Math 8 Winter 2010 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1. xcos 6xdx = 4. = x2 4
|
|
|
- Colin York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions Evaluate xcos 2 3x Solution: First rewrite cos 2 3x using the half-angle formula: ( ) 1 + cos 6x xcos 2 3x = x = 1 x + 1 xcos 6x Now use integration by parts to evaluate xcos 6x, setting u = x and dv = cos 6x, which makes du = and v = sin 6x/6: 1 x xcos 6x = x2 4 = x2 4 xsin 6x + 12 xsin 6x + 12 sin 6x 12 + cos 6x 72 + C 2 Evaluate e 2x sinx. Solution: We use integration by parts twice. Set I = e 2x sin x. Now, using integration by parts with u = e 2x and dv = sin x (the other choice of u and dv works just as well), so du = 2e 2x and v = cos x, we have I = e 2x cos x 2e 2x cos x. Using integration by parts again with u = 2e 2x and dv = cos x, we get ( ) I = e 2x cos x 2e 2x sin x 4e 2x sin x = e 2x cos x + 2e 2x sin x 4 e 2x sinx + C Solving this equation for I, we see that = e 2x cos x + 2e 2x sin x 4I + C. I = e2x cos x + 2e 2x sinx 5 + C.
2 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions Could you in principle compute x 11 e x, and if so, how? Solution: Yes, using integration by parts 1 1 times, each time setting u equal to the polynomial and letting dv = e x. 4 Evaluate sin 3 xcos 4 x. Solution: Since the power of sine is odd, we convert 2 of the sines into cosines using sin 2 x+cos 2 x = 1, so sin 2 x = 1 cos 2 x: sin 3 xcos 4 x = sin x ( 1 cos 2 x ) cos 4 x. Now we make a u-substitution, setting u = cos x and du = sin x: sin x ( 1 cos 2 x ) cos 4 x = (1 u 2 )u 4 du = u 4 u 6 du = u5 5 + u7 7 + C = cos5 x 5 + cos7 x 7 + C. 5 Evaluate sec 4 xtan 4 x. Solution: Since the power of secant is even, we save a sec 2 x and convert the other secants to tangents using the identity sec 2 x = 1 + tan 2 x: sec 4 xtan 4 x = sec 2 x ( 1 + tan 2 x ) tan 4 x. Now we make a u-substitution, setting u = tan x and du = sec 2 x: sec 2 x ( 1 + tan 2 x ) tan 4 x. = (1 + u 2 )u 4 du = u 4 + u 6 du = u5 5 + u7 7 + C = tan5 x 5 + tan7 x 7 + C.
3 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions What substitution would you use to evaluate x x 2? Solution: We would like to simplify the radical 16 + x 2 using the identity 16+16tan 2 θ = 16sec 2 θ, so we would set x = 4tan θ. 7 Evaluate (9 x 2 ) 3/2. Solution: The goal is to simplify (9 x 2 ) 3/2 using the identity 9 9sin 2 θ = 9cos 2 θ, so we set x = 3sin θ, giving = 3cos θ: 3cos θ (9 x 2 ) 3/2 = (9 9sin 2 dθ θ) 3/2 3cos θ = 3 3 cos 3 θ dθ = 1 9 = 1 9 dθ cos 2 θ sec 2 θ dθ = 1 tan θ + C. 9 Now we would draw a right triangle with sin θ = x/3 to compute that tan θ = x/ 9 x 2, giving us that (9 x 2 ) 3/2 = x 9 9 x + C. 2 8 Is the angle between the vectors a = 3, 1, 2 and b = 2, 2, 4 acute, obtuse, or right? Solution: Since a b = = 12 > and a b = a b cos θ, we see that cos θ >, so the angle between a and b is acute.
4 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions Find the area of the parallelogram whose vertices are ( 1, 2, ), (, 4, 2), (2, 1, 2), and (3, 3, ). Solution: Label the points P, Q, R, and S. Then PQ = 1,2,2, PR = 3, 1, 2 and PS = 4,1,. It follows that the parallelogram is determined by PQ and PR, so it s area is PQ PR = 2,8, 7 = = If a and b are both nonzero vectors and a b = a b, what can you say about the relationship between a and b? Solution: We are given that a b = a b, and we know that a b = a b cos θ, while a b = a b sin θ It follows that we must have cos θ = sin θ, and the only value of θ which satisfies this is θ = π/4, so the two vectors are at a 45 angle to each other. 11 Consider the vectors a = 4, 1 and b = 2, 2, shown below. Compute cos θ, u, and the length x. b Note: you should not leave unevaluated trigonometric functions in your answer. θ Solution: As θ is the angle between a and b, we can find it via the dot product: so cos θ = u a b = 1 = a b cos θ = 17 8 cos θ, x a Now, u = proj a b = a b a 2 a = ,1 = 17, Finally, using the Pythagorean Theorem, x = b 2 u 2 = = = 6 16.
5 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions Find the equation of the plane which passes through the point (2, 3, 1) and contains the line x = 3t 2, y = t + 3, z = 5t 3. Solution: We need to find two vectors on this plane, so consider the vector from the point (2, 3, 1) to the point ( 2,3, 3) which lies on the given line (just set t = in the line equation). This vector is 4,6,2, and the direction vector of the given line is 3,1,5, so the normal vector to the plane is 4, 6, 2 3, 1, 5 = 28, 26, 22. The equation for the plane is then 28(x 2) + 26(y + 3) 22(z + 1) =. 13 Find the line of intersection of the planes x + y + z = 12 and 2x + 3y + z = 2. Solution: Since the line of intersection lies on both planes, it must be orthogonal to both normal vectors. Therefore its direction is given by the cross product of the normal vectors: 1,1,1 2,3,1 = 2,1,1. We also need a point on the line of intersection. To find this, let us set x = (other choices work equally well). The equations for the first plane becomes y + z = 12, so z = 12 y. Substituting this into the equation for the second plane gives 3y + (12 y) = 2, so y = 5. Thus the point (, 5,17) lies on the line of intersection, so the line is given by x = 2t, y = t 5, z = t Compute the position vector for a particle which passes through the origin at time t = and has velocity vector v(t) = 2ti + sintj + cos tk. Solution: The position vector is the antiderivative of the velocity vector, so it is r(t) = v(t)dt = t 2 i cos tj + sin tk + C,
6 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 6 where C is a vector constant of integration. The problem stated that the particle passes through origin at time t =, so need r() = : = r() = j + C; thus C = j, so we have that r(t)t 2 i + (1 cos t)j sin tk. 15 Show that if a particle moves at constant speed, then its velocity and acceleration vectors are orthogonal. Note that this does not mean that the velocity is! (Hint: consider the derivative of v v.) Solution: Suppose that the particle s speed is C, so v(t) = C. Then we have so taking the derivates of both sides gives v(t) v(t) = C 2, v(t) v (t) + v (t) v(t) =, which implies that v(t) v (t) = v(t) a(t) =, as we wanted. 16 Consider the curve defined by r(t) = 4sin ct,3ct,4cos ct. What value of c makes the arc length of the space curve traced by r(t), t 1, equal to 1? Solution: The arc length from to 1 of this curve is given by 1 speed dt = For this to equal 1, we want c = 2. = = = 5c. 16c 2 cos 2 ct + 9c c 2 sin 2 ct dt 16c 2 + 9c 2 dt 5cdt
Chapter 8 Integration Techniques and Improper Integrals
 Chapter 8 Integration Techniques and Improper Integrals 8.1 Basic Integration Rules 8.2 Integration by Parts 8.4 Trigonometric Substitutions 8.5 Partial Fractions 8.6 Numerical Integration 8.7 Integration
Chapter 8 Integration Techniques and Improper Integrals 8.1 Basic Integration Rules 8.2 Integration by Parts 8.4 Trigonometric Substitutions 8.5 Partial Fractions 8.6 Numerical Integration 8.7 Integration
CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry
 ) (Answers for Chapter 5: Analytic Trigonometry) A.5. CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry SECTION 5.: FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) csc( x) sin x Reciprocal
) (Answers for Chapter 5: Analytic Trigonometry) A.5. CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry SECTION 5.: FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) csc( x) sin x Reciprocal
Math 3c Solutions: Exam 1 Fall Graph by eliiminating the parameter; be sure to write the equation you get when you eliminate the parameter.
 Math c Solutions: Exam 1 Fall 16 1. Graph by eliiminating the parameter; be sure to write the equation you get when you eliminate the parameter. x tan t x tan t y sec t y sec t t π 4 To eliminate the parameter,
Math c Solutions: Exam 1 Fall 16 1. Graph by eliiminating the parameter; be sure to write the equation you get when you eliminate the parameter. x tan t x tan t y sec t y sec t t π 4 To eliminate the parameter,
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10
 Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration
 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Using this definition, it is possible to define an angle of any (positive or negative) measurement by recognizing how its terminal side is obtained.
 Angle in Standard Position With the Cartesian plane, we define an angle in Standard Position if it has its vertex on the origin and one of its sides ( called the initial side ) is always on the positive
Angle in Standard Position With the Cartesian plane, we define an angle in Standard Position if it has its vertex on the origin and one of its sides ( called the initial side ) is always on the positive
6.2 Trigonometric Integrals and Substitutions
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 9: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan 6. Trigonometric Integrals and Substitutions In this section, we discuss integrals with trigonometric integrands and integrals that can
Arkansas Tech University MATH 9: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan 6. Trigonometric Integrals and Substitutions In this section, we discuss integrals with trigonometric integrands and integrals that can
Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters
 Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters α( alpha), β ( beta), θ ( theta) as well as upper case letters A,B,
Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters α( alpha), β ( beta), θ ( theta) as well as upper case letters A,B,
CK- 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 MATH 214 (R1) Winter 2008 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #8 Completion Date: Friday March 14, 2008 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question 1.
MATH 214 (R1) Winter 2008 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #8 Completion Date: Friday March 14, 2008 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question 1.
PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (50 PTS.)
 Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 50 FOR PART 1, AND 100 FOR PART 2 Show all work, simplify as appropriate,
Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 50 FOR PART 1, AND 100 FOR PART 2 Show all work, simplify as appropriate,
Math F15 Rahman
 Math - 9 F5 Rahman Week3 7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following definitions: sinh x = (ex e x ) cosh x = (ex + e x ) tanh x = sinh
Math - 9 F5 Rahman Week3 7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following definitions: sinh x = (ex e x ) cosh x = (ex + e x ) tanh x = sinh
( ) Trigonometric identities and equations, Mixed exercise 10
 Trigonometric identities and equations, Mixed exercise 0 a is in the third quadrant, so cos is ve. The angle made with the horizontal is. So cos cos a cos 0 0 b sin sin ( 80 + 4) sin 4 b is in the fourth
Trigonometric identities and equations, Mixed exercise 0 a is in the third quadrant, so cos is ve. The angle made with the horizontal is. So cos cos a cos 0 0 b sin sin ( 80 + 4) sin 4 b is in the fourth
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 SECTION 4.1 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Special Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios
SECTION 4.1 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Special Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios
MATH MIDTERM 4 - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS Calculus, Fall 2017 Professor: Jared Speck. Problem 1. Approximate the integral
 MATH 8. - MIDTERM 4 - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8. Calculus, Fall 7 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Approimate the integral 4 d using first Simpson s rule with two equal intervals and then the
MATH 8. - MIDTERM 4 - SOME REVIEW PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 8. Calculus, Fall 7 Professor: Jared Speck Problem. Approimate the integral 4 d using first Simpson s rule with two equal intervals and then the
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 144 Activity #7 Trigonometric Identities
 144 p 1 Math 144 Activity #7 Trigonometric Identities What is a trigonometric identity? Trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions that are true for every single value
144 p 1 Math 144 Activity #7 Trigonometric Identities What is a trigonometric identity? Trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions that are true for every single value
6.1: Reciprocal, Quotient & Pythagorean Identities
 Math Pre-Calculus 6.: Reciprocal, Quotient & Pythagorean Identities A trigonometric identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable(s) for which the equation is defined. In this chapter
Math Pre-Calculus 6.: Reciprocal, Quotient & Pythagorean Identities A trigonometric identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable(s) for which the equation is defined. In this chapter
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r :
 Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
MATH 162. Midterm Exam 1 - Solutions February 22, 2007
 MATH 62 Midterm Exam - Solutions February 22, 27. (8 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) x sin(x 4 + 7) dx Solution: Let u = x 4 + 7, then du = 4x dx and x sin(x 4 + 7) dx = 4 sin(u) du = 4 [
MATH 62 Midterm Exam - Solutions February 22, 27. (8 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) x sin(x 4 + 7) dx Solution: Let u = x 4 + 7, then du = 4x dx and x sin(x 4 + 7) dx = 4 sin(u) du = 4 [
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r :
 Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Since 1 revolution = 1 = = Since 1 revolution = 1 = =
 Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 8A Fall 2015! 207 Since 1 revolution = 1 = = Since 1 revolution = 1 = = Convert to revolutions (or back to degrees and/or radians) a) 45! = b) 120! = c) 450! =
Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 8A Fall 2015! 207 Since 1 revolution = 1 = = Since 1 revolution = 1 = = Convert to revolutions (or back to degrees and/or radians) a) 45! = b) 120! = c) 450! =
Math 205, Winter 2018, Assignment 3
 Math 05, Winter 08, Assignment 3 Solutions. Calculate the following integrals. Show your steps and reasoning. () a) ( + + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e + e = ( )e + e + c = ( + )e + c This uses
Math 05, Winter 08, Assignment 3 Solutions. Calculate the following integrals. Show your steps and reasoning. () a) ( + + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e + e = ( )e + e + c = ( + )e + c This uses
Worksheet 1.8: Geometry of Vector Derivatives
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.8: Geometry of Vector Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Calc I: Computing derivatives of single-variable functions y = f (t).
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.8: Geometry of Vector Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Calc I: Computing derivatives of single-variable functions y = f (t).
b) The trend is for the average slope at x = 1 to decrease. The slope at x = 1 is 1.
 Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
1. Vectors and Matrices
 E. 8.02 Exercises. Vectors and Matrices A. Vectors Definition. A direction is just a unit vector. The direction of A is defined by dir A = A, (A 0); A it is the unit vector lying along A and pointed like
E. 8.02 Exercises. Vectors and Matrices A. Vectors Definition. A direction is just a unit vector. The direction of A is defined by dir A = A, (A 0); A it is the unit vector lying along A and pointed like
( ) + ( ) ( ) ( ) Exercise Set 6.1: Sum and Difference Formulas. β =, π π. π π. β =, evaluate tan β. Simplify each of the following expressions.
 Simplify each of the following expressions ( x cosx + cosx ( + x ( 60 θ + ( 60 + θ 6 cos( 60 θ + cos( 60 + θ 7 cosx + cosx+ 8 x+ + x 6 6 9 ( θ 80 + ( θ + 80 0 cos( 90 + θ + cos( 90 θ 7 Given that tan (
Simplify each of the following expressions ( x cosx + cosx ( + x ( 60 θ + ( 60 + θ 6 cos( 60 θ + cos( 60 + θ 7 cosx + cosx+ 8 x+ + x 6 6 9 ( θ 80 + ( θ + 80 0 cos( 90 + θ + cos( 90 θ 7 Given that tan (
n=0 ( 1)n /(n + 1) converges, but not
 Math 07H Topics for the third exam (and beyond) (Technically, everything covered on the first two exams plus...) Absolute convergence and alternating series A series a n converges absolutely if a n converges.
Math 07H Topics for the third exam (and beyond) (Technically, everything covered on the first two exams plus...) Absolute convergence and alternating series A series a n converges absolutely if a n converges.
MATH 32A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW. 1. Vectors. v v = 1 22
 MATH 3A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Let v = 3,, 3. a. Find e v. Solution: v = 9 + 4 + 9 =, so 1. Vectors e v = 1 v v = 1 3,, 3 b. Find the vectors parallel to v which lie on the sphere of radius two
MATH 3A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Let v = 3,, 3. a. Find e v. Solution: v = 9 + 4 + 9 =, so 1. Vectors e v = 1 v v = 1 3,, 3 b. Find the vectors parallel to v which lie on the sphere of radius two
Math 102 Spring 2008: Solutions: HW #3 Instructor: Fei Xu
 Math Spring 8: Solutions: HW #3 Instructor: Fei Xu. section 7., #8 Evaluate + 3 d. + We ll solve using partial fractions. If we assume 3 A + B + C, clearing denominators gives us A A + B B + C +. Then
Math Spring 8: Solutions: HW #3 Instructor: Fei Xu. section 7., #8 Evaluate + 3 d. + We ll solve using partial fractions. If we assume 3 A + B + C, clearing denominators gives us A A + B B + C +. Then
MATH Final Review
 MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 2 Trigonometry. People often use the acronym SOHCAHTOA to help remember which is which. In the triangle below: = 15
 Math 2 Trigonometry 1 RATIOS OF SIDES OF A RIGHT TRIANGLE Trigonometry is all about the relationships of sides of right triangles. In order to organize these relationships, each side is named in relation
Math 2 Trigonometry 1 RATIOS OF SIDES OF A RIGHT TRIANGLE Trigonometry is all about the relationships of sides of right triangles. In order to organize these relationships, each side is named in relation
MA 351 Fall 2007 Exam #1 Review Solutions 1
 MA 35 Fall 27 Exam # Review Solutions THERE MAY BE TYPOS in these solutions. Please let me know if you find any.. Consider the two surfaces ρ 3 csc θ in spherical coordinates and r 3 in cylindrical coordinates.
MA 35 Fall 27 Exam # Review Solutions THERE MAY BE TYPOS in these solutions. Please let me know if you find any.. Consider the two surfaces ρ 3 csc θ in spherical coordinates and r 3 in cylindrical coordinates.
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester Practice Final Exam
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2010-11 Practice Final Exam 1. A ship is moving northwest at a speed of 50 mi/h. A passenger is walking due southeast on the deck at 4 mi/h. Find the speed of the passenger
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2010-11 Practice Final Exam 1. A ship is moving northwest at a speed of 50 mi/h. A passenger is walking due southeast on the deck at 4 mi/h. Find the speed of the passenger
MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART
 Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and
Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and
Math 181, Exam 2, Fall 2014 Problem 1 Solution. sin 3 (x) cos(x) dx.
 Math 8, Eam 2, Fall 24 Problem Solution. Integrals, Part I (Trigonometric integrals: 6 points). Evaluate the integral: sin 3 () cos() d. Solution: We begin by rewriting sin 3 () as Then, after using the
Math 8, Eam 2, Fall 24 Problem Solution. Integrals, Part I (Trigonometric integrals: 6 points). Evaluate the integral: sin 3 () cos() d. Solution: We begin by rewriting sin 3 () as Then, after using the
Notes on Radian Measure
 MAT 170 Pre-Calculus Notes on Radian Measure Radian Angles Terri L. Miller Spring 009 revised April 17, 009 1. Radian Measure Recall that a unit circle is the circle centered at the origin with a radius
MAT 170 Pre-Calculus Notes on Radian Measure Radian Angles Terri L. Miller Spring 009 revised April 17, 009 1. Radian Measure Recall that a unit circle is the circle centered at the origin with a radius
Precalculus Review. Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions. Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties. Constants. Linear.
 Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Multiple Choice. 1.(6 pts) Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (2, 5, 1) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9.
 Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
A. Incorrect! For a point to lie on the unit circle, the sum of the squares of its coordinates must be equal to 1.
 Algebra - Problem Drill 19: Basic Trigonometry - Right Triangle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? (A) 1, 1 (B) 1, (C) (D) (E), 3, 3, For a point to lie on the unit circle,
Algebra - Problem Drill 19: Basic Trigonometry - Right Triangle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following points lies on the unit circle? (A) 1, 1 (B) 1, (C) (D) (E), 3, 3, For a point to lie on the unit circle,
2. Pythagorean Theorem:
 Chapter 4 Applications of Trigonometric Functions 4.1 Right triangle trigonometry; Applications 1. A triangle in which one angle is a right angle (90 0 ) is called a. The side opposite the right angle
Chapter 4 Applications of Trigonometric Functions 4.1 Right triangle trigonometry; Applications 1. A triangle in which one angle is a right angle (90 0 ) is called a. The side opposite the right angle
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON. a b. Name: Problem 1
 BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
NOTES 10: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY
 NOTES 0: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 0. USING FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC INDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin csc cos sec
NOTES 0: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 0. USING FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC INDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin csc cos sec
x n cos 2x dx. dx = nx n 1 and v = 1 2 sin(2x). Andreas Fring (City University London) AS1051 Lecture Autumn / 36
 We saw in Example 5.4. that we sometimes need to apply integration by parts several times in the course of a single calculation. Example 5.4.4: For n let S n = x n cos x dx. Find an expression for S n
We saw in Example 5.4. that we sometimes need to apply integration by parts several times in the course of a single calculation. Example 5.4.4: For n let S n = x n cos x dx. Find an expression for S n
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Midterm 1 Review Solutions
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
6.1 Reciprocal, Quotient, and Pythagorean Identities.notebook. Chapter 6: Trigonometric Identities
 Chapter 6: Trigonometric Identities 1 Chapter 6 Complete the following table: 6.1 Reciprocal, Quotient, and Pythagorean Identities Pages 290 298 6.3 Proving Identities Pages 309 315 Measure of
Chapter 6: Trigonometric Identities 1 Chapter 6 Complete the following table: 6.1 Reciprocal, Quotient, and Pythagorean Identities Pages 290 298 6.3 Proving Identities Pages 309 315 Measure of
As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: Figure 1
 Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Trigonometry Basic Functions As we know, the three basic trigonometric functions are as follows: sin θ = cos θ = opposite hypotenuse adjacent hypotenuse tan θ = opposite adjacent Where θ represents an
Fall 2013 Hour Exam 2 11/08/13 Time Limit: 50 Minutes
 Math 8 Fall Hour Exam /8/ Time Limit: 5 Minutes Name (Print): This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page) and 7 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter all requested information
Math 8 Fall Hour Exam /8/ Time Limit: 5 Minutes Name (Print): This exam contains 9 pages (including this cover page) and 7 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter all requested information
PRELIM 2 REVIEW QUESTIONS Math 1910 Section 205/209
 PRELIM 2 REVIEW QUESTIONS Math 9 Section 25/29 () Calculate the following integrals. (a) (b) x 2 dx SOLUTION: This is just the area under a semicircle of radius, so π/2. sin 2 (x) cos (x) dx SOLUTION:
PRELIM 2 REVIEW QUESTIONS Math 9 Section 25/29 () Calculate the following integrals. (a) (b) x 2 dx SOLUTION: This is just the area under a semicircle of radius, so π/2. sin 2 (x) cos (x) dx SOLUTION:
Math Analysis Chapter 5 Notes: Analytic Trigonometric
 Math Analysis Chapter 5 Notes: Analytic Trigonometric Day 9: Section 5.1-Verifying Trigonometric Identities Fundamental Trig Identities Reciprocal Identities: 1 1 1 sin u = cos u = tan u = cscu secu cot
Math Analysis Chapter 5 Notes: Analytic Trigonometric Day 9: Section 5.1-Verifying Trigonometric Identities Fundamental Trig Identities Reciprocal Identities: 1 1 1 sin u = cos u = tan u = cscu secu cot
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide
 Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide 1. The Final Exam is on December 10 at 8:00-9:45pm in Hitchcock Hall (HI) 031 2. Take your BuckID to the exam. The use of notes, calculators, or other electronic
Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide 1. The Final Exam is on December 10 at 8:00-9:45pm in Hitchcock Hall (HI) 031 2. Take your BuckID to the exam. The use of notes, calculators, or other electronic
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Evaluate trigonometric
4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.3 Right Triangle Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Evaluate trigonometric
32 +( 2) ( 4) ( 2)
 Math 241 Exam 1 Sample 2 Solutions 1. (a) If ā = 3î 2ĵ+1ˆk and b = 4î+0ĵ 2ˆk, find the sine and cosine of the angle θ between [10 pts] ā and b. We know that ā b = ā b cosθ and so cosθ = ā b ā b = (3)(
Math 241 Exam 1 Sample 2 Solutions 1. (a) If ā = 3î 2ĵ+1ˆk and b = 4î+0ĵ 2ˆk, find the sine and cosine of the angle θ between [10 pts] ā and b. We know that ā b = ā b cosθ and so cosθ = ā b ā b = (3)(
Answer Key. 7.1 Tangent Ratio. Chapter 7 Trigonometry. CK-12 Geometry Honors Concepts 1. Answers
 7.1 Tangent Ratio 1. Right triangles with 40 angles have two pairs of congruent angles and therefore are similar. This means that the ratio of the opposite leg to adjacent leg is constant for all 40 right
7.1 Tangent Ratio 1. Right triangles with 40 angles have two pairs of congruent angles and therefore are similar. This means that the ratio of the opposite leg to adjacent leg is constant for all 40 right
Calculus 1: Sample Questions, Final Exam
 Calculus : Sample Questions, Final Eam. Evaluate the following integrals. Show your work and simplify your answers if asked. (a) Evaluate integer. Solution: e 3 e (b) Evaluate integer. Solution: π π (c)
Calculus : Sample Questions, Final Eam. Evaluate the following integrals. Show your work and simplify your answers if asked. (a) Evaluate integer. Solution: e 3 e (b) Evaluate integer. Solution: π π (c)
Chapter 5 Notes. 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
 Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 1. Simplify each expression to its lowest terms. Write the answer to part as the product of factors. (a) sin x csc x cot x ( 1+ sinσ + cosσ ) (c) 1 tanx
Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 1. Simplify each expression to its lowest terms. Write the answer to part as the product of factors. (a) sin x csc x cot x ( 1+ sinσ + cosσ ) (c) 1 tanx
MATH 2412 Sections Fundamental Identities. Reciprocal. Quotient. Pythagorean
 MATH 41 Sections 5.1-5.4 Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Quotient Pythagorean 5 Example: If tanθ = and θ is in quadrant II, find the exact values of the other 1 trigonometric functions using only fundamental
MATH 41 Sections 5.1-5.4 Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Quotient Pythagorean 5 Example: If tanθ = and θ is in quadrant II, find the exact values of the other 1 trigonometric functions using only fundamental
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON
 BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
BROWN UNIVERSITY MATH 0350 MIDTERM 19 OCTOBER 2017 INSTRUCTOR: SAMUEL S. WATSON Name: Problem 1 In this problem, we will use vectors to show that an angle formed by connecting a point on a circle to two
October 15 MATH 1113 sec. 51 Fall 2018
 October 15 MATH 1113 sec. 51 Fall 2018 Section 5.5: Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Base-Exponent Equality For any a > 0 with a 1, and for any real numbers x and y a x = a y if and only if
October 15 MATH 1113 sec. 51 Fall 2018 Section 5.5: Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Base-Exponent Equality For any a > 0 with a 1, and for any real numbers x and y a x = a y if and only if
SET 1. (1) Solve for x: (a) e 2x = 5 3x
 () Solve for x: (a) e x = 5 3x SET We take natural log on both sides: ln(e x ) = ln(5 3x ) x = 3 x ln(5) Now we take log base on both sides: log ( x ) = log (3 x ln 5) x = log (3 x ) + log (ln(5)) x x
() Solve for x: (a) e x = 5 3x SET We take natural log on both sides: ln(e x ) = ln(5 3x ) x = 3 x ln(5) Now we take log base on both sides: log ( x ) = log (3 x ln 5) x = log (3 x ) + log (ln(5)) x x
MATH 1080 Test 2 -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval.
 MATH 8 Test -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall 4. Consider the curve defined by y = ln( sec x), x. a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval. sec x tan x = = tan x sec x L = + tan x =
MATH 8 Test -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall 4. Consider the curve defined by y = ln( sec x), x. a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval. sec x tan x = = tan x sec x L = + tan x =
Section 7.3 Double Angle Identities
 Section 7.3 Double Angle Identities 3 Section 7.3 Double Angle Identities Two special cases of the sum of angles identities arise often enough that we choose to state these identities separately. Identities
Section 7.3 Double Angle Identities 3 Section 7.3 Double Angle Identities Two special cases of the sum of angles identities arise often enough that we choose to state these identities separately. Identities
Math 234. What you should know on day one. August 28, You should be able to use general principles like. x = cos t, y = sin t, 0 t π.
 Math 234 What you should know on day one August 28, 2001 1 You should be able to use general principles like Length = ds, Area = da, Volume = dv For example the length of the semi circle x = cos t, y =
Math 234 What you should know on day one August 28, 2001 1 You should be able to use general principles like Length = ds, Area = da, Volume = dv For example the length of the semi circle x = cos t, y =
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Chapter 1. Functions 1.3. Trigonometric Functions
 1.3 Trigonometric Functions 1 Chapter 1. Functions 1.3. Trigonometric Functions Definition. The number of radians in the central angle A CB within a circle of radius r is defined as the number of radius
1.3 Trigonometric Functions 1 Chapter 1. Functions 1.3. Trigonometric Functions Definition. The number of radians in the central angle A CB within a circle of radius r is defined as the number of radius
Alpha Trigonometry Solutions MA National Convention. Answers:
 Answers: 1 A C C D 5 A 6 C 7 B 8 A 9 A 10 A 11 C 1 D 1 E 1 B 15 C 16 C 17 D 18 C 19 B 0 C 1 E A C C 5 E 6 B 7 E 8 D 9 D 0 B 1 Solutions: 1 A Need to check each answer to 1 k60 and 1 (60 ) = 06. C An even
Answers: 1 A C C D 5 A 6 C 7 B 8 A 9 A 10 A 11 C 1 D 1 E 1 B 15 C 16 C 17 D 18 C 19 B 0 C 1 E A C C 5 E 6 B 7 E 8 D 9 D 0 B 1 Solutions: 1 A Need to check each answer to 1 k60 and 1 (60 ) = 06. C An even
Math 106: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS
 Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
t 2 + 2t dt = (t + 1) dt + 1 = arctan t x + 6 x(x 3)(x + 2) = A x +
 MATH 06 0 Practice Exam #. (0 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) (0 points). t +t+7 This is an irreducible quadratic; its denominator can thus be rephrased via completion of the square as a
MATH 06 0 Practice Exam #. (0 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) (0 points). t +t+7 This is an irreducible quadratic; its denominator can thus be rephrased via completion of the square as a
Sum and Difference Identities
 Sum and Difference Identities By: OpenStaxCollege Mount McKinley, in Denali National Park, Alaska, rises 20,237 feet (6,168 m) above sea level. It is the highest peak in North America. (credit: Daniel
Sum and Difference Identities By: OpenStaxCollege Mount McKinley, in Denali National Park, Alaska, rises 20,237 feet (6,168 m) above sea level. It is the highest peak in North America. (credit: Daniel
Exercise Set 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios
 Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Math 181, Exam 2, Study Guide 2 Problem 1 Solution. 1 + dx. 1 + (cos x)2 dx. 1 + cos2 xdx. = π ( 1 + cos π 2
 Math 8, Exam, Study Guide Problem Solution. Use the trapezoid rule with n to estimate the arc-length of the curve y sin x between x and x π. Solution: The arclength is: L b a π π + ( ) dy + (cos x) + cos
Math 8, Exam, Study Guide Problem Solution. Use the trapezoid rule with n to estimate the arc-length of the curve y sin x between x and x π. Solution: The arclength is: L b a π π + ( ) dy + (cos x) + cos
CHAPTER 6. Section Two angles are supplementary. 2. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 radians
 SECTION 6-5 CHAPTER 6 Section 6. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 radians. Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is 80 ( radians).. A central angle of
SECTION 6-5 CHAPTER 6 Section 6. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 radians. Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is 80 ( radians).. A central angle of
Find all solutions cos 6. Find all solutions. 7sin 3t Find all solutions on the interval [0, 2 ) sin t 15cos t sin.
 7.1 Solving Trigonometric Equations with Identities In this section, we explore the techniques needed to solve more complex trig equations: By Factoring Using the Quadratic Formula Utilizing Trig Identities
7.1 Solving Trigonometric Equations with Identities In this section, we explore the techniques needed to solve more complex trig equations: By Factoring Using the Quadratic Formula Utilizing Trig Identities
Inverse Trig Functions
 6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry
 Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Using Fundamental Identities Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations Sum and Difference Formulas
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Using Fundamental Identities Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations Sum and Difference Formulas
Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork
 Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork Given a right triangle with one of the angles named ", and the sides of the triangle relative to " named opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse (picture on
Unit 2 - The Trigonometric Functions - Classwork Given a right triangle with one of the angles named ", and the sides of the triangle relative to " named opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse (picture on
Transition to College Math
 Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
1 Chapter 2 Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients 2-2, 2-3, 2-4
 NYS Performance Indicators Chapter Learning Objectives Text Sections Days A.N. Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients. -, -5 A.A. Solve absolute value
NYS Performance Indicators Chapter Learning Objectives Text Sections Days A.N. Perform arithmetic operations with polynomial expressions containing rational coefficients. -, -5 A.A. Solve absolute value
3 = arccos. A a and b are parallel, B a and b are perpendicular, C a and b are normalized, or D this is always true.
 Math 210-101 Test #1 Sept. 16 th, 2016 Name: Answer Key Be sure to show your work! 1. (20 points) Vector Basics: Let v = 1, 2,, w = 1, 2, 2, and u = 2, 1, 1. (a) Find the area of a parallelogram spanned
Math 210-101 Test #1 Sept. 16 th, 2016 Name: Answer Key Be sure to show your work! 1. (20 points) Vector Basics: Let v = 1, 2,, w = 1, 2, 2, and u = 2, 1, 1. (a) Find the area of a parallelogram spanned
1 The six trigonometric functions
 Spring 017 Nikos Apostolakis 1 The six trigonometric functions Given a right triangle, once we select one of its acute angles, we can describe the sides as O (opposite of ), A (adjacent to ), and H ().
Spring 017 Nikos Apostolakis 1 The six trigonometric functions Given a right triangle, once we select one of its acute angles, we can describe the sides as O (opposite of ), A (adjacent to ), and H ().
Math 21B - Homework Set 8
 Math B - Homework Set 8 Section 8.:. t cos t dt Let u t, du t dt and v sin t, dv cos t dt Let u t, du dt and v cos t, dv sin t dt t cos t dt u v v du t sin t t sin t dt [ t sin t u v ] v du [ ] t sin t
Math B - Homework Set 8 Section 8.:. t cos t dt Let u t, du t dt and v sin t, dv cos t dt Let u t, du dt and v cos t, dv sin t dt t cos t dt u v v du t sin t t sin t dt [ t sin t u v ] v du [ ] t sin t
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
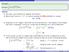 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
2.1 Limits, Rates of Change and Slopes of Tangent Lines
 2.1 Limits, Rates of Change and Slopes of Tangent Lines (1) Average rate of change of y f x over an interval x 0,x 1 : f x 1 f x 0 x 1 x 0 Instantaneous rate of change of f x at x x 0 : f x lim 1 f x 0
2.1 Limits, Rates of Change and Slopes of Tangent Lines (1) Average rate of change of y f x over an interval x 0,x 1 : f x 1 f x 0 x 1 x 0 Instantaneous rate of change of f x at x x 0 : f x lim 1 f x 0
3. On the grid below, sketch and label graphs of the following functions: y = sin x, y = cos x, and y = sin(x π/2). π/2 π 3π/2 2π 5π/2
 AP Physics C Calculus C.1 Name Trigonometric Functions 1. Consider the right triangle to the right. In terms of a, b, and c, write the expressions for the following: c a sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =. Using
AP Physics C Calculus C.1 Name Trigonometric Functions 1. Consider the right triangle to the right. In terms of a, b, and c, write the expressions for the following: c a sin θ = cos θ = tan θ =. Using
Jim Lambers Math 1B Fall Quarter Final Exam Solution (Version A)
 Jim Lambers Math 1B Fall Quarter 004-05 Final Exam Solution (Version A) 1. Suppose that a culture initially contains 500 bacteria, and that the population doubles every hours. What is the population after
Jim Lambers Math 1B Fall Quarter 004-05 Final Exam Solution (Version A) 1. Suppose that a culture initially contains 500 bacteria, and that the population doubles every hours. What is the population after
Review of Coordinate Systems
 Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
A List of Definitions and Theorems
 Metropolitan Community College Definition 1. Two angles are called complements if the sum of their measures is 90. Two angles are called supplements if the sum of their measures is 180. Definition 2. One
Metropolitan Community College Definition 1. Two angles are called complements if the sum of their measures is 90. Two angles are called supplements if the sum of their measures is 180. Definition 2. One
NYS Algebra II and Trigonometry Suggested Sequence of Units (P.I's within each unit are NOT in any suggested order)
 1 of 6 UNIT P.I. 1 - INTEGERS 1 A2.A.1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities involving linear expressions in one variable 1 A2.A.4 * Solve quadratic inequalities in one and two variables, algebraically
1 of 6 UNIT P.I. 1 - INTEGERS 1 A2.A.1 Solve absolute value equations and inequalities involving linear expressions in one variable 1 A2.A.4 * Solve quadratic inequalities in one and two variables, algebraically
True or False. Circle T if the statement is always true; otherwise circle F. for all angles θ. T F. 1 sin θ
 Math 90 Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 8-0 (Ebersole), 3.3-3.8 (Stewart) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam.
Math 90 Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 8-0 (Ebersole), 3.3-3.8 (Stewart) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam.
4 The Trigonometric Functions
 Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Sydney 8 The Trigonometric Functions The definitions in the previous section apply to between 0 and, since the angles in a right angle triangle can never be greater
Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Sydney 8 The Trigonometric Functions The definitions in the previous section apply to between 0 and, since the angles in a right angle triangle can never be greater
Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that same amount.
 Name Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit Notes #1: Basic Trig Review I. Unit Circle A circle with center point and radius. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that
Name Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit Notes #1: Basic Trig Review I. Unit Circle A circle with center point and radius. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that
Final practice, Math 31A - Lec 1, Fall 2013 Name and student ID: Question Points Score Total: 90
 Final practice, Math 31A - Lec 1, Fall 13 Name and student ID: Question Points Score 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 8 1 9 1 Total: 9 1. a) 4 points) Find all points x at which the function fx) x 4x + 3 + x
Final practice, Math 31A - Lec 1, Fall 13 Name and student ID: Question Points Score 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 6 1 7 1 8 1 9 1 Total: 9 1. a) 4 points) Find all points x at which the function fx) x 4x + 3 + x
problem score possible Total 60
 Math 32 A: Midterm 1, Oct. 24, 2008 Name: ID Number: Section: problem score possible 1. 10 2. 10 3. 10 4. 10 5. 10 6. 10 Total 60 1 1. Determine whether the following points are coplanar: a. P = (8, 14,
Math 32 A: Midterm 1, Oct. 24, 2008 Name: ID Number: Section: problem score possible 1. 10 2. 10 3. 10 4. 10 5. 10 6. 10 Total 60 1 1. Determine whether the following points are coplanar: a. P = (8, 14,
