Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL
|
|
|
- Noreen Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar Proof (a) if L is represented by a PDA M, construct a CFG G such that L(G) = L(M) (b) if w = ɛ and S is nullable, accept; otherwise reject (c) Convert G to CNF (G ) such that L(G ) = L(G) ɛ (d) Try all derivations from G using no more than 2 w 1 steps. If w derived, accept; otherwise reject Analysis Algorithm requires at most 2 w 1 steps because grammar is in CNF Time to build G independent of w, so is constant Let n = w g = search-branching factor of G : maximum number of rules with same LHS Number of derivations of length 2 w 1 g 2n 1 It takes fewer than 2n 1 steps to test each So, run time O(n2 n ) 2. PDA-based proof See below 1
2 Theorem 14.2 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL (2) Statement: Given a CFG G = (V, Σ, R, S), there is a PDA M such that L(M) = L(G) ɛ which contains no transitions of the form ((p, ɛ, α), (q, β)) Proof: By construction (see below). Discussion Algorithm convertcfgtopda-td generates PDA M that simulates derivation of a string from the given CFG M = ({p, q}, Σ, V,, p, {q}), where contains 1. A start-up transition ((p, ɛ, ɛ), (q, s)) whose sole job is to push S 2. Transitions of the form ((p, ɛ, X), (q, s 1 s 2...s n )) for each rule of the form X s 1 s 2...s n These replace X by s 1 s 2...s n in the derivation When n = 0, transition is ((p, ɛ, X), (q, ɛ)) 3. Transitions of the form ((p, c, c), (q, ɛ)) for each c Σ These replace allow consumption of input Transitions of type 1 and type 2 above are ɛ-transitions Consider a CFG in GNF 1. Rules containing S are of form S cs 1 s 2...s n, where s 1, s 2,..., s n V Σ No need to push S Simply read the c and push s 1 s 2...s n 2. Other rules are of form X cs 1 s 2...s n (X S) Rather than (a) Push c, and then (b) Immediately pop c in next transition (ala sequence of rules of type 2 and 3 above) Can simply read the c and push s 1 s 2...s n Algorithm: 1. Convert G to GNF 2. Use the above to build PDA M 2
3 Theorem 14.3 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL (3) Statement: Let M be a PDA that contains no ɛ-transitions. Consider operations of M on w Σ where w = n. 1. M will halt and either accept or reject w. 2. Each computation will halt within n steps. 3. The total number of computations pursued by M is less than or equal to b n, where b is the maximum number of competing transitions from any state of M. 4. The maximum number of steps executed by any computation of m is nb n. Proof: (See p 317) Proof of Theorem 14.1, part 2: Using a PDA Algorithm 1. If L represented by a PDA M, convert to CFG G so that L(G) = L(M) 2. if w = ɛ and S is nullable, accept; otherwise reject 3. Convert G to GNF (G ) such that L(G) = L(G ) ɛ 4. Construct PDA M such that L(M ) = L(G ) and M has no ɛ transitions 5. By theorem 14.3, all paths of M are guaranteed to halt in a finite number of steps. Run M on w Accept if M accepts; otherwise reject Analysis M is constructed in constant time (only done once) Let w = n Time needed to analyze w is time needed to simulate all paths of M on w Total number of steps bounded by nb n Number of steps could grow exponentially, or be less than b Depends on how the simulation is performed: depth-first search is O(b n ) 3
4 Context Free Languages: Decidability of CFL Emptiness and Finiteness Theorem 14.4 Statement: Given CFL L, there is a decision procedure that determines whether 1. L = NULL 2. L is infinite Proof: By construction 1. Emptiness: L(G) is empty if S is unproductive. Boolean decidecflempty (CFG G) { G = removeunproductive(g); if (G.S not in G.V) return TRUE; else return FALSE; } 2. Non-finiteness Let G = (V, Σ, R, S) be CFG that generates L n = V Σ b = branching factor of G Longest string that can be generated without repeating a NT has length b n If G generates no strings longer than this, L is finite If G generates one string longer than this, L is infinite Cannot apply decidecf L(G, w) to all strings longer than b n Σ, as there are an infinite number of them Let t be the shortest string generated by G whose length is b n+1 + b n Pumping Theorem states that t = uvxyz vy > 0 uxz L, and uxz < t Since t is the shortest string whose length is greater than b n+1 + b n uxz b n+1 + b n 4
5 Context Free Languages: Decidability of CFL Emptiness and Finiteness (2) Since the Pumping Theorem states that vxy k (i.e., b n ), no more than b n+1 strings could be pumped out Thus, b n < uxz b n+1 + b n If L has any strings longer than b n, it must have at least one of length b n+1 + b n Algorithm: Boolean decidecflinfinite (CFG G) { lexicographically enumerate all strings W L(G) where b n < w b n+1 + b n ; for (each w) if (return decidecfl(g, w)) return TRUE; return FALSE; } 5
6 Theorem 14.5 Context Free Languages: Decidability of Equivalence Statement: Given 2 deterministic CFLs L 1 and L 2, there is a decision procedure to determine whether L 1 = L 2. Proof: (See p 320) 6
7 Context Free Languages: Questions That Are Not Decidable The following are not decidable: Given CFLs L 1 and L 2 defined over alphabet Σ 1. L 1 = Σ? 2. Is L 1 s complement a CFL? 3. Is L 1 regular? 4. L 1 = L 2? 5. L 1 L 2? 6. L 1 L 2 = NULL? 7. Is L 1 inherently ambiguous? 8. Is CFG G ambiguous? 7
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA) Objectives Introduce the Pumping Lemma for CFL Show that some languages are non- CFL Discuss the DPDA, which
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA) Objectives Introduce the Pumping Lemma for CFL Show that some languages are non- CFL Discuss the DPDA, which
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages
 Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3
 SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
Functions on languages:
 MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
2.1 Solution. E T F a. E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a
 . Solution E T F a E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a E E + T E + T + T T + T + T F + T + T a + T + T a + F + T a + a + T a + a + F a + a + a E T F ( E) ( T ) ( F) (( E)) (( T )) (( F)) (( a)) . Solution
. Solution E T F a E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a E E + T E + T + T T + T + T F + T + T a + T + T a + F + T a + a + T a + a + F a + a + a E T F ( E) ( T ) ( F) (( E)) (( T )) (( F)) (( a)) . Solution
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
ECS 120: Theory of Computation UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, Midterm Exam
 ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
Context Free Grammars: Introduction. Context Free Grammars: Simplifying CFGs
 Context Free Grammars: Introduction CFGs are more powerful than RGs because of the following 2 properties: 1. Recursion Rule is recursive if it is of the form X w 1 Y w 2, where Y w 3 Xw 4 and w 1, w 2,
Context Free Grammars: Introduction CFGs are more powerful than RGs because of the following 2 properties: 1. Recursion Rule is recursive if it is of the form X w 1 Y w 2, where Y w 3 Xw 4 and w 1, w 2,
Context-Free Languages
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Non-Context-Free Languages Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.3. Proving context-freeness
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Non-Context-Free Languages Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.3. Proving context-freeness
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Context Free Grammars: Introduction
 Context Free Grammars: Introduction Context free grammar (CFG) G = (V, Σ, R, S), where V is a set of grammar symbols Σ V is a set of terminal symbols R is a set of rules, where R (V Σ) V S is a distinguished
Context Free Grammars: Introduction Context free grammar (CFG) G = (V, Σ, R, S), where V is a set of grammar symbols Σ V is a set of terminal symbols R is a set of rules, where R (V Σ) V S is a distinguished
CS481F01 Solutions 8
 CS481F01 Solutions 8 A. Demers 7 Dec 2001 1. Prob. 111 from p. 344 of the text. One of the following sets is r.e. and the other is not. Which is which? (a) { i L(M i ) contains at least 481 elements }
CS481F01 Solutions 8 A. Demers 7 Dec 2001 1. Prob. 111 from p. 344 of the text. One of the following sets is r.e. and the other is not. Which is which? (a) { i L(M i ) contains at least 481 elements }
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability.
 Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
What languages are Turing-decidable? What languages are not Turing-decidable? Is there a language that isn t even Turingrecognizable?
 } We ll now take a look at Turing Machines at a high level and consider what types of problems can be solved algorithmically and what types can t: What languages are Turing-decidable? What languages are
} We ll now take a look at Turing Machines at a high level and consider what types of problems can be solved algorithmically and what types can t: What languages are Turing-decidable? What languages are
CS 301. Lecture 18 Decidable languages. Stephen Checkoway. April 2, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 18 Decidable languages Stephen Checkoway April 2, 2018 1 / 26 Decidable language Recall, a language A is decidable if there is some TM M that 1 recognizes A (i.e., L(M) = A), and 2 halts
CS 301 Lecture 18 Decidable languages Stephen Checkoway April 2, 2018 1 / 26 Decidable language Recall, a language A is decidable if there is some TM M that 1 recognizes A (i.e., L(M) = A), and 2 halts
Non-context-Free Languages. CS215, Lecture 5 c
 Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
NPDA, CFG equivalence
 NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions
 Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Annotated version with some (sometimes rather sketchy) answers and notes. This is a collection of sample theory bridge exam questions. This is just to get some idea
Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Annotated version with some (sometimes rather sketchy) answers and notes. This is a collection of sample theory bridge exam questions. This is just to get some idea
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages. Foundations of Computer Science Theory
 Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
The Unsolvability of the Halting Problem. Chapter 19
 The Unsolvability of the Halting Problem Chapter 19 Languages and Machines SD D Context-Free Languages Regular Languages reg exps FSMs cfgs PDAs unrestricted grammars Turing Machines D and SD A TM M with
The Unsolvability of the Halting Problem Chapter 19 Languages and Machines SD D Context-Free Languages Regular Languages reg exps FSMs cfgs PDAs unrestricted grammars Turing Machines D and SD A TM M with
Pushdown Automata: Introduction (2)
 Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
Theory of Computation
 Fall 2002 (YEN) Theory of Computation Midterm Exam. Name:... I.D.#:... 1. (30 pts) True or false (mark O for true ; X for false ). (Score=Max{0, Right- 1 2 Wrong}.) (1) X... If L 1 is regular and L 2 L
Fall 2002 (YEN) Theory of Computation Midterm Exam. Name:... I.D.#:... 1. (30 pts) True or false (mark O for true ; X for false ). (Score=Max{0, Right- 1 2 Wrong}.) (1) X... If L 1 is regular and L 2 L
CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions
 CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions A. Demers 7 Nov 2001 1 (30 pts = 4 pts each part + 2 free points). For this question we use the following notation: x y means x is a prefix of y m k n means m n k For each of
CS481F01 Prelim 2 Solutions A. Demers 7 Nov 2001 1 (30 pts = 4 pts each part + 2 free points). For this question we use the following notation: x y means x is a prefix of y m k n means m n k For each of
Decidability: Church-Turing Thesis
 Decidability: Church-Turing Thesis While there are a countably infinite number of languages that are described by TMs over some alphabet Σ, there are an uncountably infinite number that are not Are there
Decidability: Church-Turing Thesis While there are a countably infinite number of languages that are described by TMs over some alphabet Σ, there are an uncountably infinite number that are not Are there
DM17. Beregnelighed. Jacob Aae Mikkelsen
 DM17 Beregnelighed Jacob Aae Mikkelsen January 12, 2007 CONTENTS Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Operations with languages...................... 2 2 Finite Automata 3 2.1 Regular expressions/languages....................
DM17 Beregnelighed Jacob Aae Mikkelsen January 12, 2007 CONTENTS Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Operations with languages...................... 2 2 Finite Automata 3 2.1 Regular expressions/languages....................
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars
 The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
V Honors Theory of Computation
 V22.0453-001 Honors Theory of Computation Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1 Solution: The class of languages recognized by these machines is the exactly the class of regular languages, thus this TM variant
V22.0453-001 Honors Theory of Computation Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1 Solution: The class of languages recognized by these machines is the exactly the class of regular languages, thus this TM variant
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 9 Last time: Converting a PDA to a CFG Pumping Lemma for CFLs Today: Pumping Lemma for CFLs Review of CFGs/PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 2/9/2016 Sofya Raskhodnikova;
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 9 Last time: Converting a PDA to a CFG Pumping Lemma for CFLs Today: Pumping Lemma for CFLs Review of CFGs/PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 2/9/2016 Sofya Raskhodnikova;
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs
 Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Pumping Lemma for CFLs
 Pumping Lemma for CFLs v y s Here we go again! Intuition: If L is CF, then some CFG G produces strings in L If some string in L is very long, it will have a very tall parse tree If a parse tree is taller
Pumping Lemma for CFLs v y s Here we go again! Intuition: If L is CF, then some CFG G produces strings in L If some string in L is very long, it will have a very tall parse tree If a parse tree is taller
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
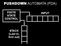 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION
 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION DECIDABILITY ( LECTURE 15) SLIDES FOR 15-453 SPRING 2011 1 / 34 TURING MACHINES-SYNOPSIS The most general model of computation Computations of a TM are described
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION DECIDABILITY ( LECTURE 15) SLIDES FOR 15-453 SPRING 2011 1 / 34 TURING MACHINES-SYNOPSIS The most general model of computation Computations of a TM are described
Cliff s notes for equivalence of CFLs and L(PDAs) LisaCFL L = L(M) for some PDA M L=L(M)forsomePDAM L = L(G) for some CFG G
 What s on our plate today? Cliff s notes for equivalence of CFLs and L(PDAs) LisaCFL L = L(M) for some PDA M L=L(M)forsomePDAM L = L(G) for some CFG G Pumping Lemma (one last time) Statement of Pumping
What s on our plate today? Cliff s notes for equivalence of CFLs and L(PDAs) LisaCFL L = L(M) for some PDA M L=L(M)forsomePDAM L = L(G) for some CFG G Pumping Lemma (one last time) Statement of Pumping
Properties of Context-Free Languages
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
SYLLABUS. Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 3 : REGULAR EXPRESSIONS AND LANGUAGES
 Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent. We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa.
 CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
Theory of Computation
 Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Before We Start. The Pumping Lemma. Languages. Context Free Languages. Plan for today. Now our picture looks like. Any questions?
 Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
Pushdown Automata. We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata.
 Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
Pushdown Automata. Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation. Chia-Ping Chen
 Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
Decidability (What, stuff is unsolvable?)
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
Computational Models: Class 5
 Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 12: Computability III (Decidable Languages relating to DFA, NFA, and CFG)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 12: Computability III (Decidable Languages relating to DFA, NFA, and CFG) Objectives Recall that decidable languages are languages that can be decided by TM (that means,
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 12: Computability III (Decidable Languages relating to DFA, NFA, and CFG) Objectives Recall that decidable languages are languages that can be decided by TM (that means,
CSE 555 Homework Three Sample Solutions
 CSE 555 Homework Three Sample Solutions Question 1 Let Σ be a fixed alphabet. A PDA M with n states and stack alphabet of size σ may recognize the empty language; if its language is non-empty then denote
CSE 555 Homework Three Sample Solutions Question 1 Let Σ be a fixed alphabet. A PDA M with n states and stack alphabet of size σ may recognize the empty language; if its language is non-empty then denote
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
Solution Scoring: SD Reg exp.: a(a
 MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
3130CIT Theory of Computation
 GRIFFITH UNIVERSITY School of Computing and Information Technology 3130CIT Theory of Computation Final Examination, Semester 2, 2006 Details Total marks: 120 (40% of the total marks for this subject) Perusal:
GRIFFITH UNIVERSITY School of Computing and Information Technology 3130CIT Theory of Computation Final Examination, Semester 2, 2006 Details Total marks: 120 (40% of the total marks for this subject) Perusal:
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CS Pushdown Automata
 Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata
 Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Laurent Vanbever. ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October,
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 19 2017 Part 5 out of 5 Last week was all about Context-Free Languages Context-Free
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 19 2017 Part 5 out of 5 Last week was all about Context-Free Languages Context-Free
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages
 Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Lecture 10 More examples of problems in P Closure properties of the class P The class NP given by Jiri Srba Lecture 10 Computability and Complexity 1/12 Example: Relatively
Computability and Complexity Lecture 10 More examples of problems in P Closure properties of the class P The class NP given by Jiri Srba Lecture 10 Computability and Complexity 1/12 Example: Relatively
CS 341 Homework 16 Languages that Are and Are Not Context-Free
 CS 341 Homework 16 Languages that Are and Are Not Context-Free 1. Show that the following languages are context-free. You can do this by writing a context free grammar or a PDA, or you can use the closure
CS 341 Homework 16 Languages that Are and Are Not Context-Free 1. Show that the following languages are context-free. You can do this by writing a context free grammar or a PDA, or you can use the closure
Introduction to Languages and Computation
 Introduction to Languages and Computation George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 400 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Languages and Computation July 2014
Introduction to Languages and Computation George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 400 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Languages and Computation July 2014
Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23)
 Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
CS154 Final Examination
 CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
CS500 Homework #2 Solutions
 CS500 Homework #2 Solutions 1. Consider the two languages Show that L 1 is context-free but L 2 is not. L 1 = {a i b j c k d l i = j k = l} L 2 = {a i b j c k d l i = k j = l} Answer. L 1 is the concatenation
CS500 Homework #2 Solutions 1. Consider the two languages Show that L 1 is context-free but L 2 is not. L 1 = {a i b j c k d l i = j k = l} L 2 = {a i b j c k d l i = k j = l} Answer. L 1 is the concatenation
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Properties of Context-free Languages. Reading: Chapter 7
 Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
CSE 105 Theory of Computation
 CSE 105 Theory of Computation http://www.jflap.org/jflaptmp/ Professor Jeanne Ferrante 1 Undecidability Today s Agenda Review and More Problems A Non-TR Language Reminders and announcements: HW 7 (Last!!)
CSE 105 Theory of Computation http://www.jflap.org/jflaptmp/ Professor Jeanne Ferrante 1 Undecidability Today s Agenda Review and More Problems A Non-TR Language Reminders and announcements: HW 7 (Last!!)
CS20a: Turing Machines (Oct 29, 2002)
 CS20a: Turing Machines (Oct 29, 2002) So far: DFA = regular languages PDA = context-free languages Today: Computability 1 Church s thesis The computable functions are the same as the partial recursive
CS20a: Turing Machines (Oct 29, 2002) So far: DFA = regular languages PDA = context-free languages Today: Computability 1 Church s thesis The computable functions are the same as the partial recursive
Notes for Lecture Notes 2
 Stanford University CS254: Computational Complexity Notes 2 Luca Trevisan January 11, 2012 Notes for Lecture Notes 2 In this lecture we define NP, we state the P versus NP problem, we prove that its formulation
Stanford University CS254: Computational Complexity Notes 2 Luca Trevisan January 11, 2012 Notes for Lecture Notes 2 In this lecture we define NP, we state the P versus NP problem, we prove that its formulation
Undecidable Problems and Reducibility
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
COMP/MATH 300 Topics for Spring 2017 June 5, Review and Regular Languages
 COMP/MATH 300 Topics for Spring 2017 June 5, 2017 Review and Regular Languages Exam I I. Introductory and review information from Chapter 0 II. Problems and Languages A. Computable problems can be expressed
COMP/MATH 300 Topics for Spring 2017 June 5, 2017 Review and Regular Languages Exam I I. Introductory and review information from Chapter 0 II. Problems and Languages A. Computable problems can be expressed
6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs
 CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs
 This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
CSCE 551: Chin-Tser Huang. University of South Carolina
 CSCE 551: Theory of Computation Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Church-Turing Thesis The definition of the algorithm came in the 1936 papers of Alonzo Church h and Alan
CSCE 551: Theory of Computation Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Church-Turing Thesis The definition of the algorithm came in the 1936 papers of Alonzo Church h and Alan
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 15 Ana Bove May 17th 2018 Recap: Context-free Languages Chomsky hierarchy: Regular languages are also context-free; Pumping lemma
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 15 Ana Bove May 17th 2018 Recap: Context-free Languages Chomsky hierarchy: Regular languages are also context-free; Pumping lemma
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions)
 Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05
 Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Part 4 out of 5 DFA NFA REX. Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY THURSDAY APRIL 3 REVIEW for Midterm TUESDAY April 8 Definition: A Turing Machine is a 7-tuple T = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q, q accept, q reject ), where: Q is a
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY THURSDAY APRIL 3 REVIEW for Midterm TUESDAY April 8 Definition: A Turing Machine is a 7-tuple T = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q, q accept, q reject ), where: Q is a
Question Bank UNIT I
 Siddhivinayak Technical Campus School of Engineering & Research Technology Department of computer science and Engineering Session 2016-2017 Subject Name- Theory of Computation Subject Code-4KS05 Sr No.
Siddhivinayak Technical Campus School of Engineering & Research Technology Department of computer science and Engineering Session 2016-2017 Subject Name- Theory of Computation Subject Code-4KS05 Sr No.
Computational Models Lecture 5
 Computational Models Lecture 5 One More PDAs Example Equivalence of PDAs and CFLs Nondeterminism adds power to PDAs (not in book) Closure Properties of CFLs Algorithmic Aspects of PDAs and CFLs DFAs and
Computational Models Lecture 5 One More PDAs Example Equivalence of PDAs and CFLs Nondeterminism adds power to PDAs (not in book) Closure Properties of CFLs Algorithmic Aspects of PDAs and CFLs DFAs and
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
