Phys 170 Lecture 4 1. Physics 170 Lecture 4. Solving for 3 Force Magnitudes in Known Directions
|
|
|
- Madlyn Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phys 170 Lecture 4 1 Physics 170 Lecture 4 Solving for 3 Force Magnitudes in Known Directions
2 Phys 170 Lecture 4 2 Mastering Engineering Issues There is definitely a problem with the campusebookstore.com company that is the middle-man between UBC Bookstore and Pearson. Some people get their access code instantly from the web. Others are told to wait for an , which never comes. We are going to move the assignment due dates back.
3 Phys 170 Lecture 4 3
4 Force Along Line Between Points 1. Position difference vector r = (end point) (start point) r = ( x end x start )î + ( y y ) ĵ + ( z z ) ˆk end start end start 2. Length of position difference vector Lr L r = r x 2 + r y 2 + r z 2 = ( x end x ) 2 start + ( y end y ) 2 start + ( z end z ) 2 start 3. Unit vector û r = r xî + r y ĵ + r z ˆk L r 4. Force vector = (force-magnitude) times unit-vector F = Fû r Phys 170 Lecture 4 4
5 Phys 170 Lecture 4 5 Setting Up Equations F R = + + F R = û B + û C + û D = u Bx + u Cx + u Dx = u By + u Cy + u Dy = u Bz + u Cz + u Dx = u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz
6 Phys 170 Lecture 4 6 Setting Up Equations F R = + + F R = û B + û C + û D = u Bx + u Cx + u Dx = u By + u Cy + u Dy = u Bz + u Cz + u Dx = u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz
7 Phys 170 Lecture 4 7 Setting Up Equations F R = + + F R = û B + û C + û D = u Bx + u Cx + u Dx = u By + u Cy + u Dy = u Bz + u Cz + u Dx = u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz
8 Phys 170 Lecture 4 8 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = u Bx = u By + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
9 Phys 170 Lecture 4 9 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = u Bx = u By + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
10 Phys 170 Lecture 4 10 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = u By + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
11 Phys 170 Lecture 4 11 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = u By + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
12 Phys 170 Lecture 4 12 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
13 Phys 170 Lecture 4 13 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
14 Phys 170 Lecture 4 14 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 + u Cy = 0 + u Cz Divide x-eqn by ubx, so upper left term is just 1 times FB Multiply new x eqn by uby and subtract that from y-eqn, so first term of new y-eqn is zero. Multiply new x eqn by ubz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first term of new z-eqn is zero.
15 Phys 170 Lecture 4 15 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 + u Cy = 0 + u Cz Divide y-eqn by u Cx, so upper middle term is just 1 times FC Multiply new y eqn by u Cz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first 2 terms of new y-eqn are zero.
16 Phys 170 Lecture 4 16 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 +1 = 0 + u Cz Divide y-eqn by u Cx, so upper middle term is just 1 times FC Multiply new y eqn by u Cz and subtract that from z-eqn, so first 2 terms of new y-eqn are zero.
17 Phys 170 Lecture 4 17 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 +1 = 0 + u Cz Divide y-eqn by u Cx, so upper middle term is just 1 times FC Multiply new y eqn by u Cz and subtract that from z-eqn, so now first two terms of new z-eqn are zero.
18 Phys 170 Lecture 4 18 Solve by Gaussian Elimination = 1 = 0 +1 = u Dz The z-equation is easy to solve for FD. Plug FD into y-equation and solve for FC. Plug FD and FC into x-equation and solve for FB.
19 Phys 170 Lecture 4 19 Diagonalization = 1 = 0 +1 = u Dz Divide the last equation by u Dz to make bottom right coef = 1.
20 Phys 170 Lecture 4 20 Diagonalization = 1 = 0 +1 = Divide the last equation by u Dz to make bottom right coef = 1.
21 Phys 170 Lecture 4 21 Diagonalization = 1 = 0 +1 = Divide the last equation by u Dz to make bottom right coef = 1. Eliminate the coefficients above the diagonal in the obvious way.
22 Phys 170 Lecture 4 22 Diagonalization = = = Divide the last equation by u Dz to make bottom right coef = 1. Eliminate the coefficients above the diagonal in the obvious way.
23 Phys 170 Lecture 4 23 Matrix Equivalent = u Bx = u By + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz = u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz
24 Phys 170 Lecture 4 24 The Augmented Matrix = u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz
25 Phys 170 Lecture 4 25 Reduced Row Echelon Form = u Bx = u By + u Cy = u Bz + u Cz u Bx u Cx u Dx u By u Cy u Dy u Bz u Cz u Dz U-matrix RREF
26 Phys 170 Lecture 4 26 Calculator Linear Equation Instructions Linear Equations on calculators Casio fx-991ms This calculator can solve linear equations for 2 or 3 variables. Enter "equation mode" by pressing MODE MODE MODE then 1 (EQN). A small EQN at the top of the display indicates that you are in "equation mode" Going into "calc mode" or "vector mode" or "matrix mode" erases any equation information. Normal calculations are not possible in "equation mode," except to calculate equation coefficients. After entering "equation mode", the screen shows Unknowns? -> (right-cursor for quadratic or cubic equations) 2 3 Enter 3 for 3 unknowns, and the screen shows a1? 0. Enter the first coefficient for the first equation (or a calculation for it) and =(equals), and the screen shows b1? 0. Enter the second coefficient for the first equation (or a calculation for it) and =(equals), and the screen shows c1? 0. Enter the third coefficient for the first equation (or a calculation for it) and =(equals), and the screen shows d1? 0. Enter the right-hand-side constant for the first equation (or a calculation for it) and =(equals), and the screen shows a2? 0. Continue this process of entering coefficients and right-hand-sides for the second equation, and third equation. After the last value (right hand side of third equation) and =(equals), the screen shows x= xx.xxxxxxxxxxx the solution for the first variable. Hit =(equals) and the screen shows y= yy.yyyyyyyyyyy the solution for the second variable. Hit =(equals) and the screen shows z= zz.zzzzzzzzzzz the solution for the third variable. Hit =(equals) and the screen shows a1= aa.aa1 the first coefficient that you entered You can use the up and down cursors to scroll through the coefficients and right-hand-sides, to check or edit them. You can also use the cursors to scroll through the solutions. The AC (all-clear) button does not clear the coefficients, nor does turning the calculator off. Exiting "equation mode" and re-entering does clear them (sets them all to zero).
27 R-matrix Using r s instead of u s F R = rb L B + r C + L C Phys 170 Lecture 4 27 r D L D = r Bx L B + r Cx L C + r Dx L D = r By L B + r Cy L C + r Dy L D = r Bz L B + r Cz L C + r Dx L D = r Bx r Cx r Dx r By r Cy r Dy r Bz r Cz r Dz L B L C L D
28 Phys 170 Lecture 4 28 Using r s instead of u s First step is finding the position difference vectors r 1, r 2, r 2 Next step is finding their lengths L1, L2, L3 But instead of doing 9 divisions to go from components of r 1, r 2, r 2 to components of û 1, û 2, û 2 to make the U-matrix which will solve for the F s directly, use the raw r1, r 2, r 2 components directly to make the R-matrix. Applying RREF to the augmented R-matrix gives so we need to do 3 multiply s at the end to get the forces. F 1 L 1, F 2 L 2, F 3 L 3
Physics 170 Lecture 5. Dot Product: Projection of Vector onto a Line & Angle Between Two Vectors
 Phys 170 Lecture 5 1 Physics 170 Lecture 5 Dot Product: Projection of Vector onto a Line & Angle etween Two Vectors Phys 170 Lecture 5 2 Mastering Engineering Introduction to M.E. and Assignment 1 moved
Phys 170 Lecture 5 1 Physics 170 Lecture 5 Dot Product: Projection of Vector onto a Line & Angle etween Two Vectors Phys 170 Lecture 5 2 Mastering Engineering Introduction to M.E. and Assignment 1 moved
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part I
 Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part I This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the first part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part I This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the first part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Algebra & Trig. I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables
 9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
Physics 170 Lecture 9. We all have our moments...
 Phys 170 Lecture 9 1 Physics 170 Lecture 9 Chapter 4 - Force System Resultants We all have our moments... Moment of a Force in 2D M = ±RF sinθ = ±RF = ±Fd = R x F y R y F x Use which ever is easiest, they
Phys 170 Lecture 9 1 Physics 170 Lecture 9 Chapter 4 - Force System Resultants We all have our moments... Moment of a Force in 2D M = ±RF sinθ = ±RF = ±Fd = R x F y R y F x Use which ever is easiest, they
1. Solve each linear system using Gaussian elimination or Gauss-Jordan reduction. The augmented matrix of this linear system is
 Solutions to Homework Additional Problems. Solve each linear system using Gaussian elimination or Gauss-Jordan reduction. (a) x + y = 8 3x + 4y = 7 x + y = 3 The augmented matrix of this linear system
Solutions to Homework Additional Problems. Solve each linear system using Gaussian elimination or Gauss-Jordan reduction. (a) x + y = 8 3x + 4y = 7 x + y = 3 The augmented matrix of this linear system
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2. where a, b, c, d, h, and k are real numbers and neither a and b nor c and d are both zero.
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
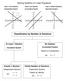 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Assignment 11 Assigned Mon Sept 27
 Assignment Assigned Mon Sept 7 Section 7., Problem 4. x sin x dx = x cos x + x cos x dx ( = x cos x + x sin x ) sin x dx u = x dv = sin x dx du = x dx v = cos x u = x dv = cos x dx du = dx v = sin x =
Assignment Assigned Mon Sept 7 Section 7., Problem 4. x sin x dx = x cos x + x cos x dx ( = x cos x + x sin x ) sin x dx u = x dv = sin x dx du = x dx v = cos x u = x dv = cos x dx du = dx v = sin x =
Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued. Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued
 Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices
 1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices We can represent a system of linear equations using an augmented matrix. In general, a matrix is just a rectangular arrays
1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices We can represent a system of linear equations using an augmented matrix. In general, a matrix is just a rectangular arrays
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Break Even. Example. 240x x This is when total cost equals total revenue.
 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations
 Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
UNIT 2B QUADRATICS II
 UNIT 2B QUADRATICS II M2 12.1-8, M2 12.10, M1 4.4 2B.1 Quadratic Graphs Objective I will be able to identify quadratic functions and their vertices, graph them and adjust the height and width of the parabolas.
UNIT 2B QUADRATICS II M2 12.1-8, M2 12.10, M1 4.4 2B.1 Quadratic Graphs Objective I will be able to identify quadratic functions and their vertices, graph them and adjust the height and width of the parabolas.
Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 9. Systems of Equations Solve the system of equations below. By this we mean, find pair(s) of numbers (x, y) (if possible) that satisfy both equations.
Chapter 9: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 9. Systems of Equations Solve the system of equations below. By this we mean, find pair(s) of numbers (x, y) (if possible) that satisfy both equations.
Unit 1 Matrices Notes Packet Period: Matrices
 Algebra 2/Trig Unit 1 Matrices Notes Packet Name: Period: # Matrices (1) Page 203 204 #11 35 Odd (2) Page 203 204 #12 36 Even (3) Page 211 212 #4 6, 17 33 Odd (4) Page 211 212 #12 34 Even (5) Page 218
Algebra 2/Trig Unit 1 Matrices Notes Packet Name: Period: # Matrices (1) Page 203 204 #11 35 Odd (2) Page 203 204 #12 36 Even (3) Page 211 212 #4 6, 17 33 Odd (4) Page 211 212 #12 34 Even (5) Page 218
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. Sections A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here, we learn another method. x + 4y = 14 5x + 3y = 2
 We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
Polynomial Functions and Models
 1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 4: Polynomial Functions and Rational Functions Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models
1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 4: Polynomial Functions and Rational Functions Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
LINEAR SYSTEMS AND MATRICES
 CHAPTER 3 LINEAR SYSTEMS AND MATRICES SECTION 3. INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR SYSTEMS This initial section takes account of the fact that some students remember only hazily the method of elimination for and
CHAPTER 3 LINEAR SYSTEMS AND MATRICES SECTION 3. INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR SYSTEMS This initial section takes account of the fact that some students remember only hazily the method of elimination for and
Core Mathematics 3 Algebra
 http://kumarmathsweeblycom/ Core Mathematics 3 Algebra Edited by K V Kumaran Core Maths 3 Algebra Page Algebra fractions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Simplify
http://kumarmathsweeblycom/ Core Mathematics 3 Algebra Edited by K V Kumaran Core Maths 3 Algebra Page Algebra fractions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Simplify
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations
 6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
Linear Algebra I Lecture 8
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 8 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 25, 2019 Outline 1 2 Gauss-Jordan Elimination Given a system of linear equations f 1 (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) = 0 f 2 (x 1, x 2,..., x n
Linear Algebra I Lecture 8 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 25, 2019 Outline 1 2 Gauss-Jordan Elimination Given a system of linear equations f 1 (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) = 0 f 2 (x 1, x 2,..., x n
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. Sections A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Matrix Solutions to Linear Equations
 Matrix Solutions to Linear Equations Augmented matrices can be used as a simplified way of writing a system of linear equations. In an augmented matrix, a vertical line is placed inside the matrix to represent
Matrix Solutions to Linear Equations Augmented matrices can be used as a simplified way of writing a system of linear equations. In an augmented matrix, a vertical line is placed inside the matrix to represent
Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination
 Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination Winfried Just, Ohio University September 22, 2017 Review: The coefficient matrix Consider a system of m linear equations in n variables.
Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination Winfried Just, Ohio University September 22, 2017 Review: The coefficient matrix Consider a system of m linear equations in n variables.
Section 5.3 Systems of Linear Equations: Determinants
 Section 5. Systems of Linear Equations: Determinants In this section, we will explore another technique for solving systems called Cramer's Rule. Cramer's rule can only be used if the number of equations
Section 5. Systems of Linear Equations: Determinants In this section, we will explore another technique for solving systems called Cramer's Rule. Cramer's rule can only be used if the number of equations
Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm
 Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm All course information is available on Moodle. Text: Nicholson, Linear algebra with applications, 7th edition. We shall cover Chapters 1,2,3,4,5:
Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm All course information is available on Moodle. Text: Nicholson, Linear algebra with applications, 7th edition. We shall cover Chapters 1,2,3,4,5:
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA II. 2 nd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA II 2 nd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Algebra II Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA II 2 nd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Algebra II Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
A supplementary reader
 A supplementary reader for CASIO fx-991ms/fx-570ms/fx-115ms/fx-100ms fx-95ms/fx-82ms/fx-350ms/fx-85ms SA0204-010002B Printed in Japan Worldwide Education Web http://world.casio.com/edu_e/ About this book...
A supplementary reader for CASIO fx-991ms/fx-570ms/fx-115ms/fx-100ms fx-95ms/fx-82ms/fx-350ms/fx-85ms SA0204-010002B Printed in Japan Worldwide Education Web http://world.casio.com/edu_e/ About this book...
Polynomial Functions
 Polynomial Functions Equations and Graphs Characteristics The Factor Theorem The Remainder Theorem http://www.purplemath.com/modules/polyends5.htm 1 A cross-section of a honeycomb has a pattern with one
Polynomial Functions Equations and Graphs Characteristics The Factor Theorem The Remainder Theorem http://www.purplemath.com/modules/polyends5.htm 1 A cross-section of a honeycomb has a pattern with one
MATH 2050 Assignment 6 Fall 2018 Due: Thursday, November 1. x + y + 2z = 2 x + y + z = c 4x + 2z = 2
 MATH 5 Assignment 6 Fall 8 Due: Thursday, November [5]. For what value of c does have a solution? Is it unique? x + y + z = x + y + z = c 4x + z = Writing the system as an augmented matrix, we have c R
MATH 5 Assignment 6 Fall 8 Due: Thursday, November [5]. For what value of c does have a solution? Is it unique? x + y + z = x + y + z = c 4x + z = Writing the system as an augmented matrix, we have c R
MA 1128: Lecture 19 4/20/2018. Quadratic Formula Solving Equations with Graphs
 MA 1128: Lecture 19 4/20/2018 Quadratic Formula Solving Equations with Graphs 1 Completing-the-Square Formula One thing you may have noticed when you were completing the square was that you followed the
MA 1128: Lecture 19 4/20/2018 Quadratic Formula Solving Equations with Graphs 1 Completing-the-Square Formula One thing you may have noticed when you were completing the square was that you followed the
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS. Chapter 5
 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 5.1 EXPLORING THE GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 5.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE EQUATIONS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What s a polynomial? A polynomial
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 5.1 EXPLORING THE GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 5.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE EQUATIONS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What s a polynomial? A polynomial
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall Integrating a vector field over a surface
 MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall 2011 Definition Integrating a vector field over a surface We are given a vector field F in space and an oriented surface in the domain of F as shown in the figure below
MATH 280 Multivariate Calculus Fall 2011 Definition Integrating a vector field over a surface We are given a vector field F in space and an oriented surface in the domain of F as shown in the figure below
(x + 1)(x 2) = 4. x
 dvanced Integration Techniques: Partial Fractions The method of partial fractions can occasionally make it possible to find the integral of a quotient of rational functions. Partial fractions gives us
dvanced Integration Techniques: Partial Fractions The method of partial fractions can occasionally make it possible to find the integral of a quotient of rational functions. Partial fractions gives us
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MAC 0 Module 0 Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the system by using Gaussian elimination with backward substitution
MAC 0 Module 0 Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the system by using Gaussian elimination with backward substitution
MATH H53 : Final exam
 MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
Section 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition
 Section 8.6 Lecture Notes Page 1 of 10 Section 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Partial fraction decomposition involves decomposing a rational function, or reversing the process of combining two or more
Section 8.6 Lecture Notes Page 1 of 10 Section 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Partial fraction decomposition involves decomposing a rational function, or reversing the process of combining two or more
Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics. The Basics of Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
Lecture Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics The Basics of Linear Algebra Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved Last Updated November 30, 2015 2 Preface Linear algebra
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING. Lectures
 FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 8 MATRICES III Rank of a matrix 2 General systems of linear equations 3 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors Rank of a matrix
FACULTY OF MATHEMATICAL STUDIES MATHEMATICS FOR PART I ENGINEERING Lectures MODULE 8 MATRICES III Rank of a matrix 2 General systems of linear equations 3 Eigenvalues and eigenvectors Rank of a matrix
( 3) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
 81 Instruction: Determining the Possible Rational Roots using the Rational Root Theorem Consider the theorem stated below. Rational Root Theorem: If the rational number b / c, in lowest terms, is a root
81 Instruction: Determining the Possible Rational Roots using the Rational Root Theorem Consider the theorem stated below. Rational Root Theorem: If the rational number b / c, in lowest terms, is a root
MTH 215: Introduction to Linear Algebra
 MTH 215: Introduction to Linear Algebra Lecture 5 Jonathan A. Chávez Casillas 1 1 University of Rhode Island Department of Mathematics September 20, 2017 1 LU Factorization 2 3 4 Triangular Matrices Definition
MTH 215: Introduction to Linear Algebra Lecture 5 Jonathan A. Chávez Casillas 1 1 University of Rhode Island Department of Mathematics September 20, 2017 1 LU Factorization 2 3 4 Triangular Matrices Definition
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
7x 5 x 2 x + 2. = 7x 5. (x + 1)(x 2). 4 x
 Advanced Integration Techniques: Partial Fractions The method of partial fractions can occasionally make it possible to find the integral of a quotient of rational functions. Partial fractions gives us
Advanced Integration Techniques: Partial Fractions The method of partial fractions can occasionally make it possible to find the integral of a quotient of rational functions. Partial fractions gives us
Chapter Practice Test Name: Period: Date:
 Name: Period: Date: 1. Draw the graph of the following system: 3 x+ 5 y+ 13 = 0 29 x 11 y 7 = 0 3 13 y = x 3x+ 5y+ 13= 0 5 5 29x 11y 7 = 0 29 7 y = x 11 11 Practice Test Page 1 2. Determine the ordered
Name: Period: Date: 1. Draw the graph of the following system: 3 x+ 5 y+ 13 = 0 29 x 11 y 7 = 0 3 13 y = x 3x+ 5y+ 13= 0 5 5 29x 11y 7 = 0 29 7 y = x 11 11 Practice Test Page 1 2. Determine the ordered
Chapter 2. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions 1 / 33 23 Chapter 2 Homework 2.5 p335 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 34, 38, 42, 46, 50, 52 2 / 33 23 3 / 33 23 Objectives:
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.5 Zeros of Polynomial Functions 1 / 33 23 Chapter 2 Homework 2.5 p335 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 34, 38, 42, 46, 50, 52 2 / 33 23 3 / 33 23 Objectives:
System of Linear Equations. Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2
 System of Linear Equations Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2 Function A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level. How does one quantity
System of Linear Equations Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2 Function A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level. How does one quantity
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Simultaneous Linear Equations
 Simultaneous Linear Equations PHYSICAL PROBLEMS Truss Problem Pressure vessel problem a a b c b Polynomial Regression We are to fit the data to the polynomial regression model Simultaneous Linear Equations
Simultaneous Linear Equations PHYSICAL PROBLEMS Truss Problem Pressure vessel problem a a b c b Polynomial Regression We are to fit the data to the polynomial regression model Simultaneous Linear Equations
6x 2 8x + 5 ) = 12x 8
 Example. If f(x) = x 3 4x + 5x + 1, then f (x) = 6x 8x + 5 Observation: f (x) is also a differentiable function... d dx ( f (x) ) = d dx ( 6x 8x + 5 ) = 1x 8 The derivative of f (x) is called the second
Example. If f(x) = x 3 4x + 5x + 1, then f (x) = 6x 8x + 5 Observation: f (x) is also a differentiable function... d dx ( f (x) ) = d dx ( 6x 8x + 5 ) = 1x 8 The derivative of f (x) is called the second
pset3-sol September 7, 2017
 pset3-sol September 7, 2017 1 18.06 pset 3 Solutions 1.1 Problem 1 Suppose that you solve AX = B with and find that X is 1 1 1 1 B = 0 2 2 2 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 X = 1 0 1 3 1 0 2 1 1.1.1 (a) What is A 1? (You
pset3-sol September 7, 2017 1 18.06 pset 3 Solutions 1.1 Problem 1 Suppose that you solve AX = B with and find that X is 1 1 1 1 B = 0 2 2 2 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 X = 1 0 1 3 1 0 2 1 1.1.1 (a) What is A 1? (You
1.2. Indices. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Indices.2 Introduction Indices, or powers, provide a convenient notation when we need to multiply a number by itself several times. In this section we explain how indices are written, and state the rules
Indices.2 Introduction Indices, or powers, provide a convenient notation when we need to multiply a number by itself several times. In this section we explain how indices are written, and state the rules
Topics. Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij
 Topics Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij or a ij lives in row i and column j Definition of a matrix
Topics Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij or a ij lives in row i and column j Definition of a matrix
4.3 Row operations. As we have seen in Section 4.1 we can simplify a system of equations by either:
 4.3 Row operations As we have seen in Section 4.1 we can simplify a system of equations by either: 1. Swapping the order of the equations around. For example: can become 3x 1 + 7x 2 = 9 x 1 2x 1 = 2 x
4.3 Row operations As we have seen in Section 4.1 we can simplify a system of equations by either: 1. Swapping the order of the equations around. For example: can become 3x 1 + 7x 2 = 9 x 1 2x 1 = 2 x
Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics
 Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs. Definition of a Polynomial Function: numbers, with a n 0. The function defined by
 Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs Definition of a Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative number and let a n, a n 1, a 2, a 1, a 0 be real numbers, with a n 0. The function defined by f(x) = a
Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs Definition of a Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative number and let a n, a n 1, a 2, a 1, a 0 be real numbers, with a n 0. The function defined by f(x) = a
8 + 6) x 2 ) y = h(x)
 . a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
. a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511)
 GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
Section Matrices and Systems of Linear Eqns.
 QUIZ: strings Section 14.3 Matrices and Systems of Linear Eqns. Remembering matrices from Ch.2 How to test if 2 matrices are equal Assume equal until proved wrong! else? myflag = logical(1) How to test
QUIZ: strings Section 14.3 Matrices and Systems of Linear Eqns. Remembering matrices from Ch.2 How to test if 2 matrices are equal Assume equal until proved wrong! else? myflag = logical(1) How to test
Partial Fraction Decomposition
 Partial Fraction Decomposition As algebra students we have learned how to add and subtract fractions such as the one show below, but we probably have not been taught how to break the answer back apart
Partial Fraction Decomposition As algebra students we have learned how to add and subtract fractions such as the one show below, but we probably have not been taught how to break the answer back apart
Relationships Between Planes
 Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Algebra Review. Finding Zeros (Roots) of Quadratics, Cubics, and Quartics. Kasten, Algebra 2. Algebra Review
 Kasten, Algebra 2 Finding Zeros (Roots) of Quadratics, Cubics, and Quartics A zero of a polynomial equation is the value of the independent variable (typically x) that, when plugged-in to the equation,
Kasten, Algebra 2 Finding Zeros (Roots) of Quadratics, Cubics, and Quartics A zero of a polynomial equation is the value of the independent variable (typically x) that, when plugged-in to the equation,
Basics. A VECTOR is a quantity with a specified magnitude and direction. A MATRIX is a rectangular array of quantities
 Some Linear Algebra Basics A VECTOR is a quantity with a specified magnitude and direction Vectors can exist in multidimensional space, with each element of the vector representing a quantity in a different
Some Linear Algebra Basics A VECTOR is a quantity with a specified magnitude and direction Vectors can exist in multidimensional space, with each element of the vector representing a quantity in a different
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Chapter 1 Linear Equations. 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
 Chapter Linear Equations. Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation in the n variables x, x 2,..., x n is one that can be expressed in the form a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a, a 2,..., a n and
Chapter Linear Equations. Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation in the n variables x, x 2,..., x n is one that can be expressed in the form a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a, a 2,..., a n and
Lecture 2e Row Echelon Form (pages 73-74)
 Lecture 2e Row Echelon Form (pages 73-74) At the end of Lecture 2a I said that we would develop an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations, and now that we have our matrix notation, we can proceed
Lecture 2e Row Echelon Form (pages 73-74) At the end of Lecture 2a I said that we would develop an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations, and now that we have our matrix notation, we can proceed
ME201 ADVANCED CALCULUS MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number: Instructions
 ME201 ADVANCED CALCULUS MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 13, 2018 8:30 am - 10:30 am Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted aids
ME201 ADVANCED CALCULUS MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 13, 2018 8:30 am - 10:30 am Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted aids
MATH 019: Final Review December 3, 2017
 Name: MATH 019: Final Review December 3, 2017 1. Given f(x) = x 5, use the first or second derivative test to complete the following (a) Calculate f (x). If using the second derivative test, calculate
Name: MATH 019: Final Review December 3, 2017 1. Given f(x) = x 5, use the first or second derivative test to complete the following (a) Calculate f (x). If using the second derivative test, calculate
EBG # 3 Using Gaussian Elimination (Echelon Form) Gaussian Elimination: 0s below the main diagonal
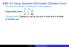 EBG # 3 Using Gaussian Elimination (Echelon Form) Gaussian Elimination: 0s below the main diagonal [ x y Augmented matrix: 1 1 17 4 2 48 (Replacement) Replace a row by the sum of itself and a multiple
EBG # 3 Using Gaussian Elimination (Echelon Form) Gaussian Elimination: 0s below the main diagonal [ x y Augmented matrix: 1 1 17 4 2 48 (Replacement) Replace a row by the sum of itself and a multiple
Math 1314 Week #14 Notes
 Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 276, Spring 2007 Additional Notes on Vectors
 Math 276, Spring 2007 Additional Notes on Vectors 1.1. Real Vectors. 1. Scalar Products If x = (x 1,..., x n ) is a vector in R n then the length of x is x = x 2 1 + + x2 n. We sometimes use the notation
Math 276, Spring 2007 Additional Notes on Vectors 1.1. Real Vectors. 1. Scalar Products If x = (x 1,..., x n ) is a vector in R n then the length of x is x = x 2 1 + + x2 n. We sometimes use the notation
y b where U. matrix inverse A 1 ( L. 1 U 1. L 1 U 13 U 23 U 33 U 13 2 U 12 1
 LU decomposition -- manual demonstration Instructor: Nam Sun Wang lu-manualmcd LU decomposition, where L is a lower-triangular matrix with as the diagonal elements and U is an upper-triangular matrix Just
LU decomposition -- manual demonstration Instructor: Nam Sun Wang lu-manualmcd LU decomposition, where L is a lower-triangular matrix with as the diagonal elements and U is an upper-triangular matrix Just
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations
 Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
MAC Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II
 MAC 1140 Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. represent systems of linear equations with matrices. 2. transform a
MAC 1140 Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. represent systems of linear equations with matrices. 2. transform a
Math123 Lecture 1. Dr. Robert C. Busby. Lecturer: Office: Korman 266 Phone :
 Lecturer: Math1 Lecture 1 Dr. Robert C. Busby Office: Korman 66 Phone : 15-895-1957 Email: rbusby@mcs.drexel.edu Course Web Site: http://www.mcs.drexel.edu/classes/calculus/math1_spring0/ (Links are case
Lecturer: Math1 Lecture 1 Dr. Robert C. Busby Office: Korman 66 Phone : 15-895-1957 Email: rbusby@mcs.drexel.edu Course Web Site: http://www.mcs.drexel.edu/classes/calculus/math1_spring0/ (Links are case
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form
 Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes. Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway
 Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway November 6, 23 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 2 Introduction 2 2 Elementary Row
Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway November 6, 23 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 2 Introduction 2 2 Elementary Row
Chapter 1: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 : Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions
 39 Algebra 2 Honors Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Section 2.1: Use Properties of Exponents Evaluate each expression (3 4 ) 2 ( 5 8 ) 3 ( 2) 3 ( 2) 9 ( a2 3 ( y 2 ) 5 y 2 y 12 rs
39 Algebra 2 Honors Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Section 2.1: Use Properties of Exponents Evaluate each expression (3 4 ) 2 ( 5 8 ) 3 ( 2) 3 ( 2) 9 ( a2 3 ( y 2 ) 5 y 2 y 12 rs
Spring 2015 Midterm 1 03/04/15 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman
 Math 0 Spring 05 Midterm 03/04/5 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print): Teaching Assistant This exam contains pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if
Math 0 Spring 05 Midterm 03/04/5 Lecturer: Jesse Gell-Redman Time Limit: 50 minutes Name (Print): Teaching Assistant This exam contains pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if
Updated: January 16, 2016 Calculus II 7.4. Math 230. Calculus II. Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University
 Math 30 Calculus II Brian Veitch Fall 015 Northern Illinois University Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something
Math 30 Calculus II Brian Veitch Fall 015 Northern Illinois University Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something
5-5 Solving Polynomial Equations
 Factor completely. If the polynomial is not factorable, write prime. 1. 3ax + 2ay az + 3bx + 2by bz (a + b)(3x + 2y z) 2. 2kx + 4mx 2nx 3ky 6my + 3ny (2x 3y)(k + 2m n) 3. 2x 3 + 5y 3 prime 4. 16g 3 + 2h
Factor completely. If the polynomial is not factorable, write prime. 1. 3ax + 2ay az + 3bx + 2by bz (a + b)(3x + 2y z) 2. 2kx + 4mx 2nx 3ky 6my + 3ny (2x 3y)(k + 2m n) 3. 2x 3 + 5y 3 prime 4. 16g 3 + 2h
1 - Systems of Linear Equations
 1 - Systems of Linear Equations 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Almost every problem in linear algebra will involve solving a system of equations. ü LINEAR EQUATIONS IN n VARIABLES We are
1 - Systems of Linear Equations 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Almost every problem in linear algebra will involve solving a system of equations. ü LINEAR EQUATIONS IN n VARIABLES We are
College Algebra. Systems of Equations and Inequalities with Matrices addendum to Lesson2. Dr. Francesco Strazzullo, Reinhardt University
 College Algebra Systems of Equations and Inequalities with Matrices addendum to Lesson2 Dr. Francesco Strazzullo, Reinhardt University Objectives These notes concern topics covered in our textbook, at
College Algebra Systems of Equations and Inequalities with Matrices addendum to Lesson2 Dr. Francesco Strazzullo, Reinhardt University Objectives These notes concern topics covered in our textbook, at
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework 6. Be prepared to answer the following oral questions if asked in the supervision class:
 MATH0 Linear Algebra B Homework 6 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra its Applications Pearson, 006 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
MATH0 Linear Algebra B Homework 6 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay, Linear Algebra its Applications Pearson, 006 (or other editions) Normally, homework assignments
Galois Theory Overview/Example Part 1: Extension Fields. Overview:
 Galois Theory Overview/Example Part 1: Extension Fields I ll start by outlining very generally the way Galois theory works. Then, I will work through an example that will illustrate the Fundamental Theorem
Galois Theory Overview/Example Part 1: Extension Fields I ll start by outlining very generally the way Galois theory works. Then, I will work through an example that will illustrate the Fundamental Theorem
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3
 ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
USE OF THE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR
 USE OF THE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR Below are some exercises to introduce the basic functions of the scientific calculator that you need to be familiar with in General Chemistry. These instructions will work
USE OF THE SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR Below are some exercises to introduce the basic functions of the scientific calculator that you need to be familiar with in General Chemistry. These instructions will work
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan , Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic
 1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan 14 18 1.2, 1.3... Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca Winter 2019 What
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan 14 18 1.2, 1.3... Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca Winter 2019 What
Chapter 8 Linear Algebraic Equations
 PowerPoint to accompany Introduction to MATLAB for Engineers, Third Edition William J. Palm III Chapter 8 Linear Algebraic Equations Copyright 2010. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. This work is only for
PowerPoint to accompany Introduction to MATLAB for Engineers, Third Edition William J. Palm III Chapter 8 Linear Algebraic Equations Copyright 2010. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. This work is only for
Chapter 2 Formulas and Definitions:
 Chapter 2 Formulas and Definitions: (from 2.1) Definition of Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n,a n 1,...,a 2,a 1,a 0 be real numbers with a n 0. The function given by f (x)
Chapter 2 Formulas and Definitions: (from 2.1) Definition of Polynomial Function: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n,a n 1,...,a 2,a 1,a 0 be real numbers with a n 0. The function given by f (x)
1.2 Supplement: Mathematical Models: A Catalog of Essential Functions
 Math 131 -copyright Angela Allen, Fall 2011 1 1.2 Supplement: Mathematical Models: A Catalog of Essential Functions Note: Some of these examples and figures come from your textbook Single Variable Calculus:
Math 131 -copyright Angela Allen, Fall 2011 1 1.2 Supplement: Mathematical Models: A Catalog of Essential Functions Note: Some of these examples and figures come from your textbook Single Variable Calculus:
Chapter 1: System of Linear Equations 1.3 Application of Li. (Read Only) Satya Mandal, KU. Summer 2017: Fall 18 Update
 Chapter 1: System of Linear Equations 1.3 Application of Linear systems (Read Only) Summer 2017: Fall 18 Update Goals In this section, we do a few applications of linear systems, as follows. Fitting polynomials,
Chapter 1: System of Linear Equations 1.3 Application of Linear systems (Read Only) Summer 2017: Fall 18 Update Goals In this section, we do a few applications of linear systems, as follows. Fitting polynomials,
Exercise Sketch these lines and find their intersection.
 These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday August 21, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say today. They are not guaranteed to be correct. 1. Solving systems of linear
These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday August 21, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say today. They are not guaranteed to be correct. 1. Solving systems of linear
Alg2 - CH4 Practice Test
 lg2 - CH4 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Evaluate + C, if possible. 2 7 8 6 a. Not possible c. b. 2 8 2 8 2. Find the product,
lg2 - CH4 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Evaluate + C, if possible. 2 7 8 6 a. Not possible c. b. 2 8 2 8 2. Find the product,
