A FEW E-COMMERCE APPLICATIONS. CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography. This is based on Chapter 9 of Trappe and Washington
|
|
|
- Darrell Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A FEW E-COMMERCE APPLICATIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 9 of Trappe and Washington
2 E-COMMERCE: SET SET = Secure Electronic Transaction Consider a credit card transaction over the net. We want: Authenticity No impersonations. No forgeries. Integrity Documents cannot be altered after the fact. Privacy The details of the transaction should be private. Security Credit card numbers & the like must be protected. SET - a collection of crypto protocols for credit card transactions ( 1997) 1
3 Characters Cardholder Merchant Bank SET EXAMPLE H - a public hash function PKC - say RSA These guys don t trust one another Encryption/Decryption Functions E C E M E B Public Private D C D M D B Cardholder GSO - goods and services order (cardholder s name, merchant s name, prices, etc.) PI - payment instructions (merchant s name, card number, total price, etc.) 2
4 SET EXAMPLE CONTINUED Q: Who knows what from the transactions? Cardholder Computes GSO md = H(E M (GSO)) PI md = H(E B (PI)) PO md = H(PI md GSO md ) DS = D C (PO md ) Sends E M (GSO), DS, PI md, E B (PI) to Merchant Merchant (on receiving E M (GSO), DS, PI md, E B (PI)) Computes Checks gso md gso md = H(E M (GSO)) b = H(PI md gso md )? = H(EM (gso)) & b? = c Sends GSO md, E B (PI), DS to the Bank gso = D M (E M (GSO)) c = E C (DS) 3
5 SET EXAMPLE, CONTINUED Bank (on receiving GSO md, E B (PI), DS) Computes Checks b? = c pi md = H(E B (PI)) c = E C (DS) pi = D B (E B (PI)) b = H(pi md GSO md ) Sends E M (a payment auth. + signature) to Merchant. Merchant Sends E C (receipt + signature) to Cardholder. 4
6 DIGITAL CASH Okamoto & Ohta s Criteria Cash can be sent securely through computer networks Cash cannot be copied or reused. The spender can remain anonymous neither the merchant nor the bank can id the spender The transactions can be done off-line the bank does not have to be involved. Cash can be transfered to others. Cash can be divided into smaller amounts. 5
7 Characters BRANDS S DIGITAL CASH SCHEME Bank Spender Merchant Central Authority Central Authority Chooses: Eve L. Dewar A prime p q = (p 1)/2 is also prime. α a primitive element of Z p. g = α 2 (mod p). (So: g e 1 g e 2 (mod p) e 1 e 2 (mod q)) e 1, e 2 Z p 1 secret exponents. g 1 = g e 1 and g 2 = g e 2. H: Z 5 Z q and H 0 : Z 4 Z q. Hash functions Public: p, q, g, g 1, g 2, H, and H 0. Private: e 1 and e 2 6
8 BRANDS S DIGITAL CASH: THE SETUP CONTINUED The Bank Chooses x ran Z q The bank s private ID Computes h = g x, h 1 = g1 x, and h 2 = g2 x. (All (mod p)) h, h 1, h 2 the bank s public ID The Spender Chooses u ran Z q The spender s private ID Computes I = g1 u (mod p) & sends I to the bank. The Bank Saves I + info on the spender Computes z = (Ig 2 ) x (mod p) and sends z to the spender. The Merchant Chooses an ID number M and sends it to the bank. 7
9 Coin (A, B, z, a, b, r) Z 6 CREATING A COIN Spender Asks bank for a coin and sends ID I. Bank Chooses: w ran Z q and computes: Sends g w and β to the spender. In number theory we trust. g w g w β (Ig 2 ) w Spender Chooses (s, x 1, x 2, α 1, α 2 ) ran Z 5 Computes: A (Ig 2 ) s B g x } 1 1 gx 2 2 z (z ) s a g α 1 w g α 2 b β sα 1A α 2 A=1 not allowed. } (mod p) (mod p) 8
10 CREATING A COIN, CONTINUED Spender continued Computes c α 1 1 H(A, B, z, a, b) (mod q). Sends c to the bank. Bank Computes c 1 (c x + w) (mod q). Sends c 1 to the spender. Spender Computes r (α 1 c 1 + α 2 ) (mod q). The coin (A, B, z, a, b, r) is complete. The amount of the coin is removed from the spender s bank account. 9
11 SPENDING THE COIN Spender Gives the coin (A, B, z, a, b, r) to the merchant. Merchant g r ah H(A,B,z,a,b) Checks: A r z H(A,B,z,a,b) (Check on board) b (mod q) Computes d = H 0 (A, B, M, t), where t = a time stamp. Sends d to spender. Spender Computes r 1 d u s + x 1 r 2 d s + x 2 Sends r 1 and r 2 to merchant. } (mod q) Merchant Checks: g r 1 1 gr 2 2 Ad B (mod p) (Check on board) Accepts the coint iff this holds. 10
12 DEPOSITING THE COIN IN THE BANK Merchant Sends (A, B, z, a, b, r) and (r 1, r 2, d) to the bank. Bank Checks that the coin has not yet be deposited. Fraud control (If it has, call the cops.) Checks that g r a h H(A,B,z,a,b) A r z H(A,B,z,a,b) b g r 1 1 gr 2 2 Ad B Accepts the coin iff these check out. (mod p) 11
13 FRAUD CONTROL: I The spender tries to spend the same coin with the merchant and the vendor. Merchant Sends the coin and (r 1, r 2, d) to the bank. Vendor Sends the coin and (r 1, r 2, d ) to the bank. Bank Since r 1 r 1 us(d d ) (mod q) r 2 r 2 s(d d ) (mod q) we have u (r 1 r 1 )(r 2 r 2 ) 1 (mod q) I g1 u (mod q) the ID of the spender 12
14 FRAUD CONTROL: II The merchant tries to deposit the same coin twice Once with (r 1, r 2, d) legit Once with (r 1, r 2, d ) forged This is hard to do. The merchant has to produce r 1, r 2, and d g r 1 1 gr 2 2 Ad B (mod p). 13
15 FRAUD CONTROL: III Someone tries to make an unauthorized coin This requires finding numbers } g r a h H(A,B,z,a,b) A r z H(A,B,z,a,b) b (mod p) } Discrete logs and worse! Eve L. Dewer dot com receives a coin from the spender and tries to spend the coin with the merchant Merchant Computes d for Eve, which is unlikely to equal d. Etc. see text 14
16 ANONYMITY The spender never needs to show the merchant an ID. The bank never sees the values of A, B, z, a, b, r until the coin is deposited. the bank and the merchant cannot figure out the ID of the spender unless there is double spending. See text for fuller details 15
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS. CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography
 SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
ECash and Anonymous Credentials
 ECash and Anonymous Credentials CS/ECE 598MAN: Applied Cryptography Nikita Borisov November 9, 2009 1 E-cash Chaum s E-cash Offline E-cash 2 Anonymous Credentials e-cash-based Credentials Brands Credentials
ECash and Anonymous Credentials CS/ECE 598MAN: Applied Cryptography Nikita Borisov November 9, 2009 1 E-cash Chaum s E-cash Offline E-cash 2 Anonymous Credentials e-cash-based Credentials Brands Credentials
Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 13
 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 13 Benny Pinkas June 5, 2011 Introduction to Cryptography, Benny Pinkas page 1 Electronic cash June 5, 2011 Introduction to Cryptography, Benny Pinkas page 2 Simple
Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 13 Benny Pinkas June 5, 2011 Introduction to Cryptography, Benny Pinkas page 1 Electronic cash June 5, 2011 Introduction to Cryptography, Benny Pinkas page 2 Simple
is caused by the urgent need to protect against account-holders who doublespend their electronic cash, since hardly anything is easier to copy than di
 Untraceable O-line Cash in Wallets with Observers (Extended abstract) Stefan Brands CWI, PO Box 4079 Amsterdam, The Netherlands. E-mail: brands@cwi.nl Abstract. Incorporating the property of untraceability
Untraceable O-line Cash in Wallets with Observers (Extended abstract) Stefan Brands CWI, PO Box 4079 Amsterdam, The Netherlands. E-mail: brands@cwi.nl Abstract. Incorporating the property of untraceability
Fairness realized with Observer
 Fairness realized with Observer Heike Neumann Mathematical Institute University of Giessen Arndtstr. 2 G-35392 Giessen Heike.B.Neumann@math.uni-giessen.de Thomas Schwarzpaul Mathematical Institute University
Fairness realized with Observer Heike Neumann Mathematical Institute University of Giessen Arndtstr. 2 G-35392 Giessen Heike.B.Neumann@math.uni-giessen.de Thomas Schwarzpaul Mathematical Institute University
Divisible E-cash Made Practical
 Divisible E-cash Made Practical Sébastien Canard (1), David Pointcheval (2), Olivier Sanders (1,2) and Jacques Traoré (1) (1) Orange Labs, Caen, France (2) École Normale Supérieure, CNRS & INRIA, Paris,
Divisible E-cash Made Practical Sébastien Canard (1), David Pointcheval (2), Olivier Sanders (1,2) and Jacques Traoré (1) (1) Orange Labs, Caen, France (2) École Normale Supérieure, CNRS & INRIA, Paris,
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model
 Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Cryptographical Security in the Quantum Random Oracle Model Center for Advanced Security Research Darmstadt (CASED) - TU Darmstadt, Germany June, 21st, 2012 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security. Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography
 CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography 1 Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange 2 Diffie-Hellman Protocol For negotiating a shared secret key using only public communication
CIS 6930/4930 Computer and Network Security Topic 5.2 Public Key Cryptography 1 Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange 2 Diffie-Hellman Protocol For negotiating a shared secret key using only public communication
Chapter 7: Signature Schemes. COMP Lih-Yuan Deng
 Chapter 7: Signature Schemes COMP 7120-8120 Lih-Yuan Deng lihdeng@memphis.edu Overview Introduction Security requirements for signature schemes ElGamal signature scheme Variants of ElGamal signature scheme
Chapter 7: Signature Schemes COMP 7120-8120 Lih-Yuan Deng lihdeng@memphis.edu Overview Introduction Security requirements for signature schemes ElGamal signature scheme Variants of ElGamal signature scheme
18734: Foundations of Privacy. Anonymous Cash. Anupam Datta. CMU Fall 2018
 18734: Foundations of Privacy Anonymous Cash Anupam Datta CMU Fall 2018 Today: Electronic Cash Goals Alice can ask for Bank to issue coins from her account. Alice can spend coins. Bank cannot track what
18734: Foundations of Privacy Anonymous Cash Anupam Datta CMU Fall 2018 Today: Electronic Cash Goals Alice can ask for Bank to issue coins from her account. Alice can spend coins. Bank cannot track what
Blind Signature Protocol Based on Difficulty of. Simultaneous Solving Two Difficult Problems
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 202, no. 39, 6903-690 Blind Signature Protocol Based on Difficulty of Simultaneous Solving Two Difficult Problems N. H. Minh, D. V. Binh 2, N. T. Giang 3 and N. A.
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 202, no. 39, 6903-690 Blind Signature Protocol Based on Difficulty of Simultaneous Solving Two Difficult Problems N. H. Minh, D. V. Binh 2, N. T. Giang 3 and N. A.
INTRODUCTION N A S D A Q - U T I L I S I N G L I N Q B L O C K C H A I N L E D G E R T E C H N O L O G Y S I N C E
 currency as means of payment in retail, e -commerce a 1 2 INTRODUCTION I N T E R N A T I O N A L M A R K E T S H A V E A C C E P T E D A N D R E C O G N I S E D C R Y P T O C U R R E N C I E S A N D B
currency as means of payment in retail, e -commerce a 1 2 INTRODUCTION I N T E R N A T I O N A L M A R K E T S H A V E A C C E P T E D A N D R E C O G N I S E D C R Y P T O C U R R E N C I E S A N D B
Lecture 10: Zero-Knowledge Proofs
 Lecture 10: Zero-Knowledge Proofs Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Applebaum Tel-Aviv University Fall Semester, 2011 12 Some of these slides are based on note by Boaz Barak. Quo vadis? Eo Romam
Lecture 10: Zero-Knowledge Proofs Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Applebaum Tel-Aviv University Fall Semester, 2011 12 Some of these slides are based on note by Boaz Barak. Quo vadis? Eo Romam
Question: Total Points: Score:
 University of California, Irvine COMPSCI 134: Elements of Cryptography and Computer and Network Security Midterm Exam (Fall 2016) Duration: 90 minutes November 2, 2016, 7pm-8:30pm Name (First, Last): Please
University of California, Irvine COMPSCI 134: Elements of Cryptography and Computer and Network Security Midterm Exam (Fall 2016) Duration: 90 minutes November 2, 2016, 7pm-8:30pm Name (First, Last): Please
Introduction to Modern Cryptography. Benny Chor
 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor RSA: Review and Properties Factoring Algorithms Trapdoor One Way Functions PKC Based on Discrete Logs (Elgamal) Signature Schemes Lecture 8 Tel-Aviv University
Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor RSA: Review and Properties Factoring Algorithms Trapdoor One Way Functions PKC Based on Discrete Logs (Elgamal) Signature Schemes Lecture 8 Tel-Aviv University
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 October 7, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 11 1/37 Digital Signature Algorithms Signatures from commutative cryptosystems Signatures from
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 11 October 7, 2015 CPSC 467, Lecture 11 1/37 Digital Signature Algorithms Signatures from commutative cryptosystems Signatures from
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018 Secret Sharing Vault should only open if both Alice and Bob are present Vault should only open if Alice, Bob, and Charlie are
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2018 Secret Sharing Vault should only open if both Alice and Bob are present Vault should only open if Alice, Bob, and Charlie are
Cryptology. Vilius Stakėnas autumn
 Cryptology Vilius Stakėnas 2010 autumn 2.22 Cryptographic protocols 2 Key distribution............................................ 3 Zero-knowledge proofs...................................... 4 ZKP concept.............................................
Cryptology Vilius Stakėnas 2010 autumn 2.22 Cryptographic protocols 2 Key distribution............................................ 3 Zero-knowledge proofs...................................... 4 ZKP concept.............................................
Lecture Notes. (electronic money/cash) Michael Nüsken b-it. IPEC winter 2008
 Lecture Notes ee (electronic money/cash) Michael Nüsken b-it (Bonn-Aachen International Center for Information Technology) IPEC winter 2008 c 2008 Michael Nüsken Workshop
Lecture Notes ee (electronic money/cash) Michael Nüsken b-it (Bonn-Aachen International Center for Information Technology) IPEC winter 2008 c 2008 Michael Nüsken Workshop
ABSTRACT. Haejung Park, Master of Arts, Department of Mathematics
 ABSTRACT Title of thesis: VARIOUS ASPECTS OF DIGITAL CASH Haejung Park, Master of Arts, 2008 Thesis directed by: Professor Lawrence C. Washington Department of Mathematics In this thesis, we study various
ABSTRACT Title of thesis: VARIOUS ASPECTS OF DIGITAL CASH Haejung Park, Master of Arts, 2008 Thesis directed by: Professor Lawrence C. Washington Department of Mathematics In this thesis, we study various
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Previously Digital Signatures Algorithms: Gen() à (sk,pk) Sign(sk,m) à σ Ver(pk,m,σ) à 0/1 Correctness: Pr[Ver(pk,m,Sign(sk,m))=1:
Uncloneable Quantum Money
 1 Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo Joint work with Michele Mosca CQISC 2006 1 Supported by NSERC, Sun Microsystems, CIAR, CFI, CSE, MITACS, ORDCF. Outline Introduction Requirements
1 Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo Joint work with Michele Mosca CQISC 2006 1 Supported by NSERC, Sun Microsystems, CIAR, CFI, CSE, MITACS, ORDCF. Outline Introduction Requirements
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 Outline Authentication CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Lecture 18 Michael J. Fischer Department of Computer Science Yale University March 29, 2010 Michael J. Fischer CPSC 467b, Lecture 18
Outline Authentication CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Lecture 18 Michael J. Fischer Department of Computer Science Yale University March 29, 2010 Michael J. Fischer CPSC 467b, Lecture 18
Cryptographic e-cash. Jan Camenisch. IBM Research ibm.biz/jancamenisch. IACR Summerschool Blockchain Technologies
 IACR Summerschool Blockchain Technologies Cryptographic e-cash Jan Camenisch IBM Research Zurich @JanCamenisch ibm.biz/jancamenisch ecash scenario & requirements Bank Withdrawal User Spend Deposit Merchant
IACR Summerschool Blockchain Technologies Cryptographic e-cash Jan Camenisch IBM Research Zurich @JanCamenisch ibm.biz/jancamenisch ecash scenario & requirements Bank Withdrawal User Spend Deposit Merchant
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Can I still get paid via direct deposit? Can I use e- wallet to pay for USANA auto ship orders? Can I use e- wallet to pay for USANA products? Can I use e- wallet to pay for
Frequently Asked Questions Can I still get paid via direct deposit? Can I use e- wallet to pay for USANA auto ship orders? Can I use e- wallet to pay for USANA products? Can I use e- wallet to pay for
Overview. Public Key Algorithms II
 Public Key Algorithms II Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70810 Durresi@csc.lsu.Edu These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc4601-04/ Louisiana State
Public Key Algorithms II Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70810 Durresi@csc.lsu.Edu These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc4601-04/ Louisiana State
A Knapsack Cryptosystem Based on The Discrete Logarithm Problem
 A Knapsack Cryptosystem Based on The Discrete Logarithm Problem By K.H. Rahouma Electrical Technology Department Technical College in Riyadh Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia E-mail: kamel_rahouma@yahoo.com
A Knapsack Cryptosystem Based on The Discrete Logarithm Problem By K.H. Rahouma Electrical Technology Department Technical College in Riyadh Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia E-mail: kamel_rahouma@yahoo.com
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011
 ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
Colluding Attacks to a Payment Protocol and Two Signature Exchange Schemes
 Colluding Attacks to a Payment Protocol and Two Signature Exchange Schemes Feng Bao Institute for Infocomm Research 21 Heng Mui Keng Terrace, Singapore 119613 Email: baofeng@i2r.a-star.edu.sg Abstract.
Colluding Attacks to a Payment Protocol and Two Signature Exchange Schemes Feng Bao Institute for Infocomm Research 21 Heng Mui Keng Terrace, Singapore 119613 Email: baofeng@i2r.a-star.edu.sg Abstract.
Theme : Cryptography. Instructor : Prof. C Pandu Rangan. Speaker : Arun Moorthy CS
 1 C Theme : Cryptography Instructor : Prof. C Pandu Rangan Speaker : Arun Moorthy 93115 CS 2 RSA Cryptosystem Outline of the Talk! Introduction to RSA! Working of the RSA system and associated terminology!
1 C Theme : Cryptography Instructor : Prof. C Pandu Rangan Speaker : Arun Moorthy 93115 CS 2 RSA Cryptosystem Outline of the Talk! Introduction to RSA! Working of the RSA system and associated terminology!
Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography
 Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography Thomas Johansson T. Johansson (Lund University) 1 / 44 Key distribution Symmetric key cryptography: Alice and Bob share a common secret key. Some means
Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography Thomas Johansson T. Johansson (Lund University) 1 / 44 Key distribution Symmetric key cryptography: Alice and Bob share a common secret key. Some means
Lecture V : Public Key Cryptography
 Lecture V : Public Key Cryptography Internet Security: Principles & Practices John K. Zao, PhD (Harvard) SMIEEE Amir Rezapoor Computer Science Department, National Chiao Tung University 2 Outline Functional
Lecture V : Public Key Cryptography Internet Security: Principles & Practices John K. Zao, PhD (Harvard) SMIEEE Amir Rezapoor Computer Science Department, National Chiao Tung University 2 Outline Functional
Exam Security January 19, :30 11:30
 Exam Security January 19, 2016. 8:30 11:30 You can score a maximum of 100. Each question indicates how many it is worth. You are NOT allowed to use books or notes, or a (smart) phone. You may answer in
Exam Security January 19, 2016. 8:30 11:30 You can score a maximum of 100. Each question indicates how many it is worth. You are NOT allowed to use books or notes, or a (smart) phone. You may answer in
Network Security Technology Spring, 2018 Tutorial 3, Week 4 (March 23) Due Date: March 30
 Network Security Technology Spring, 2018 Tutorial 3, Week 4 (March 23) LIU Zhen Due Date: March 30 Questions: 1. RSA (20 Points) Assume that we use RSA with the prime numbers p = 17 and q = 23. (a) Calculate
Network Security Technology Spring, 2018 Tutorial 3, Week 4 (March 23) LIU Zhen Due Date: March 30 Questions: 1. RSA (20 Points) Assume that we use RSA with the prime numbers p = 17 and q = 23. (a) Calculate
Practice Final Exam Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017
 Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
Practice Final Exam Name: Winter 2017, CS 485/585 Crypto March 14, 2017 Portland State University Prof. Fang Song Instructions This exam contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and 5 questions. Total
Public-Key Cryptosystems CHAPTER 4
 Public-Key Cryptosystems CHAPTER 4 Introduction How to distribute the cryptographic keys? Naïve Solution Naïve Solution Give every user P i a separate random key K ij to communicate with every P j. Disadvantage:
Public-Key Cryptosystems CHAPTER 4 Introduction How to distribute the cryptographic keys? Naïve Solution Naïve Solution Give every user P i a separate random key K ij to communicate with every P j. Disadvantage:
Blind Collective Signature Protocol
 Computer Science Journal of Moldova, vol.19, no.1(55), 2011 Blind Collective Signature Protocol Nikolay A. Moldovyan Abstract Using the digital signature (DS) scheme specified by Belarusian DS standard
Computer Science Journal of Moldova, vol.19, no.1(55), 2011 Blind Collective Signature Protocol Nikolay A. Moldovyan Abstract Using the digital signature (DS) scheme specified by Belarusian DS standard
Digital Signatures. p1.
 Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
II. Digital signatures
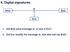 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
Dan Boneh. Introduction. Course Overview
 Online Cryptography Course Introduction Course Overview Welcome Course objectives: Learn how crypto primitives work Learn how to use them correctly and reason about security My recommendations: Take notes
Online Cryptography Course Introduction Course Overview Welcome Course objectives: Learn how crypto primitives work Learn how to use them correctly and reason about security My recommendations: Take notes
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 18 November 6, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 18 1/52 Authentication While Preventing Impersonation Challenge-response authentication protocols
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 18 November 6, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 18 1/52 Authentication While Preventing Impersonation Challenge-response authentication protocols
Unlinkable Divisible Electronic Cash
 Unlinkable Divisible Electronic Cash Toru Nakanishi and Yuji Sugiyama Department of Communication Network Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University, 3-1-1 Tsushimanaka, Okayama 700-8530,
Unlinkable Divisible Electronic Cash Toru Nakanishi and Yuji Sugiyama Department of Communication Network Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University, 3-1-1 Tsushimanaka, Okayama 700-8530,
Cryptanalysis of Threshold-Multisignature Schemes
 Cryptanalysis of Threshold-Multisignature Schemes Lifeng Guo Institute of Systems Science, Academy of Mathematics and System Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, P.R. China E-mail address:
Cryptanalysis of Threshold-Multisignature Schemes Lifeng Guo Institute of Systems Science, Academy of Mathematics and System Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, P.R. China E-mail address:
Lecture 10. Public Key Cryptography: Encryption + Signatures. Identification
 Lecture 10 Public Key Cryptography: Encryption + Signatures 1 Identification Public key cryptography can be also used for IDENTIFICATION Identification is an interactive protocol whereby one party: prover
Lecture 10 Public Key Cryptography: Encryption + Signatures 1 Identification Public key cryptography can be also used for IDENTIFICATION Identification is an interactive protocol whereby one party: prover
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK
 George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
George Danezis Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
Group Blind Digital Signatures: A Scalable Solution to Electronic Cash
 Group Blind Digital Signatures: A Scalable Solution to Electronic Cash Anna Lysyanskaya 1 and Zulfikar Ramzan 1 Laboratory for Computer Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge MA 02139,
Group Blind Digital Signatures: A Scalable Solution to Electronic Cash Anna Lysyanskaya 1 and Zulfikar Ramzan 1 Laboratory for Computer Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge MA 02139,
Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 11
 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 11 January 10, 2017 Instructor: Benny Chor Teaching Assistant: Orit Moskovich School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv University Fall Semester, 2016 17 Tuesday 12:00
Introduction to Modern Cryptography Lecture 11 January 10, 2017 Instructor: Benny Chor Teaching Assistant: Orit Moskovich School of Computer Science Tel-Aviv University Fall Semester, 2016 17 Tuesday 12:00
Dr George Danezis University College London, UK
 Dr George Danezis University College London, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
Dr George Danezis University College London, UK Identity as a proxy to check credentials Username decides access in Access Control Matrix Sometime it leaks too much information Real world examples Tickets
New Variant of ElGamal Signature Scheme
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 2010, no. 34, 1653-1662 New Variant of ElGamal Signature Scheme Omar Khadir Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science and Technology University of Hassan II-Mohammedia,
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 2010, no. 34, 1653-1662 New Variant of ElGamal Signature Scheme Omar Khadir Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science and Technology University of Hassan II-Mohammedia,
Number Theory in Cryptography
 Number Theory in Cryptography Introduction September 20, 2006 Universidad de los Andes 1 Guessing Numbers 2 Guessing Numbers (person x) (last 6 digits of phone number of x) 3 Guessing Numbers (person x)
Number Theory in Cryptography Introduction September 20, 2006 Universidad de los Andes 1 Guessing Numbers 2 Guessing Numbers (person x) (last 6 digits of phone number of x) 3 Guessing Numbers (person x)
MATH 158 FINAL EXAM 20 DECEMBER 2016
 MATH 158 FINAL EXAM 20 DECEMBER 2016 Name : The exam is double-sided. Make sure to read both sides of each page. The time limit is three hours. No calculators are permitted. You are permitted one page
MATH 158 FINAL EXAM 20 DECEMBER 2016 Name : The exam is double-sided. Make sure to read both sides of each page. The time limit is three hours. No calculators are permitted. You are permitted one page
Lecture 18 - Secret Sharing, Visual Cryptography, Distributed Signatures
 Lecture 18 - Secret Sharing, Visual Cryptography, Distributed Signatures Boaz Barak November 27, 2007 Quick review of homework 7 Existence of a CPA-secure public key encryption scheme such that oracle
Lecture 18 - Secret Sharing, Visual Cryptography, Distributed Signatures Boaz Barak November 27, 2007 Quick review of homework 7 Existence of a CPA-secure public key encryption scheme such that oracle
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05
 Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05 Fangguo Zhang 1 and Xiaofeng Chen 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sun Yat-sen
Cryptanalysis and improvement of an ID-based ad-hoc anonymous identification scheme at CT-RSA 05 Fangguo Zhang 1 and Xiaofeng Chen 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sun Yat-sen
Insecurity of An Anonymous Authentication For Privacy-preserving IoT Target-driven Applications
 Insecurity of An Anonymous Authentication For Privacy-preserving IoT Target-driven Applications Xi-Jun Lin and Lin Sun November 8, 03 Abstract: The Internet of Things (IoT) will be formed by smart objects
Insecurity of An Anonymous Authentication For Privacy-preserving IoT Target-driven Applications Xi-Jun Lin and Lin Sun November 8, 03 Abstract: The Internet of Things (IoT) will be formed by smart objects
Elliptic Curve Cryptography
 Areas for Discussion Elliptic Curve Cryptography Joseph Spring Department of Computer Science 7COM1027 - Distributed Systems Security Lecture - Elliptic Curves 1 1 Motivation Elliptic Curves Security of
Areas for Discussion Elliptic Curve Cryptography Joseph Spring Department of Computer Science 7COM1027 - Distributed Systems Security Lecture - Elliptic Curves 1 1 Motivation Elliptic Curves Security of
Security Analysis of Some Batch Verifying Signatures from Pairings
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.3, No.2, PP.138 143, Sept. 2006 (http://ijns.nchu.edu.tw/) 138 Security Analysis of Some Batch Verifying Signatures from Pairings Tianjie Cao 1,2,3, Dongdai
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.3, No.2, PP.138 143, Sept. 2006 (http://ijns.nchu.edu.tw/) 138 Security Analysis of Some Batch Verifying Signatures from Pairings Tianjie Cao 1,2,3, Dongdai
Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers
 Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers Computer Security Lecture 7 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 31st January 2011 Outline Background RSA Diffie-Hellman ElGamal Summary Outline
Cryptography IV: Asymmetric Ciphers Computer Security Lecture 7 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 31st January 2011 Outline Background RSA Diffie-Hellman ElGamal Summary Outline
Chapter 4 Asymmetric Cryptography
 Chapter 4 Asymmetric Cryptography Introduction Encryption: RSA Key Exchange: Diffie-Hellman [NetSec/SysSec], WS 2008/2009 4.1 Asymmetric Cryptography General idea: Use two different keys -K and +K for
Chapter 4 Asymmetric Cryptography Introduction Encryption: RSA Key Exchange: Diffie-Hellman [NetSec/SysSec], WS 2008/2009 4.1 Asymmetric Cryptography General idea: Use two different keys -K and +K for
Asymmetric Cryptography
 Asymmetric Cryptography Chapter 4 Asymmetric Cryptography Introduction Encryption: RSA Key Exchange: Diffie-Hellman General idea: Use two different keys -K and +K for encryption and decryption Given a
Asymmetric Cryptography Chapter 4 Asymmetric Cryptography Introduction Encryption: RSA Key Exchange: Diffie-Hellman General idea: Use two different keys -K and +K for encryption and decryption Given a
Lecture Notes 15 : Voting, Homomorphic Encryption
 6.857 Computer and Network Security October 29, 2002 Lecture Notes 15 : Voting, Homomorphic Encryption Lecturer: Ron Rivest Scribe: Ledlie/Ortiz/Paskalev/Zhao 1 Introduction The big picture and where we
6.857 Computer and Network Security October 29, 2002 Lecture Notes 15 : Voting, Homomorphic Encryption Lecturer: Ron Rivest Scribe: Ledlie/Ortiz/Paskalev/Zhao 1 Introduction The big picture and where we
Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures
 Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures v 1. Introduction to Public-key Cryptography 2. Example of Public-key Algorithm: Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange Scheme 3. RSA Encryption and Digital
Chapter 8 Public-key Cryptography and Digital Signatures v 1. Introduction to Public-key Cryptography 2. Example of Public-key Algorithm: Diffie- Hellman Key Exchange Scheme 3. RSA Encryption and Digital
Cryptography. Course 1: Remainder: RSA. Jean-Sébastien Coron. September 21, Université du Luxembourg
 Course 1: Remainder: RSA Université du Luxembourg September 21, 2010 Public-key encryption Public-key encryption: two keys. One key is made public and used to encrypt. The other key is kept private and
Course 1: Remainder: RSA Université du Luxembourg September 21, 2010 Public-key encryption Public-key encryption: two keys. One key is made public and used to encrypt. The other key is kept private and
Digital Signatures. Adam O Neill based on
 Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
Digital Signatures Adam O Neill based on http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~mihir/cse207/ Signing by hand COSMO ALICE ALICE Pay Bob $100 Cosmo Alice Alice Bank =? no Don t yes pay Bob Signing electronically SIGFILE
A new message authentication code based on the non-associativity of quasigroups. Kristen Ann Meyer. A dissertation submitted to the graduate faculty
 A new message authentication code based on the non-associativity of quasigroups by Kristen Ann Meyer A dissertation submitted to the graduate faculty in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
A new message authentication code based on the non-associativity of quasigroups by Kristen Ann Meyer A dissertation submitted to the graduate faculty in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the
A New RSA-Based Signature Scheme
 1 / 13 A New RSA-Based Signature Scheme Sven Schäge, Jörg Schwenk Horst Görtz Institute for IT-Security Africacrypt 2010 2 / 13 RSA-Based Signature Schemes Naïve RSA signature scheme not secure under the
1 / 13 A New RSA-Based Signature Scheme Sven Schäge, Jörg Schwenk Horst Görtz Institute for IT-Security Africacrypt 2010 2 / 13 RSA-Based Signature Schemes Naïve RSA signature scheme not secure under the
P4R: Privacy-Preserving Pre-Payments with Refunds for Transportation Systems
 P4R: Privacy-Preserving Pre-Payments with Refunds for Transportation Systems ndy Rupp1, Gesine Hinterwälder2, Foteini3 Baldimtsi, Christof Paar2,4 Karlsruhe Institute of Technology University of Massachusetts
P4R: Privacy-Preserving Pre-Payments with Refunds for Transportation Systems ndy Rupp1, Gesine Hinterwälder2, Foteini3 Baldimtsi, Christof Paar2,4 Karlsruhe Institute of Technology University of Massachusetts
CHAPTER 6: OTHER CRYPTOSYSTEMS, PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS and HASH FUNCTIONS. Part VI
 CHAPTER 6: OTHER CRYPTOSYSTEMS, PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMER GENERATORS and HASH FUNCTIONS Part VI Public-key cryptosystems, II. Other cryptosystems, security, PRG, hash functions A large number of interesting
CHAPTER 6: OTHER CRYPTOSYSTEMS, PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMER GENERATORS and HASH FUNCTIONS Part VI Public-key cryptosystems, II. Other cryptosystems, security, PRG, hash functions A large number of interesting
On the Big Gap Between p and q in DSA
 On the Big Gap Between p and in DSA Zhengjun Cao Department of Mathematics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, 200444. caozhj@shu.edu.cn Abstract We introduce a message attack against DSA and show that
On the Big Gap Between p and in DSA Zhengjun Cao Department of Mathematics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China, 200444. caozhj@shu.edu.cn Abstract We introduce a message attack against DSA and show that
Public Key Cryptography
 T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F B R I T I S H C O L U M B I A Public Key Cryptography EECE 412 1 What is it? Two keys Sender uses recipient s public key to encrypt Receiver uses his private key to decrypt
T H E U N I V E R S I T Y O F B R I T I S H C O L U M B I A Public Key Cryptography EECE 412 1 What is it? Two keys Sender uses recipient s public key to encrypt Receiver uses his private key to decrypt
A METHOD FOR REVOCATION IN GROUP SIGNATURE SCHEMES
 Mathematica Moravica Vol. 7 (2003), 51 59 A METHOD FOR REVOCATION IN GROUP SIGNATURE SCHEMES Constantin Popescu Abstract. A group signature scheme allows any group member to sign on behalf of the group
Mathematica Moravica Vol. 7 (2003), 51 59 A METHOD FOR REVOCATION IN GROUP SIGNATURE SCHEMES Constantin Popescu Abstract. A group signature scheme allows any group member to sign on behalf of the group
Some Security Comparisons of GOST R and ECDSA Signature Schemes
 Some Security Comparisons of GOST R 34.10-2012 and ECDSA Signature Schemes Trieu Quang Phong Nguyen Quoc Toan Institute of Cryptography Science and Technology Gover. Info. Security Committee, Viet Nam
Some Security Comparisons of GOST R 34.10-2012 and ECDSA Signature Schemes Trieu Quang Phong Nguyen Quoc Toan Institute of Cryptography Science and Technology Gover. Info. Security Committee, Viet Nam
Applied cryptography
 Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
Applied cryptography Identity-based Cryptography Andreas Hülsing 19 November 2015 1 / 37 The public key problem How to obtain the correct public key of a user? How to check its authenticity? General answer:
Introduction to Cryptography. Susan Hohenberger
 Introduction to Cryptography Susan Hohenberger 1 Cryptography -- from art to science -- more than just encryption -- essential today for non-military applications 2 Symmetric Crypto Shared secret K =>
Introduction to Cryptography Susan Hohenberger 1 Cryptography -- from art to science -- more than just encryption -- essential today for non-military applications 2 Symmetric Crypto Shared secret K =>
L7. Diffie-Hellman (Key Exchange) Protocol. Rocky K. C. Chang, 5 March 2015
 L7. Diffie-Hellman (Key Exchange) Protocol Rocky K. C. Chang, 5 March 2015 1 Outline The basic foundation: multiplicative group modulo prime The basic Diffie-Hellman (DH) protocol The discrete logarithm
L7. Diffie-Hellman (Key Exchange) Protocol Rocky K. C. Chang, 5 March 2015 1 Outline The basic foundation: multiplicative group modulo prime The basic Diffie-Hellman (DH) protocol The discrete logarithm
Improved Algebraic MACs and Practical Keyed-Verification Anonymous Credentials
 Improved Algebraic MACs and Practical Keyed-Verification Anonymous Credentials Amira Barki, Solenn Brunet, Nicolas Desmoulins and Jacques Traoré August 11th, 2016 Selected Areas in Cryptography SAC 2016
Improved Algebraic MACs and Practical Keyed-Verification Anonymous Credentials Amira Barki, Solenn Brunet, Nicolas Desmoulins and Jacques Traoré August 11th, 2016 Selected Areas in Cryptography SAC 2016
Lecture 6. Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography. Constructing CPA-secure ciphers
 1 Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 6 Portland State University Jan. 25, 2018 Lecturer: Fang Song Draft note. Version: February 4, 2018. Email fang.song@pdx.edu for comments and
1 Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 6 Portland State University Jan. 25, 2018 Lecturer: Fang Song Draft note. Version: February 4, 2018. Email fang.song@pdx.edu for comments and
LECTURE NOTES ON Quantum Cryptography
 Department of Software The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON Quantum Cryptography By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@itnet.uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Software The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON Quantum Cryptography By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@itnet.uobabylon.edu.iq
On the Key-collisions in the Signature Schemes
 On the Key-collisions in the Signature Schemes Tomáš Rosa ICZ a.s., Prague, CZ Dept. of Computer Science, FEE, CTU in Prague, CZ tomas.rosa@i.cz Motivation to study k-collisions Def. Non-repudiation [9,10].
On the Key-collisions in the Signature Schemes Tomáš Rosa ICZ a.s., Prague, CZ Dept. of Computer Science, FEE, CTU in Prague, CZ tomas.rosa@i.cz Motivation to study k-collisions Def. Non-repudiation [9,10].
arxiv: v1 [cs.cr] 16 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cr] 16 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.cr] 16 Dec 2015](/thumbs/72/67087738.jpg) A Note on Efficient Algorithms for Secure Outsourcing of Bilinear Pairings arxiv:1512.05413v1 [cs.cr] 16 Dec 2015 Lihua Liu 1 Zhengjun Cao 2 Abstract. We show that the verifying equations in the scheme
A Note on Efficient Algorithms for Secure Outsourcing of Bilinear Pairings arxiv:1512.05413v1 [cs.cr] 16 Dec 2015 Lihua Liu 1 Zhengjun Cao 2 Abstract. We show that the verifying equations in the scheme
18733: Applied Cryptography Anupam Datta (CMU) Course Overview
 18733: Applied Cryptography Anupam Datta (CMU) Course Overview Logistics Introductions Instructor: Anupam Datta Office hours: SV Bldg 23, #208 + Google Hangout (id: danupam) Office hours: Mon 1:30-2:30
18733: Applied Cryptography Anupam Datta (CMU) Course Overview Logistics Introductions Instructor: Anupam Datta Office hours: SV Bldg 23, #208 + Google Hangout (id: danupam) Office hours: Mon 1:30-2:30
CPE 776:DATA SECURITY & CRYPTOGRAPHY. Some Number Theory and Classical Crypto Systems
 CPE 776:DATA SECURITY & CRYPTOGRAPHY Some Number Theory and Classical Crypto Systems Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Computer Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Jordan Some Number Theory
CPE 776:DATA SECURITY & CRYPTOGRAPHY Some Number Theory and Classical Crypto Systems Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Computer Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Jordan Some Number Theory
Threshold Undeniable RSA Signature Scheme
 Threshold Undeniable RSA Signature Scheme Guilin Wang 1, Sihan Qing 1, Mingsheng Wang 1, and Zhanfei Zhou 2 1 Engineering Research Center for Information Security Technology; State Key Laboratory of Information
Threshold Undeniable RSA Signature Scheme Guilin Wang 1, Sihan Qing 1, Mingsheng Wang 1, and Zhanfei Zhou 2 1 Engineering Research Center for Information Security Technology; State Key Laboratory of Information
Untraceable Fair Network Payment Protocols with Off-Line TTP
 Untraceable Fair Network Payment Protocols with Off-Line TTP Chih-Hung Wang Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Chiayi University 300 University Road, Chiayi, Taiwan 600,
Untraceable Fair Network Payment Protocols with Off-Line TTP Chih-Hung Wang Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Chiayi University 300 University Road, Chiayi, Taiwan 600,
MATH UN Midterm 2 November 10, 2016 (75 minutes)
 Name: UNI: Instructor: Shrenik Shah MATH UN3025 - Midterm 2 November 10, 2016 (75 minutes) This examination booklet contains 6 problems. There are 10 sheets of paper including the front cover. This is
Name: UNI: Instructor: Shrenik Shah MATH UN3025 - Midterm 2 November 10, 2016 (75 minutes) This examination booklet contains 6 problems. There are 10 sheets of paper including the front cover. This is
Introduction to Modern Cryptography. Benny Chor
 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor RSA Public Key Encryption Factoring Algorithms Lecture 7 Tel-Aviv University Revised March 1st, 2008 Reminder: The Prime Number Theorem Let π(x) denote the
Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor RSA Public Key Encryption Factoring Algorithms Lecture 7 Tel-Aviv University Revised March 1st, 2008 Reminder: The Prime Number Theorem Let π(x) denote the
Suppose F is a field and a1,..., a6 F. Definition 1. An elliptic curve E over a field F is a curve given by an equation:
 Elliptic Curve Cryptography Jim Royer CIS 428/628: Introduction to Cryptography November 6, 2018 Suppose F is a field and a 1,..., a 6 F. Definition 1. An elliptic curve E over a field F is a curve given
Elliptic Curve Cryptography Jim Royer CIS 428/628: Introduction to Cryptography November 6, 2018 Suppose F is a field and a 1,..., a 6 F. Definition 1. An elliptic curve E over a field F is a curve given
Foundations of Network and Computer Security
 Foundations of Network and Computer Security John Black Lecture #6 Sep 8 th 2005 CSCI 6268/TLEN 5831, Fall 2005 Announcements Quiz #1 later today Still some have not signed up for class mailing list Perhaps
Foundations of Network and Computer Security John Black Lecture #6 Sep 8 th 2005 CSCI 6268/TLEN 5831, Fall 2005 Announcements Quiz #1 later today Still some have not signed up for class mailing list Perhaps
Homework 3 Solutions
 5233/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, Fall 205 Instructor Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 3 Solutions 7-Dec-205 Scribe Amir Rezapour. Consider an unfair coin with head probability 0.5. Assume that the coin
5233/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, Fall 205 Instructor Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 3 Solutions 7-Dec-205 Scribe Amir Rezapour. Consider an unfair coin with head probability 0.5. Assume that the coin
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model. A. Hülsing
 Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Lecture 16 Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko. 1 Digital Signature Schemes. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
Basics in Cryptology. Outline. II Distributed Cryptography. Key Management. Outline. David Pointcheval. ENS Paris 2018
 Basics in Cryptology II Distributed Cryptography David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA ENS Paris 2018 NS/CNRS/INRIA Cascade David Pointcheval 1/26ENS/CNRS/INRIA Cascade David Pointcheval
Basics in Cryptology II Distributed Cryptography David Pointcheval Ecole normale supérieure, CNRS & INRIA ENS Paris 2018 NS/CNRS/INRIA Cascade David Pointcheval 1/26ENS/CNRS/INRIA Cascade David Pointcheval
Post-Quantum Cryptography & Privacy. Andreas Hülsing
 Post-Quantum Cryptography & Privacy Andreas Hülsing Privacy? Too abstract? How to achieve privacy? Under the hood... Public-key crypto ECC RSA DSA Secret-key crypto AES SHA2 SHA1... Combination of both
Post-Quantum Cryptography & Privacy Andreas Hülsing Privacy? Too abstract? How to achieve privacy? Under the hood... Public-key crypto ECC RSA DSA Secret-key crypto AES SHA2 SHA1... Combination of both
Cryptanalysis of a Group Key Transfer Protocol Based on Secret Sharing: Generalization and Countermeasures
 Cryptanalysis of a Group Key Transfer Protocol Based on Secret Sharing: Generalization and Countermeasures Kallepu Raju, Appala Naidu Tentu, V. Ch. Venkaiah Abstract: Group key distribution protocol is
Cryptanalysis of a Group Key Transfer Protocol Based on Secret Sharing: Generalization and Countermeasures Kallepu Raju, Appala Naidu Tentu, V. Ch. Venkaiah Abstract: Group key distribution protocol is
Algorithmic Number Theory and Public-key Cryptography
 Algorithmic Number Theory and Public-key Cryptography Course 3 University of Luxembourg March 22, 2018 The RSA algorithm The RSA algorithm is the most widely-used public-key encryption algorithm Invented
Algorithmic Number Theory and Public-key Cryptography Course 3 University of Luxembourg March 22, 2018 The RSA algorithm The RSA algorithm is the most widely-used public-key encryption algorithm Invented
Notes on Zero Knowledge
 U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 9 Professor Luca Trevisan 4/21/2015 Notes on Zero Knowledge These notes on zero knowledge protocols for quadratic residuosity are based
U.C. Berkeley CS172: Automata, Computability and Complexity Handout 9 Professor Luca Trevisan 4/21/2015 Notes on Zero Knowledge These notes on zero knowledge protocols for quadratic residuosity are based
Winter 2008 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor and Rani Hod. Assignment #2
 0368.3049.01 Winter 2008 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor and Rani Hod Assignment #2 Published Sunday, February 17, 2008 and very slightly revised Feb. 18. Due Tues., March 4, in Rani Hod
0368.3049.01 Winter 2008 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor and Rani Hod Assignment #2 Published Sunday, February 17, 2008 and very slightly revised Feb. 18. Due Tues., March 4, in Rani Hod
2. Cryptography 2.5. ElGamal cryptosystems and Discrete logarithms
 CRYPTOGRAPHY 19 Cryptography 5 ElGamal cryptosystems and Discrete logarithms Definition Let G be a cyclic group of order n and let α be a generator of G For each A G there exists an uniue 0 a n 1 such
CRYPTOGRAPHY 19 Cryptography 5 ElGamal cryptosystems and Discrete logarithms Definition Let G be a cyclic group of order n and let α be a generator of G For each A G there exists an uniue 0 a n 1 such
Risk Management for E-Cash Systems with Partial Real-Time Audit
 Netnomics 3, 119 127, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Risk Management for E-Cash Systems with Partial Real-Time Audit YACOV YACOBI Microsoft Research, One Microsoft
Netnomics 3, 119 127, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Risk Management for E-Cash Systems with Partial Real-Time Audit YACOV YACOBI Microsoft Research, One Microsoft
