O. Benzineb H. Mekki D. Boukhetala M. Tadjine M. S. Boucherit
|
|
|
- Camron Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O. Benzineb H. Mekki D. Boukhetala M. Tajine M. S. Boucheit J. Electical Systems: special issue N (: 9- Regula pape Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Technique Base Backstepping: Application to Inuction Moto The aim of this pape is to apply a esent implicit fault toleant contol (FTC technique base backstepping to inuction moto (IM. Mathematical moels of the moto, the istubances as well as the faults signals have been evelope. Using these moels, the ynamic behavio of moto is stuie. A backstepping contol is then synthesize an applie to the system. Base on the simulation esults, it is evient that this contol law is obust to the unknown toque loa an paametic vaiations but is not to the ejection of the faults effect. In oe to etect an compensate this late, a ecent FTC technique is then stuie an applie to the moto moel. The pefomances of the applie technique ae highlighte by simulations. about the consequent benefits as fo EMC of this ive ae also pesente. Keywos: Fault Toleant Contol, Backstepping Contol, Mathematical Moel, Inuction Moto, Fault Detection an Isolation.. θ s NOMENCLATURE s, Stato, oto inex., q Synchonous efeence fame inexes. α, β Fixe stato efeence fame inexes. V, i, Φ Voltage, cuent, flux. L s, L Stato, oto inuctance. R s, R Stato, oto esistance. T s, T Stato, oto time constant. M Mutual inuctance. Ω Roto spee. Roto flux angula position. Coesponing autho : Pocess Contol Laboatoy, Ecole Nationale supéieu Polytechnique (ENP, BP 6, Elhaach, Algies, Algeia. Copyight JES on-line : jounals/esgoups.og/jes
2 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M. INTRODUCTION Fault toleance is an issue that has been aesse by many authos. Compehensive intouction to this aea can fo example be foun in [] an []. Reseach on fault toleant contol systems has eceive incease attention ecently ue to significantly inceasing eman fo eliability, maintainability an suvivability of safety-citical systems, such as automotive an aeospace systems, nuclea powe [3]. Many effots have ecently been evote to stuy fault toleant contol systems []. The inuction moto is efinitely one of the most use electic machines in the wol. When supplie by a symmetical an balance sinusoial theephase voltage an opeating accoing to manufactues instuctions namely egaing the envionment an loa type the inuction moto is a vey obust machine [5]. A beakown in the motos can cause the stop of the pouction facility o equie the use of eunant equipment to cicumvent the poblem. Seveal failues can affect electical moto ives [6] an can appea on the level of oto o stato of inuction moto [7]. They can be electic, mechanical o magnetic. Thei causes vey vaie. Inee, of the stuies showe that each faults eveale hamonics at specific fequencies in the cuents of the machine [8], [9] an []. These fequencies epen on the moto chaacteistics. The objective of this pape is to esign a obust contol (backstepping [], [] compae to the toque of loa an to the paametic istubances but on t pesent an insufficiency as fo the ejection of the faults effect. Into this case, we intouce the intenal moel which geneates an aitive tem that we as to the nominal contol to compensate the faults effect on the system an which epouces the unknown state exactly a pioi exogenos system simulating the faults [3].. INDUCTION MOTOR DISTURBANCE AND FAULTS MODELISATION.. Inuction Moto Moeling The setting in the state fom of the inuction moto moel allows the simulation of the latte, in a stationay efeence ( α β fame choosing us like states vaiables the stato cuents, oto flux an the mechanic spee Ω [], []. An like contol vecto the stato tensions. The moel of the IM is given by the state fom: = f ( x + Bu + TL ( The state vecto, the enty matix B an the vecto ae given by:
3 J. Electical Systems SI (: 9- T 3 5 sα sβ α β T x = [ x x x x x ] = [ i i Φ Φ Ω] b B = b [ ] T = With the following expession of fiel vecto f(: f( = ax + ax3 + a3xx5 f( = ax + a5x3x5 + a6x f3( = a7x + a8x3 + a9xx5 ( f = + + ( ax ax3x5 ax f5( = a3xx + axx3 + a5x5 The components of this vecto ae expesse accoing to the paametes of the IM as follows: σ σ n = = + p ( σ a a ; a = a6 = ; a3 = a5 = ; T s σ T σ T Mσ Mσ M a 7 = a = ; a8 = a = ; a9 = a = np ; a 3 T np M = a = ; JL M With: σ = L, L s.. Distubance Moeling a T f = J 5 ; L T = et R s T s =. Rs T b = b = ; = ; σ J An unknown tem Δ( x, Δai but all the time limite is ae in the moel ( which takes the fom: = f ( + Bu + TL +Δ( x, Δai (3 A way of simulating the paametic vaiations effect on the behavio of the moto is to cause at a given moment, a anom change in the system ( coefficients: ai a i + Δai, bi b i + Δbi an + Δ The istubances Δ x, Δa will take the following fom: ( i L L s
4 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M Δ ax +Δ ax 3+Δ ax 3 x5+δbu ax ax 5 3x5 ax 6 bu Δ +Δ +Δ +Δ Δ( x, Δ ai = Δ a7x+δ a8x3+δa9xx 5 Δ ax +Δ ax3x5 +Δax a3xx axx3 a5x5 T Δ +Δ +Δ +Δ L.3. Faults moeling In this section we uneline the change of the IM moel in the pesence of faults. A tem V epesenting an unknown istubance but all the time limite [3] -which esults fom the pesence of one o moe faults in the moto- is ae in moel ( which witten in the fom: = f ( + Bu + TL +σv (5 In absence of faults, V is ientically invali an we have: T V σ = an V = (6 V A way of intoucing the hamonics which affecting the stato cuents in the state system ( is to use a stable linea iffeential system epesente in this fom: z = S z (7 The ynamic matix S being the only known chaacteistic of the system, it is consiste of the pulsations ωi = π f i whee f i pesents the fequency chaacteistic of the faults: S = iag( Si ω i (8 Si = ωi We can wite the faults istubances V in this fom: aq + Q S V = z = Γz aqq + QqS (9 Γ [ aq + Q S] Γ = = [ ] Γ aqq + QqS Finally in the pesence of faults an paametic istubances the moel of the IM becomes: = f ( + Bu + T +Δ( x, Δ a +σv ( L i (
5 J. Electical Systems SI (: 9-3. BACKSTEPPING CONTROL BASEE ON THE PRINCIPLE OF FIELD-ORIENTED 3.. Pinciple of Fiel-Oiente Contol: The objective of fiel oiente contol is to have an electomagnetic toque popotional to the stato cuent of the moto (as in the case of a DC machine with an aim of contolling the electomagnetic toque an consequently the mechanical spee of the moto []. This metho consists in oienting oto flux accoing to the iection of the evolving axis (, which makes it possible to tansfom the moto moel given by ( in the efeence mak tuning ( q [3], [5]. In these new cooinates. The oto position is efine by the angle θ s as follows: Φβ θs = actan ( Φα The tansfomation αβ q is one as follows: x x s sq cos( θs = sin( θs sin( θs x cos( θs x sα sβ ( With ( can be use fo the cuent, flux an tension. The new moel of machine in ( q efeence is given by: = ax + θ s x + ax 3 + bu = θ s x + ax + a5x 3x 5 + bu 3 = a8x 3 + ax = 5 = ax x 3 + a5x 5 + TL (3 T With: x x x x3 x x5 is isq q = [ ] = [ Φ Φ Ω] Φ = Φ = Φα + Φβ ; θs x θ s = =Ω+ a7 t x Backstepping Contol The backstepping contol technique is a metho of synthesis into nonlinea when it is ifficult to apply the iect metho of Lyapunov. It is a question of choosing at the stat a Lyapunov function fo the fist subsystem an of inceasing it as we stability the vaious successive subsystems, to lea finally T 3
6 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M to a total Lyapunov function which stabilizes the total system. The backstepping esign poceue consists of the following two steps [], []. Step : This fist step consists to ientify the eos ε an ε which espectively epesent the eo between eal spee Ω an efeence Ω as well as the moule of flux Φ an that of efeence Φ. ε = x ε = x x3 The eo eivative is given by: ε = 5 5 = 5 axx3 a5x5 T ε = = a x a x 5 3 x L ( (5 The fist Lyapunov function is efine by: v = ( ε + ε (6 We selecte stabilizing functions as follows: ( x ( k x a x T ef = ε L ax3 ( x ( k x a x ef = ε a Then the eos ynamics is given by: ε = kε ε = k ε The eivative of (6 compae to time is: (7 (8 = kε kε < v (9 With k an k ae positive esign constants. So the contol in (7 is asymptotically stabilizing. Step : In this step, we efinite two new eos of the components of the stato cuent given by: ( ε ε = ( x x = k + x a x T x 3 ef L ax3 ( ε ε = ( x x = k + x a x x ef a (5 will be: Then the equation
7 J. Electical Systems SI (: 9- ε = kε + aε3 ε = k ε + a ε The eivative of (9 gives us: ε = ( = ( 3 ε = ( ef ef = ( ef ef f ( + bu f ( + bu ( ( Whee: f ( = ax + θs x + ax3 f ( x = θs x + a x + a x x To efine the contol laws, we aopt a new Lyapunov function escibe by the following expession: v = ( ε + ε + ε 3 + ε ( Thus the eivative of the final Lyapunov function is: v = ε ε + ε ε + ε ε + ε Its eivative is given by: v 3 3 ε = k + ε + ε ε 3 k ( k3ε 3 + ( ef f( bu ( k ε + ( f ( bu ε k 3ε 3 ef k ε < We choice k 3 > an k >. Finely to make ( v the eivative of the complete Lyapunov function be negative efinite, the voltage contol input is chosen as follows: u = Vs = ( ef + kε f( b (3 u = Vsq = ( ef + k3ε 3 f( b The eo eivativeε 3 an ε will be as follows: ε 3 = k3ε 3 ax3ε ( ε = a ε k ε. A RECENT IMPLICIT FAULTS TOLERANT CONTROL The iea behin implicit FTC is that of esigning a contol unit able to automatically offset the faults effect, without nee of an explicit FDI pocess an consequent explicit econfiguation [3]. This objective will be pusue fo the IM by means of the contol scheme sketche in Fig.. 5
8 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M By supposing that the faults effects on the system can be suitably moele by an exogenos signal esulting fom a stable autonomous system calle "exosystem ". An aitive contol is ae to the nominal contol an setting to compensate the faults effect (aspect FTC. This aitive contol esults fom the intenal moel whose ole is to epouce the signal epesenting the faults effect (aspect FDI. Exosystem Refeences Faults Nominal contol FDI ξ u nom + + u u a Intenal moel V System Output Fig. Stuctue of an implicit faults toleant contol. The toque of loa an the istubances paametic ae compensate by the nominal contol. Fo this ( becomes: = f ( + Bu + σv (5 The new contol is expesse by: u = u + u nom a u unom = + ua (6 u = u unom ua On the basis of which we calculate the unknown tem u a with the expession which we etaine fom the nominal contol (7 an (3. The instantaneous iffeence between the state eivative of the system an the efeence becomes: + Γ kx bu a z x + Γ k3x bu a z = 3 = 3 = ax k 3 x3 (7 x x 5 5 axx3 + k 5 x5 Let us notice that the fist two equations o not epen on the vaiables x 3, xan x 5. 6
9 J. Electical Systems SI (: 9- in the thi equation if x x3 in the fouth equation we have x = = in the fifth equation if x x5 In the continuation, fo the etemination of u a let us consie the subsystem: x x = (8 x Whose ynamics esults fom the system (7. z = S z kx + bu Γ z a (9 = = k3x + bu Γ a z Fom system (9 we can wite it in a matix fom: x = H( + Bua Γz (3 = k b H ( Ax et A = B = k (3 3 b In this case fo the etemination of intenal moel we intouce a esent implicit fault toleant contol appoach which oes not est on the esolution of the Sylveste equation. The intenal moel takes then this fom: ξ = Sξ + N( (3 im( ξ = im( z = n f Fo the calculation of the aitive contol we intouce a new vaiable. χ = M ( ξ z Gx χ = M ( ξ z Gx (33 Afte eplacement we fin: χ = MS ( ξ z + M N( G ( H( ua + Γz (3 Then ua is chosen like: u = a B Γξ (35 Consie the systems (3 an the aitive tem given by (35 in this case we have: = H ( + Γ ( ξ z (36 The new vaiable of eo is consiee: e = ( ξ z (37 Its eivative compae to time: e = ξ z = S ξ + N( + S z e = S e + N( (38 7
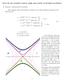
10 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M The equations escibing the ynamics of the eos in close loop ae thus: = A x + Γ e (39 e = S e + N( It is necessay to fin the expession of N (x which cancels the eo of obsevation of the faults e an makes it possible at the same time to eject thei effect fo it cancels also x. That is to say the Lyapunov function of the system (39: T T V = x x + e e Afte evelop of calculatesv becomes: V T T T T = x A x + e Γ x + e N( x ( In this case the choice of N(x is given by: T N( = Γ x ( Finally V is witten: V T = x A x (3 The system (39 becomes: Γ e = e = S e ( The objective of the contol is achieve by aopting the poceue suggeste an we able to compensate the faults effect on the system ( x an to epouce ( e thanks to the intenal moel. ( 5. SIMULATION RESULTS In the Fig. we intouce at t=. sec a loa toque equal to the nominal toque then at t =. sec a vaiation of 8% in the electical an mechanical paametes of machine, afte that the effect of only one fault in the stato geneating one hamonic of fequency 5Hz, amplitue 8 an null phase at t =.6 sec. Fo Fig.3 we consie the same situation (Fig. but in this case we intouce at t=.6 sec the effect of two faults one in the stato an anothe one in the oto geneating thee hamonics of null phases, fequency, 5, Hz an of amplitue 8,, 5 espectively. In Fig. an Fig.5, we simulate the close loop system with the ecent implicit FTC appoach. The FTC appoach which we synthesize ejects the effect of the loa toque, the paametic istubances an also the effect of one fault o two faults (in the stato an oto. 8
11 J. Electical Systems SI (: 9- Ωef (e an Ω (blue ( a s.5 Φ ef (e an Φ (blue (Wb 5 Fault I s (A I sq (A Fig. Simulations of backstepping contol in the pesence of one fault in the stato. 9
12 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M Ωef (e an Ω (blue ( a s Φ ef (e an Φ (blue (Wb Faults I s (A (A (A (A I sq (A (A (A Fig.3 Simulations of backstepping contol in the pesence of two faults (stato an oto.
13 J. Electical Systems SI (: 9- Ωef (e an Ω (blue ( a.5 Φ ef (e an Φ (blue (W 5 Fault (A I s (A (A I sq (A (A V s (e an V sq (blue (V (A z Obsevation eo Fig. Simulations of the ecent FTC appoach in the pesence of one fault.
14 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M Ωef (e an Ω (blue ( a s.5 Φ ef (e an Φ (blue (Wb 5 Faults I s (A I sq (A V s (e an V sq (blue (V. z Obsevation eo z Obsevation eo z 3 Obsevation eo Fig. 5 Simulations of the ecent FTC appoach in the pesence of two faults.
15 6. CONCLUSION J. Electical Systems SI (: 9- In this pape, a ecent implicit FTC technique is stuie an applie to inuction moto. The backstepping contol (nominal contol which we have synthesizes pesent obustness compae to the paametic istubances an the loa toque. But, pesent an insufficiency as fo the ejection of the effect of one fault (in the stato o two faults (in the stato an oto. We have shown how a esent implicit FTC appoach can be esigne in oe to compensate the faults effect stating with geneating fom the intenal moel state, an aitive tem wish we a to the nominal contol. The appoach that we ew fom the liteatue ests on the esolution of Sylveste equation which is at the oigin of its isavantages. These isavantages wee eliminate by the intoucing of a esent implicit fault toleant contol appoach fo the calculation of the intenal moel. Simulation esults have been pesente in oe to show the effectiveness of this ecent appoach. REFERENCES [] R. Patton, P. Fank an R. Clak, Issues of Fault Diagnosis fo Dynamic Systems. Spinge-Velag, Belin,. [] R. Isemann, Supevision, Fault-Detection an Fault Diagnosis Methos- an Intouction. Contol Engineeing Pactice, Vol. 5, pp , 997. [3] F. Tahami, A. Shojaei an D. Ahmai Khati, A Divesity Base Reconfiguable Metho fo Fault Toleant Contol of Inuction Motos SPEEDAM 6, S [] M. E. H. Benbouzi, D. Diallo an M. Zeaoulia, Avance Fault-Toleant Contol of Inuction-Moto Dives fo EV/HEV Taction Applications: Fom Conventional to Moen an Intelligent Contol Techniques. IEEE Tansaction on vehicula technology, vol. 56, no., Ma. 7. [5] A. S. M. Menes an A. J. Maques Caoso, A Fault-Toleant Opeating stategies appelie to Tee-phase Inuction Moto Dives IEEE tansactions on inustial electonics, vol. 53, no. 6, Dec. 6. [6] D. Diallo, M. E. H. Benbouzi an A. Makouf, A Fault-Toleant Contol Achitectue fo Inuction Moto Dives in Automotive Applications IEEE tansactions on vehicula technology, vol. 53, no. 6, Nov.. [7] S. Moeau, J.C. Tigeassou, G. Champenois, J.P. Gaubet, Diagnosis of Inuction Machines: a poceue fo electical fault etection an localization. SDEMPED 99, Gijon, Spain, pp. 5-9, Sep [8] M. E. H. Benbouzi, M. Vieia an C. Theys, Inuction motos faults etection an localization using stato cuent avance signal pocessing techniques. IEEE Tansaction on Powe Electonics, Vol., N, pp, Jan [9] S. Nani, A. Toliyat Hami, an L. Xiaoong, Conition Monitoing an Fault Diagnosis of Electical Motos IEEE Tansactions on enegy convesion, ( 5. pp [] D. Diallo, M. E. H. Benbouzi, D. Hama an X. Piee, Fault Detection an Diagnosis in an Inuction Machine Dive: A Patten Recognition Appoach Base 3
16 O. Benzineb et al: Implicit Fault Toleant Contol Tech Base Backstepping: Application to I M on Concoia Stato Mean Cuent Vecto. IEEE Tansactions on Enegy Convesion, vol., no. 3, Sep. 5. [] M. Belkheii an F. Boujema, Backstepping contol of an Inuction machine augmente by a Neual netwok. th Intenational Multi-Confeence (SSD 7, Volume I: Confeence on Systems Analysis & Automatic Contol, Tunisia, Ma. 7. [] S. Chaouch, A. Heizi, H. Seai an M. S. Naït-Saï, Lyapunov an Backstepping Contol Design of Inuction Moto System. th Intenational Multi-Confeence (SSD 7, Volume II: Confeence on Powe Electical Systems, Tunisia, Ma. 7. [3] C. Bonivento, A. Isioi, I. Maconi an A. Paoli, Implicit Fault Toleant Contol: Application to Inuction Motos. Automatica,, Rate Values Powe.8 KW Voltage / 38 V Fequency 5 Hz n p Rate Paametes R s Ω R 6.3 Ω L.6 H s L.6 H M. H Kg.m J. f.5 IS
DQ Modeling Of Induction Motor With Broken Rotor Bars In MATLAB Simulink
 DQ Moeling Of Inuction Moto With Boken Roto Bas In MATLAB Simulink Pincy P 1 an Gayathi Vijayachanan 2 1,2 Depatment. Of Electical an Electonics, See Buha College of Engineeing, Keala Abstact To analyze
DQ Moeling Of Inuction Moto With Boken Roto Bas In MATLAB Simulink Pincy P 1 an Gayathi Vijayachanan 2 1,2 Depatment. Of Electical an Electonics, See Buha College of Engineeing, Keala Abstact To analyze
Passivity-Based Control of Saturated Induction Motors
 Passivity-Base Contol of Satuate Inuction otos Levent U. Gökee, embe, IEEE, awan A. Simaan, Fellow, IEEE, an Chales W. Bice, Senio embe, IEEE Depatment of Electical Engineeing Univesity of South Caolina
Passivity-Base Contol of Satuate Inuction otos Levent U. Gökee, embe, IEEE, awan A. Simaan, Fellow, IEEE, an Chales W. Bice, Senio embe, IEEE Depatment of Electical Engineeing Univesity of South Caolina
Rotor Flux Estimation of Induction Motors Using Sliding-Mode Observer
 5th Intenational Confeence on Sustainable Enegy and Envionment Engineeing (ICSEEE 2016) Roto Flux Estimation of Induction Motos Using Sliding-Mode Obseve Yong Feng1,a, Minghao Zhou1,b and Fengling Han2,c
5th Intenational Confeence on Sustainable Enegy and Envionment Engineeing (ICSEEE 2016) Roto Flux Estimation of Induction Motos Using Sliding-Mode Obseve Yong Feng1,a, Minghao Zhou1,b and Fengling Han2,c
Vector Control. Application to Induction Motor Control. DSP in Motion Control - Seminar
 Vecto Contol Application to Induction Moto Contol Vecto Contol - Pinciple The Aim of Vecto Contol is to Oient the Flux Poducing Component of the Stato Cuent to some Suitable Flux Vecto unde all Opeating
Vecto Contol Application to Induction Moto Contol Vecto Contol - Pinciple The Aim of Vecto Contol is to Oient the Flux Poducing Component of the Stato Cuent to some Suitable Flux Vecto unde all Opeating
2.3. SLIDING MODE BASED OUTER CONTROL LOOP FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES WITH FORCED DYNAMICS
 2.3. SLIDING MODE BASED OUTER CONTROL LOOP FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES WITH FORCED DYNAMICS Abstact: Though the loa toque estimation, the basic FDC base IM ive contol system pesente in the last two sections
2.3. SLIDING MODE BASED OUTER CONTROL LOOP FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES WITH FORCED DYNAMICS Abstact: Though the loa toque estimation, the basic FDC base IM ive contol system pesente in the last two sections
CHAPTER 2 DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE. 2.1 Derivation of Machine Equations
 1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
Jerk and Hyperjerk in a Rotating Frame of Reference
 Jek an Hypejek in a Rotating Fame of Refeence Amelia Caolina Spaavigna Depatment of Applie Science an Technology, Politecnico i Toino, Italy. Abstact: Jek is the eivative of acceleation with espect to
Jek an Hypejek in a Rotating Fame of Refeence Amelia Caolina Spaavigna Depatment of Applie Science an Technology, Politecnico i Toino, Italy. Abstact: Jek is the eivative of acceleation with espect to
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5
 Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
Steady State and Transient Performance Analysis of Three Phase Induction Machine using MATLAB Simulations
 Intenational Jounal of Recent Tends in Engineeing, Vol, No., May 9 Steady State and Tansient Pefomance Analysis of Thee Phase Induction Machine using MATAB Simulations Pof. Himanshu K. Patel Assistant
Intenational Jounal of Recent Tends in Engineeing, Vol, No., May 9 Steady State and Tansient Pefomance Analysis of Thee Phase Induction Machine using MATAB Simulations Pof. Himanshu K. Patel Assistant
N igerian Journal of M athematics and Applications V olume 24, (2015),
 N igeian Jounal of M athematics an Applications V olume 24, 205), 228 236 c N ig. J. M ath. Appl. http : //www.kwsman.com Flow of an Incompessible MHD Thi Gae Flui Though a Cylinical Pipe with Isothemal
N igeian Jounal of M athematics an Applications V olume 24, 205), 228 236 c N ig. J. M ath. Appl. http : //www.kwsman.com Flow of an Incompessible MHD Thi Gae Flui Though a Cylinical Pipe with Isothemal
Equilibria of a cylindrical plasma
 // Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
// Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
SLIDING-MODE DIRECT FIELD-ORIENTED CONTROL OF SIX-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 TECHNICAL TRANSACTIONS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING CZASOPISMO TECHNICZNE ELEKTROTECHNIKA DOI: 10.4467/2353737XCT.16.250.6049 2-E/2016 JACEK LISTWAN, KRZYSZTOF PIEŃKOWSKI SLIDING-MODE DIRECT FIELD-ORIENTED CONTROL
TECHNICAL TRANSACTIONS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING CZASOPISMO TECHNICZNE ELEKTROTECHNIKA DOI: 10.4467/2353737XCT.16.250.6049 2-E/2016 JACEK LISTWAN, KRZYSZTOF PIEŃKOWSKI SLIDING-MODE DIRECT FIELD-ORIENTED CONTROL
An Adaptive Neural-Network Model-Following Speed Control of PMSM Drives for Electric Vehicle Applications
 Poceedings of the 9th WSEAS Intenational Confeence on Applied Mathematics, Istanbul, Tuey, May 27-29, 2006 (pp412-417) An Adaptive Neual-Netwo Model-Following Speed Contol of PMSM Dives fo Electic Vehicle
Poceedings of the 9th WSEAS Intenational Confeence on Applied Mathematics, Istanbul, Tuey, May 27-29, 2006 (pp412-417) An Adaptive Neual-Netwo Model-Following Speed Contol of PMSM Dives fo Electic Vehicle
PH126 Exam I Solutions
 PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
Fuzzy Adaptive Neural-Network Model-Following Speed Control for PMSM Drives
 Fuzzy Adaptive Neual-Netwok Model-Following Speed Contol fo PMSM Dives FAYEZ F. M. EL-SOUSY MAGED N. F. NASHED Powe Electonics & Enegy Convesion Depatment Electonics Reseach Institute (ERI) Al-Tahi Steet,
Fuzzy Adaptive Neual-Netwok Model-Following Speed Contol fo PMSM Dives FAYEZ F. M. EL-SOUSY MAGED N. F. NASHED Powe Electonics & Enegy Convesion Depatment Electonics Reseach Institute (ERI) Al-Tahi Steet,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF FUZZY BASED FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF FUZZY BASED FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES FOR HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES ABSTRACT 1 Maiam Khan, Student Membe, IEEE and 2 Naayan C. Ka, Membe, IEEE Electical Machine
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF FUZZY BASED FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES FOR HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES ABSTRACT 1 Maiam Khan, Student Membe, IEEE and 2 Naayan C. Ka, Membe, IEEE Electical Machine
Dynamic Performances of Self-Excited Induction Generator Feeding Different Static Loads
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 3, No. 1, June 2006, 63-76 Dynamic Pefomances of Self-Excited Induction Geneato Feeding Diffeent Static Loads Ali Nesba 1, Rachid Ibtiouen 2, Oma Touhami
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 3, No. 1, June 2006, 63-76 Dynamic Pefomances of Self-Excited Induction Geneato Feeding Diffeent Static Loads Ali Nesba 1, Rachid Ibtiouen 2, Oma Touhami
COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS
 Pogess In Electomagnetics Reseach, PIER 73, 93 105, 2007 COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS T.-X. Song, Y.-H. Liu, and J.-M. Xiong School of Mechanical Engineeing
Pogess In Electomagnetics Reseach, PIER 73, 93 105, 2007 COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS T.-X. Song, Y.-H. Liu, and J.-M. Xiong School of Mechanical Engineeing
J. Electrical Systems 1-3 (2005): Regular paper
 K. Saii D. Rahem S. Saii A Miaoui Regula pape Coupled Analytical-Finite Element Methods fo Linea Electomagnetic Actuato Analysis JES Jounal of Electical Systems In this pape, a linea electomagnetic actuato
K. Saii D. Rahem S. Saii A Miaoui Regula pape Coupled Analytical-Finite Element Methods fo Linea Electomagnetic Actuato Analysis JES Jounal of Electical Systems In this pape, a linea electomagnetic actuato
Feedback Linearizing Control of Induction Motor Drive by P-I Controllers in RTDS Environment
 Jounal of Automation and Contol Engineeing Vol., No. 4, Decembe 03 Feedback ineaizing Contol of Induction Moto Dive by P-I Contolles in TDS Envionment Kanungo Baada Mohanty and Madhu Singh Dept. of Electical
Jounal of Automation and Contol Engineeing Vol., No. 4, Decembe 03 Feedback ineaizing Contol of Induction Moto Dive by P-I Contolles in TDS Envionment Kanungo Baada Mohanty and Madhu Singh Dept. of Electical
A Nonlinear Controller for Photovoltaic Water Pumping System
 Intenational Jounal of Engineeing Tens an Technology (IJETT) - Volume4Issue5- ay 013 A Nonlinea Contolle fo Photovoltaic Wate Pumping System Hai Kishnan P 1, Ashokkuma K, Bhaathkuma S 3 1 Assistant pofesso,
Intenational Jounal of Engineeing Tens an Technology (IJETT) - Volume4Issue5- ay 013 A Nonlinea Contolle fo Photovoltaic Wate Pumping System Hai Kishnan P 1, Ashokkuma K, Bhaathkuma S 3 1 Assistant pofesso,
Fuzzy Sliding Mode Speed Controller Design of Induction Motor Drives
 Poceedings of the Intenational Confeence on Industial Engineeing and Opeations Management Istanbul, Tukey, July 3 6, Fuzzy Sliding Mode Speed Contolle Design of Induction Moto Dives F. Nacei, T. Laamayad
Poceedings of the Intenational Confeence on Industial Engineeing and Opeations Management Istanbul, Tukey, July 3 6, Fuzzy Sliding Mode Speed Contolle Design of Induction Moto Dives F. Nacei, T. Laamayad
Simultaneous state and unknown inputs estimation with PI and PMI observers for Takagi Sugeno model with unmeasurable premise variables
 Simultaneous state an unknown inputs estimation with PI an PMI obseves fo Takagi Sugeno moel with unmeasuable pemise vaiables Dalil Ichalal, Benoît Max, José Ragot an Diie Maquin Abstact In this pape,
Simultaneous state an unknown inputs estimation with PI an PMI obseves fo Takagi Sugeno moel with unmeasuable pemise vaiables Dalil Ichalal, Benoît Max, José Ragot an Diie Maquin Abstact In this pape,
Speed Sensorless Rotor Flux Estimation in Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive
 25 WSEAS Int. Conf. on DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS and CONTROL, Venice, Italy, Novembe 2-4, 25 (pp49-414) Speed Sensoless Roto Flux Estimation in Vecto Contolled Induction Moto Dive J. S. THONGAM and M.OUHROUCHE
25 WSEAS Int. Conf. on DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS and CONTROL, Venice, Italy, Novembe 2-4, 25 (pp49-414) Speed Sensoless Roto Flux Estimation in Vecto Contolled Induction Moto Dive J. S. THONGAM and M.OUHROUCHE
STABILITY AND PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSES OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR
 HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRY AND CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 42(2) pp. 109 113 (2014) STABILITY AND PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSES OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR ATTILA FODOR 1, ROLAND BÁLINT 1, ATTILA MAGYAR 1, AND
HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRY AND CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 42(2) pp. 109 113 (2014) STABILITY AND PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSES OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR ATTILA FODOR 1, ROLAND BÁLINT 1, ATTILA MAGYAR 1, AND
Two simple and novel SISO controllers for induction motors based on adaptive passivity
 ISA Tansactions 47 (2008) 60 79 www.elsevie.com/locate/isatans Two simple and novel SISO contolles fo induction motos based on adaptive passivity Juan C. Tavieso-Toes a, Manuel A. Duate-Memoud b, a Univesity
ISA Tansactions 47 (2008) 60 79 www.elsevie.com/locate/isatans Two simple and novel SISO contolles fo induction motos based on adaptive passivity Juan C. Tavieso-Toes a, Manuel A. Duate-Memoud b, a Univesity
Design and Control of High-Speed Solid-Rotor Synchronous Reluctance Drive with Three-Phase LC Filter
 Design an Contol of High-Spee Soli-Roto Synchonous Reluctance Dive with Thee-Phase LC Filte Jae-Do Pak The Pennsylvania State Univesity 11 Electical Engineeing East Univesity Pak, PA 168 Email: jaeo@psu.eu
Design an Contol of High-Spee Soli-Roto Synchonous Reluctance Dive with Thee-Phase LC Filte Jae-Do Pak The Pennsylvania State Univesity 11 Electical Engineeing East Univesity Pak, PA 168 Email: jaeo@psu.eu
EKF- BASED SENSORLESS DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR: COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO DIFFERENT SELECTION TABLES
 ansaction in Machine, Powe electonics an Dives ISSN: 1985-946 Online Publication, June 21 www.pcoglobal.com/gjto.htm MD-C17/GJO EKF- BASED SENSORLESS DIREC ORQUE CONROL OF PERMANEN MAGNE SYNCHRONOUS MOOR:
ansaction in Machine, Powe electonics an Dives ISSN: 1985-946 Online Publication, June 21 www.pcoglobal.com/gjto.htm MD-C17/GJO EKF- BASED SENSORLESS DIREC ORQUE CONROL OF PERMANEN MAGNE SYNCHRONOUS MOOR:
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
SENSORLESS VECTOR-CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE SYSTEM WITH ROTOR RESISTANCE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL PROCESSING WITH FLOATING POINT DSP
 Wokshop on ELECTRICAL MACHINES' PARAMETERS Technical Univesity of Cluj-Napoca, 26 th of May 2001 SENSORLESS VECTOR-CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE SYSTEM WITH ROTOR RESISTANCE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL
Wokshop on ELECTRICAL MACHINES' PARAMETERS Technical Univesity of Cluj-Napoca, 26 th of May 2001 SENSORLESS VECTOR-CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE SYSTEM WITH ROTOR RESISTANCE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL
ROBUST CONTROL FOR A SCARA ROBOT WITH PARAMETRIC UNCERTAINTY. Víctor Mosquera, Andrés Vivas
 ROBUS CONROL FOR A SCARA ROBO WIH PARAMERIC UNCERAINY Vícto Mosuea, Anés Vivas Depatment of Electonic, Instumentation an Contol, Univesity of Cauca, Popayán, Colombia Abstact: his pape pesents a obust
ROBUS CONROL FOR A SCARA ROBO WIH PARAMERIC UNCERAINY Vícto Mosuea, Anés Vivas Depatment of Electonic, Instumentation an Contol, Univesity of Cauca, Popayán, Colombia Abstact: his pape pesents a obust
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
Theoretical comparison between Field Oriented and Generalized Predictive Control for an Induction Motor
 Int. Jounal on Sciences and echniques of Automatic contol Vol., N heoetical compaison between Field Oiented and Genealized Pedictive Contol fo an Induction Moto aek Gallah (, Adel Khedhe (, Mohamed Faouzi
Int. Jounal on Sciences and echniques of Automatic contol Vol., N heoetical compaison between Field Oiented and Genealized Pedictive Contol fo an Induction Moto aek Gallah (, Adel Khedhe (, Mohamed Faouzi
b) The array factor of a N-element uniform array can be written
 to Eam in Antenna Theo Time: 18 Mach 010, at 8.00 13.00. Location: Polacksbacken, Skivsal You ma bing: Laboato epots, pocket calculato, English ictiona, Råe- Westegen: Beta, Noling-Östeman: Phsics Hanbook,
to Eam in Antenna Theo Time: 18 Mach 010, at 8.00 13.00. Location: Polacksbacken, Skivsal You ma bing: Laboato epots, pocket calculato, English ictiona, Råe- Westegen: Beta, Noling-Östeman: Phsics Hanbook,
Torque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Motor Using Neural Network Controller
 Toque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Moto Using Neual Netwok Contolle K. Naga Sujatha 1, and K.Vaisakh 2 Associate Pofesso, Dept of EEE, JNTUHCEJ, Kaimnaga Dist. Pofesso, Dept of EE, AU EnggCollege,Visakapatnam.
Toque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Moto Using Neual Netwok Contolle K. Naga Sujatha 1, and K.Vaisakh 2 Associate Pofesso, Dept of EEE, JNTUHCEJ, Kaimnaga Dist. Pofesso, Dept of EE, AU EnggCollege,Visakapatnam.
Hammerstein Model Identification Based On Instrumental Variable and Least Square Methods
 Intenational Jounal of Emeging Tends & Technology in Compute Science (IJETTCS) Volume 2, Issue, Januay Febuay 23 ISSN 2278-6856 Hammestein Model Identification Based On Instumental Vaiable and Least Squae
Intenational Jounal of Emeging Tends & Technology in Compute Science (IJETTCS) Volume 2, Issue, Januay Febuay 23 ISSN 2278-6856 Hammestein Model Identification Based On Instumental Vaiable and Least Squae
Solutions to Problems : Chapter 19 Problems appeared on the end of chapter 19 of the Textbook
 Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
R dt 2. INDIRECT FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR
 Indiect Field Oiented Contol of Induction Moto Using Fuzzy Logic Aun Kuma R PG Schola, PED, SELECT, VIT Univesity, Chennai Campus aunkumalmc@gmail.com Abstact: This pape pesents a fuzzy logic based speed
Indiect Field Oiented Contol of Induction Moto Using Fuzzy Logic Aun Kuma R PG Schola, PED, SELECT, VIT Univesity, Chennai Campus aunkumalmc@gmail.com Abstact: This pape pesents a fuzzy logic based speed
SEARCH-BASED DYNAMIC IDENTIFICATION OF INDUCTION MOTORS
 SEARCH-BASED DYNAMIC IDENTIFICATION OF INDUCTION MOTORS Alexande Vladimiovich Nesteovskiy Veniamin Geogievich ashiskikh Valey Mihailovich Zavyalov and Iina Yuyevna Semykina uzbass State Technical Univesity
SEARCH-BASED DYNAMIC IDENTIFICATION OF INDUCTION MOTORS Alexande Vladimiovich Nesteovskiy Veniamin Geogievich ashiskikh Valey Mihailovich Zavyalov and Iina Yuyevna Semykina uzbass State Technical Univesity
4. Compare the electric force holding the electron in orbit ( r = 0.53
 Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Maximum Torque Control of Induction Traction Motor Based on DQ Axis Voltage Regulation
 6th Intenational Confeence on Machiney, Mateials, Envionent, Biotechnology and Copute (MMEBC 016) Maxiu Toque Contol of Induction Taction Moto Based on DQ Axis Voltage Regulation Guo-Bin SUN1,a, Shu-Jia
6th Intenational Confeence on Machiney, Mateials, Envionent, Biotechnology and Copute (MMEBC 016) Maxiu Toque Contol of Induction Taction Moto Based on DQ Axis Voltage Regulation Guo-Bin SUN1,a, Shu-Jia
A Crash Course in (2 2) Matrices
 A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
Lecture Set 6 Brushless DC Machines
 Lectue Set 6 Bushless DC Machines S.D. Sudhoff Sping 2018 Reading Chapte 8, Electomechanical Motion Devices, 2 nd Edition 2 A Bushless DC Machine 3 Sample Applications Low Powe: Disk dive motos Medium
Lectue Set 6 Bushless DC Machines S.D. Sudhoff Sping 2018 Reading Chapte 8, Electomechanical Motion Devices, 2 nd Edition 2 A Bushless DC Machine 3 Sample Applications Low Powe: Disk dive motos Medium
Sensitivity Analysis of SAW Technique: the Impact of Changing the Decision Making Matrix Elements on the Final Ranking of Alternatives
 Ianian Jounal of Opeations Reseach Vol. 5, No. 1, 2014, pp. 82-94 Sensitivity Analysis of SAW Technique: the Impact of Changing the Decision Maing Matix Elements on the Final Raning of Altenatives A. Alinezha
Ianian Jounal of Opeations Reseach Vol. 5, No. 1, 2014, pp. 82-94 Sensitivity Analysis of SAW Technique: the Impact of Changing the Decision Maing Matix Elements on the Final Raning of Altenatives A. Alinezha
Electric Potential and Gauss s Law, Configuration Energy Challenge Problem Solutions
 Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
A THEORETICAL ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROSTATIC FILTERS
 PUBLISHING HOUS PROCDINGS OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY, Seies A, OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY Volume 5, Numbe /4, pp.- A THORTICAL ANALYSIS OF TH LCTROSTATIC FILTRS Gleb DRAGAN* Romanian Acaem Calea Victoiei 5, 7 Bucaest,
PUBLISHING HOUS PROCDINGS OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY, Seies A, OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY Volume 5, Numbe /4, pp.- A THORTICAL ANALYSIS OF TH LCTROSTATIC FILTRS Gleb DRAGAN* Romanian Acaem Calea Victoiei 5, 7 Bucaest,
STRIP THICKNESS ESTIMATION IN ROLLING MILLS FROM ELECTRICAL VARIABLES IN AC DRIVES
 Latin Ameican Applied Reseach 39:353-359(2009) STRIP THICKNESS ESTIMATION IN ROLLING MILLS FROM ELECTRICAL VARIABLES IN AC DRIVES N.S. MARCELLOS, J.F. DENTI and G.C.D. SOUSA Pof. Eletotécnica, CEFETES,
Latin Ameican Applied Reseach 39:353-359(2009) STRIP THICKNESS ESTIMATION IN ROLLING MILLS FROM ELECTRICAL VARIABLES IN AC DRIVES N.S. MARCELLOS, J.F. DENTI and G.C.D. SOUSA Pof. Eletotécnica, CEFETES,
Section 5: Magnetostatics
 ection 5: Magnetostatics In electostatics, electic fiels constant in time ae pouce by stationay chages. In magnetostatics magnetic fiels constant in time ae pouces by steay cuents. Electic cuents The electic
ection 5: Magnetostatics In electostatics, electic fiels constant in time ae pouce by stationay chages. In magnetostatics magnetic fiels constant in time ae pouces by steay cuents. Electic cuents The electic
GRAVITATION. Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., New Delhi -18 PG 1
 Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa Plaza, Vikas Pui Extn., New Delhi -8 Ph. : 96905, 857, E-mail einsteinclasses00@gmail.com, PG GRAVITATION Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa Plaza, Vikas Pui Extn., New Delhi -8 Ph. : 96905, 857, E-mail einsteinclasses00@gmail.com, PG GRAVITATION Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa
Online Compensation of Parameter Variation Effects for Robust Interior PM Synchronous Motor Drives
 Online Compensation of Paamete Vaiation Effects fo Robust Inteio PM Synchonous Moto Dives 713 JPE 11-5-11 Online Compensation of Paamete Vaiation Effects fo Robust Inteio PM Synchonous Moto Dives Rajenda
Online Compensation of Paamete Vaiation Effects fo Robust Inteio PM Synchonous Moto Dives 713 JPE 11-5-11 Online Compensation of Paamete Vaiation Effects fo Robust Inteio PM Synchonous Moto Dives Rajenda
Voltage-Behind-Reactance Model of Six-Phase Synchronous Machine Considering Stator Mutual Leakage Inductance
 Voltage-Behind-Reactance Model of Six-Phase Synchonous Machine Consideing Stato Mutual eakage Inductance Navid Amii, Seyyedmilad Ebahimi, Jui Jatskevich and Hemann W. Dommel Abstact Six-phase machines
Voltage-Behind-Reactance Model of Six-Phase Synchonous Machine Consideing Stato Mutual eakage Inductance Navid Amii, Seyyedmilad Ebahimi, Jui Jatskevich and Hemann W. Dommel Abstact Six-phase machines
Speed Sensorless Variable Structure Torque Control of Induction Motor
 ISSN 0005-1144 ATKAFF 51(1), 33 40(2010) Kael Jezenik, Asif Šabanović, Mian Roič Spee Sensoless Vaiable Stuctue Toque Contol of Inuction Moto UDK IFAC 621.313.333.072.1 5.5.4; 4.0.1 Oiginal scientific
ISSN 0005-1144 ATKAFF 51(1), 33 40(2010) Kael Jezenik, Asif Šabanović, Mian Roič Spee Sensoless Vaiable Stuctue Toque Contol of Inuction Moto UDK IFAC 621.313.333.072.1 5.5.4; 4.0.1 Oiginal scientific
A Simple Method to Control of Variable Speed Wind Generation System Coupled with Squirrel Cage Induction Generator
 Austalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(5): 319-328, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 A Simple Method to Contol of Vaiale Speed Wind Geneation System Coupled with Squiel Cage Induction Geneato M. Najafi,
Austalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(5): 319-328, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 A Simple Method to Contol of Vaiale Speed Wind Geneation System Coupled with Squiel Cage Induction Geneato M. Najafi,
Conventional Paper-I (a) Explain the concept of gradient. Determine the gradient of the given field: ( )
 EE-Conventional Pape-I IES-013 www.gatefoum.com Conventional Pape-I-013 1. (a) Eplain the concept of gadient. Detemine the gadient of the given field: V ρzsin φ+ z cos φ+ρ What is polaization? In a dielectic
EE-Conventional Pape-I IES-013 www.gatefoum.com Conventional Pape-I-013 1. (a) Eplain the concept of gadient. Detemine the gadient of the given field: V ρzsin φ+ z cos φ+ρ What is polaization? In a dielectic
Analysis of high speed machining center spindle dynamic unit structure performance Yuan guowei
 Intenational Confeence on Intelligent Systems Reseach and Mechatonics Engineeing (ISRME 0) Analysis of high speed machining cente spindle dynamic unit stuctue pefomance Yuan guowei Liaoning jidian polytechnic,dan
Intenational Confeence on Intelligent Systems Reseach and Mechatonics Engineeing (ISRME 0) Analysis of high speed machining cente spindle dynamic unit stuctue pefomance Yuan guowei Liaoning jidian polytechnic,dan
Notes for the standard central, single mass metric in Kruskal coordinates
 Notes fo the stana cental, single mass metic in Kuskal cooinates I. Relation to Schwazschil cooinates One oiginally elates the Kuskal cooinates to the Schwazschil cooinates in the following way: u = /2m
Notes fo the stana cental, single mass metic in Kuskal cooinates I. Relation to Schwazschil cooinates One oiginally elates the Kuskal cooinates to the Schwazschil cooinates in the following way: u = /2m
A Comparative Analysis of Different MRAS Schemes for Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drives Employing PI and Fuzzy Controllers
 A Compaative Analysis of Diffeent MRAS Schemes fo Speed Sensoless Induction Moto Dives Employing PI and Fuzzy Contolles M.Ankaao 1, M.Vijaya Kuma 2, K.Tija 3 1 Ph.D. Reseach Schola, Depatment of Electical
A Compaative Analysis of Diffeent MRAS Schemes fo Speed Sensoless Induction Moto Dives Employing PI and Fuzzy Contolles M.Ankaao 1, M.Vijaya Kuma 2, K.Tija 3 1 Ph.D. Reseach Schola, Depatment of Electical
An Experimental Estimation of a Rotor Speed MRAS Based on ANN for Sensorless Control of IM
 An Expeiental Estiation of a Roto Speed MRAS Based on ANN fo Sensoless Contol of IM Kai Negadi Ibn Khaldoun Univesity, BP 78 iaet, Algeia, aboatoy of Autoatics and Systes Analysis (.A.A.S.), Depatent of
An Expeiental Estiation of a Roto Speed MRAS Based on ANN fo Sensoless Contol of IM Kai Negadi Ibn Khaldoun Univesity, BP 78 iaet, Algeia, aboatoy of Autoatics and Systes Analysis (.A.A.S.), Depatent of
Model Reference Adaptive System Sensorless Vector Control of an Induction Motor Using a Novel Fractional Order PI Controller Adaptation Mechanism
 215 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 3 Pint ISSN : 2395-199 Online ISSN : 2394-499 Themed Section: Engineeing and Technology Refeence Adaptive System Sensoless Vecto Contol of an Induction Moto Using a Novel Factional
215 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 3 Pint ISSN : 2395-199 Online ISSN : 2394-499 Themed Section: Engineeing and Technology Refeence Adaptive System Sensoless Vecto Contol of an Induction Moto Using a Novel Factional
Hidden Two-Step Phase Transition and Competing
 Suppoting Infomation fo Hien Two-Step Phase Tansition an Competing Reaction Pathways in LiFePO 4 Yukinoi Koyama, Takeshi Uyama, Yuki Oikasa, Takahio Naka, Hieyuki Komatsu, Keiji Shimoa, Hauno Muayama,
Suppoting Infomation fo Hien Two-Step Phase Tansition an Competing Reaction Pathways in LiFePO 4 Yukinoi Koyama, Takeshi Uyama, Yuki Oikasa, Takahio Naka, Hieyuki Komatsu, Keiji Shimoa, Hauno Muayama,
ON THE TWO-BODY PROBLEM IN QUANTUM MECHANICS
 ON THE TWO-BODY PROBLEM IN QUANTUM MECHANICS L. MICU Hoia Hulubei National Institute fo Physics and Nuclea Engineeing, P.O. Box MG-6, RO-0775 Buchaest-Maguele, Romania, E-mail: lmicu@theoy.nipne.o (Received
ON THE TWO-BODY PROBLEM IN QUANTUM MECHANICS L. MICU Hoia Hulubei National Institute fo Physics and Nuclea Engineeing, P.O. Box MG-6, RO-0775 Buchaest-Maguele, Romania, E-mail: lmicu@theoy.nipne.o (Received
Tutorial 5 Drive dynamics & control
 UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES Electic Dive Sytem School o Electical Engineeing & Telecommunication ELEC463 Electic Dive Sytem Tutoial 5 Dive dynamic & contol. The ollowing paamete ae known o two high peomance
UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES Electic Dive Sytem School o Electical Engineeing & Telecommunication ELEC463 Electic Dive Sytem Tutoial 5 Dive dynamic & contol. The ollowing paamete ae known o two high peomance
OPTIMISATION OF A DRIVE SYSTEM AND ITS EPICYCLIC GEAR SET
 OPTIISATION OF A DRIVE SYSTE AND ITS EPICYCLIC GEAR SET Nicolas Bellegade, Philippe Dessante, Piee Vidal, Jean-Claude Vannie To cite this vesion: Nicolas Bellegade, Philippe Dessante, Piee Vidal, Jean-Claude
OPTIISATION OF A DRIVE SYSTE AND ITS EPICYCLIC GEAR SET Nicolas Bellegade, Philippe Dessante, Piee Vidal, Jean-Claude Vannie To cite this vesion: Nicolas Bellegade, Philippe Dessante, Piee Vidal, Jean-Claude
Modified Euler integration based control of a five-phase induction motor drive
 MultiCaft Intenational Jounal of Engineeing, Science an echnology Vol., No. 6, 00, pp. 8-30 INERNAIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND ECHNOLOGY www.ijest-ng.com 00 MultiCaft Limite. All ights eseve
MultiCaft Intenational Jounal of Engineeing, Science an echnology Vol., No. 6, 00, pp. 8-30 INERNAIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND ECHNOLOGY www.ijest-ng.com 00 MultiCaft Limite. All ights eseve
Detuning Minimization of Induction Motor Drive System for Alternative Energy Vehicles
 Enegies 2015, 8, 9117-9136; doi:10.3390/en8099117 Aticle OPEN ACCESS enegies ISSN 1996-1073 www.mdpi.com/jounal/enegies Detuning Minimization of Induction Moto Dive System fo Altenative Enegy Vehicles
Enegies 2015, 8, 9117-9136; doi:10.3390/en8099117 Aticle OPEN ACCESS enegies ISSN 1996-1073 www.mdpi.com/jounal/enegies Detuning Minimization of Induction Moto Dive System fo Altenative Enegy Vehicles
That is, the acceleration of the electron is larger than the acceleration of the proton by the same factor the electron is lighter than the proton.
 PHY 8 Test Pactice Solutions Sping Q: [] A poton an an electon attact each othe electically so, when elease fom est, they will acceleate towa each othe. Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
PHY 8 Test Pactice Solutions Sping Q: [] A poton an an electon attact each othe electically so, when elease fom est, they will acceleate towa each othe. Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
A High Performance Rotor-Flux Oriented Indirect Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Fuzzy Logic Control
 A High Pefomance Roto-Flux Oiented Indiect Vecto Contolled Induction Moto Dive using Fuzzy ogic Contol Anjali.S 1, Radhika.R 2 M.Tech Student, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Kottayam, India 1 Asst.
A High Pefomance Roto-Flux Oiented Indiect Vecto Contolled Induction Moto Dive using Fuzzy ogic Contol Anjali.S 1, Radhika.R 2 M.Tech Student, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Kottayam, India 1 Asst.
State tracking control for Takagi-Sugeno models
 State tacing contol fo Taagi-Sugeno models Souad Bezzaoucha, Benoît Max,3,DidieMaquin,3 and José Ragot,3 Abstact This wo addesses the model efeence tacing contol poblem It aims to highlight the encouteed
State tacing contol fo Taagi-Sugeno models Souad Bezzaoucha, Benoît Max,3,DidieMaquin,3 and José Ragot,3 Abstact This wo addesses the model efeence tacing contol poblem It aims to highlight the encouteed
A DETAILED STUDY OF THE HIGH ORDER SERIAL RESONANT INVERTER FOR INDUCTION HEATING
 ELECTRONICS 005 1 3 Septembe, Sozopol, BULGARIA A DETAILED STUDY OF THE HIGH ORDER SERIAL RESONANT INVERTER FOR INDUCTION HEATING Evgeniy Ivanov Popov, Liliya Ivanova Pindeva, Elisaveta Histova Mileva,
ELECTRONICS 005 1 3 Septembe, Sozopol, BULGARIA A DETAILED STUDY OF THE HIGH ORDER SERIAL RESONANT INVERTER FOR INDUCTION HEATING Evgeniy Ivanov Popov, Liliya Ivanova Pindeva, Elisaveta Histova Mileva,
Uncertainty in Operational Modal Analysis of Hydraulic Turbine Components
 Intenational Jounal of Fluid Machiney and Systems Vol. 2, No. 4, Octobe-Decembe 2009 Oiginal Pape (Invited) Uncetainty in Opeational Modal Analysis of Hydaulic Tubine Components Matin Gagnon 1, S.-Antoine
Intenational Jounal of Fluid Machiney and Systems Vol. 2, No. 4, Octobe-Decembe 2009 Oiginal Pape (Invited) Uncetainty in Opeational Modal Analysis of Hydaulic Tubine Components Matin Gagnon 1, S.-Antoine
Much that has already been said about changes of variable relates to transformations between different coordinate systems.
 MULTIPLE INTEGRLS I P Calculus Cooinate Sstems Much that has alea been sai about changes of vaiable elates to tansfomations between iffeent cooinate sstems. The main cooinate sstems use in the solution
MULTIPLE INTEGRLS I P Calculus Cooinate Sstems Much that has alea been sai about changes of vaiable elates to tansfomations between iffeent cooinate sstems. The main cooinate sstems use in the solution
Antennas & Propagation
 Antennas & Popagation 1 Oveview of Lectue II -Wave Equation -Example -Antenna Radiation -Retaded potential THE KEY TO ANY OPERATING ANTENNA ot H = J +... Suppose: 1. Thee does exist an electic medium,
Antennas & Popagation 1 Oveview of Lectue II -Wave Equation -Example -Antenna Radiation -Retaded potential THE KEY TO ANY OPERATING ANTENNA ot H = J +... Suppose: 1. Thee does exist an electic medium,
Construction Monitoring of Cable-stayed Bridges Based on Gray Prediction Model
 Sen Oes fo Repints to epints@benthamscience.ae 736 The Open Civil Engineeing Jounal, 25, 9, 736-742 Open Access Constuction Monitoing of Cable-staye Biges Base on Gay Peiction Moel Wu Fangwen *, Ji Zhengi
Sen Oes fo Repints to epints@benthamscience.ae 736 The Open Civil Engineeing Jounal, 25, 9, 736-742 Open Access Constuction Monitoing of Cable-staye Biges Base on Gay Peiction Moel Wu Fangwen *, Ji Zhengi
Physics Courseware Physics II Electric Field and Force
 Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
CHAPTER 3 DIODES. NTUEE Electronics L. H. Lu 3-1
 CHAPER 3 OE Chapte Outline 3.1 he eal ioe 3.2 eminal Chaacteistics of Junction ioes 3.3 Moeling the ioe Fowa Chaacteistics 3.4 Opeation in the Reese Beakown Region ene ioes 3.5 Rectifie Cicuits 3.6 Limiting
CHAPER 3 OE Chapte Outline 3.1 he eal ioe 3.2 eminal Chaacteistics of Junction ioes 3.3 Moeling the ioe Fowa Chaacteistics 3.4 Opeation in the Reese Beakown Region ene ioes 3.5 Rectifie Cicuits 3.6 Limiting
15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA
 15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA In this Section we will examine some simple examples of MHD equilibium configuations. These will all be in cylinical geomety. They fom the basis fo moe the complicate equilibium
15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA In this Section we will examine some simple examples of MHD equilibium configuations. These will all be in cylinical geomety. They fom the basis fo moe the complicate equilibium
Chapter 5 Linear Equations: Basic Theory and Practice
 Chapte 5 inea Equations: Basic Theoy and actice In this chapte and the next, we ae inteested in the linea algebaic equation AX = b, (5-1) whee A is an m n matix, X is an n 1 vecto to be solved fo, and
Chapte 5 inea Equations: Basic Theoy and actice In this chapte and the next, we ae inteested in the linea algebaic equation AX = b, (5-1) whee A is an m n matix, X is an n 1 vecto to be solved fo, and
Description of TEAM Workshop Problem 33.b: Experimental Validation of Electric Local Force Formulations.
 1 Desciption of TEAM Wokshop Poblem 33.b: Expeimental Validation of Electic Local Foce Fomulations. Olivie Baé, Pascal Bochet, Membe, IEEE Abstact Unde extenal stesses, the esponse of any mateial is a
1 Desciption of TEAM Wokshop Poblem 33.b: Expeimental Validation of Electic Local Foce Fomulations. Olivie Baé, Pascal Bochet, Membe, IEEE Abstact Unde extenal stesses, the esponse of any mateial is a
HYBRID FDI ON CHEMICAL PLANTS. Ferreiro García, Ramón; Pardo Martínez, Xoán C. & Vidal Paz, José
 HYBRID FDI ON CHEMICL PLNTS Feeio Gacía, Ramón; Pado Matínez, Xoán C. & Vidal Paz, José Gupo de Enxeñeia de Sistemas e Contol utomático. Depatamento de Electónica e Sistemas. Univesidade da Couña. E.S.
HYBRID FDI ON CHEMICL PLNTS Feeio Gacía, Ramón; Pado Matínez, Xoán C. & Vidal Paz, José Gupo de Enxeñeia de Sistemas e Contol utomático. Depatamento de Electónica e Sistemas. Univesidade da Couña. E.S.
Independent Control of two PM motors using a single inverter: Application to Elevator Doors.
 Independent Contol of two PM motos using a single invete: Application to Elevato Doos. John Chiasson, Danbing Seto, Fanping Sun, Alex Stankovic and Scott Botoff Abstact This wok consides the contol of
Independent Contol of two PM motos using a single invete: Application to Elevato Doos. John Chiasson, Danbing Seto, Fanping Sun, Alex Stankovic and Scott Botoff Abstact This wok consides the contol of
A Generic Reentry Trajectory Planning Algorithm for Reusable Launch Vehicle Missions
 NSC Confeence Pape No.9 A Geneic Reenty ajectoy Planning Algoithm fo Reusable Launch ehicle Missions Ashok Joshi *, K. Sivan @ Inian Institute of echnology Bombay, Mumbai 7, Inia an B. N. Suesh $, S. Savithi
NSC Confeence Pape No.9 A Geneic Reenty ajectoy Planning Algoithm fo Reusable Launch ehicle Missions Ashok Joshi *, K. Sivan @ Inian Institute of echnology Bombay, Mumbai 7, Inia an B. N. Suesh $, S. Savithi
Implicit Constraint Enforcement for Rigid Body Dynamic Simulation
 Implicit Constaint Enfocement fo Rigid Body Dynamic Simulation Min Hong 1, Samuel Welch, John app, and Min-Hyung Choi 3 1 Division of Compute Science and Engineeing, Soonchunhyang Univesity, 646 Eupnae-i
Implicit Constaint Enfocement fo Rigid Body Dynamic Simulation Min Hong 1, Samuel Welch, John app, and Min-Hyung Choi 3 1 Division of Compute Science and Engineeing, Soonchunhyang Univesity, 646 Eupnae-i
Modelling and Power Factor Improvement of Switched Reluctance Motor Drive
 odelling and Powe Facto Impovement of Switched Reluctance oto Dive X. D. XUE, K. W. E. HENG, S.. HO and Y.P.B.YEUNG Depatment of Electical Engineeing The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univesity Hung Hom, Kowloon,
odelling and Powe Facto Impovement of Switched Reluctance oto Dive X. D. XUE, K. W. E. HENG, S.. HO and Y.P.B.YEUNG Depatment of Electical Engineeing The Hong Kong Polytechnic Univesity Hung Hom, Kowloon,
( )( )( ) ( ) + ( ) ( ) ( )
 3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
Integral Control via Bias Estimation
 1 Integal Contol via Bias stimation Consie the sstem ẋ = A + B +, R n, R p, R m = C +, R q whee is an nknown constant vecto. It is possible to view as a step istbance: (t) = 0 1(t). (If in fact (t) vaies
1 Integal Contol via Bias stimation Consie the sstem ẋ = A + B +, R n, R p, R m = C +, R q whee is an nknown constant vecto. It is possible to view as a step istbance: (t) = 0 1(t). (If in fact (t) vaies
CAPACITANCE REQUIRED ANALYSIS FOR SELF- EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATEUR
 3 th Septembe 3. Vol. 55 No.3 5-3 JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.o E-ISSN: 87-395 CAPACITANCE REQUIRED ANALYSIS FOR SELF- ECITED INDUCTION ENERATEUR A. ABBOU,. BARARA, A. OUCHATTI,.
3 th Septembe 3. Vol. 55 No.3 5-3 JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.o E-ISSN: 87-395 CAPACITANCE REQUIRED ANALYSIS FOR SELF- ECITED INDUCTION ENERATEUR A. ABBOU,. BARARA, A. OUCHATTI,.
Electric Power Systems Research
 Electic Powe Systems Reseach 89 (2012) 11 22 Contents lists available at SciVese ScienceDiect Electic Powe Systems Reseach jou n al h om epage: www.elsevie.com/locate/eps Diect field oiented contol of
Electic Powe Systems Reseach 89 (2012) 11 22 Contents lists available at SciVese ScienceDiect Electic Powe Systems Reseach jou n al h om epage: www.elsevie.com/locate/eps Diect field oiented contol of
[2007] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from [Jiaxin Chen, Jianguo Zhu, Youguang Guo, A 2-D nonlinear FEA tool embedded in Matlab/Simulink
![[2007] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from [Jiaxin Chen, Jianguo Zhu, Youguang Guo, A 2-D nonlinear FEA tool embedded in Matlab/Simulink [2007] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from [Jiaxin Chen, Jianguo Zhu, Youguang Guo, A 2-D nonlinear FEA tool embedded in Matlab/Simulink](/thumbs/86/93644244.jpg) [2007] IEEE. Repinted, with pemission, fom [Jiaxin Chen, Jianguo Zhu, Youguang Guo, A 2-D nonlinea FEA tool embedded in Matlab/Simulin suounding fo application of electomagnetic field analysis in powe
[2007] IEEE. Repinted, with pemission, fom [Jiaxin Chen, Jianguo Zhu, Youguang Guo, A 2-D nonlinea FEA tool embedded in Matlab/Simulin suounding fo application of electomagnetic field analysis in powe
THE HERMITE POLYNOMIAL & QUANTIZATION OF THE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR
 THE HERMITE POLYNOMIAL & QUANTIZATION OF THE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR TIMOTHY JONES Abstact. The hamonic oscillato possesses a singula place in quantum mechanics. It is use in a wie vaiety of moels. Hee we
THE HERMITE POLYNOMIAL & QUANTIZATION OF THE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR TIMOTHY JONES Abstact. The hamonic oscillato possesses a singula place in quantum mechanics. It is use in a wie vaiety of moels. Hee we
Power efficiency and optimum load formulas on RF rectifiers featuring flow-angle equations
 LETTE IEICE Electonics Expess, Vol.10, No.11, 1 9 Powe efficiency and optimum load fomulas on F ectifies featuing flow-angle equations Takashi Ohia a) Toyohashi Univesity of Technology, 1 1 Hibaigaoka,
LETTE IEICE Electonics Expess, Vol.10, No.11, 1 9 Powe efficiency and optimum load fomulas on F ectifies featuing flow-angle equations Takashi Ohia a) Toyohashi Univesity of Technology, 1 1 Hibaigaoka,
The Impact of Power Structures on Supply Chain Enterprises with Carbon Emission Reduction Decisions
 Intenational Jounal of Business an Manageent; Vol., No. 8; 08 ISSN 8-850 E-ISSN 8-89 Publishe by Canaian Cente of Science an Eucation The Ipact of Powe Stuctues on Supply Chain Entepises with Cabon Eission
Intenational Jounal of Business an Manageent; Vol., No. 8; 08 ISSN 8-850 E-ISSN 8-89 Publishe by Canaian Cente of Science an Eucation The Ipact of Powe Stuctues on Supply Chain Entepises with Cabon Eission
Finite Element Computational Model for Defect Simulation and Detection by Eddy Currents Non Destructive Testing
 Finite Element Computational Model fo Defect Simulation and Detection by Eddy Cuents Non Destuctive Testing M. RACHEK, M. ZAOUA, H. DENOUN, C. BROUCHE Faculté de Génie Electique et de l nfomatique. Dépatement
Finite Element Computational Model fo Defect Simulation and Detection by Eddy Cuents Non Destuctive Testing M. RACHEK, M. ZAOUA, H. DENOUN, C. BROUCHE Faculté de Génie Electique et de l nfomatique. Dépatement
Stability of a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Allee Effect
 Nonlinea Analsis an Diffeential Equations, Vol. 4, 6, no. 5, 5-33 HIKARI Lt, www.m-hikai.com http://.oi.og/.988/nae.6.633 Stabilit of a Discete-Time Peato-Pe Sstem with Allee Effect Ming Zhao an Yunfei
Nonlinea Analsis an Diffeential Equations, Vol. 4, 6, no. 5, 5-33 HIKARI Lt, www.m-hikai.com http://.oi.og/.988/nae.6.633 Stabilit of a Discete-Time Peato-Pe Sstem with Allee Effect Ming Zhao an Yunfei
LC transfer of energy between the driving source and the circuit will be a maximum.
 The Q of oscillatos efeences: L.. Fotney Pinciples of Electonics: Analog and Digital, Hacout Bace Jovanovich 987, Chapte (AC Cicuits) H. J. Pain The Physics of Vibations and Waves, 5 th edition, Wiley
The Q of oscillatos efeences: L.. Fotney Pinciples of Electonics: Analog and Digital, Hacout Bace Jovanovich 987, Chapte (AC Cicuits) H. J. Pain The Physics of Vibations and Waves, 5 th edition, Wiley
A NEW VARIABLE STIFFNESS SPRING USING A PRESTRESSED MECHANISM
 Poceedings of the ASME 2010 Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences & Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE 2010 August 15-18, 2010, Monteal, Quebec, Canada DETC2010-28496
Poceedings of the ASME 2010 Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences & Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE 2010 August 15-18, 2010, Monteal, Quebec, Canada DETC2010-28496
Quaternion Based Inverse Kinematics for Industrial Robot Manipulators with Euler Wrist
 Quatenion Based Invese Kinematics fo Industial Robot Manipulatos with Eule Wist Yavuz Aydın Electonics and Compute Education Kocaeli Univesity Umuttepe Kocaeli Tukey yavuz_98@hotmailcom Seda Kucuk Electonics
Quatenion Based Invese Kinematics fo Industial Robot Manipulatos with Eule Wist Yavuz Aydın Electonics and Compute Education Kocaeli Univesity Umuttepe Kocaeli Tukey yavuz_98@hotmailcom Seda Kucuk Electonics
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 2013](/thumbs/89/100795062.jpg) A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
A note on the electostatic enegy of two point chages axiv:1306.0401v1 [physics.pop-ph] 3 Jun 013 A C Tot Instituto de Física Univesidade Fedeal do io de Janeio Caixa Postal 68.58; CEP 1941-97 io de Janeio,
Terminal Sliding Control for a SCARA Robot
 Intenational Confeence on Contol, Instumentation and Mechatonics Engineeing (CIM '7), Joho Bahu, Joho, Malaysia, May 8-9, 7 Teminal Sliding Contol fo a SCARA Robot E. Muñoz, C. Gaviia, A. Vivas Depatment
Intenational Confeence on Contol, Instumentation and Mechatonics Engineeing (CIM '7), Joho Bahu, Joho, Malaysia, May 8-9, 7 Teminal Sliding Contol fo a SCARA Robot E. Muñoz, C. Gaviia, A. Vivas Depatment
Induction Motor Identification Using Elman Neural Network
 Poceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int Conf on Signal Pocessing, Robotics and Autoation, Madid, Spain, Febuay 15-17, 2006 (pp153-157) Induction Moto Identification Using Elan Neual Netwok AA AKBARI 1, K RAHBAR
Poceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int Conf on Signal Pocessing, Robotics and Autoation, Madid, Spain, Febuay 15-17, 2006 (pp153-157) Induction Moto Identification Using Elan Neual Netwok AA AKBARI 1, K RAHBAR
A scaling-up methodology for co-rotating twin-screw extruders
 A scaling-up methodology fo co-otating twin-scew extudes A. Gaspa-Cunha, J. A. Covas Institute fo Polymes and Composites/I3N, Univesity of Minho, Guimaães 4800-058, Potugal Abstact. Scaling-up of co-otating
A scaling-up methodology fo co-otating twin-scew extudes A. Gaspa-Cunha, J. A. Covas Institute fo Polymes and Composites/I3N, Univesity of Minho, Guimaães 4800-058, Potugal Abstact. Scaling-up of co-otating
