The Aharanov Bohm Effect
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplement 6-A The Aharanov Bohm Effect Let us return to the description of an electron of charge e and mass m e, in a timeindependent magnetic field. The system is described by the Hamiltonian and the time-independent Schrödinger equation reads In the absence of a vector potential the Hamiltonian reads and the Schrödinger equation reads (6A-) (6A-2) (6A-3) (6A-4) We can show that formally the solution of (6A-4) and (6A-2) are related by a simple phase factor. Let us write a general expression It follows that We now observe that if we choose such that then H When this is repeated, we obtain (i ea(r)) 2 e(r) H 0 H(r) E(r) (i ) 2 e(r) H 0 0 (r) E 0 (r) (r) e ie(r) 0 (r) (i ea) e e ie 0 e ie (i ea) 0 e ea 0 (i ea) e ie (i ) 0 H e ie H 0 0 e ie E 0 E (6A-5) (6A-6) (6A-7) (6A-8) (6A-9) What we have just shown is that we can relate a solution of the Schrodinger equation with a vector potential A(r) to one of the Schrodinger equation without a vector potential by performing the gauge transformation shown in Eq. (6A-5). This depended, however, on our ability for find a gauge function (r) that satisfies Eq. (6A-7). This can only happen if B(r) A(r) (r) 0 You may wonder why we bother to go through this, since if B 0, we did not have to write out the Schrodinger equation in the form (6A-). The point is that in quantum mechanics it is the potentials that matter, and there are circumstances where their presence creates physical W-75
2 W-76 Supplement 6-A The Aharanov Bohm Effect r r Figure 6A- The integrals r r 0 A(r) dr along path and path 2 are generally not the same, since the difference is equal to the magnetic flux enclosed by the closed loop. effects even when the magnetic field vanishes. We can write out the dependence on the vector potential by noting that Eq. (6A-7) can be solved by a line integral, (r) r P dl A(r) which starts at some fixed point P and goes to r. In terms of this (6A-5) takes the form (6A-0) Is the line integral in the phase is independent of the path taken between P and r? Let us consider two paths as shown in Fig. 6A-. The difference between the line integrals is 2 By Stokes theorem we have dl A (r) e i(e/) r P da(r) 0 (r) dl A encl. surface dl A counterclockwise dl A ds A ds B S (6A-) (6A-2) This shows that for all paths that do not enclose any magnetic flux, the integral in the phase factor is the same, so that the phase factor does not depend on the path taken. The important point is that there may be situations when there is a local magnetic field, and paths that go around the flux tube are not equivalent. In 959 Y. Aharanov and D. Bohm pointed out a previously overlooked aspect of the quantum mechanics of a charged particle in the presence of electromagnetic fields namely, that even in a field free region, in which B 0, the presence in a field elsewhere can have physical consequences because A 0. Consider, for example, a two-slit diffraction experiment carried out with electrons, as shown in Fig. 6A-2. Suppose that there is a solenoid perpendicular to the plane in which the electrons move, located as in Fig. 6A-2(a) away from the slits. The interference pattern at the screen depends on the difference in phase between the wave functions for the Actually the A-B effect was discovered in an earlier paper by W. Ehrenberg and R. E. Siday (949). Since the effects of potentials were not of central interest in the paper, their important remarks on this subject were completely overlooked.
3 The Aharanov Bohm Effect W-77 Solenoid Electron source Path Path 2 (a) Screen Solenoid Path Electron source (b) Path 2 Screen Figure 6A-2 Schematic sketch of experiment measuring shift of electron interference pattern by confined magnetic flux. electrons passing through the two slits. In the absence of a magnetic field the interference pattern emerges from the relative phases of and s2 in 2 R e i S R 2 e i S 2 e i S (R e i(s 2S ) R 2 ) (6A-3) In the presence of a solenoid, (6A-3) is replaced by e ie e ie d A(r ) e ie 2d A(r ) 2 d A(r ) e is (R i(s R 2 e 2 S )ie/ ) (6A-4) If the solenoid is placed as in Fig. 6A-2(a), then no flux is enclosed by the paths of the electrons and there is no change in the interference pattern. If the flux is placed between the slits, as in Fig. 6A-2(b), then there is an additional contribution to the phase difference between and 2, so that the optical path difference is changed by a constant that depends on the enclosed flux. This has the effect of shifting the peak interference pattern from the previous center, by an amount that depends on the enclosed flux. The first experimental confirmation of the effect is due to R. G. Chambers in 960. The definitive experiments were done by A. Tonomura and collaborators in 980. The A-B paper generated a certain amount of controversy, because many people believed that since only electric and magnetic fields were physical nothing could depend on vector potentials. As was pointed out by M. Peshkin and others, the existence of the A-B effect is intimately tied to the quantization of angular momentum, and its absence would raise serious questions about quantum mechanics. Consider a particle of charge e confined to a very thin torus with radius lying in the x-y plane. A solenoid with radius a V is placed along the z-axis. The magnetic field B inside the solenoid points in the positive z-direction. The vector potential in a convenient, cylindrically symmetric gauge is A 2 r B
4 W-78 Supplement 6-A The Aharanov Bohm Effect that is, A A z 0 A 2 B (6A-5) The Hamiltonian operator has the form (i ea) 2 V() Now ( 2 2 2ie A e 2 A 2 ) V() ie B so that the Hamiltonian operator takes the form L 2 z ebl z e2 B m e L z eb2 2 2 V() (6A-6) (6A-7) (6A-8) Let us now takev() such that the electron is confined to a torus, so narrow that we may treat as constant. In that case the Hamiltonian becomes H aside from a constant. The eigenfunctions of H are eigenfunctions of L z. With where m 0,, 2,..., we find the energy eigenvalues to be E L z i L 2 z e 2 2 L z m V() 2 e m (6A-9) (6A-20) (6A-2) It is clear that the energy depends on the flux, even though the electron wave function nowhere overlaps the external magnetic field. To avoid this one would have to abandon quantization of angular momentum when the x-y plane has holes in it, or one would have to abandon the Schrödinger equation, or the measurability of energies (or rather energy differences) in the presence of such confined fluxes. There is no question of the correctness of this effect. There is an interesting sidelight to the A-B effect. Consider a ring made of a superconductor placed in an external magnetic field, at a temperature above the critical temperature T c below which the material becomes superconducting. When the temperature is lowered the superconductor expels the magnetic field (Fig. 6A-3) except for a thin surface layer so that B 0 inside the material (this is the so-called Meissner effect), 2 and e 2 B 2 2 V() 8m e 2 Chapter 2 in the Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol III contains an excellent discussion of these macroscopic manifestations of quantum mechanics.
5 The Aharanov Bohm Effect W-79 Figure 6A-3 A superconductor at temperature T T c (the critical temperature) acts like any other metal, and magnetic flux lines can penetrate it. When the temperature is lowered until T T c, the ring becomes superconducting, and expels magnetic flux lines. Some of these become trapped inside the ring. It is the trapped flux that is found to be quantized. magnetic flux is trapped inside the ring. The wave function of the superconductor is single-valued, and this implies that the phase factor that appears in (6A-0), when taken around a path that is inside the superconducting ring and encircles the flux region, must be unity. This implies that e ie/ Thus the flux inside the ring is quantized, with e 2n (6A-22) (6A-23) This is almost right. The only modification that must be made is that the superconductor consists of a condensate of correlated electron pairs, so that the appropriate charge that appears in eq. (6A-23) is 2e, and the flux quantization reads 2 2e n (6A-24) where n is an integer. The effect has been measured and the prediction (6A-24) was confirmed.
6 Supplement 6-B A Little About Bessel Functions The solution of the equation with n integral, are known as Bessel functions, for the regular solutions and Neumann functions for the irregular solutions N n (z) 2 J n(z) log z 2 z 2 n (log ) They have the asymptotic behavior d 2 u du 2 dz z dz n2 z2 u 0 J n (z) z 2 n l0 l0 (iz /2) 2l (iz/2) 2l l!(n l)! l!(n l)! a n l 2 z n l0 a nl l m J n (z) z 2 /2 cos z n z N n (z) z 2 /2 sin z n z A detailed discussion of their properties may be found in any book on the special functions of mathematical physics. m n m ln m (n l )! l! z 2 2l W-80
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 23 Jun 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 23 Jun 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 23 Jun 2005](/thumbs/94/119381439.jpg) The Paradoxical Forces for the Classical Electromagnetic Lag Associated with the Aharonov-Bohm Phase Shift arxiv:physics/0506180v1 [physics.class-ph] 23 Jun 2005 Timothy H. Boyer Department of Physics,
The Paradoxical Forces for the Classical Electromagnetic Lag Associated with the Aharonov-Bohm Phase Shift arxiv:physics/0506180v1 [physics.class-ph] 23 Jun 2005 Timothy H. Boyer Department of Physics,
Aharonov Bohm Effect, Magnetic Monopoles, and Charge Quantization
 Aharonov Bohm Effect, Magnetic Monopoles, and Charge Quantization Aharonov Bohm Effect In classical mechanics, the motion of a charged particle depends only on the electric and magnetic tension fields
Aharonov Bohm Effect, Magnetic Monopoles, and Charge Quantization Aharonov Bohm Effect In classical mechanics, the motion of a charged particle depends only on the electric and magnetic tension fields
Time part of the equation can be separated by substituting independent equation
 Lecture 9 Schrödinger Equation in 3D and Angular Momentum Operator In this section we will construct 3D Schrödinger equation and we give some simple examples. In this course we will consider problems where
Lecture 9 Schrödinger Equation in 3D and Angular Momentum Operator In this section we will construct 3D Schrödinger equation and we give some simple examples. In this course we will consider problems where
~ r sm e ae r sm e 2r. r-da. 2 2r
 384 ~hapter 10 The Adiabatic Approximation For Equation 10.51 we need the curl of this quantity: ~ r sm e ae r sm e 2r t"7 ( It; } 1 a [. (i sin 2 (ej2))] A i v X X+ v X+ = -.-- sm e. r = -2 r.. [10.60]
384 ~hapter 10 The Adiabatic Approximation For Equation 10.51 we need the curl of this quantity: ~ r sm e ae r sm e 2r t"7 ( It; } 1 a [. (i sin 2 (ej2))] A i v X X+ v X+ = -.-- sm e. r = -2 r.. [10.60]
1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate
 Physics 223b Lecture 4 Caltech, 04/11/18 1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate 1.6 Superfluid phase: topological defect Besides such smooth gapless excitations, superfluid can also support a very
Physics 223b Lecture 4 Caltech, 04/11/18 1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate 1.6 Superfluid phase: topological defect Besides such smooth gapless excitations, superfluid can also support a very
Aharonov Bohm Effect and Magnetic Monopoles
 Aharonov Bohm Effect and Magnetic Monopoles Aharonov Bohm Effect In classical mechanics, the motion of a charged particle depends only on the electric and magnetic tension fields E and B; the potentials
Aharonov Bohm Effect and Magnetic Monopoles Aharonov Bohm Effect In classical mechanics, the motion of a charged particle depends only on the electric and magnetic tension fields E and B; the potentials
The Aharonov-Bohm Effect
 Michael Florian Wondrak The Aharonov-Bohm Effect 1 The Aharonov-Bohm Effect Michael Florian Wondrak wondrak@fias.uni-frankfurt.de Frankfurt Institute (FIAS) Institut für Theoretische Physik Goethe-Universität
Michael Florian Wondrak The Aharonov-Bohm Effect 1 The Aharonov-Bohm Effect Michael Florian Wondrak wondrak@fias.uni-frankfurt.de Frankfurt Institute (FIAS) Institut für Theoretische Physik Goethe-Universität
An introduction to topological defects in field theories
 An introduction to topological defects in field theories Dept. Daniel B Reeves Physics and Astronomy, Dartmouth College (Dated: Mar. 7, 014) Topology is a relative newcomer to mathematics, but its application
An introduction to topological defects in field theories Dept. Daniel B Reeves Physics and Astronomy, Dartmouth College (Dated: Mar. 7, 014) Topology is a relative newcomer to mathematics, but its application
On the paper Role of potentials in the Aharonov-Bohm effect. A. M. Stewart
 On the paper Role of potentials in the Aharonov-Bohm effect A. M. Stewart Emeritus Faculty, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia. http://www.anu.edu.au/emeritus/members/pages/a_stewart/
On the paper Role of potentials in the Aharonov-Bohm effect A. M. Stewart Emeritus Faculty, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia. http://www.anu.edu.au/emeritus/members/pages/a_stewart/
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis. SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2
 Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
The Aharonov - Bohm effect
 Univerza v Ljubljani Fakulteta za matematiko in fiziko Oddelek za fiziko The Aharonov - Bohm effect Seminar I Author: Amina Alić Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Anton Ramšak April 17, 2016 Contents 1 Introduction
Univerza v Ljubljani Fakulteta za matematiko in fiziko Oddelek za fiziko The Aharonov - Bohm effect Seminar I Author: Amina Alić Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Anton Ramšak April 17, 2016 Contents 1 Introduction
From Last Time. Partially full bands = metal Bands completely full or empty = insulator / seminconductor
 From Last Time Solids are large numbers of atoms arranged in a regular crystal structure. Each atom has electron quantum states, but interactions shift the energies. End result is each type atomic electron
From Last Time Solids are large numbers of atoms arranged in a regular crystal structure. Each atom has electron quantum states, but interactions shift the energies. End result is each type atomic electron
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Aharonov-Bohm effect in spherical billiard
 June 10, 2007 / Vol 5, No 6 / CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS 311 Aharonov-Bohm effect in spherical billiard Dehua Wang (fißu) College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Ludong University, Yantai 264025 Received
June 10, 2007 / Vol 5, No 6 / CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS 311 Aharonov-Bohm effect in spherical billiard Dehua Wang (fißu) College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Ludong University, Yantai 264025 Received
Lecture 35. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 35 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Induced electric fields A long, thin solenoid is encircled by a circular conducting loop. Electric field in the loop is what must drive the current. When the solenoid current
Lecture 35 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Induced electric fields A long, thin solenoid is encircled by a circular conducting loop. Electric field in the loop is what must drive the current. When the solenoid current
QUANTUM MECHANICS Intro to Basic Features
 PCES 4.21 QUANTUM MECHANICS Intro to Basic Features 1. QUANTUM INTERFERENCE & QUANTUM PATHS Rather than explain the rules of quantum mechanics as they were devised, we first look at a more modern formulation
PCES 4.21 QUANTUM MECHANICS Intro to Basic Features 1. QUANTUM INTERFERENCE & QUANTUM PATHS Rather than explain the rules of quantum mechanics as they were devised, we first look at a more modern formulation
QUANTUM MECHANICS. Franz Schwabl. Translated by Ronald Kates. ff Springer
 Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Lecture 33. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
Lecture 33 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Faraday s law of induction When the magnetic flux through a single closed loop changes with time, there is an induced emf that can drive a current around the loop: Recall
A Superfluid Universe
 A Superfluid Universe Lecture 2 Quantum field theory & superfluidity Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU Lecture 2. Quantum fields The dynamical vacuum Vacuumscalar field Superfluidity Ginsburg Landau theory BEC
A Superfluid Universe Lecture 2 Quantum field theory & superfluidity Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU Lecture 2. Quantum fields The dynamical vacuum Vacuumscalar field Superfluidity Ginsburg Landau theory BEC
1 Quantum Theory of Matter
 Quantum Theory of Matter: Superfluids & Superconductors Lecturer: Derek Lee Condensed Matter Theory Blackett 809 Tel: 020 7594 7602 dkk.lee@imperial.ac.uk Level 4 course: PT4.5 (Theory Option) http://www.cmth.ph.ic.ac.uk/people/dkk.lee/teach/qtm
Quantum Theory of Matter: Superfluids & Superconductors Lecturer: Derek Lee Condensed Matter Theory Blackett 809 Tel: 020 7594 7602 dkk.lee@imperial.ac.uk Level 4 course: PT4.5 (Theory Option) http://www.cmth.ph.ic.ac.uk/people/dkk.lee/teach/qtm
 Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
LECTURE 23 INDUCED EMF. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 23 INDUCED EMF Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 23 2 Reading chapter 23.1 to 23.4. Induced emf Magnetic flux Faraday s law Lenz s law Quiz: 1 3 Consider the circuits shown. Which of the following
LECTURE 23 INDUCED EMF Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 23 2 Reading chapter 23.1 to 23.4. Induced emf Magnetic flux Faraday s law Lenz s law Quiz: 1 3 Consider the circuits shown. Which of the following
Scattering theory for the Aharonov-Bohm effect
 Scattering theory for the Aharonov-Bohm effect Takuya MINE Kyoto Institute of Technology 5th September 2017 Tosio Kato Centennial Conference at University of Tokyo Takuya MINE (KIT) Aharonov-Bohm effect
Scattering theory for the Aharonov-Bohm effect Takuya MINE Kyoto Institute of Technology 5th September 2017 Tosio Kato Centennial Conference at University of Tokyo Takuya MINE (KIT) Aharonov-Bohm effect
chmy361 Lec42 Tue 29nov16
 chmy361 Lec42 Tue 29nov16 1 Quantum Behavior & Quantum Mechanics Applies to EVERYTHING But most evident for particles with mass equal or less than proton Absolutely NECESSARY for electrons and light (photons),
chmy361 Lec42 Tue 29nov16 1 Quantum Behavior & Quantum Mechanics Applies to EVERYTHING But most evident for particles with mass equal or less than proton Absolutely NECESSARY for electrons and light (photons),
Quantum Mechanics. Problem 1
 Quantum Mechanics August 21, 2015 Work 4 (and only 4) of the 5 problems. Please put each problem solution on a separate sheet of paper and your name on each sheet. Problem 1 Calculate the scattering amplitude
Quantum Mechanics August 21, 2015 Work 4 (and only 4) of the 5 problems. Please put each problem solution on a separate sheet of paper and your name on each sheet. Problem 1 Calculate the scattering amplitude
The Aharonov - Bohm effect
 Univerza v Ljubljani Fakulteta za matematiko in fiziko Oddelek za fiziko The Aharonov - Bohm effect Seminar Ia Author: Amina Alić Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Anton Ramšak 24. 4. 2016. Contents 1 Introduction
Univerza v Ljubljani Fakulteta za matematiko in fiziko Oddelek za fiziko The Aharonov - Bohm effect Seminar Ia Author: Amina Alić Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Anton Ramšak 24. 4. 2016. Contents 1 Introduction
VORTICES in SUPERFLUIDS & SUPERCONDUCTORS. CIFAR Q MATERIALS SUMMER SCHOOL (May 14-16, 2012) LECTURE 2 VORTICES
 VORTICES in SUPERFLUIDS & SUPERCONDUCTORS CIFAR Q MATERIALS SUMMER SCHOOL (May 14-16, 2012) LECTURE 2 VORTICES Quantum Vortices in Superfluids Suppose we look at a vortex in a superfluid- ie., fluid circulating
VORTICES in SUPERFLUIDS & SUPERCONDUCTORS CIFAR Q MATERIALS SUMMER SCHOOL (May 14-16, 2012) LECTURE 2 VORTICES Quantum Vortices in Superfluids Suppose we look at a vortex in a superfluid- ie., fluid circulating
Lecture 10. Central potential
 Lecture 10 Central potential 89 90 LECTURE 10. CENTRAL POTENTIAL 10.1 Introduction We are now ready to study a generic class of three-dimensional physical systems. They are the systems that have a central
Lecture 10 Central potential 89 90 LECTURE 10. CENTRAL POTENTIAL 10.1 Introduction We are now ready to study a generic class of three-dimensional physical systems. They are the systems that have a central
Interferences in Photodetachment of a Negative Molecular Ion Model
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 1401 1406 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 6, December 15, 2008 Interferences in Photodetachment of a Negative Molecular Ion Model A. Afaq 1,
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 1401 1406 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 6, December 15, 2008 Interferences in Photodetachment of a Negative Molecular Ion Model A. Afaq 1,
which implies that we can take solutions which are simultaneous eigen functions of
 Module 1 : Quantum Mechanics Chapter 6 : Quantum mechanics in 3-D Quantum mechanics in 3-D For most physical systems, the dynamics is in 3-D. The solutions to the general 3-d problem are quite complicated,
Module 1 : Quantum Mechanics Chapter 6 : Quantum mechanics in 3-D Quantum mechanics in 3-D For most physical systems, the dynamics is in 3-D. The solutions to the general 3-d problem are quite complicated,
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 4, April 7, 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 4, April 7, 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Vector and Scalar Potentials
 APPENDIX G Vector and Scalar Potentials Maxwell Equations The electromagnetic field is described by two vector fields: the electric field intensity E and the magnetic field intensity H, which both depend
APPENDIX G Vector and Scalar Potentials Maxwell Equations The electromagnetic field is described by two vector fields: the electric field intensity E and the magnetic field intensity H, which both depend
11 Group Theory and Standard Model
 Physics 129b Lecture 18 Caltech, 03/06/18 11 Group Theory and Standard Model 11.2 Gauge Symmetry Electromagnetic field Before we present the standard model, we need to explain what a gauge symmetry is.
Physics 129b Lecture 18 Caltech, 03/06/18 11 Group Theory and Standard Model 11.2 Gauge Symmetry Electromagnetic field Before we present the standard model, we need to explain what a gauge symmetry is.
Chapter 28 Quantum Theory Lecture 24
 Chapter 28 Quantum Theory Lecture 24 28.1 Particles, Waves, and Particles-Waves 28.2 Photons 28.3 Wavelike Properties Classical Particles 28.4 Electron Spin 28.5 Meaning of the Wave Function 28.6 Tunneling
Chapter 28 Quantum Theory Lecture 24 28.1 Particles, Waves, and Particles-Waves 28.2 Photons 28.3 Wavelike Properties Classical Particles 28.4 Electron Spin 28.5 Meaning of the Wave Function 28.6 Tunneling
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Physics of Semiconductors (Problems for report)
 Physics of Semiconductors (Problems for report) Shingo Katsumoto Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo July, 0 Choose two from the following eight problems and solve them. I. Fundamentals
Physics of Semiconductors (Problems for report) Shingo Katsumoto Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo July, 0 Choose two from the following eight problems and solve them. I. Fundamentals
Superconductivity. Superconductivity. Superconductivity was first observed by HK Onnes in 1911 in mercury at T ~ 4.2 K (Fig. 1).
 Superconductivity Superconductivity was first observed by HK Onnes in 9 in mercury at T ~ 4. K (Fig. ). The temperature at which the resistivity falls to zero is the critical temperature, T c. Superconductivity
Superconductivity Superconductivity was first observed by HK Onnes in 9 in mercury at T ~ 4. K (Fig. ). The temperature at which the resistivity falls to zero is the critical temperature, T c. Superconductivity
Paradoxes of the Aharonov-Bohm and the Aharonov-Casher effects.
 Paradoxes of the Aharonov-Bohm and the Aharonov-Casher effects. L. Vaidman Raymond and Beverly Sackler School of Physics and Astronomy Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 69978, Israel For a believer in locality
Paradoxes of the Aharonov-Bohm and the Aharonov-Casher effects. L. Vaidman Raymond and Beverly Sackler School of Physics and Astronomy Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 69978, Israel For a believer in locality
Physics 8.861: Advanced Topics in Superfluidity
 Physics 8.861: Advanced Topics in Superfluidity My plan for this course is quite different from the published course description. I will be focusing on a very particular circle of ideas around the concepts:
Physics 8.861: Advanced Topics in Superfluidity My plan for this course is quite different from the published course description. I will be focusing on a very particular circle of ideas around the concepts:
Lecture 10: Supercurrent Equation
 Lecture 10: Supercurrent Equation Outline 1. Macroscopic Quantum Model 2. Supercurrent Equation and the London Equations 3. Fluxoid Quantization 4. The Normal State 5. Quantized Vortices October 13, 2005
Lecture 10: Supercurrent Equation Outline 1. Macroscopic Quantum Model 2. Supercurrent Equation and the London Equations 3. Fluxoid Quantization 4. The Normal State 5. Quantized Vortices October 13, 2005
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 3 (9/13/06) Bound States in One Dimensional Systems Particle in a Square Well
 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 3 (9/13/06) Bound States in One Dimensional Systems Particle in a Square Well References - R. L. Liboff, Introductory Quantum Mechanics (Holden Day, New
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 3 (9/13/06) Bound States in One Dimensional Systems Particle in a Square Well References - R. L. Liboff, Introductory Quantum Mechanics (Holden Day, New
(n, l, m l ) 3/2/2016. Quantum Numbers (QN) Plots of Energy Level. Roadmap for Exploring Hydrogen Atom
 PHYS 34 Modern Physics Atom III: Angular Momentum and Spin Roadmap for Exploring Hydrogen Atom Today Contents: a) Orbital Angular Momentum and Magnetic Dipole Moment b) Electric Dipole Moment c) Stern
PHYS 34 Modern Physics Atom III: Angular Momentum and Spin Roadmap for Exploring Hydrogen Atom Today Contents: a) Orbital Angular Momentum and Magnetic Dipole Moment b) Electric Dipole Moment c) Stern
On the Claim of the Observation of Macro-quantum effects of Magnetic Vector Potential in the Classical Domain
 arxiv:quant-ph/0408023v1 3 Aug 2004 On the Claim of the Observation of Macro-quantum effects of Magnetic Vector Potential in the Classical Domain C. S. Unnikrishnan Gravitation Group, Tata Institute of
arxiv:quant-ph/0408023v1 3 Aug 2004 On the Claim of the Observation of Macro-quantum effects of Magnetic Vector Potential in the Classical Domain C. S. Unnikrishnan Gravitation Group, Tata Institute of
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2005 Assignment 5
 Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2005 Assignment 5 Tuesday March 1, 2005 Due Tuesday March 8, 2005 Readings The reading assignment for this problem set and part of the next one is: Griffiths all of Chapter
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2005 Assignment 5 Tuesday March 1, 2005 Due Tuesday March 8, 2005 Readings The reading assignment for this problem set and part of the next one is: Griffiths all of Chapter
For a complex order parameter the Landau expansion of the free energy for small would be. hc A. (9)
 Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Superconductivity: Ginzburg-Landau Theory Some of the key ideas for the Landau mean field description of phase transitions were developed in the context of superconductivity.
Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Superconductivity: Ginzburg-Landau Theory Some of the key ideas for the Landau mean field description of phase transitions were developed in the context of superconductivity.
3. Quantum Mechanics in 3D
 3. Quantum Mechanics in 3D 3.1 Introduction Last time, we derived the time dependent Schrödinger equation, starting from three basic postulates: 1) The time evolution of a state can be expressed as a unitary
3. Quantum Mechanics in 3D 3.1 Introduction Last time, we derived the time dependent Schrödinger equation, starting from three basic postulates: 1) The time evolution of a state can be expressed as a unitary
Physics 208 Review Questions
 Physics 208 Review Questions These problems are shorter than exam problems, closer to a sub-part of a problem or slightly more, so that you can move through several of them quickly. 1) Two charges of 1.0
Physics 208 Review Questions These problems are shorter than exam problems, closer to a sub-part of a problem or slightly more, so that you can move through several of them quickly. 1) Two charges of 1.0
Quantum Physics in the Nanoworld
 Hans Lüth Quantum Physics in the Nanoworld Schrödinger's Cat and the Dwarfs 4) Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 General and Historical Remarks 1 1.2 Importance for Science and Technology 3 1.3 Philosophical
Hans Lüth Quantum Physics in the Nanoworld Schrödinger's Cat and the Dwarfs 4) Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 General and Historical Remarks 1 1.2 Importance for Science and Technology 3 1.3 Philosophical
Electron in a Box. A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time.
 Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Assignment 11
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment 11 Readings Most of the reading needed for this problem set was already given on Problem Set 9. The new readings are: Phase shifts are discussed in Cohen-Tannoudji
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment 11 Readings Most of the reading needed for this problem set was already given on Problem Set 9. The new readings are: Phase shifts are discussed in Cohen-Tannoudji
EE 4395 Special Topics Applied Quantum Mechanics for Electrical Engineers Homework Problems
 EE 4395 Special Topics Applied Quantum Mechanics for Electrical Engineers Homework Problems Part II: Electromagnetic Waves 2.1 Use the relativistic formulas for total energy (γmc 2 )and momentum (γmv)
EE 4395 Special Topics Applied Quantum Mechanics for Electrical Engineers Homework Problems Part II: Electromagnetic Waves 2.1 Use the relativistic formulas for total energy (γmc 2 )and momentum (γmv)
Chapter 6. Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom
 Chapter 6 Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 1 6.1 Schrodinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom Symmetry suggests spherical polar coordinates Fig. 6.1 (a) Spherical polar coordinates. (b) A line of constant
Chapter 6 Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 1 6.1 Schrodinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom Symmetry suggests spherical polar coordinates Fig. 6.1 (a) Spherical polar coordinates. (b) A line of constant
SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY LECTURE
 Lecture 4 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY LECTURE 4 017 Anthony J. Leggett Department of Physics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA and Director, Center for Complex Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong
Lecture 4 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY LECTURE 4 017 Anthony J. Leggett Department of Physics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA and Director, Center for Complex Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Multiple Integrals 3. 2 Vector Fields 9
 MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
MATH 32B-2 (8W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Multiple Integrals 3 2 Vector Fields 9 3 Line and Surface Integrals 5 4 The Classical Integral Theorems 9 MATH 32B-2 (8W)
Angular momentum. Quantum mechanics. Orbital angular momentum
 Angular momentum 1 Orbital angular momentum Consider a particle described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z r and their conjugate momenta (p x, p y, p z p. The classical definition of the orbital angular
Angular momentum 1 Orbital angular momentum Consider a particle described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z r and their conjugate momenta (p x, p y, p z p. The classical definition of the orbital angular
QUALIFYING EXAMINATION, Part 1. Solutions. Problem 1: Mathematical Methods. r r r 2 r r2 = 0 r 2. d 3 r. t 0 e t dt = e t
 QUALIFYING EXAMINATION, Part 1 Solutions Problem 1: Mathematical Methods (a) For r > we find 2 ( 1 r ) = 1 ( ) 1 r 2 r r2 = 1 ( 1 ) r r r 2 r r2 = r 2 However for r = we get 1 because of the factor in
QUALIFYING EXAMINATION, Part 1 Solutions Problem 1: Mathematical Methods (a) For r > we find 2 ( 1 r ) = 1 ( ) 1 r 2 r r2 = 1 ( 1 ) r r r 2 r r2 = r 2 However for r = we get 1 because of the factor in
Abrikosov vortex lattice solution
 Abrikosov vortex lattice solution A brief exploration O. Ogunnaike Final Presentation Ogunnaike Abrikosov vortex lattice solution Physics 295b 1 / 31 Table of Contents 1 Background 2 Quantization 3 Abrikosov
Abrikosov vortex lattice solution A brief exploration O. Ogunnaike Final Presentation Ogunnaike Abrikosov vortex lattice solution Physics 295b 1 / 31 Table of Contents 1 Background 2 Quantization 3 Abrikosov
Computation of the scattering amplitude in the spheroidal coordinates
 Computation of the scattering amplitude in the spheroidal coordinates Takuya MINE Kyoto Institute of Technology 12 October 2015 Lab Seminar at Kochi University of Technology Takuya MINE (KIT) Spheroidal
Computation of the scattering amplitude in the spheroidal coordinates Takuya MINE Kyoto Institute of Technology 12 October 2015 Lab Seminar at Kochi University of Technology Takuya MINE (KIT) Spheroidal
Faraday's Law ds B B G G ΦB B ds Φ ε = d B dt
 Faraday's Law ds ds ε= d Φ dt Φ Global Review Electrostatics» motion of q in external E-field» E-field generated by Σq i Magnetostatics» motion of q and i in external -field» -field generated by I Electrodynamics»
Faraday's Law ds ds ε= d Φ dt Φ Global Review Electrostatics» motion of q in external E-field» E-field generated by Σq i Magnetostatics» motion of q and i in external -field» -field generated by I Electrodynamics»
Physics 127c: Statistical Mechanics. Application of Path Integrals to Superfluidity in He 4
 Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Application of Path Integrals to Superfluidity in He 4 The path integral method, and its recent implementation using quantum Monte Carlo methods, provides both an intuitive
Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Application of Path Integrals to Superfluidity in He 4 The path integral method, and its recent implementation using quantum Monte Carlo methods, provides both an intuitive
On the Electric Charge Quantization from the Aharonov-Bohm Potential
 On the Electric Charge Quantization from the Aharonov-Bohm Potential F.A. Barone and J.A. Helayël-Neto Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas Rua Dr. Xavier Sigaud 150, Urca 90-180 Rio de Janeiro, RJ,
On the Electric Charge Quantization from the Aharonov-Bohm Potential F.A. Barone and J.A. Helayël-Neto Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas Rua Dr. Xavier Sigaud 150, Urca 90-180 Rio de Janeiro, RJ,
Chapter 4 Section 2 Notes
 Chapter 4 Section 2 Notes Vocabulary Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. Quantum
Chapter 4 Section 2 Notes Vocabulary Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. Quantum
Ampere s Law. Outline. Objectives. BEE-Lecture Notes Anurag Srivastava 1
 Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II
 CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 The Schrödinger Wave Equation Expectation Values Infinite Square-Well Potential Finite Square-Well Potential Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 The Schrödinger Wave Equation Expectation Values Infinite Square-Well Potential Finite Square-Well Potential Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential
CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter
 CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan22 1 1. Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter 1.1. Absorption (excitation), emission, diffraction, scattering, refraction
CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan22 1 1. Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter 1.1. Absorption (excitation), emission, diffraction, scattering, refraction
Select/ Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Select/ Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 06 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics Greetings, we will begin
Select/ Special Topics in Atomic Physics Prof. P. C. Deshmukh Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 06 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics Greetings, we will begin
1. Mathematical Tools
 1. Mathematical Tools 1.1 Coordinate Systems Suppose u 1, u 2, and u 3 are the coordinates of a general coordinate coordinate system in which the (ê 1, ê 2, ê 3 ) unit or basis vectors specify the directions
1. Mathematical Tools 1.1 Coordinate Systems Suppose u 1, u 2, and u 3 are the coordinates of a general coordinate coordinate system in which the (ê 1, ê 2, ê 3 ) unit or basis vectors specify the directions
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Electromagnetic
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Electromagnetic
The Ginzburg-Landau Theory
 The Ginzburg-Landau Theory A normal metal s electrical conductivity can be pictured with an electron gas with some scattering off phonons, the quanta of lattice vibrations Thermal energy is also carried
The Ginzburg-Landau Theory A normal metal s electrical conductivity can be pictured with an electron gas with some scattering off phonons, the quanta of lattice vibrations Thermal energy is also carried
Interference by Wavefront Division
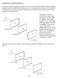 nterference by Wavefront Division One of the seminal experiments in physics was conducted in 1801 by Thomas Young, an English physicist who cut a small hole in an opaque screen, set a second screen in
nterference by Wavefront Division One of the seminal experiments in physics was conducted in 1801 by Thomas Young, an English physicist who cut a small hole in an opaque screen, set a second screen in
August 2006 Written Comprehensive Exam Day 1
 Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia August 006 Written Comprehensive Exam Day 1 This is a closed-book, closed-note exam. You may use a calculator, but only for arithmetic functions
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia August 006 Written Comprehensive Exam Day 1 This is a closed-book, closed-note exam. You may use a calculator, but only for arithmetic functions
Ampere s law. Lecture 15. Chapter 32. Physics II. Course website:
 Lecture 15 Chapter 32 Physics II Ampere s law Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Ampere s Law Electric Field From Coulomb s law 1 4 Magnetic Field Bio-Savart law 4
Lecture 15 Chapter 32 Physics II Ampere s law Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Ampere s Law Electric Field From Coulomb s law 1 4 Magnetic Field Bio-Savart law 4
Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems: 5,7,9,10,11,13,15,17,20,21,28,29,31,32,33,34,49,50,52,58,63,64. Faraday's Law of Induction We learned that e. current produces magnetic field. Now we want
Chapter 9 FARADAY'S LAW Recommended Problems: 5,7,9,10,11,13,15,17,20,21,28,29,31,32,33,34,49,50,52,58,63,64. Faraday's Law of Induction We learned that e. current produces magnetic field. Now we want
Magneto-Excitons in Semiconductor Quantum Rings
 phys. stat. sol. (a) 190, No. 3, 781 785 (2002) Magneto-Excitons in Semiconductor Quantum Rings I. Galbraith 1 ), F. J. Braid, and R. J. Warburton Department of Physics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh,
phys. stat. sol. (a) 190, No. 3, 781 785 (2002) Magneto-Excitons in Semiconductor Quantum Rings I. Galbraith 1 ), F. J. Braid, and R. J. Warburton Department of Physics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh,
Qualifying Exam. Aug Part II. Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets!
 Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Weak Link Probes and Space-Time Translation Symmetry Breaking
 Weak Link Probes and Space-Time Translation Symmetry Breaking Frank Wilczek Center for Theoretical Physics, MIT, Cambridge MA 02139 USA August 10, 2013 Abstract Intermittent weak link (Josephson type)
Weak Link Probes and Space-Time Translation Symmetry Breaking Frank Wilczek Center for Theoretical Physics, MIT, Cambridge MA 02139 USA August 10, 2013 Abstract Intermittent weak link (Josephson type)
Electromagnetism Answers to Problem Set 9 Spring 2006
 Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
Electromagnetism 70006 Answers to Problem et 9 pring 006. Jackson Prob. 5.: Reformulate the Biot-avart law in terms of the solid angle subtended at the point of observation by the current-carrying circuit.
2 Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field
 2 Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field 2.1 Basics Starting point of the quantization of the electromagnetic field are Maxwell s equations in the vacuum (source free): where B = µ 0 H, D = ε 0 E, µ
2 Quantization of the Electromagnetic Field 2.1 Basics Starting point of the quantization of the electromagnetic field are Maxwell s equations in the vacuum (source free): where B = µ 0 H, D = ε 0 E, µ
Quantum Interference in Josephson Junctions *
 ournal of Modern Physics, 15, 6, 56-535 Published Online April 15 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp http://dx.doi.org/1.436/jmp.15.6557 Quantum Interference in osephson unctions * Roberto De
ournal of Modern Physics, 15, 6, 56-535 Published Online April 15 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp http://dx.doi.org/1.436/jmp.15.6557 Quantum Interference in osephson unctions * Roberto De
The Central Force Problem: Hydrogen Atom
 The Central Force Problem: Hydrogen Atom B. Ramachandran Separation of Variables The Schrödinger equation for an atomic system with Z protons in the nucleus and one electron outside is h µ Ze ψ = Eψ, r
The Central Force Problem: Hydrogen Atom B. Ramachandran Separation of Variables The Schrödinger equation for an atomic system with Z protons in the nucleus and one electron outside is h µ Ze ψ = Eψ, r
Physics 342 Lecture 23. Radial Separation. Lecture 23. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 23 Radial Separation Lecture 23 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, March 26th, 2010 We begin our spherical solutions with the simplest possible case zero potential. Aside from
Physics 342 Lecture 23 Radial Separation Lecture 23 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, March 26th, 2010 We begin our spherical solutions with the simplest possible case zero potential. Aside from
( ) ( ) Last Time. 3-D particle in box: summary. Modified Bohr model. 3-dimensional Hydrogen atom. Orbital magnetic dipole moment
 Last Time 3-dimensional quantum states and wave functions Decreasing particle size Quantum dots (particle in box) Course evaluations Thursday, Dec. 10 in class Last HW assignment available : for practice
Last Time 3-dimensional quantum states and wave functions Decreasing particle size Quantum dots (particle in box) Course evaluations Thursday, Dec. 10 in class Last HW assignment available : for practice
Physics 582, Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Physics 582, Problem Set 4 Solutions TAs: Hart Goldman and Ramanjit Sohal Fall 2018 1. PATH INTEGRAL FOR A PARTICLE IN A DOUBLE POTENTIAL WELL 1. In real time, q 0, T/2 q 0, T/2 = q 0 e i HT q 0 = where
Physics 582, Problem Set 4 Solutions TAs: Hart Goldman and Ramanjit Sohal Fall 2018 1. PATH INTEGRAL FOR A PARTICLE IN A DOUBLE POTENTIAL WELL 1. In real time, q 0, T/2 q 0, T/2 = q 0 e i HT q 0 = where
Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields
 Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields Electric Currents Create Magnetic Fields A long, straight wire A current loop A solenoid Slide 24-14 Biot-Savart Law Current produces a magnetic field The Biot-Savart
Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields Electric Currents Create Magnetic Fields A long, straight wire A current loop A solenoid Slide 24-14 Biot-Savart Law Current produces a magnetic field The Biot-Savart
221A Lecture Notes Electromagnetic Couplings
 221A Lecture Notes Electromagnetic Couplings 1 Classical Mechanics The coupling of the electromagnetic field with a charged point particle of charge e is given by a term in the action (MKSA system) S int
221A Lecture Notes Electromagnetic Couplings 1 Classical Mechanics The coupling of the electromagnetic field with a charged point particle of charge e is given by a term in the action (MKSA system) S int
PART I Qualifying Examination. August 22, 2017, 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m.
 UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI-COLUMBIA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PART I Qualifying Examination August 22, 2017, 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Instructions: The only material you are allowed in the examination room is a writing
UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI-COLUMBIA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PART I Qualifying Examination August 22, 2017, 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Instructions: The only material you are allowed in the examination room is a writing
Physics Lecture 6
 Physics 3313 - Lecture 6 Monday February 8, 2010 Dr. Andrew Brandt 1. HW1 Due today HW2 weds 2/10 2. Electron+X-rays 3. Black body radiation 4. Compton Effect 5. Pair Production 2/8/10 3313 Andrew Brandt
Physics 3313 - Lecture 6 Monday February 8, 2010 Dr. Andrew Brandt 1. HW1 Due today HW2 weds 2/10 2. Electron+X-rays 3. Black body radiation 4. Compton Effect 5. Pair Production 2/8/10 3313 Andrew Brandt
Hamiltonian approach to Yang- Mills Theories in 2+1 Dimensions: Glueball and Meson Mass Spectra
 Hamiltonian approach to Yang- Mills Theories in 2+1 Dimensions: Glueball and Meson Mass Spectra Aleksandr Yelnikov Virginia Tech based on hep-th/0512200 hep-th/0604060 with Rob Leigh and Djordje Minic
Hamiltonian approach to Yang- Mills Theories in 2+1 Dimensions: Glueball and Meson Mass Spectra Aleksandr Yelnikov Virginia Tech based on hep-th/0512200 hep-th/0604060 with Rob Leigh and Djordje Minic
Slide 1 / 24. Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger
 Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Slide 1 / 24 Electromagnetic Induction 2011 by Bryan Pflueger Slide 2 / 24 Induced Currents If we have a galvanometer attached to a coil of wire we can induce a current simply by changing the magnetic
Superconductivity at nanoscale
 Superconductivity at nanoscale Superconductivity is the result of the formation of a quantum condensate of paired electrons (Cooper pairs). In small particles, the allowed energy levels are quantized and
Superconductivity at nanoscale Superconductivity is the result of the formation of a quantum condensate of paired electrons (Cooper pairs). In small particles, the allowed energy levels are quantized and
Quantum Theory of Matter
 Quantum Theory of Matter Overview Lecture Derek Lee Imperial College London January 2007 Outline 1 Course content Introduction Superfluids Superconductors 2 Course Plan Resources Outline 1 Course content
Quantum Theory of Matter Overview Lecture Derek Lee Imperial College London January 2007 Outline 1 Course content Introduction Superfluids Superconductors 2 Course Plan Resources Outline 1 Course content
An introduction to the vector potential
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 249 256 EUROPEANJOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)68734-4 An introduction to the vector potential DIencinella 1,3 and G Matteucci 2 1 Department
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 249 256 EUROPEANJOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)68734-4 An introduction to the vector potential DIencinella 1,3 and G Matteucci 2 1 Department
Lecture Notes in Physics
 Lecture Notes in Physics Edited by H. Araki, Kyoto, J. Ehlers, MLinchen, K. Hepp, ZUrich R. Kippenhahn, ML~nchen, D. Ruelle, Bures-sur-Yvette H.A. WeidenmSIler, Heidelberg, J. Wess, Karlsruhe and J. Zittartz,
Lecture Notes in Physics Edited by H. Araki, Kyoto, J. Ehlers, MLinchen, K. Hepp, ZUrich R. Kippenhahn, ML~nchen, D. Ruelle, Bures-sur-Yvette H.A. WeidenmSIler, Heidelberg, J. Wess, Karlsruhe and J. Zittartz,
Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics 1 Introduction Syllabus for Fall 2009 This is essentially a standard first-year course in quantum mechanics, the basic language for describing physics at the atomic and subatomic
Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics 1 Introduction Syllabus for Fall 2009 This is essentially a standard first-year course in quantum mechanics, the basic language for describing physics at the atomic and subatomic
Coaxial cable. Coaxial cable. Magnetic field inside a solenoid
 Divergence and circulation Surface S Ampere s Law A vector field is generally characterized by 1) how field lines possibly diverge away from or converge upon (point) sources plus 2) how field lines circulate,
Divergence and circulation Surface S Ampere s Law A vector field is generally characterized by 1) how field lines possibly diverge away from or converge upon (point) sources plus 2) how field lines circulate,
Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics
 Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics 3.1 Photons - Light: e.m "waves" - interference, diffraction, refraction, reflection with y E y Velocity = c Direction of Propagation z B z Fig. 3.1: The classical view
Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics 3.1 Photons - Light: e.m "waves" - interference, diffraction, refraction, reflection with y E y Velocity = c Direction of Propagation z B z Fig. 3.1: The classical view
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
CHAPTER 7 ELECTRODYNAMICS Outlines 1. Electromotive Force 2. Electromagnetic Induction 3. Maxwell s Equations Michael Faraday James C. Maxwell 2 Summary of Electrostatics and Magnetostatics ρ/ε This semester,
Magnetism. March 10, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 27 1
 Magnetism March 10, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 27 1 Notes! Homework is due on We night! Exam 4 next Tuesday Covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 in the book Magnetism, Magnetic Fields, Electromagnetic
Magnetism March 10, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 27 1 Notes! Homework is due on We night! Exam 4 next Tuesday Covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 in the book Magnetism, Magnetic Fields, Electromagnetic
Azimuthal eddy currents in a wire
 Problem 1. Azimuthal eddy currents in a wire A longitudinal AC magnetic field B(t) = ẑb o cos(ωt) is driven through the interior of a (solid) ohmic tube with length L and radius R L, drawn rather schematically
Problem 1. Azimuthal eddy currents in a wire A longitudinal AC magnetic field B(t) = ẑb o cos(ωt) is driven through the interior of a (solid) ohmic tube with length L and radius R L, drawn rather schematically
