Lecture 7: Interpolation
|
|
|
- Scot Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 7: Interpolation ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 2/9/2017
2 1 Sampling Review 2 Interpolation and Upsampling 3 Spectrum of Interpolated Signals
3 Outline 1 Sampling Review 2 Interpolation and Upsampling 3 Spectrum of Interpolated Signals
4 On-Board Practice x(t) is sampled at F s,1 = 16, 000 samples/second, creating a signal x[n]. x[n] is then played back through an ideal D/A at a different sampling rate, F s,2 = 8, 000 samples/second, to create a signal y(t). What is y(t)? x(t) = cos (2000πt) + sin (20, 000πt)
5 Outline 1 Sampling Review 2 Interpolation and Upsampling 3 Spectrum of Interpolated Signals
6 Interpolation and Upsampling Today we ll learn upsampling, and four types of interpolation. 1 Upsampling: put zeros between the samples. 2 Piece-wise constant interpolation 3 Piece-wise linear interpolation 4 Piece-wise cubic spline interpolation 5 Sinc interpolation
7 Upsampling Upsampling changes the sampling rate by inserting zeros. Suppose x[n] is sampled at F s,1, and we want to change the sampling rate to F s,2 = MF s,1 for some integer M. Upsampling creates the signal y[n]: { x[m] n = mm y ups [n] = 0 otherwise
8 Piece-Wise Constant Piece-wise constant interpolation creates ( n ) y PWC [n] = x[m], m = int M where the int operator takes the integer part. PWC interpolation can also be used as a kind of D/A, to create a continuous-time signal: ( t ) y PWC (t) = x[m], m = int T where T = 1 F s is the sampling period of x[m]. A PWC signal is discontinuous once every M samples.
9 Piece-Wise Linear Piece-wise linear interpolation creates ( ) ( n mm n (m + 1)M y PWC [n] = g x[m] + g M M PWL can also create a continuous-time signal: ( ) ( t mt t (m + 1)T y PWC (t) = g x[m] + g T T PWL creates a continuous signal by using a continuous interpolation kernel: g(t) = max(0, 1 t ) ) x[m + 1] ) x[m + 1]
10 Piece-Wise Cubic Spline Piece-wise cubic spline interpolation creates y PWCS [n] = n/m+2 m=n/m 2 ( n mm g M PWCS can also create a continuous-time signal: y PWCS (t) = n/m+2 m=n/m 2 ( t mt g T ) x[m] ) x[m] PWCS creates a continuous signal with continuous first derivatives. This is done by using an interpolation function that has continuous first derivatives: g(t) = 1 t 2 0 t 1 2(2 t ) 3 2(2 t ) 2 1 t 2 0 otherwise
11 Sinc Interpolation Sinc interpolation creates y SINC [n] = m= ( n mm g M ) x[m] Sinc interpolation can also create a continuous-time signal: y SINC (t) = m= ( t mt g T ) x[m] Sinc interpolation creates a continuous signal with all of its derivatives continuous. It does this by using an interpolation function that has all continuous derivatives: { sin(πt) g(t) = sinc(πt) πt t 0 1 t = 0
12 Outline 1 Sampling Review 2 Interpolation and Upsampling 3 Spectrum of Interpolated Signals
13 Upsampling Suppose a cosine with period T 0 is upsampled by a factor of M: x[n] = cos (2πn/T 0 ) { x[m] n = mm y[n] = 0 otherwise Then y[n] is periodic with period MT 0.
14 Fourier Series of an Upsampled Cosine Since y[n] has period MT 0, it can be written with a Fourier series: y[n] = MT 0 1 k=0 Y k e jkω 0n/M, ω 0 = 2π T 0 The coefficients Y k can be derived using Fourier series formula: Y k = 1 MT 0 1 MT 0 n=0 y[n]e jkω 0n/M Since y[n] is zero except at n = mm, we can write this as: = { 1 2M Y k = 1 T 0 1 MT 0 m=0 kω 0 = ± 2π T 0 + l2π, 0 otherwise x[m]e jkω 0m any integer l
15 Spectrum of an Upsampled Cosine So Then y[n] has the spectrum x[n] = cos (2πn/T 0 ) { x[m] n = mm y[n] = 0 otherwise Y ω = { 1 2M ω = ± 2π MT 0 + l 2π M, 0 otherwise for any integer l
16 Spectrum of an Interpolated Cosine An interpolated cosine (PWC, PWL, or PWCS) has energy only at the frequencies where the upsampled cosine has energy, that is, at ω = ± 2π MT 0 + l 2π M The energy at the lowest harmonics (±2π/MT 0 ) is nearly the same for interpolation as for upsampling. The better the interpolation, the more it damps out the high-frequency harmonics: Y PWCS,ω 2 < Y PWL,ω 2 < Y PWC,ω 2 < Y UPS,ω 2, ω > 2π MT 0
17 Spectrum of Sinc Interpolation Sinc interpolation completely eliminates the higher harmonics. ( ) 2πm x[m] = cos y[n] = m= T 0 ( ) π(n mm) sinc x[m] M Gives the following result exactly: ( ) 2πn y[n] = cos MT 0 It works in continuous time, too: ( ) ( ) π(t mt ) 2πt y(t) = sinc x[m] = cos T TT 0 m=
Lecture 13: Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Lecture 13: Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 3/9/2017 1 Sampled Systems Review 2 DTFT and Convolution 3 Inverse DTFT 4 Ideal Lowpass Filter
Lecture 13: Discrete Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 3/9/2017 1 Sampled Systems Review 2 DTFT and Convolution 3 Inverse DTFT 4 Ideal Lowpass Filter
George Mason University Signals and Systems I Spring 2016
 George Mason University Signals and Systems I Spring 206 Problem Set #6 Assigned: March, 206 Due Date: March 5, 206 Reading: This problem set is on Fourier series representations of periodic signals. The
George Mason University Signals and Systems I Spring 206 Problem Set #6 Assigned: March, 206 Due Date: March 5, 206 Reading: This problem set is on Fourier series representations of periodic signals. The
ECE 301 Fall 2010 Division 2 Homework 10 Solutions. { 1, if 2n t < 2n + 1, for any integer n, x(t) = 0, if 2n 1 t < 2n, for any integer n.
 ECE 3 Fall Division Homework Solutions Problem. Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal from its samples. Consider the following periodic signal, depicted below: {, if n t < n +, for any integer n,
ECE 3 Fall Division Homework Solutions Problem. Reconstruction of a continuous-time signal from its samples. Consider the following periodic signal, depicted below: {, if n t < n +, for any integer n,
Representing a Signal
 The Fourier Series Representing a Signal The convolution method for finding the response of a system to an excitation takes advantage of the linearity and timeinvariance of the system and represents the
The Fourier Series Representing a Signal The convolution method for finding the response of a system to an excitation takes advantage of the linearity and timeinvariance of the system and represents the
Signals & Systems. Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform. Alp Ertürk
 Signals & Systems Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation: x t = a k e jkω
Signals & Systems Lecture 5 Continuous-Time Fourier Transform Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation: x t = a k e jkω
Fourier series for continuous and discrete time signals
 8-9 Signals and Systems Fall 5 Fourier series for continuous and discrete time signals The road to Fourier : Two weeks ago you saw that if we give a complex exponential as an input to a system, the output
8-9 Signals and Systems Fall 5 Fourier series for continuous and discrete time signals The road to Fourier : Two weeks ago you saw that if we give a complex exponential as an input to a system, the output
Signals & Systems. Lecture 4 Fourier Series Properties & Discrete-Time Fourier Series. Alp Ertürk
 Signals & Systems Lecture 4 Fourier Series Properties & Discrete-Time Fourier Series Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation:
Signals & Systems Lecture 4 Fourier Series Properties & Discrete-Time Fourier Series Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Fourier Series Representation of Continuous-Time Periodic Signals Synthesis equation:
Homework: 4.50 & 4.51 of the attachment Tutorial Problems: 7.41, 7.44, 7.47, Signals & Systems Sampling P1
 Homework: 4.50 & 4.51 of the attachment Tutorial Problems: 7.41, 7.44, 7.47, 7.49 Signals & Systems Sampling P1 Undersampling & Aliasing Undersampling: insufficient sampling frequency ω s < 2ω M Perfect
Homework: 4.50 & 4.51 of the attachment Tutorial Problems: 7.41, 7.44, 7.47, 7.49 Signals & Systems Sampling P1 Undersampling & Aliasing Undersampling: insufficient sampling frequency ω s < 2ω M Perfect
Lecture 3 January 23
 EE 123: Digital Signal Processing Spring 2007 Lecture 3 January 23 Lecturer: Prof. Anant Sahai Scribe: Dominic Antonelli 3.1 Outline These notes cover the following topics: Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
EE 123: Digital Signal Processing Spring 2007 Lecture 3 January 23 Lecturer: Prof. Anant Sahai Scribe: Dominic Antonelli 3.1 Outline These notes cover the following topics: Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
ECE 301: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3
 ECE 31: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3 Due on October 14, 215 Professor: Aly El Gamal A: Xianglun Mao 1 Aly El Gamal ECE 31: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3 Problem 1 Problem 1 Consider
ECE 31: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3 Due on October 14, 215 Professor: Aly El Gamal A: Xianglun Mao 1 Aly El Gamal ECE 31: Signals and Systems Homework Assignment #3 Problem 1 Problem 1 Consider
EE Homework 13 - Solutions
 EE3054 - Homework 3 - Solutions. (a) The Laplace transform of e t u(t) is s+. The pole of the Laplace transform is at which lies in the left half plane. Hence, the Fourier transform is simply the Laplace
EE3054 - Homework 3 - Solutions. (a) The Laplace transform of e t u(t) is s+. The pole of the Laplace transform is at which lies in the left half plane. Hence, the Fourier transform is simply the Laplace
Problem Value
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 30-Apr-04 COURSE: ECE-2025 NAME: GT #: LAST, FIRST Recitation Section: Circle the date & time when your Recitation
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 30-Apr-04 COURSE: ECE-2025 NAME: GT #: LAST, FIRST Recitation Section: Circle the date & time when your Recitation
Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall Midterm 2 Solutions
 8-90 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 08 Midterm Solutions Name: Andrew ID: Problem Score Max 8 5 3 6 4 7 5 8 6 7 6 8 6 9 0 0 Total 00 Midterm Solutions. (8 points) Indicate whether
8-90 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 08 Midterm Solutions Name: Andrew ID: Problem Score Max 8 5 3 6 4 7 5 8 6 7 6 8 6 9 0 0 Total 00 Midterm Solutions. (8 points) Indicate whether
Lecture 8: Signal Reconstruction, DT vs CT Processing. 8.1 Reconstruction of a Band-limited Signal from its Samples
 EE518 Digital Signal Processing University of Washington Autumn 2001 Dept. of Electrical Engineering Lecture 8: Signal Reconstruction, D vs C Processing Oct 24, 2001 Prof: J. Bilmes
EE518 Digital Signal Processing University of Washington Autumn 2001 Dept. of Electrical Engineering Lecture 8: Signal Reconstruction, D vs C Processing Oct 24, 2001 Prof: J. Bilmes
4.1 Introduction. 2πδ ω (4.2) Applications of Fourier Representations to Mixed Signal Classes = (4.1)
 4.1 Introduction Two cases of mixed signals to be studied in this chapter: 1. Periodic and nonperiodic signals 2. Continuous- and discrete-time signals Other descriptions: Refer to pp. 341-342, textbook.
4.1 Introduction Two cases of mixed signals to be studied in this chapter: 1. Periodic and nonperiodic signals 2. Continuous- and discrete-time signals Other descriptions: Refer to pp. 341-342, textbook.
Chapter 12 Variable Phase Interpolation
 Chapter 12 Variable Phase Interpolation Contents Slide 1 Reason for Variable Phase Interpolation Slide 2 Another Need for Interpolation Slide 3 Ideal Impulse Sampling Slide 4 The Sampling Theorem Slide
Chapter 12 Variable Phase Interpolation Contents Slide 1 Reason for Variable Phase Interpolation Slide 2 Another Need for Interpolation Slide 3 Ideal Impulse Sampling Slide 4 The Sampling Theorem Slide
ECE 301 Division 1 Final Exam Solutions, 12/12/2011, 3:20-5:20pm in PHYS 114.
 ECE 301 Division 1 Final Exam Solutions, 12/12/2011, 3:20-5:20pm in PHYS 114. The exam for both sections of ECE 301 is conducted in the same room, but the problems are completely different. Your ID will
ECE 301 Division 1 Final Exam Solutions, 12/12/2011, 3:20-5:20pm in PHYS 114. The exam for both sections of ECE 301 is conducted in the same room, but the problems are completely different. Your ID will
Multirate signal processing
 Multirate signal processing Discrete-time systems with different sampling rates at various parts of the system are called multirate systems. The need for such systems arises in many applications, including
Multirate signal processing Discrete-time systems with different sampling rates at various parts of the system are called multirate systems. The need for such systems arises in many applications, including
Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Digital Signal Processing Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Chang-Su Kim Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital processing of a CT signal involves three basic steps 1. Conversion
Digital Signal Processing Chap 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Chang-Su Kim Digital Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Digital processing of a CT signal involves three basic steps 1. Conversion
Bridge between continuous time and discrete time signals
 6 Sampling Bridge between continuous time and discrete time signals Sampling theorem complete representation of a continuous time signal by its samples Samplingandreconstruction implementcontinuous timesystems
6 Sampling Bridge between continuous time and discrete time signals Sampling theorem complete representation of a continuous time signal by its samples Samplingandreconstruction implementcontinuous timesystems
Fourier Series Representation of
 Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Outline The response of LIT system
Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Outline The response of LIT system
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 GEORGIA INSIUE OF ECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECRICAL and COMPUER ENGINEERING ECE 6250 Spring 207 Problem Set # his assignment is due at the beginning of class on Wednesday, January 25 Assigned: 6-Jan-7 Due
GEORGIA INSIUE OF ECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECRICAL and COMPUER ENGINEERING ECE 6250 Spring 207 Problem Set # his assignment is due at the beginning of class on Wednesday, January 25 Assigned: 6-Jan-7 Due
Cubic Splines; Bézier Curves
 Cubic Splines; Bézier Curves 1 Cubic Splines piecewise approximation with cubic polynomials conditions on the coefficients of the splines 2 Bézier Curves computer-aided design and manufacturing MCS 471
Cubic Splines; Bézier Curves 1 Cubic Splines piecewise approximation with cubic polynomials conditions on the coefficients of the splines 2 Bézier Curves computer-aided design and manufacturing MCS 471
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing Introduction Moslem Amiri, Václav Přenosil Embedded Systems Laboratory Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic amiri@mail.muni.cz prenosil@fi.muni.cz February
Digital Signal Processing Introduction Moslem Amiri, Václav Přenosil Embedded Systems Laboratory Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic amiri@mail.muni.cz prenosil@fi.muni.cz February
Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9
 Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9 (3/4/04). The convolution Property of the CTFT 2. Frequency Response and LTI Systems Revisited 3. Multiplication Property and Parseval s Relation 4. The DT Fourier
Signals and Systems Spring 2004 Lecture #9 (3/4/04). The convolution Property of the CTFT 2. Frequency Response and LTI Systems Revisited 3. Multiplication Property and Parseval s Relation 4. The DT Fourier
Shift-Variance and Nonstationarity of Generalized Sampling-Reconstruction Processes
 Shift-Variance and Nonstationarity of Generalized Sampling-Reconstruction Processes Runyi Yu Eastern Mediterranean University Gazimagusa, North Cyprus Web: faraday.ee.emu.edu.tr/yu Emails: runyi.yu@emu.edu.tr
Shift-Variance and Nonstationarity of Generalized Sampling-Reconstruction Processes Runyi Yu Eastern Mediterranean University Gazimagusa, North Cyprus Web: faraday.ee.emu.edu.tr/yu Emails: runyi.yu@emu.edu.tr
5. THE CLASSES OF FOURIER TRANSFORMS
 5. THE CLASSES OF FOURIER TRANSFORMS There are four classes of Fourier transform, which are represented in the following table. So far, we have concentrated on the discrete Fourier transform. Table 1.
5. THE CLASSES OF FOURIER TRANSFORMS There are four classes of Fourier transform, which are represented in the following table. So far, we have concentrated on the discrete Fourier transform. Table 1.
16.362: Signals and Systems: 1.0
 16.362: Signals and Systems: 1.0 Prof. K. Chandra ECE, UMASS Lowell September 1, 2016 1 Background The pre-requisites for this course are Calculus II and Differential Equations. A basic understanding of
16.362: Signals and Systems: 1.0 Prof. K. Chandra ECE, UMASS Lowell September 1, 2016 1 Background The pre-requisites for this course are Calculus II and Differential Equations. A basic understanding of
Series FOURIER SERIES. Graham S McDonald. A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis
 Series FOURIER SERIES Graham S McDonald A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 24 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk 1. Theory
Series FOURIER SERIES Graham S McDonald A self-contained Tutorial Module for learning the technique of Fourier series analysis Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 24 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk 1. Theory
Final Exam ECE301 Signals and Systems Friday, May 3, Cover Sheet
 Name: Final Exam ECE3 Signals and Systems Friday, May 3, 3 Cover Sheet Write your name on this page and every page to be safe. Test Duration: minutes. Coverage: Comprehensive Open Book but Closed Notes.
Name: Final Exam ECE3 Signals and Systems Friday, May 3, 3 Cover Sheet Write your name on this page and every page to be safe. Test Duration: minutes. Coverage: Comprehensive Open Book but Closed Notes.
Sinc Functions. Continuous-Time Rectangular Pulse
 Sinc Functions The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE114 Digital Signal Processing Lecture Notes: Sinc Functions and Sampling Theory October 7, 2011 A rectangular pulse in time/frequency
Sinc Functions The Cooper Union Department of Electrical Engineering ECE114 Digital Signal Processing Lecture Notes: Sinc Functions and Sampling Theory October 7, 2011 A rectangular pulse in time/frequency
Problem Value
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 30-Apr-04 COURSE: ECE-2025 NAME: GT #: LAST, FIRST Recitation Section: Circle the date & time when your Recitation
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 30-Apr-04 COURSE: ECE-2025 NAME: GT #: LAST, FIRST Recitation Section: Circle the date & time when your Recitation
Question Paper Code : AEC11T02
 Hall Ticket No Question Paper Code : AEC11T02 VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Affiliated to JNTUH, Hyderabad Four Year B. Tech III Semester Tutorial Question Bank 2013-14 (Regulations: VCE-R11)
Hall Ticket No Question Paper Code : AEC11T02 VARDHAMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Affiliated to JNTUH, Hyderabad Four Year B. Tech III Semester Tutorial Question Bank 2013-14 (Regulations: VCE-R11)
6.003: Signals and Systems. Sampling and Quantization
 6.003: Signals and Systems Sampling and Quantization December 1, 2009 Last Time: Sampling and Reconstruction Uniform sampling (sampling interval T ): x[n] = x(nt ) t n Impulse reconstruction: x p (t) =
6.003: Signals and Systems Sampling and Quantization December 1, 2009 Last Time: Sampling and Reconstruction Uniform sampling (sampling interval T ): x[n] = x(nt ) t n Impulse reconstruction: x p (t) =
Lecture 18: Stability
 Lecture 18: Stability ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 4/18/2017 1 Stability 2 Impulse Response 3 Z Transform Outline 1 Stability 2 Impulse Response 3 Z Transform BIBO Stability
Lecture 18: Stability ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 4/18/2017 1 Stability 2 Impulse Response 3 Z Transform Outline 1 Stability 2 Impulse Response 3 Z Transform BIBO Stability
CH.4 Continuous-Time Fourier Series
 CH.4 Continuous-Time Fourier Series First step to Fourier analysis. My mathematical model is killing me! The difference between mathematicians and engineers is mathematicians develop mathematical tools
CH.4 Continuous-Time Fourier Series First step to Fourier analysis. My mathematical model is killing me! The difference between mathematicians and engineers is mathematicians develop mathematical tools
Solution 10 July 2015 ECE301 Signals and Systems: Midterm. Cover Sheet
 Solution 10 July 2015 ECE301 Signals and Systems: Midterm Cover Sheet Test Duration: 60 minutes Coverage: Chap. 1,2,3,4 One 8.5" x 11" crib sheet is allowed. Calculators, textbooks, notes are not allowed.
Solution 10 July 2015 ECE301 Signals and Systems: Midterm Cover Sheet Test Duration: 60 minutes Coverage: Chap. 1,2,3,4 One 8.5" x 11" crib sheet is allowed. Calculators, textbooks, notes are not allowed.
Chapter 2: The Fourier Transform
 EEE, EEE Part A : Digital Signal Processing Chapter Chapter : he Fourier ransform he Fourier ransform. Introduction he sampled Fourier transform of a periodic, discrete-time signal is nown as the discrete
EEE, EEE Part A : Digital Signal Processing Chapter Chapter : he Fourier ransform he Fourier ransform. Introduction he sampled Fourier transform of a periodic, discrete-time signal is nown as the discrete
Ver 3808 E1.10 Fourier Series and Transforms (2014) E1.10 Fourier Series and Transforms. Problem Sheet 1 (Lecture 1)
 Ver 88 E. Fourier Series and Transforms 4 Key: [A] easy... [E]hard Questions from RBH textbook: 4., 4.8. E. Fourier Series and Transforms Problem Sheet Lecture. [B] Using the geometric progression formula,
Ver 88 E. Fourier Series and Transforms 4 Key: [A] easy... [E]hard Questions from RBH textbook: 4., 4.8. E. Fourier Series and Transforms Problem Sheet Lecture. [B] Using the geometric progression formula,
Solutions. Number of Problems: 10
 Final Exam February 9th, 2 Signals & Systems (5-575-) Prof. R. D Andrea Solutions Exam Duration: 5 minutes Number of Problems: Permitted aids: One double-sided A4 sheet. Questions can be answered in English
Final Exam February 9th, 2 Signals & Systems (5-575-) Prof. R. D Andrea Solutions Exam Duration: 5 minutes Number of Problems: Permitted aids: One double-sided A4 sheet. Questions can be answered in English
Discrete Fourier Transform
 Discrete Fourier Transform Valentina Hubeika, Jan Černocký DCGM FIT BUT Brno, {ihubeika,cernocky}@fit.vutbr.cz Diskrete Fourier transform (DFT) We have just one problem with DFS that needs to be solved.
Discrete Fourier Transform Valentina Hubeika, Jan Černocký DCGM FIT BUT Brno, {ihubeika,cernocky}@fit.vutbr.cz Diskrete Fourier transform (DFT) We have just one problem with DFS that needs to be solved.
Continuous-Time Frequency Response (II) Lecture 28: EECS 20 N April 2, Laurent El Ghaoui
 EECS 20 N April 2, 2001 Lecture 28: Continuous-Time Frequency Response (II) Laurent El Ghaoui 1 annoucements homework due on Wednesday 4/4 at 11 AM midterm: Friday, 4/6 includes all chapters until chapter
EECS 20 N April 2, 2001 Lecture 28: Continuous-Time Frequency Response (II) Laurent El Ghaoui 1 annoucements homework due on Wednesday 4/4 at 11 AM midterm: Friday, 4/6 includes all chapters until chapter
EE301 Signals and Systems In-Class Exam Exam 3 Thursday, Apr. 20, Cover Sheet
 NAME: NAME EE301 Signals and Systems In-Class Exam Exam 3 Thursday, Apr. 20, 2017 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 75 minutes. Coverage: Chaps. 5,7 Open Book but Closed Notes. One 8.5 in. x 11 in. crib sheet
NAME: NAME EE301 Signals and Systems In-Class Exam Exam 3 Thursday, Apr. 20, 2017 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 75 minutes. Coverage: Chaps. 5,7 Open Book but Closed Notes. One 8.5 in. x 11 in. crib sheet
EE301 Signals and Systems In-Class Exam Exam 3 Thursday, Apr. 19, Cover Sheet
 EE301 Signals and Systems In-Class Exam Exam 3 Thursday, Apr. 19, 2012 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 75 minutes. Coverage: Chaps. 5,7 Open Book but Closed Notes. One 8.5 in. x 11 in. crib sheet Calculators
EE301 Signals and Systems In-Class Exam Exam 3 Thursday, Apr. 19, 2012 Cover Sheet Test Duration: 75 minutes. Coverage: Chaps. 5,7 Open Book but Closed Notes. One 8.5 in. x 11 in. crib sheet Calculators
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems
 Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
Chapter 5 Frequency Domain Analysis of Systems CT, LTI Systems Consider the following CT LTI system: xt () ht () yt () Assumption: the impulse response h(t) is absolutely integrable, i.e., ht ( ) dt< (this
Up-Sampling (5B) Young Won Lim 11/15/12
 Up-Sampling (5B) Copyright (c) 9,, Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version. or any later version
Up-Sampling (5B) Copyright (c) 9,, Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version. or any later version
11.6. Parametric Differentiation. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Parametric Differentiation 11.6 Introduction Often, the equation of a curve may not be given in Cartesian form y f(x) but in parametric form: x h(t), y g(t). In this section we see how to calculate the
Parametric Differentiation 11.6 Introduction Often, the equation of a curve may not be given in Cartesian form y f(x) but in parametric form: x h(t), y g(t). In this section we see how to calculate the
Homework 3 Solutions
 EECS Signals & Systems University of California, Berkeley: Fall 7 Ramchandran September, 7 Homework 3 Solutions (Send your grades to ee.gsi@gmail.com. Check the course website for details) Review Problem
EECS Signals & Systems University of California, Berkeley: Fall 7 Ramchandran September, 7 Homework 3 Solutions (Send your grades to ee.gsi@gmail.com. Check the course website for details) Review Problem
Lecture 5. The Digital Fourier Transform. (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith)
 Lecture 5 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2-1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2 -. 2. 4. 6. 8 1
Lecture 5 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2-1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2 -. 2. 4. 6. 8 1
OSE801 Engineering System Identification. Lecture 05: Fourier Analysis
 OSE81 Engineering System Identification Lecture 5: Fourier Analysis What we will study in this lecture: A short introduction of Fourier analysis Sampling the data Applications Example 1 Fourier Analysis
OSE81 Engineering System Identification Lecture 5: Fourier Analysis What we will study in this lecture: A short introduction of Fourier analysis Sampling the data Applications Example 1 Fourier Analysis
Assignment #09 - Solution Manual
 Assignment #09 - Solution Manual 1. Choose the correct statements about representation of a continuous signal using Haar wavelets. 1.5 points The signal is approximated using sin and cos functions. The
Assignment #09 - Solution Manual 1. Choose the correct statements about representation of a continuous signal using Haar wavelets. 1.5 points The signal is approximated using sin and cos functions. The
ELEN 4810 Midterm Exam
 ELEN 4810 Midterm Exam Wednesday, October 26, 2016, 10:10-11:25 AM. One sheet of handwritten notes is allowed. No electronics of any kind are allowed. Please record your answers in the exam booklet. Raise
ELEN 4810 Midterm Exam Wednesday, October 26, 2016, 10:10-11:25 AM. One sheet of handwritten notes is allowed. No electronics of any kind are allowed. Please record your answers in the exam booklet. Raise
Plane Curves and Parametric Equations
 Plane Curves and Parametric Equations MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction We typically think of a graph as a curve in the xy-plane generated by the
Plane Curves and Parametric Equations MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction We typically think of a graph as a curve in the xy-plane generated by the
GATE EE Topic wise Questions SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
 www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
x(t) = t[u(t 1) u(t 2)] + 1[u(t 2) u(t 3)]
![x(t) = t[u(t 1) u(t 2)] + 1[u(t 2) u(t 3)] x(t) = t[u(t 1) u(t 2)] + 1[u(t 2) u(t 3)]](/thumbs/96/128551587.jpg) ECE30 Summer II, 2006 Exam, Blue Version July 2, 2006 Name: Solution Score: 00/00 You must show all of your work for full credit. Calculators may NOT be used.. (5 points) x(t) = tu(t ) + ( t)u(t 2) u(t
ECE30 Summer II, 2006 Exam, Blue Version July 2, 2006 Name: Solution Score: 00/00 You must show all of your work for full credit. Calculators may NOT be used.. (5 points) x(t) = tu(t ) + ( t)u(t 2) u(t
Chapter 5. Fourier Analysis for Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Chapter
 Chapter 5. Fourier Analysis for Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Chapter Objec@ves 1. Learn techniques for represen3ng discrete-)me periodic signals using orthogonal sets of periodic basis func3ons. 2.
Chapter 5. Fourier Analysis for Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Chapter Objec@ves 1. Learn techniques for represen3ng discrete-)me periodic signals using orthogonal sets of periodic basis func3ons. 2.
11.6. Parametric Differentiation. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Parametric Differentiation 11.6 Introduction Sometimes the equation of a curve is not be given in Cartesian form y f(x) but in parametric form: x h(t), y g(t). In this Section we see how to calculate the
Parametric Differentiation 11.6 Introduction Sometimes the equation of a curve is not be given in Cartesian form y f(x) but in parametric form: x h(t), y g(t). In this Section we see how to calculate the
EE 16B Final, December 13, Name: SID #:
 EE 16B Final, December 13, 2016 Name: SID #: Important Instructions: Show your work. An answer without explanation is not acceptable and does not guarantee any credit. Only the front pages will be scanned
EE 16B Final, December 13, 2016 Name: SID #: Important Instructions: Show your work. An answer without explanation is not acceptable and does not guarantee any credit. Only the front pages will be scanned
EE123 Digital Signal Processing
 EE123 Digital Signal Processing Lecture 19 Practical ADC/DAC Ideal Anti-Aliasing ADC A/D x c (t) Analog Anti-Aliasing Filter HLP(jΩ) sampler t = nt x[n] =x c (nt ) Quantizer 1 X c (j ) and s < 2 1 T X
EE123 Digital Signal Processing Lecture 19 Practical ADC/DAC Ideal Anti-Aliasing ADC A/D x c (t) Analog Anti-Aliasing Filter HLP(jΩ) sampler t = nt x[n] =x c (nt ) Quantizer 1 X c (j ) and s < 2 1 T X
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C1 HANDOUT 6a. Dr David Corrigan 1. Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept.
 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C HANDOUT 6a. Dr David Corrigan. Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. corrigad@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ corrigad FOURIER SERIES Have seen how the behaviour of systems can
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C HANDOUT 6a. Dr David Corrigan. Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. corrigad@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ corrigad FOURIER SERIES Have seen how the behaviour of systems can
Problem Score Total
 UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 417 Principles of Signal Analysis Spring 14 EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS Friday, May 9, 14 This is a CLOSED BOOK exam.
UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 417 Principles of Signal Analysis Spring 14 EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS Friday, May 9, 14 This is a CLOSED BOOK exam.
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Final Exam January 31, Solutions
 Final Exam January 31, 014 Signals & Systems (151-0575-01) Prof. R. D Andrea & P. Reist Solutions Exam Duration: Number of Problems: Total Points: Permitted aids: Important: 150 minutes 7 problems 50 points
Final Exam January 31, 014 Signals & Systems (151-0575-01) Prof. R. D Andrea & P. Reist Solutions Exam Duration: Number of Problems: Total Points: Permitted aids: Important: 150 minutes 7 problems 50 points
Grades will be determined by the correctness of your answers (explanations are not required).
 6.00 (Fall 2011) Final Examination December 19, 2011 Name: Kerberos Username: Please circle your section number: Section Time 2 11 am 1 pm 4 2 pm Grades will be determined by the correctness of your answers
6.00 (Fall 2011) Final Examination December 19, 2011 Name: Kerberos Username: Please circle your section number: Section Time 2 11 am 1 pm 4 2 pm Grades will be determined by the correctness of your answers
Homework 9 Solutions
 8-290 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 207 Homework 9 Solutions Part One. (6 points) Compute the convolution of the following continuous-time aperiodic signals. (Hint: Use the
8-290 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 207 Homework 9 Solutions Part One. (6 points) Compute the convolution of the following continuous-time aperiodic signals. (Hint: Use the
Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives with respect to those variables. Most (but
Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives with respect to those variables. Most (but
4.5. Applications of Trigonometry to Waves. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Applications of Trigonometry to Waves 4.5 Introduction Waves and vibrations occur in many contexts. The water waves on the sea and the vibrations of a stringed musical instrument are just two everyday
Applications of Trigonometry to Waves 4.5 Introduction Waves and vibrations occur in many contexts. The water waves on the sea and the vibrations of a stringed musical instrument are just two everyday
Final Exam of ECE301, Prof. Wang s section 8 10am Tuesday, May 6, 2014, EE 129.
 Final Exam of ECE301, Prof. Wang s section 8 10am Tuesday, May 6, 2014, EE 129. 1. Please make sure that it is your name printed on the exam booklet. Enter your student ID number, e-mail address, and signature
Final Exam of ECE301, Prof. Wang s section 8 10am Tuesday, May 6, 2014, EE 129. 1. Please make sure that it is your name printed on the exam booklet. Enter your student ID number, e-mail address, and signature
Math 333 Qualitative Results: Forced Harmonic Oscillators
 Math 333 Qualitative Results: Forced Harmonic Oscillators Forced Harmonic Oscillators. Recall our derivation of the second-order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients: my
Math 333 Qualitative Results: Forced Harmonic Oscillators Forced Harmonic Oscillators. Recall our derivation of the second-order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients: my
6.003: Signals and Systems Lecture 18 April 13, 2010
 6.003: Signals and Systems Lecture 8 April 3, 200 6.003: Signals and Systems Discrete-Time Frequency Representations Signals and/or Systems Two perspectives: feedback and control (focus on systems) X +
6.003: Signals and Systems Lecture 8 April 3, 200 6.003: Signals and Systems Discrete-Time Frequency Representations Signals and/or Systems Two perspectives: feedback and control (focus on systems) X +
We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by
![We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by We start with a simple result from Fourier analysis. Given a function f : [0, 1] C, we define the Fourier coefficients of f by](/thumbs/74/71304729.jpg) Chapter 9 The functional equation for the Riemann zeta function We will eventually deduce a functional equation, relating ζ(s to ζ( s. There are various methods to derive this functional equation, see
Chapter 9 The functional equation for the Riemann zeta function We will eventually deduce a functional equation, relating ζ(s to ζ( s. There are various methods to derive this functional equation, see
Problem Value
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 2-May-05 COURSE: ECE-2025 NAME: GT #: LAST, FIRST (ex: gtz123a) Recitation Section: Circle the date & time when
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 2-May-05 COURSE: ECE-2025 NAME: GT #: LAST, FIRST (ex: gtz123a) Recitation Section: Circle the date & time when
Lecture 4: Oscillators to Waves
 Matthew Schwartz Lecture 4: Oscillators to Waves Review two masses Last time we studied how two coupled masses on springs move If we take κ=k for simplicity, the two normal modes correspond to ( ) ( )
Matthew Schwartz Lecture 4: Oscillators to Waves Review two masses Last time we studied how two coupled masses on springs move If we take κ=k for simplicity, the two normal modes correspond to ( ) ( )
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.01
 ENGI 940 Lecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.01 8. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
ENGI 940 Lecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.01 8. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
Assignment 3 Solutions
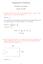 Assignment Solutions Networks and systems August 8, 7. Consider an LTI system with transfer function H(jw) = input is sin(t + π 4 ), what is the output? +jw. If the Solution : C For an LTI system with
Assignment Solutions Networks and systems August 8, 7. Consider an LTI system with transfer function H(jw) = input is sin(t + π 4 ), what is the output? +jw. If the Solution : C For an LTI system with
Review of Frequency Domain Fourier Series: Continuous periodic frequency components
 Today we will review: Review of Frequency Domain Fourier series why we use it trig form & exponential form how to get coefficients for each form Eigenfunctions what they are how they relate to LTI systems
Today we will review: Review of Frequency Domain Fourier series why we use it trig form & exponential form how to get coefficients for each form Eigenfunctions what they are how they relate to LTI systems
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing
 ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 9: February 13th, 2018 Downsampling/Upsampling and Practical Interpolation Lecture Outline! CT processing of DT signals! Downsampling! Upsampling 2 Continuous-Time
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 9: February 13th, 2018 Downsampling/Upsampling and Practical Interpolation Lecture Outline! CT processing of DT signals! Downsampling! Upsampling 2 Continuous-Time
Sampling Signals of Finite Rate of Innovation*
 Sampling Signals of Finite Rate of Innovation* Martin Vetterli http://lcavwww.epfl.ch/~vetterli EPFL & UCBerkeley.15.1.1.5.5.5.5.1.1.15.2 128 128 256 384 512 64 768 896 124 1152.15 128 128 256 384 512
Sampling Signals of Finite Rate of Innovation* Martin Vetterli http://lcavwww.epfl.ch/~vetterli EPFL & UCBerkeley.15.1.1.5.5.5.5.1.1.15.2 128 128 256 384 512 64 768 896 124 1152.15 128 128 256 384 512
Signals and Systems: Introduction
 Dependent variable Signals and Systems: Introduction What is a signal? Signals may describe a wide variety of physical phenomena. The information in a signal is contained in a pattern of variations of
Dependent variable Signals and Systems: Introduction What is a signal? Signals may describe a wide variety of physical phenomena. The information in a signal is contained in a pattern of variations of
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing
 ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 8: February 7th, 2017 Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture Outline! Review " Ideal sampling " Frequency response of sampled signal " Reconstruction " Anti-aliasing
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 8: February 7th, 2017 Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture Outline! Review " Ideal sampling " Frequency response of sampled signal " Reconstruction " Anti-aliasing
New Mexico State University Klipsch School of Electrical Engineering EE312 - Signals and Systems I Fall 2015 Final Exam
 New Mexico State University Klipsch School of Electrical Engineering EE312 - Signals and Systems I Fall 2015 Name: Solve problems 1 3 and two from problems 4 7. Circle below which two of problems 4 7 you
New Mexico State University Klipsch School of Electrical Engineering EE312 - Signals and Systems I Fall 2015 Name: Solve problems 1 3 and two from problems 4 7. Circle below which two of problems 4 7 you
! Downsampling/Upsampling. ! Practical Interpolation. ! Non-integer Resampling. ! Multi-Rate Processing. " Interchanging Operations
 Lecture Outline ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 10: February 14th, 2017 Practical and Non-integer Sampling, Multirate Sampling! Downsampling/! Practical Interpolation! Non-integer Resampling! Multi-Rate
Lecture Outline ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 10: February 14th, 2017 Practical and Non-integer Sampling, Multirate Sampling! Downsampling/! Practical Interpolation! Non-integer Resampling! Multi-Rate
LAB 6: FIR Filter Design Summer 2011
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 311: Digital Signal Processing Lab Chandra Radhakrishnan Peter Kairouz LAB 6: FIR Filter Design Summer 011
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 311: Digital Signal Processing Lab Chandra Radhakrishnan Peter Kairouz LAB 6: FIR Filter Design Summer 011
Variational construction of periodic and connecting orbits in the planar Sitnikov problem. Mitsuru Shibayama(Kyoto University)
 Variational construction of periodic and connecting orbits in the planar Sitnikov problem Mitsuru Shibayama(Kyoto University) 1 The three-body problem Consider the planar three-body problem which is governed
Variational construction of periodic and connecting orbits in the planar Sitnikov problem Mitsuru Shibayama(Kyoto University) 1 The three-body problem Consider the planar three-body problem which is governed
EE 3054: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal.
 EE 34: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer 7 Test No notes, closed book. Show your work. Simplify your answers. 3. It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal = 3 u(t) produces
EE 34: Signals, Systems, and Transforms Summer 7 Test No notes, closed book. Show your work. Simplify your answers. 3. It is observed of some continuous-time LTI system that the input signal = 3 u(t) produces
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing
 ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 8: February 12th, 2019 Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture Outline! Review " Ideal sampling " Frequency response of sampled signal " Reconstruction " Anti-aliasing
ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 8: February 12th, 2019 Sampling and Reconstruction Lecture Outline! Review " Ideal sampling " Frequency response of sampled signal " Reconstruction " Anti-aliasing
ECE 301 Fall 2011 Division 1. Homework 1 Solutions.
 ECE 3 Fall 2 Division. Homework Solutions. Reading: Course information handout on the course website; textbook sections.,.,.2,.3,.4; online review notes on complex numbers. Problem. For each discrete-time
ECE 3 Fall 2 Division. Homework Solutions. Reading: Course information handout on the course website; textbook sections.,.,.2,.3,.4; online review notes on complex numbers. Problem. For each discrete-time
Discrete Time Fourier Transform
 Discrete Time Fourier Transform Recall that we wrote the sampled signal x s (t) = x(kt)δ(t kt). We calculate its Fourier Transform. We do the following: Ex. Find the Continuous Time Fourier Transform of
Discrete Time Fourier Transform Recall that we wrote the sampled signal x s (t) = x(kt)δ(t kt). We calculate its Fourier Transform. We do the following: Ex. Find the Continuous Time Fourier Transform of
Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS)
 ELEC264: Signals And Systems Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS) o o o o Introduction to frequency analysis of signals CT FS Fourier series of CT periodic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Fourier Series Properties
ELEC264: Signals And Systems Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS) o o o o Introduction to frequency analysis of signals CT FS Fourier series of CT periodic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Fourier Series Properties
The Johns Hopkins University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Introduction to Linear Systems Fall 2002.
 The Johns Hopkins University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 505.460 Introduction to Linear Systems Fall 2002 Final exam Name: You are allowed to use: 1. Table 3.1 (page 206) & Table
The Johns Hopkins University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 505.460 Introduction to Linear Systems Fall 2002 Final exam Name: You are allowed to use: 1. Table 3.1 (page 206) & Table
Final Exam of ECE301, Section 1 (Prof. Chih-Chun Wang) 1 3pm, Friday, December 13, 2016, EE 129.
 Final Exam of ECE301, Section 1 (Prof. Chih-Chun Wang) 1 3pm, Friday, December 13, 2016, EE 129. 1. Please make sure that it is your name printed on the exam booklet. Enter your student ID number, and
Final Exam of ECE301, Section 1 (Prof. Chih-Chun Wang) 1 3pm, Friday, December 13, 2016, EE 129. 1. Please make sure that it is your name printed on the exam booklet. Enter your student ID number, and
Fourier Analysis Overview (0A)
 CTFS: Fourier Series CTFT: Fourier Transform DTFS: Fourier Series DTFT: Fourier Transform DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform Copyright (c) 2011-2016 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute
CTFS: Fourier Series CTFT: Fourier Transform DTFS: Fourier Series DTFT: Fourier Transform DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform Copyright (c) 2011-2016 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.01
 ENGI 940 ecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.0 8. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
ENGI 940 ecture Notes 8 - PDEs Page 8.0 8. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
Homework 4. May An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt
 Homework 4 May 2017 1. An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt Determine the impulse response of the system. Rewriting as y(t) = t e (t
Homework 4 May 2017 1. An LTI system has an input, x(t) and output y(t) related through the equation y(t) = t e (t t ) x(t 2)dt Determine the impulse response of the system. Rewriting as y(t) = t e (t
Signal Processing Signal and System Classifications. Chapter 13
 Chapter 3 Signal Processing 3.. Signal and System Classifications In general, electrical signals can represent either current or voltage, and may be classified into two main categories: energy signals
Chapter 3 Signal Processing 3.. Signal and System Classifications In general, electrical signals can represent either current or voltage, and may be classified into two main categories: energy signals
EE 313 Linear Systems and Signals The University of Texas at Austin. Solution Set for Homework #1 on Sinusoidal Signals
 Solution Set for Homework #1 on Sinusoidal Signals By Mr. Houshang Salimian and Prof. Brian L. Evans September 7, 2018 1. Prologue: This problem helps you to identify the points of interest in a sinusoidal
Solution Set for Homework #1 on Sinusoidal Signals By Mr. Houshang Salimian and Prof. Brian L. Evans September 7, 2018 1. Prologue: This problem helps you to identify the points of interest in a sinusoidal
Lecture 11: Spectral Analysis
 Lecture 11: Spectral Analysis Methods For Estimating The Spectrum Walid Sharabati Purdue University Latest Update October 27, 2016 Professor Sharabati (Purdue University) Time Series Analysis October 27,
Lecture 11: Spectral Analysis Methods For Estimating The Spectrum Walid Sharabati Purdue University Latest Update October 27, 2016 Professor Sharabati (Purdue University) Time Series Analysis October 27,
Practice Problems For Test 3
 Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Background. Video 17
 Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Background Video 17 Daniel J. Bodony Department of Aerospace Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign In this video you will learn... 1 What ODEs are
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Background Video 17 Daniel J. Bodony Department of Aerospace Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign In this video you will learn... 1 What ODEs are
Detailed Solutions to Exercises
 Detailed Solutions to Exercises Digital Signal Processing Mikael Swartling Nedelko Grbic rev. 205 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Detailed solution to problem E3.4 A
Detailed Solutions to Exercises Digital Signal Processing Mikael Swartling Nedelko Grbic rev. 205 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Detailed solution to problem E3.4 A
