To be submitted to Appl. Phys. Lett. Domain Dynamics in Piezoresponse Force Microscopy: Quantitative Deconvolution. and Hysteresis Loop Fine Structure
|
|
|
- Bernadette Ball
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 To be submitted to Appl. Phys. Lett. Domain Dynamics in Piezoresponse Force Microscopy: Quantitative Deconvolution and Hysteresis Loop Fine tructure Igor Bdikin and Andrei Kholkin Department of Ceramics and Glass Engineering, CICECO, University of Aveiro, 8-9 Aveiro, Portugal, Anna N. Morozovska * and ergei V. vechnikov V. Lashkaryov Institute of emiconductor Physics, National Academy of cience of Ukraine, 4, Prospect, Nauki, 8 Kiev, Ukraine eung-hyun Kim INOTEK Inc., Gyeonggi Technopark, Ansan, Gyeonggi 46-9,. Korea ergei V. Kalinin The Center for Nanoscale Materials ciences and Materials cience and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 78, U..A. * Corresponding author, morozo@i.com.ua Corresponding author, sergei@ornl.gov
2 Domain dynamics in the Piezoresponse Force pectroscopy (PF) experiment is studied using the combination of local hysteresis loop acquisition with simultaneous domain imaging. The analytical theory for PF signal from domain of arbitrary cross-section is developed and used for the analysis of experimental data on Pb(Zr,Ti)O polycrystalline films. The results suggest formation of oblate domain at early stage of the domain nucleation and growth, consistent with icient screening of depolarization field within the material. The fine structure of the hysteresis loop is shown to be related to the observed jumps in the domain geometry during domain wall propagation (nanoscale Barkhausen jumps), indicative of strong domain-defect interactions.
3 Local polarization switching in ferroelectric materials by a biased Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM) tip has emerged as a perspective approach for ultra high density data storage,, ferroelectric lithography, and nanostructure fabrication. 4,5 ubsequent imaging of the switched domain provides direct insight into domain growth mechanism 6 and relaxation kinetics 7, from which the ect of macroscopic defects, 8 microscopic disorder, 9 and surface state on domain wall dynamics and pinning can be established. The primary limitation of this approach is the (a) uncontrollable ect of surface charge migration, inevitable in ambient conditions on observed growth and relaxation kinetics, and (b) extremely large times (~s hours) required for studies even at a single location. ingle-point Piezoresponse Force pectroscopy (PF) allows probing the domain growth process by detecting the changes in local electromechanical response due to nucleation and growth of domain below the tip. Increase of acquisition speed to ~. s/loop enabled witching-pectroscopy PFM, in which PF loops are collected at each point in the image to yield D maps of parameters such as imprint, nucleation biases, or work of switching. The development of PF and PFM necessitated the quantitative interpretation of the spectroscopic data, establishing the relationship between the electromechanical response and the geometric parameters of the domain formed below the tip. Recently, the theoretical framework for the interpretation of the PF data for cylindrical domain geometry was established in Ref.[]. Here, we report the results of the combined spectroscopic-imaging experiments and correlate the changes in domain geometry and the loop shape. The PFM spectroscopy and domain imaging at each step of spectroscopic process were preformed as described elsewhere. 4 The films of Pb(Zr. Ti.7 )O (PZT) used in this study were produced by sol-gel method and commercialized by INOTEK 5. The thickness
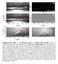
4 of the films was about 4 µm and grain size varied in the range -5 nm. The films had columnar structure with random orientation of the grains. ufficiently big grains of the size about -4 nm with strong initial piezoelectric contrast were used for the local measurements. The representative local PF hysteresis loop, corresponding evolution of domain sizes, and in-situ domain images are shown in Fig.. The data were taken with poling pulse duration s and imaging of the resulting domain structure immediately after poling. Note that a sharp change in response in PF hysteresis loop at -5 V corresponds to domain nucleation. The subsequent lateral growth of the domain corresponds to the increase in PFM signal, which finally saturates at about V. (a) 6nm 6nm 6nm d (a.u.) Bias V (V) 6nm Domain diameter ( µm ),6,5,4,,,, Negative domain (b) Positive domain U dc ( Volts ) Fig.. (a) Effective piezoresponse d via applied bias V: filled squires is experimental data for examined Pb(Zr. Ti.7 )O 4µm film 6 ; solid and dashed curves are theoretical fitting based on Eqs.(-) and Eqs.(A.4), respectively. Domain radius r s for both curves was determined from PFM images and shown in part (b). olid curve in Fig. (a) corresponds to the size of nascent domain (dark and bright), while dashed curve is calculated for the difference between the fully switched area for bright domain and nascent dark domain. 4
5 To correlate local electromechanical response measured in a PF experiment to the size of ferroelectric domain formed below the tip, we utilized the decoupling approximation 7,8 combined with Pade approximation method. Here, we develop the generalized analytical relationship between the PFM signal and ective domain size R (V), as: d d πd 8R ( V ) d π d 8R ( V ) +. () 4 4 πd + 8R ( V ) 4 πd + 8R ( V ) ( R V )) d + ( + 4ν) 5 ( Equation () is valid for dielectrically isotropic materials with γ 9, are strain piezoelectric coicients, and ν.5 is the Poisson ratio. The bias-dependent ective domain size R(V) was derived as ( π 6) + l π 6 d nm lr R ( V ), () r ( ) where l(v) is the ective domain length, radius π r ( V ) dα r( α), α is the angle, as π defined in Fig. (a). Below we compare the hysteresis loop measurements with the in-situ imaging studies. For domains of irregular shape, ective radius, r s, was determined experimentally as a square root of domain cross-section determined from PFM images. Additionally, we introduce the domain center shift with respect to the probe apex axis, a(v), that can be significant at early stages of domain growth process due to the presence of local defects and inhomogeneities. Here, we regard a(v) as a fitting parameter. For high aspect ratio (r s /l<<) tip-induced domains R s (V) r s (V) and a(v), so the radius r s can be directly extracted from ective piezoresponse d ( ) deconvolution by means of Eqs.(-). For small shifts a<<rs, V 5
6 it is possible to estimate domain length using both ective radius r s (V) extracted from PFM images and R s (V) extracted from piezoresponse data d ( V ) as following: l( V ) 6 R r. () π r R Domain parameters determination for PZT films is shown in Fig.. The accuracy of the proposed deconvolution method and results presented in Fig. can be estimated from Fig.(a). Note that the solid and dashed curves in Fig.(a) do not coincide with experimental symbols at negative bias, indicating that the contribution of small dark domain into piezoresponse was underestimated (actually we have in-situ PFM data for r s of bright domain only). At the same time, dotted and solid curve coincide almost everywhere, indicative of relatively minor contribution of domain center displacement, a(v ), to measured signal. 6
7 x Length (µm) Defect (a) r(α). - - r α R x / l (c) a θ a x Probe Domain of irregular shape a= ize (µm) Eq.(A.4).4. Eq.(-) Bias V (V) (b) r Bias V (V). (d) R a r / /l r 9/ /l - 5 Bias V (V) Fig.. (a) Problem geometry. (b) Effective domain size via applied bias: filled squires are R values deconvoluted from d using Eq.(); empty squires are average radius r values obtained from in-situ PFM data shown in Fig. b; dotted curve is domain shift a deconvoluted from d using in-situ r values in Eqs.(A.4). (c) Effective domain length via applied bias: filled triangles were deconvoluted from d using in-situ r values in Eqs.(A.4) and a ; empty squares are deconvoluted from d using in-situ r values in Eqs.(-) and a=. (d) The ratios / r l (invariant for prolate domains in Molotskii model ) and 9 / r l (almost constant in our case) calculated from r values in Eqs.(A.4) (labels near the curves, arbitrary units). For Pb(Zr. Ti.7 )O constants d =-.4, d =6. pm/v 5 γ and d=4nm; vertical offset caused by electrostatic forces is -6. a.u. The deconvolution results are independent of d 5 within the range.5 d d 5.5d. 7
8 The fitting for strongly anisotropic domains, r s /l<<, is shown to lead to unphysically large tip sizes, d nm, or lateral domain shifts, a nm, inconsistent with d 5-4nm as determined from observed ferroelectric domain wall width. To account for this discrepancy, we treated domain penetration length as a fitting parameter, and deconvolution results are shown in Fig. (c-d). The fitting of piezoresponse loop and contrast of PFM images at small voltages V suggest that the domains are oblate at nucleation and initial growth stages. This domain geometry necessitates icient depolarization field screening in bulk of the sample, since in the rigid dielectric material depolarization field favors needle-like domain (depolarization energy is ~/l ). This behavior is possible when screening charges are captured by the moving domain wall. For d=4nm, maximal domain radius r s =nm~d at bias V can be explained by ective mechanism of depolarization field surface screening in examined PZT film. The careful inspection of domain evolution in Fig. illustrates that often domain growth proceeds through the rapid jumps of domain walls, resulting in irregular domain shapes. Interestingly, these jumps can be associated with the fine structures of the local hysteresis loop, as illustrated in Fig.. Almost all hysteretic curves taken at higher magnification demonstrate visible kinks under increasing voltages. These kinks are reproducible upon repeating voltage excursions and thus could be attributed to the defects and associated pinning of domain walls. These features can be naturally explained by the presence of local defects and long range electroelastic fields as it was theoretically predicted in the past (see, e.g., Ref. 4 ). Based on result shown in Fig., each reproducible feature on the hysteresis curve could be related to a separate metastable domain state pinned by the nearest 8
9 defect site. Future improvement of the PF technique is required to relate each kink in the hysteresis curve to an individual jump of the domain wall (nanoscale Barkhausen jump). d ( a.u. ) - - 6nm U dc ( V ) 6nm Fig.. Example of the proposed relationship between the fine structure of the piezoresponse hysteresis loops and jumps of domain walls observed in the investigated PZT films under increasing bias. To summarize, we have analyzed hysteresis loop formation in Piezoresponse Force Microscopy. Direct comparison of the induced domain size and the PF signal deconvoluted using self-consistent probe calibration has demonstrated that domain shape deviates significantly from simple needle-like geometry. In fact, the oblate domains are formed at nucleation and early growth stages. As a consequence, a new invariant 9 / r l was introduced for the description of the domain growth in polycrystalline PZT films. The fine structure features on piezoresponse spectra were demonstrated and tentatively related to the nanoscale jumps in domain geometry due to domain-defect interactions. Thus, high-resolution PFM 9
10 spectroscopy offers the pathway to study the nanoscale mechanism of defect-mediated domain nucleation and growth. Authors gratefully acknowledge multiple discussions and technical support of Dr. E. A. Eliseev. Research was sponsored in part (VK) by the Division of Materials ciences and Engineering, Office of Basic Energy ciences, U.. Department of Energy, under contract DE-AC5-OR75 with Oak Ridge National Laboratory, managed and operated by UT- Battelle, LLC. User proposal CNM7-65 (ORNL), FCT project PTDC/FI/844/6 and FAME Nework of Excellence (NMP-CT-4-559) are also acknowledged.
11 upplementary ) Appendix A Measured in a PF experiment is the electromechanical response related to the size of ferroelectric domain formed below the tip. Hence, to calculate the shape of the PFM hysteresis loop, the electromechanical response change induced by the domain is required. Within the framework of linearized theory by Felten et al, 7 the surface displacement vector ui ( x) at position x is u G ( x, ξ ) ij p i( x ) = dξ dξ dξ Ek ( ξ ) d kmn ( ξ ) c nmjl (A.) ξl where ξ is the coordinate system related to the material, ( x,ξ ) G is Green tensor in isotropic elastic approximation 5 (anisotropy of elastic properties is assumed to be much smaller then ij that of dielectric and piezoelectric properties), d nmp are strain piezoelectric coicients distribution, c nmjl are elastic stiffness and the Einstein summation convention is used. The electric field E ( ρ ) is created by the biased probe. Using an ective p k, x) = ϕ p ( ρ, x x k point charge approximation, the probe is represented by a single charge Q located at distance, d, from a sample surface. The potential ϕ p at x has the form: V d ϕ p( ρ, x). (A.) ρ + ( x γ + d ) Here x = ρ and is the radial and vertical coordinate respectively, V is the bias + x x applied to the probe, γ = ε ε is the dielectric anisotropy factor; d = R π for a flattened tip represented by a disk in contact.
12 Integration of Eq. (A.) for x = yields the expression for ective vertical piezoresponse, d u V, as = ( V ) d ( f w ( V )) + d ( f w ( V )) + d ( f w ( V )) d 5 =, (A.) The functions f = ( ( + γ) ν + ) ( + γ), f = γ ( + ), = ( + γ)( + γ) γ f define the electromechanical response in the initial and final states of switching process; 6 ν is the Poisson ratio. The bias dependence of PF signal, w i, is determined by the domain sizes and shape. Domain shape affected by defects is approximated by cross-section with radius vector r(α) and length l [see Fig.(a)]. For this case, wi components are 6 : w ( ) [ r( l] = dα dθ cos θ ( + ν) π π π cosθ R R G ( θ, r( l) ( θ, r( l), (A.4a) θ R ( θ, r( l) ( θ, r( l) π π γ d + cot w [ ] α θ r( l = d d cos θsin θ, (A.4b) π RG w [ r( l] = π π dα π dθcos R θ R G ( θ, r( l) ( θ, r( l). (A.4c) where the shape factors are introduced as ( θ, r, l) = rl tan θ r + l tan θ R ( ) + γ R ( θ, r l) ( θ, r, l) = γ d + cot θ R ( θ, r, l) G, Pade approximations theory, Eqs.(A.4) can be simplified as: w ( cos θ ( + ν) ) π cosθ [ r( l] θ α π d R ( γ d + cotθ R) + γ R R and. Using Lagrange mean point theorem, and [ r( )], (A.5a) π γ d + cot θ R [ ] [ r( α) ] w r( l dθcos θsin θ π, (A.5b) ( ) γ d + cot θ R + γ R
13 π dθcos θ R [ r( α) ] ( γ d + cotθ R ) + γ w [ r( l] π. (A.5c) R Where π * dα rl tan θi R i[ r( α) ] (A.5d) * r + l tan θ i and * θ i is mean point. Further interpolation by Pade at a=, γ, r(α) const and arbitrary l (or alternatively r<<l and arbitrary r(α)) leads to for i=,, where ( π 6) l r Ri (A.5e) r + ( π ) l 6 π r dα r( α). (A.5f) π This approximation is good (less than -5% discrepancy) for d contribution at arbitrary r/l ratio, moderate for d (about 5% discrepancy) and poor (more than 5% discrepancy) for d 5 for r>>l, while d 5 contribution is negligibly small at r>>l. Then direct integration on polar angle θ leads to expression: d d πd 8R ( V ) d π d 8R ( V ) + (A.6a) 4 4 πd + 8R ( V ) 4 πd + 8R ( V ) ( R V )) d + ( + 4ν) 5 ( Under the condition <a<<r and r <<l one obtains using concept of ective piezoresponse volume that and therefore: d ( ) ( r a) d ( r a) + d ( r + a) d ( r a),, (A.6b) 4r r a
14 ( πd + 4r ) a + r ( ) πd + 8r ( πd + 4r ) a πd ( π + ) r d 8r * 6r d + 8πd 4 ( ) πd + 8r d r, a (A.7) d 5 + 6r πd + 8r The case a~r should fitted numerically on the base of exact expressions (A.4). Appendix B Pt Pt Intensity ( a.u. ) PZT PZT PZT PZT + PZT PZT + PZT PZT + PZT PZT PZT + PZT Θ ( o ) Fig. X-ray diffraction pattern of Pb(Zr -x Ti x )O, x =.7, thickness 4 µm. This is no textured film. All orientations are present in the film. Data on this film Pb(Zr -x Ti x )O x =.7 (INOTEK): Thickness 4 µm Orientation Dielectric constant Random (XRD plots available) ~45 (poled) 4
15 ~6 (unpoled) Remanent polarization 5 µc/cm Coercive field d (clamped) e (wafer texture technique) 75 kv/cm 5 pm/v - C/m Assuming that values of piezoelectric modulus from the table are ective values, related to intrinsic ones as d film E s film c = d d, e = e e (see e.g. Ref. 7 ) and using E s + c E E E s elastic compliances from Ref. [ 8 ] s =8.5 and s =-.8 - Pa -, we obtained d =-.4, and d =6. pm/v. The deconvolution was performed for d 5 =.5d for bulk and d 5 =.5d for ceramics, and the results are shown to be weakly dependent on d 5. 5
16 References.H. Ahn, W.W. Jung, and.k. Choi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 79 (5). Y. Cho,. Hashimoto, N. Odagawa, K. Tanaka, and Y. Hiranaga, Nanotechnology 7, 7 (6). D.B. Li, D.R. trachan, J. H. Ferris, D.A. Bonnell, J. Mat. Res., 95 (6). 4 X. Zhang, D. Xue and K. Kitamura, J. of Alloys and Compounds 449, 9 (8). 5 V.Ya. hur, E. hishkin, E. Rumyantsev, E. Nikolaeva, A. hur, R. Batchko, M. Fejer, K. Gallo,. Kurimura, K. Terabe, K. Kitamura, Ferroelectrics 4, (4). 6 A. Gruverman, B.J. Rodriguez, C. Dehoff, J.D. Waldrep, A.I. Kingon, R.J. Nemanich, and J.. Cross, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 89 (5). 7 K.. Wong, J.Y. Dai, X.Y. Zhao, and H.. Luo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 9, 697 (7). 8 A. Agronin, Y. Rosenwaks, and G. Rosenman, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 79 (6). 9 P. Paruch, T. Giamarchi, and J.-M. Triscone, Phys.Rev.Lett. 94, 976 (5).. Bühlmann, E. Colla, and P. Muralt, Phys. Rev. B 7, 4 (5). D. Dahan, M. Molotskii, G. Rosenman, and Y. Rosenwaks, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 59 (6). Jesse, H.N. Lee, and.v. Kalinin, Rev. ci. Instrum. 77, 77 (6). A.N. Morozovska,.V. vechnikov, E.A. Eliseev,. Jesse, B.J. Rodriguez, and.v. Kalinin. J. Appl. Phys., 48 (7). 4 A.L. Kholkin, A.L. Kholkin, I.K. Bdikin, D.A. Kiselev, V.V. hvartsman, and.h. Kim, J. of Electroceramics 9, 8 (7)
17 6 A. Kholkin, I.K. Bdikin, V.V. hvartsman, A. Orlova, D.A. Kiselev, A.A. Bogomolov, Mater. Res. oc. Proc. 88E, O7.6 (5). 7 F. Felten, G.A. chneider, J. Muñoz aldaña, and.v. Kalinin, J. Appl. Phys. 96, 56 (4). 8 D.A. crymgeour and V. Gopalan, Phys. Rev. B 7, 4 (5). 9 A.N. Morozovska,.V. vechnikov, E.A. Eliseev, B.J. Rodriguez,. Jesse, and.v. Kalinin. arxiv/7.46, submitted to PRB. M. Molotskii, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 9, p.64 ().V. Kalinin,. Jesse, B.J. Rodriguez, E.A. Eliseev, V. Gopalan, and A.N. Morozovska. Appl. Phys. Lett. 9, 95 (7). R. Landauer, J. Appl. Phys. 8, 7 (957)..V. Kalinin et al, submitted 4 B. A. trukov and A. P. Levanyuk, Physical Principles of Ferroelectric Phenomena in Crystals [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (98) 5 L.D. Landau and E.M. Lifshitz, Theory of Elasticity. Theoretical Physics, Vol. 7 (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 976). 6.V. Kalinin, E.A. Eliseev, and A.N. Morozovska, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 94 (6). 7 N. etter, D. Damjanovic, L. Eng, G. Fox,. Gevorgian,. Hong, A. Kingon, H. Kohlstedt, N.Y. Park, G.B. tephenson, I. tolitchnov, A.K. Taganstev, D.V. Taylor, T. Yamada, and. treiffer. J. Appl. Phys., 566 (6). 8 N. A. Pertsev, V. G. Kukhar, H. Kohlstedt, and R. Waser, Phys. Rev. B 67, 547 (). 7
Polarization Reversal by Tip of Scanning Probe Microscope in SBN
 IV Sino-Russian ASRTU Symposium on Advanced Materials and Processing Technology (2016), Volume 2016 Conference Paper Polarization Reversal by Tip of Scanning Probe Microscope in SBN E.A. Neradovskaya 1,
IV Sino-Russian ASRTU Symposium on Advanced Materials and Processing Technology (2016), Volume 2016 Conference Paper Polarization Reversal by Tip of Scanning Probe Microscope in SBN E.A. Neradovskaya 1,
Online publication date: 23 June 2010 PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [Shur, Vladimir][NEICON Consortium] On: 24 June 2010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 781557264] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in
This article was downloaded by: [Shur, Vladimir][NEICON Consortium] On: 24 June 2010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 781557264] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in
Piezoresponse Force Microscopy in Its Applications
 Application Note 083 Piezoresponse Force Microscopy in Its Applications Ferrroelectric domains imaging Hysteresis loops measurements Local ferroelectric behavior investigation Sergei Magonov, NT-MDT Development
Application Note 083 Piezoresponse Force Microscopy in Its Applications Ferrroelectric domains imaging Hysteresis loops measurements Local ferroelectric behavior investigation Sergei Magonov, NT-MDT Development
Supplementary Figures:
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Thermodynamics Study on the Decay Properties of Reversed Domains in LiNbO 3. Single Crystals
 DOI: 1.4172/221-6212.1178 Thermodynamics Study on the Decay Properties of Reversed Domains in LiNbO Single rystals Li LB 1,2*, Li GL 1, Kan Y 2, Lu XM 2 and Zhu JS 2 1 School of Physics and Engineering,
DOI: 1.4172/221-6212.1178 Thermodynamics Study on the Decay Properties of Reversed Domains in LiNbO Single rystals Li LB 1,2*, Li GL 1, Kan Y 2, Lu XM 2 and Zhu JS 2 1 School of Physics and Engineering,
Depolarization of a piezoelectric film under an alternating current field
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 054108 2007 Depolarization of a piezoelectric film under an alternating current field K. W. Kwok, a M. K. Cheung, H. L. W. Chan, and C. L. Choy Department of Applied Physics
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 101, 054108 2007 Depolarization of a piezoelectric film under an alternating current field K. W. Kwok, a M. K. Cheung, H. L. W. Chan, and C. L. Choy Department of Applied Physics
Newcastle University eprints
 Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Nanosecond Structural Visualization of the Reproducibility of Polarization Switching in Ferroelectrics
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 85: 165 173, 2006 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN 1058-4587 print / 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580601085842 Nanosecond Structural Visualization of the Reproducibility
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 85: 165 173, 2006 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN 1058-4587 print / 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580601085842 Nanosecond Structural Visualization of the Reproducibility
Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 902E 2006 Materials Research Society 0902-T06-09.1 Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale Alexei Grigoriev 1, Dal-Hyun Do 1, Dong Min Kim 1, Chang-Beom
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 902E 2006 Materials Research Society 0902-T06-09.1 Structural dynamics of PZT thin films at the nanoscale Alexei Grigoriev 1, Dal-Hyun Do 1, Dong Min Kim 1, Chang-Beom
More ferroelectrics discovered by switching spectroscopy. piezoresponse force microscopy?
 More ferroelectrics discovered by switching spectroscopy piezoresponse force microscopy? Hongchen Miao 1, Chi Tan 1, Xilong Zhou 1, Xiaoyong Wei, Faxin Li 1,3,a) 1 LTCS and College of Engineering, Peking
More ferroelectrics discovered by switching spectroscopy piezoresponse force microscopy? Hongchen Miao 1, Chi Tan 1, Xilong Zhou 1, Xiaoyong Wei, Faxin Li 1,3,a) 1 LTCS and College of Engineering, Peking
Piezoresponse force microscopy and recent
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Alexei Gruverman Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 1-1-2006 Piezoresponse force microscopy and recent
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Alexei Gruverman Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 1-1-2006 Piezoresponse force microscopy and recent
Vortex Ferroelectric Domains. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, NE
 Vortex Ferroelectric Domains A. Gruverman, 1 D. Wu, 2 H.-J. Fan, 3 I. Vrejoiu, 4 M. Alexe, 4 R. J. Harrison, 3 and J. F. Scott 3 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln,
Vortex Ferroelectric Domains A. Gruverman, 1 D. Wu, 2 H.-J. Fan, 3 I. Vrejoiu, 4 M. Alexe, 4 R. J. Harrison, 3 and J. F. Scott 3 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln,
Nanoscale polarization manipulation and imaging in ferroelectric Langmuir-Blodgett polymer films
 Nanoscale polarization manipulation and imaging in ferroelectric Langmuir-Blodgett polymer films Brian J. Rodriguez 1, Stephen Jesse 1, Sergei V. Kalinin 1, *, Jihee Kim 2, Stephen Ducharme 2, **, & V.
Nanoscale polarization manipulation and imaging in ferroelectric Langmuir-Blodgett polymer films Brian J. Rodriguez 1, Stephen Jesse 1, Sergei V. Kalinin 1, *, Jihee Kim 2, Stephen Ducharme 2, **, & V.
Statistical switching kinetics in ferroelectrics
 Statistical switching kinetics in ferroelectrics X.J. Lou Department of Materials Science and Engineering, National University of Singapore, 117574, Singapore Abstract: By assuming a more realistic nucleation
Statistical switching kinetics in ferroelectrics X.J. Lou Department of Materials Science and Engineering, National University of Singapore, 117574, Singapore Abstract: By assuming a more realistic nucleation
Domain Nucleation And Relaxation Kinetics In Ferroelectric Thin Films. Ramesh
 Domain Nucleation And Relaxation Kinetics In Ferroelectric Thin Films C. S. Ganpule a), V. Nagarajan, S. B. Ogale, A. L. Roytburd, E. D. Williams and R. Ramesh Materials Research Science and Engineering
Domain Nucleation And Relaxation Kinetics In Ferroelectric Thin Films C. S. Ganpule a), V. Nagarajan, S. B. Ogale, A. L. Roytburd, E. D. Williams and R. Ramesh Materials Research Science and Engineering
5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes
 5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes 5.1 New candidates for nanoelectronics: ferroelectric nanotubes In this chapter, one of the core elements for a complex building
5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes 5.1 New candidates for nanoelectronics: ferroelectric nanotubes In this chapter, one of the core elements for a complex building
Piezoelectric materials for MEMS applications Hiroshi Funakubo Tokyo Institute of Technology
 Piezoelectric materials for MEMS applications Hiroshi Funakubo Tokyo Institute of Technology MEMS Engineer Forum 2016/5/11 11:50-12:15 Content 1. Introduction 2. Processing 3. Materials Matter Content
Piezoelectric materials for MEMS applications Hiroshi Funakubo Tokyo Institute of Technology MEMS Engineer Forum 2016/5/11 11:50-12:15 Content 1. Introduction 2. Processing 3. Materials Matter Content
Epitaxial piezoelectric heterostructures for ultrasound micro-transducers
 15 th Korea-U.S. Forum on Nanotechnology Epitaxial piezoelectric heterostructures for ultrasound micro-transducers Seung-Hyub Baek Center for Electronic Materials Korea Institute of Science and Technology
15 th Korea-U.S. Forum on Nanotechnology Epitaxial piezoelectric heterostructures for ultrasound micro-transducers Seung-Hyub Baek Center for Electronic Materials Korea Institute of Science and Technology
High tunable dielectric response of Pb 0.87 Ba 0.1 La 0.02 (Zr 0.6 Sn 0.33 Ti 0.07 ) O 3 thin film
 Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, Volume 108, Issue 4, paper number 044107 High tunable dielectric response of Pb 0.87 Ba 0.1 La 0.02 (Zr 0.6 Sn 0.33 Ti 0.07 ) O 3 thin film T. M. Correia and Q. Zhang*
Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, Volume 108, Issue 4, paper number 044107 High tunable dielectric response of Pb 0.87 Ba 0.1 La 0.02 (Zr 0.6 Sn 0.33 Ti 0.07 ) O 3 thin film T. M. Correia and Q. Zhang*
Switching Current Study: Hysteresis Measurement of Ferroelectric Capacitors using Current-Voltage Measurement Method
 Chapter 7 Switching Current Study: Hysteresis Measurement of Ferroelectric Capacitors using Current-Voltage Measurement Method 7-1. Introduction Over the past few decades, various methods for obtaining
Chapter 7 Switching Current Study: Hysteresis Measurement of Ferroelectric Capacitors using Current-Voltage Measurement Method 7-1. Introduction Over the past few decades, various methods for obtaining
Polarization Control of Electron Tunneling into Ferroelectric Surfaces
 Submitted: Science Date: 01/20/2009 Revised: 05/07/2009 Polarization Control of Electron Tunneling into Ferroelectric Surfaces Peter Maksymovych* 1, Stephen Jesse 1, Pu Yu 2, Ramamoorthy Ramesh 2, Arthur
Submitted: Science Date: 01/20/2009 Revised: 05/07/2009 Polarization Control of Electron Tunneling into Ferroelectric Surfaces Peter Maksymovych* 1, Stephen Jesse 1, Pu Yu 2, Ramamoorthy Ramesh 2, Arthur
Characteristics of Lead Free Ferroelectric Thin Films Consisted of (Na 0.5 Bi 0.5 )TiO 3 and Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-04-24 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 684, pp 307-311 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.684.307 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Characteristics of Lead Free Ferroelectric
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2013-04-24 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vol. 684, pp 307-311 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.684.307 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Characteristics of Lead Free Ferroelectric
Effects of niobium doping on the piezoelectric properties of sol gel-derived lead zirconate titanate films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 95, NUMBER 3 1 FEBRUARY 2004 Effects of niobium doping on the piezoelectric properties of sol gel-derived lead zirconate titanate films K. W. Kwok, a) R. C. W. Tsang,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 95, NUMBER 3 1 FEBRUARY 2004 Effects of niobium doping on the piezoelectric properties of sol gel-derived lead zirconate titanate films K. W. Kwok, a) R. C. W. Tsang,
Supplementary Information for. Effect of Ag nanoparticle concentration on the electrical and
 Supplementary Information for Effect of Ag nanoparticle concentration on the electrical and ferroelectric properties of Ag/P(VDF-TrFE) composite films Haemin Paik 1,2, Yoon-Young Choi 3, Seungbum Hong
Supplementary Information for Effect of Ag nanoparticle concentration on the electrical and ferroelectric properties of Ag/P(VDF-TrFE) composite films Haemin Paik 1,2, Yoon-Young Choi 3, Seungbum Hong
Imry-Ma disordered state induced by defects of "random local anisotropy" type in the system with O(n) symmetry
 1 Imry-Ma disordered state induced by defects of "random local anisotropy" type in the system with O(n) symmetry A.A. Berzin 1, A.I. Morosov 2, and A.S. Sigov 1 1 Moscow Technological University (MIREA),
1 Imry-Ma disordered state induced by defects of "random local anisotropy" type in the system with O(n) symmetry A.A. Berzin 1, A.I. Morosov 2, and A.S. Sigov 1 1 Moscow Technological University (MIREA),
Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates.
 Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates. Abstract S. Dunn and R. W. Whatmore Building 70, Nanotechnology,
Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates. Abstract S. Dunn and R. W. Whatmore Building 70, Nanotechnology,
Electrochemical Strain Microscopy of Silica Glasses
 Electrochemical Strain Microscopy of Silica Glasses R. Proksch 1 Asylum Research, an Oxford Instruments Company, 6310 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, CA 93117 USA Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM)
Electrochemical Strain Microscopy of Silica Glasses R. Proksch 1 Asylum Research, an Oxford Instruments Company, 6310 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, CA 93117 USA Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM)
Effect of interfacial dislocations on ferroelectric phase stability and domain morphology in a thin film a phase-field model
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 4 15 AUGUST 2003 Effect of interfacial dislocations on ferroelectric phase stability and domain morphology in a thin film a phase-field model S. Y. Hu, Y. L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 4 15 AUGUST 2003 Effect of interfacial dislocations on ferroelectric phase stability and domain morphology in a thin film a phase-field model S. Y. Hu, Y. L.
Micron 43 (2012) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Micron. j our na l ho me p age:
 Micron 43 (2012) 1121 1126 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Micron j our na l ho me p age: www.elsevier.com/locate/micron Direct observation of ferroelectric domain switching in varying
Micron 43 (2012) 1121 1126 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Micron j our na l ho me p age: www.elsevier.com/locate/micron Direct observation of ferroelectric domain switching in varying
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field
 Lecture 7-1 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field - Electrostriction The electrostrictive effect is a quadratic dependence of strain or stress on the polarization P
Lecture 7-1 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field - Electrostriction The electrostrictive effect is a quadratic dependence of strain or stress on the polarization P
Virtual piezoforce microscopy of polycrystalline ferroelectric films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 064105 2006 Virtual piezoforce microscopy of polycrystalline ferroelectric films R. Edwin García a School of Materials Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 064105 2006 Virtual piezoforce microscopy of polycrystalline ferroelectric films R. Edwin García a School of Materials Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
NANOSCALE PHENOMENA IN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS
 NANOSCALE PHENOMENA IN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS NANOSCALEPHENOMENAIN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS edited by Seungbum Hong Samsung Advanced Institute oftechnology, Korea SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, LLC
NANOSCALE PHENOMENA IN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS NANOSCALEPHENOMENAIN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS edited by Seungbum Hong Samsung Advanced Institute oftechnology, Korea SPRINGER-SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, LLC
APPENDIX A Landau Free-Energy Coefficients
 APPENDIX A Landau Free-Energy Coefficients Long-Qing Chen Department of Materials Science and Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania 180 USA The thermodynamics of
APPENDIX A Landau Free-Energy Coefficients Long-Qing Chen Department of Materials Science and Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania 180 USA The thermodynamics of
Contrast Mechanism for Visualization of Ferroelectric Domains with Scanning Force Microscopy
 Ferroelectrics, 334:29 34, 2006 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190600689654 Contrast Mechanism for Visualization of Ferroelectric Domains
Ferroelectrics, 334:29 34, 2006 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190600689654 Contrast Mechanism for Visualization of Ferroelectric Domains
PHYSICAL BASIS OF THE DOMAIN ENGINEERING IN THE BULK FERROELECTRICS
 Ferroelectrics, V. 221, pp. 157-167 (1999) PHYSICAL BASIS OF THE DOMAIN ENGINEERING IN THE BULK FERROELECTRICS VLADIMIR SHUR, a EVGENII RUMYANTSEV, a ROBERT BATCHKO, b GREGORY MILLER, b MARTIN FEJER b
Ferroelectrics, V. 221, pp. 157-167 (1999) PHYSICAL BASIS OF THE DOMAIN ENGINEERING IN THE BULK FERROELECTRICS VLADIMIR SHUR, a EVGENII RUMYANTSEV, a ROBERT BATCHKO, b GREGORY MILLER, b MARTIN FEJER b
Deepam Maurya 1*, Yuan Zhou 1, Yaojin Wang 2, Yongke Yan 1, Jiefang Li 2, Dwight Viehland 2, and Shashank Priya 1*
 Giant strain with ultra-low hysteresis and high temperature stability in grain oriented lead-free K0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BaTiO3-Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 piezoelectric materials: supplementary information Deepam Maurya 1*,
Giant strain with ultra-low hysteresis and high temperature stability in grain oriented lead-free K0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BaTiO3-Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 piezoelectric materials: supplementary information Deepam Maurya 1*,
Polarization switching and patterning in self-assembled peptide tubular structures
 Polarization switching and patterning in self-assembled peptide tubular structures Igor Bdikin, Vladimir Bystrov, Ivonne Delgadillo, José Gracio, Svitlana Kopyl et al. Citation: J. Appl. Phys. 111, 074104
Polarization switching and patterning in self-assembled peptide tubular structures Igor Bdikin, Vladimir Bystrov, Ivonne Delgadillo, José Gracio, Svitlana Kopyl et al. Citation: J. Appl. Phys. 111, 074104
Domain-size dependence of piezoelectric properties of ferroelectrics
 Domain-size dependence of piezoelectric properties of ferroelectrics Rajeev Ahluwalia, 1 Turab Lookman, 1 Avadh Saxena, 1 and Wenwu Cao 2 1 Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos,
Domain-size dependence of piezoelectric properties of ferroelectrics Rajeev Ahluwalia, 1 Turab Lookman, 1 Avadh Saxena, 1 and Wenwu Cao 2 1 Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos,
Processing and characterization of ferroelectric thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition
 ELECTROCERAMICS IX, Cherbourg, 2004. Symp. D: Pyro, Piezo, Ferroelectrics: B1-P-578 Processing and characterization of ferroelectric thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition F. Craciun a,*, M. Dinescu
ELECTROCERAMICS IX, Cherbourg, 2004. Symp. D: Pyro, Piezo, Ferroelectrics: B1-P-578 Processing and characterization of ferroelectric thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition F. Craciun a,*, M. Dinescu
Micro-Brilouin scattering study of field cooling effects on ferroelectric relaxor PZN-9%PT single crystals
 Micro-Brilouin scattering study of field cooling effects on ferroelectric relaxor PZN-9%PT single crystals Jae-Hyeon Ko 1 *, Do Han Kim 2, Seiji Kojima 2, D. C. Feng 3 1 Department of Physics, Hallym University,
Micro-Brilouin scattering study of field cooling effects on ferroelectric relaxor PZN-9%PT single crystals Jae-Hyeon Ko 1 *, Do Han Kim 2, Seiji Kojima 2, D. C. Feng 3 1 Department of Physics, Hallym University,
Monte Carlo Simulation of Ferroelectric Domain Structure: Electrostatic and Elastic Strain Energy Contributions
 Monte Carlo Simulation of Ferroelectric Domain Structure: Electrostatic and Elastic Strain Energy Contributions B.G. Potter, Jr., B.A. Tuttle, and V. Tikare Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, NM
Monte Carlo Simulation of Ferroelectric Domain Structure: Electrostatic and Elastic Strain Energy Contributions B.G. Potter, Jr., B.A. Tuttle, and V. Tikare Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque, NM
Domain switching and electromechanical properties of pulse poled Pb Zn 1Õ3 Nb 2Õ3 O 3 PbTiO 3 crystals
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 89, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 2001 Domain switching and electromechanical properties of pulse poled Pb Zn 1Õ3 Nb 2Õ3 O 3 PbTiO 3 crystals Hanxing Yu, Venkat Gopalan, Jürgen Sindel,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 89, NUMBER 1 1 JANUARY 2001 Domain switching and electromechanical properties of pulse poled Pb Zn 1Õ3 Nb 2Õ3 O 3 PbTiO 3 crystals Hanxing Yu, Venkat Gopalan, Jürgen Sindel,
A Nanoscale Shape Memory Oxide
 A Nanoscale Shape Memory Oxide Jinxing Zhang 1,2*, Xiaoxing Ke 3*, Gaoyang Gou 4, Jan Seidel 2,5, Bin Xiang 6,9, Pu Yu 2,7, Wen-I Liang 8, Andrew M. Minor 9,10, Ying-hao Chu 8, Gustaaf Van Tendeloo 3,
A Nanoscale Shape Memory Oxide Jinxing Zhang 1,2*, Xiaoxing Ke 3*, Gaoyang Gou 4, Jan Seidel 2,5, Bin Xiang 6,9, Pu Yu 2,7, Wen-I Liang 8, Andrew M. Minor 9,10, Ying-hao Chu 8, Gustaaf Van Tendeloo 3,
A Hydrothermally Deposited Epitaxial PbTiO 3 Thin Film on SrRuO 3 Bottom Electrode for the Ferroelectric Ultra-High Density Storage Medium
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 64: 247 257, 2004 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580490894645 A Hydrothermally Deposited Epitaxial PbTiO 3 Thin Film
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 64: 247 257, 2004 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580490894645 A Hydrothermally Deposited Epitaxial PbTiO 3 Thin Film
Ferroelectric (FE) thin films and nanostructures continue
 Finite Curvature-Mediated Ferroelectricity Stephen S. Nonnenmann, Oren D. Leaffer, Eric M. Gallo, Michael T. Coster, and Jonathan E. Spanier* pubs.acs.org/nanolett Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
Finite Curvature-Mediated Ferroelectricity Stephen S. Nonnenmann, Oren D. Leaffer, Eric M. Gallo, Michael T. Coster, and Jonathan E. Spanier* pubs.acs.org/nanolett Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
4. Electric scanning probe imaging and modification of ferroelectric surfaces
 4. Electric scanning probe imaging and modification of ferroelectric surfaces Sergei V. Kalinin * and Dawn A. Bonnell University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 1914 * Condensed Matter Sciences Division,
4. Electric scanning probe imaging and modification of ferroelectric surfaces Sergei V. Kalinin * and Dawn A. Bonnell University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 1914 * Condensed Matter Sciences Division,
Laser Interferometric Displacement Measurements of Multi-Layer Actuators and PZT Ceramics
 Ferroelectrics, 320:161 169, 2005 Copyright Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190590967026 Laser Interferometric Displacement Measurements of Multi-Layer
Ferroelectrics, 320:161 169, 2005 Copyright Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190590967026 Laser Interferometric Displacement Measurements of Multi-Layer
Control of periodic ferroelastic domains in ferroelectric Pb1-xSrxTiO3 thin films for nanoscaled
 University of Groningen Control of periodic ferroelastic domains in ferroelectric Pb1-xSrxTiO3 thin films for nanoscaled memory devices Nesterov, Oleksiy IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
University of Groningen Control of periodic ferroelastic domains in ferroelectric Pb1-xSrxTiO3 thin films for nanoscaled memory devices Nesterov, Oleksiy IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
Quantitative Measurements of Electromechanical Response with a Metrological Atomic Force Microscope
 Quantitative Measurements of Electromechanical Response with a Metrological Atomic Force Microscope Aleksander Labuda and Roger Proksch Asylum Research an Oxford Instruments Company, Santa Barbara, CA,
Quantitative Measurements of Electromechanical Response with a Metrological Atomic Force Microscope Aleksander Labuda and Roger Proksch Asylum Research an Oxford Instruments Company, Santa Barbara, CA,
Stabilizing the forming process in unipolar resistance switching
 Stabilizing the forming process in unipolar resistance switching using an improved compliance current limiter S. B. Lee, 1 S. H. Chang, 1 H. K. Yoo, 1 and B. S. Kang 2,a) 1 ReCFI, Department of Physics
Stabilizing the forming process in unipolar resistance switching using an improved compliance current limiter S. B. Lee, 1 S. H. Chang, 1 H. K. Yoo, 1 and B. S. Kang 2,a) 1 ReCFI, Department of Physics
PHASE-FIELD SIMULATION OF DOMAIN STRUCTURE EVOLUTION IN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 652 2001 Materials Research Society PHASE-FIELD SIMULATION OF DOMAIN STRUCTURE EVOLUTION IN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS Y. L. Li, S. Y. Hu, Z. K. Liu, and L. Q. Chen Department
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 652 2001 Materials Research Society PHASE-FIELD SIMULATION OF DOMAIN STRUCTURE EVOLUTION IN FERROELECTRIC THIN FILMS Y. L. Li, S. Y. Hu, Z. K. Liu, and L. Q. Chen Department
Supporting Information for: Flexible Energy Conversion
 Supporting Inormation or: Piezoelectric Nanoribbons Printed onto Rubber or Flexible Energy Conversion Yi Qi, Noah T. Jaeris, Kenneth Lyons, Jr., Christine M. Lee, Habib Ahmad, Michael C. McAlpine *, Department
Supporting Inormation or: Piezoelectric Nanoribbons Printed onto Rubber or Flexible Energy Conversion Yi Qi, Noah T. Jaeris, Kenneth Lyons, Jr., Christine M. Lee, Habib Ahmad, Michael C. McAlpine *, Department
Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine Ukraine 88000
 Supplementary Material: CuInP S 6 - Room emperature Layered Ferroelectric A. Belianinov, 1 Q. He, 1 A. Dziaugys, P. Maksymovych, 1 E. Eliseev, a A. Borisevich, 1 A. Morozovska, J. Banys, Y. Vysochanskii,
Supplementary Material: CuInP S 6 - Room emperature Layered Ferroelectric A. Belianinov, 1 Q. He, 1 A. Dziaugys, P. Maksymovych, 1 E. Eliseev, a A. Borisevich, 1 A. Morozovska, J. Banys, Y. Vysochanskii,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Structural Evidence for Strong Coupling between Polarization Rotation and Lattice Strain in Monoclinic Relaxor Ferroelectrics Hui Liu, Jun Chen,*, Longlong Fan, Yang Ren, Lei Hu,
Supporting Information Structural Evidence for Strong Coupling between Polarization Rotation and Lattice Strain in Monoclinic Relaxor Ferroelectrics Hui Liu, Jun Chen,*, Longlong Fan, Yang Ren, Lei Hu,
Ferroelectricity in Strain-Free SrTiO 3 Thin Films
 Ferroelectricity in Strain-Free SrTiO 3 Thin Films H. W. Jang, 1 A. Kumar, 2 S. Denev, 2 M. D. Biegalski, 3 P. Maksymovych, 3 C.W. Bark, 1 C. T. Nelson, 4 C. M. Folkman, 1 S. H. Baek, 1 N. Balke, 3 C.
Ferroelectricity in Strain-Free SrTiO 3 Thin Films H. W. Jang, 1 A. Kumar, 2 S. Denev, 2 M. D. Biegalski, 3 P. Maksymovych, 3 C.W. Bark, 1 C. T. Nelson, 4 C. M. Folkman, 1 S. H. Baek, 1 N. Balke, 3 C.
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 19 Mar 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 19 Mar 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 19 Mar 2002](/thumbs/84/89168837.jpg) Domain wall creep in epitaxial ferroelectric Pb(Zr 0.2 Ti 0.8 )O 3 thin films arxiv:cond-mat/0203381v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 19 Mar 2002 T. Tybell, 1,2 P. Paruch, 1 T. Giamarchi, 3 and J.-M. Triscone 1 1 DPMC,
Domain wall creep in epitaxial ferroelectric Pb(Zr 0.2 Ti 0.8 )O 3 thin films arxiv:cond-mat/0203381v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 19 Mar 2002 T. Tybell, 1,2 P. Paruch, 1 T. Giamarchi, 3 and J.-M. Triscone 1 1 DPMC,
Investigation of microstructure and piezoelectric properties of Zr- and Smdoped PbTiO 3 nanostructured thin films derived by sol gel technology
 Sensors and Actuators B 109 (2005) 97 101 Investigation of microstructure and piezoelectric properties of Zr- and Smdoped PbTiO 3 nanostructured thin films derived by sol gel technology Arturas Ulcinas
Sensors and Actuators B 109 (2005) 97 101 Investigation of microstructure and piezoelectric properties of Zr- and Smdoped PbTiO 3 nanostructured thin films derived by sol gel technology Arturas Ulcinas
Mechanism of Polarization Fatigue in BiFeO 3 : the Role of Schottky Barrier
 Mechanism of Polarization Fatigue in BiFeO 3 : the Role of Schottky Barrier Yang Zhou, 1 Xi Zou, 1 Lu You, 1 Rui Guo, 1 Zhi Shiuh Lim, 1 Lang Chen, 1 Guoliang Yuan, 2,a) and Junling Wang 1,b) 1 School
Mechanism of Polarization Fatigue in BiFeO 3 : the Role of Schottky Barrier Yang Zhou, 1 Xi Zou, 1 Lu You, 1 Rui Guo, 1 Zhi Shiuh Lim, 1 Lang Chen, 1 Guoliang Yuan, 2,a) and Junling Wang 1,b) 1 School
Formation of Self-Organized Nanodomain Patterns During Spontaneous Backswitching in Lithium Niobate
 Ferroelectrics, 2001, Vol. 253, pp. 105-114 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 2001 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license under
Ferroelectrics, 2001, Vol. 253, pp. 105-114 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 2001 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license under
Self-consistent theory of nanodomain formation on non-polar surfaces of ferroelectrics
 To be submitted to Phys.Rev.B. Self-consistent eory of nanodomain formation on non-polar surfaces of ferroelectrics Anna N. Morozovsa 1*, Anton Ievlev, Vyacheslav V. Obuhovsii 3, Yevhen Fomichov 4, Olesandr
To be submitted to Phys.Rev.B. Self-consistent eory of nanodomain formation on non-polar surfaces of ferroelectrics Anna N. Morozovsa 1*, Anton Ievlev, Vyacheslav V. Obuhovsii 3, Yevhen Fomichov 4, Olesandr
Electrical Characterization with SPM Application Modules
 Electrical Characterization with SPM Application Modules Metrology, Characterization, Failure Analysis: Data Storage Magnetoresistive (MR) read-write heads Semiconductor Transistors Interconnect Ferroelectric
Electrical Characterization with SPM Application Modules Metrology, Characterization, Failure Analysis: Data Storage Magnetoresistive (MR) read-write heads Semiconductor Transistors Interconnect Ferroelectric
Nanometer-Scale Materials Contrast Imaging with a Near-Field Microwave Microscope
 Nanometer-Scale Materials Contrast Imaging with a Near-Field Microwave Microscope Atif Imtiaz 1 and Steven M. Anlage Center for Superconductivity Research, Department of Physics, University of Maryland,
Nanometer-Scale Materials Contrast Imaging with a Near-Field Microwave Microscope Atif Imtiaz 1 and Steven M. Anlage Center for Superconductivity Research, Department of Physics, University of Maryland,
The anomalies of the properties of nanomaterials related to the distribution of the grain sizes
 The anomalies of the properties of nanomaterials related to the distribution of the grain sizes M.D.Glinchuk, P.I.Bykov Institute for Problems of Materials Science, NASc of Ukraine, Kjijanovskogo 3, 368
The anomalies of the properties of nanomaterials related to the distribution of the grain sizes M.D.Glinchuk, P.I.Bykov Institute for Problems of Materials Science, NASc of Ukraine, Kjijanovskogo 3, 368
I. INTRODUCTION II. SAMPLE PREPARATION JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER 2002 Longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients of lead zirconate titanateõvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene composites with different
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 5 1 SEPTEMBER 2002 Longitudinal and transverse piezoelectric coefficients of lead zirconate titanateõvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene composites with different
Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 29 Milan Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting M. Guizzetti* 1, V. Ferrari 1, D. Marioli 1 and T. Zawada 2 1 Dept.
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 29 Milan Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting M. Guizzetti* 1, V. Ferrari 1, D. Marioli 1 and T. Zawada 2 1 Dept.
Using the surface spontaneous depolarization field of ferroelectrics to direct the assembly of virus particles
 Appl. Phys. Lett. Vol 85, Issue 16, 3537 (2004) Using the surface spontaneous depolarization field of ferroelectrics to direct the assembly of virus particles Working Title: Directed assembly of biological
Appl. Phys. Lett. Vol 85, Issue 16, 3537 (2004) Using the surface spontaneous depolarization field of ferroelectrics to direct the assembly of virus particles Working Title: Directed assembly of biological
Spectro-microscopic photoemission evidence of surface dissociation and charge uncompensated areas in Pb(Zr,Ti)O 3 (001) layers
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information - Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. Spectro-microscopic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information - Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. Spectro-microscopic
ACOUSTIC EMISSION MEASUREMENTS ON PIEZOELECTRIC/ FERROELECTRIC MATERIALS
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION MEASUREMENTS ON PIEZOELECTRIC/ FERROELECTRIC MATERIALS HIDEAKI ABURATANI Kitakyushu National College of Technology, Kokura-minami, Kitakyushu, Fukuoka, Japan Abstract Ferroelectric materials
ACOUSTIC EMISSION MEASUREMENTS ON PIEZOELECTRIC/ FERROELECTRIC MATERIALS HIDEAKI ABURATANI Kitakyushu National College of Technology, Kokura-minami, Kitakyushu, Fukuoka, Japan Abstract Ferroelectric materials
ONR Grant No. N C Fabrication of Electrostrictive Ceramic Rings for Navy Sonar Transducers
 > ONR Grant No. N00014-93-C-0231 Fabrication of Electrostrictive Ceramic Rings for Navy Sonar Transducers Final Report Period September 19,1993-March 19,1994 Sponsored by Office of Naval Research (ONR)
> ONR Grant No. N00014-93-C-0231 Fabrication of Electrostrictive Ceramic Rings for Navy Sonar Transducers Final Report Period September 19,1993-March 19,1994 Sponsored by Office of Naval Research (ONR)
Online publication date: 23 June 2010 PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [Shur, Vladimir][NEICON Consortium] On: 24 June 2010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 781557264] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in
This article was downloaded by: [Shur, Vladimir][NEICON Consortium] On: 24 June 2010 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 781557264] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Large Electrocaloric Effect in Relaxor Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric Lanthanum Doped Lead Zirconate Titanate Ceramics Biao Lu, Peilian Li, Zhenghua Tang, Yingbang Yao, Xingsen
Supplementary Information Large Electrocaloric Effect in Relaxor Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric Lanthanum Doped Lead Zirconate Titanate Ceramics Biao Lu, Peilian Li, Zhenghua Tang, Yingbang Yao, Xingsen
On Domain Wall Broadening in Ferroelectric Lithium Niobate and Tantalate
 Page 277, AIP Conference Proceedings, Fundamental Physics of Ferroelectrics 2002. On Domain Wall Broadening in Ferroelectric Lithium Niobate and Tantalate Sungwon Kim*, B. Steiner, A. Gruverman, V. Gopalan*
Page 277, AIP Conference Proceedings, Fundamental Physics of Ferroelectrics 2002. On Domain Wall Broadening in Ferroelectric Lithium Niobate and Tantalate Sungwon Kim*, B. Steiner, A. Gruverman, V. Gopalan*
Scaling behaviors of RESET voltages and currents in unipolar
 Scaling behaviors of RESET voltages and currents in unipolar resistance switching S. B. Lee, 1 S. C. Chae, 1 S. H. Chang, 1 J. S. Lee, 2 S. Seo, 3 B. Kahng, 2 and T. W. Noh 1,a) 1 ReCOE & FPRD, Department
Scaling behaviors of RESET voltages and currents in unipolar resistance switching S. B. Lee, 1 S. C. Chae, 1 S. H. Chang, 1 J. S. Lee, 2 S. Seo, 3 B. Kahng, 2 and T. W. Noh 1,a) 1 ReCOE & FPRD, Department
Chapter 12. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Chapter 12 Nanometrology Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands in relation to a meter and sub divisions of meter. Nanometrology
Generalized continuum theory for ferroelectric thin films
 Generalized continuum theory for ferroelectric thin films Tianquan Lü* and Wenwu Cao Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, 83 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Generalized continuum theory for ferroelectric thin films Tianquan Lü* and Wenwu Cao Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, 83 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
Solid State Physics (condensed matter): FERROELECTRICS
 Solid State Physics (condensed matter): FERROELECTRICS Prof. Igor Ostrovskii The University of Mississippi Department of Physics and Astronomy Oxford, UM: May, 2012 1 People: Solid State Physics Condensed
Solid State Physics (condensed matter): FERROELECTRICS Prof. Igor Ostrovskii The University of Mississippi Department of Physics and Astronomy Oxford, UM: May, 2012 1 People: Solid State Physics Condensed
Mesoscopic harmonic mapping of electromechanical response in a relaxor ferroelectric
 Mesoscopic harmonic mapping of electromechanical response in a relaxor ferroelectric Rama K. Vasudevan, 1 Shujun Zhang, 2 Jilai Ding, 3 M. Baris Okatan, 1 Stephen Jesse, 1 Sergei V. Kalinin, 1 and Nazanin
Mesoscopic harmonic mapping of electromechanical response in a relaxor ferroelectric Rama K. Vasudevan, 1 Shujun Zhang, 2 Jilai Ding, 3 M. Baris Okatan, 1 Stephen Jesse, 1 Sergei V. Kalinin, 1 and Nazanin
From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view
 From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view Pablo Aguado-Puente Javier Junquera Ferroelectricity: Basic definitions Existence
From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view Pablo Aguado-Puente Javier Junquera Ferroelectricity: Basic definitions Existence
Accumulation of charged defects at. local and bulk properties of
 Accumulation of charged defects at domain walls and its implication to local and bulk properties of polycrystalline lli BiFeO 3 Tadej Rojac Andreja Bencan, Hana Ursic, Bostjan Jancar, Gasper Tavcar, Maja
Accumulation of charged defects at domain walls and its implication to local and bulk properties of polycrystalline lli BiFeO 3 Tadej Rojac Andreja Bencan, Hana Ursic, Bostjan Jancar, Gasper Tavcar, Maja
Piezoelectric properties of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 thin films annealed in different atmospheres
 Materials Research Bulletin 42 (2007) 967 974 www.elsevier.com/locate/matresbu Piezoelectric properties of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 thin films annealed in different atmospheres A.Z. Simões *, C.S. Riccardi, A.H.M.
Materials Research Bulletin 42 (2007) 967 974 www.elsevier.com/locate/matresbu Piezoelectric properties of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 thin films annealed in different atmospheres A.Z. Simões *, C.S. Riccardi, A.H.M.
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light. Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film
 Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Scanning capacitance spectroscopy of an Al x Ga 1Àx NÕGaN heterostructure field-effect transistor structure: Analysis of probe tip effects
 Scanning capacitance spectroscopy of an Al x Ga 1Àx NÕGaN heterostructure field-effect transistor structure: Analysis of probe tip effects D. M. Schaadt and E. T. Yu a) Department of Electrical and Computer
Scanning capacitance spectroscopy of an Al x Ga 1Àx NÕGaN heterostructure field-effect transistor structure: Analysis of probe tip effects D. M. Schaadt and E. T. Yu a) Department of Electrical and Computer
An investigation of magnetic reversal in submicron-scale Co dots using first order reversal curve diagrams
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 85, NUMBER 9 1 MAY 1999 An investigation of magnetic reversal in submicron-scale Co dots using first order reversal curve diagrams Chris Pike a) Department of Geology,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 85, NUMBER 9 1 MAY 1999 An investigation of magnetic reversal in submicron-scale Co dots using first order reversal curve diagrams Chris Pike a) Department of Geology,
3rd International Symposium on Instrumentation Science and Technology
 Measurement of Longitudinal Piezoelectric Coefficients (d 33 of Pb(Zr 0.50,Ti 0.50 O 3 Thin Films with Atomic Force Microscopy LIU Meng-wei a, DONG Wei-jie b, TONG Jian-hua a, WANG Jing b, CUI Yan a, CUI
Measurement of Longitudinal Piezoelectric Coefficients (d 33 of Pb(Zr 0.50,Ti 0.50 O 3 Thin Films with Atomic Force Microscopy LIU Meng-wei a, DONG Wei-jie b, TONG Jian-hua a, WANG Jing b, CUI Yan a, CUI
G. Ravichandran Aeronautics & Mechanical Engineering Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories California Institute of Technology
 Multi-Disciplinary University Initiative Army Research Office Engineering Microstructural Complexity in Ferroelectric Devices Mechanical Characterization G. Ravichandran Aeronautics & Mechanical Engineering
Multi-Disciplinary University Initiative Army Research Office Engineering Microstructural Complexity in Ferroelectric Devices Mechanical Characterization G. Ravichandran Aeronautics & Mechanical Engineering
Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5
 Preamble In recent years bismuth-based, layer-structured perovskites such as SrBi 2 Nb 2 O 9 (SBN) and SrBi 2 Ta 2 O 9 (SBT) have been investigated extensively, because of their potential use in ferroelectric
Preamble In recent years bismuth-based, layer-structured perovskites such as SrBi 2 Nb 2 O 9 (SBN) and SrBi 2 Ta 2 O 9 (SBT) have been investigated extensively, because of their potential use in ferroelectric
Recent Achievements in Domain Engineering in Lithium Niobate and Lithium Tantalate
 Ferroelectrics, 2001, Vol. 257, pp. 191-202 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 2001 Taylor & Francis Recent Achievements in Domain Engineering in Lithium
Ferroelectrics, 2001, Vol. 257, pp. 191-202 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 2001 Taylor & Francis Recent Achievements in Domain Engineering in Lithium
Equilibrium orientation of an ellipsoidal particle inside a dielectric medium with a finite electric conductivity in the external electric field
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 71, 056611 005 Equilibrium orientation of an ellipsoidal particle inside a dielectric medium with a finite electric conductivity in the external electric field Yu. Dolinsky* and T. Elperin
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 71, 056611 005 Equilibrium orientation of an ellipsoidal particle inside a dielectric medium with a finite electric conductivity in the external electric field Yu. Dolinsky* and T. Elperin
Piezoelectric Composites as Bender Actuators
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 71: 221 232, 2005 Copyright Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN 1058-4587 print / 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580590964673 Piezoelectric Composites as Bender Actuators Karla Mossi,
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 71: 221 232, 2005 Copyright Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN 1058-4587 print / 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580590964673 Piezoelectric Composites as Bender Actuators Karla Mossi,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
6th NDT in Progress Lamb waves in an anisotropic plate of a single crystal silicon wafer
 6th NDT in Progress 2011 International Workshop of NDT Experts, Prague, 10-12 Oct 2011 Lamb waves in an anisotropic plate of a single crystal silicon wafer Young-Kyu PARK 1, Young H. KIM 1 1 Applied Acoustics
6th NDT in Progress 2011 International Workshop of NDT Experts, Prague, 10-12 Oct 2011 Lamb waves in an anisotropic plate of a single crystal silicon wafer Young-Kyu PARK 1, Young H. KIM 1 1 Applied Acoustics
Electric Field- and Temperature-Induced Phase Transitions in High-Strain Relaxor- Based Ferroelectric Pb(Mg1 /3Nb2/3)1 - xtixo3 Single Crystals
 Electric Field- and Temperature-Induced Phase Transitions in High-Strain Relaxor- Based Ferroelectric Pb(Mg1 /3Nb2/3)1 - xtixo3 Single Crystals Authors: R. R. Chien, V. Hugo Schmidt, C.-S. Tu, F.-T. Wang,
Electric Field- and Temperature-Induced Phase Transitions in High-Strain Relaxor- Based Ferroelectric Pb(Mg1 /3Nb2/3)1 - xtixo3 Single Crystals Authors: R. R. Chien, V. Hugo Schmidt, C.-S. Tu, F.-T. Wang,
Chapter 10. Nanometrology. Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Chapter 10 Nanometrology Oxford University Press 2013. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Nanometrology is the science of measurement at the nanoscale level. Figure illustrates where nanoscale stands
Interaction of Stern layer and domain structure on photochemistry of lead-zirconate-titanate.
 Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Volume 42, Number 6, 21 March 2009, 065408 Interaction of Stern layer and domain structure on photochemistry of lead-zirconate-titanate. P M Jones and S Dunn Bld.
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Volume 42, Number 6, 21 March 2009, 065408 Interaction of Stern layer and domain structure on photochemistry of lead-zirconate-titanate. P M Jones and S Dunn Bld.
Ferroelectric domain and surface nano-engineering of a near-stoichiometric LiNbO 3 single crystal
 Ferroelectric domain and surface nano-engineering of a near-stoichiometric LiNbO 3 single crystal K. Terabe*, M. Nakamura, S. Takekawa, and K. Kitamura, National Institute for Materials Science, Japan;
Ferroelectric domain and surface nano-engineering of a near-stoichiometric LiNbO 3 single crystal K. Terabe*, M. Nakamura, S. Takekawa, and K. Kitamura, National Institute for Materials Science, Japan;
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Leakage Current-Voltage Characteristics of Ferroelectric Thin Film Capacitors
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 38, No. 6, June 2001, pp. 723 728 Leakage Current-Voltage Characteristics of Ferroelectric Thin Film Capacitors Kwangbae Lee and Byung Roh Rhee Department of
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 38, No. 6, June 2001, pp. 723 728 Leakage Current-Voltage Characteristics of Ferroelectric Thin Film Capacitors Kwangbae Lee and Byung Roh Rhee Department of
Acoustic study of nano-crystal embedded PbO P 2 O 5 glass
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 9, No. 4, August 6, pp. 357 363. Indian Academy of Sciences. Acoustic study of nano-crystal embedded PbO P O 5 glass SUDIP K BATABYAL, A PAUL, P ROYCHOUDHURY and C BASU* Department
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 9, No. 4, August 6, pp. 357 363. Indian Academy of Sciences. Acoustic study of nano-crystal embedded PbO P O 5 glass SUDIP K BATABYAL, A PAUL, P ROYCHOUDHURY and C BASU* Department
Direct Observation of Capacitor Switching Using Planar Electrodes
 www.materialsviews.com Direct Observation of Capacitor Switching Using Planar Electrodes www.afm-journal.de By Nina Balke, * Martin Gajek, Alexander K. Tagantsev, Lane W. Martin, Ying-Hao Chu, Ramamoorthy
www.materialsviews.com Direct Observation of Capacitor Switching Using Planar Electrodes www.afm-journal.de By Nina Balke, * Martin Gajek, Alexander K. Tagantsev, Lane W. Martin, Ying-Hao Chu, Ramamoorthy
