Avoiding collisions Cryptographic hash functions. Table of contents
|
|
|
- Ami Avice Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Avoiding collisions Cryptographic hash functions Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction Collision resistance Birthday attacks Merkle-Damgärd Transform Hash-and-MAC
2 Hash functions Hash functions take arbitrary-length strings and compress them into shorter strings. The functions you studied in CS230 are examples where hashes are used to achieve O(1) lookup time in set implementations. Collisions are not good for data-retrieval complexity. They are disastrous in cryptographic applications. Defining collisions A collision in a function H is a pair of distinct inputs x and x 0 such that H(x) =H(x 0 ); we say that x and x 0 collide under H. A function H is collision resistant if it is infeasible for any probabilistic polynomial-time algorithm to find a collision in H. Typically, H is a compression function with infinite domain and finite range, so collisions must exist. Our goal is to make them hard to find.
3 Keyed hash functions Formally, we deal with a family of hash functions indexed by a key. More precisely, H will be a two-input function that takes as inputs a key s and a string x, and outputs a string H s (x) def = H(s, x). It must be hard to find a collision in H s for a randomly-generated s. Formal definition of a hash function Definition 5.1. A hash function is a pair of probabilistic polynomial-time algorithms (Gen, H) satisfying the following: Gen is a probabilistic algorithm which takes as input a security parameter 1 n and outputs a key s. Weassumethat1 n is implicit in s. There exists a polynomial ` such that H takes as input a key s and a string x 2 {0, 1} and outputs a string H s (x) 2 {0, 1}`(n). If H s is defined only for inputs x 2 {0, 1}`0(n) and `0(n) > `(n), then we say that (Gen, H) is a fixed-length hash function for inputs of length `0(n).
4 Collision-finding experiments and collision resistance The collision-finding experiment Hash-coll A, (n): 1. Akeys is generated by running Gen(1 n ). 2. The adversary A is given s and outputs x, x 0.(If is a fixed length hash function for inputs of length `0(n) thenwerequire x, x 0 2 {0, 1}`0(n).) 3. The output of the experiment is defined to be 1 if and only if x 6= x 0 and H s (x) =H s (x 0 ). In such a case we say that A has found a collision. Definition 5.2. A hash function =(Gen, H) is collision resistant if for all probabilistic polynomial-time adversaries A there exists a negligible function negl such that Pr[Hash-coll A, (n) = 1] apple negl(n). A generic birthday attack There is a generic attack that finds collisions in any hash function. This attack implies a minimal output length needed for a hash function to be secure. Model the keyed hash function by a truly random function, H : {0, 1}! {0, 1}`. Choose q arbitrary inputs x 1,...,x q 2 {0, 1} 2`, compute y i := H(x i )and check whether any two y i are equal.
5 Analysis of the birthday problem We did half of the analysis a couple of lectures ago: Lemma A.15. Let y 1,...,y q be q elements chosen uniformly at random from a set of of size N. The probability that there exists distinct i, j with y i = y j is at most q2 2N. This time we prove: Lemma A.16. Fix a positive integer N, andsayq apple p 2N elements y 1,...,y q are chosen uniformly and independently at random from a set of size N. Then the probability that there exists distinct i, j with y i = y j is at least q(q 1) 4N. Remark. These lemmas imply that the birthday attack finds a collision with high probability using q = (2`/2 ) hash-function evaluations. (Sorting the outputs and scanning for collisions requires an additional O(` 2`/2 )time). Proof of Lemma A.16 Lemma A.10. Fix a positive integer N, andsayq apple p 2N elements y 1,...,y q are chosen uniformly and independently at random from a set of size N. Then the probability that there exists distinct i, j with y i = y j is at least q(q 1) 4N. Proof. Let Coll denote the event of a collision and let NoColl i be the event that there is no collision among y 1,...,y i.then NoColl q = Coll is the event that there is no collision at all.
6 Calculating Pr[NoColl q ] If NoColl q occurs then NoColl i must also have occurred for all i apple q. Thus, Pr[NoColl q ] = Pr[NoColl 1 ] Pr[NoColl 2 NoColl 1 ] Pr[NoColl q NoColl q 1 ]. Certainly Pr[NoColl 1 ] = 1, and if {y 1,...,y i } are distinct, the probability that y i+1 does not collide with any of these values is. In other words, 1 i N so Pr[NoColl i+1 NoColl i ]=1 Pr[NoColl q ]= q 1 Y i=1 1 i. N i N, Math 115 returns with a vengeance From the first two terms of the Taylor series expansion of e x, 1 i N apple e i/n,so We conclude that Pr[NoColl q ] = apple q 1 Y 1 i=1 qy 1 e i/n i=1 i N = e P q 1 i=1 (i/n) = e q(q 1)/2N. Pr[Coll] = 1 Pr[NoColl q ] 1 e q(q 1)/2N q(q 1) 4N. *The last line uses the fact that for all 0 apple x apple 1, e x apple 1 x/2.
7 Birthday attacks matter A hash function designed with output length 128 bits seems secure since running steps to find a collision seems infeasible. However, the generic birthday attack requires only 2 64 steps, large but not impossible. Furthermore, evil doers may use collisions to their advantage. Constructing collision-resistant hashes: Merkle-Damgärd transform The Merkle-Damgärd transform is widely used to convert fixed-length hash functions to full-fledged hashes. Assume we are given a fixed-length collision-resistant hash function, (Gen, h), that compresses its input length by half; i.e., `0(n) =2`(n). We construct a collision-resistant hash (Gen, H) that maps any length inputs to outputs of length `(n).
8 The construction Construction 5.3. Let (Gen, h) be a fixed-length collision-resistent hash function for inputs of length 2`(n) and with output length `(n). Construct a variable-length hash function (Gen, H) as follows: Gen: Remains unchanged. H: Oninputakeys and a string x 2 {0, 1} of length L < 2`(n), do the following: 1. Set B := d L` e. Padx with zeros so its length is a multiple of `. Parse the padded result as the sequence of `-bit blocks x 1,...,x B.Setx B+1 := L, wherel is encoded using exactly ` bits. 2. Set z 0 := 0`. 3. For i =1,...,B + 1, compute z i := h s (z i 1 kx i ). 4. Output z B+1. Collision-resistance results Theorem 5.4. If (Gen, h) is a fixed-length collision-resistant hash function, then (Gen, H) is a collision-resistent hash function. Proof. We show that for any s, a collision in H s yields a collision in h s. Let x and x 0 be two di erent strings of respective lengths L and L 0 such that H s (x) =H s (x 0 ). Let x 1,...,x B be the B blocks of the padded x, andletx 0 1,...,x 0 B 0 be the B 0 blocks of the padded x 0. Recall that x B+1 = L and x 0 B 0 +1 = L0.
9 The first of two cases Case 1: L 6= L 0. The last step of the computation of H s (x) is z B+1 := h s (Z B kl) and the last step of the computation of H s (x 0 ) is z 0 B 0 +1 := hs (z 0 B 0 kl 0 ). Since H s (x) =H s (x 0 ) it follows that h s (z B kl) =h s (z 0 B 0 kl 0 ). Collision city: z B kl 6= z 0 B 0 kl 0,whileL 6= L 0. The second of two cases Case 2: L = L 0.ThenB = B 0 and x B+1 = x 0 B+1.Letz i, z 0 i be intermediate values of x, x 0 during the computation of H s (x), H s (x 0 ) respectively. There must be at least one index i such that x i 6= xi 0.Leti be the highest index for which z i 1kx i 6= zi 0 1 kx i 0.Ifi = B +1then z B kx B+1 and zb 0 kx B+1 0 are di erent strings that collide for hs,because h s (z B kx B+1 )=z B+1 = H s (x) =H s (x 0 )=z 0 B+1 = h s (z 0 Bkx 0 B+1). If i apple B, then the maximality of i implies z i = z 0 i. Once again, z i 1kx i 6= z 0 i 1 kx 0 i are two strings that collide for hs.
10 Collision-resistant hash functions in practice SHA-1, a common iterated hash, inputs a string of any length up to , and produces an output of length 160 bits.* SHA-1 starts with a compression function that compresses fixed-length inputs by a small amount. A Merkle-Damgärd transform is applied to obtain a collision-resistant hash function. Think of pigeons (the bit strings) roosting in pigeon holes. Things have got to be crowded. However, nobody has found a hole with two or more pigeons. *MD4, MD5,and SHA are ancestors (not be trusted); SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512 descendants. Big MACs We built our MACs from pseudorandom functions. Here we will see another approach that relies on collision-resistant hashing along with message authentication code. A another common* approach is based on collision-resistant hash functions constructed using the Merkel-Damgärd transformation. We will save that for next time. *Not to mention more e cient.
11 Hash-and-MAC The idea is simple: A long message m is hashed down to a fixed-length string H s (m) using a collision-resistant has function, then a fixed-length MAC is applied. Construction 5.5 Let = (Mac, Vrfy) be a MAC for message of length `(n), and let H =(Gen H, H) be a hash function with output of length `(n). Construct a Mac 0 =(Gen 0, Mac 0, Vrfy 0 ) for arbitrary-length messages as follows Gen : On input 1 n, choose uniform k 2 {0, 1} and run Gen H (1 n )to obtain a key s. Thekeyisk 0 := hk, si. Mac : On input hk, si and message m 2 {0, 1}, output the tag t Mac k (H s (m)). Vrfy : On input a key hk, si, a message m 2 {0, 1}, and a MAC tag t, output 1 if and only if Vrfy k (H s (m), t)? =1. If is secure, then so is 0 Theorem 5.6. If is a secure MAC for message of length ` and H is collision resistant, then Contruction 5.5 is a secure MAC for arbitrary length messages. Proof. let 0 denote Construction 5.5, and let A 0 be a PPT adversary attacking 0. In Mac-forge A 0, 0,letk0 = hk, si denote the MAC key, Q denote the set of messages whose tags were requested by A 0,and(m, t) be the final output of A 0. Assume WLOG that m /2 Q and define coll to be the event that there is an m 2 Q for which H s (m )=H s (m). We have Pr[Mac-forge A 0, 0(n) = 1] = Pr[Mac-forge A0, 0(n) =1^ coll] + Pr[Mac-forge A 0, 0(n) =1^coll] apple Pr[coll] + Pr[Mac-forge A0, 0(n) =1^ coll]. We show both terms above are negligible.
12 Algorithm for finding a collision in H Algorithm C The algorithm is given s as an input. Choose uniform k 2 {0, 1} n. Run A 0 (1 n ). When A 0 requests a tag on m i 2 {0, 1},return t i Mac k (H s (m i )). When A 0 outputs (m, t), then if there exists an i for which H s (m )=H s (m i ), output (m, m i ). When the input s to C is generated by running Gen H (1 n ), then the view of A 0 is distributed identically to its view in Mac-forge A 0,,(n). Since C outputs a collision exactly when coll occurs, we have Pr[Hash-coll C, H (n) = 1] = Pr[coll]. Since H is collision resistant, we conclude that Pr[coll] is negligible. We show Pr[Mac-forge A0, 0(n) =1^coll] is negligible Algorithm A Compute Gen H (1 n ) to obtain s. Run A 0 (1 n ). When A 0 requests a tag on m i 2 {0, 1}, then (1) compute ˆm i := H s (m i ); (2) obtain a tag t i on ˆm i from the MAC oracle; and (3) give t i to A 0. When A 0 outputs (m, t), then output (H s (m ), t). In the experiment Mac-forge A, (n), the view of A 0 when run as a subroutine by A is distributed identically to its view in experiment Mac-forge A0,,(n). Whenever both Mac-forge A0,,(n) = 1 and coll do not occur, A outputs a valid forgery. Therefore, Pr[Mac-forge A, (n) = 1] = Pr[Mac-forge A0, 0(n) =1^coll], ] and security of implies that the former probability is negligible.
Constructing secure MACs Message authentication in action. Table of contents
 Constructing secure MACs Message authentication in action Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time Recall the definition of message
Constructing secure MACs Message authentication in action Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time Recall the definition of message
Hash Functions. Ali El Kaafarani. Mathematical Institute Oxford University. 1 of 34
 Hash Functions Ali El Kaafarani Mathematical Institute Oxford University 1 of 34 Outline 1 Definition and Notions of Security 2 The Merkle-damgård Transform 3 MAC using Hash Functions 4 Cryptanalysis:
Hash Functions Ali El Kaafarani Mathematical Institute Oxford University 1 of 34 Outline 1 Definition and Notions of Security 2 The Merkle-damgård Transform 3 MAC using Hash Functions 4 Cryptanalysis:
Avoiding collisions Cryptographic hash functions. Table of contents
 Avoiding collisions Cryptographic hash functions Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction Davies-Meyer Hashes in Practice Hash
Avoiding collisions Cryptographic hash functions Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction Davies-Meyer Hashes in Practice Hash
Notes for Lecture 9. 1 Combining Encryption and Authentication
 U.C. Berkeley CS276: Cryptography Handout N9 Luca Trevisan February 17, 2009 Notes for Lecture 9 Notes scribed by Joel Weinberger, posted March 1, 2009 Summary Last time, we showed that combining a CPA-secure
U.C. Berkeley CS276: Cryptography Handout N9 Luca Trevisan February 17, 2009 Notes for Lecture 9 Notes scribed by Joel Weinberger, posted March 1, 2009 Summary Last time, we showed that combining a CPA-secure
Block Ciphers/Pseudorandom Permutations
 Block Ciphers/Pseudorandom Permutations Definition: Pseudorandom Permutation is exactly the same as a Pseudorandom Function, except for every key k, F k must be a permutation and it must be indistinguishable
Block Ciphers/Pseudorandom Permutations Definition: Pseudorandom Permutation is exactly the same as a Pseudorandom Function, except for every key k, F k must be a permutation and it must be indistinguishable
Lecture 14: Cryptographic Hash Functions
 CSE 599b: Cryptography (Winter 2006) Lecture 14: Cryptographic Hash Functions 17 February 2006 Lecturer: Paul Beame Scribe: Paul Beame 1 Hash Function Properties A hash function family H = {H K } K K is
CSE 599b: Cryptography (Winter 2006) Lecture 14: Cryptographic Hash Functions 17 February 2006 Lecturer: Paul Beame Scribe: Paul Beame 1 Hash Function Properties A hash function family H = {H K } K K is
1 Cryptographic hash functions
 CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 24 October 2012 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 24 October 2012 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
CSA E0 235: Cryptography (19 Mar 2015) CBC-MAC
 CSA E0 235: Cryptography (19 Mar 2015) Instructor: Arpita Patra CBC-MAC Submitted by: Bharath Kumar, KS Tanwar 1 Overview In this lecture, we will explore Cipher Block Chaining - Message Authentication
CSA E0 235: Cryptography (19 Mar 2015) Instructor: Arpita Patra CBC-MAC Submitted by: Bharath Kumar, KS Tanwar 1 Overview In this lecture, we will explore Cipher Block Chaining - Message Authentication
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes. Table of contents
 John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
John Hancock enters the 21th century Digital signature schemes Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents From last time: Good news and bad There
Introduction to Cryptography
 B504 / I538: Introduction to Cryptography Spring 2017 Lecture 12 Recall: MAC existential forgery game 1 n Challenger (C) k Gen(1 n ) Forger (A) 1 n m 1 m 1 M {m} t 1 MAC k (m 1 ) t 1 m 2 m 2 M {m} t 2
B504 / I538: Introduction to Cryptography Spring 2017 Lecture 12 Recall: MAC existential forgery game 1 n Challenger (C) k Gen(1 n ) Forger (A) 1 n m 1 m 1 M {m} t 1 MAC k (m 1 ) t 1 m 2 m 2 M {m} t 2
Lecture 11: Hash Functions, Merkle-Damgaard, Random Oracle
 CS 7880 Graduate Cryptography October 20, 2015 Lecture 11: Hash Functions, Merkle-Damgaard, Random Oracle Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Tanay Mehta 1 Topics Covered Review Collision-Resistant Hash Functions
CS 7880 Graduate Cryptography October 20, 2015 Lecture 11: Hash Functions, Merkle-Damgaard, Random Oracle Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Tanay Mehta 1 Topics Covered Review Collision-Resistant Hash Functions
1 Cryptographic hash functions
 CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 23 February 2011 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
CSCI 5440: Cryptography Lecture 6 The Chinese University of Hong Kong 23 February 2011 1 Cryptographic hash functions Last time we saw a construction of message authentication codes (MACs) for fixed-length
El Gamal A DDH based encryption scheme. Table of contents
 El Gamal A DDH based encryption scheme Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction El Gamal Practical Issues The El Gamal encryption
El Gamal A DDH based encryption scheme Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Fall 2016 Table of contents Introduction El Gamal Practical Issues The El Gamal encryption
ENEE 459-C Computer Security. Message authentication (continue from previous lecture)
 ENEE 459-C Computer Security Message authentication (continue from previous lecture) Last lecture Hash function Cryptographic hash function Message authentication with hash function (attack?) with cryptographic
ENEE 459-C Computer Security Message authentication (continue from previous lecture) Last lecture Hash function Cryptographic hash function Message authentication with hash function (attack?) with cryptographic
Cryptographic Hashes. Yan Huang. Credits: David Evans, CS588
 Cryptographic Hashes Yan Huang Credits: David Evans, CS588 Recap: CPA 1. k KeyGen(1 n ). b {0,1}. Give Enc(k, ) to A. 2. A chooses as many plaintexts as he wants, and receives the corresponding ciphertexts
Cryptographic Hashes Yan Huang Credits: David Evans, CS588 Recap: CPA 1. k KeyGen(1 n ). b {0,1}. Give Enc(k, ) to A. 2. A chooses as many plaintexts as he wants, and receives the corresponding ciphertexts
Lecture 1. Crypto Background
 Lecture 1 Crypto Background This lecture Crypto background hash functions random oracle model digital signatures and applications Cryptographic Hash Functions Hash function takes a string of arbitrary
Lecture 1 Crypto Background This lecture Crypto background hash functions random oracle model digital signatures and applications Cryptographic Hash Functions Hash function takes a string of arbitrary
12 Hash Functions Defining Security
 12 Hash Functions A hash function is any function that takes arbitrary-length input and has fixed-length output, so H : {0, 1} {0, 1} n. Think of H (m) as a fingerprint of m. Calling H (m) a fingerprint
12 Hash Functions A hash function is any function that takes arbitrary-length input and has fixed-length output, so H : {0, 1} {0, 1} n. Think of H (m) as a fingerprint of m. Calling H (m) a fingerprint
Lecture 6. Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography. Constructing CPA-secure ciphers
 1 Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 6 Portland State University Jan. 25, 2018 Lecturer: Fang Song Draft note. Version: February 4, 2018. Email fang.song@pdx.edu for comments and
1 Winter 2018 CS 485/585 Introduction to Cryptography Lecture 6 Portland State University Jan. 25, 2018 Lecturer: Fang Song Draft note. Version: February 4, 2018. Email fang.song@pdx.edu for comments and
New Attacks on the Concatenation and XOR Hash Combiners
 New Attacks on the Concatenation and XOR Hash Combiners Itai Dinur Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University, Israel Abstract. We study the security of the concatenation combiner H 1(M) H 2(M)
New Attacks on the Concatenation and XOR Hash Combiners Itai Dinur Department of Computer Science, Ben-Gurion University, Israel Abstract. We study the security of the concatenation combiner H 1(M) H 2(M)
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 14 October 16, 2013 CPSC 467, Lecture 14 1/45 Message Digest / Cryptographic Hash Functions Hash Function Constructions Extending
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 14 October 16, 2013 CPSC 467, Lecture 14 1/45 Message Digest / Cryptographic Hash Functions Hash Function Constructions Extending
Lecture 7: CPA Security, MACs, OWFs
 CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography September 27, 2017 Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Lecture 7: CPA Security, MACs, OWFs Scribe: Eysa Lee 1 Topic Covered Chosen Plaintext Attack (CPA) MACs One Way Functions (OWFs)
CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography September 27, 2017 Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Lecture 7: CPA Security, MACs, OWFs Scribe: Eysa Lee 1 Topic Covered Chosen Plaintext Attack (CPA) MACs One Way Functions (OWFs)
Attacks on hash functions. Birthday attacks and Multicollisions
 Attacks on hash functions Birthday attacks and Multicollisions Birthday Attack Basics In a group of 23 people, the probability that there are at least two persons on the same day in the same month is greater
Attacks on hash functions Birthday attacks and Multicollisions Birthday Attack Basics In a group of 23 people, the probability that there are at least two persons on the same day in the same month is greater
Authentication. Chapter Message Authentication
 Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
Chapter 5 Authentication 5.1 Message Authentication Suppose Bob receives a message addressed from Alice. How does Bob ensure that the message received is the same as the message sent by Alice? For example,
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 09/19/16. Lecture 6 Message Authentication Codes and Hash Functions
 ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 09/19/16 Lecture 6 Message Authentication Codes and Hash Functions Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security 09/19/16 Lecture 6 Message Authentication Codes and Hash Functions Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland,
Cryptography CS 555. Topic 13: HMACs and Generic Attacks
 Cryptography CS 555 Topic 13: HMACs and Generic Attacks 1 Recap Cryptographic Hash Functions Merkle-Damgård Transform Today s Goals: HMACs (constructing MACs from collision-resistant hash functions) Generic
Cryptography CS 555 Topic 13: HMACs and Generic Attacks 1 Recap Cryptographic Hash Functions Merkle-Damgård Transform Today s Goals: HMACs (constructing MACs from collision-resistant hash functions) Generic
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography. Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017
 COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Authenticated Encryption Syntax Syntax: Enc: K M à C Dec: K C à M { } Correctness: For all k K, m M, Dec(k, Enc(k,m) ) = m Unforgeability
COS433/Math 473: Cryptography Mark Zhandry Princeton University Spring 2017 Authenticated Encryption Syntax Syntax: Enc: K M à C Dec: K C à M { } Correctness: For all k K, m M, Dec(k, Enc(k,m) ) = m Unforgeability
Leftovers from Lecture 3
 Leftovers from Lecture 3 Implementing GF(2^k) Multiplication: Polynomial multiplication, and then remainder modulo the defining polynomial f(x): (1,1,0,1,1) *(0,1,0,1,1) = (1,1,0,0,1) For small size finite
Leftovers from Lecture 3 Implementing GF(2^k) Multiplication: Polynomial multiplication, and then remainder modulo the defining polynomial f(x): (1,1,0,1,1) *(0,1,0,1,1) = (1,1,0,0,1) For small size finite
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography
 Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Katz, Lindell Introduction to Modern Cryptrography Slides Chapter 12 Markus Bläser, Saarland University Digital signature schemes Goal: integrity of messages Signer signs a message using a private key
Lecture 5, CPA Secure Encryption from PRFs
 CS 4501-6501 Topics in Cryptography 16 Feb 2018 Lecture 5, CPA Secure Encryption from PRFs Lecturer: Mohammad Mahmoody Scribe: J. Fu, D. Anderson, W. Chao, and Y. Yu 1 Review Ralling: CPA Security and
CS 4501-6501 Topics in Cryptography 16 Feb 2018 Lecture 5, CPA Secure Encryption from PRFs Lecturer: Mohammad Mahmoody Scribe: J. Fu, D. Anderson, W. Chao, and Y. Yu 1 Review Ralling: CPA Security and
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signa
 Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
Lecture 18: Message Authentication Codes & Digital Signatures MACs and Signatures Both are used to assert that a message has indeed been generated by a party MAC is the private-key version and Signatures
An introduction to Hash functions
 An introduction to Hash functions Anna Rimoldi eriscs - Universitée de la Méditerranée, Marseille Secondo Workshop di Crittografia BunnyTN 2011 A. Rimoldi (eriscs) Hash function 12 September 2011 1 / 27
An introduction to Hash functions Anna Rimoldi eriscs - Universitée de la Méditerranée, Marseille Secondo Workshop di Crittografia BunnyTN 2011 A. Rimoldi (eriscs) Hash function 12 September 2011 1 / 27
Lecture 16 Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko. 1 Digital Signature Schemes. CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004
 CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
CMSC 858K Advanced Topics in Cryptography March 18, 2004 Lecturer: Jonathan Katz Lecture 16 Scribe(s): Chiu Yuen Koo Nikolai Yakovenko Jeffrey Blank 1 Digital Signature Schemes In this lecture, we introduce
REU 2015: Complexity Across Disciplines. Introduction to Cryptography
 REU 2015: Complexity Across Disciplines Introduction to Cryptography Symmetric Key Cryptosystems Iterated Block Ciphers Definition Let KS : K K s be a function that produces a set of subkeys k i K, 1 i
REU 2015: Complexity Across Disciplines Introduction to Cryptography Symmetric Key Cryptosystems Iterated Block Ciphers Definition Let KS : K K s be a function that produces a set of subkeys k i K, 1 i
Provable Security in Symmetric Key Cryptography
 Provable Security in Symmetric Key Cryptography Jooyoung Lee Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics, Sejong University July 5, 2012 Outline 1. Security Proof of Blockcipher-based Hash Functions K i E X
Provable Security in Symmetric Key Cryptography Jooyoung Lee Faculty of Mathematics and Statistics, Sejong University July 5, 2012 Outline 1. Security Proof of Blockcipher-based Hash Functions K i E X
Lecture 24: MAC for Arbitrary Length Messages. MAC Long Messages
 Lecture 24: MAC for Arbitrary Length Messages Recall Previous lecture, we constructed MACs for fixed length messages The GGM Pseudo-random Function (PRF) Construction Given. Pseudo-random Generator (PRG)
Lecture 24: MAC for Arbitrary Length Messages Recall Previous lecture, we constructed MACs for fixed length messages The GGM Pseudo-random Function (PRF) Construction Given. Pseudo-random Generator (PRG)
1 Number Theory Basics
 ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
ECS 289M (Franklin), Winter 2010, Crypto Review 1 Number Theory Basics This section has some basic facts about number theory, mostly taken (or adapted) from Dan Boneh s number theory fact sheets for his
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 16 October 30, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 16 1/52 Properties of Hash Functions Hash functions do not always look random Relations among
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 16 October 30, 2017 CPSC 467, Lecture 16 1/52 Properties of Hash Functions Hash functions do not always look random Relations among
CPA-Security. Definition: A private-key encryption scheme
 CPA-Security The CPA Indistinguishability Experiment PrivK cpa A,Π n : 1. A key k is generated by running Gen 1 n. 2. The adversary A is given input 1 n and oracle access to Enc k, and outputs a pair of
CPA-Security The CPA Indistinguishability Experiment PrivK cpa A,Π n : 1. A key k is generated by running Gen 1 n. 2. The adversary A is given input 1 n and oracle access to Enc k, and outputs a pair of
Lecture 15: Message Authentication
 CSE 599b: Cryptography (Winter 2006) Lecture 15: Message Authentication 22 February 2006 Lecturer: Paul Beame Scribe: Paul Beame 1 Message Authentication Recall that the goal of message authentication
CSE 599b: Cryptography (Winter 2006) Lecture 15: Message Authentication 22 February 2006 Lecturer: Paul Beame Scribe: Paul Beame 1 Message Authentication Recall that the goal of message authentication
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 15 October 20, 2014 CPSC 467, Lecture 15 1/37 Common Hash Functions SHA-2 MD5 Birthday Attack on Hash Functions Constructing New
CPSC 467: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 15 October 20, 2014 CPSC 467, Lecture 15 1/37 Common Hash Functions SHA-2 MD5 Birthday Attack on Hash Functions Constructing New
Problem 1. k zero bits. n bits. Block Cipher. Block Cipher. Block Cipher. Block Cipher. removed
 Problem 1 n bits k zero bits IV Block Block Block Block removed January 27, 2011 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 2 Problem 1 IV Inverse Inverse Inverse Inverse Missing bits January 27, 2011 Practical
Problem 1 n bits k zero bits IV Block Block Block Block removed January 27, 2011 Practical Aspects of Modern Cryptography 2 Problem 1 IV Inverse Inverse Inverse Inverse Missing bits January 27, 2011 Practical
Cryptographic Hash Functions
 Cryptographic Hash Functions Çetin Kaya Koç koc@ece.orst.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Oregon State University Corvallis, Oregon 97331 Technical Report December 9, 2002 Version 1.5 1 1 Introduction
Cryptographic Hash Functions Çetin Kaya Koç koc@ece.orst.edu Electrical & Computer Engineering Oregon State University Corvallis, Oregon 97331 Technical Report December 9, 2002 Version 1.5 1 1 Introduction
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS. CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography
 SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
SIGNATURE SCHEMES & CRYPTOGRAPHIC HASH FUNCTIONS CIS 400/628 Spring 2005 Introduction to Cryptography This is based on Chapter 8 of Trappe and Washington DIGITAL SIGNATURES message sig 1. How do we bind
On High-Rate Cryptographic Compression Functions
 On High-Rate Cryptographic Compression Functions Richard Ostertág and Martin Stanek Department o Computer Science Faculty o Mathematics, Physics and Inormatics Comenius University Mlynská dolina, 842 48
On High-Rate Cryptographic Compression Functions Richard Ostertág and Martin Stanek Department o Computer Science Faculty o Mathematics, Physics and Inormatics Comenius University Mlynská dolina, 842 48
Hash Functions. A hash function h takes as input a message of arbitrary length and produces as output a message digest of fixed length.
 Hash Functions 1 Hash Functions A hash function h takes as input a message of arbitrary length and produces as output a message digest of fixed length. 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 Long Message Hash Function 1 1 1
Hash Functions 1 Hash Functions A hash function h takes as input a message of arbitrary length and produces as output a message digest of fixed length. 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 Long Message Hash Function 1 1 1
Foundations of Network and Computer Security
 Foundations of Network and Computer Security John Black Lecture #5 Sep 7 th 2004 CSCI 6268/TLEN 5831, Fall 2004 Announcements Please sign up for class mailing list by end of today Quiz #1 will be on Thursday,
Foundations of Network and Computer Security John Black Lecture #5 Sep 7 th 2004 CSCI 6268/TLEN 5831, Fall 2004 Announcements Please sign up for class mailing list by end of today Quiz #1 will be on Thursday,
Foundations of Network and Computer Security
 Foundations of Network and Computer Security John Black Lecture #6 Sep 8 th 2005 CSCI 6268/TLEN 5831, Fall 2005 Announcements Quiz #1 later today Still some have not signed up for class mailing list Perhaps
Foundations of Network and Computer Security John Black Lecture #6 Sep 8 th 2005 CSCI 6268/TLEN 5831, Fall 2005 Announcements Quiz #1 later today Still some have not signed up for class mailing list Perhaps
Chapter 5. Hash Functions. 5.1 The hash function SHA1
 Chapter 5 Hash Functions A hash function usually means a function that compresses, meaning the output is shorter than the input. Often, such a function takes an input of arbitrary or almost arbitrary length
Chapter 5 Hash Functions A hash function usually means a function that compresses, meaning the output is shorter than the input. Often, such a function takes an input of arbitrary or almost arbitrary length
Cryptanalysis of a Message Authentication Code due to Cary and Venkatesan
 Cryptanalysis of a Message Authentication Code due to Cary and Venkatesan Simon R. Blackburn and Kenneth G. Paterson Department of Mathematics Royal Holloway, University of London Egham, Surrey, TW20 0EX,
Cryptanalysis of a Message Authentication Code due to Cary and Venkatesan Simon R. Blackburn and Kenneth G. Paterson Department of Mathematics Royal Holloway, University of London Egham, Surrey, TW20 0EX,
Lecture 10: NMAC, HMAC and Number Theory
 CS 6903 Modern Cryptography April 10, 2008 Lecture 10: NMAC, HMAC and Number Theory Instructor: Nitesh Saxena Scribes: Jonathan Voris, Md. Borhan Uddin 1 Recap 1.1 MACs A message authentication code (MAC)
CS 6903 Modern Cryptography April 10, 2008 Lecture 10: NMAC, HMAC and Number Theory Instructor: Nitesh Saxena Scribes: Jonathan Voris, Md. Borhan Uddin 1 Recap 1.1 MACs A message authentication code (MAC)
Introduction to Cryptography k. Lecture 5. Benny Pinkas k. Requirements. Data Integrity, Message Authentication
 Common Usage of MACs for message authentication Introduction to Cryptography k Alice α m, MAC k (m) Isα= MAC k (m)? Bob k Lecture 5 Benny Pinkas k Alice m, MAC k (m) m,α Got you! α MAC k (m )! Bob k Eve
Common Usage of MACs for message authentication Introduction to Cryptography k Alice α m, MAC k (m) Isα= MAC k (m)? Bob k Lecture 5 Benny Pinkas k Alice m, MAC k (m) m,α Got you! α MAC k (m )! Bob k Eve
Digital signature schemes
 Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Digital signature schemes Martin Stanek Department of Computer Science Comenius University stanek@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Cryptology 1 (2017/18) Content Introduction digital signature scheme security of digital
Domain Extender for Collision Resistant Hash Functions: Improving Upon Merkle-Damgård Iteration
 Domain Extender for Collision Resistant Hash Functions: Improving Upon Merkle-Damgård Iteration Palash Sarkar Cryptology Research Group Applied Statistics Unit Indian Statistical Institute 203, B.T. Road,
Domain Extender for Collision Resistant Hash Functions: Improving Upon Merkle-Damgård Iteration Palash Sarkar Cryptology Research Group Applied Statistics Unit Indian Statistical Institute 203, B.T. Road,
Lecture 10: NMAC, HMAC and Number Theory
 CS 6903 Modern Cryptography April 13, 2011 Lecture 10: NMAC, HMAC and Number Theory Instructor: Nitesh Saxena Scribes: Anand Desai,Manav Singh Dahiya,Amol Bhavekar 1 Recap 1.1 MACs A Message Authentication
CS 6903 Modern Cryptography April 13, 2011 Lecture 10: NMAC, HMAC and Number Theory Instructor: Nitesh Saxena Scribes: Anand Desai,Manav Singh Dahiya,Amol Bhavekar 1 Recap 1.1 MACs A Message Authentication
H Definition - hash function. Cryptographic Hash Functions - Introduction. Cryptographic hash functions. Lars R. Knudsen.
 Definition - hash function Cryptographic Hash Functions - Introduction Lars R. Knudsen April 21, 2008 Located in the southernmost part of Europe with an artic climate, Hotel Finse 1222 provides the perfect
Definition - hash function Cryptographic Hash Functions - Introduction Lars R. Knudsen April 21, 2008 Located in the southernmost part of Europe with an artic climate, Hotel Finse 1222 provides the perfect
Technische Universität München (I7) Winter 2013/14 Dr. M. Luttenberger / M. Schlund SOLUTION. Cryptography Endterm
 Technische Universität München (I7) Winter 2013/14 Dr. M. Luttenberger / M. Schlund SOLUTION Cryptography Endterm Exercise 1 One Liners 1.5P each = 12P For each of the following statements, state if it
Technische Universität München (I7) Winter 2013/14 Dr. M. Luttenberger / M. Schlund SOLUTION Cryptography Endterm Exercise 1 One Liners 1.5P each = 12P For each of the following statements, state if it
3C - A Provably Secure Pseudorandom Function and Message Authentication Code. A New mode of operation for Cryptographic Hash Function
 3C - A Provably Secure Pseudorandom Function and Message Authentication Code. A New mode of operation for Cryptographic Hash Function Praveen Gauravaram 1, William Millan 1, Juanma Gonzalez Neito 1, Edward
3C - A Provably Secure Pseudorandom Function and Message Authentication Code. A New mode of operation for Cryptographic Hash Function Praveen Gauravaram 1, William Millan 1, Juanma Gonzalez Neito 1, Edward
Notes for Lecture A can repeat step 3 as many times as it wishes. We will charge A one unit of time for every time it repeats step 3.
 COS 533: Advanced Cryptography Lecture 2 (September 18, 2017) Lecturer: Mark Zhandry Princeton University Scribe: Mark Zhandry Notes for Lecture 2 1 Last Time Last time, we defined formally what an encryption
COS 533: Advanced Cryptography Lecture 2 (September 18, 2017) Lecturer: Mark Zhandry Princeton University Scribe: Mark Zhandry Notes for Lecture 2 1 Last Time Last time, we defined formally what an encryption
New Proofs for NMAC and HMAC: Security without Collision-Resistance
 A preliminary version of this paper appears in Advances in Cryptology CRYPTO 06, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol. 4117, C. Dwork ed., Springer-Verlag, 2006. This is the full version. New Proofs for
A preliminary version of this paper appears in Advances in Cryptology CRYPTO 06, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol. 4117, C. Dwork ed., Springer-Verlag, 2006. This is the full version. New Proofs for
Cryptographic Hardness Assumptions
 Chapter 2 Cryptographic Hardness Assumptions As noted in the previous chapter, it is impossible to construct a digital signature scheme that is secure against an all-powerful adversary. Instead, the best
Chapter 2 Cryptographic Hardness Assumptions As noted in the previous chapter, it is impossible to construct a digital signature scheme that is secure against an all-powerful adversary. Instead, the best
Lecture 10 - MAC s continued, hash & MAC
 Lecture 10 - MAC s continued, hash & MAC Boaz Barak March 3, 2010 Reading: Boneh-Shoup chapters 7,8 The field GF(2 n ). A field F is a set with a multiplication ( ) and addition operations that satisfy
Lecture 10 - MAC s continued, hash & MAC Boaz Barak March 3, 2010 Reading: Boneh-Shoup chapters 7,8 The field GF(2 n ). A field F is a set with a multiplication ( ) and addition operations that satisfy
Digital Signatures. p1.
 Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
Digital Signatures p1. Digital Signatures Digital signature is the same as MAC except that the tag (signature) is produced using the secret key of a public-key cryptosystem. Message m MAC k (m) Message
REU 2015: Complexity Across Disciplines. Introduction to Cryptography
 REU 2015: Complexity Across Disciplines Introduction to Cryptography Iterated Block Ciphers Definition Let KS : K K s be a function that produces a set of subkeys k i K, 1 i s from any key k K. A block
REU 2015: Complexity Across Disciplines Introduction to Cryptography Iterated Block Ciphers Definition Let KS : K K s be a function that produces a set of subkeys k i K, 1 i s from any key k K. A block
HASH FUNCTIONS 1 /62
 HASH FUNCTIONS 1 /62 What is a hash function? By a hash function we usually mean a map h : D {0,1} n that is compressing, meaning D > 2 n. E.g. D = {0,1} 264 is the set of all strings of length at most
HASH FUNCTIONS 1 /62 What is a hash function? By a hash function we usually mean a map h : D {0,1} n that is compressing, meaning D > 2 n. E.g. D = {0,1} 264 is the set of all strings of length at most
Breaking H 2 -MAC Using Birthday Paradox
 Breaking H 2 -MAC Using Birthday Paradox Fanbao Liu 1,2, Tao Xie 1 and Changxiang Shen 2 1 School of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, 410073, Hunan, P. R. China 2 School of
Breaking H 2 -MAC Using Birthday Paradox Fanbao Liu 1,2, Tao Xie 1 and Changxiang Shen 2 1 School of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, 410073, Hunan, P. R. China 2 School of
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes
 From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
From Fixed-Length Messages to Arbitrary-Length Messages Practical RSA Signature Padding Schemes [Published in D. Naccache, Ed., Topics in Cryptology CT-RSA 2001, vol. 2020 of Lecture Notes in Computer
A Composition Theorem for Universal One-Way Hash Functions
 A Composition Theorem for Universal One-Way Hash Functions Victor Shoup IBM Zurich Research Lab, Säumerstr. 4, 8803 Rüschlikon, Switzerland sho@zurich.ibm.com Abstract. In this paper we present a new scheme
A Composition Theorem for Universal One-Way Hash Functions Victor Shoup IBM Zurich Research Lab, Säumerstr. 4, 8803 Rüschlikon, Switzerland sho@zurich.ibm.com Abstract. In this paper we present a new scheme
Block ciphers And modes of operation. Table of contents
 Block ciphers And modes of operation Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Table of contents Introduction Pseudorandom permutations Block Ciphers Modes of Operation
Block ciphers And modes of operation Foundations of Cryptography Computer Science Department Wellesley College Table of contents Introduction Pseudorandom permutations Block Ciphers Modes of Operation
CTR mode of operation
 CSA E0 235: Cryptography 13 March, 2015 Dr Arpita Patra CTR mode of operation Divya and Sabareesh 1 Overview In this lecture, we formally prove that the counter mode of operation is secure against chosen-plaintext
CSA E0 235: Cryptography 13 March, 2015 Dr Arpita Patra CTR mode of operation Divya and Sabareesh 1 Overview In this lecture, we formally prove that the counter mode of operation is secure against chosen-plaintext
ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011
 ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
ECS 127: Cryptography Handout F UC Davis Phillip Rogaway June 9, 2011 ECS 189A Final Cryptography Spring 2011 Hints for success: Good luck on the exam. I don t think it s all that hard (I do believe I
II. Digital signatures
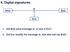 II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
II. Digital signatures Alice m Bob Eve 1. Did Bob send message m, or was it Eve? 2. Did Eve modify the message m, that was sent by Bob? 1 Digital signatures Digital signature - are equivalent of handwritten
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall
 5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
5199/IOC5063 Theory of Cryptology, 2014 Fall Homework 2 Reference Solution 1. This is about the RSA common modulus problem. Consider that two users A and B use the same modulus n = 146171 for the RSA encryption.
Forgery and Partial Key-Recovery Attacks on HMAC and NMAC Using Hash Collisions
 Forgery and Partial Key-Recovery Attacks on HMAC and NMAC Using Hash Collisions Scott Contini 1 and Yiqun Lisa Yin 2 1 Macquarie University, Centre for Advanced Computing ACAC, NSW 2109, Australia scontini@comp.mq.edu.au
Forgery and Partial Key-Recovery Attacks on HMAC and NMAC Using Hash Collisions Scott Contini 1 and Yiqun Lisa Yin 2 1 Macquarie University, Centre for Advanced Computing ACAC, NSW 2109, Australia scontini@comp.mq.edu.au
Introduction to Information Security
 Introduction to Information Security Lecture 4: Hash Functions and MAC 2007. 6. Prof. Byoungcheon Lee sultan (at) joongbu. ac. kr Information and Communications University Contents 1. Introduction - Hash
Introduction to Information Security Lecture 4: Hash Functions and MAC 2007. 6. Prof. Byoungcheon Lee sultan (at) joongbu. ac. kr Information and Communications University Contents 1. Introduction - Hash
Provable Chosen-Target-Forced-Midx Preimage Resistance
 Provable Chosen-Target-Forced-Midx Preimage Resistance Elena Andreeva and Bart Mennink (K.U.Leuven) Selected Areas in Cryptography Toronto, Canada August 11, 2011 1 / 15 Introduction Hash Functions 2 /
Provable Chosen-Target-Forced-Midx Preimage Resistance Elena Andreeva and Bart Mennink (K.U.Leuven) Selected Areas in Cryptography Toronto, Canada August 11, 2011 1 / 15 Introduction Hash Functions 2 /
2 Message authentication codes (MACs)
 CS276: Cryptography October 1, 2015 Message Authentication Codes and CCA2 Instructor: Alessandro Chiesa Scribe: David Field 1 Previous lecture Last time we: Constructed a CPA-secure encryption scheme from
CS276: Cryptography October 1, 2015 Message Authentication Codes and CCA2 Instructor: Alessandro Chiesa Scribe: David Field 1 Previous lecture Last time we: Constructed a CPA-secure encryption scheme from
Cryptography and Security Final Exam
 Cryptography and Security Final Exam Serge Vaudenay 29.1.2018 duration: 3h no documents allowed, except one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes a pocket calculator is allowed communication devices are not
Cryptography and Security Final Exam Serge Vaudenay 29.1.2018 duration: 3h no documents allowed, except one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes a pocket calculator is allowed communication devices are not
Introduction to Hash Tables
 Introduction to Hash Tables Hash Functions A hash table represents a simple but efficient way of storing, finding, and removing elements. In general, a hash table is represented by an array of cells. In
Introduction to Hash Tables Hash Functions A hash table represents a simple but efficient way of storing, finding, and removing elements. In general, a hash table is represented by an array of cells. In
The Security of Abreast-DM in the Ideal Cipher Model
 The Security of breast-dm in the Ideal Cipher Model Jooyoung Lee, Daesung Kwon The ttached Institute of Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea 305-390 jlee05@ensec.re.kr,ds
The Security of breast-dm in the Ideal Cipher Model Jooyoung Lee, Daesung Kwon The ttached Institute of Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, Korea 305-390 jlee05@ensec.re.kr,ds
Week 12: Hash Functions and MAC
 Week 12: Hash Functions and MAC 1. Introduction Hash Functions vs. MAC 2 Hash Functions Any Message M Hash Function Generate a fixed length Fingerprint for an arbitrary length message. No Key involved.
Week 12: Hash Functions and MAC 1. Introduction Hash Functions vs. MAC 2 Hash Functions Any Message M Hash Function Generate a fixed length Fingerprint for an arbitrary length message. No Key involved.
Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures
 CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
CS 7810 Graduate Cryptography October 30, 2017 Lecture 15 & 16: Trapdoor Permutations, RSA, Signatures Lecturer: Daniel Wichs Scribe: Willy Quach & Giorgos Zirdelis 1 Topic Covered. Trapdoor Permutations.
Collapsing sponges: Post-quantum security of the sponge construction
 Collapsing sponges: Post-quantum security of the sponge construction Dominique Unruh University of Tartu March 27, 2017 Abstract We investigate the post-quantum security of hash functions based on the
Collapsing sponges: Post-quantum security of the sponge construction Dominique Unruh University of Tartu March 27, 2017 Abstract We investigate the post-quantum security of hash functions based on the
Cryptography and Security Final Exam
 Cryptography and Security Final Exam Solution Serge Vaudenay 29.1.2018 duration: 3h no documents allowed, except one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes a pocket calculator is allowed communication devices
Cryptography and Security Final Exam Solution Serge Vaudenay 29.1.2018 duration: 3h no documents allowed, except one 2-sided sheet of handwritten notes a pocket calculator is allowed communication devices
SPCS Cryptography Homework 13
 1 1.1 PRP For this homework, use the ollowing PRP: E(k, m) : {0, 1} 3 {0, 1} 3 {0, 1} 3 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 m 000 011 001 111 010 000 101 110 100 001 101 110 010 000 111 100 001 011 010 001
1 1.1 PRP For this homework, use the ollowing PRP: E(k, m) : {0, 1} 3 {0, 1} 3 {0, 1} 3 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 m 000 011 001 111 010 000 101 110 100 001 101 110 010 000 111 100 001 011 010 001
CBC MAC for Real-Time Data Sources. Abstract. The Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) Message Authentication Code (MAC) is an
 CBC MAC for Real-Time Data Sources Erez Petrank Charles Racko y Abstract The Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) Message Authentication Code (MAC) is an authentication method which is widely used in practice.
CBC MAC for Real-Time Data Sources Erez Petrank Charles Racko y Abstract The Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) Message Authentication Code (MAC) is an authentication method which is widely used in practice.
Winter 2008 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor and Rani Hod. Assignment #2
 0368.3049.01 Winter 2008 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor and Rani Hod Assignment #2 Published Sunday, February 17, 2008 and very slightly revised Feb. 18. Due Tues., March 4, in Rani Hod
0368.3049.01 Winter 2008 Introduction to Modern Cryptography Benny Chor and Rani Hod Assignment #2 Published Sunday, February 17, 2008 and very slightly revised Feb. 18. Due Tues., March 4, in Rani Hod
Limits on the Efficiency of One-Way Permutation-Based Hash Functions
 Limits on the Efficiency of One-Way Permutation-Based Hash Functions Jeong Han Kim Daniel R. Simon Prasad Tetali Abstract Naor and Yung show that a one-bit-compressing universal one-way hash function (UOWHF)
Limits on the Efficiency of One-Way Permutation-Based Hash Functions Jeong Han Kim Daniel R. Simon Prasad Tetali Abstract Naor and Yung show that a one-bit-compressing universal one-way hash function (UOWHF)
Solution of Exercise Sheet 7
 saarland Foundations of Cybersecurity (Winter 16/17) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes CISPA / Saarland University university computer science Solution of Exercise Sheet 7 1 Variants of Modes of Operation Let (K,
saarland Foundations of Cybersecurity (Winter 16/17) Prof. Dr. Michael Backes CISPA / Saarland University university computer science Solution of Exercise Sheet 7 1 Variants of Modes of Operation Let (K,
Online Cryptography Course. Collision resistance. Introduc3on. Dan Boneh
 Online Cryptography Course Collision resistance Introduc3on Recap: message integrity So far, four MAC construc3ons: PRFs ECBC- MAC, CMAC : commonly used with AES (e.g. 802.11i) NMAC : basis of HMAC (this
Online Cryptography Course Collision resistance Introduc3on Recap: message integrity So far, four MAC construc3ons: PRFs ECBC- MAC, CMAC : commonly used with AES (e.g. 802.11i) NMAC : basis of HMAC (this
Foundations of Cryptography
 - 111 - Foundations of Cryptography Notes of lecture No. 10B & 11 (given on June 11 & 18, 1989) taken by Sergio Rajsbaum Summary In this lecture we define unforgeable digital signatures and present such
- 111 - Foundations of Cryptography Notes of lecture No. 10B & 11 (given on June 11 & 18, 1989) taken by Sergio Rajsbaum Summary In this lecture we define unforgeable digital signatures and present such
Security II: Cryptography
 Security II: Cryptography Markus Kuhn Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/teaching/1415/securityii/ Lent 2015 Part II 1 Related textbooks Main reference: Jonathan Katz,
Security II: Cryptography Markus Kuhn Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/teaching/1415/securityii/ Lent 2015 Part II 1 Related textbooks Main reference: Jonathan Katz,
Modern Cryptography Lecture 4
 Modern Cryptography Lecture 4 Pseudorandom Functions Block-Ciphers Modes of Operation Chosen-Ciphertext Security 1 October 30th, 2018 2 Webpage Page for first part, Homeworks, Slides http://pub.ist.ac.at/crypto/moderncrypto18.html
Modern Cryptography Lecture 4 Pseudorandom Functions Block-Ciphers Modes of Operation Chosen-Ciphertext Security 1 October 30th, 2018 2 Webpage Page for first part, Homeworks, Slides http://pub.ist.ac.at/crypto/moderncrypto18.html
Adaptive Preimage Resistance Analysis Revisited: Requirements, Subtleties and Implications
 Adaptive Preimage Resistance Analysis Revisited: Requirements, Subtleties and Implications Donghoon Chang 1 and Moti Yung 2 1 The Computer Security Division, National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Adaptive Preimage Resistance Analysis Revisited: Requirements, Subtleties and Implications Donghoon Chang 1 and Moti Yung 2 1 The Computer Security Division, National Institute of Standards and Technology,
Public-key Cryptography: Theory and Practice
 Public-key Cryptography Theory and Practice Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Appendix A: Symmetric Techniques Block Ciphers A block cipher f of block-size
Public-key Cryptography Theory and Practice Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Appendix A: Symmetric Techniques Block Ciphers A block cipher f of block-size
Understanding Cryptography A Textbook for Students and Practitioners by Christof Paar and Jan Pelzl. Chapter 11 Hash Functions ver.
 Understanding Cryptography A Textbook for Students and Practitioners by Christof Paar and Jan Pelzl www.crypto-textbook.com Chapter 11 Hash Functions ver. October 29, 2009 These slides were prepared by
Understanding Cryptography A Textbook for Students and Practitioners by Christof Paar and Jan Pelzl www.crypto-textbook.com Chapter 11 Hash Functions ver. October 29, 2009 These slides were prepared by
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model. A. Hülsing
 Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
Digital Signature Schemes and the Random Oracle Model A. Hülsing Today s goal Review provable security of in use signature schemes. (PKCS #1 v2.x) PAGE 1 Digital Signature Source: http://hari-cio-8a.blog.ugm.ac.id/files/2013/03/dsa.jpg
HASH FUNCTIONS. Mihir Bellare UCSD 1
 HASH FUNCTIONS Mihir Bellare UCSD 1 Hashing Hash functions like MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA512, SHA3,... are amongst the most widely-used cryptographic primitives. Their primary purpose is collision-resistant
HASH FUNCTIONS Mihir Bellare UCSD 1 Hashing Hash functions like MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA512, SHA3,... are amongst the most widely-used cryptographic primitives. Their primary purpose is collision-resistant
Homework 7 Solutions
 Homework 7 Solutions Due: March 22, 2018 CS 151: Intro. to Cryptography and Computer Security 1 Fun with PRFs a. F a s = F 0 k(x) F s (x) is not a PRF, for any choice of F. Consider a distinguisher D a
Homework 7 Solutions Due: March 22, 2018 CS 151: Intro. to Cryptography and Computer Security 1 Fun with PRFs a. F a s = F 0 k(x) F s (x) is not a PRF, for any choice of F. Consider a distinguisher D a
Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography
 Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography Thomas Johansson T. Johansson (Lund University) 1 / 44 Key distribution Symmetric key cryptography: Alice and Bob share a common secret key. Some means
Lecture 1: Introduction to Public key cryptography Thomas Johansson T. Johansson (Lund University) 1 / 44 Key distribution Symmetric key cryptography: Alice and Bob share a common secret key. Some means
Full Key-Recovery Attacks on HMAC/NMAC-MD4 and NMAC-MD5
 Full Attacks on HMAC/NMAC- and NMAC-MD5 Pierre-Alain Fouque, Gaëtan Leurent, Phong Nguyen Laboratoire d Informatique de l École Normale Supérieure CRYPTO 2007 1/26 WhatisaMACalgorithm? M Alice wants to
Full Attacks on HMAC/NMAC- and NMAC-MD5 Pierre-Alain Fouque, Gaëtan Leurent, Phong Nguyen Laboratoire d Informatique de l École Normale Supérieure CRYPTO 2007 1/26 WhatisaMACalgorithm? M Alice wants to
