b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root. Ans. (D) x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 Ans. (C)
|
|
|
- Laurence Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root The solution set of x 2 2x < 8 is given by the inequality (A) x < 4 (B) x > -2 (C) -2 < x < 4 (D) -2 x 4 (D) x > 4 x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 3. If sin x = , then sec x = (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) sin x = 0.618, therefore, x = sin -1 (0.6018) = 37. Now, sec x = = = An equation of line l in Figure 6 is (A) x = 2 (B) y = 2 (C) x = 0 (D) y = x + 2 (E) x + y = 2 As shown in the figure, x = 2 5. If 0 < x < 1, then (A) 0 < ln < 1 (B) ln > 1 (C) ln < 0 (D) ln > 0 (E) none of these is true 0 < x < 1, therefore, ln x < 0. But, ln = ln (x) -1 = (-1) ln x. Since ln x < 0, we get ln = (-)(-) > 0.
2 6. When (a + b) 4 is expanded, what is the coefficient of the third term? (A) 10 (B) 11 (C) 6 (D) -11 (E) The sum cannot be determined. Refer to Binomial Expansion ( + ) =. Using n = 4, r = 2, we get the coefficient of the third term, 4 C 2 = What is the approximate x-intercept of f (x) = (A) (B) 1.73 (C) (D) 0.58 (E) 3? To get the x intercept, we get y = f (x) = 0, f (x) = Thus, x + 3 = 0. x = 3 = = If f (x) = + 4 and g(x) = 2x 2-3, then f (g(2)) = (A) 6.16 (B) 3.61 (C) 2.24 (D) 3.00 (E) 6.00 This problem is about composite function. f (g(2)) means, first we get g(2) = 2(2) 2-3 = 5, and then plug it into f (x) function. f (5) = = 9 = 3 9. Let the symbol be defined as A B = cos A sin B - sin A cos B. What is the approximate value of 76 36? (A).766 (B).643 (C).125 (D) 0 (E) Just replacing A = 76, and B = 36, we get cos (76 ) sin (36 ) - sin (76 ) cos (36 ) = (-) Ans. (E) 10. The slope of a line perpendicular to the line whose equation is + = 1 is (A) (B) - (C) - + = 1 into a standard eq., we get y = 3 4 x + 3. Now, to be perpendicular to this line, we need the slope m, which is a negative reciprocal of 3 4. m = =. (D) (E) -3
3 11. Approximately, what is lim (A) 3.02 (B) 3.13 (C) 3.24 (D) 3.35 (E) 3.46? To find the limit of this eq., notice that the degrees of numerator and denominator are both the same degrees of 3. Thus, the limit on this will be the ratio of the highest degree coefficient, which is = Limit for Horizontal Asymptotes & Vertical Asymptotes; Vertical Asymptotes is the vertical line that the curve is approaching, but never cross over as x a. In most cases, the rational function has its VA, when we find its denominator equals to zero. Horizontal Asymptotes is the horizontal line that the curve is approaching as x. To find HA, we need to know 3 different cases. That is, HA, y = lim ( ). 1. When the degree of Numerator = the degree of Denominator, then HA is just the ratio of the coef. of the highest degree terms. 2. When the degree of the Num > the degree of denominator, then it is ZERO. 3. When the degree of Num < the degree of Denom, then it is UNDEFINED. For example, let y =, where x -1, 1. Then, since the degrees of numerator and denominator are both two, the HA is the limit value, which is the ratio of the leading coefficients. That is, our horizontal asymptote is y = = 1. Now, to get the vertical asymptotes, where the function is undefined, we set its denominator equal zero. That is, x 2-1 = 0. Our vertical asymptotes are x = 1, x = -1. (Note: Be careful about removable discontinuity ) In general, for Math IIC test when time management is very important, we may just use a graphing calculator, which is a much more effective way to solve quickly during the exam. You may find from the graphing of y =, two vertical asymptotes at x = 1, x = -1, and one horizontal asymptote at y = 1.
4 12. The maximum value of 3 sin x cos x + is (A) (B) (C) 3 (D) (E) 6 Using graphing calculator, we get max = 3. Or, since 3sin x cos x + = (2sin x cos x) +, and 2sin x cos x = sin 2x, we get (sin 2x) +. The amplitude of this function is, but the function has been shifted up by. Therefore, the maximum value becomes ( + ) = 3. Trigonometry A) 6 Basic Trig Functions; sin θ =, cos θ =, tan θ = SOH-CAH-TOA csc θ =, sec θ =, cot θ = B) The property of the angle sum and difference sin (A±B) = sin A cos B ± cos A sin B cos (A±B) = cos A cos B sin A sin B ± tan (A±B) = sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A cos 2A = cos 2 A sin 2 A = 1 2sin 2 A = 2cos 2 A - 1 sin 2 A + cos 2 A = 1 1+ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ. C) Heron s formula to find the area, given 3 sides; Area = ( )( )( ), where s = The Law of Sine: = = The law of Cosine: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2ab cos C Area with 2 side, and angle θ: Area = bc sin θ D) For a general form: y = a cos b(x - h) + k, we have, a = amplitude, b = # of frequency, = period, h = units of translation horizontally, k = units of shifting vertically.
5 E) Cofunctions sin θ = cos(90 -θ) = cos( - θ), (ie) sin 30 = cos 60 tan θ = cot(90 -θ) = cot( - θ), (ie) tan 15 = cot 75 sec θ = csc(90 -θ) = csc( - θ), (ie) sec 45 = csc 45 F) Sign changes by Quadrants: all seniors take calculus by I-II-III-IV Qtr 13. As angle x increases from 0 to 2π radians, sin x increases in (A) no quadrants (B) the first and third quadrants only (C) the second and fourth quadrants only (D) all four quadrants (E) the first and fourth quadrants only As shown in this graph, y = sin x increases in (I) and (IV). Ans. (E) 14. The solution set of 2x 5y < 3 lies in which quadrants? (A) I only (B) I and II (C) I, II, and III (D) II, III, and IV (E) I, II, III, and IV 2x - 5y < 3, or 2x - 3 < 5y x - < y As shown here, the graph covers all four quadrants. Ans. (E) 15. If f (x) = 2 e x - 4 and g(x) = ln x, then f (g(9)) = (A) 6.83 (B) 12 (C) 14 (D) (E) As in question #8, we get g(9) = ln 9, and then f (g(9)) = f (ln 9) = 2 (9 ln e ) - 4 = 18-4 = 14. (note: a ln b = b ln a ) Properties of log function: (1) log x y = log x + log y (2) log = log x - log y (3) log x m = m log x (4) log x y= = (5) log x x = 1, log x 1 = 0 (6) y = log a x, if and only if x = a y
6 16. Find the positive value of cos (sin ). (A) (B) 1 (C) (D) 3 (E) 2 Here, sin -1 = 30. cos (30 ) =. 17. How many different hands, each consisting of four cards, can be drawn, from a deck of 52 different cards? (A) 132,600 (B) (C) 270,725 (D) (E) 2652 To solve this problem, we need to understand the following ideas on probability and combination. 1) The total possible number of combination on n objects is n (eg) (A, B, C) = 3, because A-B-C, A-C-B, B-A-C, B-C-A, C-A-B, C-B-A, total of 6 = 3 (A, B, C, D) = 4, (A, B, C, D, E) = 5 etc. 2) The total number of combination on n objects, but with the repetition of k and r objects is (eg) COFFEE = ( )( ) Minimum = ( )( ) 3) The total number of combination on n objects, but with k group with n, and n 2 member in them is k(n 1 )(n 2 ) (eg) A, B, C, D, E into 2 grouping of (A, B), (C, D, E) will be (2 grouping)(2 on A, B)(3 on C, D, E) = (2)(2)(3) 4) Permutation is with a consideration of "Ordering", np r = ( ) (eg) Suggest I choose 3 students with the best score out of 10 students in my Math IIc class, and then buy them lunch, steak for the best, hamburger for the second best, and tacos for the third best. Then, this will a permutation, because "Order" matters by having different lunches with their rank, thus 10 P 3 = ( ) = 5) Combination is without a consideration of "ordering", nc r = ( ) (eg) Suppose that I choose 3 students with the top best scores in my Math IIc class, and then buy them lunch, but this time, all hamburgers. Then, in this case, "order" does not matter, because they all eat hamburgers. Thus, it is Combination, 10 C 3 = ( ) = Now, notice that 10 C 3 and 10 P 3 are exactly the same, except that 10 C 3 is being divided by 3, while 10 P 3 isn t. That is because in 10 C 3 case, those 3 students selected will have the same lunch, hamburger - hamburger - hamburger, or H - H - H repetition of 3, therefore, being divided by 3. Based on the above ideas on Combination, we choose 4 cards out of 52 cards, but without any particular ordering. Therefore, it will be combination, 52 C 4 = = 270,725.
7 18. The area of a triangle with sides 4, 5, and 8 is (A) 7.5 (B) 8.18 (C) 3.75 (D) 13.0 (E) 2.4 Here, we are given the lengths of 3 sides only, without any angle information. Therefore, we use Heron s formula to find the area, that is s = = = 8.5 Area = ( )( )( ) = 8.5(8.5 4)(8.5 5)(8.5 8) = 8.18 Now, in addition to Heron s formula, we also need to review following formulas for Math IIc - exam: 1) The Law of Sine: = = 2) The law of Cosine: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2ab cos C 3) Area with 2 side, and angle θ: Area = bc sin θ 19. One side of a given triangle is 6 inches. Inside the triangle a line segment is drawn parallel to this side, cutting off a triangle whose area is one-thirds that of the given triangle. Find the length of this segment in inches. (A) 2 (B) 2 3 (C) 3 3 (D) 6 3 (E) 9 Since the ratio of the area DBE is 1:, we get the ratio of the line segment A C:D E = 1:. (Note) Length : Area : Volume :
8 20. Given the statement, "Only if it snows will the class be cancelled", if it is known that it did not snow, what conclusion can be drawn? (A) The class is cancelled. (B) The class is not cancelled. (C) The class might be cancelled. (D) No conclusion can be drawn. (E) None of the above. As mentioned in the previous test #1, it is a logic problem with negation. LOGIC : There are 4 different logic cases; Let s make a statement. If p, then q. Using mathematical symbol for this statement is, p q. Negation: If p, then NOT q, or, p ~ q, where "~" sign represents "NOT". Inverse: If NOT p, then NOT q, or ~ p ~ q. Converse: If q, then p, or q p. Contra Positive: If NOT q, then NOT p, or ~ q ~ p. Of all these, the Contra Positive is the most important one to remember. Here, the Contra Positive is exactly the same statement as the original statement. Often, if we cannot prove the original statement, then we may use the logic of Contra Positive to prove the original statement. 21. What is the domain of the function f (x) = (A) x < (B) x 1.36 (C) x > 1.36 (D) x 1.36 (E) x < or x > 1.36? In most case, a domain problem in Rational Function involves with the condition of its denominator. In this problem, the denominator 2 5 0, and at the same time, 2x 3 5 > 0. 2x 3 5 > 0 or x > The hyperbola 9x 2 4y 2 = 16 intersects the x-axis at approximately which of the following points? (A) (2, 0) (B) (0, 2) (C) (1.33, 0) (D) (0, 1.33) (E) (0, -1.33) This problem involves with the topics on Conic Sections. However, the question only asks about the x-intercept, when y = 0, we only need to plug in y = 0 into equation. 9x 2 4(0) 2 = 16 x 2 = x = ± 16 9 = ± = ±1.33 (1.33, 0)
9 (Note) For the future reference, I want to go over topics on Conic Sections as follows: 1) Circle: Let P 1 be the plane that cuts the cone in a horizontal direction. Then it creates a circle, formed by its intersection. Given (x - h) 2 + (y - k) 2 = r 2, center = (h, k) radius = r 2) Ellipse: Let P 2 be the plane that cuts the cone in a tilted direction. Then it creates an elliptical figure, formed by intersection. Given ( ) + ( ) = 1, center = (h, k) length of Major axis = 2a, when a > b length of Minor axis = 2b vertex = (±a + h, o + k) Foci = (h ± c, k), where c 2 = a 2 b 2 d 1 + d 2 = 2a + = 1, a > b a < b
10 3) Hyperbola: Let P 3 be the plane that cuts the cone in a vertical direction. Then it creates a hyperbolic figure, formed by its intersection. Given ( ) ( ) = 1, or ( ) ( ) = 1, center = (h, k) vertex = (±a + h, o + k) Asymptotes: y - k = ± (x h), where the slope is. Foci = (±c + h, o + k), where c 2 = a 2 + b 2 d 1 d 2 = 2a - = 1 - = 1 4) Parabola: Let P 4 be the plane that cuts the cone in a parallel to slant edge direction. Then it creates a parabolic figure, formed by its intersection. Given 4P(y - k) = (x - h) 2, or 4P(x - h) = (y - k) 2, vertex = (h, k) Foci = (o + h, p + k ) or (p + h, o + k) Directrix line: y = -p + k or x = -p + h 23. The length of the vector that could correctly be used to represent in the complex plane the number i is (A) 11 (B) 11 (C) 3 2 (D) 5 (E) 13 The length of a vector, or the magnitude of a vector, z = a + bi = < a, b > is given by z = a + bi = +. Therefore, z = i = ( 7) + 2 = 11.
11 24. In a cube, the ratio of the longest diagonal to a side is (A) 2 : 3 (B) 6 : 2 (C) 6 : 2 (D) 3 : 2 (E) 3 : 1 c = = 3 b = = 2 Thus, c:a = 3:1 Ans. (E) 25. What is the measure of the smallest angle in a right triangle with sides of lengths 5, 12 and 13? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Referring to the topics of Trig. Functions previously, we may use the Law of cosine, c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2ab cos C. Here, the shortest side is = cos C. C = cos -1 = What is the period of the curve whose equation is y = 4sin x cos x? (A) 60 (B) 120 (C) 180 (D) 360 (E) 720 y = 4sin x cos x = 2(2sin x cos x). But 2sin x cos x = sin 2x. y = 2 sin 2x p = 2 = π = Let f (x) be a polynomial function. If f ( 2) = 0 and f (- 2) = 0, then f (x) is divisible by (A) x 3 (B) x 2 2 (C) x (D) x 2-3x + 2 (E) x 2 + 3x + 2 Refer to the previous test #1, we have stated Factor Theorem, that is, if f (x) has f (a) = 0, then it must have a factor of (x - a). Here, f ( 2) = 0 and f (- 2) = 0. we have (x - 2)(x + 2) factors. Therefore, f (x) must be division by (x 2-2). 28. How many real roots does the following equation have? 5e x + e -x 4 = 0 (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) an infinite number Using a Graphing utility, let y 1 = 5e x + e -x - 4, and then check how many x-intercept it has. There is no real root.
12 29. If f (x) = ln x and g(x) = f (x) f -1 (x), what does g(2) equal? (A) 8.1 (B) 7.5 (C) 8.3 (D) 5.1 (E) 7.4 f (x) = y = ln x. Now, to get the inverse f -1 (x) by switching x and y's, x = ln y or y = e x = f -1 (x) g(x) = f (x) f -1 (x) = (ln x) (e x ) g(2) = (ln 2) (e 2 ) = If the 3rd term of a geometric progression is and the 6th term is, what is the 12 th term of the progression? (A) a (B) 2a (C) (D) (E) a 2 Recall the Geometric series with the following formulas: a n = a 1 r n-1, r =, s n = a 1 And also, the infinite series, s = a 1, r < 1. Here, a 3 = and a₆ =. = = r 3, which is, = r 3, or = r 3 r =. Therefore, a 12 = a 6 r 6 = ( ) 6 = =. (Note) For Arithmetic series, a n = a 1 + (n - 1)d, d = a n - a n-1, s n = where d is the "Common Difference" n, 31. If f (x, y, z) = 3x - 5y + 6z and f (a, b, 0) = f (0, a, b), then = (A) 0.32 (B) 2.7 (C) 8.6 (D) 0.12 (E) 1.18 f (x, y, z) = 3x - 5y + 6z (a, b, o) = 3a - 5b + 0 eq. (1) (o, a, b) = 0-5a + 6b eq. (2) By equating (1) = (2), we get 3a - 5b = - 5a + 6b, or ( 3 + 5)a = ( 6 + 5)b = = 1.18 Ans. (E) 32. What is the inverse of f (x) =? (A) y = (B) y = 5 - (C) y = y = f (x) =. To get the inverse f -1 (x) by switching x and y's, we get x = or x 2 =. Now, by reciprocal of both sides, = -y y 2 = 5 -, or y = 5 = f -1 (x). (D) y = (E) y = + 5
13 33. Find the value of P if (x + 1) is a factor of f (x) = 3x 4 + 2x 3 Px 2 2x + 1. (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 (E) 5 If (x + 1) is a factor of f (x), then f (-1) = 0. f (-1) = p = 0. p = In how many different orders can 10 students arrange themselves around a table? (A) 9 (B) 81 (C) 181,440 (D) 362,880 (E) 387,420,489 Here, the circular permutation is is (n 1) 9 = 362, If [x] is defined to represent the greatest integer less than or equal to x, and f (x) = x [x], what is the period of f (x)? (A) 1 (B) (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) f is not a periodic function. f (x) = [x] is what is called "Integer Function", and defined as the greatest integer, x [x] < x + 1. (ie) [3.5] = 3, [12.57] = 12, [-2.5] = -3,... etc. Here, the quicker way of solving it is by using a graphing utility. y 1 = abs(x - int(x) - 0.5) shows that y 1 repeats its cycle every one unit. 36. If the equation 3x 3 + 9x 2 + px q = 0 has 3 equal roots, then (A) q = 0 (B) p = 0 (C) q = 1 (D) each root = 1 (E) each root = -1 For a given cubic function, f (x) = ax 3 + bx 2 + cx + d, the sum of the three roots, x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = (-) and the product of the roots, = Here, the sum of 3 equal roots is x 1 + x 2 + x 3 = x 1 + x 1 + x 1 = 3x 1 = (-) = (-)3. x 1 = (-)1 Ans. (E) 37. Each term of a sequence, after the first, is inversely proportional to the term preceding it. If the first two terms are 3 and 9, what is the 100th term? (A) 3 (B) 9 (C) (D) 3 99 (E) The 100th term cannot be determined. a 1 = 3, a 2 = 9, a 3, a 4,... Since the second term 9 is inversely proportion to the proceeding term 3, we get 9 = k, k = 27. Therefore the general term a n = k = 27. Using this sequence, a 3 = 27 = 27 = 3, a 4 = 27 = 27 = 9,... etc., which creates the sequence of 3, 9, 3, 9,... Every even term is 9. a 100 = 9
14 38. The point whose polar coordinates are (3, 45 ) is the same as the point whose polar coordinates are (A) (-3, 45 ) (B) (-3, 225 ) (C) (3, -45 ) (D) (-3, 135 ) (E) (3, 225 ) As shown in the figure, the point Q is in the opposite side of the point P. Now, for the point Q(3, 225 ) to be the same point as P(3, 45 ), we need to change r = (+)3 of point Q to r = (-)3 to move the direction backward (-3, 225 ) = (3, 45 ) In general, (r, θ) = (-r, θ ). 39. If log x 2 log 8 + log x, then (A) x 2 (B) x 2 (C) x 4 (D) x 4 (E) x 1 Referring to the properties of logarithmic function, log AB = log A + log B, log = log A - log B, we get log x 2 log 8 log 0, or 1 1 x2 8 x ( - 8) 0. Since 0, we get x 4. However, this algebraic manipulation takes too long. Therefore, my recommendation is to use a graphing utility, let y 1 = log x 2, and y 2 = log 8 + look for the solution for y 1 y 2 x 4. log x, and then, 40. A right circular cylinder is circumscribed about a sphere. If V s represents the volume of the sphere and V c represents the volume of the cylinder, then Refer to the figure shown, V c = πr 2 h = πr 2 (2r) = 2πr 3. V s = πr 3 (A) V s = V c V s = V c (B) V s < V c (C) V s > V c (D) V s V c (E) V s V c
15 41. If f (x) =, when x 3 If f (x) = k, when x = 3, what must the value of k be in order for f (x) to be a continuous function? (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 0 (D) -2 (E) No value of k will make f (x) a continuous function. In order to be a continuous function, the discontinuity at x = 3 must be removed. That means, for the given function, f (x) = = ( )( ) must be ( ) reduced to f (x) = ( )( ) = (x + 1), x 3. ( ) Now, with this function f (x) = (x + 1), f (3) = = 4, and k must be equal to f (3) for f (x) to be a continuous function. 42. Write the complex number 3 - i in polar form. (A) 2(cos + i sin ) (B) -2(cos + i sin ) (C) 2(cos + i sin ) (D) -2(cos + i sin ) Let z = a + bi = 3 - i, where a = 3, b = (-)1. Then, from the course of Polar coordinates, r = + = 4 = 2, θ = tan -1 (- ) = -, or in the 4th quadrant. Therefore, using z = a + bi = r(cos θ + i sin θ) in polar form, z = 3 - i =2(cos + i sin ). Ans. (E) (E) 2(cos + i sin ) 43. If = 2 3, then θ = (A) 15 (B) 30 (C) 45 (D) 60 (E) 75 Using a graphing utility, let y 1 =, y 2 = 2 3, and then find the intersection. The result is θ = What is the degree measure of the angle x of a triangle that has sides of length of 5 and 7 as shown in the figure (1)? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Using the Law of sine, we get sin x = = x = sin = =
16 45. In ABC, a = 2, b = 5, C = 60. What is the area of ABC? (A) 4.3 (B) 3.6 (C) 3.2 (D) 2.9 (E) 2.3 Area of ABC = a b sin c = (2)(5) sin 60 =. 46. If f (x, y) = x 3 xy 2 + 3y 4, which of the following is (are) true? I. f (x, y) = f (x, -y) II. f (x, y) = f (-x, y) III. f (x, y) = f (-x, -y) (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III Since f (x, y) = x 3 - xy 2 + 3y 4 has y terms with even powers, f (x, -y) should have the same result as f (x, y), while f (-x, y) should have effect on its x terms with odd powers. Therefore, the only right choice is (I). 47. Figure 5 shows a cube with edge of length 4 centimeters. If points A and C are midpoints of the edges of the cube, what is the area of region ABCD? B A D = = 20 = 2 5. Area of ABCD = 2 5 = 20cm 2 A C D (A) cm 2 (B) cm 2 (C) cm 2 (D) cm 2 (E) cm 2
17 48. If (x, y) represents a point on the graph of y = 2 + 1, which of the following could be a portion of the graph of the set of points (x, y 2 )? (A) 1 2 y (B) 1 2 y For a given function, y = 2 + 1, we transform our coordinates from (x, y) to (x, y 2 ). Therefore, letting Y = y 2, we get Y = y 2 = = 2x + 1, or Y = 2x + 1 in (x, Y) coordinate system. 1 x 1 x (C) 2 y (D) 2 y x 1 x (E) 2 y 1 1 x 49. If the parameter is eliminated from the equations x = 4t and y = 2t, then the relation between x and y is (A) y = x 1 (B) y = 1 x (C) y 2 = x 1 (D) y 2 = (x 1) 2 (E) y 2 = 4x - 4 In this problem of parametric equation, we need to eliminate "t" from x and y equations, and set up the two equation into one equation with x and y variables only. Since y = 2t, and x = 4t 2 + 1, we replace 4t 2 with y 2. x = 4t = (2t) = y y 2 = x If 8 people shook hands with each other, how many handshakes were exchanged? (A) 8 (B) 16 (C) 21 (D) 28 (E) 56 Shaking hands implies between 2 people. Therefore, 8 C 2 = 28.
1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to
 SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
Since x + we get x² + 2x = 4, or simplifying it, x² = 4. Therefore, x² + = 4 2 = 2. Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
ALGEBRA 2 X. Final Exam. Review Packet
 ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
Algebra 2 Khan Academy Video Correlations By SpringBoard Activity
 SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
SB Activity Activity 1 Creating Equations 1-1 Learning Targets: Create an equation in one variable from a real-world context. Solve an equation in one variable. 1-2 Learning Targets: Create equations in
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers
 Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Coach Stones Expanded Standard Pre-Calculus Algorithm Packet Page 1 Section: P.1 Algebraic Expressions, Mathematical Models and Real Numbers CLASSIFICATIONS OF NUMBERS NATURAL NUMBERS = N = {1,2,3,4,...}
Curriculum Catalog
 2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents PRE-CALCULUS COURSE OVERVIEW...1 UNIT 1: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 2: FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT
2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents PRE-CALCULUS COURSE OVERVIEW...1 UNIT 1: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 2: FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT
Algebra and Trigonometry
 Algebra and Trigonometry 978-1-63545-098-9 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Jay Abramson, Arizona State
Algebra and Trigonometry 978-1-63545-098-9 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Jay Abramson, Arizona State
The American School of Marrakesh. AP Calculus AB Summer Preparation Packet
 The American School of Marrakesh AP Calculus AB Summer Preparation Packet Summer 2016 SKILLS NEEDED FOR CALCULUS I. Algebra: *A. Exponents (operations with integer, fractional, and negative exponents)
The American School of Marrakesh AP Calculus AB Summer Preparation Packet Summer 2016 SKILLS NEEDED FOR CALCULUS I. Algebra: *A. Exponents (operations with integer, fractional, and negative exponents)
PreCalculus. Curriculum (447 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Lone Star College-CyFair Formula Sheet
 Lone Star College-CyFair Formula Sheet The following formulas are critical for success in the indicated course. Student CANNOT bring these formulas on a formula sheet or card to tests and instructors MUST
Lone Star College-CyFair Formula Sheet The following formulas are critical for success in the indicated course. Student CANNOT bring these formulas on a formula sheet or card to tests and instructors MUST
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus
 DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
1. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y 3x
 MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
HHS Pre-Calculus Reference Book
 HHS Pre-Calculus Reference Book Purpose: To create a reference book to review topics for your final exam and to prepare you for Calculus. Instructions: Students are to compose a reference book containing
HHS Pre-Calculus Reference Book Purpose: To create a reference book to review topics for your final exam and to prepare you for Calculus. Instructions: Students are to compose a reference book containing
PRE-CALCULUS FORM IV. Textbook: Precalculus with Limits, A Graphing Approach. 4 th Edition, 2005, Larson, Hostetler & Edwards, Cengage Learning.
 PRE-CALCULUS FORM IV Tetbook: Precalculus with Limits, A Graphing Approach. 4 th Edition, 2005, Larson, Hostetler & Edwards, Cengage Learning. Course Description: This course is designed to prepare students
PRE-CALCULUS FORM IV Tetbook: Precalculus with Limits, A Graphing Approach. 4 th Edition, 2005, Larson, Hostetler & Edwards, Cengage Learning. Course Description: This course is designed to prepare students
Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 261-pilot)
 Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10023 Sp 11 253 Topics (was 261-pilot) Intermediate Algebra (2011), 3rd Ed. [open all close all] R-Review of Basic Algebraic Concepts Section R.2 Ordering integers Plotting
Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10023 Sp 11 253 Topics (was 261-pilot) Intermediate Algebra (2011), 3rd Ed. [open all close all] R-Review of Basic Algebraic Concepts Section R.2 Ordering integers Plotting
Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 217-pilot)
 Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10024 Sp 11 213 Topics (was 217-pilot) College Algebra, 9th Ed. [open all close all] R-Basic Algebra Operations Section R.1 Integers and rational numbers Rational and irrational
Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10024 Sp 11 213 Topics (was 217-pilot) College Algebra, 9th Ed. [open all close all] R-Basic Algebra Operations Section R.1 Integers and rational numbers Rational and irrational
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Textbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012
 Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
Polynomials and Rational Functions. Quadratic Equations and Inequalities. Remainder and Factor Theorems. Rational Root Theorem
 Pre-Calculus Pre-AP Scope and Sequence - Year at a Glance Pre-Calculus Pre-AP - First Semester Pre-calculus with Limits; Larson/Hostetler Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks
Pre-Calculus Pre-AP Scope and Sequence - Year at a Glance Pre-Calculus Pre-AP - First Semester Pre-calculus with Limits; Larson/Hostetler Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks
How to use this Algebra II - Semester 2 Study Packet
 Excellence is not an act, but a habit. Aristotle Dear Algebra II Student, First of all, Congrats! for making it this far in your math career. Passing Algebra II is a huge mile-stone Give yourself a pat
Excellence is not an act, but a habit. Aristotle Dear Algebra II Student, First of all, Congrats! for making it this far in your math career. Passing Algebra II is a huge mile-stone Give yourself a pat
ACT MATH MUST-KNOWS Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions
 Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
Pre-Algebra and Elementary Algebra: 24 questions Basic operations using whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimals and percents Natural (Counting) Numbers: 1, 2, 3 Whole Numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3 Integers:
Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part)
 Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW
 NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW Algebra II Honors is a full-year, high school math course intended for the student who has successfully completed the prerequisite course Algebra I. This course focuses on algebraic
NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW Algebra II Honors is a full-year, high school math course intended for the student who has successfully completed the prerequisite course Algebra I. This course focuses on algebraic
Portable Assisted Study Sequence ALGEBRA IIB
 SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
Algebra III INSTRUCTIONAL PACING GUIDE (Days Based on 90 minutes)
 EA, IA, PC-1. Connect algebra and trigonometry with other branches of mathematics. EA, IA, PC-1.7 G-1. G-1.8 G-1.9 Understand how to represent algebraic and trigonometric relationships by using tools such
EA, IA, PC-1. Connect algebra and trigonometry with other branches of mathematics. EA, IA, PC-1.7 G-1. G-1.8 G-1.9 Understand how to represent algebraic and trigonometric relationships by using tools such
College Algebra & Trig w Apps
 WTCS Repository 10-804-197 College Algebra & Trig w Apps Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 5.00 This course covers those skills needed for success in Calculus and many
WTCS Repository 10-804-197 College Algebra & Trig w Apps Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Total Credits 5.00 This course covers those skills needed for success in Calculus and many
CURRICULUM GUIDE. Honors Algebra II / Trigonometry
 CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Algebra II / Trigonometry The Honors course is fast-paced, incorporating the topics of Algebra II/ Trigonometry plus some topics of the pre-calculus course. More emphasis is placed
CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Algebra II / Trigonometry The Honors course is fast-paced, incorporating the topics of Algebra II/ Trigonometry plus some topics of the pre-calculus course. More emphasis is placed
Math 370 Semester Review Name
 Math 370 Semester Review Name 1) State the following theorems: (a) Remainder Theorem (b) Factor Theorem (c) Rational Root Theorem (d) Fundamental Theorem of Algebra (a) If a polynomial f(x) is divided
Math 370 Semester Review Name 1) State the following theorems: (a) Remainder Theorem (b) Factor Theorem (c) Rational Root Theorem (d) Fundamental Theorem of Algebra (a) If a polynomial f(x) is divided
NON-AP CALCULUS SUMMER PACKET
 NON-AP CALCULUS SUMMER PACKET These problems are to be completed to the best of your ability by the first day of school. You will be given the opportunity to ask questions about problems you found difficult
NON-AP CALCULUS SUMMER PACKET These problems are to be completed to the best of your ability by the first day of school. You will be given the opportunity to ask questions about problems you found difficult
Summer 2017 Review For Students Entering AP Calculus AB/BC
 Summer 2017 Review For Students Entering AP Calculus AB/BC Holy Name High School AP Calculus Summer Homework 1 A.M.D.G. AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet Holy Name High School Welcome to AP Calculus
Summer 2017 Review For Students Entering AP Calculus AB/BC Holy Name High School AP Calculus Summer Homework 1 A.M.D.G. AP Calculus AB Summer Review Packet Holy Name High School Welcome to AP Calculus
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW
 CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
PRECALCULUS BISHOP KELLY HIGH SCHOOL BOISE, IDAHO. Prepared by Kristina L. Gazdik. March 2005
 PRECALCULUS BISHOP KELLY HIGH SCHOOL BOISE, IDAHO Prepared by Kristina L. Gazdik March 2005 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Course Description.3 Scope and Sequence 4 Content Outlines UNIT I: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
PRECALCULUS BISHOP KELLY HIGH SCHOOL BOISE, IDAHO Prepared by Kristina L. Gazdik March 2005 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Course Description.3 Scope and Sequence 4 Content Outlines UNIT I: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
5.4 - Quadratic Functions
 Fry TAMU Spring 2017 Math 150 Notes Section 5.4 Page! 92 5.4 - Quadratic Functions Definition: A function is one that can be written in the form f (x) = where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. (What
Fry TAMU Spring 2017 Math 150 Notes Section 5.4 Page! 92 5.4 - Quadratic Functions Definition: A function is one that can be written in the form f (x) = where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. (What
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ALGEBRA II
 UNIT: Review of Basic Algebra Skills as Needed SR1 and any Supplemental Materials UNIT : What skills from Algebra I are used in Algebra II? Review Algebra I Skills as Needed SR1 and any additional resources
UNIT: Review of Basic Algebra Skills as Needed SR1 and any Supplemental Materials UNIT : What skills from Algebra I are used in Algebra II? Review Algebra I Skills as Needed SR1 and any additional resources
Unit 1. Revisiting Parent Functions and Graphing
 Unit 1 Revisiting Parent Functions and Graphing Precalculus Analysis Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Understand how the algebraic properties of an equation transform the geometric properties of its graph.
Unit 1 Revisiting Parent Functions and Graphing Precalculus Analysis Pacing Guide First Nine Weeks Understand how the algebraic properties of an equation transform the geometric properties of its graph.
Course Catalog. Pre-calculus Glynlyon, Inc.
 Course Catalog Pre-calculus 2016 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 2: FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT 4: CIRCULAR
Course Catalog Pre-calculus 2016 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 2: FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT 4: CIRCULAR
PreCalculus. Curriculum (637 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Algebra 2. Curriculum (384 topics additional topics)
 Algebra 2 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Algebra 2 This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).
 Review You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).. Arithmetic You should know how to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and work with the integers Z = {...,,,
Review You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).. Arithmetic You should know how to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and work with the integers Z = {...,,,
Math Level 2. Mathematics Level 2
 Math Reference Information THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS FOR YOUR REFERENCE IN ANSWERING SOME OF THE SAMPLE QUESTIONS. THIS INFORMATION IS ALSO PROVIDED ON THE ACTUAL SUBJECT TEST IN MATHEMATICS LEVEL.
Math Reference Information THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS FOR YOUR REFERENCE IN ANSWERING SOME OF THE SAMPLE QUESTIONS. THIS INFORMATION IS ALSO PROVIDED ON THE ACTUAL SUBJECT TEST IN MATHEMATICS LEVEL.
ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY FOR CALCULUS MATH 1340
 ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY FOR CALCULUS Course Description: MATH 1340 A combined algebra and trigonometry course for science and engineering students planning to enroll in Calculus I, MATH 1950. Topics include:
ALGEBRA & TRIGONOMETRY FOR CALCULUS Course Description: MATH 1340 A combined algebra and trigonometry course for science and engineering students planning to enroll in Calculus I, MATH 1950. Topics include:
Algebra 2 Honors Final Exam StudyGuide
 Name: Score: 0 / 80 points (0%) Algebra 2 Honors Final Exam StudyGuide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Simplify. 2. D Multiply the numerator
Name: Score: 0 / 80 points (0%) Algebra 2 Honors Final Exam StudyGuide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Simplify. 2. D Multiply the numerator
Functions and their Graphs
 Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
Chapter One Due Monday, December 12 Functions and their Graphs Functions Domain and Range Composition and Inverses Calculator Input and Output Transformations Quadratics Functions A function yields a specific
STEM-Prep Pathway SLOs
 STEM-Prep Pathway SLOs Background: The STEM-Prep subgroup of the MMPT adopts a variation of the student learning outcomes for STEM from the courses Reasoning with Functions I and Reasoning with Functions
STEM-Prep Pathway SLOs Background: The STEM-Prep subgroup of the MMPT adopts a variation of the student learning outcomes for STEM from the courses Reasoning with Functions I and Reasoning with Functions
DRAFT. Pre-calculus Curriculum Map Quarter 1 Chapters P 2. Extraneous Critical numbers Test intervals
 Quarter 1 Chapters P 2 Plot points in the coordinate plane and use distance and midpoint formulas. Sketch graphs of equations. Find and use slope of a line to write and graph linear equations. Solve equations:
Quarter 1 Chapters P 2 Plot points in the coordinate plane and use distance and midpoint formulas. Sketch graphs of equations. Find and use slope of a line to write and graph linear equations. Solve equations:
1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
 Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math Review for AP Calculus
 Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
Contents. CHAPTER P Prerequisites 1. CHAPTER 1 Functions and Graphs 69. P.1 Real Numbers 1. P.2 Cartesian Coordinate System 14
 CHAPTER P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers 1 Representing Real Numbers ~ Order and Interval Notation ~ Basic Properties of Algebra ~ Integer Exponents ~ Scientific Notation P.2 Cartesian Coordinate System
CHAPTER P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers 1 Representing Real Numbers ~ Order and Interval Notation ~ Basic Properties of Algebra ~ Integer Exponents ~ Scientific Notation P.2 Cartesian Coordinate System
Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet. Calculator Questions
 Name: Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet Calculator Questions 1. Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (Sec. 1.6) 2 8 37 2. Graph the inequality 31. (Sec. 2.8) 3. If y varies directly
Name: Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet Calculator Questions 1. Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (Sec. 1.6) 2 8 37 2. Graph the inequality 31. (Sec. 2.8) 3. If y varies directly
Math 370 Semester Review Name
 Math 370 Semester Review Name These problems will give you an idea of what may be included on the final exam. Don't worry! The final exam will not be this long! 1) State the following theorems: (a) Remainder
Math 370 Semester Review Name These problems will give you an idea of what may be included on the final exam. Don't worry! The final exam will not be this long! 1) State the following theorems: (a) Remainder
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Grade XI Mathematics
 Grade XI Mathematics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter Wise - Important Questions and Solutions #GrowWithGreen Questions Sets Q1. For two disjoint sets A and B, if n [P ( A B )] = 32 and n [P ( A B )] =
Grade XI Mathematics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter Wise - Important Questions and Solutions #GrowWithGreen Questions Sets Q1. For two disjoint sets A and B, if n [P ( A B )] = 32 and n [P ( A B )] =
PreCalculus Honors Curriculum Pacing Guide First Half of Semester
 Unit 1 Introduction to Trigonometry (9 days) First Half of PC.FT.1 PC.FT.2 PC.FT.2a PC.FT.2b PC.FT.3 PC.FT.4 PC.FT.8 PC.GCI.5 Understand that the radian measure of an angle is the length of the arc on
Unit 1 Introduction to Trigonometry (9 days) First Half of PC.FT.1 PC.FT.2 PC.FT.2a PC.FT.2b PC.FT.3 PC.FT.4 PC.FT.8 PC.GCI.5 Understand that the radian measure of an angle is the length of the arc on
Topic 1: Fractional and Negative Exponents x x Topic 2: Domain. 2x 9 2x y x 2 5x y logg 2x 12
 AP Calculus BC Summer Packet Name INSTRUCTIONS: Where applicable, put your solutions in interval notation. Do not use any calculator (ecept on Topics 5:#5 & :#6). Please do all work on separate paper and
AP Calculus BC Summer Packet Name INSTRUCTIONS: Where applicable, put your solutions in interval notation. Do not use any calculator (ecept on Topics 5:#5 & :#6). Please do all work on separate paper and
1 x. II. CHAPTER 2: (A) Graphing Rational Functions: Show Asymptotes using dotted lines, Intercepts, Holes(Coordinates, if any.)
 FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
CHAPTERS 5-7 TRIG. FORMULAS PACKET
 CHAPTERS 5-7 TRIG. FORMULAS PACKET PRE-CALCULUS SECTION 5-2 IDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin x = ( 1 / csc x ) csc x = ( 1 / sin x ) cos x = ( 1 / sec x ) sec x = ( 1 / cos x ) tan x = ( 1 / cot x
CHAPTERS 5-7 TRIG. FORMULAS PACKET PRE-CALCULUS SECTION 5-2 IDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin x = ( 1 / csc x ) csc x = ( 1 / sin x ) cos x = ( 1 / sec x ) sec x = ( 1 / cos x ) tan x = ( 1 / cot x
Math Prep for Statics
 Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
function independent dependent domain range graph of the function The Vertical Line Test
 Functions A quantity y is a function of another quantity x if there is some rule (an algebraic equation, a graph, a table, or as an English description) by which a unique value is assigned to y by a corresponding
Functions A quantity y is a function of another quantity x if there is some rule (an algebraic equation, a graph, a table, or as an English description) by which a unique value is assigned to y by a corresponding
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
Copyright 2018 UC Regents and ALEKS Corporation. ALEKS is a registered trademark of ALEKS Corporation. 2/10
 Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review
 Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
AP Calculus Summer Assignment Summer 2017 Expectations for Summer Assignment on the first day of the school year.
 Summer 07 Expectations for Summer Assignment This packet is to be submitted to your Calculus BC teacher on the first day of the school year. All work must be shown in the packet OR on separate paper attached
Summer 07 Expectations for Summer Assignment This packet is to be submitted to your Calculus BC teacher on the first day of the school year. All work must be shown in the packet OR on separate paper attached
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 5
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Algebraic. techniques1
 techniques Algebraic An electrician, a bank worker, a plumber and so on all have tools of their trade. Without these tools, and a good working knowledge of how to use them, it would be impossible for them
techniques Algebraic An electrician, a bank worker, a plumber and so on all have tools of their trade. Without these tools, and a good working knowledge of how to use them, it would be impossible for them
International Baccalaureate MYP Pacing Guide
 International Baccalaureate MYP Pacing Guide Subject Area: Algebra II / Trigonometry Grade: 9,10,11,12 Year: 2012-2013 No. of Wk. 1 1.5 Unit title Preliminary topics in Algebra Absolute Value Equations
International Baccalaureate MYP Pacing Guide Subject Area: Algebra II / Trigonometry Grade: 9,10,11,12 Year: 2012-2013 No. of Wk. 1 1.5 Unit title Preliminary topics in Algebra Absolute Value Equations
Solutions Math is Cool HS Championships Mental Math
 Mental Math 9/11 Answer Solution 1 30 There are 5 such even numbers and the formula is n(n+1)=5(6)=30. 2 3 [ways] HHT, HTH, THH. 3 6 1x60, 2x30, 3x20, 4x15, 5x12, 6x10. 4 9 37 = 3x + 10, 27 = 3x, x = 9.
Mental Math 9/11 Answer Solution 1 30 There are 5 such even numbers and the formula is n(n+1)=5(6)=30. 2 3 [ways] HHT, HTH, THH. 3 6 1x60, 2x30, 3x20, 4x15, 5x12, 6x10. 4 9 37 = 3x + 10, 27 = 3x, x = 9.
Region 16 Board of Education. Precalculus Curriculum
 Region 16 Board of Education Precalculus Curriculum 2008 1 Course Description This course offers students an opportunity to explore a variety of concepts designed to prepare them to go on to study calculus.
Region 16 Board of Education Precalculus Curriculum 2008 1 Course Description This course offers students an opportunity to explore a variety of concepts designed to prepare them to go on to study calculus.
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Advanced Math A Units and s Advanced Math A Unit 1 Functions and Math Models (7 days) 10% of grade s 1. I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Advanced Math A Units and s Advanced Math A Unit 1 Functions and Math Models (7 days) 10% of grade s 1. I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description
Pre-Calculus EOC Review 2016
 Pre-Calculus EOC Review 2016 Name The Exam 50 questions, multiple choice, paper and pencil. I. Limits 8 questions a. (1) decide if a function is continuous at a point b. (1) understand continuity in terms
Pre-Calculus EOC Review 2016 Name The Exam 50 questions, multiple choice, paper and pencil. I. Limits 8 questions a. (1) decide if a function is continuous at a point b. (1) understand continuity in terms
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
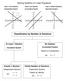 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student,
 Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall Section 1.1. Section objectives. Section 1.3. Section objectives. Section A.10. Section objectives
 Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall 2013 Learning Objectives Section 1.1 1. Use the Distance Formula 2. Use the Midpoint Formula 4. Graph Equations Using a Graphing Utility 5. Use a Graphing Utility to Create Tables
Pre-Calculus MATH 119 Fall 2013 Learning Objectives Section 1.1 1. Use the Distance Formula 2. Use the Midpoint Formula 4. Graph Equations Using a Graphing Utility 5. Use a Graphing Utility to Create Tables
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Precalculus
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Precalculus Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Mathematics Course Number MAT 187 Title Precalculus Credits 5 Developed by Adam Stinchcombe Lecture/Lab Ratio 5 Lecture/0
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Precalculus Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Mathematics Course Number MAT 187 Title Precalculus Credits 5 Developed by Adam Stinchcombe Lecture/Lab Ratio 5 Lecture/0
REQUIRED MATHEMATICAL SKILLS FOR ENTERING CADETS
 REQUIRED MATHEMATICAL SKILLS FOR ENTERING CADETS The Department of Applied Mathematics administers a Math Placement test to assess fundamental skills in mathematics that are necessary to begin the study
REQUIRED MATHEMATICAL SKILLS FOR ENTERING CADETS The Department of Applied Mathematics administers a Math Placement test to assess fundamental skills in mathematics that are necessary to begin the study
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Winter 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
MATH Spring 2010 Topics per Section
 MATH 101 - Spring 2010 Topics per Section Chapter 1 : These are the topics in ALEKS covered by each Section of the book. Section 1.1 : Section 1.2 : Ordering integers Plotting integers on a number line
MATH 101 - Spring 2010 Topics per Section Chapter 1 : These are the topics in ALEKS covered by each Section of the book. Section 1.1 : Section 1.2 : Ordering integers Plotting integers on a number line
0615a2. Algebra 2/Trigonometry Regents Exam x 2 y? 4 x. y 2. x 3 y
 Algebra /Trigonometry Regents Exam 065 www.jmap.org 065a Which list of ordered pairs does not represent a one-to-one function? ) (, ),(,0),(,),(4,) ) (,),(,),(,4),(4,6) ) (,),(,4),(,),(4,) 4) (,5),(,4),(,),(4,0)
Algebra /Trigonometry Regents Exam 065 www.jmap.org 065a Which list of ordered pairs does not represent a one-to-one function? ) (, ),(,0),(,),(4,) ) (,),(,),(,4),(4,6) ) (,),(,4),(,),(4,) 4) (,5),(,4),(,),(4,0)
Math 2412 Final Exam Review
 Math 41 Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor and simplify the algebraic expression. 1) (x + 4) /5 - (x + 4) 1/5
Math 41 Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor and simplify the algebraic expression. 1) (x + 4) /5 - (x + 4) 1/5
College Algebra with Trigonometry
 College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (556 topics + 614 additional
College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (556 topics + 614 additional
Course Outline and Objectives. MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators
 Effective Fall 2011 Course Outline and Objectives MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators TEXT: Precalculus, 5 th Edition, by Faires and DeFranza ISBN 978-0-8400-6862-0 NOTE: A graphing calculator
Effective Fall 2011 Course Outline and Objectives MA 1453 Precalculus with Graphing Calculators TEXT: Precalculus, 5 th Edition, by Faires and DeFranza ISBN 978-0-8400-6862-0 NOTE: A graphing calculator
MCPS Algebra 2 and Precalculus Standards, Categories, and Indicators*
 Content Standard 1.0 (HS) Patterns, Algebra and Functions Students will algebraically represent, model, analyze, and solve mathematical and real-world problems involving functional patterns and relationships.
Content Standard 1.0 (HS) Patterns, Algebra and Functions Students will algebraically represent, model, analyze, and solve mathematical and real-world problems involving functional patterns and relationships.
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
 Review Polynomials A1.1.4 A1.2.5 Add, subtract, multiply and simplify polynomials and rational expressions Solve polynomial equations and equations involving rational expressions Review Chapter 1 and their
Review Polynomials A1.1.4 A1.2.5 Add, subtract, multiply and simplify polynomials and rational expressions Solve polynomial equations and equations involving rational expressions Review Chapter 1 and their
Algebra II Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 Algebra II Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Algebra II Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Appendix C: Event Topics per Meet
 Appendix C: Event Topics per Meet Meet 1 1A Pre-algebra Topics Fractions to add and express as the quotient of two relatively prime integers Complex fractions and continued fractions Decimals, repeating
Appendix C: Event Topics per Meet Meet 1 1A Pre-algebra Topics Fractions to add and express as the quotient of two relatively prime integers Complex fractions and continued fractions Decimals, repeating
MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT100 is a fast-paced and thorough tour of precalculus mathematics, where the choice of topics is primarily motivated by the conceptual and technical knowledge
MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT100 is a fast-paced and thorough tour of precalculus mathematics, where the choice of topics is primarily motivated by the conceptual and technical knowledge
ax 2 + bx + c = 0 where
 Chapter P Prerequisites Section P.1 Real Numbers Real numbers The set of numbers formed by joining the set of rational numbers and the set of irrational numbers. Real number line A line used to graphically
Chapter P Prerequisites Section P.1 Real Numbers Real numbers The set of numbers formed by joining the set of rational numbers and the set of irrational numbers. Real number line A line used to graphically
Math 1012 Precalculus Functions Final Exam Review Page 1 of 5
 Math 1012 Precalculus Functions Final Exam Review Page 1 of 5 Final Exam Preparation The final exam will be 10 questions long, some with two parts. Material for the final can be drawn from anything we
Math 1012 Precalculus Functions Final Exam Review Page 1 of 5 Final Exam Preparation The final exam will be 10 questions long, some with two parts. Material for the final can be drawn from anything we
AP CALCULUS AB. Summer Assignment. Page 1
 AP CALCULUS AB Summer Assignment Page 1 Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This will be the toughest class yet in your mathematical careers but the benefit you will receive by having this experience in high school
AP CALCULUS AB Summer Assignment Page 1 Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This will be the toughest class yet in your mathematical careers but the benefit you will receive by having this experience in high school
Step 1: Greatest Common Factor Step 2: Count the number of terms If there are: 2 Terms: Difference of 2 Perfect Squares ( + )( - )
 Review for Algebra 2 CC Radicals: r x p 1 r x p p r = x p r = x Imaginary Numbers: i = 1 Polynomials (to Solve) Try Factoring: i 2 = 1 Step 1: Greatest Common Factor Step 2: Count the number of terms If
Review for Algebra 2 CC Radicals: r x p 1 r x p p r = x p r = x Imaginary Numbers: i = 1 Polynomials (to Solve) Try Factoring: i 2 = 1 Step 1: Greatest Common Factor Step 2: Count the number of terms If
ALGEBRA II (COMMON CORE) FACTS YOU MUST KNOW COLD FOR THE REGENTS EXAM
 ALGEBRA II (COMMON CORE) FACTS YOU MUST KNOW COLD FOR THE REGENTS EXAM NYS Mathematics Regents Preparation Created by Trevor Clark Algebra II [Common Core] Regents Exam Study Guide ALGEBRA & FUNCTIONS
ALGEBRA II (COMMON CORE) FACTS YOU MUST KNOW COLD FOR THE REGENTS EXAM NYS Mathematics Regents Preparation Created by Trevor Clark Algebra II [Common Core] Regents Exam Study Guide ALGEBRA & FUNCTIONS
ALGEBRA 2. Background Knowledge/Prior Skills Knows what operation properties hold for operations with matrices
 ALGEBRA 2 Numbers and Operations Standard: 1 Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
ALGEBRA 2 Numbers and Operations Standard: 1 Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
Saxon Advanced Mathematics Scope and Sequence
 hmhco.com Saxon Advanced Mathematics Scope and Sequence Foundations Calculator Perform two-variable analysis Use graphing calculators Find roots of equations Solve systems of equations Exponentials and
hmhco.com Saxon Advanced Mathematics Scope and Sequence Foundations Calculator Perform two-variable analysis Use graphing calculators Find roots of equations Solve systems of equations Exponentials and
Curriculum Scope & Sequence
 Book: Sullivan Pre-Calculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Curriculum Scope & Sequence Course: PRE-CALCULUS CP/HONORS ***The goals and standards addressed
Book: Sullivan Pre-Calculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities Subject/Grade Level: MATHEMATICS/HIGH SCHOOL Curriculum Scope & Sequence Course: PRE-CALCULUS CP/HONORS ***The goals and standards addressed
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE ALGEBRA II
 CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE ALGEBRA II Course Number 5116 Department Mathematics Qualification Guidelines Successful completion of both semesters of Algebra 1 or Algebra 1
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE ALGEBRA II Course Number 5116 Department Mathematics Qualification Guidelines Successful completion of both semesters of Algebra 1 or Algebra 1
Quantile Textbook Report
 Quantile Textbook Report Algebra 2 Author Charles, Randall I., et al StateEdition West Virginia Grade Algebra 2 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities 1.1 Patterns and Expressions 930Q 1.2 Properties
Quantile Textbook Report Algebra 2 Author Charles, Randall I., et al StateEdition West Virginia Grade Algebra 2 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities 1.1 Patterns and Expressions 930Q 1.2 Properties
