative velocity is equal to difference in velocities of bodies (V r = V V ). 3. STATEMENT A body, what ever its motion, is always at rest in a frame of reference which is fixed to the body itself. STATEMENT The releative velocity of a body with respect to itself is zero. (a) A body has no relative motion with respect to itself. Hence in frame of reference attached to body itself its velocity is zero. SECTION - IV (Passage ased Question) This section contains one () paragraph based upon the paragraph three(3) multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each question has four(4) options (a),, (c), (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Two parallel rail tracks run north south. Train A moves north with a speed of 54 km/h and train moves south with a speed of 9 km/ h. 4. The relative velocity of with respect to A is (a) 9 km/h 44 km/h (c) 3 km/h (d) none of these Let v A = 54 km/h then v = 9 km/h S ( ) N (+) 54 km/h 9 km/h Relative velocity of with respect to A v A 9 54 = 44 km/h The velocity of train with respect to train A appears 44 km/h along south. 5. The relative velocity of ground with respect to is (a) 9 km/h 44 km/h (c) 7 km/h (d) 6 km/h (a) Relative velocity of ground with respect to train = v ground v = 9 = 9 km/h To train, the ground appears to move with a speed of 9 km/h along south. 6. The velocity of a monkey running on the roof of the train A against its motion (with a velocity of 8 km/ h with respect to the train A) as observed by a man standing on the ground is (a) 33 km/h 36 km/h (c) 99 km/h (d) zero 6 Relative Velocity
7 The velocity of monkey with respect to train A [v monkey ] train A = [v monkey ] ground [v train A ] ground or [v monkey ] ground = [v monkey ] train A + [ v train A ] ground = 36 km/h. SECTION - V (Matrix Match Type) This section contains one () question. It contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. Statements in column I are labelled as A,, C and whereas statements in column II are labelled as p, q, r and s. The answers to these questions have to be appropriately bubbled as illustrated in the following example. If the correct matches are A p, r ; q, s; C r and q, then the correctly bubbled matrix will look like the following: 7. Match the following columns. Column I p q r s p q r s p p p q q q r r r s s s Fig. 3.4 Relative Velocity 7 A C Column II (a) It is raining verticaly at 3 m s. If wind blows horizontally at m s,. The apparent velocity of rainfall is (p) m s A boat is moving at m s towards north and another boat is moving at m s towards north-west. Find the relative velocity of the second boat with respect to the first is equal to (q) 5 m s (c) From the top of a tower, two particles are dropped at an interval of s. Find the relative velocity and relative acceleration of the particles during the fall. Acceleration due to gravity = m s. (r) 4 m s (d) A police jeep is chasing with velocity of.5 m s a thief in another jeep moving with velocity 4.5 m s. Police fires a bullet with muzzle velocity of 8 m s. The velocity with which it will strike the car of the thief is (s) m s (a) (r) ; (s) ; (c) (p) ; (d) (q) (d) Effective speed of the bullet = speed of bullet + speed of police jeep = 8 m s +.5 m s = (8 +.5) m s = 9.5 m s speed of thief's jeep = 4.5 m s Velocity of bullet w.r.t thief's car = = 5 m s SECTION - VI (Integer Type) This section contains three (3) questions. The answer to each of the question is a single digit integer, ranging from to Velocity of a boat in still water is 5 km h. The boat takes 5 min to cross a river of width km perpendicularly. The velocity of current is The boat crosses a river of width km in 5 min or in. 4 h The resultant of the velocity of the boat and current is w (say) and u v w u w 4 km h / 4
8 Let the velocity of the boat in still water be v and the velocity of current be u. From Fig v = u + w or, u = v + w or, u v w km. h. 9. It is raining vertically at 3 m. s. If wind blows horizontally at m. s, what will be the apparent velocity and direction of rainfall? V R = 3.ms V W = ms Let the resualt velocity be R R m / s irection of wind y V w O V w x x R V R. A boat is moving at 5 km. h towards north and another boat is moving at 5 km. h towards north-west. Find the relative velocity of the second boat with respect to the first. Required relative velocity of the second boat w.r. to the first boat is R N 5 km / h y 5 km/h 5 km/h V w W R O E 3 km/h R 5 5 R R 5 S 8 Relative Velocity
Q1. In a circular track (distance 400 m) an athlete runs 1/4 the of the ground. So what would be the displacement?
 Class: 9 Subject: Physics Topic: Motion in a straight line No. of Questions: 20 Q1. In a circular track (distance 400 m) an athlete runs 1/4 the of the ground. So what would be the displacement? Given,
Class: 9 Subject: Physics Topic: Motion in a straight line No. of Questions: 20 Q1. In a circular track (distance 400 m) an athlete runs 1/4 the of the ground. So what would be the displacement? Given,
Q3.1. A. 100 m B. 200 m C. 600 m D m E. zero. 500 m. 400 m. 300 m Pearson Education, Inc.
 Q3.1 P 400 m Q A bicyclist starts at point P and travels around a triangular path that takes her through points Q and R before returning to point P. What is the magnitude of her net displacement for the
Q3.1 P 400 m Q A bicyclist starts at point P and travels around a triangular path that takes her through points Q and R before returning to point P. What is the magnitude of her net displacement for the
Physics 12. Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions
 Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Full file at
 Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
CHAPTER 2: VECTOR COMPONENTS DESCRIBE MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS
 CHAPTER 2: VECTOR COMPOETS DESCRIBE MOTIO I TWO DIMESIOS 2.1 Vector Methods in One Dimension Vectors may be pictured with sketches in which arrows represent quantities such as displacement, force and velocity.
CHAPTER 2: VECTOR COMPOETS DESCRIBE MOTIO I TWO DIMESIOS 2.1 Vector Methods in One Dimension Vectors may be pictured with sketches in which arrows represent quantities such as displacement, force and velocity.
Chapter 3. Vectors. θ that the vector forms with i ˆ is 15. I. Vectors and Scalars
 Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Chapter 3. Vectors I. Vectors and Scalars 1. What type of quantity does the odometer of a car measure? a) vector; b) scalar; c) neither scalar nor vector; d) both scalar and vector. 2. What type of quantity
Components of a Vector
 Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Avanti Learning Centres
 9P01 Motion 1 Avanti Learning Centres 016 Edition 9P01. Motion TABLE OF CONTENTS 9P01. Motion 1 9P01.1 Distance, Displacement & Speed....... 9P01. Velocity & Acceleration.......4 9P01.3 Graphical Representation
9P01 Motion 1 Avanti Learning Centres 016 Edition 9P01. Motion TABLE OF CONTENTS 9P01. Motion 1 9P01.1 Distance, Displacement & Speed....... 9P01. Velocity & Acceleration.......4 9P01.3 Graphical Representation
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction
 Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
Answer: Scalars: Volume, mass, speed, density, number of moles, angular frequency. Vectors: Acceleration, velocity, displacement, angular velocity.
 Question State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement, angular
Question State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement, angular
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes
 Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
MOTION IN A PLANE. Chapter Four MCQ I. (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180
 Chapter Four MOTION IN A PLANE MCQ I 4.1 The angle between A = ˆi + ˆj and B = ˆi ˆj is (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180 4.2 Which one of the following statements is true? (a) A scalar quantity is the one
Chapter Four MOTION IN A PLANE MCQ I 4.1 The angle between A = ˆi + ˆj and B = ˆi ˆj is (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180 4.2 Which one of the following statements is true? (a) A scalar quantity is the one
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. All questions are of equal value. Answer all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 PAGE NO.: 1 of 5 All questions are of equal value. Answer all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
PAGE NO.: 1 of 5 All questions are of equal value. Answer all questions. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
Chapter 01: Motion in one-dimension:- Basic definitions. Equations of motion(both horizontal & vertical motions). Graphical representation( x-t
 MECHANICS Chapter 01: Motion in one-dimension:- Basic definitions. Equations of motion(both horizontal & vertical motions). Graphical representation(x-t, v-t and a-t) & Significance of different graphs.
MECHANICS Chapter 01: Motion in one-dimension:- Basic definitions. Equations of motion(both horizontal & vertical motions). Graphical representation(x-t, v-t and a-t) & Significance of different graphs.
Electric Flux Holiday Homework
 Physics 1. Evaluate (999) 1/3 upto four places of decimal.. Solve (1001) 1/3 upto six places of decimal. 3. Plot graph y = x 4. Plot graph x² + y² = 9 5. Integrate the following functions w.r.t.x and find
Physics 1. Evaluate (999) 1/3 upto four places of decimal.. Solve (1001) 1/3 upto six places of decimal. 3. Plot graph y = x 4. Plot graph x² + y² = 9 5. Integrate the following functions w.r.t.x and find
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTER 3
 Solutions to Phsics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTE 3 1. We choose the west and south coordinate sstem shown. For the components of the resultant we have W W = D 1 + D cos
Solutions to Phsics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTE 3 1. We choose the west and south coordinate sstem shown. For the components of the resultant we have W W = D 1 + D cos
Page 1 of 35 Website: Mobile:
 Question 4.1: State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement,
Question 4.1: State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement,
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction
Relative Motion. David Teichrob UBC Physics 2006
 Relative Motion David Teichrob UBC Physics 2006 What is Relative Motion? First of all the physics concept involved is KINEMATICS (the study of motion of objects - the relation among displacement, velocity,
Relative Motion David Teichrob UBC Physics 2006 What is Relative Motion? First of all the physics concept involved is KINEMATICS (the study of motion of objects - the relation among displacement, velocity,
Q1. The density of aluminum is 2700 kg/m 3. Find the mass of a uniform solid aluminum cylinder of radius cm and height cm.
 Coordinator: W. Al-Basheer Sunday, June 28, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. The density of aluminum is 2700 kg/m 3. Find the mass of a uniform solid aluminum cylinder of radius 10.00 cm and height 30.48 cm. A) 25.85
Coordinator: W. Al-Basheer Sunday, June 28, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. The density of aluminum is 2700 kg/m 3. Find the mass of a uniform solid aluminum cylinder of radius 10.00 cm and height 30.48 cm. A) 25.85
Downloaded from
 Motion 1. A train travels 40 km at a uniform speed of 30 km h -1. Its average speed after travelling another 40 km is 45 km h -1 for the whole journey. Its speed in the second half of the journey is (A)
Motion 1. A train travels 40 km at a uniform speed of 30 km h -1. Its average speed after travelling another 40 km is 45 km h -1 for the whole journey. Its speed in the second half of the journey is (A)
Ans: (c) [1988] Ans: (b) Q8. (a) zero (b) A (c) zero vector (d) unit vector Ans: (c) (c) 1: 3. (d) 3:1 Ans: (b) Q11.
![Ans: (c) [1988] Ans: (b) Q8. (a) zero (b) A (c) zero vector (d) unit vector Ans: (c) (c) 1: 3. (d) 3:1 Ans: (b) Q11. Ans: (c) [1988] Ans: (b) Q8. (a) zero (b) A (c) zero vector (d) unit vector Ans: (c) (c) 1: 3. (d) 3:1 Ans: (b) Q11.](/thumbs/91/107309181.jpg) Motion in a Plane Q1. π/2 cos 1 0.6 tan 1 7/5 π/4 Q2. [1988] MockTime.com Q6. An electric fan has blades of length 30 cm measured from the axis of rotation. If the fan is rotating at 120 rpm, the acceleration
Motion in a Plane Q1. π/2 cos 1 0.6 tan 1 7/5 π/4 Q2. [1988] MockTime.com Q6. An electric fan has blades of length 30 cm measured from the axis of rotation. If the fan is rotating at 120 rpm, the acceleration
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Physics 231. Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion. Alex Brown September MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Trigonometry Basics. Which side is opposite? It depends on the angle. θ 2. Y is opposite to θ 1 ; Y is adjacent to θ 2.
 Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
CHAPTER 8. Motion (NCERT SOLVED) CBSE CLASS IX. Dr. SIMIL RAHMAN
 CHAPTER 8 Motion (NCERT SOLVED) CBSE CLASS IX Dr. SIMIL RAHMAN Chapter8 www.similphysics.weebly.com MOTION (NCERT QUESTIONS SOLVED) 1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement?
CHAPTER 8 Motion (NCERT SOLVED) CBSE CLASS IX Dr. SIMIL RAHMAN Chapter8 www.similphysics.weebly.com MOTION (NCERT QUESTIONS SOLVED) 1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement?
Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars.
 1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
Physics ( (Chapter 4) (Motion in a Plane)
 () Question 4.1: State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: Volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement,
() Question 4.1: State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: Volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement,
Niraj Sir SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 3
 SOLUTIONS TO ONEPTS HPTER 3 1. a) Distance travelled = 50 + 40 + 0 = 110 m b) F = F = D = 50 0 = 30 M His displacement is D D = F DF 30 40 50m In ED tan = DE/E = 30/40 = 3/4 = tan 1 (3/4) His displacement
SOLUTIONS TO ONEPTS HPTER 3 1. a) Distance travelled = 50 + 40 + 0 = 110 m b) F = F = D = 50 0 = 30 M His displacement is D D = F DF 30 40 50m In ED tan = DE/E = 30/40 = 3/4 = tan 1 (3/4) His displacement
Motion in one dimension
 Work Sheet - 1 1. Define rest and motion. 2. Define distance and displacement. Write their S.I unit. 3. Distinguish between distance and displacement. Write five points of differences. Work Sheet - 2 1.
Work Sheet - 1 1. Define rest and motion. 2. Define distance and displacement. Write their S.I unit. 3. Distinguish between distance and displacement. Write five points of differences. Work Sheet - 2 1.
State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector:
 Question 4.1: State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement,
Question 4.1: State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector: volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement,
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PHYS 101 Fall 2013 (Purcell), Fake Midterm #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a
PHYS 101 Fall 2013 (Purcell), Fake Midterm #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a
Class 11 Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Motion in a Straight Line
 Class 11 Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Motion in a Straight Line Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Among the four graphs shown in the figure, there is only one graph for which
Class 11 Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Motion in a Straight Line Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Among the four graphs shown in the figure, there is only one graph for which
 Question 1: An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example. Yes. An object that has moved through a distance can have zero displacement.
Question 1: An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example. Yes. An object that has moved through a distance can have zero displacement.
Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review
 Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Multiple Choice 1. The position of a particle moving along the x axis is given by 2 x = ( 21+ 22t 6 0. t )m, where t is in s. What is the average velocity during the time
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Multiple Choice 1. The position of a particle moving along the x axis is given by 2 x = ( 21+ 22t 6 0. t )m, where t is in s. What is the average velocity during the time
Today s Lecture: Kinematics in Two Dimensions (continued) A little bit of chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion (next time)
 Today s Lecture: Kinematics in Two Dimensions (continued) Relative Velocity - 2 Dimensions A little bit of chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion (next time) 27 September 2009 1 Relative Velocity
Today s Lecture: Kinematics in Two Dimensions (continued) Relative Velocity - 2 Dimensions A little bit of chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion (next time) 27 September 2009 1 Relative Velocity
What is Relative Motion
 RELATIVE MOTION What is Relative Motion Strictly speaking all motion is relative to something. Usually that something is a reference point that is assumed to be at rest (i.e. the earth). Motion can be
RELATIVE MOTION What is Relative Motion Strictly speaking all motion is relative to something. Usually that something is a reference point that is assumed to be at rest (i.e. the earth). Motion can be
PHYS 100 Mid-Term #1
 D.W. Poppy Secondary School Physics 12 PHYS 100 Mid-Term #1 Name: Directions: Fill in the scantron form with the following information: 1. ID number (student number) 2. Name at top of form 3. Name bubbled
D.W. Poppy Secondary School Physics 12 PHYS 100 Mid-Term #1 Name: Directions: Fill in the scantron form with the following information: 1. ID number (student number) 2. Name at top of form 3. Name bubbled
Section Distance and displacment
 Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Phys 201, Lecture 5 Feb.2. Chapter 3: Mo;on in Two and Three Dimensions
 Phys 201, Lecture 5 Feb.2 Chapter 3: Mo;on in Two and Three Dimensions Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Displacement describes the location change of a particle Velocity is rate of change of displacement
Phys 201, Lecture 5 Feb.2 Chapter 3: Mo;on in Two and Three Dimensions Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Displacement describes the location change of a particle Velocity is rate of change of displacement
Answers !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
 11 th Grade Physics Workbook METU Development Foundation High chool 1 Answers 11th Grade Chapter-1 Relative Motion Activity - 1.2.1 Moving observer 1. 2. Velocity of the motorcycle with respect to ground
11 th Grade Physics Workbook METU Development Foundation High chool 1 Answers 11th Grade Chapter-1 Relative Motion Activity - 1.2.1 Moving observer 1. 2. Velocity of the motorcycle with respect to ground
Find graphically, using scaled diagram, following vectors (both magnitude and direction):
 1 HOMEWORK 1 on VECTORS: use ruler and protractor, please!!! 1. v 1 = 3m/s, E and v = 4m/s, 3 Find graphically, using scaled diagram, following vectors (both magnitude and direction): a. v = v 1 + v b.
1 HOMEWORK 1 on VECTORS: use ruler and protractor, please!!! 1. v 1 = 3m/s, E and v = 4m/s, 3 Find graphically, using scaled diagram, following vectors (both magnitude and direction): a. v = v 1 + v b.
Vector x-component (N) y-component (N)
 Name AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2014 Where calculations are required, show your work. Be smart about significant figures. Print these sheets and hand them in (neatly done) on the first day of class.
Name AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2014 Where calculations are required, show your work. Be smart about significant figures. Print these sheets and hand them in (neatly done) on the first day of class.
ISSUED BY K V - DOWNLOADED FROM KINEMATICS
 KINEMATICS *rest and Motion are relative terms, nobody can exist in a state of absolute rest or of absolute motion. *One dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion
KINEMATICS *rest and Motion are relative terms, nobody can exist in a state of absolute rest or of absolute motion. *One dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Physics 1A. Lecture 3B. "More than anything else... any guy here would love to have a monkey. A pet monkey." -- Dane Cook
 Physics 1A Lecture 3B "More than anything else... any guy here would love to have a monkey. A pet monkey." -- Dane Cook Trajectories Since there is no horizontal acceleration (a x = 0) the horizontal position,
Physics 1A Lecture 3B "More than anything else... any guy here would love to have a monkey. A pet monkey." -- Dane Cook Trajectories Since there is no horizontal acceleration (a x = 0) the horizontal position,
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16)
 Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion. Section 4 Relative Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Today s Lecture: Kinematics in Two Dimensions (continued) A little bit of chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion (next time)
 Today s Lecture: Kinematics in Two Dimensions (continued) Relative Velocity - 2 Dimensions A little bit of chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion (next time) 29 September 2009 1 Question the moving
Today s Lecture: Kinematics in Two Dimensions (continued) Relative Velocity - 2 Dimensions A little bit of chapter 4: Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion (next time) 29 September 2009 1 Question the moving
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS (P1) COMMON TEST JUNE 2014
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS (P1) COMMON TEST JUNE 2014 MARKS: 100 TIME: 2 hours This question paper consists of 9 pages and 2 data sheets. *PHSCE1* Physical Sciences
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS (P1) COMMON TEST JUNE 2014 MARKS: 100 TIME: 2 hours This question paper consists of 9 pages and 2 data sheets. *PHSCE1* Physical Sciences
Scalar Quantities - express only magnitude ie. time, distance, speed
 Chapter 6 - Vectors Scalar Quantities - express only magnitude ie. time, distance, speed Vector Quantities - express magnitude and direction. ie. velocity 80 km/h, 58 displacement 10 km (E) acceleration
Chapter 6 - Vectors Scalar Quantities - express only magnitude ie. time, distance, speed Vector Quantities - express magnitude and direction. ie. velocity 80 km/h, 58 displacement 10 km (E) acceleration
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review
 AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
y(t) = y 0 t! 1 2 gt 2. With y(t final ) = 0, we can solve this for v 0 : v 0 A ĵ. With A! ĵ =!2 and A! = (2) 2 + (!
 1. The angle between the vector! A = 3î! 2 ĵ! 5 ˆk and the positive y axis, in degrees, is closest to: A) 19 B) 71 C) 90 D) 109 E) 161 The dot product between the vector! A = 3î! 2 ĵ! 5 ˆk and the unit
1. The angle between the vector! A = 3î! 2 ĵ! 5 ˆk and the positive y axis, in degrees, is closest to: A) 19 B) 71 C) 90 D) 109 E) 161 The dot product between the vector! A = 3î! 2 ĵ! 5 ˆk and the unit
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics. f i i
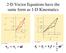 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
Circular motion. Announcements:
 Circular motion Announcements: Clicker scores through Wednesday are now posted on DL. Scoring is points for a wrong answer, 3 points for a right answer. 13 clicker questions so far, so max is 39 points.
Circular motion Announcements: Clicker scores through Wednesday are now posted on DL. Scoring is points for a wrong answer, 3 points for a right answer. 13 clicker questions so far, so max is 39 points.
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion Chapter 2: 2-Dimensional Motion 2.1 Position 2.2 Distance and Displacement 2.3 Average Speed and Average Velocity 2.4 Instant Speed and Instant
vector of point will be and if the point P is in a space and its coordinates are (x, y, z) then position vector can be expressed as
 2.1 Motion in One Dimension : Position Position of any point is completely expressed by two factors : Its distance from the observer and its direction with respect to observer. That is why position is
2.1 Motion in One Dimension : Position Position of any point is completely expressed by two factors : Its distance from the observer and its direction with respect to observer. That is why position is
Physics 125: Classical Physics A. 1 Practice Problems for Midterm Exam 1
 Physics 125: Classical Physics A 1 Practice Problems for Midterm Exam 1 Problem 1 The Figure 1 depicts velocity as a function of time for a short run. Find: a) The acceleration at t = 5 seconds. b) The
Physics 125: Classical Physics A 1 Practice Problems for Midterm Exam 1 Problem 1 The Figure 1 depicts velocity as a function of time for a short run. Find: a) The acceleration at t = 5 seconds. b) The
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
Downloaded from APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY Write the correct answer for each of the following : 1. Write the altitude of the sun is at 60 o, then the height of the vertical tower that will cost
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY Write the correct answer for each of the following : 1. Write the altitude of the sun is at 60 o, then the height of the vertical tower that will cost
1. Less than before. 2. Greater than before. 3. No change. correct
 Version One Homework 3 Schemm 54321 Oct 22, 2004 1 This print-out should have 19 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. The due
Version One Homework 3 Schemm 54321 Oct 22, 2004 1 This print-out should have 19 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. The due
D) sin A = D) tan A = D) cos B =
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
During the second part of the trip then we travelled at 50 km/hr for hour so x = v avg t =
 PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
PH 2213 : Chapter 02 Homework Solutions Problem 2.6 : You are driving home from school steadily at 90 km/hr for 130 km. It then begins to rain and you slow to 50 km/hr. You arrive home after driving 3
Phys101-T121-First Major Exam Zero Version, choice A is the correct answer
 Phys101-T121-First Major Exam Zero Version, choice A is the correct answer Q1. Find the mass of a solid cylinder of copper with a radius of 5.00 cm and a height of 10.0 inches if the density of copper
Phys101-T121-First Major Exam Zero Version, choice A is the correct answer Q1. Find the mass of a solid cylinder of copper with a radius of 5.00 cm and a height of 10.0 inches if the density of copper
FIITJEE PET IX (REG_1 ST YEAR)
 FIITJEE PET IX (REG_1 ST YEAR) MAINS DATE: 1.08.017 Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 360 INSTRUCTIONS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball Point
FIITJEE PET IX (REG_1 ST YEAR) MAINS DATE: 1.08.017 Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 360 INSTRUCTIONS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball Point
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit:
 Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Using Units in Science
 Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Name: Class: Date: Solution x 1 = units y 1 = 0. x 2 = d 2 cos = = tan 1 y
 Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
Contents. Objectives Circular Motion Velocity and Acceleration Examples Accelerating Frames Polar Coordinates Recap. Contents
 Physics 121 for Majors Today s Class You will see how motion in a circle is mathematically similar to motion in a straight line. You will learn that there is a centripetal acceleration (and force) and
Physics 121 for Majors Today s Class You will see how motion in a circle is mathematically similar to motion in a straight line. You will learn that there is a centripetal acceleration (and force) and
a railway carriage moving without jerks between two stations. a monkey sitting on top of a man cycling smoothly on a circular track.
 Question 3.1: In which of the following examples of motion, can the body be considered approximately a point object: a railway carriage moving without jerks between two stations. a monkey sitting on top
Question 3.1: In which of the following examples of motion, can the body be considered approximately a point object: a railway carriage moving without jerks between two stations. a monkey sitting on top
Chapter 4 Kinematics II: Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Kinematics II: Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Demonstrations: 1) Ball falls down and another falls out 2) Parabolic and straight line motion from two different frames. The truck with a dropping
Chapter 4 Kinematics II: Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Demonstrations: 1) Ball falls down and another falls out 2) Parabolic and straight line motion from two different frames. The truck with a dropping
Physics. TOPIC : Newton s law of Motion
 OPIC : ewton s law of Motion Date : Marks : 10 mks ime : ½ hr 1. A person sitting in an open car moving at constant velocity throws a ball vertically up into air. Outside the car In the car to the side
OPIC : ewton s law of Motion Date : Marks : 10 mks ime : ½ hr 1. A person sitting in an open car moving at constant velocity throws a ball vertically up into air. Outside the car In the car to the side
Kinematics WORKSHEETS. KEEP IT SIMPLE SCIENCE Physics Module 1. Motion Graphs. KISS Resources for NSW Syllabuses & Australian Curriculum
 Worksheet 1 Fill in the blank spaces. KEEP IT IMPLE CIENCE Physics Module 1 Kinematics WORKHEET peed & Velocity The average speed of a moving object is equal to the a)... travelled, divided by... taken.
Worksheet 1 Fill in the blank spaces. KEEP IT IMPLE CIENCE Physics Module 1 Kinematics WORKHEET peed & Velocity The average speed of a moving object is equal to the a)... travelled, divided by... taken.
PHYSICS STD 9 ICSE ( ) MOTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 PHYSICS STD 9 ICSE (2017-2018) MOTION IN ONE DIMENSION IMPORTANT FORMULAE 1. Speed = Distance Time or v = S t 2. Average speed = Total distance travelled Total time taken 3. Average velocity = Displacement
PHYSICS STD 9 ICSE (2017-2018) MOTION IN ONE DIMENSION IMPORTANT FORMULAE 1. Speed = Distance Time or v = S t 2. Average speed = Total distance travelled Total time taken 3. Average velocity = Displacement
These physical quantities can be classified into two categories, depending on their dependent or independent existence.
 Chapter Motion The branch of Science which deals with the study of nature and natural phenomena is called Physics. In Physics, we deal with inanimate matter, energy and radiation. The quantities in terms
Chapter Motion The branch of Science which deals with the study of nature and natural phenomena is called Physics. In Physics, we deal with inanimate matter, energy and radiation. The quantities in terms
Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Please write your CID Colton
 Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Phys101 First Major-111 Zero Version Monday, October 17, 2011 Page: 1
 Monday, October 17, 011 Page: 1 Q1. 1 b The speed-time relation of a moving particle is given by: v = at +, where v is the speed, t t + c is the time and a, b, c are constants. The dimensional formulae
Monday, October 17, 011 Page: 1 Q1. 1 b The speed-time relation of a moving particle is given by: v = at +, where v is the speed, t t + c is the time and a, b, c are constants. The dimensional formulae
Class 11 GURU GOBIND SINGH PUBLIC SCHOOL PHYSICS CHAPTER 1: UNITS & MEASUREMENT
 CHAPTER 1: UNITS & MEASUREMENT 1. Assuming that the mass (m) of the largest stone that can be moved by a flowing river depends only upon the velocity, the density ρ of water and the acceleration due to
CHAPTER 1: UNITS & MEASUREMENT 1. Assuming that the mass (m) of the largest stone that can be moved by a flowing river depends only upon the velocity, the density ρ of water and the acceleration due to
 Laws of Motion. A fighter aircraft is looping in a vertical plane. The minimum velocity at the highest point is (Given r = radius of the loop) a) gr b) gr c) gr d) 3gr. In non-inertial frame, the second
Laws of Motion. A fighter aircraft is looping in a vertical plane. The minimum velocity at the highest point is (Given r = radius of the loop) a) gr b) gr c) gr d) 3gr. In non-inertial frame, the second
Need to have some new mathematical techniques to do this: however you may need to revise your basic trigonometry. Basic Trigonometry
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions Kinematics in 2-dimensions. By the end of this you will 1. Remember your Trigonometry 2. Know how to handle vectors 3. be able to handle problems in 2-dimensions 4. understand
Kinematics in Two Dimensions Kinematics in 2-dimensions. By the end of this you will 1. Remember your Trigonometry 2. Know how to handle vectors 3. be able to handle problems in 2-dimensions 4. understand
What part has zero acceleration? Where is the object stationary? Is there a region of constant acceleration?
 What part has zero acceleration? Where is the object stationary? Is there a region of constant acceleration? What part has zero acceleration? Only if not turning Where is the object stationary? Is there
What part has zero acceleration? Where is the object stationary? Is there a region of constant acceleration? What part has zero acceleration? Only if not turning Where is the object stationary? Is there
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems
 Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
Kinematics in Two-Dimensions
 Slide 1 / 92 Slide 2 / 92 Kinematics in Two-Dimensions www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 92 How to Use this File Each topic is composed of brief direct instruction There are formative assessment questions after
Slide 1 / 92 Slide 2 / 92 Kinematics in Two-Dimensions www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 92 How to Use this File Each topic is composed of brief direct instruction There are formative assessment questions after
CHAPTER 2 LINEAR MOTION
 0 CHAPTER LINEAR MOTION HAPTER LINEAR MOTION 1 Motion o an object is the continuous change in the position o that object. In this chapter we shall consider the motion o a particle in a straight line, which
0 CHAPTER LINEAR MOTION HAPTER LINEAR MOTION 1 Motion o an object is the continuous change in the position o that object. In this chapter we shall consider the motion o a particle in a straight line, which
An object moves back and forth, as shown in the position-time graph. At which points is the velocity positive?
 1 The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the instantaneous velocity 2 The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: displacement from the original position to its position
1 The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the instantaneous velocity 2 The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: displacement from the original position to its position
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4 Main points of last lecture Scalars vs. Vectors Vectors A: (A x, A y ) or A & θ Addition/Subtraction Projectile Motion X-direction: a x = 0 (v x = constant)
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4 Main points of last lecture Scalars vs. Vectors Vectors A: (A x, A y ) or A & θ Addition/Subtraction Projectile Motion X-direction: a x = 0 (v x = constant)
NCERT Solutions. 95% Top Results. 12,00,000+ Hours of LIVE Learning. 1,00,000+ Happy Students. About Vedantu. Awesome Master Teachers
 Downloaded from Vedantu NCERT Solutions About Vedantu Vedantu is India s biggest LIVE online teaching platform with over 450+ best teachers from across the country. Every week we are coming up with awesome
Downloaded from Vedantu NCERT Solutions About Vedantu Vedantu is India s biggest LIVE online teaching platform with over 450+ best teachers from across the country. Every week we are coming up with awesome
Motion in Two Dimensions An Algebraic Approach
 . Motion in Two Dimensions An Algebraic Approach In ection.1 you learned how to solve motion problems in two dimensions by using vector scale diagrams. This method has some limitations. First, the method
. Motion in Two Dimensions An Algebraic Approach In ection.1 you learned how to solve motion problems in two dimensions by using vector scale diagrams. This method has some limitations. First, the method
ISP209 Fall Exam #1. Name: Student #:
 ISP209 Fall 2012 Exam #1 Name: Student #: Please write down your name and student # on both the exam and the scoring sheet. After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside the
ISP209 Fall 2012 Exam #1 Name: Student #: Please write down your name and student # on both the exam and the scoring sheet. After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside the
VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home.
 VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home. a. What distance did you travel? b. What was the displacement
VEL A Distance & Displacement & VEL B Speed and Velocity 1. You run from your house to a friend's house that is 3 miles away. You then walk home. a. What distance did you travel? b. What was the displacement
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions. Examples: non-linear motion (circles, planetary orbits, etc.) flight of projectiles (shells, golf balls, etc.
 Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Examples: HPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO & THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors the displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion
Motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Examples: HPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO & THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors the displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion
The exam has 20 questions (questions 2-21) and you have 1 hour and 15 minutes to complete the exam.
 Exam 1 Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on your scatron. Also fill in your section
Exam 1 Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on your scatron. Also fill in your section
A train begins a journey from a station and travels 60 km in a time of 20 minutes. The graph shows how the speed of each runner changes with time.
 1 train begins a journey from a station and travels 6 km in a of 2 minutes. What is the average of the train? 3. m / s 5. m / s 5 m / s 6 m / s 2 Two runners take part in a race. The graph shows how the
1 train begins a journey from a station and travels 6 km in a of 2 minutes. What is the average of the train? 3. m / s 5. m / s 5 m / s 6 m / s 2 Two runners take part in a race. The graph shows how the
= M. L 2. T 3. = = cm 3
 Phys101 First Major-1 Zero Version Sunday, March 03, 013 Page: 1 Q1. Work is defined as the scalar product of force and displacement. Power is defined as the rate of change of work with time. The dimension
Phys101 First Major-1 Zero Version Sunday, March 03, 013 Page: 1 Q1. Work is defined as the scalar product of force and displacement. Power is defined as the rate of change of work with time. The dimension
 Horizontal Motion 1 An object is said to be at rest, if the position of the object does not change with time with respect to its surroundings An object is said to be in motion, if its position changes
Horizontal Motion 1 An object is said to be at rest, if the position of the object does not change with time with respect to its surroundings An object is said to be in motion, if its position changes
