Supporting Information for The substorm cycle as reproduced by community-available global MHD models
|
|
|
- Pauline Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SPACE WEATHER Supporting Information for The substorm cycle as reproduced by community-available global MHD models E. Gordeev 1, V. Sergeev 1, N. Tsyganenko 1, M. Kuznetsova 2, L. Rastätter 2, J. Raeder 3, G. Tóth 4, J. Lyon 5, V. Merkin 6 and M. Wiltberger 7 Corresponding author: Evgeny Gordeev, Saint-Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg, Russia. (evgeny.i.gordeev@spbu.ru) 1 Saint-Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg, Russia 2 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD, USA 3 Space Science Center, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH, USA 4 Center for Space Environment Modelling, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA 5 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, USA 6 Applied Physics Laboratory, John Hopkins University, Laurel, MD, USA
2 X - 2 GORDEEV ET AL.: GLOBAL MHD SUBSTORM Content of this file 1. Introduction 2. Table S1 3. Table S2 Additional Supporting Information (Files uploaded separately) 1. Movie (gif) S1 Introduction As a supplement to the paper, here we present two additional tables and one gif movie file. The Table S1 contains the summary of the main numerical details of the used global MHD simulations. The Table S2 collects the input solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field components for 19 simulations as well as their names. All simulation results can be found at NASA Community Coordinated Modelling Center webpage [ under the names shown in the table. The Figure S1 (gif movie) contain supplementary movies demonstrating the dynamics of magnetospheric configuration and main parameter distributions in the meridional (top row) and equatorial (botom row) planes during the artificial event. Three different GMHD 7 High-Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, USA
3 GORDEEV ET AL.: GLOBAL MHD SUBSTORM X - 3 models (from left to right: BATSRUS, LFM, Open GGCM) are used with the same corresponding solar wind input #02: 2 hour northward B z = +3nT followed by 2 hours southward B z = 5nT, other parameters are: IMF B x = +4nT, B y = 2nT, solar wind speed V x = 400km/s, V y = V z = 0, temperature T = 1e5K, and density N = 7cm 3. Each plate of the top row shows the meridional view of magnetic field lines, logarithm of plasma pressure (color) and plasma velocity (arrows). Each plate of the botom row shows the equatorial view of logarithm of magnetic field magnitude (isocontour lines), logarithm of electric field (color, to characterize the amplitude of magnetic flux transport) and plasma velocity (arrows). There are also three panels at the top wich demonstrate the variation of (from left to right): IMF Bz, lobe magnetic field and cross-tail electric potential.
4 X - 4 GORDEEV ET AL.: GLOBAL MHD SUBSTORM Table S1. Summary of features and settings of global MHD models used in this study, see the text for details BATS-R-US v General properties: MHD equations Ideal, conservative, Solver notes Eight-wave approximate Order of MHD discretization spatial/temporal GUMICS 4-HC Ideal, conservative, Mostly Roe, subcycling, divb cleaning LFM LTR Ideal, semi-conservative, Total variation diminishing (TVD), constrained transport (CT) Riemann 2/2 1/1 8/2 4/2 MHD grid type Cartesian, static, block-refined Characteristics of our set of runs: Spatial grid resolution, [RE] 2M cells SS point PS (X=-10) Cartesian, dynamic, cell-refined 100K cells SS point PS (X=-10) MP (X=-15) Distorted spherical, static, not refined 160K cells SS point x**x0.8 PS (X=-10) x**x0.8 MP (X=-15) x**x1.5 OpenGGCM 4.0 semi-conservative with resistivity TVD, CT Stretched Cartesian, static, not refined 3.5M cells SS point x0.3x0.3 PS (X=-10) -0.2x0.3x0.3 MP(X=-15) -0.25x0.35x1.5 MP (X=-15) Ionospheric Constant Auroral Constant Constant conductance F10.7 = Wm 2 Hz 1 Ionospheric grid Lat=1 o Lon=2 o Triangular adaptive Lat=2 o Lon=2 o Lat=0.5 o Lon=3 o resolution, [deg] min=0.9 o max=3.6 o Comments: Simulations with enhanced spatial resolution does not show significant changes in results for the set of used system parameters.
5 GORDEEV ET AL.: GLOBAL MHD SUBSTORM X - 5 Table S2. Parameters of 19 standard input data sets and their run names in the CCMC simulation database Standard Solar Wind & IMF inputs Name extensions of CCMC runs: Full name of the run is Gordeev [extension] Vx, N, T, Pd Bx, By, (Bz0,Bz1,Bz2), MA, Ey1/Ey2 [km/s] [cm 3 ] [10 3 K] [npa] [nt] [nt] [nt] BATSRUS Open GGCM LFM , 7, 100, , -2, (-5,+3,-2) / , 7, 100, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 7, 100, , -2, (-5,+3,-8) / , 7, 100, , -2, (-5,+6,-5) / , 4, 250, , -2, (-5,+3,-2) / , 4, 250, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 4, 250, , -2, (-5,+3,-8) / , 4, 250, , -2, (-5,+6,-5) / , 12, 35, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 2, 350, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 4, 100, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 10, 100, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 2, 250, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 6, 250, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 5, 50, , (-2,-2,-8), (-5,+3,-6) / , 5, 50, , (-2,-2,-10), (-5,+3,-10) / , 5, 50, , (-2,-2,-16), (-5,+3,-10) / , 6, 500, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / , 5, 500, , -2, (-5,+3,-5) / The results of simulations can be found at CCMC website, Indices used with Bz and Ey: 0 - preconditioning ( 1h), 1 - next 2h of northward Bz, 3 - next 2h of southward Bz.
On the origin of plasma sheet evolution during the substorm growth phase
 On the origin of plasma sheet evolution during the substorm growth phase Evgeny Gordeev Victor Sergeev Maria Shukhtina Viacheslav Merkin Maria Kuznetsova (SPSU) (SPSU) (SPSU) (APL) (GSFC) [Hsieh and Otto,
On the origin of plasma sheet evolution during the substorm growth phase Evgeny Gordeev Victor Sergeev Maria Shukhtina Viacheslav Merkin Maria Kuznetsova (SPSU) (SPSU) (SPSU) (APL) (GSFC) [Hsieh and Otto,
Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation
 Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation Kyung Sun Park 1, Dae-Young Lee 1, Myeong Joon Kim 1, Rok Soon Kim 2, Kyungsuk
Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation Kyung Sun Park 1, Dae-Young Lee 1, Myeong Joon Kim 1, Rok Soon Kim 2, Kyungsuk
Relation of polar auroral arcs to magnetotail twisting and IMF rotation: a systematic MHD simulation study
 Annales Geophysicae (24) 22: 951 97 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/24-22-951 European Geosciences Union 24 Annales Geophysicae Relation of polar auroral arcs to magnetotail twisting and IMF rotation: a systematic
Annales Geophysicae (24) 22: 951 97 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/24-22-951 European Geosciences Union 24 Annales Geophysicae Relation of polar auroral arcs to magnetotail twisting and IMF rotation: a systematic
Dynamics of ring current and electric fields in the inner magnetosphere during disturbed periods: CRCM BATS R US coupled model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014621, 2010 Dynamics of ring current and electric fields in the inner magnetosphere during disturbed periods:
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014621, 2010 Dynamics of ring current and electric fields in the inner magnetosphere during disturbed periods:
Numerical Methods Used in the Lyon-Fedder-Mobarry Global Code to Model the Magnetosphere
 Advanced Methods for Space Simulations, edited by H. Usui and Y. Omura, pp. 101 109. c TERRAPUB, Tokyo, 2007. Numerical Methods Used in the Lyon-Fedder-Mobarry Global Code to Model the Magnetosphere John
Advanced Methods for Space Simulations, edited by H. Usui and Y. Omura, pp. 101 109. c TERRAPUB, Tokyo, 2007. Numerical Methods Used in the Lyon-Fedder-Mobarry Global Code to Model the Magnetosphere John
Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere. Outline
 Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere P. K. Toivanen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Outline Introduction to large-scale electromagnetic fields Magnetic field geometry Modelling
Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere P. K. Toivanen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Outline Introduction to large-scale electromagnetic fields Magnetic field geometry Modelling
Magnetopause erosion: A global view from MHD simulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A6, 1235, doi:10.1029/2002ja009564, 2003 Magnetopause erosion: A global view from MHD simulation M. Wiltberger High Altitude Observatory, National Center
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A6, 1235, doi:10.1029/2002ja009564, 2003 Magnetopause erosion: A global view from MHD simulation M. Wiltberger High Altitude Observatory, National Center
Comparison between vortices created and evolving during fixed and dynamic solar wind conditions
 EGU Journal Logos (RGB) doi:10.5194/angeo-31-1463-2013 Author(s) 2013. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences Annales Geophysicae N Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Atmospheric Chemistry
EGU Journal Logos (RGB) doi:10.5194/angeo-31-1463-2013 Author(s) 2013. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences Annales Geophysicae N Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Atmospheric Chemistry
Magnetospheric Model Performance during Conjugate Aurora
 18 Magnetospheric Model Performance during Conjugate Aurora William Longley 1, Patricia Reiff 1, Jone Peter Reistad 2, and Nikolai Østgaard 2 Video of Yosemite Talk, URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.15142/t3h01c
18 Magnetospheric Model Performance during Conjugate Aurora William Longley 1, Patricia Reiff 1, Jone Peter Reistad 2, and Nikolai Østgaard 2 Video of Yosemite Talk, URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.15142/t3h01c
Magnetospheric modes and solar wind energy coupling efficiency
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014737, 2010 Magnetospheric modes and solar wind energy coupling efficiency T. I. Pulkkinen, 1 M. Palmroth, 1 H.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014737, 2010 Magnetospheric modes and solar wind energy coupling efficiency T. I. Pulkkinen, 1 M. Palmroth, 1 H.
Structures in the Magnetosphere 2. Hover the curser over a point on the image. The coordinates and value at that point should appear.
 Investigating the Magnetosphere Introduction In this investigation, you will explore the properties of the regions of the magnetosphere using simulation results from the BATS-R-US model from the magnetosphere
Investigating the Magnetosphere Introduction In this investigation, you will explore the properties of the regions of the magnetosphere using simulation results from the BATS-R-US model from the magnetosphere
Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field
 Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field I. Alexeev, V. Kalegaev The solar wind influence on the magnetospheric state is sufficiently nonlinear
Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field I. Alexeev, V. Kalegaev The solar wind influence on the magnetospheric state is sufficiently nonlinear
Why Study Magnetic Reconnection?
 Why Study Magnetic Reconnection? Fundamental Process Sun: Solar flares, Flare loops, CMEs Interplanetary Space Planetary Magnetosphere: solar wind plasma entry, causes Aurora Ultimate goal of the project
Why Study Magnetic Reconnection? Fundamental Process Sun: Solar flares, Flare loops, CMEs Interplanetary Space Planetary Magnetosphere: solar wind plasma entry, causes Aurora Ultimate goal of the project
Dependence of magnetic field just inside the magnetopause on subsolar standoff distance: Global MHD results
 Article SPECIAL ISSUE Basic Plasma Processes in Solar-Terrestrial Activities April 2012 Vol.57 No.12: 1438 1442 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4961-6 SPECIAL TOPICS: Dependence of magnetic field just inside the
Article SPECIAL ISSUE Basic Plasma Processes in Solar-Terrestrial Activities April 2012 Vol.57 No.12: 1438 1442 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4961-6 SPECIAL TOPICS: Dependence of magnetic field just inside the
Geomagnetic Disturbance Report Reeve Observatory
 Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling During Storms and Substorms
 Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling During Storms and Substorms Bill Lotko Bin Zhang Oliver Brambles Sheng Xi John Lyon Tian Luo Roger Varney Jeremy Ouellette Mike Wiltberger 2 3 4 CEDAR: Storms
Magnetosphere-Ionosphere-Thermosphere Coupling During Storms and Substorms Bill Lotko Bin Zhang Oliver Brambles Sheng Xi John Lyon Tian Luo Roger Varney Jeremy Ouellette Mike Wiltberger 2 3 4 CEDAR: Storms
Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm
 ESS 7 Lecture 13 October 27, 2010 Substorms Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm This set of images in the ultra-violet from the Polar satellite shows changes that occur during an auroral substorm.
ESS 7 Lecture 13 October 27, 2010 Substorms Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm This set of images in the ultra-violet from the Polar satellite shows changes that occur during an auroral substorm.
Investigation of the viscous potential using an MHD simulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017022, 2012 Investigation of the viscous potential using an MHD simulation R. Bruntz, 1 R. E. Lopez, 1 M. Wiltberger, 2 and J. G. Lyon 3 Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011ja017022, 2012 Investigation of the viscous potential using an MHD simulation R. Bruntz, 1 R. E. Lopez, 1 M. Wiltberger, 2 and J. G. Lyon 3 Received
Perpendicular Flow Separation in a Magnetized Counterstreaming Plasma: Application to the Dust Plume of Enceladus
 Perpendicular Flow Separation in a Magnetized Counterstreaming Plasma: Application to the Dust Plume of Enceladus Y.-D. Jia, Y. J. Ma, C.T. Russell, G. Toth, T.I. Gombosi, M.K. Dougherty Magnetospheres
Perpendicular Flow Separation in a Magnetized Counterstreaming Plasma: Application to the Dust Plume of Enceladus Y.-D. Jia, Y. J. Ma, C.T. Russell, G. Toth, T.I. Gombosi, M.K. Dougherty Magnetospheres
Time history effects at the magnetopause: Hysteresis in power input and its implications to substorm processes
 219 Time history effects at the magnetopause: Hysteresis in power input and its implications to substorm processes M. Palmroth, T. I. Pulkkinen, T. V. Laitinen, H. E. J. Koskinen, and P. Janhunen 1. Introduction
219 Time history effects at the magnetopause: Hysteresis in power input and its implications to substorm processes M. Palmroth, T. I. Pulkkinen, T. V. Laitinen, H. E. J. Koskinen, and P. Janhunen 1. Introduction
CRCM + BATS-R-US two-way coupling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SPACE PHYSICS, VOL. 118, 135 15, doi:1.1/jgra.51, 13 CRCM + BATS-R-US two-way coupling A. Glocer, 1 M. Fok, 1 X. Meng, G. Toth, N. Buzulukova, 3, S. Chen, 5 and K. Lin
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SPACE PHYSICS, VOL. 118, 135 15, doi:1.1/jgra.51, 13 CRCM + BATS-R-US two-way coupling A. Glocer, 1 M. Fok, 1 X. Meng, G. Toth, N. Buzulukova, 3, S. Chen, 5 and K. Lin
X-ray imaging of the magnetosphere
 X-ray imaging of the magnetosphere T. R. Sun 1, C. Wang 1, F. Wei 1, S. F. Sembay 2, J. A. Carter 2, S. Milan 2, A. M. Read 2, G. Branduardi-Raymont 3, J. Rae 3, H. Hietala 4, J. Eastwood 4, W. Yuan 5,
X-ray imaging of the magnetosphere T. R. Sun 1, C. Wang 1, F. Wei 1, S. F. Sembay 2, J. A. Carter 2, S. Milan 2, A. M. Read 2, G. Branduardi-Raymont 3, J. Rae 3, H. Hietala 4, J. Eastwood 4, W. Yuan 5,
Andrew Keen, Inari, Finland 18 Feb º C spaceweather.com
 ESS 7 Lecture 17 May 14, 2010 The Aurora Aurora Amazing Light Show Andrew Keen, Inari, Finland 18 Feb 2010-31º C spaceweather.com Athabasca Aurora Oct 3 2003 Courtesy Mikko Syrjäsuo There is a Long Record
ESS 7 Lecture 17 May 14, 2010 The Aurora Aurora Amazing Light Show Andrew Keen, Inari, Finland 18 Feb 2010-31º C spaceweather.com Athabasca Aurora Oct 3 2003 Courtesy Mikko Syrjäsuo There is a Long Record
The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction
 The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction Research seminar on Sun-Earth connections Eija Tanskanen Friday January 27, 2006 12-14 a.m., D115 Outline 1. Basics of the Earth s magnetosphere
The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction Research seminar on Sun-Earth connections Eija Tanskanen Friday January 27, 2006 12-14 a.m., D115 Outline 1. Basics of the Earth s magnetosphere
RCM Modeling of Penetration Electric Fields During Magnetic Storms
 RCM Modeling of Penetration Electric Fields During Magnetic Storms S. Sazykin, R. A. Wolf, R. W. Spiro, Haystack Workshop on Penetration Electric Fields November 8, 2005 Low Latitude E-field: Massive Undershielding
RCM Modeling of Penetration Electric Fields During Magnetic Storms S. Sazykin, R. A. Wolf, R. W. Spiro, Haystack Workshop on Penetration Electric Fields November 8, 2005 Low Latitude E-field: Massive Undershielding
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere
 An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere Charles Jackman & Dean Pesnell NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD International Workshop
An Overview of the Impact of Energetic Particle Precipitation (EPP) on the Mesosphere and Stratosphere Charles Jackman & Dean Pesnell NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD International Workshop
A numerical study of solar wind magnetosphere interaction for northward interplanetary magnetic field
 To appear in Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999. A numerical study of solar wind magnetosphere interaction for northward interplanetary magnetic field P. Song, D.L. DeZeeuw, T.I. Gombosi, C. P. T. Groth
To appear in Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999. A numerical study of solar wind magnetosphere interaction for northward interplanetary magnetic field P. Song, D.L. DeZeeuw, T.I. Gombosi, C. P. T. Groth
Search for an onset mechanism that operates for both CMEs and substorms
 Ann. Geophys., 27, 3141 3146, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Search for an onset mechanism that operates for both
Ann. Geophys., 27, 3141 3146, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Search for an onset mechanism that operates for both
Numerical Simulation of Jovian and Kronian Magnetospheric Configuration
 Feb. 16, 2015 Numerical Simulation of Jovian and Kronian Magnetospheric Configuration Keiichiro FUKAZAWA 1, 2 1.Academic Center for Computing and Media Studies, Kyoto University 2.CREST, JST Context Jovian
Feb. 16, 2015 Numerical Simulation of Jovian and Kronian Magnetospheric Configuration Keiichiro FUKAZAWA 1, 2 1.Academic Center for Computing and Media Studies, Kyoto University 2.CREST, JST Context Jovian
Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (<200 kev) at geostationary orbit
 Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (
Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (
CHAPTER 2 DATA. 2.1 Data Used
 CHAPTER DATA For the analysis, it is required to use geomagnetic indices, which are representatives of geomagnetic activity, and Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) data in addition to f F,which is used
CHAPTER DATA For the analysis, it is required to use geomagnetic indices, which are representatives of geomagnetic activity, and Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) data in addition to f F,which is used
THE ACCURACY OF PRESENT MODELS OF THE HIGH ALTITUDE POLAR MAGNETOSPHERE
 THE ACCURAC OF PRESENT MODELS OF THE HIGH ALTITUDE POLAR MAGNETOSPHERE C. T. Russell 1, J. G. Luhmann 2 and F. R. Fenrich 3 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California Los Angeles
THE ACCURAC OF PRESENT MODELS OF THE HIGH ALTITUDE POLAR MAGNETOSPHERE C. T. Russell 1, J. G. Luhmann 2 and F. R. Fenrich 3 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California Los Angeles
Initiation of Ballooning Instability by Reconnection in the Near-Earth Plasma Sheet
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL., XXXX, DOI:1.19/, 1 Initiation of Ballooning Instability by Reconnection in the Near-Earth Plasma Sheet P. Zhu, 1 J. Raeder, K. Germaschewski, A. Bhattacharjee, and C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL., XXXX, DOI:1.19/, 1 Initiation of Ballooning Instability by Reconnection in the Near-Earth Plasma Sheet P. Zhu, 1 J. Raeder, K. Germaschewski, A. Bhattacharjee, and C.
Computational Plasma Physics in the Solar System and Beyond. Ofer Cohen HPC Day 2017 at UMass Dartmouth
 Computational Plasma Physics in the Solar System and Beyond Ofer Cohen HPC Day 2017 at UMass Dartmouth Plasma physics (not medical!!!) - studying the interaction between charged particles and electromagnetic
Computational Plasma Physics in the Solar System and Beyond Ofer Cohen HPC Day 2017 at UMass Dartmouth Plasma physics (not medical!!!) - studying the interaction between charged particles and electromagnetic
CISM Model Timeline, Years 6-10
 Solar-Heliosphere Models 1 Black = capabilities to incoporate in coupled model Green = evaluations, test CORHEL 3.4 MAS,, CONE models. Inputs from full set of observatories (NSO/KP, Wilcox, Mt. Wilson,
Solar-Heliosphere Models 1 Black = capabilities to incoporate in coupled model Green = evaluations, test CORHEL 3.4 MAS,, CONE models. Inputs from full set of observatories (NSO/KP, Wilcox, Mt. Wilson,
Effects of the surface conductivity and IMF strength on dynamics of planetary ions in Mercury s magnetosphere
 1! 5 th SERENA-HEWG workshop (6/16/2014)! Effects of the surface conductivity and IMF strength on dynamics of planetary ions in Mercury s magnetosphere K. Seki 1, M. Yagi 2, Y. Matsumoto 3, N. Terada 4,!
1! 5 th SERENA-HEWG workshop (6/16/2014)! Effects of the surface conductivity and IMF strength on dynamics of planetary ions in Mercury s magnetosphere K. Seki 1, M. Yagi 2, Y. Matsumoto 3, N. Terada 4,!
Dynamics of the Jovian magnetosphere for northward interplanetary magnetic field (IMF)
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L03202, doi:10.1029/2004gl021392, 2005 Dynamics of the Jovian magnetosphere for northward interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) Keiichiro Fukazawa and Tatsuki Ogino
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L03202, doi:10.1029/2004gl021392, 2005 Dynamics of the Jovian magnetosphere for northward interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) Keiichiro Fukazawa and Tatsuki Ogino
1 Introduction. Cambridge University Press Physics of Space Plasma Activity Karl Schindler Excerpt More information
 1 Introduction Space plasma phenomena have attracted particular interest since the beginning of the exploration of space about half a century ago. Already a first set of pioneering observations (e.g.,
1 Introduction Space plasma phenomena have attracted particular interest since the beginning of the exploration of space about half a century ago. Already a first set of pioneering observations (e.g.,
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 16698 First edition 2013-05-01 Space environment (natural and artificial) Methods for estimation of future geomagnetic activity Environnement spatial (naturel et artificiel)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 16698 First edition 2013-05-01 Space environment (natural and artificial) Methods for estimation of future geomagnetic activity Environnement spatial (naturel et artificiel)
Substorms: Externally Driven Transition to Unstable State a few Minutes Before Onset
 Substorms: Externally Driven Transition to Unstable State a few Minutes Before Onset L. R. Lyons 1, I. O Voronkov 2, J. M. Ruohoniemi 3, E. F. Donovan 4 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
Substorms: Externally Driven Transition to Unstable State a few Minutes Before Onset L. R. Lyons 1, I. O Voronkov 2, J. M. Ruohoniemi 3, E. F. Donovan 4 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University
Alfvén Mach number and IMF clock angle dependencies of sunward flow channels in the magnetosphere
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 1257 1262, doi:1.12/grl.537, 213 Alfvén Mach number and IMF clock angle dependencies of sunward flow channels in the magnetosphere S. Eriksson 1 and L. Rastätter 2
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 1257 1262, doi:1.12/grl.537, 213 Alfvén Mach number and IMF clock angle dependencies of sunward flow channels in the magnetosphere S. Eriksson 1 and L. Rastätter 2
CROSS POLAR MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA DRIFT AS OBSERVED BY CLUSTER EDI: STATISTICAL RESULTS
 CROSS POLAR MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA DRIFT AS OBSERVED BY CLUSTER EDI: STATISTICAL RESULTS 1 M. Förster 1, S. Haaland 2, G. Paschmann 3, J. B. Baker 4, H. Vaith 5, J.M. Quinn 5, and R. B. Torbert 5 1 Max-Planck
CROSS POLAR MAGNETOSPHERIC PLASMA DRIFT AS OBSERVED BY CLUSTER EDI: STATISTICAL RESULTS 1 M. Förster 1, S. Haaland 2, G. Paschmann 3, J. B. Baker 4, H. Vaith 5, J.M. Quinn 5, and R. B. Torbert 5 1 Max-Planck
Plasma interaction at Io and Europa
 Plasma interaction at Io and Europa Camilla D. K. Harris Tidal Heating: Lessons from Io and the Jovian System Thursday, Oct 18 2018 1. Jupiter s Magnetosphere 2. Moon-Magnetosphere Plasma Interaction 3.
Plasma interaction at Io and Europa Camilla D. K. Harris Tidal Heating: Lessons from Io and the Jovian System Thursday, Oct 18 2018 1. Jupiter s Magnetosphere 2. Moon-Magnetosphere Plasma Interaction 3.
MHD simulation of solar wind using solar photospheric magnetic field data
 6-16P, LWS workshop 2004 March, Boulder MHD simulation of solar wind using solar photospheric magnetic field data Keiji Hayashi (Stanford University) keiji@quake.stanford.edu Introduction Time-dependent
6-16P, LWS workshop 2004 March, Boulder MHD simulation of solar wind using solar photospheric magnetic field data Keiji Hayashi (Stanford University) keiji@quake.stanford.edu Introduction Time-dependent
Relation of substorm disturbances triggered by abrupt solar-wind changes to physics of plasma sheet transport
 1 Relation of substorm disturbances triggered by abrupt solar-wind changes to physics of plasma sheet transport L. R. Lyons, D.-Y. Lee, C.-P. Wang, and S. B. Mende 1. Introduction Abstract: Substorm onset
1 Relation of substorm disturbances triggered by abrupt solar-wind changes to physics of plasma sheet transport L. R. Lyons, D.-Y. Lee, C.-P. Wang, and S. B. Mende 1. Introduction Abstract: Substorm onset
Role of IMF B x in the solar wind magnetosphere ionosphere coupling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015454, 2010 Role of IMF B x in the solar wind magnetosphere ionosphere coupling Z. Peng, 1 C. Wang, 1 and Y. Q. Hu 2 Received 14 March 2010;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015454, 2010 Role of IMF B x in the solar wind magnetosphere ionosphere coupling Z. Peng, 1 C. Wang, 1 and Y. Q. Hu 2 Received 14 March 2010;
Magnetic Effects Change Our View of the Heliosheath
 Magnetic Effects Change Our View of the Heliosheath M. Opher Λ, P. C. Liewer Λ, M. Velli, T. I. Gombosi ΛΛ, W.Manchester ΛΛ,D. L. DeZeeuw ΛΛ,G.Toth ΛΛ and I. Sokolov ΛΛ Λ Jet Propulsion Laboratory, MS
Magnetic Effects Change Our View of the Heliosheath M. Opher Λ, P. C. Liewer Λ, M. Velli, T. I. Gombosi ΛΛ, W.Manchester ΛΛ,D. L. DeZeeuw ΛΛ,G.Toth ΛΛ and I. Sokolov ΛΛ Λ Jet Propulsion Laboratory, MS
Substorms at Mercury: Old Questions and New Insights. Daniel N. Baker Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP)
 Substorms at Mercury: Old Questions and New Insights Daniel N. Baker Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) Outline of Presentation Introduction Substorms in the Earth s Magnetosphere Prior
Substorms at Mercury: Old Questions and New Insights Daniel N. Baker Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) Outline of Presentation Introduction Substorms in the Earth s Magnetosphere Prior
Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events
 Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) and Stepan Dubyagin (1) Special thanks to Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez (3) (1) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki,
Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) and Stepan Dubyagin (1) Special thanks to Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez (3) (1) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki,
Solar-Wind/Magnetosphere Coupling
 Solar-Wind/Magnetosphere Coupling Joe Borovsky Space Science Institute --- University of Michigan 1. Get a feeling for how the coupling works 2. Get an understanding of how reconnection works 3. Look at
Solar-Wind/Magnetosphere Coupling Joe Borovsky Space Science Institute --- University of Michigan 1. Get a feeling for how the coupling works 2. Get an understanding of how reconnection works 3. Look at
Modeling magnetospheric current response to solar wind dynamic pressure enhancements during magnetic storms: 2. Application to different storm phases
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013420, 2008 Modeling magnetospheric current response to solar wind dynamic pressure enhancements during magnetic storms: 2. Application to
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013420, 2008 Modeling magnetospheric current response to solar wind dynamic pressure enhancements during magnetic storms: 2. Application to
Magnetic Energy Storage and the Nightside Magnetosphere Ionosphere Coupling
 1 Magnetic Energy Storage and the Nightside Magnetosphere Ionosphere Coupling W. Horton, M. Pekker Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 I. Doxas Dept. of Astrophysical
1 Magnetic Energy Storage and the Nightside Magnetosphere Ionosphere Coupling W. Horton, M. Pekker Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 I. Doxas Dept. of Astrophysical
Ionospheric Tomography II: Ionospheric Tomography II: Applications to space weather and the high-latitude ionosphere
 Ionospheric Tomography II: Ionospheric Tomography II: Applications to space weather and the high-latitude ionosphere Why tomography at high latitudes? Why tomography at high latitudes? Magnetic field railway
Ionospheric Tomography II: Ionospheric Tomography II: Applications to space weather and the high-latitude ionosphere Why tomography at high latitudes? Why tomography at high latitudes? Magnetic field railway
Global MHD Eigenmodes of the Outer Magnetosphere
 Global MHD Eigenmodes of the Outer Magnetosphere Andrew Wright UNIVERSITY OF ST ANDREWS Magnetospheric Structure: Cavities and Waveguides The Earth s magnetosphere is structured by magnetic fields and
Global MHD Eigenmodes of the Outer Magnetosphere Andrew Wright UNIVERSITY OF ST ANDREWS Magnetospheric Structure: Cavities and Waveguides The Earth s magnetosphere is structured by magnetic fields and
Does the polar cap area saturate?
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09107, doi:10.1029/2007gl029357, 2007 Does the polar cap area saturate? V. G. Merkin 1 and C. C. Goodrich 1 Received 15 January 2007;
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09107, doi:10.1029/2007gl029357, 2007 Does the polar cap area saturate? V. G. Merkin 1 and C. C. Goodrich 1 Received 15 January 2007;
Solar Wind Parameters for Magnetospheric Magnetic Field Modeling
 July 10, 2007, revised manuscript submitted to SW Solar Wind Parameters for Magnetospheric Magnetic Field Modeling Z. Qin 1, R. E. Denton 1, N. A. Tsyganenko 2, S. Wolf 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
July 10, 2007, revised manuscript submitted to SW Solar Wind Parameters for Magnetospheric Magnetic Field Modeling Z. Qin 1, R. E. Denton 1, N. A. Tsyganenko 2, S. Wolf 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Magnetic Reconnection
 Magnetic Reconnection? On small scale-lengths (i.e. at sharp gradients), a diffusion region (physics unknown) can form where the magnetic field can diffuse through the plasma (i.e. a breakdown of the frozenin
Magnetic Reconnection? On small scale-lengths (i.e. at sharp gradients), a diffusion region (physics unknown) can form where the magnetic field can diffuse through the plasma (i.e. a breakdown of the frozenin
A global MHD simulation of an event with a quasi-steady northward IMF component
 European Geosciences Union 2007 Annales Geophysicae A global MHD simulation of an event with a quasi-steady northward IMF component V. G. Merkin 1, J. G. Lyon 2, B. J. Anderson 3, H. Korth 3, C. C. Goodrich
European Geosciences Union 2007 Annales Geophysicae A global MHD simulation of an event with a quasi-steady northward IMF component V. G. Merkin 1, J. G. Lyon 2, B. J. Anderson 3, H. Korth 3, C. C. Goodrich
Mercury s magnetosphere-solar wind interaction for northward and southward interplanetary magnetic field during the MESSENGER Flybys
 Mercury s magnetosphere-solar wind interaction for northward and southward interplanetary magnetic field during the MESSENGER Flybys P. M. Trávníček 1,3, D. Schriver 2, D. Herčík 3, P. Hellinger 3, J.
Mercury s magnetosphere-solar wind interaction for northward and southward interplanetary magnetic field during the MESSENGER Flybys P. M. Trávníček 1,3, D. Schriver 2, D. Herčík 3, P. Hellinger 3, J.
Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System
 Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System Robert Fear 1,2 R.C.Fear@soton.ac.uk 1 Space Environment Physics group University of Southampton 2 Radio & Space Plasma Physics group University of Leicester
Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System Robert Fear 1,2 R.C.Fear@soton.ac.uk 1 Space Environment Physics group University of Southampton 2 Radio & Space Plasma Physics group University of Leicester
Magnetopause energy and mass transfer: results from a global MHD simulation
 Ann. Geophys., 24, 3467 348, 26 www.ann-geophys.net/24/3467/26/ European Geosciences Union 26 Annales Geophysicae Magnetopause energy and mass transfer: results from a global MHD simulation M. Palmroth,
Ann. Geophys., 24, 3467 348, 26 www.ann-geophys.net/24/3467/26/ European Geosciences Union 26 Annales Geophysicae Magnetopause energy and mass transfer: results from a global MHD simulation M. Palmroth,
DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE
 DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE PROF JIM WILD j.wild@lancaster.ac.uk @jim_wild With thanks to: Stan Cowley, Rob Fear & Steve Milan OUTLINE So far: Dungey cycle - the stirring of the magnetosphere
DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE PROF JIM WILD j.wild@lancaster.ac.uk @jim_wild With thanks to: Stan Cowley, Rob Fear & Steve Milan OUTLINE So far: Dungey cycle - the stirring of the magnetosphere
Effect of the altitudinal variation of the gravitational acceleration on the thermosphere simulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013081, 2008 Effect of the altitudinal variation of the gravitational acceleration on the thermosphere simulation Yue Deng, 1 Aaron J. Ridley,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013081, 2008 Effect of the altitudinal variation of the gravitational acceleration on the thermosphere simulation Yue Deng, 1 Aaron J. Ridley,
Magnetotail response to prolonged southward IMF B z intervals: Loading, unloading, and continuous magnetospheric dissipation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010561, 2005 Magnetotail response to prolonged southward IMF B z intervals: Loading, unloading, and continuous magnetospheric dissipation E.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010561, 2005 Magnetotail response to prolonged southward IMF B z intervals: Loading, unloading, and continuous magnetospheric dissipation E.
Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2), Stepan Dubyagin (1), Ilkka Sillanpää (1)
 From studying electron motion in the electromagnetic fields in the inner magnetosphere to the operational nowcast model for low energy (< 200 kev) electron fluxes responsible for surface charging Natalia
From studying electron motion in the electromagnetic fields in the inner magnetosphere to the operational nowcast model for low energy (< 200 kev) electron fluxes responsible for surface charging Natalia
Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter?
 Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter? N. Ganushkina (1, 2), S. Dubyagin (1), I. Sillanpää (1), D.
Substorm-associated effects in the variations of low energy electron fluxes in the inner magnetosphere: Does the substorm s strength matter? N. Ganushkina (1, 2), S. Dubyagin (1), I. Sillanpää (1), D.
Plasma depletion layer: its dependence on solar wind conditions and the Earth dipole tilt
 Annales Geophysicae (2) 22: 273 29 SRef-ID: 132-576/ag/2-22-273 European Geosciences Union 2 Annales Geophysicae Plasma depletion layer: its dependence on solar wind conditions and the Earth dipole tilt
Annales Geophysicae (2) 22: 273 29 SRef-ID: 132-576/ag/2-22-273 European Geosciences Union 2 Annales Geophysicae Plasma depletion layer: its dependence on solar wind conditions and the Earth dipole tilt
Advanced modeling of low energy electrons responsible for surface charging
 Advanced modeling of low energy electrons responsible for surface charging Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2), Stepan Dubyagin (1), Ilkka Sillanpää (1), Jean-Charles Matéo Vélez (3), Dave Pitchford (4) (1) Finnish
Advanced modeling of low energy electrons responsible for surface charging Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2), Stepan Dubyagin (1), Ilkka Sillanpää (1), Jean-Charles Matéo Vélez (3), Dave Pitchford (4) (1) Finnish
From the Chapman-Ferraro Magnetosphere To the Dungey-Alfvén Magnetosphere
 From the Chapman-Ferraro Magnetosphere To the Dungey-Alfvén Magnetosphere Two Magnetosphere Types Chapman-Ferraro Dungey-Alfvén Chapman-Ferraro Type Hands-off, no-touch vacuum coupling Dungey-Alfvén Type
From the Chapman-Ferraro Magnetosphere To the Dungey-Alfvén Magnetosphere Two Magnetosphere Types Chapman-Ferraro Dungey-Alfvén Chapman-Ferraro Type Hands-off, no-touch vacuum coupling Dungey-Alfvén Type
STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM
 Prosiding Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan Penerapan MIPA Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 16 Mei 2009 STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM L. Muhammad
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan Penerapan MIPA Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 16 Mei 2009 STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM L. Muhammad
Disruption of a heliospheric current sheet fold
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047822, 2011 Disruption of a heliospheric current sheet fold V. G. Merkin, 1 J. G. Lyon, 2 S. L. McGregor, 2 and D. M. Pahud 3 Received 16 April
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl047822, 2011 Disruption of a heliospheric current sheet fold V. G. Merkin, 1 J. G. Lyon, 2 S. L. McGregor, 2 and D. M. Pahud 3 Received 16 April
How changes in the tilt angle of the geomagnetic dipole affect the coupled magnetosphere-ionosphere-thermosphere system
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012ja018056, 2012 How changes in the tilt angle of the geomagnetic dipole affect the coupled magnetosphere-ionosphere-thermosphere system Ingrid
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012ja018056, 2012 How changes in the tilt angle of the geomagnetic dipole affect the coupled magnetosphere-ionosphere-thermosphere system Ingrid
Chapter 8 Geospace 1
 Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Drift-bounce resonance between Pc5 wave and ions: Arase and MMS study
 Drift-bounce resonance between Pc5 wave and ions: Arase and MMS study S. Oimatsu1, M. Nosé2, M. Teramoto2, K. Yamamoto1, A. Matsuoka3, S. Kasahara4, S. Yokota5, K. Keika4, G. Le6, R. Nomura7, A. Fujimoto8,
Drift-bounce resonance between Pc5 wave and ions: Arase and MMS study S. Oimatsu1, M. Nosé2, M. Teramoto2, K. Yamamoto1, A. Matsuoka3, S. Kasahara4, S. Yokota5, K. Keika4, G. Le6, R. Nomura7, A. Fujimoto8,
Solar Wind Magnetosphere Coupling
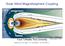 Solar Wind Magnetosphere Coupling Frank Toffoletto, Rice University thanks to R. W. Spiro, R. A. Wolf and T. W. Hill, Rice U. Figure courtesy T. W. Hill Outline Introduction Properties of the Solar Wind
Solar Wind Magnetosphere Coupling Frank Toffoletto, Rice University thanks to R. W. Spiro, R. A. Wolf and T. W. Hill, Rice U. Figure courtesy T. W. Hill Outline Introduction Properties of the Solar Wind
Assessment of ionospheric Joule heating by GUMICS-4 MHD simulation, AMIE, and satellite-based statistics: towards a synthesis
 Annales Geophysicae, 23, 251 268, 25 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/25-23-251 European Geosciences Union 25 Annales Geophysicae Assessment of ionospheric Joule heating by GUMICS-4 MHD simulation, AMIE, and satellite-based
Annales Geophysicae, 23, 251 268, 25 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/25-23-251 European Geosciences Union 25 Annales Geophysicae Assessment of ionospheric Joule heating by GUMICS-4 MHD simulation, AMIE, and satellite-based
Geosynchronous magnetic field response to solar wind dynamic pressure pulse
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003ja010076, 2004 Geosynchronous magnetic field response to solar wind dynamic pressure pulse D.-Y. Lee Department of Astronomy and Space Science,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003ja010076, 2004 Geosynchronous magnetic field response to solar wind dynamic pressure pulse D.-Y. Lee Department of Astronomy and Space Science,
Ionospheric Outflow and the Magnetosphere: A Poorly Understood, Non- Linear Relationship
 Ionospheric Outflow and the Magnetosphere: A Poorly Understood, Non- Linear Relationship D. Welling University of Michigan Climate and Space 10/1/15 The Unsolved Problem: The importance of ionospheric
Ionospheric Outflow and the Magnetosphere: A Poorly Understood, Non- Linear Relationship D. Welling University of Michigan Climate and Space 10/1/15 The Unsolved Problem: The importance of ionospheric
Database development of global Jovian magnetospheric simulation
 Feb. 24, 2016 Database development of global Jovian magnetospheric simulation K. Fukazawa 1, T. Kimura 2, F. Tsuchiya 3, G. Murakami 4, H. Kita 3, C. Tao 5 1. Academic Center for Computing and Media Studies,
Feb. 24, 2016 Database development of global Jovian magnetospheric simulation K. Fukazawa 1, T. Kimura 2, F. Tsuchiya 3, G. Murakami 4, H. Kita 3, C. Tao 5 1. Academic Center for Computing and Media Studies,
Real-time Earth magnetosphere simulator with three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic code
 SPACE WEATHER, VOL. 4,, doi:10.1029/2004sw000100, 2006 Real-time Earth magnetosphere simulator with three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic code M. Den, 1 T. Tanaka, 2,3 S. Fujita, 4,5 T. Obara, 5,6 H. Shimazu,
SPACE WEATHER, VOL. 4,, doi:10.1029/2004sw000100, 2006 Real-time Earth magnetosphere simulator with three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic code M. Den, 1 T. Tanaka, 2,3 S. Fujita, 4,5 T. Obara, 5,6 H. Shimazu,
Low energy electrons in the inner Earth s magnetosphere
 Low energy electrons in the inner Earth s magnetosphere Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) (1) University of Michigan, Ann Arbor MI, USA (2) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland The research leading
Low energy electrons in the inner Earth s magnetosphere Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) (1) University of Michigan, Ann Arbor MI, USA (2) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland The research leading
Crater FTEs: Simulation results and THEMIS observations
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L17S06, doi:10.1029/2008gl033568, 2008 Crater FTEs: Simulation results and THEMIS observations D. G. Sibeck, 1 M. Kuznetsova, 1 V. Angelopoulos,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L17S06, doi:10.1029/2008gl033568, 2008 Crater FTEs: Simulation results and THEMIS observations D. G. Sibeck, 1 M. Kuznetsova, 1 V. Angelopoulos,
Effects of causally driven cusp O + outflow on the storm time magnetosphere ionosphere system using a multifluid global simulation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015469, 2010 Effects of causally driven cusp O + outflow on the storm time magnetosphere ionosphere system using a multifluid global simulation
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015469, 2010 Effects of causally driven cusp O + outflow on the storm time magnetosphere ionosphere system using a multifluid global simulation
Convection dynamics and driving mechanism of a small substorm during dominantly IMF By+, Bz+ conditions
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L08803, doi:10.1029/2003gl018878, 2004 Convection dynamics and driving mechanism of a small substorm during dominantly IMF By+, Bz+ conditions Jun Liang, 1 G. J.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L08803, doi:10.1029/2003gl018878, 2004 Convection dynamics and driving mechanism of a small substorm during dominantly IMF By+, Bz+ conditions Jun Liang, 1 G. J.
Earth s Magnetosphere
 Earth s Magnetosphere General Description of the Magnetosphere Shape Pressure Balance The Earth s Magnetic Field The Geodynamo, Magnetic Reversals, Discovery Current Systems Chapman Ferraro Cross Tail
Earth s Magnetosphere General Description of the Magnetosphere Shape Pressure Balance The Earth s Magnetic Field The Geodynamo, Magnetic Reversals, Discovery Current Systems Chapman Ferraro Cross Tail
Using This Flip Chart
 Using This Flip Chart Solar storms can cause fluctuations in the magnetosphere called magnetic storms. These magnetic storms have disabled satellites and burned out transformers shutting down power grids.
Using This Flip Chart Solar storms can cause fluctuations in the magnetosphere called magnetic storms. These magnetic storms have disabled satellites and burned out transformers shutting down power grids.
A Correlation Study of Steady Magnetospheric Convection in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
 A Correlation Study of Steady Magnetospheric Convection in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres Caroline M. McElhenny 1, Dr. Anna DeJong 1 1 Christopher Newport University Abstract: The purpose of this
A Correlation Study of Steady Magnetospheric Convection in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres Caroline M. McElhenny 1, Dr. Anna DeJong 1 1 Christopher Newport University Abstract: The purpose of this
The Physics of Space Plasmas
 The Physics of Space Plasmas Magnetic Storms and Substorms William J. Burke 14 November 2012 University of Massachusetts, Lowell Lecture 9 Course term-paper topics Geomagnetic Storms: (continued ) Volland-Stern
The Physics of Space Plasmas Magnetic Storms and Substorms William J. Burke 14 November 2012 University of Massachusetts, Lowell Lecture 9 Course term-paper topics Geomagnetic Storms: (continued ) Volland-Stern
Large-scale flow vortices following a magnetospheric sudden impulse
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SPACE PHYSICS, VOL. 118, 3 364, doi:1.12/jgra.329, 213 Large-scale flow vortices following a magnetospheric sudden impulse A. A. Samsonov 1 and D. G. Sibeck 2 Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SPACE PHYSICS, VOL. 118, 3 364, doi:1.12/jgra.329, 213 Large-scale flow vortices following a magnetospheric sudden impulse A. A. Samsonov 1 and D. G. Sibeck 2 Received
A PARALLEL ADAPTIVE 3D MHD SCHEME FOR MODELING CORONAL AND SOLAR WIND PLASMA FLOWS
 A PARALLEL ADAPTIVE 3D MHD SCHEME FOR MODELING CORONAL AND SOLAR WIND PLASMA FLOWS C. P. T. GROTH, D. L. DE ZEEUW and T. I. GOMBOSI Space Physics Research Laboratory, Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic
A PARALLEL ADAPTIVE 3D MHD SCHEME FOR MODELING CORONAL AND SOLAR WIND PLASMA FLOWS C. P. T. GROTH, D. L. DE ZEEUW and T. I. GOMBOSI Space Physics Research Laboratory, Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic
Long-term evolution of magnetospheric current systems during storms
 Annales Geophysicae () : 1317 133 SRef-ID: 13-76/ag/--1317 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Long-term evolution of magnetospheric current systems during storms N. Yu. Ganushkina 1, T. I.
Annales Geophysicae () : 1317 133 SRef-ID: 13-76/ag/--1317 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Long-term evolution of magnetospheric current systems during storms N. Yu. Ganushkina 1, T. I.
ROTATIONAL ASYMMETRY OF EARTH S BOW SHOCK
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol.53, No.2, 2010, pp: 198 208 ROTATIONAL ASYMMETRY OF EARTH S BOW SHOCK HU You-Qiu 1, PENG Zhong 2, WANG Chi 2 1 CAS Key Laboratory of Basic Plasma Physics, School of Earth
CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol.53, No.2, 2010, pp: 198 208 ROTATIONAL ASYMMETRY OF EARTH S BOW SHOCK HU You-Qiu 1, PENG Zhong 2, WANG Chi 2 1 CAS Key Laboratory of Basic Plasma Physics, School of Earth
Modeling Interactions between the Magnetosphere, Ionosphere & Thermosphere. M.Wiltberger NCAR/HAO
 Modeling Interactions between the Magnetosphere, Ionosphere & Thermosphere M.Wiltberger NCAR/HAO Outline Overview of MIT circuit Modeling Magnetospheric impacts on the Ionosphere Energetic Particle Fluxes
Modeling Interactions between the Magnetosphere, Ionosphere & Thermosphere M.Wiltberger NCAR/HAO Outline Overview of MIT circuit Modeling Magnetospheric impacts on the Ionosphere Energetic Particle Fluxes
Chapter 15. The Role and Form of Modelling in Space Weather
 Chapter 15 The Role and Form of Modelling in Space Weather Konstantinos Papadopoulos Departments of Physics and Astronomy, University of Maryland College Park, MD 20782, USA Abstract Keywords A critical
Chapter 15 The Role and Form of Modelling in Space Weather Konstantinos Papadopoulos Departments of Physics and Astronomy, University of Maryland College Park, MD 20782, USA Abstract Keywords A critical
Multi Spacecraft Observation of Compressional Mode ULF Waves Excitation and Relativistic Electron Acceleration
 Multi Spacecraft Observation of Compressional Mode ULF Waves Excitation and Relativistic Electron Acceleration X. Shao 1, L. C. Tan 1, A. S. Sharma 1, S. F. Fung 2, Mattias Tornquist 3,Dimitris Vassiliadis
Multi Spacecraft Observation of Compressional Mode ULF Waves Excitation and Relativistic Electron Acceleration X. Shao 1, L. C. Tan 1, A. S. Sharma 1, S. F. Fung 2, Mattias Tornquist 3,Dimitris Vassiliadis
Introduction to the Sun-Earth system Steve Milan
 Introduction to the Sun-Earth system Steve Milan steve.milan@ion.le.ac.uk The solar-terrestrial system Corona is so hot that the Sun s gravity cannot hold it down it flows outwards as the solar wind A
Introduction to the Sun-Earth system Steve Milan steve.milan@ion.le.ac.uk The solar-terrestrial system Corona is so hot that the Sun s gravity cannot hold it down it flows outwards as the solar wind A
STATISTICAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DAYSIDE HIGH-ALTITUDE/-LATITUDE O + OUTFLOWS, SOLAR WINDS, AND GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY
 1 STATISTICAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DAYSIDE HIGH-ALTITUDE/-LATITUDE O + OUTFLOWS, SOLAR WINDS, AND GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY Sachiko Arvelius 1, M. Yamauchi 1, H. Nilsson 1, R. Lundin 1, H. Rème 2,
1 STATISTICAL STUDY OF RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DAYSIDE HIGH-ALTITUDE/-LATITUDE O + OUTFLOWS, SOLAR WINDS, AND GEOMAGNETIC ACTIVITY Sachiko Arvelius 1, M. Yamauchi 1, H. Nilsson 1, R. Lundin 1, H. Rème 2,
Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT
![Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT](/thumbs/89/99030303.jpg) Space Weather S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Outline Overview of Space Weather I. Space disasters II. Space weather III. Sun IV. Solar wind (interplanetary space) V. Magnetosphere VI. Recent Space
Space Weather S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Outline Overview of Space Weather I. Space disasters II. Space weather III. Sun IV. Solar wind (interplanetary space) V. Magnetosphere VI. Recent Space
PROBLEM 1 (15 points) In a Cartesian coordinate system, assume the magnetic flux density
 PROBLEM 1 (15 points) In a Cartesian coordinate system, assume the magnetic flux density varies as ( ) where is a constant, is the unit vector in x direction. a) Sketch the magnetic flux density and the
PROBLEM 1 (15 points) In a Cartesian coordinate system, assume the magnetic flux density varies as ( ) where is a constant, is the unit vector in x direction. a) Sketch the magnetic flux density and the
Fast flow, dipolarization, and substorm evolution: Cluster/Double Star multipoint observations
 197 Fast flow, dipolarization, and substorm evolution: /Double Star multipoint observations R. Nakamura, T. Takada, W. Baumjohann, M. Volwerk, T. L. Zhang, Y. Asano, A. Runov, Z. Vörös, E. Lucek, C. Carr,
197 Fast flow, dipolarization, and substorm evolution: /Double Star multipoint observations R. Nakamura, T. Takada, W. Baumjohann, M. Volwerk, T. L. Zhang, Y. Asano, A. Runov, Z. Vörös, E. Lucek, C. Carr,
