Clifford algebras, Fermions and Spin chains
|
|
|
- Audra Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clifford algebras, Fermions and Spin chains 1 Birgit Wehefritz-Kaufmann Physics Department, University of Connecticut, U-3046, 15 Hillside Road, Storrs, CT Abstract. We show how using Clifford algebras and their representations can greatly simplify the analysis of integrable systems. In particular, we apply this approach to the XX-model with non-diagonal boundaries which is among others related to growing and fluctuating interfaces and stochastic reaction-diffusion systems. Using this approach, we can not only diagonalize the system, but also find new hidden symmetries. Acknowledgments We would like to thank the organizers of the conference for their wonderful job. Our presentation of spin chains and Clifford algebras is a direct consequence of the invitation to speak at this conference. We also thank V. Rittenberg for pointing us to the total Fermion number operator. 1 Introduction There are three complex vector spaces which happen to have the same dimension (1) V 1 = (C ) () V = Λ C and (3) V 3, the unique irreducible representation of the complex Clifford algebra Cl (see e.g. [1 for the last statement). These three vector spaces are basically studied by two groups of people, the ones working in integrable systems and the ones working on math/physics related to group theory. Each group has their own intrinsic reasons and interpretation for
2 each of these spaces. Our aim is to bring these two groups of people together by providing a general framework linking these spaces and interpretations together. We apply this philosophy to a concrete problem of the boundary XX chain and present new results that can be obtained by systematically following this connection which we first explicate. Clifford algebras and Spin Systems: A digest The shortest way to define the Clifford algebra for a given R vector space W of dimension n with a fixed quadratic form Q is to give a presentation in terms of generators and relations. et e i be a basis of W and let, be the bilinear form associated to Q. Then C(W,Q) := e i : {e i,e j } = e i,e j 1 ; in particular C k := C(R k, 1 k ) and Cl k := C R C k. Here {e i,e j } = e i e j e j e i and 1 k is the k k identity matrix. Notice that for all non degenerate Q, C R C(R k,q) Cl k. We will first focus on two standard quadratic forms on C. The first is Q = 1 = diag(1,...,1) where we used the basis c + 1,..., c +, c 1,..., c. The algebra Cl is then presented as {c µ m,c ν n} = δ µ,ν m,n (1) The generators in this presentation are usually ( called ) Clifford Operators. The second form is Q = ω = where we used the basis b 1,..., b, a 1,..., a. This leads to the Fermion representation {b n,a m } = δ n,m, {b n,b m } = 0, {a n,a m } = 0 () These two presentations of the same algebra are related by b n = 1 (c+ n +ic n ),a n = 1 (c+ n ic n ); c + n = b n +a n,c n = 1 i (b n a n ) A (spin 1/) spin chain is an operator H End((C ) ). Notice that due to the general properties of Clifford algebras [1, Cl 1 We will usually not distinguish in notation between elements of W and elements in the Clifford algebra. If this becomes necessary, we denote the inclusion of W into C(W,Q) by ı.
3 Cl ˆ M (C) ˆ. Here ˆ is the tensor product for Z/Z graded algebras. So, although Cl End(C ) = M (C) the Clifford algebra Cl does not readily act on V = (C ) due to the inequality of graded ˆ and non graded tensor products. The remedy is the Jordan Wigner transformation (JWT) [3 which is highly non local. Cl Cl ; τ+, j 1 j ( i=1 3 σi z x,y )σ j (3) Here σ x,σ y,σ z are the Pauli Spin matrices and we used the notation σ j := j 1 k=1 1 σ k= j+1 1 ; we also set σ ± = 1 (σ x ± iσ y ). 3 Fermionization of Spin chains With the help of the JWT one can write many spin chain problems in terms of Fermions [4, 5 (see also [6, 7 for more examples). The main point is that simple quadratic forms in the non local operators τ H = Λ n iτn τ n + = Λ n b n a n Λ n = Λ n N n + E 0 (4) give rise to physically interesting operators which are naturally written in terms of the σ matrices and vice versa. The problem of Fermionization is to determine if a given Hamiltonian can be brought into the form H = 1 M m,n µ,ν τ mτ µ n ν and then diagonalized, i.e. brought into the form (4). Here is the sum over all (m, µ) (n,ν). In this expression H is a symmetric form on the odd vector space ı(c ). This problem is equivalent to diagonalizing the anti symmetric form M on the even vector space C. This is done by a change of base Ψ. With Λ = diag(λ ) 1,..., Λ ) the resulting matrix equation reads Ψ t MΨ =. In order to preserve the Clifford presentation ( 0 i Λ iλ 0 (1), we also need that Ψ t Ψ = 1. Notice if we work with Fermions instead then a base change Ψ would have to satisfy Φ t ω Φ = ω.
4 4 The XX-chain with boundaries and a new conserved quantity By enlarging the vector space to C C C [8 the rationale of the sections above can be applied to the XX chain with boundaries[9 H = 1 1[ σ + j σ j+1 +σ j σ + j [ α σ 8 1 +α +σ 1 + +α zσ1 z +β +σ + +β σ +β zσ z j=1 The projection to the original problem [9 is non trivial and its understanding in terms of Clifford representations is still an interesting open problem; in particular, since it seems that complex Clifford algebras of odd dimensional vector spaces make an appearance [10. Having obtained this we can pull back operators that commute with H in the form (4) to get new conserved quantities. One such operator is total Fermion number operator F tot = +1 b na n (for another such operator see [11). We include the expression in terms of the σ matrices [1 to show the power of the transformation. [ + F tot = χ( j k) +1 ) ( π( j k) + ) (+1) [ ( 1) +k+ k= keven ( 1) j+k+1 (σ z j+1... σ k 1 z ) j,k=1 j+k odd, j<k χ( j+k) +1 ) 1 k=1 k odd χ( j+k) +1 ) x π( j+k) + ))(σ j σ y k σ y j σ y k ) + ( π( j+k) + ) )(σ y j σ y k σ x j σk x ) [ χk ( 1) k+1 +1 ) + πk )σz 1 σ z... σ k 1 z σ k x χk +1 ) k+ + πk )σx k + ( 1) χk +1 ) πk + )σy k 4 (σ z k+1... σ z 1 σ z Since we have super-selection rules for the state space, we can look at the partition function Z m of H restricted to the sector with m Fermions. In the continuum limit [13, we obtain (see [1 for further details) Z m = lim (tr z π n=0 λ nn n ) = z mχ π + m z m(m+1) + (1 z m )z (m 1)m (1 z)(1 z )... (1 z m ) (6) ) (5)
5 5 References [1 Bröcker T and tom Dieck T 1985, Representations of compact ie groups. (New York: Springer-Verlag) [ Chevalley C 1997 The algebraic theory of spinors and Clifford algebras. Collected works. Vol.. (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) [3 Jordan P and Wigner E 198 Z. f. Phys [4 ieb E, Schultz T and Mattis D 1961 Ann. Phys., NY [5 Kramers H A 1957 Quantum Mechanics (New York: Interscience) Meyer K 1956 Z. Narturforsch 11A 865 Rodriguez S 1959 Phys. Rev Nambu Y 1950 Progr. Theoret. Phys. Japan 5 1 [6 de Crombrugghe M and Rittenberg V 1983 Ann. Phys., NY Korepin V E, Bogoliubov N M and A G Izergin 1993 Quantum Inverse Scattering Method and Correlation Functions (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) Hinrichsen H J. Phys. A: Math. Gen de Gier J, Nienhuis B, Pearce P A and Rittenberg V 00 Phys. Rev. E Pearce P A, Rittenberg V, de Gier J and Nienhuis B 00 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen [7 Takahashi M 1999 Thermodynamics of One-Dimensional Solvable Models (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) [8 Bariev R Z and Peschel I 1991 Phys. ett. A Hinrichsen H, Krebs K and Peschel I 1996 Zeitschrift für Physik B [9 Bilstein U and Wehefritz B 1999 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen [10 Wehefritz Kaufmann B Clifford representations in integrable systems. Preprint. [11 Bilstein U and Rittenberg V 000 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen [1 Wehefritz Kaufmann B New results for the XX model with boundaries. Preprint. [13 Saleur H 199 Aspects topologiques de la physique en basse dimension/topological aspects of low dimensional systems (es Ulis: EDP Sci) p
Introduction to the Mathematics of the XY -Spin Chain
 Introduction to the Mathematics of the XY -Spin Chain Günter Stolz June 9, 2014 Abstract In the following we present an introduction to the mathematical theory of the XY spin chain. The importance of this
Introduction to the Mathematics of the XY -Spin Chain Günter Stolz June 9, 2014 Abstract In the following we present an introduction to the mathematical theory of the XY spin chain. The importance of this
On the Random XY Spin Chain
 1 CBMS: B ham, AL June 17, 2014 On the Random XY Spin Chain Robert Sims University of Arizona 2 The Isotropic XY-Spin Chain Fix a real-valued sequence {ν j } j 1 and for each integer n 1, set acting on
1 CBMS: B ham, AL June 17, 2014 On the Random XY Spin Chain Robert Sims University of Arizona 2 The Isotropic XY-Spin Chain Fix a real-valued sequence {ν j } j 1 and for each integer n 1, set acting on
Bethe Ansatz solution of the open XX spin chain with nondiagonal boundary terms
 UMTG 231 Bethe Ansatz solution of the open XX spin chain with nondiagonal boundary terms arxiv:hep-th/0110081v1 9 Oct 2001 Rafael I. Nepomechie Physics Department, P.O. Box 248046, University of Miami
UMTG 231 Bethe Ansatz solution of the open XX spin chain with nondiagonal boundary terms arxiv:hep-th/0110081v1 9 Oct 2001 Rafael I. Nepomechie Physics Department, P.O. Box 248046, University of Miami
Frustration and Area law
 Frustration and Area law When the frustration goes odd S. M. Giampaolo Institut Ruder Bošković, Zagreb, Croatia Workshop: Exactly Solvable Quantum Chains Natal 18-29 June 2018 Coauthors F. Franchini Institut
Frustration and Area law When the frustration goes odd S. M. Giampaolo Institut Ruder Bošković, Zagreb, Croatia Workshop: Exactly Solvable Quantum Chains Natal 18-29 June 2018 Coauthors F. Franchini Institut
Random Fermionic Systems
 Random Fermionic Systems Fabio Cunden Anna Maltsev Francesco Mezzadri University of Bristol December 9, 2016 Maltsev (University of Bristol) Random Fermionic Systems December 9, 2016 1 / 27 Background
Random Fermionic Systems Fabio Cunden Anna Maltsev Francesco Mezzadri University of Bristol December 9, 2016 Maltsev (University of Bristol) Random Fermionic Systems December 9, 2016 1 / 27 Background
arxiv:quant-ph/ v1 15 Dec 2004
 Entanglement in the XX Spin Chain with Energy Current V. Eisler, and Z. Zimborás 2, Institute for Theoretical Physics, Eötvös University, 7 Budapest, Pázmány sétány /a, Hungary 2 Research Institute for
Entanglement in the XX Spin Chain with Energy Current V. Eisler, and Z. Zimborás 2, Institute for Theoretical Physics, Eötvös University, 7 Budapest, Pázmány sétány /a, Hungary 2 Research Institute for
The Quantum Heisenberg Ferromagnet
 The Quantum Heisenberg Ferromagnet Soon after Schrödinger discovered the wave equation of quantum mechanics, Heisenberg and Dirac developed the first successful quantum theory of ferromagnetism W. Heisenberg,
The Quantum Heisenberg Ferromagnet Soon after Schrödinger discovered the wave equation of quantum mechanics, Heisenberg and Dirac developed the first successful quantum theory of ferromagnetism W. Heisenberg,
ANTICOMMUTING INTEGRALS AND FERMIONIC FIELD THEORIES FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL ISING MODELS. V.N. Plechko
 ANTICOMMUTING INTEGRALS AND FERMIONIC FIELD THEORIES FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL ISING MODELS V.N. Plechko Bogoliubov Theoretical Laboratory, Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, JINR-Dubna, 141980 Dubna, Moscow
ANTICOMMUTING INTEGRALS AND FERMIONIC FIELD THEORIES FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL ISING MODELS V.N. Plechko Bogoliubov Theoretical Laboratory, Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, JINR-Dubna, 141980 Dubna, Moscow
Generalization of the matrix product ansatz for integrable chains
 arxiv:cond-mat/0608177v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 7 Aug 006 Generalization of the matrix product ansatz for integrable chains F. C. Alcaraz, M. J. Lazo Instituto de Física de São Carlos, Universidade de São Paulo,
arxiv:cond-mat/0608177v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 7 Aug 006 Generalization of the matrix product ansatz for integrable chains F. C. Alcaraz, M. J. Lazo Instituto de Física de São Carlos, Universidade de São Paulo,
The Dirac Equation. Topic 3 Spinors, Fermion Fields, Dirac Fields Lecture 13
 The Dirac Equation Dirac s discovery of a relativistic wave equation for the electron was published in 1928 soon after the concept of intrisic spin angular momentum was proposed by Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck
The Dirac Equation Dirac s discovery of a relativistic wave equation for the electron was published in 1928 soon after the concept of intrisic spin angular momentum was proposed by Goudsmit and Uhlenbeck
Hidden structures in quantum mechanics
 Journal of Generalized Lie Theory and Applications Vol. 3 (2009), No. 1, 33 38 Hidden structures in quantum mechanics Vladimir DZHUNUSHALIEV 1 Department of Physics and Microelectronics Engineering, Kyrgyz-Russian
Journal of Generalized Lie Theory and Applications Vol. 3 (2009), No. 1, 33 38 Hidden structures in quantum mechanics Vladimir DZHUNUSHALIEV 1 Department of Physics and Microelectronics Engineering, Kyrgyz-Russian
Physics 557 Lecture 5
 Physics 557 Lecture 5 Group heory: Since symmetries and the use of group theory is so much a part of recent progress in particle physics we will take a small detour to introduce the basic structure (as
Physics 557 Lecture 5 Group heory: Since symmetries and the use of group theory is so much a part of recent progress in particle physics we will take a small detour to introduce the basic structure (as
Fully Packed Loops Model: Integrability and Combinatorics. Plan
 ully Packed Loops Model 1 Fully Packed Loops Model: Integrability and Combinatorics Moscow 05/04 P. Di Francesco, P. Zinn-Justin, Jean-Bernard Zuber, math.co/0311220 J. Jacobsen, P. Zinn-Justin, math-ph/0402008
ully Packed Loops Model 1 Fully Packed Loops Model: Integrability and Combinatorics Moscow 05/04 P. Di Francesco, P. Zinn-Justin, Jean-Bernard Zuber, math.co/0311220 J. Jacobsen, P. Zinn-Justin, math-ph/0402008
Construction of spinors in various dimensions
 Construction of spinors in various dimensions Rhys Davies November 23 2011 These notes grew out of a desire to have a nice Majorana representation of the gamma matrices in eight Euclidean dimensions I
Construction of spinors in various dimensions Rhys Davies November 23 2011 These notes grew out of a desire to have a nice Majorana representation of the gamma matrices in eight Euclidean dimensions I
A New Formalism of Arbitrary Spin Particle Equations. Abstract
 A New Formalism of Arbitrary Spin Particle Equations S.R. Shi Huiyang Radio and TV station,daishui,huiyang,huizhou,guangdong,china,56 (Dated: October 4, 6) Abstract In this paper, a new formalism of arbitrary
A New Formalism of Arbitrary Spin Particle Equations S.R. Shi Huiyang Radio and TV station,daishui,huiyang,huizhou,guangdong,china,56 (Dated: October 4, 6) Abstract In this paper, a new formalism of arbitrary
Temperature Correlation Functions in the XXO Heisenberg Chain
 CONGRESSO NAZIONALE DI FISICA DELLA MATERIA Brescia, 13-16 June, 1994 Temperature Correlation Functions in the XXO Heisenberg Chain F. Colomo 1, A.G. Izergin 2,3, V.E. Korepin 4, V. Tognetti 1,5 1 I.N.F.N.,
CONGRESSO NAZIONALE DI FISICA DELLA MATERIA Brescia, 13-16 June, 1994 Temperature Correlation Functions in the XXO Heisenberg Chain F. Colomo 1, A.G. Izergin 2,3, V.E. Korepin 4, V. Tognetti 1,5 1 I.N.F.N.,
The Dirac Field. Physics , Quantum Field Theory. October Michael Dine Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz
 Michael Dine Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz October 2013 Lorentz Transformation Properties of the Dirac Field First, rotations. In ordinary quantum mechanics, ψ σ i ψ (1) is
Michael Dine Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz October 2013 Lorentz Transformation Properties of the Dirac Field First, rotations. In ordinary quantum mechanics, ψ σ i ψ (1) is
Topological invariants for 1-dimensional superconductors
 Topological invariants for 1-dimensional superconductors Eddy Ardonne Jan Budich 1306.4459 1308.soon SPORE 13 2013-07-31 Intro: Transverse field Ising model H TFI = L 1 i=0 hσ z i + σ x i σ x i+1 σ s:
Topological invariants for 1-dimensional superconductors Eddy Ardonne Jan Budich 1306.4459 1308.soon SPORE 13 2013-07-31 Intro: Transverse field Ising model H TFI = L 1 i=0 hσ z i + σ x i σ x i+1 σ s:
An ingenious mapping between integrable supersymmetric chains
 An ingenious mapping between integrable supersymmetric chains Jan de Gier University of Melbourne Bernard Nienhuis 65th birthday, Amsterdam 2017 György Fehér Sasha Garbaly Kareljan Schoutens Jan de Gier
An ingenious mapping between integrable supersymmetric chains Jan de Gier University of Melbourne Bernard Nienhuis 65th birthday, Amsterdam 2017 György Fehér Sasha Garbaly Kareljan Schoutens Jan de Gier
Tutorial 5 Clifford Algebra and so(n)
 Tutorial 5 Clifford Algebra and so(n) 1 Definition of Clifford Algebra A set of N Hermitian matrices γ 1, γ,..., γ N obeying the anti-commutator γ i, γ j } = δ ij I (1) is the basis for an algebra called
Tutorial 5 Clifford Algebra and so(n) 1 Definition of Clifford Algebra A set of N Hermitian matrices γ 1, γ,..., γ N obeying the anti-commutator γ i, γ j } = δ ij I (1) is the basis for an algebra called
Particle Notes. Ryan D. Reece
 Particle Notes Ryan D. Reece July 9, 2007 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Overview of Special Relativity 1.1.1 Lorentz Boosts Searches in the later part 19th century for the coordinate transformation that
Particle Notes Ryan D. Reece July 9, 2007 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Overview of Special Relativity 1.1.1 Lorentz Boosts Searches in the later part 19th century for the coordinate transformation that
and S is in the state ( )
 Physics 517 Homework Set #8 Autumn 2016 Due in class 12/9/16 1. Consider a spin 1/2 particle S that interacts with a measuring apparatus that is another spin 1/2 particle, A. The state vector of the system
Physics 517 Homework Set #8 Autumn 2016 Due in class 12/9/16 1. Consider a spin 1/2 particle S that interacts with a measuring apparatus that is another spin 1/2 particle, A. The state vector of the system
Lorentz-covariant spectrum of single-particle states and their field theory Physics 230A, Spring 2007, Hitoshi Murayama
 Lorentz-covariant spectrum of single-particle states and their field theory Physics 30A, Spring 007, Hitoshi Murayama 1 Poincaré Symmetry In order to understand the number of degrees of freedom we need
Lorentz-covariant spectrum of single-particle states and their field theory Physics 30A, Spring 007, Hitoshi Murayama 1 Poincaré Symmetry In order to understand the number of degrees of freedom we need
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Sep 1997
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Sep 1997 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Sep 1997](/thumbs/86/93807033.jpg) Z. Phys. B 92 (1993) 307 LPSN-93-LT2 arxiv:cond-mat/9306013v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Sep 1997 Surface magnetization of aperiodic Ising quantum chains 1. Introduction L Turban and B Berche Laboratoire
Z. Phys. B 92 (1993) 307 LPSN-93-LT2 arxiv:cond-mat/9306013v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Sep 1997 Surface magnetization of aperiodic Ising quantum chains 1. Introduction L Turban and B Berche Laboratoire
Supersymmetrization of Quaternionic Quantum Mechanics
 Supersymmetrization of Quaternionic Quantum Mechanics Seema Rawat 1), A. S. Rawat ) and O. P. S. Negi 3) 1) Department of Physics Zakir Hussain Delhi College, Jawahar Nehru Marg New Delhi-11, India ) Department
Supersymmetrization of Quaternionic Quantum Mechanics Seema Rawat 1), A. S. Rawat ) and O. P. S. Negi 3) 1) Department of Physics Zakir Hussain Delhi College, Jawahar Nehru Marg New Delhi-11, India ) Department
ADVANCED TOPICS IN STATISTICAL PHYSICS
 ADVANCED TOPICS IN STATISTICAL PHYSICS Spring term 2013 EXERCISES Note : All undefined notation is the same as employed in class. Exercise 1301. Quantum spin chains a. Show that the 1D Heisenberg and XY
ADVANCED TOPICS IN STATISTICAL PHYSICS Spring term 2013 EXERCISES Note : All undefined notation is the same as employed in class. Exercise 1301. Quantum spin chains a. Show that the 1D Heisenberg and XY
PHY 396 K. Solutions for homework set #9.
 PHY 396 K. Solutions for homework set #9. Problem 2(a): The γ 0 matrix commutes with itself but anticommutes with the space-indexed γ 1,2,3. At the same time, the parity reflects the space coordinates
PHY 396 K. Solutions for homework set #9. Problem 2(a): The γ 0 matrix commutes with itself but anticommutes with the space-indexed γ 1,2,3. At the same time, the parity reflects the space coordinates
Clifford Algebras and Spin Groups
 Clifford Algebras and Spin Groups Math G4344, Spring 2012 We ll now turn from the general theory to examine a specific class class of groups: the orthogonal groups. Recall that O(n, R) is the group of
Clifford Algebras and Spin Groups Math G4344, Spring 2012 We ll now turn from the general theory to examine a specific class class of groups: the orthogonal groups. Recall that O(n, R) is the group of
Supplementary Figure 3: Interaction effects in the proposed state preparation with Bloch oscillations. The numerical results are obtained by
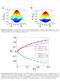 Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Quantum Physics 2006/07
 Quantum Physics 6/7 Lecture 7: More on the Dirac Equation In the last lecture we showed that the Dirac equation for a free particle i h t ψr, t = i hc α + β mc ψr, t has plane wave solutions ψr, t = exp
Quantum Physics 6/7 Lecture 7: More on the Dirac Equation In the last lecture we showed that the Dirac equation for a free particle i h t ψr, t = i hc α + β mc ψr, t has plane wave solutions ψr, t = exp
Entanglement, quantum critical phenomena and efficient simulation of quantum dynamics
 Entanglement, quantum critical phenomena and efficient simulation of quantum dynamics Simons Conference on Reversible and Quantum Computation Stony Brook, May 28-31 2003 Guifre Vidal Institute for Quantum
Entanglement, quantum critical phenomena and efficient simulation of quantum dynamics Simons Conference on Reversible and Quantum Computation Stony Brook, May 28-31 2003 Guifre Vidal Institute for Quantum
THE NUMBER OF ORTHOGONAL CONJUGATIONS
 THE NUMBER OF ORTHOGONAL CONJUGATIONS Armin Uhlmann University of Leipzig, Institute for Theoretical Physics After a short introduction to anti-linearity, bounds for the number of orthogonal (skew) conjugations
THE NUMBER OF ORTHOGONAL CONJUGATIONS Armin Uhlmann University of Leipzig, Institute for Theoretical Physics After a short introduction to anti-linearity, bounds for the number of orthogonal (skew) conjugations
Lecture 11: Clifford algebras
 Lecture 11: Clifford algebras In this lecture we introduce Clifford algebras, which will play an important role in the rest of the class. The link with K-theory is the Atiyah-Bott-Shapiro construction
Lecture 11: Clifford algebras In this lecture we introduce Clifford algebras, which will play an important role in the rest of the class. The link with K-theory is the Atiyah-Bott-Shapiro construction
in-medium pair wave functions the Cooper pair wave function the superconducting order parameter anomalous averages of the field operators
 (by A. A. Shanenko) in-medium wave functions in-medium pair-wave functions and spatial pair particle correlations momentum condensation and ODLRO (off-diagonal long range order) U(1) symmetry breaking
(by A. A. Shanenko) in-medium wave functions in-medium pair-wave functions and spatial pair particle correlations momentum condensation and ODLRO (off-diagonal long range order) U(1) symmetry breaking
Topological Phases in One Dimension
 Topological Phases in One Dimension Lukasz Fidkowski and Alexei Kitaev arxiv:1008.4138 Topological phases in 2 dimensions: - Integer quantum Hall effect - quantized σ xy - robust chiral edge modes - Fractional
Topological Phases in One Dimension Lukasz Fidkowski and Alexei Kitaev arxiv:1008.4138 Topological phases in 2 dimensions: - Integer quantum Hall effect - quantized σ xy - robust chiral edge modes - Fractional
1 The spin homomorphism SL 2 (C) SO 1,3 (R)
 1 The spin homomorphism SL 2 (C) SO 1,3 (R) A summary from multiple sources written by Y. Feng and Katherine E. Stange Abstract We will discuss the spin homomorphism SL 2 (C) SO 1,3 (R) in three manners.
1 The spin homomorphism SL 2 (C) SO 1,3 (R) A summary from multiple sources written by Y. Feng and Katherine E. Stange Abstract We will discuss the spin homomorphism SL 2 (C) SO 1,3 (R) in three manners.
Introduction to Quantum Spin Systems
 1 Introduction to Quantum Spin Systems Lecture 2 Sven Bachmann (standing in for Bruno Nachtergaele) Mathematics, UC Davis MAT290-25, CRN 30216, Winter 2011, 01/10/11 2 Basic Setup For concreteness, consider
1 Introduction to Quantum Spin Systems Lecture 2 Sven Bachmann (standing in for Bruno Nachtergaele) Mathematics, UC Davis MAT290-25, CRN 30216, Winter 2011, 01/10/11 2 Basic Setup For concreteness, consider
The Homogenous Lorentz Group
 The Homogenous Lorentz Group Thomas Wening February 3, 216 Contents 1 Proper Lorentz Transforms 1 2 Four Vectors 2 3 Basic Properties of the Transformations 3 4 Connection to SL(2, C) 5 5 Generators of
The Homogenous Lorentz Group Thomas Wening February 3, 216 Contents 1 Proper Lorentz Transforms 1 2 Four Vectors 2 3 Basic Properties of the Transformations 3 4 Connection to SL(2, C) 5 5 Generators of
The continuum limit of the integrable open XYZ spin-1/2 chain
 arxiv:hep-th/9809028v2 8 Sep 1998 The continuum limit of the integrable open XYZ spin-1/2 chain Hiroshi Tsukahara and Takeo Inami Department of Physics, Chuo University, Kasuga, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 112-8551
arxiv:hep-th/9809028v2 8 Sep 1998 The continuum limit of the integrable open XYZ spin-1/2 chain Hiroshi Tsukahara and Takeo Inami Department of Physics, Chuo University, Kasuga, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 112-8551
Light-Cone Quantization of Electrodynamics
 Light-Cone Quantization of Electrodynamics David G. Robertson Department of Physics, The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Abstract Light-cone quantization of (3+1)-dimensional electrodynamics is
Light-Cone Quantization of Electrodynamics David G. Robertson Department of Physics, The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Abstract Light-cone quantization of (3+1)-dimensional electrodynamics is
IDEMPOTENTS OF CLIFFORD ALGEBRAS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS TECHNICAL REPORT IDEMPOTENTS OF CLIFFORD ALGEBRAS DR.R.AB lamowicz DR.B.FAUSER DR.K.PODLASKI DR.J.REMBIELIŃSKI OCTOBER 2003 No. 2003-6 TENNESSEE TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Cookeville,
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS TECHNICAL REPORT IDEMPOTENTS OF CLIFFORD ALGEBRAS DR.R.AB lamowicz DR.B.FAUSER DR.K.PODLASKI DR.J.REMBIELIŃSKI OCTOBER 2003 No. 2003-6 TENNESSEE TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY Cookeville,
CLASSIFICATION OF NON-ABELIAN CHERN-SIMONS VORTICES
 CLASSIFICATION OF NON-ABELIAN CHERN-SIMONS VORTICES arxiv:hep-th/9310182v1 27 Oct 1993 Gerald V. Dunne Department of Physics University of Connecticut 2152 Hillside Road Storrs, CT 06269 USA dunne@hep.phys.uconn.edu
CLASSIFICATION OF NON-ABELIAN CHERN-SIMONS VORTICES arxiv:hep-th/9310182v1 27 Oct 1993 Gerald V. Dunne Department of Physics University of Connecticut 2152 Hillside Road Storrs, CT 06269 USA dunne@hep.phys.uconn.edu
The 1+1-dimensional Ising model
 Chapter 4 The 1+1-dimensional Ising model The 1+1-dimensional Ising model is one of the most important models in statistical mechanics. It is an interacting system, and behaves accordingly. Yet for a variety
Chapter 4 The 1+1-dimensional Ising model The 1+1-dimensional Ising model is one of the most important models in statistical mechanics. It is an interacting system, and behaves accordingly. Yet for a variety
Symmetries and Supersymmetries in Trapped Ion Hamiltonian Models
 Proceedings of Institute of Mathematics of NAS of Ukraine 004, Vol. 50, Part, 569 57 Symmetries and Supersymmetries in Trapped Ion Hamiltonian Models Benedetto MILITELLO, Anatoly NIKITIN and Antonino MESSINA
Proceedings of Institute of Mathematics of NAS of Ukraine 004, Vol. 50, Part, 569 57 Symmetries and Supersymmetries in Trapped Ion Hamiltonian Models Benedetto MILITELLO, Anatoly NIKITIN and Antonino MESSINA
NOTES ON FOCK SPACE PETER TINGLEY
 NOTES ON FOCK SPACE PETER TINGLEY Abstract. These notes are intended as a fairly self contained explanation of Fock space and various algebras that act on it, including a Clifford algebras, a Weyl algebra,
NOTES ON FOCK SPACE PETER TINGLEY Abstract. These notes are intended as a fairly self contained explanation of Fock space and various algebras that act on it, including a Clifford algebras, a Weyl algebra,
Quantum entanglement and symmetry
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Quantum entanglement and symmetry To cite this article: D Chrucisi and A Kossaowsi 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 87 012008 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Quantum entanglement and symmetry To cite this article: D Chrucisi and A Kossaowsi 2007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 87 012008 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
NOTES FOR 128: COMBINATORIAL REPRESENTATION THEORY OF COMPLEX LIE ALGEBRAS AND RELATED TOPICS
 NOTES FOR 128: COMBINATORIAL REPRESENTATION THEORY OF COMPLEX LIE ALGEBRAS AND RELATED TOPICS (FIRST COUPLE LECTURES MORE ONLINE AS WE GO) Recommended reading [Bou] N. Bourbaki, Elements of Mathematics:
NOTES FOR 128: COMBINATORIAL REPRESENTATION THEORY OF COMPLEX LIE ALGEBRAS AND RELATED TOPICS (FIRST COUPLE LECTURES MORE ONLINE AS WE GO) Recommended reading [Bou] N. Bourbaki, Elements of Mathematics:
Appendix A Notational Conventions
 Appendix A Notational Conventions Throughout the book we use Einstein s implicit summation convention: repeated indices in an expression are automatically summed over. We work in natural units where the
Appendix A Notational Conventions Throughout the book we use Einstein s implicit summation convention: repeated indices in an expression are automatically summed over. We work in natural units where the
Introduction to supersymmetry
 Introduction to supersymmetry Vicente Cortés Institut Élie Cartan Université Henri Poincaré - Nancy I cortes@iecn.u-nancy.fr August 31, 2005 Outline of the lecture The free supersymmetric scalar field
Introduction to supersymmetry Vicente Cortés Institut Élie Cartan Université Henri Poincaré - Nancy I cortes@iecn.u-nancy.fr August 31, 2005 Outline of the lecture The free supersymmetric scalar field
Lecture 4 - Relativistic wave equations. Relativistic wave equations must satisfy several general postulates. These are;
 Lecture 4 - Relativistic wave equations Postulates Relativistic wave equations must satisfy several general postulates. These are;. The equation is developed for a field amplitude function, ψ 2. The normal
Lecture 4 - Relativistic wave equations Postulates Relativistic wave equations must satisfy several general postulates. These are;. The equation is developed for a field amplitude function, ψ 2. The normal
Disclaimer. [disclaimer]
![Disclaimer. [disclaimer] Disclaimer. [disclaimer]](/thumbs/87/97074168.jpg) Disclaimer This is a problem set (as turned in) for the module physics755. This problem set is not reviewed by a tutor. This is just what I have turned in. All problem sets for this module can be found
Disclaimer This is a problem set (as turned in) for the module physics755. This problem set is not reviewed by a tutor. This is just what I have turned in. All problem sets for this module can be found
Non-abelian statistics
 Non-abelian statistics Paul Fendley Non-abelian statistics are just plain interesting. They probably occur in the ν = 5/2 FQHE, and people are constructing time-reversal-invariant models which realize
Non-abelian statistics Paul Fendley Non-abelian statistics are just plain interesting. They probably occur in the ν = 5/2 FQHE, and people are constructing time-reversal-invariant models which realize
Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions. Takahiro Morimoto.
 QMath13, 10 th October 2016 Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions Takahiro Morimoto UC Berkeley Collaborators Akira Furusaki
QMath13, 10 th October 2016 Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions Takahiro Morimoto UC Berkeley Collaborators Akira Furusaki
11 Spinor solutions and CPT
 11 Spinor solutions and CPT 184 In the previous chapter, we cataloged the irreducible representations of the Lorentz group O(1, 3. We found that in addition to the obvious tensor representations, φ, A
11 Spinor solutions and CPT 184 In the previous chapter, we cataloged the irreducible representations of the Lorentz group O(1, 3. We found that in addition to the obvious tensor representations, φ, A
Clifford Algebras and Their Decomposition into Conjugate Fermionic Heisenberg Algebras
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Clifford Algebras and Their Decomposition into Conugate Fermionic Heisenberg Algebras To cite this article: Sultan Catto et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Clifford Algebras and Their Decomposition into Conugate Fermionic Heisenberg Algebras To cite this article: Sultan Catto et al 016 J. Phys.: Conf.
Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport. Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, / 21
 Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, 2017 1 / 21 This notes are predominately based on: J.K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány
Topological Insulator Surface States and Electrical Transport Alexander Pearce Intro to Topological Insulators: Week 11 February 2, 2017 1 / 21 This notes are predominately based on: J.K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány
0 T (L int (x 1 )...L int (x n )) = i
 LORENTZ INVARIANT RENORMALIZATION IN CAUSAL PERTURBATION THEORY K. BRESSER, G. PINTER AND D. PRANGE II. Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Hamburg Luruper Chaussee 149 22761 Hamburg Germany e-mail:
LORENTZ INVARIANT RENORMALIZATION IN CAUSAL PERTURBATION THEORY K. BRESSER, G. PINTER AND D. PRANGE II. Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Hamburg Luruper Chaussee 149 22761 Hamburg Germany e-mail:
Solution of the Dirac equation in presence of an uniform magnetic field
 Solution of the Dirac equation in presence of an uniform magnetic field arxiv:75.4275v2 [hep-th] 3 Aug 27 Kaushik Bhattacharya Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico,
Solution of the Dirac equation in presence of an uniform magnetic field arxiv:75.4275v2 [hep-th] 3 Aug 27 Kaushik Bhattacharya Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico,
Outline. Motivation: Numerical Ranges as Measuring Sticks for Optimising Quantum Dynamics. I Symmetry Approach to Quantum Systems Theory
 Some Remarks on Quantum Systems Theory as Pertaining to Numerical Ranges A Unified Lie-Geometric Viewpoint Thomas Schulte-Herbrüggen relating to (joint) work with G. Dirr, R. Zeier, C.K. Li, Y.T. Poon,
Some Remarks on Quantum Systems Theory as Pertaining to Numerical Ranges A Unified Lie-Geometric Viewpoint Thomas Schulte-Herbrüggen relating to (joint) work with G. Dirr, R. Zeier, C.K. Li, Y.T. Poon,
arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 8 Nov 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 8 Nov 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 8 Nov 2008](/thumbs/79/80291227.jpg) SUBSPACES OF 7 7 SKEW-SYMMETRIC MATRICES RELATED TO THE GROUP G 2 arxiv:0811.1298v1 [math.gr] 8 Nov 2008 ROD GOW Abstract. Let K be a field of characteristic different from 2 and let C be an octonion algebra
SUBSPACES OF 7 7 SKEW-SYMMETRIC MATRICES RELATED TO THE GROUP G 2 arxiv:0811.1298v1 [math.gr] 8 Nov 2008 ROD GOW Abstract. Let K be a field of characteristic different from 2 and let C be an octonion algebra
J. Stat. Mech. (2005) P01006
 Journal of Statistical Mechanics: An IOP and SISSA journal Theory and Experiment Jan de Gier 1 and Bernard Nienhuis 2 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of Melbourne, VIC 3010,
Journal of Statistical Mechanics: An IOP and SISSA journal Theory and Experiment Jan de Gier 1 and Bernard Nienhuis 2 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of Melbourne, VIC 3010,
Supersymmetry and Quantum Hall effect in graphene
 Supersymmetry and Quantum Hall effect in graphene Ervand Kandelaki Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Festköperphysik Institut für Theoretische Physik IV Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg March 14, 007 1 Introduction
Supersymmetry and Quantum Hall effect in graphene Ervand Kandelaki Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Festköperphysik Institut für Theoretische Physik IV Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg March 14, 007 1 Introduction
Geometry of a qubit. Maris Ozols (ID ) December 22, 2007
 Geometry of a qubit Maris Ozols (ID 20286921 December 22, 2007 1 Introduction Initially my plan was to write about geometry of quantum states of an n-level quantum system. When I was about to finish the
Geometry of a qubit Maris Ozols (ID 20286921 December 22, 2007 1 Introduction Initially my plan was to write about geometry of quantum states of an n-level quantum system. When I was about to finish the
THE BORDER BETWEEN RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM THEORY
 THE BORDER BETWEEN RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM THEORY Tevian Dray I: Attempts at Unification II: Spinors III: The Future Abstract Many efforts have been made to fulfill Einstein s dream of unifying general
THE BORDER BETWEEN RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM THEORY Tevian Dray I: Attempts at Unification II: Spinors III: The Future Abstract Many efforts have been made to fulfill Einstein s dream of unifying general
Lecture notes: Quantum gates in matrix and ladder operator forms
 Phys 7 Topics in Particles & Fields Spring 3 Lecture v.. Lecture notes: Quantum gates in matrix and ladder operator forms Jeffrey Yepez Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Hawai i at Manoa
Phys 7 Topics in Particles & Fields Spring 3 Lecture v.. Lecture notes: Quantum gates in matrix and ladder operator forms Jeffrey Yepez Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Hawai i at Manoa
The sl(2) loop algebra symmetry of the XXZ spin chain at roots of unity and applications to the superintegrable chiral Potts model 1
 The sl(2) loop algebra symmetry of the XXZ spin chain at roots of unity and applications to the superintegrable chiral Potts model 1 Tetsuo Deguchi Department of Physics, Ochanomizu Univ. In collaboration
The sl(2) loop algebra symmetry of the XXZ spin chain at roots of unity and applications to the superintegrable chiral Potts model 1 Tetsuo Deguchi Department of Physics, Ochanomizu Univ. In collaboration
1 Time reversal. 1.1 Without spin. Time-dependent Schrödinger equation: 2m + V (r) ψ (r, t) (7) Local time-reversal transformation, T :
 1 Time reversal 1.1 Without spin Time-dependent Schrödinger equation: i t ψ (r, t = Local time-reversal transformation, T : Transformed Schrödinger equation d (f T (t dt ] 2m + V (r ψ (r, t (1 t 1 < t
1 Time reversal 1.1 Without spin Time-dependent Schrödinger equation: i t ψ (r, t = Local time-reversal transformation, T : Transformed Schrödinger equation d (f T (t dt ] 2m + V (r ψ (r, t (1 t 1 < t
Lie Algebra and Representation of SU(4)
 EJTP, No. 8 9 6 Electronic Journal of Theoretical Physics Lie Algebra and Representation of SU() Mahmoud A. A. Sbaih, Moeen KH. Srour, M. S. Hamada and H. M. Fayad Department of Physics, Al Aqsa University,
EJTP, No. 8 9 6 Electronic Journal of Theoretical Physics Lie Algebra and Representation of SU() Mahmoud A. A. Sbaih, Moeen KH. Srour, M. S. Hamada and H. M. Fayad Department of Physics, Al Aqsa University,
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.dg] 6 Feb 1998
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.dg] 6 Feb 1998 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.dg] 6 Feb 1998](/thumbs/93/114520081.jpg) Cartan Spinor Bundles on Manifolds. Thomas Friedrich, Berlin November 5, 013 arxiv:math/980033v1 [math.dg] 6 Feb 1998 1 Introduction. Spinor fields and Dirac operators on Riemannian manifolds M n can be
Cartan Spinor Bundles on Manifolds. Thomas Friedrich, Berlin November 5, 013 arxiv:math/980033v1 [math.dg] 6 Feb 1998 1 Introduction. Spinor fields and Dirac operators on Riemannian manifolds M n can be
Problem Set 2 Due Tuesday, September 27, ; p : 0. (b) Construct a representation using five d orbitals that sit on the origin as a basis: 1
 Problem Set 2 Due Tuesday, September 27, 211 Problems from Carter: Chapter 2: 2a-d,g,h,j 2.6, 2.9; Chapter 3: 1a-d,f,g 3.3, 3.6, 3.7 Additional problems: (1) Consider the D 4 point group and use a coordinate
Problem Set 2 Due Tuesday, September 27, 211 Problems from Carter: Chapter 2: 2a-d,g,h,j 2.6, 2.9; Chapter 3: 1a-d,f,g 3.3, 3.6, 3.7 Additional problems: (1) Consider the D 4 point group and use a coordinate
3.3 Lagrangian and symmetries for a spin- 1 2 field
 3.3 Lagrangian and symmetries for a spin- 1 2 field The Lagrangian for the free spin- 1 2 field is The corresponding Hamiltonian density is L = ψ(i/ µ m)ψ. (3.31) H = ψ( γ p + m)ψ. (3.32) The Lagrangian
3.3 Lagrangian and symmetries for a spin- 1 2 field The Lagrangian for the free spin- 1 2 field is The corresponding Hamiltonian density is L = ψ(i/ µ m)ψ. (3.31) H = ψ( γ p + m)ψ. (3.32) The Lagrangian
Relativistic wave equations of arbitrary spin in quantum mechanics and field theory, example spin s=2
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Relativistic wave equations of arbitrary spin in quantum mechanics and field theory, example spin s= Related content - Link between the relativistic
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Relativistic wave equations of arbitrary spin in quantum mechanics and field theory, example spin s= Related content - Link between the relativistic
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 1 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 1 Oct 2017 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 1 Oct 2017](/thumbs/76/73184617.jpg) Stochastic thermodynamics of quantum maps with and without equilibrium Felipe Barra and Cristóbal Lledó Departamento de Física, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas y Matemáticas, Universidad de Chile, Santiago,
Stochastic thermodynamics of quantum maps with and without equilibrium Felipe Barra and Cristóbal Lledó Departamento de Física, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas y Matemáticas, Universidad de Chile, Santiago,
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 11 Oct 1999
 NIKHEF/99-026 Killing-Yano tensors, non-standard supersymmetries and an index theorem J.W. van Holten arxiv:gr-qc/9910035 v1 11 Oct 1999 Theoretical Physics Group, NIKHEF P.O. Box 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam
NIKHEF/99-026 Killing-Yano tensors, non-standard supersymmetries and an index theorem J.W. van Holten arxiv:gr-qc/9910035 v1 11 Oct 1999 Theoretical Physics Group, NIKHEF P.O. Box 41882, 1009 DB Amsterdam
Mathematical Analysis of a Generalized Chiral Quark Soliton Model
 Symmetry, Integrability and Geometry: Methods and Applications Vol. 2 (2006), Paper 018, 12 pages Mathematical Analysis of a Generalized Chiral Quark Soliton Model Asao ARAI Department of Mathematics,
Symmetry, Integrability and Geometry: Methods and Applications Vol. 2 (2006), Paper 018, 12 pages Mathematical Analysis of a Generalized Chiral Quark Soliton Model Asao ARAI Department of Mathematics,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 8 Jul 1998
 Fermionization and Hubbard Models P. Dargis and Z. Maassarani Département de Physique, Pav. A-Vachon Université Laval, Ste Foy, Qc, G1K 7P4 Canada arxiv:cond-mat/9806208v2 8 Jul 1998 Abstract We introduce
Fermionization and Hubbard Models P. Dargis and Z. Maassarani Département de Physique, Pav. A-Vachon Université Laval, Ste Foy, Qc, G1K 7P4 Canada arxiv:cond-mat/9806208v2 8 Jul 1998 Abstract We introduce
Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond
 Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond Jiri Vala Department of Mathematical Physics National University of Ireland at Maynooth Postdoc: PhD students: Collaborators: Graham Kells Ahmet Bolukbasi
Kitaev honeycomb lattice model: from A to B and beyond Jiri Vala Department of Mathematical Physics National University of Ireland at Maynooth Postdoc: PhD students: Collaborators: Graham Kells Ahmet Bolukbasi
Correlators of the phase model arxiv:solv-int/ v2 20 Dec 1996
 Correlators of the phase model arxiv:solv-int/96100v 0 Dec 1996 N.M. Bogoliubov Research Institute for Theoretical Physics P.O.Box 9, FIN-00014 University of Helsinki, FINLAND. A.G. Izergin, N.A. Kitanine
Correlators of the phase model arxiv:solv-int/96100v 0 Dec 1996 N.M. Bogoliubov Research Institute for Theoretical Physics P.O.Box 9, FIN-00014 University of Helsinki, FINLAND. A.G. Izergin, N.A. Kitanine
Lecture 10. The Dirac equation. WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Lecture 10 The Dirac equation WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics The Dirac equation The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist
Lecture 10 The Dirac equation WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics The Dirac equation The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by British physicist
Non-Hermitian CP-Symmetric Dirac Hamiltonians with Real Energy Eigenvalues
 Non-Hermitian CP-Symmetric irac Hamiltonians with Real Energy Eigenvalues.. lhaidari Saudi Center for Theoretical Physics, Jeddah 438, Saudi rabia bstract: We present a large class of non-hermitian non-pt-symmetric
Non-Hermitian CP-Symmetric irac Hamiltonians with Real Energy Eigenvalues.. lhaidari Saudi Center for Theoretical Physics, Jeddah 438, Saudi rabia bstract: We present a large class of non-hermitian non-pt-symmetric
Cluster Properties and Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
 Cluster Properties and Relativistic Quantum Mechanics Wayne Polyzou polyzou@uiowa.edu The University of Iowa Cluster Properties p.1/45 Why is quantum field theory difficult? number of degrees of freedom.
Cluster Properties and Relativistic Quantum Mechanics Wayne Polyzou polyzou@uiowa.edu The University of Iowa Cluster Properties p.1/45 Why is quantum field theory difficult? number of degrees of freedom.
THE DIRAC EQUATION (A REVIEW) We will try to find the relativistic wave equation for a particle.
 THE DIRAC EQUATION (A REVIEW) We will try to find the relativistic wave equation for a particle. First, we introduce four dimensional notation for a vector by writing x µ = (x, x 1, x 2, x 3 ) = (ct, x,
THE DIRAC EQUATION (A REVIEW) We will try to find the relativistic wave equation for a particle. First, we introduce four dimensional notation for a vector by writing x µ = (x, x 1, x 2, x 3 ) = (ct, x,
Lie algebraic aspects of quantum control in interacting spin-1/2 (qubit) chains
 .. Lie algebraic aspects of quantum control in interacting spin-1/2 (qubit) chains Vladimir M. Stojanović Condensed Matter Theory Group HARVARD UNIVERSITY September 16, 2014 V. M. Stojanović (Harvard)
.. Lie algebraic aspects of quantum control in interacting spin-1/2 (qubit) chains Vladimir M. Stojanović Condensed Matter Theory Group HARVARD UNIVERSITY September 16, 2014 V. M. Stojanović (Harvard)
Algebraic Quantum Thermodynamics
 Foundations of Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Algebraic Quantum Thermodynamics Carl Brannen Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract Density matrices can be used to describe ensembles
Foundations of Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Algebraic Quantum Thermodynamics Carl Brannen Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract Density matrices can be used to describe ensembles
Symmetries of the Schrödinger equation and algebra/superalgebra duality
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Symmetries of the Schrödinger equation and algebra/superalgebra duality To cite this article: Francesco Toppan 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 597 012071
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Symmetries of the Schrödinger equation and algebra/superalgebra duality To cite this article: Francesco Toppan 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 597 012071
232A Lecture Notes Representation Theory of Lorentz Group
 232A Lecture Notes Representation Theory of Lorentz Group 1 Symmetries in Physics Symmetries play crucial roles in physics. Noether s theorem relates symmetries of the system to conservation laws. In quantum
232A Lecture Notes Representation Theory of Lorentz Group 1 Symmetries in Physics Symmetries play crucial roles in physics. Noether s theorem relates symmetries of the system to conservation laws. In quantum
Angular Momentum set II
 Angular Momentum set II PH - QM II Sem, 7-8 Problem : Using the commutation relations for the angular momentum operators, prove the Jacobi identity Problem : [ˆL x, [ˆL y, ˆL z ]] + [ˆL y, [ˆL z, ˆL x
Angular Momentum set II PH - QM II Sem, 7-8 Problem : Using the commutation relations for the angular momentum operators, prove the Jacobi identity Problem : [ˆL x, [ˆL y, ˆL z ]] + [ˆL y, [ˆL z, ˆL x
Representation of Spin Group Spin(p, q)
 Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing China 48 2007 pp. 415 424 c nternational Academic Publishers Vol. 48 No. 3 September 15 2007 Representation of Spin Group Spinp q WANG Na 1 WU Ke 12 ZHANG Bo 1 1 School of
Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing China 48 2007 pp. 415 424 c nternational Academic Publishers Vol. 48 No. 3 September 15 2007 Representation of Spin Group Spinp q WANG Na 1 WU Ke 12 ZHANG Bo 1 1 School of
Parallel and Killing Spinors on Spin c Manifolds. 1 Introduction. Andrei Moroianu 1
 Parallel and Killing Spinors on Spin c Manifolds Andrei Moroianu Institut für reine Mathematik, Ziegelstr. 3a, 0099 Berlin, Germany E-mail: moroianu@mathematik.hu-berlin.de Abstract: We describe all simply
Parallel and Killing Spinors on Spin c Manifolds Andrei Moroianu Institut für reine Mathematik, Ziegelstr. 3a, 0099 Berlin, Germany E-mail: moroianu@mathematik.hu-berlin.de Abstract: We describe all simply
3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase
 Physics 3b Lecture 16 Caltech, 05/30/18 3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase 3.1 Breakdown of noninteracting SPT phases with interaction Building on our previous discussion of the Majorana chain and
Physics 3b Lecture 16 Caltech, 05/30/18 3 Symmetry Protected Topological Phase 3.1 Breakdown of noninteracting SPT phases with interaction Building on our previous discussion of the Majorana chain and
arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 12 Aug 2008
![arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 12 Aug 2008 arxiv: v2 [quant-ph] 12 Aug 2008](/thumbs/72/66366028.jpg) Complexity of thermal states in quantum spin chains arxiv:85.449v [quant-ph] Aug 8 Marko Žnidarič, Tomaž Prosen and Iztok Pižorn Department of physics, FMF, University of Ljubljana, Jadranska 9, SI- Ljubljana,
Complexity of thermal states in quantum spin chains arxiv:85.449v [quant-ph] Aug 8 Marko Žnidarič, Tomaž Prosen and Iztok Pižorn Department of physics, FMF, University of Ljubljana, Jadranska 9, SI- Ljubljana,
ON THE CHERN CHARACTER OF A THETA-SUMMABLE FREDHOLM MODULE.
 ON THE CHERN CHARACTER OF A THETA-SUMMABLE FREDHOLM MODULE. Ezra Getzler and András Szenes Department of Mathematics, Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass. 02138 USA In [3], Connes defines the notion of
ON THE CHERN CHARACTER OF A THETA-SUMMABLE FREDHOLM MODULE. Ezra Getzler and András Szenes Department of Mathematics, Harvard University, Cambridge, Mass. 02138 USA In [3], Connes defines the notion of
Efficient time evolution of one-dimensional quantum systems
 Efficient time evolution of one-dimensional quantum systems Frank Pollmann Max-Planck-Institut für komplexer Systeme, Dresden, Germany Sep. 5, 2012 Hsinchu Problems we will address... Finding ground states
Efficient time evolution of one-dimensional quantum systems Frank Pollmann Max-Planck-Institut für komplexer Systeme, Dresden, Germany Sep. 5, 2012 Hsinchu Problems we will address... Finding ground states
HIGHER SPIN PROBLEM IN FIELD THEORY
 HIGHER SPIN PROBLEM IN FIELD THEORY I.L. Buchbinder Tomsk I.L. Buchbinder (Tomsk) HIGHER SPIN PROBLEM IN FIELD THEORY Wroclaw, April, 2011 1 / 27 Aims Brief non-expert non-technical review of some old
HIGHER SPIN PROBLEM IN FIELD THEORY I.L. Buchbinder Tomsk I.L. Buchbinder (Tomsk) HIGHER SPIN PROBLEM IN FIELD THEORY Wroclaw, April, 2011 1 / 27 Aims Brief non-expert non-technical review of some old
2D CFT and the Ising Model
 2D CFT and the Ising Model Alex Atanasov December 27, 207 Abstract In this lecture, we review the results of Appendix E from the seminal paper by Belavin, Polyakov, and Zamolodchikov on the critical scaling
2D CFT and the Ising Model Alex Atanasov December 27, 207 Abstract In this lecture, we review the results of Appendix E from the seminal paper by Belavin, Polyakov, and Zamolodchikov on the critical scaling
EXCITED STATE QUANTUM PHASE TRANSITIONS AND MONODROMY
 EXCITED STATE QUANTUM PHASE TRANSITIONS AND MONODROMY Francesco Iachello Yale University Groenewold Symposium on Semi-classical Methods in Mathematics and Physics, Groningen, The Netherlands, October 19-21,
EXCITED STATE QUANTUM PHASE TRANSITIONS AND MONODROMY Francesco Iachello Yale University Groenewold Symposium on Semi-classical Methods in Mathematics and Physics, Groningen, The Netherlands, October 19-21,
1 4-dimensional Weyl spinor
 4-dimensional Weyl spinor Left moving ψ α, α =, Right moving ψ α, α =, They are related by the complex conjugation. The indices are raised or lowerd by the ϵ tensor as ψ α := ϵ αβ ψ β, α := ϵ α β β. (.)
4-dimensional Weyl spinor Left moving ψ α, α =, Right moving ψ α, α =, They are related by the complex conjugation. The indices are raised or lowerd by the ϵ tensor as ψ α := ϵ αβ ψ β, α := ϵ α β β. (.)
BRST and Dirac Cohomology
 BRST and Dirac Cohomology Peter Woit Columbia University Dartmouth Math Dept., October 23, 2008 Peter Woit (Columbia University) BRST and Dirac Cohomology October 2008 1 / 23 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Representation
BRST and Dirac Cohomology Peter Woit Columbia University Dartmouth Math Dept., October 23, 2008 Peter Woit (Columbia University) BRST and Dirac Cohomology October 2008 1 / 23 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Representation
Spinor Formulation of Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter Spinor Formulation of Relativistic Quantum Mechanics. The Lorentz Transformation of the Dirac Bispinor We will provide in the following a new formulation of the Dirac equation in the chiral representation
Chapter Spinor Formulation of Relativistic Quantum Mechanics. The Lorentz Transformation of the Dirac Bispinor We will provide in the following a new formulation of the Dirac equation in the chiral representation
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.oa] 10 Feb 2000
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.oa] 10 Feb 2000 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.oa] 10 Feb 2000](/thumbs/87/95098578.jpg) On the K-property of quantized Arnold cat maps arxiv:math/0002080v [math.oa] 0 Feb 2000 I S.V. Neshveyev Abstract We prove that some quantized Arnold cat maps are entropic K-systems. his result was formulated
On the K-property of quantized Arnold cat maps arxiv:math/0002080v [math.oa] 0 Feb 2000 I S.V. Neshveyev Abstract We prove that some quantized Arnold cat maps are entropic K-systems. his result was formulated
