Unit 5 Electricity and Magnetism
|
|
|
- Isabella Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism Overview In this unit, students explore the properties, quantities, principles, and laws of electricit, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic induction. The carr out experiments or simulations, and build a prototpe device, to demonstrate properties of magnetic fields and electromagnetic induction. Also, the identif and describe examples of domestic and industrial technologies that are applications of magnetic fields. The curriculum emphasis in this unit is technolog. This includes the design of a prototpe device that applies the principles of electromagnetism (expectation EM2.04), a description of technological sstems (expectation EM3.01), and a description of the historical development of technologies (expectation EM3.02). Chapter 12, Electricit, presents electrostatics and current electricit. Some components of this chapter are a review of the content of the electricit unit in grade 9 science. Chapter 13, Electromagnetism, explores the magnetic effects and applications of electric current. Chapter 14, Electromagnetic Induction, presents the complement of the concepts in Chapter 13, namel the induction of electric current using magnetism, and the applications of this electromagnetic induction. CONTENT SUGGESTIONS General Comments The following facts will help in planning the content of Unit 5: Individual sections do not alwas fit into one class period; some need less time, and some need more time. The ke expectations are often covered in more than one wa or in more than one section. Thus, choices can be made to save time or to adapt to the prior knowledge and skills of the students. The are meant for student practice, not for assessment. Some students ma reduce the time the spend on those questions b doing rough solutions rather than formal solutions for evaluation or assessment. (The Section Questions are meant for assessment.) As ou will notice in the Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills, students in Ontario have been exposed to the topics of electrostatics, current electricit, magnetism, and electromagnetism a lot in previous grades. Thus, it is a good idea to determine what knowledge and skills the students bring with them to class, and build on them. The Unit 5 Performance Task (pages 540 1) can be used to cover several of the specific expectations, including EM2.04, EM3.01, and EM3.02. To comfortabl complete all parts of all sections of Unit 5 will take approximatel 30 class periods. Thus, choices must be made to cover the curriculum emphases while giving the students a positive experience in the time available. TEACHING SUGGESTIONS Discuss the introductor photograph and the feature on Dr. Mehrdad on page 419 of the text. Discuss with the students the expectations for the unit and the assessment rubrics (found in this manual). Have our students work on the Are You Read? diagnostic assignment on pages SPECIFIC SUGGESTIONS The suggestions in Table 1 are based on these assumptions: Class periods are 70 to 75 min long. Five units are to be covered in a little more than 100 periods, so on average each unit should be completed within about 20 periods, including assessment and evaluation Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 295
2 Table 1 Unit 5 Planning Pathwa Topic Period Content Comments, Including Time-Saving Strategies Ch Intro; 12.1 Discuss some of the questions on pages orall. Discuss the introduction to section 12.1 briefl. Do Investigation , the Tr This Activit, and Activit as class demonstrations to review what the students learned about electrostatics in grade 9 science. Assign the Section 12.1 Questions for homework ; 12.3 The concepts in section 12.2 are introduced to help students understand magnetic fields later in the unit; however, electric fields and Coulomb s law are optional, so if time is limited the can be treated briefl or omitted. Section 12.3 should be emphasized in this period ; 12.5 Electric potential is a compulsor component of the course, so emphasize section Electric circuits and Kirchhoff s laws are optional, so section 12.5 can be treated as a brief review of electric circuits studied in grade 9 science ; 12.7 Although Ohm s law is not a written requirement in the course expectations, it is needed for the mathematical analsis of other topics, including power and the use of transformers. Thus, a brief review of the topic in section 12.6 is recommended. In section 12.7, emphasize the equation related to power. If time is limited, ou can omit the topic on the cost of electricit, pages Review Quiz Since much of Chapter 12 is a review of the grade 9 unit on electricit, the tpical chapter review and test can be replaced with a student-controlled review and self-test. Students can use the Chapter 12 Summar (page 467) and Review (pages 468 9) to complete Chapter 12. Ch Intro; 13.1 Students have not studied magnetism in the science curriculum since grade 3, so the will benefit greatl from activities and demonstrations involving magnetic forces and fields. To ensure ample time for the Tr This Activit on page 471 and Activit on page 473, some questions can be assigned for homework This section can be completed fairl easil in one class period. If ou haven t alread done so, now would be a good time to introduce the Unit 5 Performance Task, pages 540 1, so students who will be doing it can begin thinking about what the will do ; 13.4 start Since section 13.4 is relativel long and is related to section 13.3, it is a good idea to begin 13.4 in this period. Plan on getting to the end of page 483 or finish Complete the parts of section 13.4 not done in the previous period. 296 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
3 Topic Period Content Comments, Including Time-Saving Strategies ; 13.6 start Section 13.5 can easil be done in a single period, but if ou intend to have the students build an electric motor (in Activit ), ou should begin section 13.6 in this period. To save time, Investigation could be done as a class demonstration finish If ou intend to have students work on the Unit 5 Performance Task, then the construction of a simple DC motor (Activit ) is not mandator. However, an student not doing the Performance Task should consider building the motor or another device that operates on the principles of electromagnetism. (See expectation EM2.04.) The Case Stud on pages can be done fairl quickl, but the Explore an Issue feature on page 501 will require extra time for researching and reporting on the issue. 12 Review Some items on pages can be assigned as compulsor and some as optional, and some can be discussed orall. 13 Test After the test, students can begin working on Chapter 14. Ch Intro; 14.1 start The Chapter 14 introduction leads directl to section Plan on completing to the end of Investigation (pages 508 9) in this period. Complete section 14.1, and do section To save time, Activit could be done as a class demonstration finish; See the Teaching Suggestions for section 14.3 for ideas on demonstrations and activities to engage the students in this topic The planning of this section is straightforward ; Career Section 14.5 can be combined with the Career feature on page Review Some items on pages can be assigned as compulsor and some Test as optional, and some can be discussed orall. Review 20 Unit Review Make a list of questions on pages that ou recommend students work on for their review of Unit 5. Test 21 Unit Test After the Unit 5 test, students can begin working on a review for the final examination Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 297
4 Curriculum and Assessment Map for Unit 5 Overall Expectations EMV.01 demonstrate an understanding of the properties, phsical quantities, principles, and laws related to electricit, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic induction EMV.02 carr out experiments or simulations, and construct a prototpe device, to demonstrate characteristic properties of magnetic fields and electromagnetic induction EMV.03 identif and describe examples of domestic and industrial technologies that were developed on the basis of the scientific understanding of magnetic fields Section Overall Expectations Electrostatics Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) q. 1 6 Section 12.1 Questions q. 1 7 Section 12.1 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 8 9 Investigation Analsis a f, Evaluation g h Communication Activit Tr This Activit Section 12.1 Questions Making, q Reflecting, q. 13 Making Section 12.1 Questions Making, q Assessment Tools 298 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
5 Section 12.2 Electric Fields and Electric Charge 12.3 Electric Current 12.4 Electric Potential Difference Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Communication Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) q. 1 2 Section 12.2 Questions q. 1 7 Section 12.2 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q Lab Exercise Analsis, a b Section 12.2 Questions Reflecting, q. 11 Making Lab Exercise Analsis, b Inquir Communication Making q. 1 5 Section 12.3 Questions q. 1 6, EM1.08 Section 12.3 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 10 Section 12.3 Questions q. 7 9 Reflecting, q. 12, EM 1.02 Section 12.3 Questions Making, q. 11, EM 1.02 q. 1 6 Section 12.4 Questions q. 1 6 Assessment Tools 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 299
6 Section 12.5 Kirchhoff s Laws for Electric Circuits 12.6 Electric Resistance Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Communication Making Inquir Communication Making Inquir Communication Making Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) Section 12.4 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q Section 12.4 Questions q. 7 Section 12.4 Questions q q. 1 Section 12.5 Questions q. 1 6 Section 12.5 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 7 Activit Analsis, a b Section 12.5 Questions Reflecting, q. 10 Section 12.5 Questions Making, q. 8 9 q Section 12.6 Questions q. 1 7 Section 12.6 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q Section 12.6 Questions Making, q. 12 Section 12.6 Questions Making, q. 11 Assessment Tools 300 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
7 Section 12.7 Power in Electric Circuits 13.1 Magnetic Force and Fields 13.2 Magnetic Materials Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Communication Making Inquir Communication Making Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) q. 1 8 Section 12.7 Questions q Section 12.7 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 11 Section 12.7 Questions Making, q. 13 Section 12.7 Questions Making, q. 12, 14 q. 1 2, EM1.03 Section 13.1 Questions q. 1 3, EM1.03 Appling Inquir Skills, q. 3 6, EM2.01 Activit Observations, a d, EM1.03, EM2.01 Section 13.1 Questions Reflecting, q. 6, EM1.03 Section 13.1 Questions Making, q. 5 EM1.03 q. 1 6, EM1.03 Section 13.2 Questions q. 1 2, EM1.03 Assessment Tools 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 301
8 Section 13.3 Oersted s Discover 13.4 The Magnetic Field of a Coil or Solenoid Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Communication Making Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) Section 13.2 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 4 EM1.03 Tr This Activitq. a b EM1.03 Section 13.2 Questions q. 3 EM1.03 Section 13.2 Questions Making, q. 5 EM1.03 q. 1 3 EM1.04, EM1.05 Section 13.3 Questions q. 1 3 EM1.04, EM1.05 Inquir Activit Observations, a b EM1.04, EM1.05, EM2.02 Communication Section 13.3 Questions Reflecting, q. 4 EMV.03 Making Activit Observations, c EM1.04, EM1.05, EM2.02 q. 1 6 EM1.04, EM1.05 Section 13.4 Questions q. 1 8 EM1.04, EM1.05 Inquir Activit Observations, a d EM1.04, EM1.05, EM2.02 Tr This Activit EM1.04, EM1.05, EM2.02 Communication Section 13.4 Questions Making, q. 10 EM1.04, EM1.05 Making Making, q. 7 EM1.04, EM1.05 Section 13.4 Questions Making, q. 9 EM1.04, EM1.05 Assessment Tools 302 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
9 Section 13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic Field The Motor Principle 13.6 Applications of the Motor Principle 14.1 Farada s Discover Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Communication Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) Section 13.5 Questions q. 1 2 EM1.04, EM1.05, EM1.06 Section 13.5 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 3 4 EM1.04, EM1.05, EM1.06 Investigation Analsis, a e, Evaluation, f EM1.04, EM1.05, EM1.06 Section 13.5 Questions Reflecting, q. 5 EM1.06 Making Investigation Evaluation, g EM1.06 Inquir Communication Making q. 1 7 EM1.06 Section 13.6 Questions q. 1 6 EM1.06 Section 13.6 Questions Appling Inquir Skills, q. 7 8 EM1.06 Activit Analsis, a b EM1.06, EM2.04, EM3.01 Section 13.6 Questions Reflecting, q. 10 EM1.06 Explore an Issue EM3.01 Section 13.6 Questions Making, q. 9 EM1.06 q. 1 EM1.07 Section 14.1 Questions q. 1 6 EM1.07 Inquir Investigation Analsis, c d, f h EM1.07, EM2.03 Assessment Tools 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 303
10 Section 14.2 Direction of Induced Current 14.3 Electric Generators: AC and DC 14.4 The Transformer Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) Communication Investigation Evaluation, i EM1.07, EM2.03 Making Investigation Analsis, e EM1.07, EM2.03 q. 1 2 EM1.07, EM3.01, EM3.02 Section 14.2 Questions q. 1 4 EM1.07 Inquir Activit Analsis, a EM1.07, EM2.03 Communication Activit Analsis, b EM1.07, EM2.03 Making Making, q. 3 EM1.07, EM3.01, EM3.02 Inquir Making Section 14.3 Questions q. 1 4 EM1.07, EM1.08, EM3.01, EM3.02 Tr This Activit EM1.07, EM1.08 Section 14.3 Questions Making, q. 5 EM1.07, EM1.08 q. 1 5 EM1.09, EM3.01, EM 3.02 Section 14.4 Questions q. 1 6 EM1.09, EM3.01, EM 3.02 Inquir Investigation Analsis, b f, Evaluation, g h EM1.09, EM3.01, EM 3.02 Communication Section 14.4 Questions Making, q. 7c EM1.09, EM3.01, EM 3.02 Making Section 14.4 Questions Making, q. 7 EM1.09, EM3.01, EM 3.02 Assessment Tools 304 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
11 Section 14.5 Distribution of Electrical Energ Overall Expectations Achievement Chart Categories Inquir Communication Making Assessment/Evaluation Opportunities (Evidence) q. 1 3 EM1.08, EM1.09, EM3.01, EM3.02 Section 14.5 Questions q. 1 6 EM1.08, EM1.09, EM3.01, EM3.02 Explore an Issue SIS.04 Explore an Issue EM3.01, EM3.02 Career activit Making, q. 1 SIS.12 Explore an Issue Section 14.5 Questions Making, q EM1.08, EM1.09, EM3.01, EM3.02 Assessment Tools Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills The following are samples of specific expectations from Ontario s grades 7 to 9 curriculum that relate to Unit 5. (See the Ontario Guidelines for full details.) Grade 7 Heat compare the motion of particles in a solid, a liquid, and a gas using the particle theor Grade 9 The Characteristics of Electricit describe the properties of static electric charges, and explain electrostatic attraction and repulsion using scientific models of atomic structure describe charging b contact and b induction compare qualitativel static electricit and electric current describe the concepts of electric current, potential difference, and resistance, with the help of a water analog explain how electric current, potential difference, and electrical resistance are measured using an ammeter and a voltmeter state the SI units of potential difference, electric current, electrical resistance, electrical energ, and power describe the relationship among electrical resistance, potential difference, and current; solve simple problems involving the quantities describe the potential difference and current characteristics in a series and a parallel circuit compare the electrical resistance of a series and parallel connection of identical resistors to that of a single resistor determine quantitativel the percent efficienc of an electrical device that converts electrical energ to other forms of energ 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 305
12 describe the relationship among electrical energ transformed, power, and elapsed time, and solve simple problems involving these phsical quantities compare methods of producing electrical energ, including their advantages and disadvantages demonstrate knowledge of electrical safet procedures when planning and carring out an inquir and choosing and using materials, tools, and equipment demonstrate the skills required to plan and conduct an inquir into electricit, using instruments, tools, and apparatus safel, accuratel, and effectivel design, draw, and construct series and parallel circuits for a given purpose, and measure current, potential difference, and resistance at various points in the circuit, using appropriate instruments and SI units charge an electroscope b contact and b induction predict, verif, and explain the effect of a nearb charged object on a charged electroscope use appropriate instruments and techniques to investigate potential difference against current for an ohmic resistor in a simple series circuit, graph the data, and determine resistance from the slope of the graph Ke Inquir and Communication Skills As students begin this unit, the should Be familiar with the meanings, use, and conversion of metric prefixes; for a review, refer to Appendix C, page 576, in the text. Be aware of how to perform a controlled experiment involving three variables (see Investigation ); for suggestions, see Appendix A1, page Be able to write lab reports; for suggestions, refer to Appendix A4, pages Be able to appl decision making to issues related to the topics of electricit and electromagnetism; for reference, see Appendix A2, pages Be proficient in appling math skills such as writing numbers in scientific notation, rounding off answers to the correct number of significant digits, appling equations to solve problems, using dimensional analsis, and drawing and interpreting graphs; see Appendix A5, pages Be able to use a variet of resources, including the Internet, to research topics related to electricit and electromagnetism. Ke Technical and Safet Skills As students begin this unit, the should Displa wise safet practices when participating in an lab activit; refer to Appendixes B1 and B2 on pages Be able to use mechanical and electrical equipment such as a connecting wires, clips, voltmeters, ammeters, power supplies, magnets, magnetic compasses, electroscopes, and solenoids. Making As students progress through this unit, the should Be capable of recognizing and/or explaining the connections between the science principles presented and the applications to technolog, societ, and the environment. 306 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
13 Unit 5 Investigation/Activit/Lab Exercise/Tr This Activit Chart and Skills Menu Summar Chapter 12 Investigations, Activities, Lab Exercises, Tr This Activities Title Purpose Question Prediction/ Hpothesis Tr This Activit: to test students Safet and awareness and Electricit knowledge of electrical safet Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces Tr This Activit: Charging b Contact Activit Charging b Induction Lab Exercise : Investigating Data from Millikan s Oil Drop Experiment Activit : Cells in Series and in Parallel to investigate the laws of electric charge and appl the Bohr- Rutherford model of the atom to investigate how to charge a neutral object b contact to investigate how to charge an object b induction to investigate data similar to values measured b Millikan and look for patterns to investigate Kirchoff s voltage law Completed b Student Design Materials Procedure Evidence Analsis Evaluation Snthesis
14 Chapter 13 Title Purpose Question Prediction/ Hpothesis Tr This Activit: to use a bar Making a Magnet magnet to magnetize a steel paper clip Activit : Magnetic Fields Tr This Activit: Magnetic Induction Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet to investigate the properties of magnetic fields around bar magnets to investigate the properties of magnetic induction and soft and hard iron to investigate the characteristics of the magnetic field around a straight conductor to investigate the characteristics of the magnetic field around a coil to investigate the factors that can affect the strength of an electromagnet Design Materials Procedure Evidence Analsis Evaluation Snthesis
15 Title Purpose Question Prediction/ Design Materials Procedure Evidence Analsis Evaluation Snthesis Hpothesis Investigation : The Motor Principle to investigate the conditions that cause a currentcarring conductor to experience a force Activit Constructing a Simple DC Motor to construct, test, and refine a simple DC motor Chapter 14 Title Purpose Question Prediction/ Hpothesis Tr This Activit: A Demonstration of Electromagnetic Induction to investigate and note several instances of electromagnetic induction Design Materials Procedure Evidence Analsis Evaluation Snthesis Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor Tr This Activit: Farada s Iron Ring to investigate how to produce a current in a coil using a bar magnet and the factors that determine the magnitude of the induced current to investigate the conditions that produce an induced current in the secondar coil of Farada s iron ring
16 Title Purpose Question Prediction/ Hpothesis Activit : to investigate the The Direction of direction of the Induced Current induced current in a coiled conductor Tr This Activit: AC Generator Demonstration Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration) Tr This Activit: Demonstration of Edd Currents to investigate the connection between Lenz s law and the induced current from generators to investigate the relationship between the input and output voltages and the number of windings in the primar and secondar coils to investigate induced edd currents and the effect on a falling magnet Design Materials Procedure Evidence Analsis Evaluation Snthesis Performance Task Title Purpose Question Prediction/ Hpothesis Technolog Trade to allow students Show to design, create, test, and present a technological device Design Materials Procedure Evidence Analsis Evaluation Snthesis
17 Materials List for Unit 5 Students need the following items to perform the investigations, activities, lab exercises, and Tr This activities in Unit 5. The number of items required is based on a class of 30 students working in pairs. Unless stated otherwise, 15 items are required. An following the number means 15 times that number (i.e., 3 means 45 of that particular item). Where the term item is inappropriate, such as for a piece of tubing or masking tape, the teacher must look at the individual activit or investigation to obtain appropriate quantities. Activit or Investigation Text Page Materials Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12) ebonite rods or polethlene strips and fur insulated rod hanger glass rods or acetate strips and silk pith ball suspended on thread small bits of paper sawdus iron filings Tr This Activit: Charging b Contact (Chapter 12) Activit : Charging b Induction (Chapter 12) Activit : Cells in Series and in Parallel (Chapter 12) Tr This Activit: Making a Magnet (Chapter 13) Activit : Magnetic Fields (Chapter 13) Tr This Activit: Magnetic Induction (Chapter 13) Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13) Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13) 428 ebonite rods and fur glass rods and silk pith ball or leaf electroscope 429 ebonite rod and fur (or glass rod and silk) two metal rods two glass beakers pith ball or leaf electroscope 448 voltmeter two or three cells that have the same voltage connecting wires (4) load (for example, a 25-Ω resistor) 471 steel paper clips compass bar magnet 473 two bar magnets iron filings sheet of acetate (or paper) small compass 476 permanent magnet iron nail several metal washers cm of bare 12-gauge copper wire piece of stiff cardboard, 15 cm 15 cm batter (6 V 12 V) or DC power suppl iron filings connecting wires with alligator clips four compasses cm of bare 12-gauge copper wire wooden dowel (about 15 cm long 4 cm diameter) stiff cardboard and scissors batter (6 V 12 V) or DC power suppl connecting wires with alligator clips iron filings 2 compasses 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 311
18 Activit or Investigation Text Page Materials Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13) cm of bare 12-gauge copper wire wooden dowel (about 15 cm long 4 cm diameter) different substances (clinders) to be placed in core batter (6 V 12 V) or DC power suppl connecting wires with alligator clips metal washers or metal paper clips Investigation : The Motor Principle (Chapter 13) Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13) Tr This Activit: A Demonstration of Electromagnetic Induction (Chapter 14) Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14) Tr This Activit: Farada s Iron Ring (Chapter 14) Activit : The Direction of Induced Current (Chapter 14) Tr This Activit: AC Generator Demonstration (Chapter 14) Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration) (Chapter 14) Tr This Activit: Demonstration of Edd Currents (Chapter 14) insulated wire (fine) retort stand, clamp, and metre stick 5-cm length of bare 12-gauge copper wire pair of bar magnets 6-V batter or DC power suppl insulated wire tape pencil pin 2 common iron nails (about 7 cm long) 6-V batter, or DC power suppl block of wood cardboard 507 soft iron core coil bar magnet galvanometer or milliammeter connecting wires galvanometer or ammeter horseshoe magnet coil with a hollow core pair of bar magnets two similar solenoids of 300 and 600 turns 510 Farada s iron ring apparatus DC power suppl (batter) galvanometer or ammeter coiled conductor galvanometer or ammeter magnet connecting wires 520 generator (hand crank) connecting wires (if needed) small light bulb lab transformer set (iron core and several coils with different numbers of turns) variac (AC variable voltage power source) two AC multi-range voltmeters 6-V or 12-V batter DC voltmeter nichrome wire or long finishing nail water hollow dish-shaped ring of metal with wooden handle 526 long copper tube two similar clindrical pieces of metal (strong magnet, unmagnetized) 312 Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
19 Materials Activit or Investigation batter (6 V or 12 V) or DC power suppl Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13), text page 480; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484; Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13), text page 488; Investigation : The Motor Principle (Chapter 13), text pages 492 3; Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages 498 9; Tr This Activit: Farada s Iron Ring (Chapter 14), text page 510; Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration) (Chapter 14), text pages cardboard, stiff (and scissors) Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13), text page 480; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484; Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages cells, two or three that have the same voltage Activit : Cells in Series and in Parallel (Chapter 12), text page 448 coil (with a hollow core) Tr This Activit: A Demonstration of Electromagnetic Induction (Chapter 14), text page 507; Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14), text pages coiled conductor Activit : The Direction of Induced Current (Chapter 14), text pages compass Tr This Activit: Making a Magnet (Chapter 13), text page 471; Activit : Magnetic Fields (Chapter 13) text 473; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13), text page 480; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484 connecting wires (with alligator clips) Activit : Cells in Series and in Parallel (Chapter 12), text page 448; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13), text page 480; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484; Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13), text page 488; Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14), text pages 508 9; Activit : The Direction of Induced Current (Chapter 14), text pages 513 4; Tr This Activit: AC Generator Demonstration (Chapter 14), text page Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 313
20 Materials copper tube copper wire, bare 12-gauge different substances (clinders) to be placed in core dowel, wooden (15 cm long 4 cm diameter) ebonite rods or polethlene strips and fur Farada s iron ring apparatus galvanometer or milliammeter generator (hand crank) and small light bulb glass beakers glass rods or acetate strips and silk insulated rod hanger insulated wire (fine) iron core, soft Activit or Investigation Tr This Activit: Demonstration of Edd Currents (Chapter 14), text page 526 Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13), text page 480; Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484; Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13), text page 488; Investigation : The Motor Principle (Chapter 13), text pages Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13), text page 488 Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484; Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13), text page 488 Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages 425 6; Tr This Activit: Charging b Contact (Chapter 12), text page 428; Activit : Charging b Induction (Chapter 12), text page 429 Tr This Activit: Farada s Iron Ring (Chapter 14), text page 510 Tr This Activit: A Demonstration of Electromagnetic Induction (Chapter 14), text page 507; Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14), text pages (or ammeter); Tr This Activit: Farada s Iron Ring (Chapter 14), text page 510 (or ammeter); Activit : The Direction of Induced Current (Chapter 14), text pages (or ammeter), Tr This Activit: AC Generator Demonstration (Chapter 14), text page 520 Activit : Charging b Induction (Chapter 12), text page 429 Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages 425 6; Tr This Activit: Charging b Contact (Chapter 12), text page 428 Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages Investigation : The Motor Principle (Chapter 13), text pages 492 3; Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages Tr This Activit: A Demonstration of Electromagnetic Induction (Chapter 14), text page Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
21 Materials Activit or Investigation iron filings or nails Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages (filings); Activit : Magnetic Fields (Chapter 13) text 473 (filings); Tr This Activit: Magnetic Induction (Chapter 13), text page 476 (nail); Activit : Magnetic Field of a Straight Conductor (Chapter 13), text page 480 (filings); Activit : Magnetic Field of a Coil (Chapter 13), text page 484 (filings); Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages (nail) lab transformer set (iron core and several coils with Investigation : Transformers (Teacher different numbers of turns) Demonstration) (Chapter 14), text pages light bulb Tr This Activit: AC Generator Demonstration (Chapter 14), text page 520 load (for example, a 25-Ω resistor) Activit : Cells in Series and in Parallel (Chapter 12), text page 448 magnet, bar Tr This Activit: Making a Magnet (Chapter 13), text page 471; Activit : Magnetic Fields (Chapter 13) text 473; Investigation : The Motor Principle (Chapter 13), text pages 492 3; Tr This Activit: A Demonstration of Electromagnetic Induction (Chapter 14), text page 507; Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14), text pages 508 9; Activit : The Direction of Induced Current (Chapter 14), text pages magnet, horseshoe Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14), text pages magnet, permanent Tr This Activit: Magnetic Induction (Chapter 13), text page 476; Tr This Activit: Demonstration of Edd Currents (Chapter 14), text page 526 metal rods Activit : Charging b Induction (Chapter 12), text page 429 metal washers or metal paper clips Tr This Activit: Magnetic Induction (Chapter 13), text page 476; Tr This Activit: Testing an Electromagnet (Chapter 13), text page 488 nichrome wire or long finishing nail Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration) (Chapter 14), text pages paper, small bits of, or sheet Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages 425 6; Activit : Magnetic Fields (Chapter 13) text Nelson Thomson Learning Unit 5 Electricit and Magnetism 315
22 Materials Activit or Investigation pencil Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages pin Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages pith ball (suspended on thread), or leaf electroscope Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages 425 6; Tr This Activit: Charging B Contact (Chapter 12), text page 428; Activit : Charging b Induction (Chapter 12), text page 429 utilit stand, clamp, and metre stick Investigation : The Motor Principle (Chapter 13), text pages ring of metal, hollow dish-shaped with a wooden Investigation : Transformers (Teacher handle Demonstration (Chapter 14), text pages sawdust Investigation : Electric Charges and Forces (Chapter 12), text pages solenoids Investigation : Inducing Current in a Coiled Conductor (Chapter 14), text pages steel paper clips Tr This Activit: Making a Magnet (Chapter 13), text page 471 tape Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages variac (AC variable voltage power source) Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration) (Chapter 14), text pages voltmeter, AC multi-range Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration) (Chapter 14), text pages voltmeter, DC Activit : Cells in Series and in Parallel (Chapter 12), text page 448 Investigation : Transformers (Teacher Demonstration (Chapter 14), text pages wood, block of Activit : Constructing a Simple DC Motor (Chapter 13), text pages Unit 5 Overview 2002 Nelson Thomson Learning
GRADE 7: Physical processes 3. UNIT 7P.3 8 hours. Magnetism. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 7: Physical processes 3 Magnetism UNIT 7P.3 8 hours About this unit This unit is the third of five units on physical processes for Grade 7. It builds on Unit 6P.1 and leads on to work on electromagnets
GRADE 7: Physical processes 3 Magnetism UNIT 7P.3 8 hours About this unit This unit is the third of five units on physical processes for Grade 7. It builds on Unit 6P.1 and leads on to work on electromagnets
CLASSROOM KIT ELECTROMAGNETS
 CLASSROOM KIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their ideas. The
CLASSROOM KIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their ideas. The
9. Which of the following is the correct relationship among power, current, and voltage?. a. P = I/V c. P = I x V b. V = P x I d.
 Name: Electricity and Magnetism Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Resistance is measured in a unit called the. a. ohm c. ampere b. coulomb d. volt 2. The statement
Name: Electricity and Magnetism Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Resistance is measured in a unit called the. a. ohm c. ampere b. coulomb d. volt 2. The statement
Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism. Lee Wai Kit
 Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism Lee Wai Kit Electricity and Magnetism 4.1 Electrostatics 4.2 Circuits and domestic electricity 4.3 Electromagnetism 4.1 Electrostatics electric charges
Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism Lee Wai Kit Electricity and Magnetism 4.1 Electrostatics 4.2 Circuits and domestic electricity 4.3 Electromagnetism 4.1 Electrostatics electric charges
The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Properties of magnetic fields apply in nature and technology.
 UIT E UMMARY KEY COCEPT CHAPTER UMMARY 11 The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Electrical circuits Conventional current and electron flow Current, electrical
UIT E UMMARY KEY COCEPT CHAPTER UMMARY 11 The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Electrical circuits Conventional current and electron flow Current, electrical
Preliminary Course Physics Module 8.3 Electrical Energy in the Home Summative Test. Student Name:
 Summative Test Student Name: Date: / / IMPORTANT FORMULAE I = Q/t V = I.R R S = R 1 + R 2 +.. 1/R P = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 + P = V.I = I 2.R = V 2 /R Energy = V.I.t E = F/q Part A. Multiple Choice Questions 1-20.
Summative Test Student Name: Date: / / IMPORTANT FORMULAE I = Q/t V = I.R R S = R 1 + R 2 +.. 1/R P = 1/R 1 + 1/R 2 + P = V.I = I 2.R = V 2 /R Energy = V.I.t E = F/q Part A. Multiple Choice Questions 1-20.
For use with Comprehensive Secondary Physics
 For use with 139 For use with Physics Secondary Form Two Physics : Term One WEEK 1 Magnetic and nonmagnetic materials identify magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Observing attraction and repulsion of
For use with 139 For use with Physics Secondary Form Two Physics : Term One WEEK 1 Magnetic and nonmagnetic materials identify magnetic and non-magnetic materials. Observing attraction and repulsion of
GRADE 10A: Physics 6. UNIT 10AP.6 7 hours. Electrostatics and magnetism. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 10A: Physics 6 Electrostatics and magnetism UNIT 10AP.6 7 hours About this unit This unit is the sixth of seven units on physics for Grade 10 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning
GRADE 10A: Physics 6 Electrostatics and magnetism UNIT 10AP.6 7 hours About this unit This unit is the sixth of seven units on physics for Grade 10 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning
LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I. Objectives
 LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I Objectives to be able to discuss potential difference and current in a circuit in terms of electric field, work per unit charge and motion of charges to understand that
LABORATORY 4 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS I Objectives to be able to discuss potential difference and current in a circuit in terms of electric field, work per unit charge and motion of charges to understand that
PHYSICS 30 ELECTRIC FIELDS ASSIGNMENT 1 55 MARKS
 For each of the following questions complete communication must be shown. Communication consists of an introduction to the physics of the situation, diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well
For each of the following questions complete communication must be shown. Communication consists of an introduction to the physics of the situation, diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well
CLASSROOM VISIT ELECTROMAGNETS
 CLASSROOM VISIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Pre-Outreach Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their
CLASSROOM VISIT ELECTROMAGNETS Page 1 1 Pre-Outreach Activity: What Do We Already Know? Teacher A simple, yet effective learning strategy, a K-W-L chart, is used to help Background: students clarify their
AP Physics C. Electricity - Term 3
 AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
AP Physics C Electricity - Term 3 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the
AP Physics C. Magnetism - Term 4
 AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
Name: Block: Date: NNHS Introductory Physics: MCAS Review Packet #4 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS electricity and magnetism. 5.1 Recognize that an electric charge tends to be static on insulators
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS electricity and magnetism. 5.1 Recognize that an electric charge tends to be static on insulators
2. How do electrically charged objects affect neutral objects when they come in contact?
 North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
UNIT 3: Electric charge.
 UNIT 3: Electric charge Recommended Prior Knowledge Students should be aware of the two types of charge, charging by friction and by induction. They should be able to distinguish between conductors and
UNIT 3: Electric charge Recommended Prior Knowledge Students should be aware of the two types of charge, charging by friction and by induction. They should be able to distinguish between conductors and
MASTER SYLLABUS
 MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 A. Academic Division: Business, Industry and Technology B. Discipline: Physics C. Course Number and Title: PHYS1130 General Physics II D. Course Coordinator: Gary Wood Assistant
MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 A. Academic Division: Business, Industry and Technology B. Discipline: Physics C. Course Number and Title: PHYS1130 General Physics II D. Course Coordinator: Gary Wood Assistant
2. How do electrically charged objects affect neutral objects when they come in contact?
 North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
North arolina Testing Program EO Physical Science Sample Items Goal 4 1. When a plastic rod is rubbed with fur, the plastic rod becomes negatively charged. Which statement explains the charge transfer
13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic Field The Motor Principle
 13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic ield igure 1 Determining the force on an electric conductor in a magnetic field Magnetic field of the permanent magnet Magnetic field of the current-carrying conductor (c)
13.5 Conductor in a Magnetic ield igure 1 Determining the force on an electric conductor in a magnetic field Magnetic field of the permanent magnet Magnetic field of the current-carrying conductor (c)
Magnets attract some metals but not others
 Electricity and Magnetism Junior Science Magnets attract some metals but not others Some objects attract iron and steel. They are called magnets. Magnetic materials have the ability to attract some materials
Electricity and Magnetism Junior Science Magnets attract some metals but not others Some objects attract iron and steel. They are called magnets. Magnetic materials have the ability to attract some materials
OVERALL EXPECTATIONS By the end of this unit students will: SPECIFIC EXPECTATIONS By the end of this unit students will:
 OVERALL EXPECTATIONS By the end of this unit students will: D1. Analyze the operation of technologies that use gravitational, electric, or magnetic fields, and assess the technologies social and environmental
OVERALL EXPECTATIONS By the end of this unit students will: D1. Analyze the operation of technologies that use gravitational, electric, or magnetic fields, and assess the technologies social and environmental
Physics 010 Midterm #2
 Physics 010 Midterm #2 Thursday April 2, 8:30 10:00am This midterm is closed book. No books or notes allowed. Calculators are allowed There are 10 questions on this midterm, with marks noted beside each
Physics 010 Midterm #2 Thursday April 2, 8:30 10:00am This midterm is closed book. No books or notes allowed. Calculators are allowed There are 10 questions on this midterm, with marks noted beside each
TEKS Physics, Beginning with School Year Correlation to CPO Science Link
 TEKS Physics. (c) Knowledge and skills. (1) Scientific processes. The student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices.
TEKS Physics. (c) Knowledge and skills. (1) Scientific processes. The student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices.
DRAFT. Activity 16, Electromagnetic Induction! Science & Global Issues: Global Energy & Power! from! 2014 The Regents of the University of California!
 Activity 16, Electromagnetic Induction! from! Science & Global Issues: Global Energy & Power! This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. ESI 0352453.
Activity 16, Electromagnetic Induction! from! Science & Global Issues: Global Energy & Power! This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. ESI 0352453.
Jeopardy. Circuits. Electricity. Terms. Magnets This N That Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200
 Jeopardy Magnets This N That Circuits Terms Electricity Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
Jeopardy Magnets This N That Circuits Terms Electricity Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
1. A solenoid is a powerful magnet that is created by looping a conductor and passing a current through the conductor.
 Electricity and Magnetism Unit Test /60 Part A: True/False [5 K/U] In the blank provided, identify if the statement is true or false. If the statement is false, identify and correct the portion that is
Electricity and Magnetism Unit Test /60 Part A: True/False [5 K/U] In the blank provided, identify if the statement is true or false. If the statement is false, identify and correct the portion that is
Unit 3 BLM Answers UNIT 3 BLM 3-46
 UNIT 3 BLM 3-46 Unit 3 BLM Answers BLM 3-3, Charge Transfer Diagrams 1. Positively charged objects should have more (+) than ( ). Negatively charged objects should have more ( ) than (+). 2. They must
UNIT 3 BLM 3-46 Unit 3 BLM Answers BLM 3-3, Charge Transfer Diagrams 1. Positively charged objects should have more (+) than ( ). Negatively charged objects should have more ( ) than (+). 2. They must
Name: SNC1 Date: Investigation Electrostatic Series
 ACTIVITY #1 Purpose: To determine how charged objects respond to one another and what kind of charge is transferred when a charged object contacts an uncharged one. Pre Lab Questions 1. When acetate and
ACTIVITY #1 Purpose: To determine how charged objects respond to one another and what kind of charge is transferred when a charged object contacts an uncharged one. Pre Lab Questions 1. When acetate and
PHY222 Lab 8 - Magnetic Fields and Right Hand Rules Magnetic forces on wires, electron beams, coils; direction of magnetic field in a coil
 PHY222 Lab 8 - Magnetic Fields and Right Hand Rules Magnetic forces on wires, electron beams, coils; direction of magnetic field in a coil Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names You will return this
PHY222 Lab 8 - Magnetic Fields and Right Hand Rules Magnetic forces on wires, electron beams, coils; direction of magnetic field in a coil Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names You will return this
CLASS X- ELECTRICITY
 Conductor- Insulator: Materia Materials through which electric current cannot pass are called insulators. Electric Circuit: A continuous a CLASS X- ELECTRICITY als through which electric current can pass
Conductor- Insulator: Materia Materials through which electric current cannot pass are called insulators. Electric Circuit: A continuous a CLASS X- ELECTRICITY als through which electric current can pass
Study Guide. Science 3103 Electricity. Adult Basic Education Science. Prerequisite: Science Credit Value: 1
 Adult Basic Education Science Electricity Study Guide Prerequisite: Science 3102 Credit Value: 1 Text: Nelson Physics 12: College Preparation; Hirsch, Alan J.; Nelson Thomson Canada; 2004. Science Courses
Adult Basic Education Science Electricity Study Guide Prerequisite: Science 3102 Credit Value: 1 Text: Nelson Physics 12: College Preparation; Hirsch, Alan J.; Nelson Thomson Canada; 2004. Science Courses
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition 2017
 A Correlation and Narrative Summary of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition 2017 To the AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Course Description AP is a trademark registered and/or owned
A Correlation and Narrative Summary of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition 2017 To the AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Course Description AP is a trademark registered and/or owned
Symbol Meaning unit. 2. k 3. q. 4. r. 5. E 6. R Total 7. 1/R Total 8. P 9. V 10. I 11. R. 12. Q 13. N 14. e 15. F magnetic 16. v 17.
 Name period 3 rd 9 weeks test PEOPLE and SYMBOLS practice Instructions: Work in groups following Quiz-Quiz-Trade activity Date: Monday 2/25/13 Write what each symbol means, including the unit Symbol Meaning
Name period 3 rd 9 weeks test PEOPLE and SYMBOLS practice Instructions: Work in groups following Quiz-Quiz-Trade activity Date: Monday 2/25/13 Write what each symbol means, including the unit Symbol Meaning
Science Practice Exam. Chapters 5 and 14
 Science Practice Exam Chapters 5 and 14 FORMULAS Science and Technology FORMULAS C: concentration m: quantity of solute v: quantity of solution V: potential difference R: resistance I: electric current
Science Practice Exam Chapters 5 and 14 FORMULAS Science and Technology FORMULAS C: concentration m: quantity of solute v: quantity of solution V: potential difference R: resistance I: electric current
Updated: Page 1 of 6
 MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 A. Academic Division: Business, Industry, and Technology B. Discipline: Electronic Engineering Technology C. Course Number and Title: ELET1510 DC Electricity D. Course Coordinator:
MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 A. Academic Division: Business, Industry, and Technology B. Discipline: Electronic Engineering Technology C. Course Number and Title: ELET1510 DC Electricity D. Course Coordinator:
Magnetism and Electricity Unit Design Rev9.08 Grade 5
 Magnetism and Electricity Unit Design Rev9.08 Grade 5 RI Statements of Enduring Knowledge - (Established Goals): PS 1 Energy is necessary for change to occur in matter. Energy can be stored, transferred,
Magnetism and Electricity Unit Design Rev9.08 Grade 5 RI Statements of Enduring Knowledge - (Established Goals): PS 1 Energy is necessary for change to occur in matter. Energy can be stored, transferred,
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS
 5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
Fat: Who Says? Measuring Obesity by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
 Fat: Who Says? Measuring Obesity by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Circuitous Adventures Activity 3C Part 2 Objectives: Using simple electrical components, students will be able to: Identify a simple
Fat: Who Says? Measuring Obesity by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Circuitous Adventures Activity 3C Part 2 Objectives: Using simple electrical components, students will be able to: Identify a simple
Saint Lucie County Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Honors Physics 1 Course Code: 2003390 UNIT 9 TOPIC of STUDY: Electricity STANDARDS: 10: Energy ~The electric force between two charged particles depends upon the size of the charge and the distance
Course: Honors Physics 1 Course Code: 2003390 UNIT 9 TOPIC of STUDY: Electricity STANDARDS: 10: Energy ~The electric force between two charged particles depends upon the size of the charge and the distance
PLANNING EXPERIMENT (SECTION B)
 SIMPLE PENDULUM OF Period depends on length of pendulum Length increase, period increase To investigate the relationship between period and length of pendulum MV : length of pendulum RV : period FV : angle
SIMPLE PENDULUM OF Period depends on length of pendulum Length increase, period increase To investigate the relationship between period and length of pendulum MV : length of pendulum RV : period FV : angle
Material World: Electricity
 17. Coulomb s Law The force, F, between two objects with charge q1 and q2, is given by: k q q 1 2 F -, where r = distance between the two charges in meters 2 r k = Coulomb's constant = 9 X 10 9 m 2 /C
17. Coulomb s Law The force, F, between two objects with charge q1 and q2, is given by: k q q 1 2 F -, where r = distance between the two charges in meters 2 r k = Coulomb's constant = 9 X 10 9 m 2 /C
Energy and Electromagnetism
 4 th Science Notebook Energy and Electromagnetism Investigation 3: The Force of Magnetism Name: Big Question: What are the properties of magnets? 1 Alignment with New York State Science Standards & Performance
4 th Science Notebook Energy and Electromagnetism Investigation 3: The Force of Magnetism Name: Big Question: What are the properties of magnets? 1 Alignment with New York State Science Standards & Performance
GRADE 5: Physical processes 4. UNIT 5P.4 5 hours. Magnetic forces. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 5: Physical processes 4 Magnetic forces UNIT 5P.4 5 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of five units on physical processes for Grade 5. The unit is designed to guide your planning and
GRADE 5: Physical processes 4 Magnetic forces UNIT 5P.4 5 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of five units on physical processes for Grade 5. The unit is designed to guide your planning and
Electricity. Year 10 Science
 Electricity Year 10 Science What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? A stationary electrical charge that is built up on the
Electricity Year 10 Science What is electricity? The collection or flow of electrons in the form of an electric charge What is static electricity? A stationary electrical charge that is built up on the
Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter D. Other Science Courses
 Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter D. Other Science Courses Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter D issued under the Texas Education Code, 28.002,
Chapter 112. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science Subchapter D. Other Science Courses Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter D issued under the Texas Education Code, 28.002,
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism
 AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Course overview This is a calculus based course in physics. The course is the equivalent of an introductory engineering course in Physics. The main objective of the
AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Course overview This is a calculus based course in physics. The course is the equivalent of an introductory engineering course in Physics. The main objective of the
Level 1 Physics, 2016
 90937 909370 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Physics, 2016 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 15 November 2016 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit
90937 909370 1SUPERVISOR S Level 1 Physics, 2016 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 15 November 2016 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit
Lesson 9: Products of Electricity
 Magnetism and Electricity -> 9: Products of Electricity Getting Started? Big Ideas P What does electrical power produce? P How is electrical power produced? Lesson 9: Products of Electricity & Facts and
Magnetism and Electricity -> 9: Products of Electricity Getting Started? Big Ideas P What does electrical power produce? P How is electrical power produced? Lesson 9: Products of Electricity & Facts and
Electromagnetism Review Sheet
 Electromagnetism Review Sheet Electricity Atomic basics: Particle name Charge location protons electrons neutrons + in the nucleus - outside of the nucleus neutral in the nucleus What would happen if two
Electromagnetism Review Sheet Electricity Atomic basics: Particle name Charge location protons electrons neutrons + in the nucleus - outside of the nucleus neutral in the nucleus What would happen if two
Review: Magnetism and Electromagnetism
 Review: Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice: Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement. 1. Magnetism is a force of a. gravity. b. weight. c. voltage. d. attraction
Review: Magnetism and Electromagnetism Multiple Choice: Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement. 1. Magnetism is a force of a. gravity. b. weight. c. voltage. d. attraction
13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
 Assignments in cience Class X (Term I) 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 1. Magnetic field: The space surrounding a magnet in which its influence in the form of magnetic force can be detected, is
Assignments in cience Class X (Term I) 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 1. Magnetic field: The space surrounding a magnet in which its influence in the form of magnetic force can be detected, is
Equipotential Lines and Electric Fields
 Physics Equipotential Lines and Electric Fields Plotting the Electric Field MATERIALS AND RESOURCES EACH GROUP 5 alligator clip leads 2 batteries, 9 V 2 binder clips, large computer LabQuest multimeter,
Physics Equipotential Lines and Electric Fields Plotting the Electric Field MATERIALS AND RESOURCES EACH GROUP 5 alligator clip leads 2 batteries, 9 V 2 binder clips, large computer LabQuest multimeter,
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance
 Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Electricity Review completed.notebook. June 13, 2013
 Which particle in an atom has no electric charge associated with it? a. proton c. neutron b. electron d. nucleus Jun 12 9:28 PM The electrons in a metal sphere can be made to move by touching it with a
Which particle in an atom has no electric charge associated with it? a. proton c. neutron b. electron d. nucleus Jun 12 9:28 PM The electrons in a metal sphere can be made to move by touching it with a
1. Voltage is how much work is being done for a charge. 2. Lightning is the electric breakdown of air by weak electric fields and is a flow of energy.
 Chapters 17 and 18 Practice Problems True or False 1. Voltage is how much work is being done for a charge. 2. Lightning is the electric breakdown of air by weak electric fields and is a flow of energy.
Chapters 17 and 18 Practice Problems True or False 1. Voltage is how much work is being done for a charge. 2. Lightning is the electric breakdown of air by weak electric fields and is a flow of energy.
Circuits. Circuits. Electric Current & DC Circuits. current and circuits presentation March 22, How to Use this File.
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Electric Current & DC Circuits Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non commercial
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Electric Current & DC Circuits Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non commercial
SUPPLY LIST. Physics
 2018-19 SUPPLY LIST Physics Table of Contents UNIT 1: KINEMATICS... 1 UNIT 2: DYNAMICS... 2 UNIT 3: WORK AND ENERGY... 4 UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION TO WAVES... 5 UNIT 5: LIGHT... 5 UNIT 7: STATIC ELECTRICITY...
2018-19 SUPPLY LIST Physics Table of Contents UNIT 1: KINEMATICS... 1 UNIT 2: DYNAMICS... 2 UNIT 3: WORK AND ENERGY... 4 UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION TO WAVES... 5 UNIT 5: LIGHT... 5 UNIT 7: STATIC ELECTRICITY...
Electric Charge. Conductors A material that transfers charge easily Metals
 Electric Charge An electrical property of matter that creates a force between objects. Like charges repel Opposite charges attract Equal amount of positive and negative = no net charge Electrons: Negative
Electric Charge An electrical property of matter that creates a force between objects. Like charges repel Opposite charges attract Equal amount of positive and negative = no net charge Electrons: Negative
GRADE 11A: Physics 6. UNIT 11AP.6 10 hours. Electromagnetic induction. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 11A: Physics 6 Electromagnetic induction UNIT 11AP.6 10 hours About this unit This unit is the sixth of seven units on physics for Grade 11 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning and
GRADE 11A: Physics 6 Electromagnetic induction UNIT 11AP.6 10 hours About this unit This unit is the sixth of seven units on physics for Grade 11 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning and
Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs
 Name: Lab Partners: Date: Pre-Lab Assignment: Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs (Due at the beginning of lab) 1. Explain why in Activity 1.1 the plates will be charged in several
Name: Lab Partners: Date: Pre-Lab Assignment: Fundamentals of Circuits I: Current Models, Batteries & Bulbs (Due at the beginning of lab) 1. Explain why in Activity 1.1 the plates will be charged in several
Lesson Plan: Electric Circuits (~130 minutes) Concepts
 Lesson Plan: Electric Circuits (~130 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity is the flow of electric charge (electrons). 2. Electric Charge is a property of subatomic particles. 3. Current is the movement of
Lesson Plan: Electric Circuits (~130 minutes) Concepts 1. Electricity is the flow of electric charge (electrons). 2. Electric Charge is a property of subatomic particles. 3. Current is the movement of
SNC1DI Unit Review: Static & Current Electricity
 SNC1DI Unit Review: Static & Current Electricity 1. Be able to recognize the definitions for the following terms: Friction Contact Induction Lightning Electrostatic Series Pithball electroscope Insulators
SNC1DI Unit Review: Static & Current Electricity 1. Be able to recognize the definitions for the following terms: Friction Contact Induction Lightning Electrostatic Series Pithball electroscope Insulators
Title of Activity: Let there be Light! Introduction to Ohm's Law and basic series circuits.
 Title of Activity: Let there be Light! Introduction to Ohm's Law and basic series circuits. Concepts Covered: Circuitry is in all of our electronics. This circuits must be asembled in specific ways to
Title of Activity: Let there be Light! Introduction to Ohm's Law and basic series circuits. Concepts Covered: Circuitry is in all of our electronics. This circuits must be asembled in specific ways to
LESSON PLAN-1 T1-Session
 LESSON PLAN1 T1Session 20152016 For the 3rd March ity Periods: (2) Practical:(0) Concept of Charge and its properties. and its units. the components of circuit & their symbols. problems related to the
LESSON PLAN1 T1Session 20152016 For the 3rd March ity Periods: (2) Practical:(0) Concept of Charge and its properties. and its units. the components of circuit & their symbols. problems related to the
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Chapter 1. Electric Fields 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Triboelectric Effect 1.3 Experiments with Pith Balls 1.4 Experiments with a Gold-leaf Electroscope 1.5 Coulomb s Law 1.6 Electric
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Chapter 1. Electric Fields 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Triboelectric Effect 1.3 Experiments with Pith Balls 1.4 Experiments with a Gold-leaf Electroscope 1.5 Coulomb s Law 1.6 Electric
Electric Current & DC Circuits
 Electric Current & DC Circuits Circuits Click on the topic to go to that section Conductors Resistivity and Resistance Circuit Diagrams Measurement EMF & Terminal Voltage Kirchhoff's Rules Capacitors*
Electric Current & DC Circuits Circuits Click on the topic to go to that section Conductors Resistivity and Resistance Circuit Diagrams Measurement EMF & Terminal Voltage Kirchhoff's Rules Capacitors*
Curriculum Catalog
 2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog Physics 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents UNIT 1: KINEMATICS... 1 UNIT 2: DYNAMICS... 2 UNIT 3: WORK AND ENERGY... 3 UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION TO WAVES... 4 UNIT 5: LIGHT...
2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog Physics 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents UNIT 1: KINEMATICS... 1 UNIT 2: DYNAMICS... 2 UNIT 3: WORK AND ENERGY... 3 UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION TO WAVES... 4 UNIT 5: LIGHT...
Supply List. Physics. Released Glynlyon, Inc
 N Supply List Physics 2012 Glynlyon, Inc Released 4-1-12 Table of Contents UNIT 1: KINEMATICS... 1 UNIT 2: DYNAMICS... 2 UNIT 3: WORK AND ENERGY... 2 UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION TO WAVES... 3 UNIT 5: LIGHT...
N Supply List Physics 2012 Glynlyon, Inc Released 4-1-12 Table of Contents UNIT 1: KINEMATICS... 1 UNIT 2: DYNAMICS... 2 UNIT 3: WORK AND ENERGY... 2 UNIT 4: INTRODUCTION TO WAVES... 3 UNIT 5: LIGHT...
AP Physics 2 Sample Syllabus 3
 Syllabus 066439v Curricular Requirements CR Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including college-level textbooks and reference materials in print or electronic format. CRa The
Syllabus 066439v Curricular Requirements CR Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including college-level textbooks and reference materials in print or electronic format. CRa The
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields
 Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
AP Physics 2 Sample Syllabus 3
 Curricular Requirements CR CRa CRb CRc CRd CRe CRf CRg CR3 CR4 CR CR6a CR6b CR7 CR8 Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including collegelevel textbooks and reference materials
Curricular Requirements CR CRa CRb CRc CRd CRe CRf CRg CR3 CR4 CR CR6a CR6b CR7 CR8 Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including collegelevel textbooks and reference materials
Introduction to Electrical Theory
 Youth xplore Trades Skills Introduction to lectrical Theory Description Working as an electrician requires many skills. The physical demands of the job are one important part of the skills needed to succeed.
Youth xplore Trades Skills Introduction to lectrical Theory Description Working as an electrician requires many skills. The physical demands of the job are one important part of the skills needed to succeed.
Electromagnetism Checklist
 Electromagnetism Checklist Elementary Charge and Conservation of Charge 4.1.1A Convert from elementary charge to charge in coulombs What is the charge in coulombs on an object with an elementary charge
Electromagnetism Checklist Elementary Charge and Conservation of Charge 4.1.1A Convert from elementary charge to charge in coulombs What is the charge in coulombs on an object with an elementary charge
Science TEKS Verification
 Science EKS Verification (1) Scientific processes. he student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. hese investigations
Science EKS Verification (1) Scientific processes. he student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. hese investigations
Particle symbol. electron negative outside nucleus e
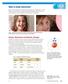 What Is Static Electricity? Have you ever had your hair stand up after putting on, or taking off, a sweater (Figure 1)? Or have you perhaps noticed that a balloon placed near your head will attract your
What Is Static Electricity? Have you ever had your hair stand up after putting on, or taking off, a sweater (Figure 1)? Or have you perhaps noticed that a balloon placed near your head will attract your
TOPIC 4 STATIC ELECTRICITY
 IGCSE Physics 0625 notes Topic 4: Static Electricity 1 TOPIC 4 STATIC ELECTRICITY ELECTRICITY: Electricity is the flow of electrical charges or power. The charges could be in the form of electrons or ions.
IGCSE Physics 0625 notes Topic 4: Static Electricity 1 TOPIC 4 STATIC ELECTRICITY ELECTRICITY: Electricity is the flow of electrical charges or power. The charges could be in the form of electrons or ions.
UNIT 1 EXPLORING THE NATURE OF ELECTROSTATIC FORCES
 UNIT 1 EXPLORING THE NATURE OF ELECTROSTATIC FORCES Objectives to learn that scientific models are based on observations and to learn how scientific models are developed from observational evidence to
UNIT 1 EXPLORING THE NATURE OF ELECTROSTATIC FORCES Objectives to learn that scientific models are based on observations and to learn how scientific models are developed from observational evidence to
Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 Student Guide
 Concepts of this Module Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 Student Guide Interactions of permanent magnets with other magnets, conductors, insulators, and electric charges. Magnetic fields of permanent
Concepts of this Module Electricity and Magnetism Module 6 Student Guide Interactions of permanent magnets with other magnets, conductors, insulators, and electric charges. Magnetic fields of permanent
Science Lab List
 2010-2011 Science Lab List Physics 2010 Glynlyon, Inc Released 6-1-10 Table of Contents PHYSICS (2010): UNIT 1 KINEMATICS... 1 PHYSICS (2010): UNIT 2 DYNAMICS... 2 PHYSICS (2010): UNIT 3 WORK AND ENERGY...
2010-2011 Science Lab List Physics 2010 Glynlyon, Inc Released 6-1-10 Table of Contents PHYSICS (2010): UNIT 1 KINEMATICS... 1 PHYSICS (2010): UNIT 2 DYNAMICS... 2 PHYSICS (2010): UNIT 3 WORK AND ENERGY...
10/11/2018 1:48 PM Approved (Changed Course) PHYS 42 Course Outline as of Fall 2017
 10/11/2018 1:48 PM Approved (Changed Course) PHYS 42 Course Outline as of Fall 2017 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: PHYS 42 Title: ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM Full Title: Electricity and Magnetism for Scientists
10/11/2018 1:48 PM Approved (Changed Course) PHYS 42 Course Outline as of Fall 2017 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: PHYS 42 Title: ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM Full Title: Electricity and Magnetism for Scientists
P4 - Electromagnetism
 Number of weeks (between 6&8) Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) Current and voltage Notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic
Number of weeks (between 6&8) Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) Current and voltage Notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic
Combined Science Physics Academic Overview
 Combined Science Physics Academic Overview 2018-19 Science Term 1.1 Term 1.2 Term 2.1 Term 2.2 Term 3.1 Term 3.1 Year 9 Motion Forces 1 Newton s Laws Forces 2 Momentum and Safety Energy Waves End of year
Combined Science Physics Academic Overview 2018-19 Science Term 1.1 Term 1.2 Term 2.1 Term 2.2 Term 3.1 Term 3.1 Year 9 Motion Forces 1 Newton s Laws Forces 2 Momentum and Safety Energy Waves End of year
Student Achievement. Physics 12
 Student Achievement Physics 12 Student Achievement PHYSICS 12 FORMULAE Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions Gravitation v + v0 v = v0 + at v = 2 F g m m = G r 1 2 2 v v ad 2 2 = 0 + 2 Vector Dynamics 1
Student Achievement Physics 12 Student Achievement PHYSICS 12 FORMULAE Vector Kinematics in Two Dimensions Gravitation v + v0 v = v0 + at v = 2 F g m m = G r 1 2 2 v v ad 2 2 = 0 + 2 Vector Dynamics 1
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *5533380653* PHYSICS 5054/02 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2007 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *5533380653* PHYSICS 5054/02 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2007 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
AP Physics 2 Syllabus
 AP Physics Syllabus Curricular Requirements CR1 Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including college-level textbooks and reference materials in print or electronic format. CRa
AP Physics Syllabus Curricular Requirements CR1 Students and teachers have access to college-level resources including college-level textbooks and reference materials in print or electronic format. CRa
Amarillo ISD Science Curriculum
 Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Circuits. Electric Current & DC Circuits. Slide 1 / 127. Slide 2 / 127. Slide 3 / 127. Slide 4 / 127. Slide 5 / 127. Slide 6 / 127
 Slide 1 / 127 Slide 2 / 127 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Electric Current & DC Circuits www.njctl.org Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org
Slide 1 / 127 Slide 2 / 127 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Electric Current & DC Circuits www.njctl.org Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org
Embedded Assessment Notes
 Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
- Memorize the terms voltage, current, resistance, and power. - Know the equations Ohm s Law and the Electric Power formula
 E: Know Circuit Vocabulary (Short Answer) Level 2 Prerequisites: Know Circuit Vocabulary (Short Answer); Recognize Insulators and Conductors Objectives: - Memorize the terms voltage, current, resistance,
E: Know Circuit Vocabulary (Short Answer) Level 2 Prerequisites: Know Circuit Vocabulary (Short Answer); Recognize Insulators and Conductors Objectives: - Memorize the terms voltage, current, resistance,
SOTM LAB: P16 OHM S LAW I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Ohm s Law DEVELOPERS OF LAB:
 SOTM LAB: P16 OHM S LAW I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Ohm s Law DEVELOPERS OF LAB: John Lane, JD853@maristb.marist.edu Taylor Pancoast, JD573@maristb.marist.edu OVERVIEW OF LAB DESCRIPTION
SOTM LAB: P16 OHM S LAW I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Ohm s Law DEVELOPERS OF LAB: John Lane, JD853@maristb.marist.edu Taylor Pancoast, JD573@maristb.marist.edu OVERVIEW OF LAB DESCRIPTION
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *6658930791* UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education PHYSIS 0625/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2011 dditional Materials: Multiple
*6658930791* UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education PHYSIS 0625/12 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2011 dditional Materials: Multiple
Magnetism and Electricity
 Magnetism and Electricity UNIT 7 Student Reader E3 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 7 Page 1 2016 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a girl with her hair standing straight up. This
Magnetism and Electricity UNIT 7 Student Reader E3 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 7 Page 1 2016 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of a girl with her hair standing straight up. This
Electron Theory. Elements of an Atom
 Electron Theory Elements of an Atom All matter is composed of molecules which are made up of a combination of atoms. Atoms have a nucleus with electrons orbiting around it. The nucleus is composed of protons
Electron Theory Elements of an Atom All matter is composed of molecules which are made up of a combination of atoms. Atoms have a nucleus with electrons orbiting around it. The nucleus is composed of protons
Read Chapter 7; pages:
 Forces Read Chapter 7; pages: 191-221 Objectives: - Describe how electrical charges exert forces on each other; Compare the strengths of electric and gravitational forces; Distinguish between conductors
Forces Read Chapter 7; pages: 191-221 Objectives: - Describe how electrical charges exert forces on each other; Compare the strengths of electric and gravitational forces; Distinguish between conductors
MPTC Electromagnetism daily calendar (draft)
 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 MPTC Electromagnetism daily calendar (draft) - Distribute workshop materials, - Pretest - Introduce leaders and participants - Discuss workshop design and course expectations. Begin
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 MPTC Electromagnetism daily calendar (draft) - Distribute workshop materials, - Pretest - Introduce leaders and participants - Discuss workshop design and course expectations. Begin
12.2 Electric Fields and Electric Charge
 9. A pith-ball electroscope may be in a charged or a neutral state. Describe the steps you would take to determine whether it is charged or neutral. If the electroscope is charged, how would you determine
9. A pith-ball electroscope may be in a charged or a neutral state. Describe the steps you would take to determine whether it is charged or neutral. If the electroscope is charged, how would you determine
Electricity and Magnetism Static Electricity, Current Electricity, and Magnets
 Electricity and Magnetism Static Electricity, Current Electricity, and Magnets Expanding Science Skills Series By John B Beaver, PhD, and DON POWERS, PhD Consultants: Schyrlet Cameron and Carolyn Craig
Electricity and Magnetism Static Electricity, Current Electricity, and Magnets Expanding Science Skills Series By John B Beaver, PhD, and DON POWERS, PhD Consultants: Schyrlet Cameron and Carolyn Craig
Physics Form 5 Syllabus
 Physics Form 5 Syllabus Theme in syllabus Topic Content Learning Outcome Magnetism Properties of Magnets Magnetic field of earth Making magnets Magnetic Properties of Steel and Iron Magnetic and Non- Magnetic
Physics Form 5 Syllabus Theme in syllabus Topic Content Learning Outcome Magnetism Properties of Magnets Magnetic field of earth Making magnets Magnetic Properties of Steel and Iron Magnetic and Non- Magnetic
8. Electric circuit: The closed path along which electric current flows is called an electric circuit.
 GIST OF THE LESSON 1. Positive and negative charges: The charge acquired by a glass rod when rubbed with silk is called positive charge and the charge acquired by an ebonite rod when rubbed with wool is
GIST OF THE LESSON 1. Positive and negative charges: The charge acquired by a glass rod when rubbed with silk is called positive charge and the charge acquired by an ebonite rod when rubbed with wool is
