Calculation of the Streaming Potential Near a Rotating Disk with Rotational Elliptic Coordinates
|
|
|
- Harvey Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6/4 (8) PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA Calculation of the Streaming Potential Near a Rotating Dis with Rotational Elliptic Coordinates F.S. Lameiras * and E.H.M. Nunes Centro de Desenvolvimento da Tecnologia Nuclear, Comissão Nacional de Energia Nuclear, Av. Antônio Carlos, 6.67, Belo Horionte, Minas Gerais, Brail Received 3 rd January 8; accepted th March 8 Abstract The calculation with rotational elliptic coordinates of the streaming potential in the vicinity of a dis-shaped sample rotating in an electrolytic solution is presented. The measurement of this streaming potential is used to determine the eta potential of planar surfaces. Rotational elliptic coordinates are favored in relation to integral transform methods because only simple mathematical methods are employed to explain the theory of this technique. Keywords: eta potential, planar surfaces, rotating dis, streaming potential, rotational elliptic coordinates. Introduction A new method and a new apparatus to measure the eta potential of a planar surface, ζ, based on the measurement of the electric potential in the vicinity of a rotating dis were described in three previous papers [,,3]. A sample in the shape of a dis is fixed to a rotating cylindrical support immersed in a fluid with electric charges. The rotation of the dis generates a radial movement of electric charges in the diffuse layer adjacent to the sample s face, resulting in an electric potential distributed in the space near the sample. This electric potential can be measured and is proportional to the eta potential. The advantage of this new method is the experimental simplicity, which allows the construction of a reliable equipment. In the first two papers [,] the authors tried to employ elliptic rotational coordinates to develop the theory of the method, but they found some disagreements between theory and practice. In the third paper [3] they corrected * Corresponding author. address: fernando.lameiras@pq.cnpq.br
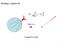
2 F.S. Lameiras and E.H.M. Nunes / Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6 (8) the theoretical flaws by using the Hanel transform according to Nanis and Kesselman [4]. However, this solution is complex and difficult to explain to most users of this new technique. The authors derived the Legendre s equation by applying the rotational elliptic coordinates to the Laplace s equation, but in the corrected application the Chebyshev s equation is derived. This paper presents the solution of the Chebyshev s equation to this problem, which is derived with simple mathematical methods and agrees with the solution of the Hanel transform. Theory Fig. shows the situation where the face of a dis is immersed in a fluid where there are negative and positive electric charges. Let the face of the dis be made of a ind of material whose surface has affinity for negative electric charges. A layer of negative electric charges adheres to this surface. After that, a layer of positive charges is attracted to this layer of negative charges. However, because of thermodynamic fluctuations, this layer presents disorganiation. Another more disorganied layer with negative charges approaches this surface. Successive layers with progressive disorganiation will follow, and after a distance d, the disorganiation between negative and positive charges will be the same as observed in the fluid. ample rotating dis disco rotativo ρ(r,) r fluid velocity ϕ Figure. Scheme of the assembly used in the measurement of the eta potential using a rotating dis. d ϕ = 37
3 F.S. Lameiras and E.H.M. Nunes / Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6 (8) The separation between positive and negative charges near the face of the dis generates electric dipoles, whose electric field can be observed. If the dis is rotated, according to the principles of the viscous fluids dynamics, the fluid layer in contact with the dis will rotate at the same velocity as the dis. The layer near the dis will rotate at a lower velocity. The difference between the velocities of these two layers is proportional to the viscosity of the fluid. The velocity of the successive layers decreases in the same way, as shown in Fig.. The rotating movement of the dis generates an outward radial movement of the fluid towards the edge of the dis. The velocity v r of this movement is given by [5,6,7] v =γ r r () /.53Ω 3/ = ν, where Ω is the angular velocity of the dis, and ν is the γ inematic viscosity of the fluid. r and are cylindrical coordinates. This radial movement generates a displacement of electric charges in the vicinity of the dis because, as shown in Fig., there are more free positive electric charges than free negative electric charges. This generates a radial electric current. The charges move outward to the edge of the dis, where they leave this layer and flow bac through the liquid toward the dis. Let ρ(r,) be the electric charge density in the fluid. This density will be different from ero only in the vicinity of the dis. Therefore, ρ(r,) will rapidly approach ero when increases. The radial electric current through a wall of fluid of radius r and height is According to Gauss s law, ir = ρ(r, )vr π r () ρ(r, ) = ε ϕ, where ϕ is the electric potential and ε is the electric permittivity of the fluid. ϕ = ( r) r ( r ϕ r) + ϕ is the Laplacian of the electric potential in cylindrical coordinates with cylindrical symmetry ( ϕ θ = ). ϕ r has a small variation for r < R (R is the radius of the dis). Thus, i r ϕ ε γ r π r (3) The radial electric current can be obtained through the integration of (3), i ϕ ϕ = π r εγ = π r εγ [ ϕ] r d (4) This radial current is confined to a layer near the face of the dis. The physical quantity 37
4 F.S. Lameiras and E.H.M. Nunes / Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6 (8) ζ ϕ (5) = [ ϕ] is defined as the eta potential. The current i R increases with the square of r until the maximum value i = πεr γζ is reached. R The radial current increment in a ring of the layer of fluid near the surface of the dis is ir = 4πεγζ r r (6) This current increment must be supplied by the fluid below the ring. Thus, the current density perpendicular to the surface of the dis, j, is j i r = = πr r εγ ζ (7) The negative sign taes to account that j is in the opposite direction of the coordinate axis. This equation shows that the current density returning to the layer of fluid near the face of the dis is uniform when r R. In a volume element sufficiently distant from the face of the dis, there is a charge balance. Thus, according to Gauss s law, ϕ =. This equation can be solved using the elliptical coordinates ξ and η, where r R[ ( + ξ )( η )] / = and = Rξη. Considering a solution such as ϕ ( ξ, η) = M ( ξ ) P( η), one obtains Chebyshev s differential equations (with real argument for η and imaginary argument for ξ). Solutions convergent for ξ and η are obtained considering M j ( ξ ) = j = a j ξ and P ( η) = j j = c j η, where j is an integer. The general solution is where ( η;b) = [ a M ( ξ;b) + a M ( ξ;b) ][ c P ( η;b) c P ( η;b) ] ϕ ξ; + (8) M M P j ξ [ ][ b ( j 4) ] L [ b ] ( j )! ( ξ;b) = b ( j ) j+ ξ [ ][ b ( j 3) ] L [ b ] ( j + ) ( ξ;b) = b ( j ) ( η;b) = ( j ) j η [ b] [( j 4) b] L [ b] ( j )!! (9a) (9b) (9c) 37
5 F.S. Lameiras and E.H.M. Nunes / Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6 (8) P ( η;b) = ( j ) j+ η [ b] [( j 3) b] L [ b] ( j + )! (9d) The first boundary condition is that the function ϕ(r;)=ϕ(ξ;η;b) must provide a current density perpendicular to the face of the dis equal to j = εγζ ϕ ϕ j = = = Rη ξ One obtains from (9) that ξ =., where is the electric conductivity of the fluid. ' ' ( ) ( ) [ ( ) ( )][ c P η;b + cp η;b ] a M ;b + a M ;b η ε γ R = () [ ]η This equation is true if c P ( η;b) + cp ( η;b) is constant. In order to fulfill this condition, c = and b =, because P ( η;) = η. Moreover, M ' ( ;) =, M ' ( ;) =, and M ( ξ;) = ξ. The solution is given by ( η;) = a c η M ( ξ;) ηξ ϕ ξ; () The second boundary condition is that the streaming potential is maximum at the center of the dis (r=;=) or (η=;ξ =) and is equal to, so that ϕ ( ξ; η;) = η[ M ( ξ;) ξ] () Discussion Equation () is true where ϕ =, that is, where there is electric charge balance in a volume of fluid. This situation exists for > d from the face of the dis (Fig. ). In the region between = and = d, ϕ, that is, there is a net electric charge. The radial electric current is confined to this region. d is related to the Debye s distance in an electrolyte [8]. In Fig., d is shown as amplified for didactical purposes, because d<<<r. The electric potential ϕ(ξ;;) can be measured by putting an electrode in (,r)=(rξ;) and another one in a position >> R, where ϕ(,r) =. Along the axis of the dis (η=), equation () gives that ( ξ;;) ϕ (3) = M ( ξ;) ξ The right hand side of (3) gives the same values for small ξ as the approximated function employed by Sides, 373
6 F.S. Lameiras and E.H.M. Nunes / Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6 (8) ( ξ;;) ϕ ξ + ξ (4) ϕ(ξ;;) is typically around. mv near the dis and falls as ξ growths. This streaming potential is not very high relative to the noise observed in practice. So, ξ should be as close as possible to ero in order to eep the streaming potential as high as possible to decrease the error of measurement. Another good procedure is to give an identifiable pattern to the rotation of the dis (e. g., a sinusoidal pattern) to separate the streaming potential from the noise. Conclusion This paper corrects the approaches previously published by using elliptic rotational coordinates to calculate the streaming potential near a rotating dis immersed in a fluid with electric charges. The rotation of a dis whose radius is R, immersed in a fluid where there are negative and positive electric charges, generates an electric potential difference between a position along the axis of the dis and another position distant from the dis given by (for R) ϕ R = M ( ξ;) R (5) where ϕ(/r) is the electric potential difference, ε is the electric permittivity of the fluid, is the electric conductivity of the fluid, ζ is the eta potential of the / surface of the dis, R is the radius of the dis,.53ω 3/ γ = ν, where Ω is the angular velocity of the dis and ν is the inematic viscosity of the fluid, and [ ( j ) ] ( j 4) [ ] ( j) M = L R! R j (6) ϕ, ν and can be measured, whereas Ω, R and can be controlled. In these conditions, it is possible to calculate the eta potential with equation (5) by measuring the electric potential in a position along the axis of the dis. Acnowledgments To CNPq (Processes n. 477/4- and 358/6-) and to CAPES. References. P.J. Sides and J.D. Hoggard, Langmuir (4) J.D. Hoggard, P.J. Sides and D.C. Prieve, Langmuir (5) P.J. Sides, J. Newman, J.D. Hoggard and D.C. Prieve, Langmuir (6)
7 F.S. Lameiras and E.H.M. Nunes / Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 6 (8) L. Nanis and W. Kesselman, J. Electrochem. Soc. 8 (97) Th. Von Kármán, Z. Angew. Math. Mech. (9) W.G. Cochran, Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. (934) M.H. Rogers and G.N. Lance, J. Fluid Mech. 7 (96) R.J. Golston and P.H. Rutherford, Introduction to Plasma Physics, Institute of Physics Publishing, Philadelphia,
NANOPARTICLE MANIPULATION BY DIELECTROPHORESIS
 Physica Macedonica 61, (1) p. 39-44 ISSN 149-7168 NANOPARTICLE MANIPULATION BY DIELECTROPHORESIS A. Neculae, R. Giugiulan and M. Lungu West University of Timisoara, Faculty of Physics, Blv. V. Parvan no.4,
Physica Macedonica 61, (1) p. 39-44 ISSN 149-7168 NANOPARTICLE MANIPULATION BY DIELECTROPHORESIS A. Neculae, R. Giugiulan and M. Lungu West University of Timisoara, Faculty of Physics, Blv. V. Parvan no.4,
Physics 2B. Lecture 24B. Gauss 10 Deutsche Mark
 Physics 2B Lecture 24B Gauss 10 Deutsche Mark Electric Flux Flux is the amount of something that flows through a given area. Electric flux, Φ E, measures the amount of electric field lines that passes
Physics 2B Lecture 24B Gauss 10 Deutsche Mark Electric Flux Flux is the amount of something that flows through a given area. Electric flux, Φ E, measures the amount of electric field lines that passes
ON VARIABLE LAMINAR CONVECTIVE FLOW PROPERTIES DUE TO A POROUS ROTATING DISK IN A MAGNETIC FIELD
 ON VARIABLE LAMINAR CONVECTIVE FLOW PROPERTIES DUE TO A POROUS ROTATING DISK IN A MAGNETIC FIELD EMMANUEL OSALUSI, PRECIOUS SIBANDA School of Mathematics, University of KwaZulu-Natal Private Bag X0, Scottsville
ON VARIABLE LAMINAR CONVECTIVE FLOW PROPERTIES DUE TO A POROUS ROTATING DISK IN A MAGNETIC FIELD EMMANUEL OSALUSI, PRECIOUS SIBANDA School of Mathematics, University of KwaZulu-Natal Private Bag X0, Scottsville
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination January 7, 28 9. am 12: pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination January 7, 28 9. am 12: pm Full credit can be achieved from completely correct answers to 4 questions.
Electric Field and Gauss s law. January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1
 Electric Field and Gauss s law January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1 Missing clickers! The following clickers are not yet registered! If your clicker number is in this list,
Electric Field and Gauss s law January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1 Missing clickers! The following clickers are not yet registered! If your clicker number is in this list,
Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 2005/10/17 Electro Dynamic
 Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 5//7 Name Electro Dynamic. () Write Gauss Law in differential form. E( r) =ρ( r)/ɛ, or D = ρ, E= electricfield,ρ=volume charge density, ɛ =permittivity
Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 5//7 Name Electro Dynamic. () Write Gauss Law in differential form. E( r) =ρ( r)/ɛ, or D = ρ, E= electricfield,ρ=volume charge density, ɛ =permittivity
Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP)
 Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP) Self-potential method (passive) Self-potential mechanism Measurement of self potentials and interpretation Induced polarization method (active)
Part II: Self Potential Method and Induced Polarization (IP) Self-potential method (passive) Self-potential mechanism Measurement of self potentials and interpretation Induced polarization method (active)
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Physics Lecture 13
 Physics 113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 113 Lecture 13 EXAM I: REVIEW A few concepts: electric force, field and potential Gravitational Force What is the force on a mass produced by other masses? Kepler s
Physics 113 Jonathan Dowling Physics 113 Lecture 13 EXAM I: REVIEW A few concepts: electric force, field and potential Gravitational Force What is the force on a mass produced by other masses? Kepler s
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE FLOW AROUND A SQUARE CYLINDER USING THE VORTEX METHOD
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE FLOW AROUND A SQUARE CYLINDER USING THE VORTEX METHOD V. G. Guedes a, G. C. R. Bodstein b, and M. H. Hirata c a Centro de Pesquisas de Energia Elétrica Departamento de Tecnologias
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE FLOW AROUND A SQUARE CYLINDER USING THE VORTEX METHOD V. G. Guedes a, G. C. R. Bodstein b, and M. H. Hirata c a Centro de Pesquisas de Energia Elétrica Departamento de Tecnologias
PHY102 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law
 PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
Gauss s Law. The first Maxwell Equation A very useful computational technique This is important!
 Gauss s Law The first Maxwell quation A very useful computational technique This is important! P05-7 Gauss s Law The Idea The total flux of field lines penetrating any of these surfaces is the same and
Gauss s Law The first Maxwell quation A very useful computational technique This is important! P05-7 Gauss s Law The Idea The total flux of field lines penetrating any of these surfaces is the same and
Chapter 23. Gauss Law. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 Electric Flux Electric field vectors and field lines pierce an imaginary, spherical Gaussian surface that encloses a particle with charge +Q. Now the enclosed particle
Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 Electric Flux Electric field vectors and field lines pierce an imaginary, spherical Gaussian surface that encloses a particle with charge +Q. Now the enclosed particle
Legendre s Equation. PHYS Southern Illinois University. October 13, 2016
 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University October 13, 2016 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Legendre s Equation October 13, 2016 1 / 10 The Laplacian in Spherical Coordinates The Laplacian is given
PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University October 13, 2016 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Legendre s Equation October 13, 2016 1 / 10 The Laplacian in Spherical Coordinates The Laplacian is given
3/22/2016. Chapter 27 Gauss s Law. Chapter 27 Preview. Chapter 27 Preview. Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2.
 Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-3 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-4 1 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-5 Chapter 27 Preview Slide
Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-3 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-4 1 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-5 Chapter 27 Preview Slide
How to define the direction of A??
 Chapter Gauss Law.1 Electric Flu. Gauss Law. A charged Isolated Conductor.4 Applying Gauss Law: Cylindrical Symmetry.5 Applying Gauss Law: Planar Symmetry.6 Applying Gauss Law: Spherical Symmetry You will
Chapter Gauss Law.1 Electric Flu. Gauss Law. A charged Isolated Conductor.4 Applying Gauss Law: Cylindrical Symmetry.5 Applying Gauss Law: Planar Symmetry.6 Applying Gauss Law: Spherical Symmetry You will
Summary: Applications of Gauss Law
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Influence of chemical reaction, Soret and Dufour effects on heat and mass transfer of a binary fluid mixture in porous medium over a rotating disk
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 10, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov - Dec. 2014), PP 73-78 Influence of chemical reaction, Soret and Dufour effects on heat and
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 10, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov - Dec. 2014), PP 73-78 Influence of chemical reaction, Soret and Dufour effects on heat and
Electric Flux. If we know the electric field on a Gaussian surface, we can find the net charge enclosed by the surface.
 Chapter 23 Gauss' Law Instead of considering the electric fields of charge elements in a given charge distribution, Gauss' law considers a hypothetical closed surface enclosing the charge distribution.
Chapter 23 Gauss' Law Instead of considering the electric fields of charge elements in a given charge distribution, Gauss' law considers a hypothetical closed surface enclosing the charge distribution.
Solution of Kirchhoff's Time-Domain Integral Equation in Acoustics
 Solution of Kirchhoff's Time-Domain Integral Equation in Acoustics Dr. George Benthien and Dr. Stephen Hobbs March 29, 2005 E-mail: george@gbenthien.net In this paper we will loo at the time-domain equivalent
Solution of Kirchhoff's Time-Domain Integral Equation in Acoustics Dr. George Benthien and Dr. Stephen Hobbs March 29, 2005 E-mail: george@gbenthien.net In this paper we will loo at the time-domain equivalent
free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]
![free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m] free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]](/thumbs/79/79624275.jpg) Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
Hydrodynamic Characterization of an Electrochemical Cell with Rotating Disc Electrode: A Three-Dimensional Biphasic Model
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL REACTOR ENGINEERING Volume 8 2010 Article A95 Hydrodynamic Characterization of an Electrochemical Cell with Rotating Disc Electrode: A Three-Dimensional Biphasic Model
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL REACTOR ENGINEERING Volume 8 2010 Article A95 Hydrodynamic Characterization of an Electrochemical Cell with Rotating Disc Electrode: A Three-Dimensional Biphasic Model
Quiz. Chapter 15. Electrical Field. Quiz. Electric Field. Electric Field, cont. 8/29/2011. q r. Electric Forces and Electric Fields
 Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields uiz Four point charges, each of the same magnitude, with varying signs as specified, are arranged at the corners of a square as shown. Which of the arrows
Chapter 15 Electric Forces and Electric Fields uiz Four point charges, each of the same magnitude, with varying signs as specified, are arranged at the corners of a square as shown. Which of the arrows
1. (3) Write Gauss Law in differential form. Explain the physical meaning.
 Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about
Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about
Liquid Sloshing in a Rotating, Laterally Oscillating Cylindrical Container
 Universal Journal of Mechanical Engineering 5(3): 97-101, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujme.2017.050304 http://www.hrpub.org Liquid Sloshing in a Rotating, Laterally Oscillating Cylindrical Container Yusuke Saito,
Universal Journal of Mechanical Engineering 5(3): 97-101, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujme.2017.050304 http://www.hrpub.org Liquid Sloshing in a Rotating, Laterally Oscillating Cylindrical Container Yusuke Saito,
Homework 4 PHYS 212 Dr. Amir
 Homework 4 PHYS Dr. Amir. (I) A uniform electric field of magnitude 5.8 passes through a circle of radius 3 cm. What is the electric flux through the circle when its face is (a) perpendicular to the field
Homework 4 PHYS Dr. Amir. (I) A uniform electric field of magnitude 5.8 passes through a circle of radius 3 cm. What is the electric flux through the circle when its face is (a) perpendicular to the field
Higher Orders Instability of a Hollow Jet Endowed with Surface Tension
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 2, No. (2008) 69 78 c Technical University of Lodz Higher Orders Instability of a Hollow Jet Endowed with Surface Tension Ahmed E. Radwan Mathematics Department,
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 2, No. (2008) 69 78 c Technical University of Lodz Higher Orders Instability of a Hollow Jet Endowed with Surface Tension Ahmed E. Radwan Mathematics Department,
PHYSICS. Chapter 24 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
Squirming Sphere in an Ideal Fluid
 Squirming Sphere in an Ideal Fluid D Rufat June 8, 9 Introduction The purpose of this wor is to derive abalytically and with an explicit formula the motion due to the variation of the surface of a squirming
Squirming Sphere in an Ideal Fluid D Rufat June 8, 9 Introduction The purpose of this wor is to derive abalytically and with an explicit formula the motion due to the variation of the surface of a squirming
Chapter 28. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 28. Gauss s Law Using Gauss s law, we can deduce electric fields, particularly those with a high degree of symmetry, simply from the shape of the charge distribution. The nearly spherical shape
Chapter 28. Gauss s Law Using Gauss s law, we can deduce electric fields, particularly those with a high degree of symmetry, simply from the shape of the charge distribution. The nearly spherical shape
 Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Number of pages in the question paper : 05 Number of questions in the question paper : 48 Modeling Transport Phenomena of Micro-particles Note: Follow the notations used in the lectures. Symbols have their
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background
 The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
The CMP Slurry Monitor - Background Abstract The CMP slurry monitor uses electroacoustic and ultrasonic attenuation measurements to determine the size and zeta potential of slurry particles. The article
CH 23. Gauss Law. A. Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface.
 CH 23 Gauss Law [SHIVOK SP212] January 4, 2016 I. Introduction to Gauss Law A. Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface.
CH 23 Gauss Law [SHIVOK SP212] January 4, 2016 I. Introduction to Gauss Law A. Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface.
The flow due to a rough rotating disk
 Z. angew. Math. Phys. 54 (2004) 1 12 0044-2275/04/050001-12 DOI 10.1007/s00033-003-2096-6 c 2004 Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP The flow due to a rough rotating
Z. angew. Math. Phys. 54 (2004) 1 12 0044-2275/04/050001-12 DOI 10.1007/s00033-003-2096-6 c 2004 Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP The flow due to a rough rotating
dt Now we will look at the E&M force on moving charges to explore the momentum conservation law in E&M.
 . Momentum Conservation.. Momentum in mechanics In classical mechanics p = m v and nd Newton s law d p F = dt If m is constant with time d v F = m = m a dt Now we will look at the &M force on moving charges
. Momentum Conservation.. Momentum in mechanics In classical mechanics p = m v and nd Newton s law d p F = dt If m is constant with time d v F = m = m a dt Now we will look at the &M force on moving charges
Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1
 Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1 Two Parallel Conducting Sheets Find the electric field to the left of the sheets, between the sheets and to the right of the sheets. 1/28/2018 2 Uniform
Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1 Two Parallel Conducting Sheets Find the electric field to the left of the sheets, between the sheets and to the right of the sheets. 1/28/2018 2 Uniform
Exact Solutions for the Incompressible Viscous Fluid of a Rotating Disk Flow
 Progress in Applied Mathematics Vol. 1, No. 1, 211, pp. 9-97 www.cscanada.org ISSN 1925-251X [Print] ISSN 1925-2528 [Online] www.cscanada.net Exact Solutions for the Incompressible Viscous Fluid of a Rotating
Progress in Applied Mathematics Vol. 1, No. 1, 211, pp. 9-97 www.cscanada.org ISSN 1925-251X [Print] ISSN 1925-2528 [Online] www.cscanada.net Exact Solutions for the Incompressible Viscous Fluid of a Rotating
Steady and unsteady diffusion
 Chapter 5 Steady and unsteady diffusion In this chapter, we solve the diffusion and forced convection equations, in which it is necessary to evaluate the temperature or concentration fields when the velocity
Chapter 5 Steady and unsteady diffusion In this chapter, we solve the diffusion and forced convection equations, in which it is necessary to evaluate the temperature or concentration fields when the velocity
Reading: Chapter 28. 4πε r. For r > a. Gauss s Law
 Reading: Chapter 8 Q 4πε r o k Q r e For r > a Gauss s Law 1 Chapter 8 Gauss s Law lectric Flux Definition: lectric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular
Reading: Chapter 8 Q 4πε r o k Q r e For r > a Gauss s Law 1 Chapter 8 Gauss s Law lectric Flux Definition: lectric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview
 Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electrophoretic Light Scattering Overview When an electric field is applied across an electrolytic solution, charged particles suspended in the electrolyte are attracted towards the electrode of opposite
Electric Field Lines. lecture 4.1.1
 Electric Field Lines Two protons, A and B, are in an electric field. Which proton has the larger acceleration? A. Proton A B. Proton B C. Both have the same acceleration. lecture 4.1.1 Electric Field Lines
Electric Field Lines Two protons, A and B, are in an electric field. Which proton has the larger acceleration? A. Proton A B. Proton B C. Both have the same acceleration. lecture 4.1.1 Electric Field Lines
NOTE. Application of Contour Dynamics to Systems with Cylindrical Boundaries
 JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS 145, 462 468 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CP986024 NOTE Application of Contour Dynamics to Systems with Cylindrical Boundaries 1. INTRODUCTION Contour dynamics (CD) is a widely used
JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL PHYSICS 145, 462 468 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CP986024 NOTE Application of Contour Dynamics to Systems with Cylindrical Boundaries 1. INTRODUCTION Contour dynamics (CD) is a widely used
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field
 Lecture 6-1 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field Electric Field and Forces Suppose a charged fixed q 1 in a space, an exploring charge q is moving toward the fixed
Lecture 6-1 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field Electric Field and Forces Suppose a charged fixed q 1 in a space, an exploring charge q is moving toward the fixed
Chapter (2) Gauss s Law
 Chapter (2) Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface! What is meant by electric flux and how you can calculate it. How
Chapter (2) Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface! What is meant by electric flux and how you can calculate it. How
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 27 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux
 Lecture 3 Chapter 23 Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter
Lecture 3 Chapter 23 Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter
Questions Chapter 23 Gauss' Law
 Questions Chapter 23 Gauss' Law 23-1 What is Physics? 23-2 Flux 23-3 Flux of an Electric Field 23-4 Gauss' Law 23-5 Gauss' Law and Coulomb's Law 23-6 A Charged Isolated Conductor 23-7 Applying Gauss' Law:
Questions Chapter 23 Gauss' Law 23-1 What is Physics? 23-2 Flux 23-3 Flux of an Electric Field 23-4 Gauss' Law 23-5 Gauss' Law and Coulomb's Law 23-6 A Charged Isolated Conductor 23-7 Applying Gauss' Law:
Chapter 21 Chapter 23 Gauss Law. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 21 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 What is Physics? Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers
Chapter 21 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 What is Physics? Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers
Characteristics of Positive Ions in the Sheath Region of Magnetized Collisional Electronegative Discharges
 Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.6, No.6, Jun. 204 Characteristics of Positive Ions in the Sheath Region of Magnetized Collisional Electronegative Discharges M. M. HATAMI, A. R. NIKNAM 2 Physics Department
Plasma Science and Technology, Vol.6, No.6, Jun. 204 Characteristics of Positive Ions in the Sheath Region of Magnetized Collisional Electronegative Discharges M. M. HATAMI, A. R. NIKNAM 2 Physics Department
Chapter 1 The Electric Force
 Chapter 1 The Electric Force 1. Properties of the Electric Charges 1- There are two kinds of the electric charges in the nature, which are positive and negative charges. - The charges of opposite sign
Chapter 1 The Electric Force 1. Properties of the Electric Charges 1- There are two kinds of the electric charges in the nature, which are positive and negative charges. - The charges of opposite sign
Gauss s Law. Chapter 22. Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition. Applications of Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Uniform Charged Sphere Infinite Line of Charge Infinite Sheet of Charge Two infinite sheets of charge Phys 2435:
Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Uniform Charged Sphere Infinite Line of Charge Infinite Sheet of Charge Two infinite sheets of charge Phys 2435:
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law
 Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Attention: the list of unregistered iclickers will be posted on our Web page after this lecture. From the concept of electric field flux to the calculation of
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Attention: the list of unregistered iclickers will be posted on our Web page after this lecture. From the concept of electric field flux to the calculation of
Electric Flux. To investigate this, we have to understand electric flux.
 Problem 21.72 A charge q 1 = +5. nc is placed at the origin of an xy-coordinate system, and a charge q 2 = -2. nc is placed on the positive x-axis at x = 4. cm. (a) If a third charge q 3 = +6. nc is now
Problem 21.72 A charge q 1 = +5. nc is placed at the origin of an xy-coordinate system, and a charge q 2 = -2. nc is placed on the positive x-axis at x = 4. cm. (a) If a third charge q 3 = +6. nc is now
l=0 The expansion coefficients can be determined, for example, by finding the potential on the z-axis and expanding that result in z.
 Electrodynamics I Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 15/11/6 Name Electrodynamic Score = 14 / 14 points Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try
Electrodynamics I Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 15/11/6 Name Electrodynamic Score = 14 / 14 points Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try
Lecture 2. Lecture 1. Forces on a rotating planet. We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their:
 Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
4.2 Concepts of the Boundary Layer Theory
 Advanced Heat by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell 4.2 Concepts of the Boundary Layer Theory It is difficult to solve the complete viscous flow fluid around a body unless the geometry is very
Advanced Heat by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell 4.2 Concepts of the Boundary Layer Theory It is difficult to solve the complete viscous flow fluid around a body unless the geometry is very
Electrodynamics Exam Solutions
 Electrodynamics Exam Solutions Name: FS 215 Prof. C. Anastasiou Student number: Exercise 1 2 3 4 Total Max. points 15 15 15 15 6 Points Visum 1 Visum 2 The exam lasts 18 minutes. Start every new exercise
Electrodynamics Exam Solutions Name: FS 215 Prof. C. Anastasiou Student number: Exercise 1 2 3 4 Total Max. points 15 15 15 15 6 Points Visum 1 Visum 2 The exam lasts 18 minutes. Start every new exercise
Chapter 23. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 23 Gauss s Law 23.1 What is Physics?: Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers a hypothetical
Chapter 23 Gauss s Law 23.1 What is Physics?: Gauss law relates the electric fields at points on a (closed) Gaussian surface to the net charge enclosed by that surface. Gauss law considers a hypothetical
E&M. 1 Capacitors. January 2009
 E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law
 Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer
 1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
1114 Langmuir 23, 19, 1114-112 On the Chemical Free Energy of the Electrical Double Layer Marian Manciu and Eli Ruckenstein* Department of Chemical Engineering, State University of New York at Buffalo,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I)
 Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Basics of Electromagnetics Maxwell s Equations (Part - I) Soln. 1. C A. dl = C. d S [GATE 1994: 1 Mark] A. dl = A. da using Stoke s Theorem = S A. ds 2. The electric field strength at distant point, P,
Distribution of induced charge
 E&M Lecture 10 Topics: (1)Distribution of induced charge on conducting plate (2)Total surface induced charge on plate (3)Point charge near grounded conducting sphere (4)Point charge near floating conducting
E&M Lecture 10 Topics: (1)Distribution of induced charge on conducting plate (2)Total surface induced charge on plate (3)Point charge near grounded conducting sphere (4)Point charge near floating conducting
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents), Ampere s Law is introduced
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law. Last Lecture: Electric Field Lines
 Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Last Lecture: Electric Field Lines 1 iclicker Charged particles are fixed on grids having the same spacing. Each charge has the same magnitude Q with signs given
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Last Lecture: Electric Field Lines 1 iclicker Charged particles are fixed on grids having the same spacing. Each charge has the same magnitude Q with signs given
Lecture 9 Electric Flux and Its Density Gauss Law in Integral Form
 Lecture 9 Electric Flux and Its Density Gauss Law in Integral Form ections: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 Homework: ee homework file Faraday s Experiment (1837), Electric Flux ΨΨ charge transfer from inner to outer sphere
Lecture 9 Electric Flux and Its Density Gauss Law in Integral Form ections: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 Homework: ee homework file Faraday s Experiment (1837), Electric Flux ΨΨ charge transfer from inner to outer sphere
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field In this chapter we investigate the sources of magnetic of magnetic field, in particular, the magnetic field produced by moving charges (i.e., currents). Ampere s Law
Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow
 OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
OCEN 678-600 Fluid Dynamics for Ocean and Environmental Engineering Homework #2 Viscous Flow Date distributed : 9.18.2005 Date due : 9.29.2005 at 5:00 pm Return your solution either in class or in my mail
Gauss s Law. Lecture 4. Chapter 27. Channel 61 (clicker) Physics II
 Lecture 4 Chapter 27 Physics II 01.30.2015 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov201415/physics2spring.html
Lecture 4 Chapter 27 Physics II 01.30.2015 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov201415/physics2spring.html
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law
 Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 22 To use the electric field at a surface to determine the charge within the surface To learn the meaning of electric flux and how to calculate
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 22 To use the electric field at a surface to determine the charge within the surface To learn the meaning of electric flux and how to calculate
Physics 351 Monday, April 27, 2015
 Physics 351 Monday, April 27, 2015 Final exam is Wednesday, May 6, from 9am-11am, in DRL A4. You can bring a sheet of your own handwritten notes. Final exam includes Ch7 (Lagrangians), Ch9 (non-inertial
Physics 351 Monday, April 27, 2015 Final exam is Wednesday, May 6, from 9am-11am, in DRL A4. You can bring a sheet of your own handwritten notes. Final exam includes Ch7 (Lagrangians), Ch9 (non-inertial
INDUCE NANOSTRUCTURES WITH ELECTRIC FIELDS
 INDUCE NANOSTRUCTURES WITH ELECTRIC FIELDS David Pei With special thanks to my advisor: Wei Lu Abstract This semester, I induced different nanoparticles with electric fields to observe their behavior under
INDUCE NANOSTRUCTURES WITH ELECTRIC FIELDS David Pei With special thanks to my advisor: Wei Lu Abstract This semester, I induced different nanoparticles with electric fields to observe their behavior under
Spherical Waves, Radiator Groups
 Waves, Radiator Groups ELEC-E5610 Acoustics and the Physics of Sound, Lecture 10 Archontis Politis Department of Signal Processing and Acoustics Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering November
Waves, Radiator Groups ELEC-E5610 Acoustics and the Physics of Sound, Lecture 10 Archontis Politis Department of Signal Processing and Acoustics Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering November
Measurement Techniques for Engineers. Motion and Vibration Measurement
 Measurement Techniques for Engineers Motion and Vibration Measurement Introduction Quantities that may need to be measured are velocity, acceleration and vibration amplitude Quantities useful in predicting
Measurement Techniques for Engineers Motion and Vibration Measurement Introduction Quantities that may need to be measured are velocity, acceleration and vibration amplitude Quantities useful in predicting
Physics 202, Lecture 3. The Electric Field
 Physics 202, Lecture 3 Today s Topics Electric Field (Review) Motion of charged particles in external E field Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium (Ch. 21.9) Gauss s Law (Ch. 22) Reminder: HW #1 due
Physics 202, Lecture 3 Today s Topics Electric Field (Review) Motion of charged particles in external E field Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium (Ch. 21.9) Gauss s Law (Ch. 22) Reminder: HW #1 due
Measurement of electric potential fields
 Measurement of electric potential fields Matthew Krupcale, Oliver Ernst Department of Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland Ohio, 44106-7079 18 November 2012 Abstract In electrostatics, Laplace
Measurement of electric potential fields Matthew Krupcale, Oliver Ernst Department of Physics, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland Ohio, 44106-7079 18 November 2012 Abstract In electrostatics, Laplace
Week 8. Topics: Next deadline: Viscous fluid flow (Study guide 14. Sections 12.4 and 12.5.) Bolus flow (Study guide 15. Section 12.6.
 8/1 Topics: Week 8 Viscous fluid flow (Study guide 14. Sections 12.4 and 12.5.) Bolus flow (Study guide 15. Section 12.6.) Pulsatile flow (Study guide 15. Section 12.7.) Next deadline: Friday October 31
8/1 Topics: Week 8 Viscous fluid flow (Study guide 14. Sections 12.4 and 12.5.) Bolus flow (Study guide 15. Section 12.6.) Pulsatile flow (Study guide 15. Section 12.7.) Next deadline: Friday October 31
Physics 11b Lecture #3. Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physics 11b Lecture #3 lectric Flux Gauss s Law What We Did Last Time Introduced electric field by Field lines and the rules From a positive charge to a negative charge No splitting, merging, or crossing
Physics 11b Lecture #3 lectric Flux Gauss s Law What We Did Last Time Introduced electric field by Field lines and the rules From a positive charge to a negative charge No splitting, merging, or crossing
Tides in Higher-Dimensional Newtonian Gravity
 Tides in Higher-Dimensional Newtonian Gravity Philippe Landry Department of Physics University of Guelph 23 rd Midwest Relativity Meeting October 25, 2013 Tides: A Familiar Example Gravitational interactions
Tides in Higher-Dimensional Newtonian Gravity Philippe Landry Department of Physics University of Guelph 23 rd Midwest Relativity Meeting October 25, 2013 Tides: A Familiar Example Gravitational interactions
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 10 Fluids
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 10 Fluids Fluids A fluid may be either a liquid or a gas Some characteristics of a fluid Flows from one place to another Shape varies according
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 10 Fluids Fluids A fluid may be either a liquid or a gas Some characteristics of a fluid Flows from one place to another Shape varies according
Unsteady Couette Flow through a Porous Medium in a Rotating System
 International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 974-3189 Volume 2, Number 3 (21), pp. 381-39 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Unsteady Couette Flow
International Journal of Computational Science and Mathematics. ISSN 974-3189 Volume 2, Number 3 (21), pp. 381-39 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Unsteady Couette Flow
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
 Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Dielectrics - III. Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 Dielectrics - III Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We continue with our discussion of dielectric medium. Example : Dielectric Sphere in a uniform
Dielectrics - III Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We continue with our discussion of dielectric medium. Example : Dielectric Sphere in a uniform
THERMAL HYDRAULIC MODELING OF THE LS-VHTR
 2013 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2013 Recife, PE, Brazil, November 24-29, 2013 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-05-2 THERMAL HYDRAULIC MODELING OF
2013 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2013 Recife, PE, Brazil, November 24-29, 2013 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-05-2 THERMAL HYDRAULIC MODELING OF
Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas )
 Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas ) Yasutomo ISHII and Andrei SMOLYAKOV 1) Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki 311-0102, Japan 1) University
Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas ) Yasutomo ISHII and Andrei SMOLYAKOV 1) Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki 311-0102, Japan 1) University
Vacuum Polarization in the Presence of Magnetic Flux at Finite Temperature in the Cosmic String Background
 Vacuum Polarization in the Presence of Magnetic Flux at Finite Temperature in the Cosmic String Background Univ. Estadual da Paraíba (UEPB), Brazil E-mail: jeanspinelly@ig.com.br E. R. Bezerra de Mello
Vacuum Polarization in the Presence of Magnetic Flux at Finite Temperature in the Cosmic String Background Univ. Estadual da Paraíba (UEPB), Brazil E-mail: jeanspinelly@ig.com.br E. R. Bezerra de Mello
Chapter 24. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Electrodynamics Qualifier Examination
 Electrodynamics Qualifier Examination August 15, 2007 General Instructions: In all cases, be sure to state your system of units. Show all your work, write only on one side of the designated paper, and
Electrodynamics Qualifier Examination August 15, 2007 General Instructions: In all cases, be sure to state your system of units. Show all your work, write only on one side of the designated paper, and
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CHAPTER 19 Molecules in Motion. 1. Matter transport is driven by concentration gradient.
 CHAPTER 19 Molecules in Motion I. Transport in Gases. A. Fick s Law of Diffusion. 1. Matter transport is driven by concentration gradient. Flux (matter) = J m = D dn dz N = number density of particles
CHAPTER 19 Molecules in Motion I. Transport in Gases. A. Fick s Law of Diffusion. 1. Matter transport is driven by concentration gradient. Flux (matter) = J m = D dn dz N = number density of particles
3 Chapter. Gauss s Law
 3 Chapter Gauss s Law 3.1 Electric Flux... 3-2 3.2 Gauss s Law (see also Gauss s Law Simulation in Section 3.10)... 3-4 Example 3.1: Infinitely Long Rod of Uniform Charge Density... 3-9 Example 3.2: Infinite
3 Chapter Gauss s Law 3.1 Electric Flux... 3-2 3.2 Gauss s Law (see also Gauss s Law Simulation in Section 3.10)... 3-4 Example 3.1: Infinitely Long Rod of Uniform Charge Density... 3-9 Example 3.2: Infinite
Electromagnetic Induction (Chapters 31-32)
 Electromagnetic Induction (Chapters 31-3) The laws of emf induction: Faraday s and Lenz s laws Inductance Mutual inductance M Self inductance L. Inductors Magnetic field energy Simple inductive circuits
Electromagnetic Induction (Chapters 31-3) The laws of emf induction: Faraday s and Lenz s laws Inductance Mutual inductance M Self inductance L. Inductors Magnetic field energy Simple inductive circuits
Confinement of toroidal non-neutral plasma in Proto-RT
 Workshop on Physics with Ultra Slow Antiproton Beams, RIKEN, March 15, 2005 Confinement of toroidal non-neutral plasma in Proto-RT H. Saitoh, Z. Yoshida, and S. Watanabe Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
Workshop on Physics with Ultra Slow Antiproton Beams, RIKEN, March 15, 2005 Confinement of toroidal non-neutral plasma in Proto-RT H. Saitoh, Z. Yoshida, and S. Watanabe Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,
Chapter 22: Gauss s Law
 Chapter 22: Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface. What is meant by electric flux, and how to calculate it. How Gauss
Chapter 22: Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface. What is meant by electric flux, and how to calculate it. How Gauss
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
V. Electrostatics Lecture 24: Diffuse Charge in Electrolytes MIT Student 1. Poisson-Nernst-Planck Equations The Nernst-Planck Equation is a conservation of mass equation that describes the influence of
Chapter 24. QUIZ 6 January 26, Example: Three Point Charges. Example: Electrostatic Potential Energy 1/30/12 1
 QUIZ 6 January 26, 2012 An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by 3.2
QUIZ 6 January 26, 2012 An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by 3.2
How Electronics Started! And JLab Hits the Wall!
 How Electronics Started! And JLab Hits the Wall! In electronics, a vacuum diode or tube is a device used to amplify, switch, otherwise modify, or create an electrical signal by controlling the movement
How Electronics Started! And JLab Hits the Wall! In electronics, a vacuum diode or tube is a device used to amplify, switch, otherwise modify, or create an electrical signal by controlling the movement
Ampere s Law. Outline. Objectives. BEE-Lecture Notes Anurag Srivastava 1
 Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
Outline Introduce as an analogy to Gauss Law. Define. Applications of. Objectives Recognise to be analogous to Gauss Law. Recognise similar concepts: (1) draw an imaginary shape enclosing the current carrying
