Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm
|
|
|
- Kelley Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 1021, Linear Algebra 1. Section: A at 10am, B at 2:30pm All course information is available on Moodle. Text: Nicholson, Linear algebra with applications, 7th edition. We shall cover Chapters 1,2,3,4,5: 1. Systems of Linear Equations: Matrix Algebra: Determinants and Diagonalization: Vector Geometry: The Vector Space R n : Evaluation: Weekly online homeworks: 10% (registration on Lyryx is free, this year only). Test 1: Tuesday, October 10, in class, 25% (Note the date change!) Test 2: Thursday, November 23, in class, 25% Final Exam: 40%
2 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam.
3 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy:
4 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy: 1. Read an exercise.
5 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy: 1. Read an exercise. 2. Read its solution without stopping to think about the exercise.
6 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy: 1. Read an exercise. 2. Read its solution without stopping to think about the exercise. 3. Proceed to the next exercise immediately.
7 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy: 1. Read an exercise. 2. Read its solution without stopping to think about the exercise. 3. Proceed to the next exercise immediately. is a complete waste of time.
8 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy: 1. Read an exercise. 2. Read its solution without stopping to think about the exercise. 3. Proceed to the next exercise immediately. is a complete waste of time. It is akin to trying to learn to ride a bike by watching YouTube videos of people riding a bike.
9 Suggested exercises from Nicholson s Linear algebra with applications, 7th ed. are available on Moodle. Important: The online Lyryx homework is a good technical drill. As such it is not a sufficient preparation for the tests and the exam. Working out the suggested exercises will provide a good preparation for the tests and the exam. The following strategy: 1. Read an exercise. 2. Read its solution without stopping to think about the exercise. 3. Proceed to the next exercise immediately. is a complete waste of time. It is akin to trying to learn to ride a bike by watching YouTube videos of people riding a bike. Mathematics is not a spectator sport.
10 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations, quick recap A linear equation in the n variables x 1,..., x n is a 1 x a n x n = b. a 1,..., a n are coefficients of x 1,..., x n. b is the constant term in the equation. A system of linear equations in variables x 1,..., x n is a finite collection of linear equations in these variables. A system of three equations in four variables looks like this: a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + a 13 x 3 + a 14 x 4 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + a 23 x 3 + a 24 x 4 = b 2 a 31 x 1 + a 32 x 2 + a 33 x 3 + a 34 x 4 = b 3
11 A solution of a system of linear equations in variables x 1,..., x n is a sequence of n real numbers s 1,..., s n which is a solution to every equation in the system. The basic problem of linear algebra: Describe and study an algorithm for solving systems on linear equations. Our goal #1: Describe an algorithm that checks whether a given system has a solution. If it does, the algorithm describes the solution in parametric form.
12 Given a system Augmented matrix of a system a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + a 13 x 3 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + a 23 x 3 = b 2 a 31 x 1 + a 32 x 2 + a 33 x 3 = b 3 of three equations in three variables. The array of numbers a 11 a 12 a 13 b 1 a 21 a 22 a 23 b 2 a 31 a 32 a 33 b 3 is the augmented matrix of the system.
13 Given a system Augmented matrix of a system a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + a 13 x 3 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + a 23 x 3 = b 2 a 31 x 1 + a 32 x 2 + a 33 x 3 = b 3 of three equations in three variables. The array of numbers a 11 a 12 a 13 b 1 a 21 a 22 a 23 b 2 a 31 a 32 a 33 b 3 is the augmented matrix of the system. The coefficient matrix is and b 1 b 2 b 3 a 11 a 21 a 12 a 22 a 13 a 23 a 31 a 32 a 33 is the constant matrix of the system.
14 1.2 Gaussian elimination Example Which of the following three systems is easiest to solve? 2x + y + 3z = 1 2y z + x = 0 9z + x 4y = 2 x + y + 3z = 1 y z = 0 z = 2 x = 1 y = 0 z = 2 (1) (2) (3)
15 A useful notational convention In the following * stands for any real number, possibly zero. So [ ] 1 0 may stand for [ ] [ or ] [ 0 2, but not 3 0 ].
16 The row-echelon form (REF) and the reduced row-echelon form (RREF) Definition A matrix is in the row-echelon form (REF) if it satisfies the following: 1. All zero rows (if any) are at the bottom. 2. The first nonzero entry in each nonzero row is a 1. It is called the leading 1 for that row. 3. Each leading 1 is to the right of all leading 1s in the rows above it.
17 The row-echelon form (REF) and the reduced row-echelon form (RREF) Definition A matrix is in the row-echelon form (REF) if it satisfies the following: 1. All zero rows (if any) are at the bottom. 2. The first nonzero entry in each nonzero row is a 1. It is called the leading 1 for that row. 3. Each leading 1 is to the right of all leading 1s in the rows above it. An REF matrix is said to be in the reduced row-echelon form (RREF) if in addition to the above conditions 4. Each leading 1 is the only nonzero entry in its column.
18 Solving systems whose augmented matrix is in the RREF This is a very short slide! If the matrix is (writing a, b, c,... in place of *s) 1 0 a 0 = b 0 1 c 0 = d = e then the system is x 1 + ax 3 = b x 2 + cx 3 = d x 4 = e
19 Solving systems whose augmented matrix is in the RREF This is a very short slide! If the matrix is (writing a, b, c,... in place of *s) 1 0 a 0 = b 0 1 c 0 = d = e then the system is or x 1 + ax 3 = b x 2 + cx 3 = d x 4 = e x 1 = b ax 3 x 2 = d cx 3 x 4 = e
20 Solving systems whose augmented matrix is in the RREF This is a very short slide! If the matrix is (writing a, b, c,... in place of *s) 1 0 a 0 = b 0 1 c 0 = d = e then the system is or and the general solution is x 1 + ax 3 = b x 2 + cx 3 = d x 4 = e x 1 = b ax 3 x 2 = d cx 3 x 4 = e x 1 = b ap, x 2 = d cp, x 3 = p, x 4 = e, where p is any parameter.
21 The described method gives a solution to any system whose augmented matrix is in the RREF. Solving systems whose augmented matrix is in the REF is very similar, but there is a little bit of extra work.
22 Gaussian elimination: Elementary operations on matrices Three types of elementary operations on matrices
23 Gaussian elimination: Elementary operations on matrices Three types of elementary operations on matrices 1. Type I: Interchange two rows of a matrix. 2. Type II: Multiply a row by a nonzero number. 3. Type III: Add a multiple of one row to a different row.
24 Gaussian elimination: Elementary operations on matrices Three types of elementary operations on matrices 1. Type I: Interchange two rows of a matrix. 2. Type II: Multiply a row by a nonzero number. 3. Type III: Add a multiple of one row to a different row. Theorem Every matrix can be brought to REF (or RREF) by a sequence of elementary row operations.
25 Gaussian elimination: Elementary operations on matrices Three types of elementary operations on matrices 1. Type I: Interchange two rows of a matrix. 2. Type II: Multiply a row by a nonzero number. 3. Type III: Add a multiple of one row to a different row. Theorem Every matrix can be brought to REF (or RREF) by a sequence of elementary row operations. We shall give a constructive proof of this theorem.
26 A proof of the theorem
27 A proof of the theorem Let s see how this works in practice.
28 Putting it all together
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Row Reduction and Echelon Forms 1 / 29 Key Concepts row echelon form, reduced row echelon form pivot position, pivot, pivot column basic variable, free variable general solution, parametric solution existence
Math "Matrix Approach to Solving Systems" Bibiana Lopez. November Crafton Hills College. (CHC) 6.3 November / 25
 Math 102 6.3 "Matrix Approach to Solving Systems" Bibiana Lopez Crafton Hills College November 2010 (CHC) 6.3 November 2010 1 / 25 Objectives: * Define a matrix and determine its order. * Write the augmented
Math 102 6.3 "Matrix Approach to Solving Systems" Bibiana Lopez Crafton Hills College November 2010 (CHC) 6.3 November 2010 1 / 25 Objectives: * Define a matrix and determine its order. * Write the augmented
March 19 - Solving Linear Systems
 March 19 - Solving Linear Systems Welcome to linear algebra! Linear algebra is the study of vectors, vector spaces, and maps between vector spaces. It has applications across data analysis, computer graphics,
March 19 - Solving Linear Systems Welcome to linear algebra! Linear algebra is the study of vectors, vector spaces, and maps between vector spaces. It has applications across data analysis, computer graphics,
Section Gaussian Elimination
 Section. - Gaussian Elimination A matrix is said to be in row echelon form (REF) if it has the following properties:. The first nonzero entry in any row is a. We call this a leading one or pivot one..
Section. - Gaussian Elimination A matrix is said to be in row echelon form (REF) if it has the following properties:. The first nonzero entry in any row is a. We call this a leading one or pivot one..
Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued. Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued
 Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
Algebra & Trig. I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Linear Equations in Linear Algebra
 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LINEAR EQUATION x 1,, x n A linear equation in the variables equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n
1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LINEAR EQUATION x 1,, x n A linear equation in the variables equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here, we learn another method. x + 4y = 14 5x + 3y = 2
 We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables
 9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
Midterm 1 Review. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015
 Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix
 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
Relationships Between Planes
 Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination
 Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination Winfried Just, Ohio University September 22, 2017 Review: The coefficient matrix Consider a system of m linear equations in n variables.
Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination Winfried Just, Ohio University September 22, 2017 Review: The coefficient matrix Consider a system of m linear equations in n variables.
1 - Systems of Linear Equations
 1 - Systems of Linear Equations 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Almost every problem in linear algebra will involve solving a system of equations. ü LINEAR EQUATIONS IN n VARIABLES We are
1 - Systems of Linear Equations 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Almost every problem in linear algebra will involve solving a system of equations. ü LINEAR EQUATIONS IN n VARIABLES We are
Math 3C Lecture 20. John Douglas Moore
 Math 3C Lecture 20 John Douglas Moore May 18, 2009 TENTATIVE FORMULA I Midterm I: 20% Midterm II: 20% Homework: 10% Quizzes: 10% Final: 40% TENTATIVE FORMULA II Higher of two midterms: 30% Homework: 10%
Math 3C Lecture 20 John Douglas Moore May 18, 2009 TENTATIVE FORMULA I Midterm I: 20% Midterm II: 20% Homework: 10% Quizzes: 10% Final: 40% TENTATIVE FORMULA II Higher of two midterms: 30% Homework: 10%
MAC Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I
 MAC 2103 Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Represent a system of linear equations as an augmented matrix.
MAC 2103 Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Represent a system of linear equations as an augmented matrix.
Elementary Matrices. MATH 322, Linear Algebra I. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Elementary Matrices MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Outline Today s discussion will focus on: elementary matrices and their properties, using elementary
Elementary Matrices MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Outline Today s discussion will focus on: elementary matrices and their properties, using elementary
Lesson U2.1 Study Guide
 Lesson U2.1 Study Guide Sunday, June 3, 2018 2:05 PM Matrix operations, The Inverse of a Matrix and Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay, Sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.5 (about 24 pages). MyMathLab: Lesson
Lesson U2.1 Study Guide Sunday, June 3, 2018 2:05 PM Matrix operations, The Inverse of a Matrix and Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay, Sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.5 (about 24 pages). MyMathLab: Lesson
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
Last Time. x + 3y = 6 x + 2y = 1. x + 3y = 6 y = 1. 2x + 4y = 8 x 2y = 1. x + 3y = 6 2x y = 7. Lecture 2
 January 9 Last Time 1. Last time we ended with saying that the following four systems are equivalent in the sense that we can move from one system to the other by a special move we discussed. (a) (b) (c)
January 9 Last Time 1. Last time we ended with saying that the following four systems are equivalent in the sense that we can move from one system to the other by a special move we discussed. (a) (b) (c)
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry
 1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca May-June 2017 Introduction: linear equations Read 1.1 (in the text that is!) Go to course, class webpages.
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca May-June 2017 Introduction: linear equations Read 1.1 (in the text that is!) Go to course, class webpages.
CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
1.4 Gaussian Elimination Gaussian elimination: an algorithm for finding a (actually the ) reduced row echelon form of a matrix. A row echelon form
 1. Gaussian Elimination Gaussian elimination: an algorithm for finding a (actually the ) reduced row echelon form of a matrix. Original augmented matrix A row echelon form 1 1 0 0 0 1!!!! The reduced row
1. Gaussian Elimination Gaussian elimination: an algorithm for finding a (actually the ) reduced row echelon form of a matrix. Original augmented matrix A row echelon form 1 1 0 0 0 1!!!! The reduced row
Math 344 Lecture # Linear Systems
 Math 344 Lecture #12 2.7 Linear Systems Through a choice of bases S and T for finite dimensional vector spaces V (with dimension n) and W (with dimension m), a linear equation L(v) = w becomes the linear
Math 344 Lecture #12 2.7 Linear Systems Through a choice of bases S and T for finite dimensional vector spaces V (with dimension n) and W (with dimension m), a linear equation L(v) = w becomes the linear
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2
 Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
Lecture 22: Section 4.7
 Lecture 22: Section 47 Shuanglin Shao December 2, 213 Row Space, Column Space, and Null Space Definition For an m n, a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = a m1 a m2 a mn, the vectors r 1 = [ a 11 a 12 a 1n
Lecture 22: Section 47 Shuanglin Shao December 2, 213 Row Space, Column Space, and Null Space Definition For an m n, a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A = a m1 a m2 a mn, the vectors r 1 = [ a 11 a 12 a 1n
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 211: Linear Algebra
 Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
System of Linear Equations
 Math 20F Linear Algebra Lecture 2 1 System of Linear Equations Slide 1 Definition 1 Fix a set of numbers a ij, b i, where i = 1,, m and j = 1,, n A system of m linear equations in n variables x j, is given
Math 20F Linear Algebra Lecture 2 1 System of Linear Equations Slide 1 Definition 1 Fix a set of numbers a ij, b i, where i = 1,, m and j = 1,, n A system of m linear equations in n variables x j, is given
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. Sections A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2. No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit.
 Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2 No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit. 1. ( 4 pts) Say which matrix is in row echelon form and which is not.
Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2 No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit. 1. ( 4 pts) Say which matrix is in row echelon form and which is not.
Name: Section Registered In:
 Name: Section Registered In: Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 21, 2006 60 points possible 1. (a) (3pts) Define what it means for a linear system to be inconsistent. Solution: A linear system is inconsistent
Name: Section Registered In: Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 21, 2006 60 points possible 1. (a) (3pts) Define what it means for a linear system to be inconsistent. Solution: A linear system is inconsistent
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces
 1.4 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 1 Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces 1.4. Solving Systems of Linear Equations Note. We give an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations (called
1.4 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 1 Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces 1.4. Solving Systems of Linear Equations Note. We give an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations (called
MAC1105-College Algebra. Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices
 MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
Linear Equations in Linear Algebra
 1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LINEAR EQUATION,, 1 n A linear equation in the variables equation that can be written in the form a a a b 1 1 2 2 n n a a is an where
1 Linear Equations in Linear Algebra 1.1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LINEAR EQUATION,, 1 n A linear equation in the variables equation that can be written in the form a a a b 1 1 2 2 n n a a is an where
Math 1314 Week #14 Notes
 Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Review for Exam Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions.
 Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
1. Solve each linear system using Gaussian elimination or Gauss-Jordan reduction. The augmented matrix of this linear system is
 Solutions to Homework Additional Problems. Solve each linear system using Gaussian elimination or Gauss-Jordan reduction. (a) x + y = 8 3x + 4y = 7 x + y = 3 The augmented matrix of this linear system
Solutions to Homework Additional Problems. Solve each linear system using Gaussian elimination or Gauss-Jordan reduction. (a) x + y = 8 3x + 4y = 7 x + y = 3 The augmented matrix of this linear system
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued
 Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. Sections A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra Sections 5.1 5.3 A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are
Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay 2.5
 Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay 2.5 October, 20 You have seen that if we know the inverse A of a matrix A, we can easily solve the equation Ax = b. Solving a large number of equations Ax = b, Ax 2 =
Matrix Factorization Reading: Lay 2.5 October, 20 You have seen that if we know the inverse A of a matrix A, we can easily solve the equation Ax = b. Solving a large number of equations Ax = b, Ax 2 =
Lecture 6 & 7. Shuanglin Shao. September 16th and 18th, 2013
 Lecture 6 & 7 Shuanglin Shao September 16th and 18th, 2013 1 Elementary matrices 2 Equivalence Theorem 3 A method of inverting matrices Def An n n matrice is called an elementary matrix if it can be obtained
Lecture 6 & 7 Shuanglin Shao September 16th and 18th, 2013 1 Elementary matrices 2 Equivalence Theorem 3 A method of inverting matrices Def An n n matrice is called an elementary matrix if it can be obtained
Lecture 2e Row Echelon Form (pages 73-74)
 Lecture 2e Row Echelon Form (pages 73-74) At the end of Lecture 2a I said that we would develop an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations, and now that we have our matrix notation, we can proceed
Lecture 2e Row Echelon Form (pages 73-74) At the end of Lecture 2a I said that we would develop an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations, and now that we have our matrix notation, we can proceed
3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse
 Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan , Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic
 1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan 14 18 1.2, 1.3... Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca Winter 2019 What
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan 14 18 1.2, 1.3... Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca Winter 2019 What
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations. Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve:
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices
 1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices We can represent a system of linear equations using an augmented matrix. In general, a matrix is just a rectangular arrays
1.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations: Gauss-Jordan Elimination and Matrices We can represent a system of linear equations using an augmented matrix. In general, a matrix is just a rectangular arrays
Linear Equation: a 1 x 1 + a 2 x a n x n = b. x 1, x 2,..., x n : variables or unknowns
 Linear Equation: a x + a 2 x 2 +... + a n x n = b. x, x 2,..., x n : variables or unknowns a, a 2,..., a n : coefficients b: constant term Examples: x + 4 2 y + (2 5)z = is linear. x 2 + y + yz = 2 is
Linear Equation: a x + a 2 x 2 +... + a n x n = b. x, x 2,..., x n : variables or unknowns a, a 2,..., a n : coefficients b: constant term Examples: x + 4 2 y + (2 5)z = is linear. x 2 + y + yz = 2 is
Linear Algebra I Lecture 8
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 8 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 25, 2019 Outline 1 2 Gauss-Jordan Elimination Given a system of linear equations f 1 (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) = 0 f 2 (x 1, x 2,..., x n
Linear Algebra I Lecture 8 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 25, 2019 Outline 1 2 Gauss-Jordan Elimination Given a system of linear equations f 1 (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) = 0 f 2 (x 1, x 2,..., x n
Lectures on Linear Algebra for IT
 Lectures on Linear Algebra for IT by Mgr. Tereza Kovářová, Ph.D. following content of lectures by Ing. Petr Beremlijski, Ph.D. Department of Applied Mathematics, VSB - TU Ostrava Czech Republic 2. Systems
Lectures on Linear Algebra for IT by Mgr. Tereza Kovářová, Ph.D. following content of lectures by Ing. Petr Beremlijski, Ph.D. Department of Applied Mathematics, VSB - TU Ostrava Czech Republic 2. Systems
UNIT 3 INTERSECTIONS OF LINES AND PLANES
 UNIT 3 INTERSECTIONS OF LINES AND PLANES UNIT 3 INTERSECTIONS OF LINES AND PLANES...1 VECTOR EQUATIONS OF LINES IN SCALAR EQUATION OF LINES IN EQUATIONS OF LINES IN 2...2 2...4 3...6 VECTOR AND SCALAR
UNIT 3 INTERSECTIONS OF LINES AND PLANES UNIT 3 INTERSECTIONS OF LINES AND PLANES...1 VECTOR EQUATIONS OF LINES IN SCALAR EQUATION OF LINES IN EQUATIONS OF LINES IN 2...2 2...4 3...6 VECTOR AND SCALAR
Section 6.3. Matrices and Systems of Equations
 Section 6.3 Matrices and Systems of Equations Introduction Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. For example: [ 4 7 π 3 2 5 Definitions
Section 6.3 Matrices and Systems of Equations Introduction Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. For example: [ 4 7 π 3 2 5 Definitions
Section 5.6. LU and LDU Factorizations
 5.6. LU and LDU Factorizations Section 5.6. LU and LDU Factorizations Note. We largely follow Fraleigh and Beauregard s approach to this topic from Linear Algebra, 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley (995). See
5.6. LU and LDU Factorizations Section 5.6. LU and LDU Factorizations Note. We largely follow Fraleigh and Beauregard s approach to this topic from Linear Algebra, 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley (995). See
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 1.1 Linear System Math 2331 Linear Algebra 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan Chiu, University
1.1 Linear System Math 2331 Linear Algebra 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan Chiu, University
Chapter 4. Solving Systems of Equations. Chapter 4
 Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Example: 2x y + 3z = 1 5y 6z = 0 x + 4z = 7. Definition: Elementary Row Operations. Example: Type I swap rows 1 and 3
 Math 0 Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination and substitution
Math 0 Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination and substitution
Row Reduced Echelon Form
 Math 40 Row Reduced Echelon Form Solving systems of linear equations lies at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems in or variables using elimination and substitution of
Math 40 Row Reduced Echelon Form Solving systems of linear equations lies at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems in or variables using elimination and substitution of
If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined
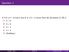 Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
MATRICES. a m,1 a m,n A =
 MATRICES Matrices are rectangular arrays of real or complex numbers With them, we define arithmetic operations that are generalizations of those for real and complex numbers The general form a matrix of
MATRICES Matrices are rectangular arrays of real or complex numbers With them, we define arithmetic operations that are generalizations of those for real and complex numbers The general form a matrix of
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511)
 GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
7.5 Operations with Matrices. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
Math 54 HW 4 solutions
 Math 54 HW 4 solutions 2.2. Section 2.2 (a) False: Recall that performing a series of elementary row operations A is equivalent to multiplying A by a series of elementary matrices. Suppose that E,...,
Math 54 HW 4 solutions 2.2. Section 2.2 (a) False: Recall that performing a series of elementary row operations A is equivalent to multiplying A by a series of elementary matrices. Suppose that E,...,
Review Solutions for Exam 1
 Definitions Basic Theorems. Finish the definition: Review Solutions for Exam (a) A linear combination of vectors {v,..., v n } is: any vector of the form c v + c v + + c n v n (b) A set of vectors {v,...,
Definitions Basic Theorems. Finish the definition: Review Solutions for Exam (a) A linear combination of vectors {v,..., v n } is: any vector of the form c v + c v + + c n v n (b) A set of vectors {v,...,
I am trying to keep these lessons as close to actual class room settings as possible.
 Greetings: I am trying to keep these lessons as close to actual class room settings as possible. They do not intend to replace the text book actually they will involve the text book. An advantage of a
Greetings: I am trying to keep these lessons as close to actual class room settings as possible. They do not intend to replace the text book actually they will involve the text book. An advantage of a
Solving Systems of Linear Equations
 LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
PH1105 Lecture Notes on Linear Algebra.
 PH05 Lecture Notes on Linear Algebra Joe Ó hógáin E-mail: johog@mathstcdie Main Text: Calculus for the Life Sciences by Bittenger, Brand and Quintanilla Other Text: Linear Algebra by Anton and Rorres Matrices
PH05 Lecture Notes on Linear Algebra Joe Ó hógáin E-mail: johog@mathstcdie Main Text: Calculus for the Life Sciences by Bittenger, Brand and Quintanilla Other Text: Linear Algebra by Anton and Rorres Matrices
MATH10212 Linear Algebra B Homework Week 5
 MATH Linear Algebra B Homework Week 5 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay Linear Algebra its Applications Pearson 6 (or other editions) Normally homework assignments
MATH Linear Algebra B Homework Week 5 Students are strongly advised to acquire a copy of the Textbook: D C Lay Linear Algebra its Applications Pearson 6 (or other editions) Normally homework assignments
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
EBG # 3 Using Gaussian Elimination (Echelon Form) Gaussian Elimination: 0s below the main diagonal
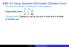 EBG # 3 Using Gaussian Elimination (Echelon Form) Gaussian Elimination: 0s below the main diagonal [ x y Augmented matrix: 1 1 17 4 2 48 (Replacement) Replace a row by the sum of itself and a multiple
EBG # 3 Using Gaussian Elimination (Echelon Form) Gaussian Elimination: 0s below the main diagonal [ x y Augmented matrix: 1 1 17 4 2 48 (Replacement) Replace a row by the sum of itself and a multiple
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
MATH 2050 Assignment 6 Fall 2018 Due: Thursday, November 1. x + y + 2z = 2 x + y + z = c 4x + 2z = 2
 MATH 5 Assignment 6 Fall 8 Due: Thursday, November [5]. For what value of c does have a solution? Is it unique? x + y + z = x + y + z = c 4x + z = Writing the system as an augmented matrix, we have c R
MATH 5 Assignment 6 Fall 8 Due: Thursday, November [5]. For what value of c does have a solution? Is it unique? x + y + z = x + y + z = c 4x + z = Writing the system as an augmented matrix, we have c R
Topics. Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij
 Topics Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij or a ij lives in row i and column j Definition of a matrix
Topics Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij or a ij lives in row i and column j Definition of a matrix
Chapter 1: Linear Equations
 Chapter : Linear Equations (Last Updated: September, 6) The material for these notes is derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed).. Systems of Linear Equations Before
Chapter : Linear Equations (Last Updated: September, 6) The material for these notes is derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed).. Systems of Linear Equations Before
5x 2 = 10. x 1 + 7(2) = 4. x 1 3x 2 = 4. 3x 1 + 9x 2 = 8
 1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
A Quick Introduction to Row Reduction
 A Quick Introduction to Row Reduction Gaussian Elimination Suppose we are asked to solve the system of equations 4x + 5x 2 + 6x 3 = 7 6x + 7x 2 + 8x 3 = 9. That is, we want to find all values of x, x 2
A Quick Introduction to Row Reduction Gaussian Elimination Suppose we are asked to solve the system of equations 4x + 5x 2 + 6x 3 = 7 6x + 7x 2 + 8x 3 = 9. That is, we want to find all values of x, x 2
Chapter 2. Systems of Equations and Augmented Matrices. Creighton University
 Chapter Section - Systems of Equations and Augmented Matrices D.S. Malik Creighton University Systems of Linear Equations Common ways to solve a system of equations: Eliminationi Substitution Elimination
Chapter Section - Systems of Equations and Augmented Matrices D.S. Malik Creighton University Systems of Linear Equations Common ways to solve a system of equations: Eliminationi Substitution Elimination
Linear Algebra Handout
 Linear Algebra Handout References Some material and suggested problems are taken from Fundamentals of Matrix Algebra by Gregory Hartman, which can be found here: http://www.vmi.edu/content.aspx?id=779979.
Linear Algebra Handout References Some material and suggested problems are taken from Fundamentals of Matrix Algebra by Gregory Hartman, which can be found here: http://www.vmi.edu/content.aspx?id=779979.
Chapter 1: Linear Equations
 Chapter : Linear Equations (Last Updated: September, 7) The material for these notes is derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed).. Systems of Linear Equations Before
Chapter : Linear Equations (Last Updated: September, 7) The material for these notes is derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed).. Systems of Linear Equations Before
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Homework 1.1 and 1.2 WITH SOLUTIONS
 Math 220 Linear Algebra (Spring 2018) Homework 1.1 and 1.2 WITH SOLUTIONS Due Thursday January 25 These will be graded in detail and will count as two (TA graded) homeworks. Be sure to start each of these
Math 220 Linear Algebra (Spring 2018) Homework 1.1 and 1.2 WITH SOLUTIONS Due Thursday January 25 These will be graded in detail and will count as two (TA graded) homeworks. Be sure to start each of these
Number of solutions of a system
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 3: Linear systems and matrices Section 7 Number of solutions of a system What you need to know already: How to solve a linear system by using Gauss- Jordan elimination.
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 3: Linear systems and matrices Section 7 Number of solutions of a system What you need to know already: How to solve a linear system by using Gauss- Jordan elimination.
(I.D) Solving Linear Systems via Row-Reduction
 (I.D) Solving Linear Systems via Row-Reduction Turning to the promised algorithmic approach to Gaussian elimination, we say an m n matrix M is in reduced-row echelon form if: the first nonzero entry of
(I.D) Solving Linear Systems via Row-Reduction Turning to the promised algorithmic approach to Gaussian elimination, we say an m n matrix M is in reduced-row echelon form if: the first nonzero entry of
Section 5.3 Systems of Linear Equations: Determinants
 Section 5. Systems of Linear Equations: Determinants In this section, we will explore another technique for solving systems called Cramer's Rule. Cramer's rule can only be used if the number of equations
Section 5. Systems of Linear Equations: Determinants In this section, we will explore another technique for solving systems called Cramer's Rule. Cramer's rule can only be used if the number of equations
Linear Methods (Math 211) - Lecture 2
 Linear Methods (Math 211) - Lecture 2 David Roe September 11, 2013 Recall Last time: Linear Systems Matrices Geometric Perspective Parametric Form Today 1 Row Echelon Form 2 Rank 3 Gaussian Elimination
Linear Methods (Math 211) - Lecture 2 David Roe September 11, 2013 Recall Last time: Linear Systems Matrices Geometric Perspective Parametric Form Today 1 Row Echelon Form 2 Rank 3 Gaussian Elimination
Homework 1 Due: Wednesday, August 27. x + y + z = 1. x y = 3 x + y + z = c 2 2x + cz = 4
 Homework 1 Due: Wednesday, August 27 1. Find all values of c for which the linear system: (a) has no solutions. (b) has exactly one solution. (c) has infinitely many solutions. (d) is consistent. x + y
Homework 1 Due: Wednesday, August 27 1. Find all values of c for which the linear system: (a) has no solutions. (b) has exactly one solution. (c) has infinitely many solutions. (d) is consistent. x + y
Math 51, Homework-2. Section numbers are from the course textbook.
 SSEA Summer 2017 Math 51, Homework-2 Section numbers are from the course textbook. 1. Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 1 1 1 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 0 t R.
SSEA Summer 2017 Math 51, Homework-2 Section numbers are from the course textbook. 1. Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 1 1 1 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 0 t R.
Math 1314 College Algebra 7.6 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination (Gauss-Jordan Elimination)
 Math 1314 College Algebra 7.6 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination (Gauss-Jordan Elimination) A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers. Size is m x n Denoted by capital letters. Entries
Math 1314 College Algebra 7.6 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination (Gauss-Jordan Elimination) A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers. Size is m x n Denoted by capital letters. Entries
Systems of Linear Equations. By: Tri Atmojo Kusmayadi and Mardiyana Mathematics Education Sebelas Maret University
 Systems of Linear Equations By: Tri Atmojo Kusmayadi and Mardiyana Mathematics Education Sebelas Maret University Standard of Competency: Understanding the properties of systems of linear equations, matrices,
Systems of Linear Equations By: Tri Atmojo Kusmayadi and Mardiyana Mathematics Education Sebelas Maret University Standard of Competency: Understanding the properties of systems of linear equations, matrices,
Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra
 1.4 Linear Combinations Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra 1.4 Linear Combinations & Systems of Linear Equations Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/
1.4 Linear Combinations Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra 1.4 Linear Combinations & Systems of Linear Equations Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/
Elementary matrices, continued. To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding
 Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations
 Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2. where a, b, c, d, h, and k are real numbers and neither a and b nor c and d are both zero.
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Evaluating Determinants by Row Reduction
 Evaluating Determinants by Row Reduction MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Objectives Reduce a matrix to row echelon form and evaluate its determinant.
Evaluating Determinants by Row Reduction MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Objectives Reduce a matrix to row echelon form and evaluate its determinant.
Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra
 3.1 Elementary Matrix Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra 3.1 Elementary Matrix Operations and Elementary Matrix Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/
3.1 Elementary Matrix Math 4377/6308 Advanced Linear Algebra 3.1 Elementary Matrix Operations and Elementary Matrix Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/
