a 1 f t t e ( ) ( 0.8) t ( 3 0.8) 1 ( ) ( ) t 1 f t e (5.70 t) 1.4(5.70t 0.8) e f t e t t ( ) ( (
|
|
|
- Alberta Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUESTION 8 a. (i) Vertical translation of a so a. Or as t, f( t) then e 0a a (ii) f t bt e.4 ( ) ( 0.8) t Using ( 3, 086) when t 3, f( t) 086 b e.4( 3) 086 ( 3 0.8) Gives b 5.70 b. f t t e.4 ( ) ( ) t Gives /.4.4 ( ) t t f t e (5.70 t).4(5.70t 0.8) e /.4t f t e t t ( ) (5.70.4( )) /.4t f t e t ( ) (.8.) f / () The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page
2 c. Find the lowest point on the graph of f '( t ). This point occurs at the stationary point on the graph of f '( t ). i.e. at t.88. or So on the graph of f () t, f (.88).34 Coordinates are (.88,.34) d. (i) y t - Area (8.87) (.8) (.609) 3.73 units The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page 3
3 (ii) Find f() t 0. or The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page
4 t-intercept at (-0.69, 0) Integral = 0.69 f () tdt f() tdt 0.69 Area = 0.8 square units (iii) Average value f () tdt ( ) Answer = The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page
5 e. (i) gt () is reflection over y-axis of f () t. This is f ( t)..4t gt ( ) ( 5.70t0.8) e (ii) k (t) is reflection over y-axis of positive t values of f () t. This is f ( t ). k t t e.4 ( ) t The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page
6 (iii) h (t) is f ( t ) then translated vertically downwards by unit. This is f( t)..4 t h(t) (5.70 t 0.8) e (iv) k(t).4 t (5.70 t 0.8) e and f t t e.4 ( ) ( ) t When t t then k( t) f ( t) when t 0.4 t k(t) (5.70 t 0.8) e and gt t e.4 ( ) ( ) t When t t then k( t) g( t) when t 0 The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page 3
7 QUESTION 9 The graph of de y is shown below: dt a. (i) de dt 0.4t y tae b y(0) 5, 5 0 bb 5 de (ii) At t = 0, 05 5 people/hr dt b. (i) dy dt e tae ae t 0.4t 0.4t 0.4t a 0.4 ( 0.4 ) Solve 0.4 t ae (0.4 t) 0 0.4t ae 0 no solution (0.4 t) 0 0.4t t.5 Giving :30 pm The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page 4
8 (ii) Let y = t tae When t =.5 Giving a 80.93e c. (i) Solve ete 0.4t Gives t ,7.374 The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page 5
9 Or graphically: Need times after midday Times (to the nearest minute) at :8pm and 7:pm (ii) As the rate is positive for all values of t (the graph is always located above the t axis), this means that more people are entering the venue as opposed to leaving, across all values over hours. e te dt 0.4t d. (i) people The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page
10 (ii) At t.5 hrs dt people 0.4t te 0 A graph The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page 3
11 de e. E is found by integrating y dt Screen shows a function with +c found by substituting the point (.5, 40) The School For Excellence 05 Unit 3 & 4 Mathematical Methods Maximising Exam Marks Page 4
12 Graph matches part d. The average value of a function f ( x ) over the interval [ ab, ] is given by b ( ) b a f x dx a Define this complicated function E as g(x) for ClassPad or e(t) for TI-inspire and find average value. Average value of E is people The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
13 QUESTION 0 a. (i) Initial number = 400 Solve t e t = to the nearest week, 3 weeks. (ii) dp 0.t 80e dt (iii) Rate of decrease after 0 weeks is rabbits per week. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
14 b. Use average value function = 5 0.t 400e dt To nearest rabbit = 443 c. (i) To find P o find P (5) where 0.t P 400e. P(5) So Po 70 to the nearest rabbit and P 70 (ii) Using P P 8t 5log t o So P 70 8t 5log t for t 5. Find P (30) : e e o The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
15 P(30) 47 rabbits d. (i) P 70 8t 5log t (ii) find dp 8 t 5 8loge t dt t e dp for t 5. dt A Stationary point found at (3.85, 64.34) Not in domain for t 5 e. Average rate of change = P(30) P(0) 30 0 where P(30) is from nd function and P(0) is from st function M 30 0 Average rate of change = 3.77 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 4
16 f. (i) Use your CAS to define the piece-wise function 0.t P400e Pt () Po 8 t5 loge t30 0 t 5 t 5 Showing meeting point at (5, 70). (ii) Differentiable for t 0,55,. 4A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 5
17 QUESTION a. b. c. (i) (ii) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 6
18 d. e. (i) (ii) Use technology to find the points of intersection. x x x e 3 ( 3 ) x x 0, Answer: (0.87,.6) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 7
19 QUESTION a. (i) When t 4, A 9 : a(4) 9 3(4) 4 4a 9 6 a 9 4 a 36 M (ii) 36t A 3 t 4 Using polynomial long division: 3t 4 36t _ 36t A M 3t 4 4 3t 4 b. D A B 4 3 D 3t 4 t 3 D 3 4 t 3 3t 4 M 3 4 c. D t 3 3t 4 D (3( t 3) 4(3t 4) ) dd dt 3 ( t 3) (3t 4) A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 8
20 dd d. Maximum value of D occurs when 0 : dt 3 0, 0 t 4. M ( t 3) (3t 4) 3 0 ( t 3) 0 ( t 3) (3t 4) 4 (3t 4) ( t 3) 4 (3t 4) t ( 3 4) 4( 3t 4 ( t 3), t 3) 3t 4 t 6 t M 3 4 When t : D = Hence the maximum difference in new influenza cases between those previously unexposed and those exposed to the virus is A Note: D is measured in hundreds. t k e. C( t) 4( t t) e C( t) 4(t ) e t k e k t k ( t t) 4 t e k t ( t k t) For maximum concentration C ( t) 0 : M t t ( t t) 0 or e k 0 M k tk k t t 0 No solution When t = 4, C ( t) 0 : 8k k k 0 0 k A 9 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 9
21 f. Let A C(t) Substitute 0 k : 9 A 4e 4e e 5 9t 0 9t 0 9t 0 t 9 0 ( t 3t 9t 0 0 3t 0 9t t) da 9 e dt 5 0 da For maximum absorption 0 : dt 9t 3t 0 9t e 38t 9t 0 0 M 9t 9 0 e t 0 9t t 3t 0 9t e 38t 0 0 t t or 7. 3 M From the graph of C (t) below it can be seen that the maximum rate of absorption occurs after 0.76 hours. A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 0
22 QUESTION 3 0 a. min C 0 max C 0 b. (i) Let T 4 C t 0 4cos 4 t 4cos 4 t cos t t t 3 pm (ii) 0 at t 3 T 4 C Period t 3 t 3 4 hrs no. cycles 0 T C at t n Z U 0 i.e. At pm every day. n, where n represents the number of cycles and The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
23 c. (i) T ABsinCt D If T T 0 then T T t 0 4cos ABsin CtD Need to identify what transformations would be required to convert the cosine curve to a sine curve. For curves to be equal, the amplitude, period and vertical translation must be the same. Sine curve must have: Amp 4 Vert Trans 0 Reflection in x axis Equation becomes 0 4sin tc A 0 B 4 C (ii) If c was equal to t i.e. 0 4sin 0 4sin 4 t i.e. sin t 3 t t = 9 hours A Bsin Ct D, the first maximum would occur at t 9 hours. Use this to identify the translation (horizontal) required to move the first sin max (at t 9 ) to the maxima on the cos curve (at t 3 ). i.e. Need to move sin 6 units to left. i.e. t6t 5 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
24 t Sine curve equation is: 0 4sin 5 Expand: Equate: 5 0 4sin t 5 D d. Let T3 T or T3 T Safer as both equations have been given and are error free. Alternatively: Move sin curve 4-6 hours = 8 hours to right t 8 t 9 t t t 8 cos sin 0 0 4cos 3 8 cos ( t ) sin ( t ) 4cos ( t ) 3 8 cos ( t ) sin ( t ) 4cos ( t ) cos ( t) sin ( t) 40 3 Case : cos ( t ) 0 3 ( t ), t 6,8 t 7,9 8 Case : sin ( t ) sin ( t ) ( t ), 3 3 t 6, 0 t 7, Therefore, the first two times are t 7, 7. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
25 e. (i) fog is defined if r g d f dg S d (0,] r r (,0] max, g f f y x r g d f -4 (ii) (0,] (0,] This is the max possible range of g. Find the corresponding domain - S. Let t cos 0 t t 6 t 7 t S x:0t 7 t f g t loge cos d d [0, 7) fog g y x The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 4
26 QUESTION 4 a. (i) PM Using right-angled triangle PMT, tan( ) x Giving PM = x tan( ) (ii) Using Pythagoras in right-angled triangle, PT = x +PM Giving PT = So PT = x x tan( ) and PT = x tan ( ) x + taking positive root. tan ( ) b. (i) L( ) = with x = 0 0 tan ( ) and simplify dl 0sin( ) Giving d cos ( ) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 5
27 dl 0sin( ) (ii) For minimum let 0 d cos ( ) Solution is 0,,,... this gives no actual triangle. Minimum is 0 so PT = TM = 0 metres. c. (i) Using chain rule dx dx d dt d dt dx d 0.5 where cos d dt Giving x x PT and cos dx d cos and sin 0.5 sin d dt d 3M dt 4sin x (ii) d dt 4sin d When then 4 dt 4sin 4 4 d radians/sec. dt The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 6
28 dt d d. (i) 4sin (ii) dt 4sin d d t 4sin and t 4cos c 0 4 cos cc 3 at t = 0 3 Giving t 4cos M Rearrange to give in terms of t: t cos 4 t 4 cos The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 7
29 e. or Graph to find absolute maximum at point 36,. Maximum time Tom can walk is 36 secs. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
30 QUESTION 5 a. (i) metres. M a amplitude (ii) Minimum height = 8 + = 0 metres = (-Amplitude + Vertical Translation) 0 b a b 70 M b. Period = 80 seconds = 3 4 minutes 4 c 3 Therefore c. h70 50sin td When 3 c M 3 t h If constn()=0 or If constant n= d is a possible value. M M 4 d. Period = minutes. 3 4 The point P reaches the maximum height once every minutes: Therefore the point P reaches its maximum height 7 times during a 36 minute ride. A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
31 sin 95 e. Solve h t, letting d = for 0 t 36. CAS gives 4 n 8 4 n t 4 where n Z or n n t where n Z 9 9 M When n, 4 t The smallest value of t satisfying 0 t 36 is t minutes. A 9 Therefore the point P first reaches a height of at least 95 metres above ground level after 9 4 minutes. f. During the first rotation P is at a height of 95 metres above the ground a second time 8 when t minutes (see part e) seconds 3 h = 95 M The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 4
32 From the graph it is clear that the number of minutes during one rotation that the point P is at least 95 metres above ground level is minutes: minutes seconds. 9 3 To nearest second, answer = 7 seconds 3 g. h70 50sin t A dh 3 75 cos t dt or dh 3 t 75 sin dt M Solve 00 dh dt graphically: The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 5
33 or M t 0. 5 minutes and t minutes minutes 4. 8 seconds. Therefore dh dt 00 m/s for 4.8 seconds, which is less than 0 seconds. The average person will not feel sick on the Southern Star Observation Wheel. A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 6
34 h. h70 50sin ct dh 50ccosct dt dh The smallest positive value of c such that 00 for no more than dt 0 seconds at a time and the wheel turns as quickly as possible is required. 0 seconds = minutes. 6 Therefore the positive value of c is required such that if t and t t are two consecutive solutions to 50c cosc( t ) 00, then t t. 6 c( t ) 00 4 c( t ) 50c cos cos c 4 c( t ) cos c 4 t cos c c 4 t cos c c and 4 t cos c c 4 t t cos c c cos 6 c c cos 4 c 4 c M M c 4.67, correct to three decimal places. A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 7
35 Further clarification about why the expression for t is made equal to. 4 i.e. c( t ) cos c As shown in screen below we have a ve solution and a +ve solution. These are: 4 4 cos cos c c and. c c 4 Rearranging the equation gave us cos( ct ( )). If we were to solve this equation or c the equation cos x 0.5, we would be concerned with finding solutions in the quadrants where cosine is positive i.e. Quadrants and 4. The rules describing the angles in Quadrants and 4 are and which is equal to. Therefore, when we rearrange the equation to create an expression for inverse cosine, these two angle solutions must be taken into consideration. Therefore, 4 t cos where the positive represents the st Quadrant angle and the c c negative sign represents the angle in the 4th Quadrant.) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 8
36 QUESTION 6 a. Amplitude =. Without a vertical translation, minimum and maximum values would be. To reach values of 0 and, the curve must be raised by, hence a. b. (i) x E sin n Let n0, x 5 5 E sin 0 4 (ii) x sin n0, E 0.75 x sin x 3.33 Therefore, a student must answer at least 4 questions. c. There are a variety of ways to score 50 marks. The student that answers the minimum number of questions would need to correctly answer the six questions that are worth 7 marks each (total = 4 marks) + one 5 mark question + one 3 mark question. Minimum Number Correct Questions = 8 Score (6 7) (5) (3) 50 When x 8, E 0.35 Maximum Number Correct Questions = i.e. The six questions that are worth 3 marks each (total = 8 marks) + five 5 mark questions + one 7 mark question. Score (63) (55) (7) 50 When x, E 0.65 Answer is 0.35 E 0.65 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 9
37 d. (i) (ii) x' 0.5 0x y' 0 3 y x' 0.5x 0.5x y' 3y 3y x' 0.5x y' 3y x4 x' 8 y ' y 3 Substitute x and y into E( x ): y' ( 4 x' 8) sin 3 n 3 4 ( x ' ) 3 y ' sin n 3 4 ( x ) 5 y sin n x e. (i) Dx ( ) e (ii) ( ) E D x exists when range D( x) domain E( x) domain E( x ): As 0n 00 then 0 x 00 range D( x) [0,00] Maximum range Dx ( ) (0,00] x (Note that e 0 ). The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 0
38 Corresponding domain: x Minimum occurs when e 0 i.e.. x Maximum occurs when e 00 i.e. x loge 00 Gives domain (,loge 00] But answer is [0, loge 00] as x represents the number of correct questions, which cannot be a negative number. de( D( x)) f. Rate of change in cheating dx Using chain rule: de( D( x)) dx x x e e cos n n Allow n 0 and find derivative when x 5, de( D( x)) dx To nearest whole number = 0985 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
39 QUESTION 7 t b x Ae cos( ct). The graph of x (t) is illustrated below. a. (i) When t 0, x Ae 0 cos(0) A Also, when t 0, x 5 so A 5. (ii) Using c and f ( 4). 39 t b xt 5e cos( t) 4 b.39 5e cos(8) 4.39 b e 5cos(8) 4.39 loge b 5cos(8) b 4.39 loge 5cos(8) Gives 4 b.39 loge 5cos(8) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
40 t 0 b. (i) x 5e cos( t) / t t 0 0 So x ( t) 5 e cos( t) e sin( t) 0 / t 0 x ( t) 5e cos( t) sin( t) 0 / t 0 x ( t) 5e cos( t) sin( t) 0 / t 0 x ( t) e cos( t) 40sin( t) t Of form ke ( ksint cos t) Gives k 0.5 and k 40. 3M ( ) cos( ) 40sin( ) No solution for e t 0. 4 / t 0 (ii) Solve x t e t t Solve cos( t) 40sin( t) 0 Simplifies to tan( t). 40 Therefore, and (iii) If tan x a then A 40 x n tan ( a), n Z tan t n n n t 0.05 Therefore, 0.05 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
41 c. (i) Period of x (t) = Period of y (t). (ii) The maximum value on the graph of cos( ct ) is always equal to. t b b Substituting cos( ct) into x Ae cos(ct) gives g( t) Ae. (iii) The minimum stationary points occur at x, which is the reflection of the maximum values, in the Xaxis. Therefore, the equation of the curve on which the minimum stationary points lie will be on the equation which is a reflection of the curve on which the maximum stationary points lie. t t b 0 i.e. gt () Ae 5e t d. / 0 f ( th) f() t hf () t where x f() t 5e cos() t t Using x( 4 ). 39 / f(4 0.) f(4) 0. f (4) Answer = -.53 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 4
42 60 t t 0 0 e. (i) Area = 5e 5e cos( t) dt 0 (ii) Area = 60 t t cos( ) e e t dt = Area = 60 0 t t 0 0 5e 5e dt = Unshaded region = = Shaded area : unshaded area = : Hence ratio is approximately :. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 5
43 QUESTION 8 a. i. cos x y e du Let u cos( x) and so sin( x) M dx u dy u y e and so e du dy dx dy du du dx e cos( x) sin( x) e sin( x) cos( x) A sin( x) e dx e 0 A o cos( x) cos( x) ii. ( e e ) A b. i. cos( x) f ( x) sin( x) e uv cos x Let u sin x and v e then dv cos(x) cos( x sin( x) e ) dx dx M du dv cos( x) cos( x) f ( x) v u = cos( x ) e sin ( x ) e dx dx A ii. If f( x) 0 then cos( cos( x) x ) e cos( x) sin ( xe ) 0 cos( x) Therefore e (cos( x) sin ( x )) = 0 Now cos(x) e can never be zero so cos( x ) sin ( x) 0 Hence cos( x ) ( cos ( x)) 0 and so cos ( x ) cos( x) 0 M Using the quadratic formula, 4 cos( x) A One of these values corresponds with what needed to be found. c. f ( g( x)) = sin cos ( x ) x ). e A ( The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 6
44 d. i. ` Intercepts (0,.44), (.98, 0), (6.0, 0). Coordinate format not necessary here. A Shape with two points of intersection at approximately (0.7,.3) and (5.3, -.4) H ii. (0.65,.34) and (5.33,.46) A e. [ f ( x) g( f ( x))] dx f ( x) dx [ f ( x) g( f ( x))] dx f ( x) dx The two difference integrals with correct lower terminals. All four integrals correct. M A Total = 4 marks The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 7
45 QUESTION 9 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 8
46 QUESTION 0 a. Dt () asin tband D ( ) 35 and D ( ) 5 6 Two equations are formed. 35 asin b and 5 asin( ) b M 6 Solving simultaneously gives a 0 and b 5 (CAS used to solve) M b. Solving D ( t) 0 gives t 7. 6 and t M Tom s parents can leave their books on the beach from 7 : 00am to : 37 pm and from 5 : 3pm to 7 : 00 pm A c. Average value is ( ) 5 0 D t dt M (using av value formula) Average value is at mean point and is therefore the only place where there are 3 distinct solutions, giving m 5 A d. A D 65 S(t) t The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 9
47 e. (i) Pr( X 8) normalcdf (8,, 5, 3) A (ii) Pr( X k X 8) 0.3 M Pr( X kx 8) 0.3 Pr( X 8) Pr( X k) 0.3 Pr( X 8) Note: If the numerator was equal to Pr( X 8), the resultant fraction would be equal to, which is not the case. Hence the numerator must equal Pr( X k). Pr( X k) Pr( X k) M invnorm( , 5, 3) k 3.55 pounds A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 0
48 QUESTION a. If Wt () is increasing then W '( t) 0 for t 0. ct ct W '( t) 3 ( c be ) a( be ) ct ct W '( t) 3 abce ( be ) i.e. ct ct 3 abce ( be ) 0 M ct As abc,, 0 then 3abce 0. As the square of a number is greater than or equal to zero, then ( be ct ) 0. Therefore, W '( t) 0 for all values of t. A b. lim Wt ( ) lim a be t t As t then e 0. ct 3 a be 3 Therefore, 3 3 a be a( 0) a A As an animal ages, its weight aproaches the value a. c. (i) y A A (ii) Substitute t 0 and f( t) 0.49 : 0 be 0.49 b 0.49 b 0.5 M (iii) f () t 0.5e ct Substitute t and f( t) 0.45 : e c c e c log e(.07843) M d. Find the Interquartile range (IQR). The interquartile range describes the values of t for which the middle 50% of the distribution lies. i.e. The difference between the 75 th percentile and the 5 th percentile. i.e. The 75 th percentile (a t value) The 5 th percentile (a t value) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
49 Let the 75 th percentile equal q. Let the 5 th percentile equal p. q Wt ( ) dt 0.75 M 0 q , 5.85 As t 0, q 5.85 p Wt ( ) dt 0.5 M 0 p 6.478,.36 As t 0, p.36 IQR A e. Binomial with n 6 and p. binompdf 6,, Pr( X 3) 0.9 A f. (i) Binomial with n n and p 0. Pr( X 3) 0. n 3 3 n3 (0.) (0.8) 0. M n (use technolgy) n 7 rats A (ii) Let X Number of overweight rats n n p 0. np( p).5 M n(0.)(0.8) (.5) n n 39 A The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page
50 QUESTION a. (i) Pr( W 00) (ii) Pr( W a) 0.75 giving Pr( W a) 0.5 Using Inverse Normal: a b. Binomial distribution. Let X = Number of underweight packs Let p = probability of pack being underweight = n = 5 Box rejected is X 3 Pr( X 3) c. (i) Binomial application but as order is important, do not apply usual rules. Use multiplication principle. Pr (Box accepted) = = Pr (Box rejected) = = Pr (First boxes only accepted) = Pr(Accepted) Pr(Accepted) Pr (Rejected) (ii) Binomial Let 0.5 Pr (Rejected) Pr (Rejected) 3 ( ) (0.066) np n p 0.5 n n Answer: n = 5 boxes. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
51 d. (i) Type Type Type 3 Profit ($) x 0 0.8x 0 0 Probability (Pr) Pr (Box accepted) = = Pr (Box rejected) = = Type = 85% of = Type = 5% of = Type 3 = Probability of box being rejected = A (ii) ( x0) 0.340(0.8x0) 0(0.06) x 0 (iii) Profit occurs when x x 0 x.5340 Profit occurs when x $.54 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 4
52 QUESTION a. (i) Pr( tuna from Boat ) (ii) Let X Number of tuna. E ( X ) b. (i) Pr( Boat / tuna) Pr( Boat tuna) Pr( tuna) Alternatively the probability may be obtained directly from the given table. Number tuna caught by Boat Total number tuna caught (ii) Pr( one is a tuna) Pr( tuna from Boat AND not from Boat ) OR Pr( tuna from Boat AND not from Boat ) c. (i) Tuna Salmon Other Number of fish Price per kilo (x$) 0 5 Probability (Pr(X=x) Pr(X=x) Price (x$) M (ii) E($) (0 0.6) ( 0.3) (5 0.) $0. 0 / kg The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 5
53 d. (i) Area = a 35 kg 35 a X z c Pr( X 35 a) 0.85 Pr( z c) 0.85 Using Inverse Normal: c c X a a.0364 (ii) Binomial. X Number acceptable fish p probability acceptable 0.70 n 5 Find Pr( X ) e. (i) Let X number of acceptable fish p p n 5 Pr( X ) p p 0 p ( p ) (ii) P' ( p) 3 0 p 3( p) ( p) 0 p and simplify 0 p( p) ( 5p) Let P '( p) 0 : 0 p ( p) ( 5p) 0 p 0,, 5 As 0 p, p. 5 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 6
54 QUESTION 4 a. 99 Binomial, p, q 300, n,000, Where np, 000, b. 99 p, n Pr( X 99) Pr( X 98) c. (i) $x Profit $.0 Loss $0.50 Pr(X=x) E(P) = ($.0 x ) - ($0.50 x ) = $. (ii) Binomial distribution: X Bi(5, ) Let X = Number of packets Pr( X 5) The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 7
55 d. (i) k x f( x) 0 0 x elsewhere f ( x) k ( x) k(x) k( x) for x0, x Graph is and f ( x) k ( x ) kx for x 0, 0 x k 4A (ii) For PDF Area = Symmetric graph so area of triangle = 0.5 Area = k So k = e. (i) Need PrX 7 PrX xdx xdx 8 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 8
56 (ii) Var( X ) 0 x f( x) dx x xdx x ( x) dx 0 where by symmetry mean = Gives Var(X) Gives sd(x) % confidence interval: X X 6 6 f. Pr( X p) 0.6 p The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 9
57 From graph means Pr( X p) 0. Need p ( xdx ) 0. Within domain gives 0 5 p. 5 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 30
58 QUESTION 5 a. Range is b. Pr(h > 9) = Pr(z > = 0 5. = 9.8 m to 30. m 9 0 ) 5. = Pr(z > 0.96) = Binomial : Pr(h 65) = 00 C 65 (0.5777) 65 (0.43) C 66 (0.5777) 66 (0.43) 34 + = c. (i) Pr(at least yellow) = Pr(y=) + Pr(y=3) = ( 3 C (0.8) (0.7) ) = 0.93 M Expected number = = 93 (ii) Pr(h 9 Y ) = ( ) {3( ) } = ( from part b) d. Conditional probability: Pr( h 6 Y 3) Pr( h 9 Y ) = = Pr( h 6 Y 3) Pr( h 9 Y ) 6 0 Pr( z ) Pr( Y 3) Pr( z ) 0.8 = e. Pr(z > ) = 0.5 z =.0364 f. 50 Pr(z < 3 = ) = 0.38 z = Solving simultaneously, 49., 9.8 k (0.93 from part c) 0.93 k M 0.7 M = 8.45 Million dollars The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
59 QUESTION 6 n a. (i) Sn T S0 Sn n car( C) public( P) A (ii) S T S 0 S S car( C) 87.5 public( P) Answer: 87 are catching public transport b. Use trial and error: Car users drop below 450 at S 8, meaning at 9 th festival. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 3
60 c. Could check with steady state S first, where S T S. 0 S car( C) public( P) P P T Q Q where T = So P Q = P Q Where Q = 500 P Giving P P = P 500 P Equate and solve: 0.75P0.(500 P) P Meaning P = 48 travelling by car. The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 33
61 d. Find, using integration where area = a Solve for a, cos x If constn()=0, a = or If n=, a= d dx e. (i) xsin x6 sin x6 x cos x6 sin x6 xcos x (ii) Mean of PDF is xf( x) dx So mean of f (x) is xf( x) dx x x dx x x dx Giving cos 6 cos 6 Using integration by recognition we know that: sin x6 xcos x6dx xsin x Simplifying and separating terms gives: sin x6dx xcos x6dx xsin x x cos x 6 dx xsin x 6 sin x6 dx The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 34
62 x cos x 6 dx 0 0 x cos x 6 dx xsin x 6 sin x 6 dx x RHS sin sin cos cos cos M Checking with CAS: Mean = 6 The School For Excellence 05 Year Mathematical Methods Exam Analysis Lecture Page 35
Written examination 2
 INSIGHT YEAR Trial Exam Paper 03 MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination s This book presents: correct solutions with full working mark allocations tips This trial examination produced by Insight
INSIGHT YEAR Trial Exam Paper 03 MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination s This book presents: correct solutions with full working mark allocations tips This trial examination produced by Insight
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) PILOT STUDY
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2004 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) PILOT STUDY Written examination 2 (Analysis task) Monday 8 November 2004 Reading time: 9.00
Victorian Certificate of Education 2004 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) PILOT STUDY Written examination 2 (Analysis task) Monday 8 November 2004 Reading time: 9.00
MATHEMATICAL METHODS
 Victorian Certificate of Education 018 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written examination 1 Friday 1 June 018 Reading time:.00 pm to.15 pm (15 minutes)
Victorian Certificate of Education 018 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written examination 1 Friday 1 June 018 Reading time:.00 pm to.15 pm (15 minutes)
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 2
 Victorian CertiÞcate of Education 2007 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 2 Monday 12 November 2007 Reading time:
Victorian CertiÞcate of Education 2007 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 2 Monday 12 November 2007 Reading time:
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) PILOT STUDY
 Victorian CertiÞcate of Education 2005 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) PILOT STUDY Written examination 2 (Analysis task) Monday
Victorian CertiÞcate of Education 2005 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) PILOT STUDY Written examination 2 (Analysis task) Monday
2017 VCE Mathematical Methods 2 examination report
 7 VCE Mathematical Methods examination report General comments There were some excellent responses to the 7 Mathematical Methods examination and most students were able to attempt the four questions in
7 VCE Mathematical Methods examination report General comments There were some excellent responses to the 7 Mathematical Methods examination and most students were able to attempt the four questions in
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS)
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2015 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1 Wednesday 4 November 2015 Reading time: 9.00 am
Victorian Certificate of Education 2015 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1 Wednesday 4 November 2015 Reading time: 9.00 am
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2010 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1 Friday 5 November 2010 Reading time:
Victorian Certificate of Education 2010 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1 Friday 5 November 2010 Reading time:
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
 Victorian Certificate of Education 07 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Monday 3 November 07 Reading time: 3.00 pm to 3.5
Victorian Certificate of Education 07 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Monday 3 November 07 Reading time: 3.00 pm to 3.5
*P46958A0244* IAL PAPER JANUARY 2016 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA. 1. f(x) = (3 2x) 4, x 3 2
 Edexcel "International A level" "C3/4" papers from 016 and 015 IAL PAPER JANUARY 016 Please use extra loose-leaf sheets of paper where you run out of space in this booklet. 1. f(x) = (3 x) 4, x 3 Find
Edexcel "International A level" "C3/4" papers from 016 and 015 IAL PAPER JANUARY 016 Please use extra loose-leaf sheets of paper where you run out of space in this booklet. 1. f(x) = (3 x) 4, x 3 Find
SOLUTIONS: Trial Exam 2013 MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written Examination 2
 The Mathematical Association of Victoria SOLUTIONS: Trial Exam 0 MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written Examination SECTION : Multiple Choice. D. C. B 4. B 5. A 6. D 7. C 8. E 9. B 0. A. D. B. D 4. E 5. D 6. E 7.
The Mathematical Association of Victoria SOLUTIONS: Trial Exam 0 MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written Examination SECTION : Multiple Choice. D. C. B 4. B 5. A 6. D 7. C 8. E 9. B 0. A. D. B. D 4. E 5. D 6. E 7.
Express g(x) in the form f(x) + ln a, where a (4)
 SL 2 SUMMER PACKET PRINT OUT ENTIRE PACKET, SHOW YOUR WORK FOR ALL EXERCISES ON SEPARATE PAPER. MAKE SURE THAT YOUR WORK IS NEAT AND ORGANIZED. WORK SHOULD BE COMPLETE AND READY TO TURN IN THE FIRST DAY
SL 2 SUMMER PACKET PRINT OUT ENTIRE PACKET, SHOW YOUR WORK FOR ALL EXERCISES ON SEPARATE PAPER. MAKE SURE THAT YOUR WORK IS NEAT AND ORGANIZED. WORK SHOULD BE COMPLETE AND READY TO TURN IN THE FIRST DAY
Express g(x) in the form f(x) + ln a, where a (4)
 SL 2 SUMMER PACKET 2013 PRINT OUT ENTIRE PACKET, SHOW YOUR WORK FOR ALL EXERCISES ON SEPARATE PAPER. MAKE SURE THAT YOUR WORK IS NEAT AND ORGANIZED. WORK SHOULD BE COMPLETE AND READY TO TURN IN THE FIRST
SL 2 SUMMER PACKET 2013 PRINT OUT ENTIRE PACKET, SHOW YOUR WORK FOR ALL EXERCISES ON SEPARATE PAPER. MAKE SURE THAT YOUR WORK IS NEAT AND ORGANIZED. WORK SHOULD BE COMPLETE AND READY TO TURN IN THE FIRST
Calculus first semester exam information and practice problems
 Calculus first semester exam information and practice problems As I ve been promising for the past year, the first semester exam in this course encompasses all three semesters of Math SL thus far. It is
Calculus first semester exam information and practice problems As I ve been promising for the past year, the first semester exam in this course encompasses all three semesters of Math SL thus far. It is
Table of Contents. Module 1
 Table of Contents Module Order of operations 6 Signed Numbers Factorization of Integers 7 Further Signed Numbers 3 Fractions 8 Power Laws 4 Fractions and Decimals 9 Introduction to Algebra 5 Percentages
Table of Contents Module Order of operations 6 Signed Numbers Factorization of Integers 7 Further Signed Numbers 3 Fractions 8 Power Laws 4 Fractions and Decimals 9 Introduction to Algebra 5 Percentages
8 M13/5/MATME/SP2/ENG/TZ1/XX/M 9 M13/5/MATME/SP2/ENG/TZ1/XX/M. x is σ = var,
 8 M/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M 9 M/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M SECTION A. (a) d N [ mark] (b) (i) into term formula () eg u 00 5 + (99), 5 + (00 ) u 00 0 N (ii) into sum formula () 00 00 eg S 00 ( (5) + 99() ),
8 M/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M 9 M/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ/XX/M SECTION A. (a) d N [ mark] (b) (i) into term formula () eg u 00 5 + (99), 5 + (00 ) u 00 0 N (ii) into sum formula () 00 00 eg S 00 ( (5) + 99() ),
MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2008 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1 Friday 7 November 2008 Reading time:
Victorian Certificate of Education 2008 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination 1 Friday 7 November 2008 Reading time:
Sec 4 Maths SET D PAPER 2
 S4MA Set D Paper Sec 4 Maths Exam papers with worked solutions SET D PAPER Compiled by THE MATHS CAFE P a g e Answer all questions. Write your answers and working on the separate Answer Paper provided.
S4MA Set D Paper Sec 4 Maths Exam papers with worked solutions SET D PAPER Compiled by THE MATHS CAFE P a g e Answer all questions. Write your answers and working on the separate Answer Paper provided.
2017 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines
 07 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer A D 3 C 4 A 5 B 6 D 7 B 8 A 9 C 0 A NESA 07 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines Section II Question (a) Provides
07 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer A D 3 C 4 A 5 B 6 D 7 B 8 A 9 C 0 A NESA 07 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines Section II Question (a) Provides
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary GCE in Mathematics (8MA0) Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in Mathematics (9MA0)
 Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary GCE in Mathematics (8MA0) Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in Mathematics (9MA0) First teaching from September 2017 First certification from June 2018 2
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary GCE in Mathematics (8MA0) Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in Mathematics (9MA0) First teaching from September 2017 First certification from June 2018 2
Add Math (4047/02) Year t years $P
 Add Math (4047/0) Requirement : Answer all questions Total marks : 100 Duration : hour 30 minutes 1. The price, $P, of a company share on 1 st January has been increasing each year from 1995 to 015. The
Add Math (4047/0) Requirement : Answer all questions Total marks : 100 Duration : hour 30 minutes 1. The price, $P, of a company share on 1 st January has been increasing each year from 1995 to 015. The
Mathematical Methods (CAS) Unit 4 Revision Lecture Presented by Samuel Goh
 Mathematical Methods (CAS) Unit 4 Revision Lecture Presented by Samuel Goh Introduction Multiple Choice Question Get familiar with the audience response software! What colour is this dress? a) Blue and
Mathematical Methods (CAS) Unit 4 Revision Lecture Presented by Samuel Goh Introduction Multiple Choice Question Get familiar with the audience response software! What colour is this dress? a) Blue and
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
 AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAM. Directions: Solve each of the following problems,
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAM. Directions: Solve each of the following problems,
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review
 Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
MATHEMATICAL METHODS
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2016 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written examination 1 Wednesday 2 November 2016 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
Victorian Certificate of Education 2016 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER MATHEMATICAL METHODS Written examination 1 Wednesday 2 November 2016 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
Written examination 2
 INSIGHT YEAR 1 Trial Exam Paper 01 MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination s This book presents: correct solutions with full working explanatory notes mark allocations tips This trial examination
INSIGHT YEAR 1 Trial Exam Paper 01 MATHEMATICAL METHODS (CAS) Written examination s This book presents: correct solutions with full working explanatory notes mark allocations tips This trial examination
May 2015 Timezone 2 IB Maths Standard Exam Worked Solutions
 May 015 Timezone IB Maths Standard Exam Worked Solutions 015, Steve Muench steve.muench@gmail.com @stevemuench Please feel free to share the link to these solutions http://bit.ly/ib-sl-maths-may-015-tz
May 015 Timezone IB Maths Standard Exam Worked Solutions 015, Steve Muench steve.muench@gmail.com @stevemuench Please feel free to share the link to these solutions http://bit.ly/ib-sl-maths-may-015-tz
Find all points where the function is discontinuous. 1) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - 1) 2) f(x) =
 Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 28, 2015
 Math 110 4. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 8, 015 1. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute the derivative of f(x = 1 at x = a. 1 + x Inserting the function into
Math 110 4. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 8, 015 1. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute the derivative of f(x = 1 at x = a. 1 + x Inserting the function into
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
 Victorian Certificate of Education 06 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Monday 7 November 06 Reading time:.5 am to.00 noon
Victorian Certificate of Education 06 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Monday 7 November 06 Reading time:.5 am to.00 noon
UNIT 2 MATHEMATICAL METHODS 2013 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM WEEK 11 EXAMINATION 2 SOLUTIONS SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 UNIT MATHEMATICAL METHODS 01 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM WEEK 11 EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION 1 QUESTION QUESTION
UNIT MATHEMATICAL METHODS 01 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM WEEK 11 EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION 1 QUESTION QUESTION
Year 2011 VCE. Mathematical Methods CAS. Trial Examination 1
 Year 0 VCE Mathematical Methods CAS Trial Examination KILBAHA MULTIMEDIA PUBLISHING PO BOX 7 KEW VIC 30 AUSTRALIA TEL: (03) 908 5376 FAX: (03) 987 4334 kilbaha@gmail.com http://kilbaha.com.au IMPORTANT
Year 0 VCE Mathematical Methods CAS Trial Examination KILBAHA MULTIMEDIA PUBLISHING PO BOX 7 KEW VIC 30 AUSTRALIA TEL: (03) 908 5376 FAX: (03) 987 4334 kilbaha@gmail.com http://kilbaha.com.au IMPORTANT
weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Trigonometry
 http://kumarmaths. weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Trigonometry Core Maths 3 Trigonometry Page 1 C3 Trigonometry In C you were introduced to radian measure and had to find areas of sectors and segments.
http://kumarmaths. weebly.com/ Core Mathematics 3 Trigonometry Core Maths 3 Trigonometry Page 1 C3 Trigonometry In C you were introduced to radian measure and had to find areas of sectors and segments.
Unit 1 & 2 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam
 Name: Teacher: Unit 1 & 2 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2 2017 Monday November 20 (1.00pm - 3.15pm) Reading time: 15 Minutes Writing time: 120 Minutes Instruction to candidates: Students are permitted to bring
Name: Teacher: Unit 1 & 2 Maths Methods (CAS) Exam 2 2017 Monday November 20 (1.00pm - 3.15pm) Reading time: 15 Minutes Writing time: 120 Minutes Instruction to candidates: Students are permitted to bring
Correct substitution. cos = (A1) For substituting correctly sin 55.8 A1
 Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) MarkScheme 1. (a) Evidence of using the cosine rule eg cos = cos Correct substitution eg cos = = 55.8 (0.973 radians) N2 (b) Area = sin For substituting
Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) MarkScheme 1. (a) Evidence of using the cosine rule eg cos = cos Correct substitution eg cos = = 55.8 (0.973 radians) N2 (b) Area = sin For substituting
MTH 122: Section 204. Plane Trigonometry. Test 1
 MTH 122: Section 204. Plane Trigonometry. Test 1 Section A: No use of calculator is allowed. Show your work and clearly identify your answer. 1. a). Complete the following table. α 0 π/6 π/4 π/3 π/2 π
MTH 122: Section 204. Plane Trigonometry. Test 1 Section A: No use of calculator is allowed. Show your work and clearly identify your answer. 1. a). Complete the following table. α 0 π/6 π/4 π/3 π/2 π
C3 PAPER JUNE 2014 *P43164A0232* 1. The curve C has equation y = f (x) where + 1. (a) Show that 9 f (x) = (3)
 PMT C3 papers from 2014 and 2013 C3 PAPER JUNE 2014 1. The curve C has equation y = f (x) where 4x + 1 f( x) =, x 2 x > 2 (a) Show that 9 f (x) = ( x ) 2 2 Given that P is a point on C such that f (x)
PMT C3 papers from 2014 and 2013 C3 PAPER JUNE 2014 1. The curve C has equation y = f (x) where 4x + 1 f( x) =, x 2 x > 2 (a) Show that 9 f (x) = ( x ) 2 2 Given that P is a point on C such that f (x)
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
 Victorian Certificate of Education 08 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Monday November 08 Reading time: 3.00 pm to 3.5
Victorian Certificate of Education 08 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Monday November 08 Reading time: 3.00 pm to 3.5
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
MATH 162 R E V I E W F I N A L E X A M FALL 2016
 MATH 6 R E V I E W F I N A L E X A M FALL 06 BASICS Graphs. Be able to graph basic functions, such as polynomials (eg, f(x) = x 3 x, x + ax + b, x(x ) (x + ) 3, know about the effect of multiplicity of
MATH 6 R E V I E W F I N A L E X A M FALL 06 BASICS Graphs. Be able to graph basic functions, such as polynomials (eg, f(x) = x 3 x, x + ax + b, x(x ) (x + ) 3, know about the effect of multiplicity of
2006 Mathematical Methods (CAS) GA 3: Examination 2
 006 Mathematical Methods (CAS) GA : Examination GENERAL COMMENTS There were 59 students who sat this examination in 006. Marks ranged from 4 to the maximum possible score of 0. Student responses showed
006 Mathematical Methods (CAS) GA : Examination GENERAL COMMENTS There were 59 students who sat this examination in 006. Marks ranged from 4 to the maximum possible score of 0. Student responses showed
Mathematical Methods (CAS) 2002 Examination 1 part 1 sample solutions Q 14 to 27
 Mathematical Methods (CAS) 00 Examination part sample solutions Q 4 to 7 Note: To use Derive efficiently, students should be familiar with the 'tick plus equals' and 'tick plus approximately equals' evaluation
Mathematical Methods (CAS) 00 Examination part sample solutions Q 4 to 7 Note: To use Derive efficiently, students should be familiar with the 'tick plus equals' and 'tick plus approximately equals' evaluation
Unit 1 Investigating Equations in 3-Space
 Mathematics 2204/2205 Teacher: Mr. J Hunt Note to The Student/Parent This package presents in depth review for Level II Advanced and Academic Mathematics. Problems indicated by * are for Advanced Math
Mathematics 2204/2205 Teacher: Mr. J Hunt Note to The Student/Parent This package presents in depth review for Level II Advanced and Academic Mathematics. Problems indicated by * are for Advanced Math
Review for the Final Exam
 Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Mathematics Extension 1
 NORTH SYDNEY GIRLS HIGH SCHOOL 05 TRIAL HSC EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading Time 5 minutes Working Time hours Write using black or blue pen Black pen is preferred Board approved
NORTH SYDNEY GIRLS HIGH SCHOOL 05 TRIAL HSC EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading Time 5 minutes Working Time hours Write using black or blue pen Black pen is preferred Board approved
Core 3 (A2) Practice Examination Questions
 Core 3 (A) Practice Examination Questions Trigonometry Mr A Slack Trigonometric Identities and Equations I know what secant; cosecant and cotangent graphs look like and can identify appropriate restricted
Core 3 (A) Practice Examination Questions Trigonometry Mr A Slack Trigonometric Identities and Equations I know what secant; cosecant and cotangent graphs look like and can identify appropriate restricted
2 M13/5/MATME/SP2/ENG/TZ1/XX 3 M13/5/MATME/SP2/ENG/TZ1/XX Full marks are not necessarily awarded for a correct answer with no working. Answers must be
 M13/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ1/XX 3 M13/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ1/XX Full marks are not necessarily awarded for a correct answer with no working. Answers must be supported by working and/or explanations. In particular,
M13/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ1/XX 3 M13/5/MATME/SP/ENG/TZ1/XX Full marks are not necessarily awarded for a correct answer with no working. Answers must be supported by working and/or explanations. In particular,
UNIT 2 MATHEMATICAL METHODS 2015 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM WEEK 11 EXAMINATION 2 SOLUTIONS SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 UNIT MATHEMATICAL METHODS 015 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM WEEK 11 EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Where possible, students
UNIT MATHEMATICAL METHODS 015 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM WEEK 11 EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Where possible, students
IB Math SL 1: Trig Practice Problems: MarkScheme Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) MarkScheme
 IB Math SL : Trig Practice Problems: MarkScheme Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) MarkScheme. (a) Evidence of using the cosine rule p + r q eg cos P Qˆ R, q p + r pr cos P Qˆ R pr
IB Math SL : Trig Practice Problems: MarkScheme Circular Functions and Trig - Practice Problems (to 07) MarkScheme. (a) Evidence of using the cosine rule p + r q eg cos P Qˆ R, q p + r pr cos P Qˆ R pr
When should technology be used?
 Using a Graphing Calculator in the Classroom When should technology be used? The graphing calculator is a wonderful tool for teaching concepts. It also can become a crutch. GOOD Examining the effects of
Using a Graphing Calculator in the Classroom When should technology be used? The graphing calculator is a wonderful tool for teaching concepts. It also can become a crutch. GOOD Examining the effects of
π π π π Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A B C D Determine the period of 15
 Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A. 0.09 B. 0.18 C. 151.83 D. 303.67. Determine the period of y = 6cos x + 8. 15 15 A. B. C. 15 D. 30 15 3. Determine the exact value of
Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A. 0.09 B. 0.18 C. 151.83 D. 303.67. Determine the period of y = 6cos x + 8. 15 15 A. B. C. 15 D. 30 15 3. Determine the exact value of
Math 152 Take Home Test 1
 Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
( and 1 degree (1 ) , there are. radians in a full circle. As the circumference of a circle is. radians. Therefore, 1 radian.
 Angles are usually measured in radians ( c ). The radian is defined as the angle that results when the length of the arc of a circle is equal to the radius of that circle. As the circumference of a circle
Angles are usually measured in radians ( c ). The radian is defined as the angle that results when the length of the arc of a circle is equal to the radius of that circle. As the circumference of a circle
(b) g(x) = 4 + 6(x 3) (x 3) 2 (= x x 2 ) M1A1 Note: Accept any alternative form that is correct. Award M1A0 for a substitution of (x + 3).
 Paper. Answers. (a) METHOD f (x) q x f () q 6 q 6 f() p + 8 9 5 p METHOD f(x) (x ) + 5 x + 6x q 6, p (b) g(x) + 6(x ) (x ) ( + x x ) Note: Accept any alternative form that is correct. Award A for a substitution
Paper. Answers. (a) METHOD f (x) q x f () q 6 q 6 f() p + 8 9 5 p METHOD f(x) (x ) + 5 x + 6x q 6, p (b) g(x) + 6(x ) (x ) ( + x x ) Note: Accept any alternative form that is correct. Award A for a substitution
Core Mathematics 3 Trigonometry
 Edexcel past paper questions Core Mathematics 3 Trigonometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Maths 3 Trigonometry Page 1 C3 Trigonometry In C you were introduced to radian measure
Edexcel past paper questions Core Mathematics 3 Trigonometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Maths 3 Trigonometry Page 1 C3 Trigonometry In C you were introduced to radian measure
Students! (1) with calculator. (2) No calculator
 Students! (1) with calculator Let R be the region bounded by the graphs of y = sin(π x) and y = x 3 4x, as shown in the figure above. (a) Find the area of R. (b) The horizontal line y = splits the region
Students! (1) with calculator Let R be the region bounded by the graphs of y = sin(π x) and y = x 3 4x, as shown in the figure above. (a) Find the area of R. (b) The horizontal line y = splits the region
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems. Answers
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems Answers. A 988 AB # 48%. D 998 AB #4 5%. E 998 BC # % 5. C 99 AB # % 6. B 998 AB #80 48% 7. C 99 AB #7 65% 8. C 998 AB # 69% 9. B 99 BC # 75% 0. C 998 BC # 80%.
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems Answers. A 988 AB # 48%. D 998 AB #4 5%. E 998 BC # % 5. C 99 AB # % 6. B 998 AB #80 48% 7. C 99 AB #7 65% 8. C 998 AB # 69% 9. B 99 BC # 75% 0. C 998 BC # 80%.
College Prep Math Final Exam Review Packet
 College Prep Math Final Exam Review Packet Name: Date of Exam: In Class 1 Directions: Complete each assignment using the due dates given by the calendar below. If you are absent from school, you are still
College Prep Math Final Exam Review Packet Name: Date of Exam: In Class 1 Directions: Complete each assignment using the due dates given by the calendar below. If you are absent from school, you are still
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference (complete below) Centre No. Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 6663 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics C Advanced Subsidiary Specimen Paper Time: hour 30 minutes Examiner
Paper Reference (complete below) Centre No. Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 6663 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics C Advanced Subsidiary Specimen Paper Time: hour 30 minutes Examiner
Principles of Mathematics 12
 Principles of Mathematics 1 Examination Booklet August 006 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EXAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS REFER TO THE RESPONSE BOOKLET. Contents: 16 pages
Principles of Mathematics 1 Examination Booklet August 006 Form A DO NOT OPEN ANY EXAMINATION MATERIALS UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. FOR FURTHER INSTRUCTIONS REFER TO THE RESPONSE BOOKLET. Contents: 16 pages
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
MATH 1207 R02 MIDTERM EXAM 2 SOLUTION
 MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
MATH 7 R MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION FALL 6 - MOON Name: Write your answer neatly and show steps. Except calculators, any electronic devices including laptops and cell phones are not allowed. () (5 pts) Find
DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
 AP Calculus AB Exam SECTION I: Multiple Choice 016 DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time 1 hour, 45 minutes Number of Questions 45 Percent of Total Score 50% Writing
AP Calculus AB Exam SECTION I: Multiple Choice 016 DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time 1 hour, 45 minutes Number of Questions 45 Percent of Total Score 50% Writing
MATHEMATICS. NORTH SYDNEY BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 2008 Trial HSC Examination STUDENT NUMBER:... QUESTION Total %
 008 Trial HSC Eamination MATHEMATICS General instructions Working time 3 hours. plus 5 minutes reading time) Write on the lined paper in the booklet provided. Each question is to commence on a new page.
008 Trial HSC Eamination MATHEMATICS General instructions Working time 3 hours. plus 5 minutes reading time) Write on the lined paper in the booklet provided. Each question is to commence on a new page.
 Note : This document might take a little longer time to print. more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more
Note : This document might take a little longer time to print. more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more
Mathematics Extension 1
 NSW Education Standards Authority 08 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Mathematics Extension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black pen Calculators approved
NSW Education Standards Authority 08 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Mathematics Extension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black pen Calculators approved
Math 116 Second Midterm March 23, 2010
 Math 6 Second Midterm March 23, 2 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note that
Math 6 Second Midterm March 23, 2 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note that
2016 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW
 FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
Paper2Practice [303 marks]
![Paper2Practice [303 marks] Paper2Practice [303 marks]](/thumbs/86/93861274.jpg) PaperPractice [0 marks] Consider the expansion of (x + ) 10. 1a. Write down the number of terms in this expansion. [1 mark] 11 terms N1 [1 mark] 1b. Find the term containing x. evidence of binomial expansion
PaperPractice [0 marks] Consider the expansion of (x + ) 10. 1a. Write down the number of terms in this expansion. [1 mark] 11 terms N1 [1 mark] 1b. Find the term containing x. evidence of binomial expansion
2 2xdx. Craigmount High School Mathematics Department
 Π 5 3 xdx 5 cosx 4 6 3 8 Help Your Child With Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
Π 5 3 xdx 5 cosx 4 6 3 8 Help Your Child With Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
b) The trend is for the average slope at x = 1 to decrease. The slope at x = 1 is 1.
 Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
2016 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines
 06 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer B C 3 B 4 A 5 B 6 A 7 A 8 D 9 C 0 D Section II Question (a) Provides correct sketch Identifies radius, or equivalent
06 HSC Mathematics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer B C 3 B 4 A 5 B 6 A 7 A 8 D 9 C 0 D Section II Question (a) Provides correct sketch Identifies radius, or equivalent
Year 2013 VCE Mathematical Methods CAS Trial Examination 2 Suggested Solutions
 Year VCE Mathematical Methods CAS Trial Examination Suggested Solutions KILBAHA MULTIMEDIA PUBLISHING PO BOX 7 KEW VIC AUSTRALIA TEL: () 98 576 FAX: () 987 44 kilbaha@gmail.com IMPORTANT COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Year VCE Mathematical Methods CAS Trial Examination Suggested Solutions KILBAHA MULTIMEDIA PUBLISHING PO BOX 7 KEW VIC AUSTRALIA TEL: () 98 576 FAX: () 987 44 kilbaha@gmail.com IMPORTANT COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review
 Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
N5 R1.2 and R1.3 Quadratics - Revision
 N5 R and R3 Quadratics - Revision This revision pack covers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level for Quadratics so you can evaluate your learning of this outcome. It is important that you prepare
N5 R and R3 Quadratics - Revision This revision pack covers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level for Quadratics so you can evaluate your learning of this outcome. It is important that you prepare
1! i 3$ (( )( x! 1+ i 3)
 Math 4C Fall 2008 Final Exam (Name) (PID) (Section) Read each question carefully; answer each question completely. Show all work: no credit for unsupported answers. Attach additional sheets if necessary.
Math 4C Fall 2008 Final Exam (Name) (PID) (Section) Read each question carefully; answer each question completely. Show all work: no credit for unsupported answers. Attach additional sheets if necessary.
Higher Mathematics Course Notes
 Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
1d C4 Integration cot4x 1 4 1e C4 Integration trig reverse chain 1
 A Assignment Nu Cover Sheet Name: Drill Current work Question Done BP Ready Topic Comment Aa C4 Integration Repeated linear factors 3 (x ) 3 (x ) + c Ab C4 Integration cos^ conversion x + sinx + c Ac C4
A Assignment Nu Cover Sheet Name: Drill Current work Question Done BP Ready Topic Comment Aa C4 Integration Repeated linear factors 3 (x ) 3 (x ) + c Ab C4 Integration cos^ conversion x + sinx + c Ac C4
Level 3, Calculus
 Level, 4 Calculus Differentiate and use derivatives to solve problems (965) Integrate functions and solve problems by integration, differential equations or numerical methods (966) Manipulate real and
Level, 4 Calculus Differentiate and use derivatives to solve problems (965) Integrate functions and solve problems by integration, differential equations or numerical methods (966) Manipulate real and
Review for the Final Exam
 Math 171 Review for the Final Exam 1 Find the limits (4 points each) (a) lim 4x 2 3; x x (b) lim ( x 2 x x 1 )x ; (c) lim( 1 1 ); x 1 ln x x 1 sin (x 2) (d) lim x 2 x 2 4 Solutions (a) The limit lim 4x
Math 171 Review for the Final Exam 1 Find the limits (4 points each) (a) lim 4x 2 3; x x (b) lim ( x 2 x x 1 )x ; (c) lim( 1 1 ); x 1 ln x x 1 sin (x 2) (d) lim x 2 x 2 4 Solutions (a) The limit lim 4x
QUESTION 6 (16 Marks) A continuous random variable X has a Weibull distribution if it has a probability distribution function given by
 QUESTION 6 (6 Marks) A continuous random variable X has a Weibull distribution if it has a probability distribution function given by x f ( x) e x / if x otherwise where and are positive constants. The
QUESTION 6 (6 Marks) A continuous random variable X has a Weibull distribution if it has a probability distribution function given by x f ( x) e x / if x otherwise where and are positive constants. The
OC = $ 3cos. 1 (5.4) 2 θ = (= radians) (M1) θ = 1. Note: Award (M1) for identifying the largest angle.
 4 + 5 7 cos α 4 5 5 α 0.5. Note: Award for identifying the largest angle. Find other angles first β 44.4 γ 4.0 α 0. (C4) Note: Award (C) if not given to the correct accuracy.. (a) p (C) 4. (a) OA A is
4 + 5 7 cos α 4 5 5 α 0.5. Note: Award for identifying the largest angle. Find other angles first β 44.4 γ 4.0 α 0. (C4) Note: Award (C) if not given to the correct accuracy.. (a) p (C) 4. (a) OA A is
Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017
 Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017 1. The terminal ray of an angle drawn in standard position on the unit circle that measures 30 has 3 1 coordinates of,. Based on this information,
Chapter 11B: Trig Graphing Review Sheet Test Wednesday 05/17/2017 1. The terminal ray of an angle drawn in standard position on the unit circle that measures 30 has 3 1 coordinates of,. Based on this information,
LUNG CHEUNG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL Mock Examination 2006 / 2007 Mathematics and Statistics
 S.7 LUNG CHEUNG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL Mock Examination 006 / 007 Mathematics and Statistics Maximum Mark: 100 Date: 1 007 Time: 8 30 11 30 1. This paper consists of Section A and Section B.. Answer
S.7 LUNG CHEUNG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL Mock Examination 006 / 007 Mathematics and Statistics Maximum Mark: 100 Date: 1 007 Time: 8 30 11 30 1. This paper consists of Section A and Section B.. Answer
(c) Find the gradient of the graph of f(x) at the point where x = 1. (2) The graph of f(x) has a local maximum point, M, and a local minimum point, N.
 Calculus Review Packet 1. Consider the function f() = 3 3 2 24 + 30. Write down f(0). Find f (). Find the gradient of the graph of f() at the point where = 1. The graph of f() has a local maimum point,
Calculus Review Packet 1. Consider the function f() = 3 3 2 24 + 30. Write down f(0). Find f (). Find the gradient of the graph of f() at the point where = 1. The graph of f() has a local maimum point,
December 2012 Maths HL Holiday Pack. Paper 1.2 Paper 1 from TZ2 Paper 2.2 Paper 2 from TZ2. Paper 1.1 Paper 1 from TZ1 Paper 2.
 December 2012 Maths HL Holiday Pack This pack contains 4 past papers from May 2011 in the following order: Paper 1.2 Paper 1 from TZ2 Paper 2.2 Paper 2 from TZ2 Paper 1.1 Paper 1 from TZ1 Paper 2.1 Paper
December 2012 Maths HL Holiday Pack This pack contains 4 past papers from May 2011 in the following order: Paper 1.2 Paper 1 from TZ2 Paper 2.2 Paper 2 from TZ2 Paper 1.1 Paper 1 from TZ1 Paper 2.1 Paper
On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions by showing ALL of your work.
 Final Exam Review Cummulative Math 20-1 Ch.1 Sequence and Series Final Exam Review On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions by showing ALL of your work. 1. The common difference in
Final Exam Review Cummulative Math 20-1 Ch.1 Sequence and Series Final Exam Review On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions by showing ALL of your work. 1. The common difference in
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
Chapter 7. 1 a The length is a function of time, so we are looking for the value of the function when t = 2:
 Practice questions Solution Paper type a The length is a function of time, so we are looking for the value of the function when t = : L( ) = 0 + cos ( ) = 0 + cos ( ) = 0 + = cm We are looking for the
Practice questions Solution Paper type a The length is a function of time, so we are looking for the value of the function when t = : L( ) = 0 + cos ( ) = 0 + cos ( ) = 0 + = cm We are looking for the
D. 6. Correct to the nearest tenth, the perimeter of the shaded portion of the rectangle is:
 Trigonometry PART 1 Machine Scored Answers are on the back page Full, worked out solutions can be found at MATH 0-1 PRACTICE EXAM 1. An angle in standard position θ has reference angle of 0 with sinθ
Trigonometry PART 1 Machine Scored Answers are on the back page Full, worked out solutions can be found at MATH 0-1 PRACTICE EXAM 1. An angle in standard position θ has reference angle of 0 with sinθ
Practice Test - Chapter 4
 Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
u x y reduces the differential equation
 CATHOLIC JUNIOR COLLEGE H MATHEMATICS 06 JC PRELIM Paper (i) Prove that the substitution (ii) (i) Given u x y, du dy x y dx dx du dy x y ----------- (I) dx dx Substitute (I) & u x y and into D.E: we get
CATHOLIC JUNIOR COLLEGE H MATHEMATICS 06 JC PRELIM Paper (i) Prove that the substitution (ii) (i) Given u x y, du dy x y dx dx du dy x y ----------- (I) dx dx Substitute (I) & u x y and into D.E: we get
Review for FINALS. FINAL CULMINATING date FINAL EXAM date
 Date: Name: Review for FINALS FINAL CULMINATING date FINAL EXAM date Success Criteria Ensure our Journals are complete and corrected. These ou ma use on the CULMINATING (but not on the EXAM) Complete the
Date: Name: Review for FINALS FINAL CULMINATING date FINAL EXAM date Success Criteria Ensure our Journals are complete and corrected. These ou ma use on the CULMINATING (but not on the EXAM) Complete the
!"#$%&'(#)%"*#%*+"),-$.)#/*01#2-31#)(.*4%5)(*6).#* * *9)"&*#2-*5$%5%.-&*#%5)(*8).#*9%$*1*'"),-$.)#/*31#2-31#)(.*5$-51$1#)%"*(%'$.
 !"#$%&'(#)%"*#%*+"),-$.)#/*0#-3#)(.*4%5)(*6).#* * 78-.-*9)"&*#-*5$%5%.-&*#%5)(*8).#*9%$**'"),-$.)#/*3#-3#)(.*5$-5$#)%"*(%'$.-:* ;)(*(%'8&**#).* )"#$%&'(#)%":*!*3*##()">**B$#-$*8$>-C*7DA*9)8-*%9*.%3-*5%..)
!"#$%&'(#)%"*#%*+"),-$.)#/*0#-3#)(.*4%5)(*6).#* * 78-.-*9)"&*#-*5$%5%.-&*#%5)(*8).#*9%$**'"),-$.)#/*3#-3#)(.*5$-5$#)%"*(%'$.-:* ;)(*(%'8&**#).* )"#$%&'(#)%":*!*3*##()">**B$#-$*8$>-C*7DA*9)8-*%9*.%3-*5%..)
Average rates of change May be used to estimate the derivative at a point
 Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
 Victorian Certificate of Education 08 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Wednesday 6 June 08 Reading time: 0.00 am to 0.5
Victorian Certificate of Education 08 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS Section Written examination Wednesday 6 June 08 Reading time: 0.00 am to 0.5
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
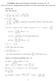 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
Active Maths 4 Book 1: Additional Questions and Solutions
 Active Maths 4 Book 1: Additional Questions and Solutions Question 1 (a) Find the vertex of y = f(x) where f(x) = x 6x 7, stating whether it is a minimum or a maximum. (b) Find where the graph of y = f(x)
Active Maths 4 Book 1: Additional Questions and Solutions Question 1 (a) Find the vertex of y = f(x) where f(x) = x 6x 7, stating whether it is a minimum or a maximum. (b) Find where the graph of y = f(x)
b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root. Ans. (D) x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
