A) At each point along the pipe, the volume of fluid passing by is given by dv dt = Av, thus, the two velocities are: v n. + ρgy 1
|
|
|
- Shanon Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1) The horizontal pipe hon in Fig. 1 ha a diameter of 4.8 cm at the ider portion and 3.7 cm at the contriction. Water i floing in the pipe and the dicharge from the pipe i 6.50 x -3 m 3 /. A) Find the flo peed at the ide and narro portion. (8 pt.) B) Find the preure difference beteen thee portion. (6 pt.) C) The difference in height beteen the mercury column in the U-haped tube. The denity of Hg i 13.6 g/cm 3. (6 pt.) A) At each point along the pipe, the volume of fluid paing by i given by dv dt Av, thu, the to velocitie are: v n v 3.7 v 4.8 n 3.59 m/. 6.5x 3 m 3 / 6.04 m/, and π(3.7x m) / 4 B) Uing Bernoulli equation: p ρv 1 + ρgy 1 p + 1 ρv + ρgy, and uing the ame height, the preure difference i jut: 1 ρv 1 1 ρv v 1 (00kg/ m3 )[(6.04m/ ) (3.59m/ ) ] 1.18 x 4 Pa. C) Again, uing Bernoulli equation, but thi time velocitie are zero, thu p ρgh h p ρg 1.18x 4 Pa 8.85 cm. 13.6g/ cm 3 3 kg/ g 9.8m/ 6 m 3 3 / cm
2 ) A 1.-kg monkey rench i pivoted 0.3 m from it center of ma and alloed to ing a a phyical pendulum. The period for mall-angle ocillation i A) What i the moment of inertia of the rench about an axi through the pivot? (6 pt.) B) f the rench i initially diplaced 0.15 radian from it equilibrium poition, hat i the angular peed of the rench a it pae through the equilibrium poition? (6 pt.) C) What i the total energy of the ytem in part B? (6 pt.) A) ω mgd mgdt 4π 1.kg 9.8m/ 0.3m (0.94) 4π 7.9 x - kg m. B) For mall angle, e aume the motion i SHM, thu, Θ(t) Θ o co(ωt +φ ). The initial condition imply that hen Θ(t) 0, the angular velocity ill be given by ωθ o π 0.15rad 1.00 rad/ C) Given that ET+U and i contant, ill calculate at Θ(t) 0, hich give, E 1 dθ dt 1 7.9x kg m (1.00rad / ) 3.95 x - Nm.
3 3) The ound of a hip onar ytem operate at a frequency of 4.0 khz. The peed of ound in ater i 148 m/. The hip i at ret in the ater. A) What i the avelength of the ave emitted by the ource? (6 pt.) B) What i the difference in frequency beteen the directly radiated ave and the ave reflected from a hale traveling directly toard the hip at 4.95m/? (6 pt.) C) The pecific gravity of eaater i 1.03, calculate the Bulk modulu of the eaater. (6 pt.) A) λ v f 148m/ 4x 3 Hz 6.18 cm. B) The hale receive the onar ignal at a frequency of: f 1+ v v f, thi i alo the frequency that the hale remit the ave, hich i detected by the hip no at ' v a frequency of: f f, o the detected frequency, in term of the emitted frequency i jut: v + v f. Thu the frequency difference i jut ' f f f v + v 1 f v 4.95m/ f 4kHz 161 Hz. 148m 4.95m/ C) v B ρ B ρv kg/ m 3 (148m/ ).6 x 9 Pa.
4 4) The lunch hitle of a local mill radiate uniformly in all direction at 0 o C. At a ditance of 50m from the hitle the ound intenity level i 75 db. The frequency i 448 Hz. For 0 o air the denity i 1. kg/m 3, the peed of ound i 344 m/ and the Bulk modulu i 1.4 x 5 Pa. A) What i the preure amplitude at thi ditance? (6 pt.) B) What i the diplacement amplitude? (6 pt.) C) At hat ditance i the ound intenity level 45 db? (6 pt.) A) p max ρv p max ( ρv, and β db log o β ), thu o p max ρv o ( β ) (1.kg/ m 3 )(344m/ )* 1 W / m * x -1 Pa. B) p max BkA A p max Bk p max v Bπf (.61x Pa)(344m/ ) π(1.4x 5 Pa)(448Hz ) 1.39 x -7 m. C) 1 r r r r 75 db 75 db 45 db 1 45 db 75 r 75 o 45 (50m) ( ) 1581 m. o
5 5) (4 pt. for each part.) A) What i required for periodic motion to occur? A retoring force and equilibrium. B) n addition to the requirement of part A) hat ele i required for Simple Harmonic Motion? The retoring force i proportional to diplacement. C) To unique function, g(x,t) and h(x,t) are olution to the ave equation derived in lecture. Will the ne function created by g(x,t)+h(x,t) alo be a olution to thi ave equation? f o, hy? The um g+h atifie the ave equation derived in cla becaue of the principle of linear uperpoition. D) Sound i a longitudinal preure ave traveling through a medium. Do the molecule of the medium move? f o, hat type of motion do they execute? The molecule of the medium execute imple harmonic motion. E) A tring, fixed at both end, vibrate at it 3 rd harmonic frequency. 1) Ho many boundary condition are there? ) Ho many node and antidnode are there? There are boundary condition. There are 4 node and 3 antinode. F) When forced ocillation on a ytem match one of the natural frequencie of the ytem, hat phenomenon occur? Thi i called reonance.
EP225 Note No. 5 Mechanical Waves
 EP5 Note No. 5 Mechanical Wave 5. Introduction Cacade connection of many ma-pring unit conitute a medium for mechanical wave which require that medium tore both kinetic energy aociated with inertia (ma)
EP5 Note No. 5 Mechanical Wave 5. Introduction Cacade connection of many ma-pring unit conitute a medium for mechanical wave which require that medium tore both kinetic energy aociated with inertia (ma)
PHYSICS 126 Fall 2010 Midterm 1
 PHYSICS 16 Fall 010 Midterm 1 Name: SOLUTIONS Student ID: Section Number: Closed book with one sheet of notes and a calculator. Answer the questions in spaces provided on each sheet. If you run out of
PHYSICS 16 Fall 010 Midterm 1 Name: SOLUTIONS Student ID: Section Number: Closed book with one sheet of notes and a calculator. Answer the questions in spaces provided on each sheet. If you run out of
Physics 2. Angular Momentum. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Phyic Angular Momentum For Campu earning Angular Momentum Thi i the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. t quantifie the momentum of a rotating object, or ytem of object. To get the angular momentum,
Phyic Angular Momentum For Campu earning Angular Momentum Thi i the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. t quantifie the momentum of a rotating object, or ytem of object. To get the angular momentum,
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
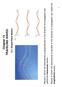 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms,
 43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
Physics 6A. Angular Momentum. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Phyic 6A Angular Momentum For Campu earning Angular Momentum Thi i the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. t quantifie the momentum of a rotating object, or ytem of object. f we imply tranlate the
Phyic 6A Angular Momentum For Campu earning Angular Momentum Thi i the rotational equivalent of linear momentum. t quantifie the momentum of a rotating object, or ytem of object. f we imply tranlate the
Lecture 23 Date:
 Lecture 3 Date: 4.4.16 Plane Wave in Free Space and Good Conductor Power and Poynting Vector Wave Propagation in Loy Dielectric Wave propagating in z-direction and having only x-component i given by: E
Lecture 3 Date: 4.4.16 Plane Wave in Free Space and Good Conductor Power and Poynting Vector Wave Propagation in Loy Dielectric Wave propagating in z-direction and having only x-component i given by: E
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section
 Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Sound waves. Content. Chapter 21. objectives. objectives. When we use Sound Waves. What are sound waves? How they work.
 Chapter 21. Sound wae Content 21.1 Propagation o ound wae 21.2 Source o ound 21.3 Intenity o ound 21.4 Beat 21.5 Doppler eect 1 2 objectie a) explain the propagation o ound wae in air in term o preure
Chapter 21. Sound wae Content 21.1 Propagation o ound wae 21.2 Source o ound 21.3 Intenity o ound 21.4 Beat 21.5 Doppler eect 1 2 objectie a) explain the propagation o ound wae in air in term o preure
Solution The light plates are at the same heights. In balance, the pressure at both plates has to be the same. m g A A A F A = F B.
 43. A piece of metal rests in a toy wood boat floating in water in a bathtub. If the metal is removed from the boat, and kept out of the water, what happens to the water level in the tub? A) It does not
43. A piece of metal rests in a toy wood boat floating in water in a bathtub. If the metal is removed from the boat, and kept out of the water, what happens to the water level in the tub? A) It does not
two equations that govern the motion of the fluid through some medium, like a pipe. These two equations are the
 Fluid and Fluid Mechanic Fluid in motion Dynamic Equation of Continuity After having worked on fluid at ret we turn to a moving fluid To decribe a moving fluid we develop two equation that govern the motion
Fluid and Fluid Mechanic Fluid in motion Dynamic Equation of Continuity After having worked on fluid at ret we turn to a moving fluid To decribe a moving fluid we develop two equation that govern the motion
UNIT # 06 (PART - II)
 EXERCSE. Wae on urface of ater are combination of longitudinal and tranere ae. ( ). m, 5m/, T f 5 UNT # 6 (PRT - ) WVE THEORY. y in t JEE-Phyic ; y 5 in t co t in t co t / / : in t. 6 / m f 5 5 Number
EXERCSE. Wae on urface of ater are combination of longitudinal and tranere ae. ( ). m, 5m/, T f 5 UNT # 6 (PRT - ) WVE THEORY. y in t JEE-Phyic ; y 5 in t co t in t co t / / : in t. 6 / m f 5 5 Number
EELE 3332 Electromagnetic II Chapter 10
 EELE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 10 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Ilamic Univerity of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 01 1 Electromagnetic wave propagation A changing magnetic
EELE 333 Electromagnetic II Chapter 10 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Ilamic Univerity of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Talal Skaik 01 1 Electromagnetic wave propagation A changing magnetic
ANSWERS 391. Chapter 9
 ANSWERS 391 ANSWERS Chapter 9 9.1 1.8 9. (a) From the given graph for a stress of 150 10 6 N m - the strain is 0.00 Approximate yield strength of the material is 3 10 8 N m - 9.3 (a) Material A Strength
ANSWERS 391 ANSWERS Chapter 9 9.1 1.8 9. (a) From the given graph for a stress of 150 10 6 N m - the strain is 0.00 Approximate yield strength of the material is 3 10 8 N m - 9.3 (a) Material A Strength
Mechanics. Free rotational oscillations. LD Physics Leaflets P Measuring with a hand-held stop-clock. Oscillations Torsion pendulum
 Mechanic Ocillation Torion pendulum LD Phyic Leaflet P.5.. Free rotational ocillation Meauring with a hand-held top-clock Object of the experiment g Meauring the amplitude of rotational ocillation a function
Mechanic Ocillation Torion pendulum LD Phyic Leaflet P.5.. Free rotational ocillation Meauring with a hand-held top-clock Object of the experiment g Meauring the amplitude of rotational ocillation a function
1. Basic introduction to electromagnetic field. wave properties and particulate properties.
 Lecture Baic Radiometric Quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation. Objective:. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field:
Lecture Baic Radiometric Quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation. Objective:. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field:
Physics 2212 G Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2018
 Phyic 2212 G Quiz #2 Solution Spring 2018 I. (16 point) A hollow inulating phere ha uniform volume charge denity ρ, inner radiu R, and outer radiu 3R. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a ditance
Phyic 2212 G Quiz #2 Solution Spring 2018 I. (16 point) A hollow inulating phere ha uniform volume charge denity ρ, inner radiu R, and outer radiu 3R. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a ditance
The Influence of Landau Damping on Multi Bunch Instabilities
 Univerität Dortmund The Influence of Landau Damping on Multi Bunch Intabilitie A Baic Coure on Landau Damping + A Few Implication Prof. Dr. Thoma Wei Department of Phyic / Dortmund Univerity Riezlern,
Univerität Dortmund The Influence of Landau Damping on Multi Bunch Intabilitie A Baic Coure on Landau Damping + A Few Implication Prof. Dr. Thoma Wei Department of Phyic / Dortmund Univerity Riezlern,
Bernoulli s equation may be developed as a special form of the momentum or energy equation.
 BERNOULLI S EQUATION Bernoulli equation may be developed a a pecial form of the momentum or energy equation. Here, we will develop it a pecial cae of momentum equation. Conider a teady incompreible flow
BERNOULLI S EQUATION Bernoulli equation may be developed a a pecial form of the momentum or energy equation. Here, we will develop it a pecial cae of momentum equation. Conider a teady incompreible flow
ME 375 EXAM #1 Tuesday February 21, 2006
 ME 375 EXAM #1 Tueday February 1, 006 Diviion Adam 11:30 / Savran :30 (circle one) Name Intruction (1) Thi i a cloed book examination, but you are allowed one 8.5x11 crib heet. () You have one hour to
ME 375 EXAM #1 Tueday February 1, 006 Diviion Adam 11:30 / Savran :30 (circle one) Name Intruction (1) Thi i a cloed book examination, but you are allowed one 8.5x11 crib heet. () You have one hour to
Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics Dynamics Using Pascal s Law = F 1 = F 2 2 = F 2 A 2
 Lecture 24: Archimedes Principle and Bernoulli s Law 1 Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics Dynamics Using Pascal s Law Example 15.1 The hydraulic lift A hydraulic lift consists of a small diameter piston of radius
Lecture 24: Archimedes Principle and Bernoulli s Law 1 Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics Dynamics Using Pascal s Law Example 15.1 The hydraulic lift A hydraulic lift consists of a small diameter piston of radius
MAE 101A. Homework 3 Solutions 2/5/2018
 MAE 101A Homework 3 Solution /5/018 Munon 3.6: What preure gradient along the treamline, /d, i required to accelerate water upward in a vertical pipe at a rate of 30 ft/? What i the anwer if the flow i
MAE 101A Homework 3 Solution /5/018 Munon 3.6: What preure gradient along the treamline, /d, i required to accelerate water upward in a vertical pipe at a rate of 30 ft/? What i the anwer if the flow i
Physics 41 Homework Set 3 Chapter 17 Serway 7 th Edition
 Pyic 41 Homework Set 3 Capter 17 Serway 7 t Edition Q: 1, 4, 5, 6, 9, 1, 14, 15 Quetion *Q17.1 Anwer. Te typically iger denity would by itelf make te peed of ound lower in a olid compared to a ga. Q17.4
Pyic 41 Homework Set 3 Capter 17 Serway 7 t Edition Q: 1, 4, 5, 6, 9, 1, 14, 15 Quetion *Q17.1 Anwer. Te typically iger denity would by itelf make te peed of ound lower in a olid compared to a ga. Q17.4
Summary PHY101 ( 2 ) T / Hanadi Al Harbi
 الكمية Physical Quantity القانون Low التعريف Definition الوحدة SI Unit Linear Momentum P = mθ be equal to the mass of an object times its velocity. Kg. m/s vector quantity Stress F \ A the external force
الكمية Physical Quantity القانون Low التعريف Definition الوحدة SI Unit Linear Momentum P = mθ be equal to the mass of an object times its velocity. Kg. m/s vector quantity Stress F \ A the external force
KEY. D. 1.3 kg m. Solution: Using conservation of energy on the swing, mg( h) = 1 2 mv2 v = 2mg( h)
 Phy 5 - Fall 206 Extra credit review eion - Verion A KEY Thi i an extra credit review eion. t will be worth 30 point of extra credit. Dicu and work on the problem with your group. You may ue your text
Phy 5 - Fall 206 Extra credit review eion - Verion A KEY Thi i an extra credit review eion. t will be worth 30 point of extra credit. Dicu and work on the problem with your group. You may ue your text
b) (6) With 10.0 N applied to the smaller piston, what pressure force F 2 (in newtons) is produced on the larger piston?
 General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 17, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 17, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
Bogoliubov Transformation in Classical Mechanics
 Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
Bogoliubov Tranformation in Claical Mechanic Canonical Tranformation Suppoe we have a et of complex canonical variable, {a j }, and would like to conider another et of variable, {b }, b b ({a j }). How
PHYSICS 111 SPRING EXAM 3: April 12, 2016; 8:15pm - 9:45pm
 PHYSICS SPRING 06 EXAM 3: April, 06; 8:5pm - 9:45pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 0 multiple-choice questions plus extra credit question, each worth
PHYSICS SPRING 06 EXAM 3: April, 06; 8:5pm - 9:45pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 0 multiple-choice questions plus extra credit question, each worth
Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter 14
 HRW 7e Chapter 4 Page of 8 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter 4. The air inside pushes outard ith a force given by p i A, here p i is the pressure inside the room and A is the area of the indo. Similarly,
HRW 7e Chapter 4 Page of 8 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter 4. The air inside pushes outard ith a force given by p i A, here p i is the pressure inside the room and A is the area of the indo. Similarly,
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam
 Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Solution to phys101-t112-final Exam Q1. An 800-N man stands halfway up a 5.0-m long ladder of negligible weight. The base of the ladder is.0m from the wall as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that the wall-ladder
Basics of a Quartz Crystal Microbalance
 Baic of a Quartz Crytal Microbalance Introduction Thi document provide an introduction to the quartz crytal microbalance (QCM) which i an intrument that allow a uer to monitor mall ma change on an electrode.
Baic of a Quartz Crytal Microbalance Introduction Thi document provide an introduction to the quartz crytal microbalance (QCM) which i an intrument that allow a uer to monitor mall ma change on an electrode.
b) (6) What is the volume of the iron cube, in m 3?
 General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 14, 2012 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 14, 2012 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
FRTN10 Exercise 3. Specifications and Disturbance Models
 FRTN0 Exercie 3. Specification and Diturbance Model 3. A feedback ytem i hown in Figure 3., in which a firt-order proce if controlled by an I controller. d v r u 2 z C() P() y n Figure 3. Sytem in Problem
FRTN0 Exercie 3. Specification and Diturbance Model 3. A feedback ytem i hown in Figure 3., in which a firt-order proce if controlled by an I controller. d v r u 2 z C() P() y n Figure 3. Sytem in Problem
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion
 Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
1. Intensity of Periodic Sound Waves 2. The Doppler Effect
 1. Intenity o Periodic Sound Wae. The Doppler Eect 1-4-018 1 Objectie: The tudent will be able to Deine the intenity o the ound wae. Deine the Doppler Eect. Undertand ome application on ound 1-4-018 3.3
1. Intenity o Periodic Sound Wae. The Doppler Eect 1-4-018 1 Objectie: The tudent will be able to Deine the intenity o the ound wae. Deine the Doppler Eect. Undertand ome application on ound 1-4-018 3.3
These are practice problems for the final exam. You should attempt all of them, but turn in only the even-numbered problems!
 Math 33 - ODE Due: 7 December 208 Written Problem Set # 4 Thee are practice problem for the final exam. You hould attempt all of them, but turn in only the even-numbered problem! Exercie Solve the initial
Math 33 - ODE Due: 7 December 208 Written Problem Set # 4 Thee are practice problem for the final exam. You hould attempt all of them, but turn in only the even-numbered problem! Exercie Solve the initial
CHAPTER 12 OSCILLATORY MOTION
 CHAPTER 1 OSCILLATORY MOTION Before starting the discussion of the chapter s concepts it is worth to define some terms we will use frequently in this chapter: 1. The period of the motion, T, is the time
CHAPTER 1 OSCILLATORY MOTION Before starting the discussion of the chapter s concepts it is worth to define some terms we will use frequently in this chapter: 1. The period of the motion, T, is the time
Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity
 Add Important Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity Page: 136 Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity NGSS Standard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objective: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Undertanding
Add Important Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity Page: 136 Linear Motion, Speed & Velocity NGSS Standard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objective: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3 Knowledge/Undertanding
@(; t) p(;,b t) +; t), (; t)) (( whih lat line follow from denition partial derivative. in relation quoted in leture. Th derive wave equation for ound
 24 Spring 99 Problem Set 5 Optional Problem Phy February 23, 999 Handout Derivation Wave Equation for Sound. one-dimenional wave equation for ound. Make ame ort Derive implifying aumption made in deriving
24 Spring 99 Problem Set 5 Optional Problem Phy February 23, 999 Handout Derivation Wave Equation for Sound. one-dimenional wave equation for ound. Make ame ort Derive implifying aumption made in deriving
Longitudinal Waves. waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation
 Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Question 1 Equivalent Circuits
 MAE 40 inear ircuit Fall 2007 Final Intruction ) Thi exam i open book You may ue whatever written material you chooe, including your cla note and textbook You may ue a hand calculator with no communication
MAE 40 inear ircuit Fall 2007 Final Intruction ) Thi exam i open book You may ue whatever written material you chooe, including your cla note and textbook You may ue a hand calculator with no communication
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
PHYS 110B - HW #6 Spring 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #6 Spring 4, Solution by David Pace Any referenced equation are from Griffith Problem tatement are paraphraed. Problem. from Griffith Show that the following, A µo ɛ o A V + A ρ ɛ o Eq..4 A
PHYS B - HW #6 Spring 4, Solution by David Pace Any referenced equation are from Griffith Problem tatement are paraphraed. Problem. from Griffith Show that the following, A µo ɛ o A V + A ρ ɛ o Eq..4 A
Chapter 9: Solids and Fluids
 Chapter 9: Solids and Fluids State of matters: Solid, Liquid, Gas and Plasma. Solids Has definite volume and shape Can be crystalline or amorphous Molecules are held in specific locations by electrical
Chapter 9: Solids and Fluids State of matters: Solid, Liquid, Gas and Plasma. Solids Has definite volume and shape Can be crystalline or amorphous Molecules are held in specific locations by electrical
Final Comprehensive Exam Physical Mechanics Friday December 15, Total 100 Points Time to complete the test: 120 minutes
 Final Comprehenive Exam Phyical Mechanic Friday December 15, 000 Total 100 Point Time to complete the tet: 10 minute Pleae Read the Quetion Carefully and Be Sure to Anwer All Part! In cae that you have
Final Comprehenive Exam Phyical Mechanic Friday December 15, 000 Total 100 Point Time to complete the tet: 10 minute Pleae Read the Quetion Carefully and Be Sure to Anwer All Part! In cae that you have
= 16.7 m. Using constant acceleration kinematics then yields a = v v E The expression for the resistance of a resistor is given as R = ρl 4 )
 016 PhyicBowl Solution # An # An # An # An # An 1 C 11 C 1 B 31 E 41 D A 1 B E 3 D 4 B 3 D 13 A 3 C 33 B 43 C 4 D 14 E 4 B 34 C 44 E 5 B 15 B 5 A 35 A 45 D 6 D 16 C 6 C 36 B 46 A 7 E 17 A 7 D 37 E 47 C
016 PhyicBowl Solution # An # An # An # An # An 1 C 11 C 1 B 31 E 41 D A 1 B E 3 D 4 B 3 D 13 A 3 C 33 B 43 C 4 D 14 E 4 B 34 C 44 E 5 B 15 B 5 A 35 A 45 D 6 D 16 C 6 C 36 B 46 A 7 E 17 A 7 D 37 E 47 C
ρ water = 1000 kg/m 3 = 1.94 slugs/ft 3 γ water = 9810 N/m 3 = 62.4 lbs/ft 3
 CEE 34 Aut 004 Midterm # Anwer all quetion. Some data that might be ueful are a follow: ρ water = 1000 kg/m 3 = 1.94 lug/ft 3 water = 9810 N/m 3 = 6.4 lb/ft 3 1 kw = 1000 N-m/ 1. (10) A 1-in. and a 4-in.
CEE 34 Aut 004 Midterm # Anwer all quetion. Some data that might be ueful are a follow: ρ water = 1000 kg/m 3 = 1.94 lug/ft 3 water = 9810 N/m 3 = 6.4 lb/ft 3 1 kw = 1000 N-m/ 1. (10) A 1-in. and a 4-in.
Fluid-structure coupling analysis and simulation of viscosity effect. on Coriolis mass flowmeter
 APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 2013, Singapore luid-tructure coupling analyi and imulation of vicoity effect on Corioli ma flowmeter *Luo Rongmo, and Wu Jian National Metrology Centre, A*STAR, 1 Science
APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 2013, Singapore luid-tructure coupling analyi and imulation of vicoity effect on Corioli ma flowmeter *Luo Rongmo, and Wu Jian National Metrology Centre, A*STAR, 1 Science
Assessment Schedule 2017 Scholarship Physics (93103)
 Scholarhip Phyic (93103) 201 page 1 of 5 Aement Schedule 201 Scholarhip Phyic (93103) Evidence Statement Q Evidence 1-4 mark 5-6 mark -8 mark ONE (a)(i) Due to the motion of the ource, there are compreion
Scholarhip Phyic (93103) 201 page 1 of 5 Aement Schedule 201 Scholarhip Phyic (93103) Evidence Statement Q Evidence 1-4 mark 5-6 mark -8 mark ONE (a)(i) Due to the motion of the ource, there are compreion
Physics 11 HW #9 Solutions
 Phyic HW #9 Solution Chapter 6: ocu On Concept: 3, 8 Problem: 3,, 5, 86, 9 Chapter 7: ocu On Concept: 8, Problem:,, 33, 53, 6 ocu On Concept 6-3 (d) The amplitude peciie the maximum excurion o the pot
Phyic HW #9 Solution Chapter 6: ocu On Concept: 3, 8 Problem: 3,, 5, 86, 9 Chapter 7: ocu On Concept: 8, Problem:,, 33, 53, 6 ocu On Concept 6-3 (d) The amplitude peciie the maximum excurion o the pot
Oscillations. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER. Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 15 Oscillations Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums 1. The displacement of a particle oscillating along the x axis is given as a function
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 15 Oscillations Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums 1. The displacement of a particle oscillating along the x axis is given as a function
Physics 41 HW Set 1 Chapter 15 Serway 8 th ( 7 th )
 Conceptual Q: 4 (7), 7 (), 8 (6) Physics 4 HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 8 th ( 7 th ) Q4(7) Answer (c). The equilibrium position is 5 cm below the starting point. The motion is symmetric about the equilibrium
Conceptual Q: 4 (7), 7 (), 8 (6) Physics 4 HW Set Chapter 5 Serway 8 th ( 7 th ) Q4(7) Answer (c). The equilibrium position is 5 cm below the starting point. The motion is symmetric about the equilibrium
A B = AB cos θ = 100. = 6t. a(t) = d2 r(t) a(t = 2) = 12 ĵ
 1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the Earth s surface and falls back to Earth. Which of the graphs below best symbolizes its speed v(t) as a function of time, neglecting air resistance: The answer
1. A ball is thrown vertically upward from the Earth s surface and falls back to Earth. Which of the graphs below best symbolizes its speed v(t) as a function of time, neglecting air resistance: The answer
A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right.
 1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
Physics 218: Exam 1. Class of 2:20pm. February 14th, You have the full class period to complete the exam.
 Phyic 218: Exam 1 Cla of 2:20pm February 14th, 2012. Rule of the exam: 1. You have the full cla period to complete the exam. 2. Formulae are provided on the lat page. You may NOT ue any other formula heet.
Phyic 218: Exam 1 Cla of 2:20pm February 14th, 2012. Rule of the exam: 1. You have the full cla period to complete the exam. 2. Formulae are provided on the lat page. You may NOT ue any other formula heet.
ANSWERS TO MA1506 TUTORIAL 7. Question 1. (a) We shall use the following s-shifting property: L(f(t)) = F (s) L(e ct f(t)) = F (s c)
 ANSWERS O MA56 UORIAL 7 Quetion. a) We hall ue the following -Shifting property: Lft)) = F ) Le ct ft)) = F c) Lt 2 ) = 2 3 ue Ltn ) = n! Lt 2 e 3t ) = Le 3t t 2 ) = n+ 2 + 3) 3 b) Here u denote the Unit
ANSWERS O MA56 UORIAL 7 Quetion. a) We hall ue the following -Shifting property: Lft)) = F ) Le ct ft)) = F c) Lt 2 ) = 2 3 ue Ltn ) = n! Lt 2 e 3t ) = Le 3t t 2 ) = n+ 2 + 3) 3 b) Here u denote the Unit
SAMPLING. Sampling is the acquisition of a continuous signal at discrete time intervals and is a fundamental concept in real-time signal processing.
 SAMPLING Sampling i the acquiition of a continuou ignal at dicrete time interval and i a fundamental concept in real-time ignal proceing. he actual ampling operation can alo be defined by the figure belo
SAMPLING Sampling i the acquiition of a continuou ignal at dicrete time interval and i a fundamental concept in real-time ignal proceing. he actual ampling operation can alo be defined by the figure belo
Honors Classical Physics I
 Honors Classical Physics PHY141 Lecture 31 Sound Waves Please set your clicker to channel 1 Lecture 31 1 Example Standing Waves A string of mass m = 00 g and length L = 4.0 m is stretched between posts
Honors Classical Physics PHY141 Lecture 31 Sound Waves Please set your clicker to channel 1 Lecture 31 1 Example Standing Waves A string of mass m = 00 g and length L = 4.0 m is stretched between posts
Lecture 3 Basic radiometric quantities.
 Lecture 3 Baic radiometric quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation.. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field: Definition,
Lecture 3 Baic radiometric quantitie. The Beer-Bouguer-Lambert law. Concept of extinction cattering plu aborption and emiion. Schwarzchild equation.. Baic introduction to electromagnetic field: Definition,
EF 152 Exam 2 - Fall, 2016 Page 1 Copy 223
 EF 152 Exam 2 - Fall, 2016 Page 1 Copy 223 Instructions Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. Do not leave if there is less than 5 minutes to go in the exam. When time is called, immediately
EF 152 Exam 2 - Fall, 2016 Page 1 Copy 223 Instructions Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. Do not leave if there is less than 5 minutes to go in the exam. When time is called, immediately
The Influence of the Load Condition upon the Radial Distribution of Electromagnetic Vibration and Noise in a Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor
 The Influence of the Load Condition upon the Radial Ditribution of Electromagnetic Vibration and Noie in a Three-Phae Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Yuta Sato 1, Iao Hirotuka 1, Kazuo Tuboi 1, Maanori Nakamura
The Influence of the Load Condition upon the Radial Ditribution of Electromagnetic Vibration and Noie in a Three-Phae Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Yuta Sato 1, Iao Hirotuka 1, Kazuo Tuboi 1, Maanori Nakamura
Physics 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #9
 Physics 07 HOMEORK ASSIGNMENT #9 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapter : Problems 6, 8, 33, 40, 44 *6 A 58-kg skier is going down a slope oriented 35 above the horizontal. The area of each ski in contact
Physics 07 HOMEORK ASSIGNMENT #9 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapter : Problems 6, 8, 33, 40, 44 *6 A 58-kg skier is going down a slope oriented 35 above the horizontal. The area of each ski in contact
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Fluids. Fluids in Motion or Fluid Dynamics
 Fluids Fluids in Motion or Fluid Dynamics Resources: Serway - Chapter 9: 9.7-9.8 Physics B Lesson 3: Fluid Flow Continuity Physics B Lesson 4: Bernoulli's Equation MIT - 8: Hydrostatics, Archimedes' Principle,
Fluids Fluids in Motion or Fluid Dynamics Resources: Serway - Chapter 9: 9.7-9.8 Physics B Lesson 3: Fluid Flow Continuity Physics B Lesson 4: Bernoulli's Equation MIT - 8: Hydrostatics, Archimedes' Principle,
Physics Exam 3 Formulas
 Phyic 10411 Exam III November 20, 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam i cloed book, and you may have only pen/pencil and a calculator (no tored equation or
Phyic 10411 Exam III November 20, 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam i cloed book, and you may have only pen/pencil and a calculator (no tored equation or
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
= s = 3.33 s s. 0.3 π 4.6 m = rev = π 4.4 m. (3.69 m/s)2 = = s = π 4.8 m. (5.53 m/s)2 = 5.
 Seat: PHYS 500 (Fall 0) Exa #, V 5 pt. Fro book Mult Choice 8.6 A tudent lie on a very light, rigid board with a cale under each end. Her feet are directly over one cale and her body i poitioned a hown.
Seat: PHYS 500 (Fall 0) Exa #, V 5 pt. Fro book Mult Choice 8.6 A tudent lie on a very light, rigid board with a cale under each end. Her feet are directly over one cale and her body i poitioned a hown.
Liquids CHAPTER 13 FLUIDS FLUIDS. Gases. Density! Bulk modulus! Compressibility. To begin with... some important definitions...
 CHAPTER 13 FLUIDS FLUIDS Liquids Gases Density! Bulk modulus! Compressibility Pressure in a fluid! Hydraulic lift! Hydrostatic paradox Measurement of pressure! Manometers and barometers Buoyancy and Archimedes
CHAPTER 13 FLUIDS FLUIDS Liquids Gases Density! Bulk modulus! Compressibility Pressure in a fluid! Hydraulic lift! Hydrostatic paradox Measurement of pressure! Manometers and barometers Buoyancy and Archimedes
Stability. ME 344/144L Prof. R.G. Longoria Dynamic Systems and Controls/Lab. Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Stability The tability of a ytem refer to it ability or tendency to eek a condition of tatic equilibrium after it ha been diturbed. If given a mall perturbation from the equilibrium, it i table if it return.
Stability The tability of a ytem refer to it ability or tendency to eek a condition of tatic equilibrium after it ha been diturbed. If given a mall perturbation from the equilibrium, it i table if it return.
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
PHYSICSBOWL March 29 April 14, 2017
 PHYSICSBOWL 2017 March 29 April 14, 2017 40 QUESTIONS 45 MINUTES The ponor of the 2017 PhyicBowl, including the American Aociation of Phyic Teacher, are providing ome of the prize to recognize outtanding
PHYSICSBOWL 2017 March 29 April 14, 2017 40 QUESTIONS 45 MINUTES The ponor of the 2017 PhyicBowl, including the American Aociation of Phyic Teacher, are providing ome of the prize to recognize outtanding
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 117.3 MIDTERM TEST February 11, 2016 Time: 90 minutes NAME: SOLUTIONS (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 117.3 MIDTERM TEST February 11, 2016 Time: 90 minutes NAME: SOLUTIONS (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION
Pulsed Magnet Crimping
 Puled Magnet Crimping Fred Niell 4/5/00 1 Magnetic Crimping Magnetoforming i a metal fabrication technique that ha been in ue for everal decade. A large capacitor bank i ued to tore energy that i ued to
Puled Magnet Crimping Fred Niell 4/5/00 1 Magnetic Crimping Magnetoforming i a metal fabrication technique that ha been in ue for everal decade. A large capacitor bank i ued to tore energy that i ued to
ME 322 Worksheet Winter 2007 Introduction to Compressible Flow
 ME 3 Workheet Winter 007 Introduction to Compreible Flow 1. A two-liter cylindrical tank, 10 cm in diameter, ha a piton that fit perfectly. The piton doe not leak, and there i no friction between the piton
ME 3 Workheet Winter 007 Introduction to Compreible Flow 1. A two-liter cylindrical tank, 10 cm in diameter, ha a piton that fit perfectly. The piton doe not leak, and there i no friction between the piton
Physics 6B. Practice Midterm #1 Solutions
 Physics 6B Practice Midterm #1 Solutions 1. A block of plastic with a density of 90 kg/m 3 floats at the interface between of density 850 kg/m 3 and of density 1000 kg/m 3, as shown. Calculate the percentage
Physics 6B Practice Midterm #1 Solutions 1. A block of plastic with a density of 90 kg/m 3 floats at the interface between of density 850 kg/m 3 and of density 1000 kg/m 3, as shown. Calculate the percentage
Physics in Faculty of
 Why we study Physics in Faculty of Engineering? Dimensional analysis Scalars and vector analysis Rotational of a rigid body about a fixed axis Rotational kinematics 1. Dimensional analysis The ward dimension
Why we study Physics in Faculty of Engineering? Dimensional analysis Scalars and vector analysis Rotational of a rigid body about a fixed axis Rotational kinematics 1. Dimensional analysis The ward dimension
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 25, 2007 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 25, 2007 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
Important because SHM is a good model to describe vibrations of a guitar string, vibrations of atoms in molecules, etc.
 Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory motion under a restoring force proportional to the amount of displacement from equilibrium A restoring force is a force that tries to move the system back to equilibrium
Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory motion under a restoring force proportional to the amount of displacement from equilibrium A restoring force is a force that tries to move the system back to equilibrium
Chap 12. Sound. Speed of sound is different in different material. Depends on the elasticity and density of the medium. T v sound = v string =
 Chap 12. Sound Sec. 12.1 - Characteristics of Sound Sound is produced due to source(vibrating object and travels in a medium (londitudinal sound waves and can be heard by a ear (vibrations. Sound waves
Chap 12. Sound Sec. 12.1 - Characteristics of Sound Sound is produced due to source(vibrating object and travels in a medium (londitudinal sound waves and can be heard by a ear (vibrations. Sound waves
Oscillatory Motion. Solutions of Selected Problems
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion. Solutions of Selected Problems 15.1 Problem 15.18 (In the text book) A block-spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.50 cm. If the spring constant is 250 N/m and
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion. Solutions of Selected Problems 15.1 Problem 15.18 (In the text book) A block-spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.50 cm. If the spring constant is 250 N/m and
Chapter 12. Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx
 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
Answers to test yourself questions
 Answers to test yourself questions Option B B Rotational dynamics ( ω + ω )t Use 0 ( +.).0 θ to get θ 46. 46 rad. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get ω.0 +. 4 and so ω 7.8 7 rad s. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get.4. + α 0 π. Hence
Answers to test yourself questions Option B B Rotational dynamics ( ω + ω )t Use 0 ( +.).0 θ to get θ 46. 46 rad. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get ω.0 +. 4 and so ω 7.8 7 rad s. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get.4. + α 0 π. Hence
s much time does it take for the dog to run a distance of 10.0m
 ATTENTION: All Diviion I tudent, START HERE. All Diviion II tudent kip the firt 0 quetion, begin on #.. Of the following, which quantity i a vector? Energy (B) Ma Average peed (D) Temperature (E) Linear
ATTENTION: All Diviion I tudent, START HERE. All Diviion II tudent kip the firt 0 quetion, begin on #.. Of the following, which quantity i a vector? Energy (B) Ma Average peed (D) Temperature (E) Linear
In-Class Problem 5: Newton s Laws of Motion
 In-Cla Problem 5: Neton La of Motion Conider a trac ith a pulley located at the end. The force enor and cart have total ma m 1. They are connected by a inextenible rope of length l (paing over the pulley)
In-Cla Problem 5: Neton La of Motion Conider a trac ith a pulley located at the end. The force enor and cart have total ma m 1. They are connected by a inextenible rope of length l (paing over the pulley)
/University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2009
 Lecture 0 /6/09 /Univerity of Wahington Department of Chemitry Chemitry 453 Winter Quarter 009. Wave Function and Molecule Can quantum mechanic explain the tructure of molecule by determining wave function
Lecture 0 /6/09 /Univerity of Wahington Department of Chemitry Chemitry 453 Winter Quarter 009. Wave Function and Molecule Can quantum mechanic explain the tructure of molecule by determining wave function
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
NARAYANA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
Chapter 11. Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves Driven Harmonic Motion and Resonance RESONANCE Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillating object,
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves Driven Harmonic Motion and Resonance RESONANCE Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillating object,
AP Physics. Harmonic Motion. Multiple Choice. Test E
 AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
Chapter 4. Oscillatory Motion. 4.1 The Important Stuff Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chapter 4 Oscillatory Motion 4.1 The Important Stuff 4.1.1 Simple Harmonic Motion In this chapter we consider systems which have a motion which repeats itself in time, that is, it is periodic. In particular
Chapter 4 Oscillatory Motion 4.1 The Important Stuff 4.1.1 Simple Harmonic Motion In this chapter we consider systems which have a motion which repeats itself in time, that is, it is periodic. In particular
Ch 15 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Ch 15 Simple Harmonic Motion Periodic (Circular) Motion Point P is travelling in a circle with a constant speed. How can we determine the x-coordinate of the point P in terms of other given quantities?
Ch 15 Simple Harmonic Motion Periodic (Circular) Motion Point P is travelling in a circle with a constant speed. How can we determine the x-coordinate of the point P in terms of other given quantities?
Class Average = 71. Counts Scores
 30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
PHYSICS 1307 FALL 2007 EXAM # 3 Thursday, November 15, 2007 SOLUTIONS. P atm = N m 2 v sound =343 m/ s
 1/9 Last Name: First Name: SMU ID: PHYSICS 1307 FALL 2007 EXAM # 3 Thursday, November 15, 2007 SOLUTIONS CQ: NQ: Total: Scientific data air =1.29 kg m 3 steel =12 10 6 0 C 1 P atm =1.013 10 5 N m 2 v sound
1/9 Last Name: First Name: SMU ID: PHYSICS 1307 FALL 2007 EXAM # 3 Thursday, November 15, 2007 SOLUTIONS CQ: NQ: Total: Scientific data air =1.29 kg m 3 steel =12 10 6 0 C 1 P atm =1.013 10 5 N m 2 v sound
Chapter 18 Solutions
 Chapter 18 Solutions 18.1 he resultant wave function has the form y A 0 cos φ sin kx ω t + φ (a) A A 0 cos φ (5.00) cos (π /4) 9.4 m f ω π 100π π 600 Hz *18. We write the second wave function as hen y
Chapter 18 Solutions 18.1 he resultant wave function has the form y A 0 cos φ sin kx ω t + φ (a) A A 0 cos φ (5.00) cos (π /4) 9.4 m f ω π 100π π 600 Hz *18. We write the second wave function as hen y
Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity continued
 Chapter 10 Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity continued Spring constants & oscillations Hooke's Law F A = k x Displacement proportional to applied force Oscillations position: velocity: acceleration:
Chapter 10 Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity continued Spring constants & oscillations Hooke's Law F A = k x Displacement proportional to applied force Oscillations position: velocity: acceleration:
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
Physics 1C. Lecture 12C
 Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
