Computations in Quantum Tensor Networks
|
|
|
- Clinton Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coputtons n Quntu Tensor etwors Thos ucle Thos Schulte-erbrüggen Konrd Wldherr Bonn 4.8.
2 Overvew () Proble settng: Coputton of Ground Sttes Physcl odel nd th. descrpton () Effcent Representton of Vectors s Tensors: () Mtr Product Sttes (MPS) nd Tensor Trns (TT): escrpton Coputtons/Contrctons orlztons (SV MRG) (b) Mtr Product Opertors (MPO) (c) tlzng syetres n the vector representton (d) Krylov ethods for egenvectors n MPS representton
3 . Coputton of ground sttes Physcl syste wth prtcles (here spn chn) 4 5 ntercton wthn the syste (e.g. nerest-neghbor ntercton) 4 5 Eternl ntercton (e.g. eteror gnetc feld) 4 5 Gol: Fnd ground stte sllest energy level of the syste nu egenvlue/vector
4 Quntu syste descrbed by ltonn opertor. The rel egenvlues of re the energy levels of sttonry sttes descrbed by the relted egenvectors: ψ > E ψ > ny stte s represented by vector ltonn tr C C 4
5 5 ltonn y be forulted s weghted su of Kronecer products of Pul trces ( ertn untry trces). Pul trces s spn opertors: σ y σ z σ Typcl spn vectors for spn up: > > Kronecer product Tensor product
6 6 Eple: sng-type ltonn z z z z z z z z σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ 4 5
7 Typcl Pttern spn chn control ltonn Sprsty: O(n log(n)) Structured: constnt long dgonls 7
8 Q Generl ltonn M α ( ) ( ) Q Q Q ( ) { σ σ σ } Pul trces ( ) y z : Proble: For 5 egenvector hs 5 coponents! Soluton: Fnd sutble vectors wth sprse representton tht llow - good pprotons of the egenvector we re loong for - esy coputtons y for nuercl egenvlue coputtons (Rylegh Quotent Vector terton. n sutble subset solve n T T eff eff 8
9 9 Typcl ltonns Open Boundry Condtons OBC otton: z y P S S S S P S P σ t ste ( ) ( ) P P P P ( ) ( ) ( ) P P P P P P z z zz y y yy P P P P OBC:
10 Typcl ltonns Perodc Boundry Condtons PBC: sotropc esenberg- J J ' yy esenberg odel P P od (generlzed) nsotropc esenberg-y J J Y yy esenberg-z J J Z zz sotropc esenberg- J J yy J zz λ esenberg-z J J yy J Z zz esenberg-yz J J Y yy J Z zz
11 Typcl ltonns Blner bqudrtc - KLT KLT odel: ( S S ) S S ( ) sn Blner bqudrtc: cos( θ ) S S ( θ )( S S ) 8 : Suton over neghbors wth nde : 4 5 SS : neghbors ( S S ) 6
12 . Sprse nd effcent representton/pproton of vector : Consder vector s bnry tensor: ( ) ( ) v bnry representton of nde. Reshpe! >... > >...
13 Grphcl otton Vector ( leg): Mtr ( legs): ( ) Generl tensor wth legs... Mtr-vector product contrcton over nde : ( ) ( ) ( y )
14 4 Frst Subset of tensor ppro: Consder ll vectors of the for R b b b b nner product: y y O() Mtr-vector product: ( ) ( ) ( ) M M Q Q Q Q α α Costs: (M) but unstsfctory pproton property. CP bd ppro. Tucer cnnot be ppled.
15 5 () Mtr Product Sttes Tensor Trn - pprotons se rn- ters le CP but n lned for tht - reflects the underlyng Physcs - llows fst coputtons Quntu Physcs: Verstrete Schollwöc Mthetcs: Tyrtyshnov Oseledets
16 6 Mtr Product Sttes cont Suton overlp reflects neghborhood relton n spn chn
17 7 Mtr Product Sttes cont. Perodc boundry condtons (Tensor chns): ( ) trce For ect representton of one needs lrger! We re only nterested n sll tr szes nd pprotons!
18 - [ ]
19 ' ' ' ' ' ' nd so on. For notton see Khoros/Kzeev: rn core product :
20 Core Tensors : trce...
21 For the coputton of y we need the nner product of two MPS vectors: ( ) ( ) p p p p p p b b b... ;... ;... Therefore we represent the sngle fctors n the bove su s sll tensors wth three legs (ndces) structured by ndces tht pper n two dfferent tensor fctors. ;... ; ) ( ; ; ere we hve to decde bout the order of the suton (contrctons).
22 MPS grphcl trce ( )
23 MPS orlzton MPS representton s not unque. Between tr products we cn nsert - wthout chngng the vector coponents. Trnsforng the trces nto untry trces v SV. Cobne the two trces t poston nto rectngulr bloc tr: trce ( ) or ( ) nfoldng or trcston of -leg tensor
24 Replce the two trces by prts of untry tr: Copute SV: Λ V Replce trces by. Multply the Λ V prt on the rght neghborng pr. n the se wy we cn consder the SV ( ) V Λ ( ) Then we cn ove the V Λ to the left neghbour pr -. So we cn replce ll by upto (the lst renng one). 4
25 For open boundry condtons ths cn be used to orthogonlze every tr pr e.g. fro the left upto the lst vector pr t the rght end u u u u ru 5
26 OBC: n the open boundry cse the fctor r n the left ost pr cn be etrcted s fctor for the whole MPS-vector nd cn be gnored. dvntge n Rylegh Quotent nzton: eff nd fster convergence. PBC: n the perodc cse we cnnot get rd of the lst tr pr. Therefore untry trces cn be cheved upto one tr pr. dvntge n Rylegh Quotent nzton: uercl stblty n eff nd fster convergence. 6
27 7 The norlzton v SV leds to the condtons or n the nonperodc cse the frst nd lst eleents re vectors wth p p p p p p p p p b b or δ δ Wrtten coponentwse: or δ δ s then clled Krus opertor.
28 Orthogonlzton v MRG Cobne two neghbourng tr prs nd pply SV: trce ( ) ( ) ( ΛV ΛV ) ( V V ) Λ Λ ΛV Strt e.g. on the left nd orthogonlze ech tr pr nd then go the rght neghbour. 8
29 9 Further Trnsforton Σ W V W V Σ se SV nonnegtve dgonl wth W B W B B B B B u u wth Σ W W W V
30 MPS MPS gves lrger MPS: ( ) ( ) B B B trce B B B trce trce b b b y So for orgnl MPS vectors wth tr sze the su s MPS vector wth tr sze. MPS MPS MPS
31 MPS wth dgonl trces CP trce
32 MPS Mnfold The spce M of MPS vectors s no lner subspce but hs certn propertes: The unt vectors re n M wth : ( e ) ( ) e δ δ δ Sprse vectors wth nnz re ebers of M for tr sze. M s so clled tr nfold Tngent spce R.Schneder e.. bsl e..
33 PEPS nner product between two PEPS tensors ( nd ): Contrcton begnnng fro down left wth the frst left colun: ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 4 ~ 4 ~ 4 ~ ~ ~ 4 ~ ~ 4 4 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 4 ~ 4 4 ~ ~ ~ ~
34 nner product of two tensors (relted to nde resp. ). Frst step: Contrcton n ll ndces
35 eltng nd to longer of length r. Contrctons prwse n frst nd second colun:
36 Meltng nd reducton to short ndces:.. { 5 5 } 4 { 4 4 } Reduce ndces to hlf length gn! { } { 4 4 } 4 4 { } { } 4 { } 4 6
37 ow ll ndces re of short length r gn Repet untl one colun left 4 7
38 MER Lyers wth untry tensors nd soetres: B 8
39 9 B ' ' ' ' ' δ δ ' ' ' B B δ untry core tensor: soetry:
40 C ; ;; ; ; ; B ;; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; B ; ; ; C ; ; ; 4
41 (b) MPO - Mtr Product Opertor O... trce ( )... σ σ wth e.g. σ σ σ z or O (... ) trce ><... >< Quntu Physcs: Verstrete Schollwöc.. Mthetcs: Oseledets Khoros R. Schneder 4
42 ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; O MPS: MPO:
43 4 [ ] ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' : : : :...
44 44 Further MPOs [ ] r r r r r r r r ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' r r r r r Y Y r r Z Y Z Y
45 45 Further MPOs r r Z Y Z Y sng r r r Z Y Z Y Z W V Y W V Z Y
46 46 Core tensor n dfferent fors: Z Y Z Y ( ) Z Z Y Y Z Z Y Y Z Y r r
47 47 MPO wth Z Y Z Y Z Y Z Y Z Z Y Y Z Z Y Y Z Y r r
48 48 dvntge: MPO MPS ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) O O O O O O O MPS b b MPS MPS MPO ' ' ' ' ' ' ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; ;; O O O MPO MPO MPO
49 (c) Syetres The consdered ltonns often hve specl syetres: J the nt-dentty: J T nd JJ T syetrc persyetrc Then the egenvlues re syetrc: J ± Other syetres: J ± Or for generl peruttons P: P ± P ± Queston: ow to odel these syetres n the MPS nstz? 49
50 ( ) tr Eple... wth the se tr pr t ech poston Ths s relted to trnslton nvrnt spn perodc spn syste or T MPS. Leds to strong syetres e.g. tr ( ) tr( ) tr( ) Mn property: trce(b) trce(b) bt shft syetry:
51 5 Slrly blocwse: ) ( C B C B tr ) ( ) ( B C B C tr B C B C tr ) ( B B B tr ) ( ) ( ) ( B B B tr B B B tr B B B tr
52 Eple Btreversl Syetry: ( ) T MPS tr wth tr tr... ( ) ( ) tr ( T T ) tr( )... T Specl cse T MPS: tr wth T ( )... 5
53 ( )... tr Eple wth B ± B b ± b Slrly f the lst tr pr hs ths property then B ± B b ± b b ± b 5
54 Persyetry Bt flp Syetry tr wth nvolutons: (( )( ) ) tr t holds:. resp.. n generl: tr tr ~ ( ) (... ~ ~ ~~ )... 54
55 55 Bt flp orl For nvoluton S - ± S ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ tr S S S S S S S S tr S S S S S S S S tr tr Ebed ll ± n nt-denty J (Jordn bloc J )
56 Qus nqueness ssue tht the MPS vector s of the for tr V V V wth untry trces V nd. ssue tht t holds J for ll possble choces of. Then t follows tht V re nvolutons for ll. 56
57 57 Full Bt Syetry Gves bt reverse/flp/shft syetry (we cn ssue sy. nvol.) J J J J J J J J tr T Wthout Persyetry: Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ B B tr tr tr T T Λ B s possble norl for.
58 dvntges Reducton n degree of freedo by usng syetres: More copct norl for. bt shft / bt reversl / bt flp / Less storge fster convergence nd hgher ccurcy n vector pproton. 58
59 (d) Krylov - MPS Replced Rylegh Quotent Mnzton by Krylov Subspce nzton n MPS spce. Generte Orthonorl bss of K n ( ) spn { n... } Proble: MPS nd prwse orthogonlzton of MPS gves MPS vectors wth lrger blocsze new. Therefore we hve to pply bc proecton nto MPS -spce MPO representton of reduces the costs for drtclly! 59
60 6 Proected Krylov Subspce terton - vod orthogonlzton - use subspces of fed sze. n n n n n n B n n n n n n Solve n y λ B n y ew egenvector pproton y y y n n new...
61 Proectons Replce n subspce y MPS_ ( o MPS vector) by proecton nto MPS spce: n y y MPS _ MPS _ O Solve ths nzton pprotely by - SV copresson - lterntng Lest Squres nzton 6
62 6 Subspce terton { } { } n n spn P P P P P P spn K... )...)) (... ( ( ))... ( ( ) ( ) ( ~ n n n n n n n n n n B Solve n y λ B n y Gves new egenvector estte ( ) n n MPS y y P...
63 6
64 64
65 65
66 66
67 - Fster convergence by proecton becuse ect egenvector s very close to MPS nfold - se soluton for s strt pproton for - Cn copute ore egenvlues/vectors - Only proecton s needed Modfctons: - Sze of subspce - - use ect Krylov tr - nclude proected orthogonlzton r : / : ; ( ) ; P( ); 67
68 Conclusons: - MPS-TT llows effcent nd hgh qulty pproton of egenvectors of huge ltonns - Mtr Product Opertors re very useful n connecton wth MPS vectors - Syetres n the vector cn be epressed n the MPS nstz - Krylov ethods cn be ppled ncludng proectons Thn you 68
8. Computing Eigenvalues in Parallel
 8. Coptng Egenles n Prllel x egenector wth egenle λ, ff: x λx, x spd, then there exsts n orthogonl ss of egenectors λ,,,,n Λ or Λ,..., n ), Λ dg λ,..., λ n ) n generl y e coplex ntry nd Λ n pper trnglr
8. Coptng Egenles n Prllel x egenector wth egenle λ, ff: x λx, x spd, then there exsts n orthogonl ss of egenectors λ,,,,n Λ or Λ,..., n ), Λ dg λ,..., λ n ) n generl y e coplex ntry nd Λ n pper trnglr
Principle Component Analysis
 Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
An Ising model on 2-D image
 School o Coputer Scence Approte Inerence: Loopy Bele Propgton nd vrnts Prolstc Grphcl Models 0-708 Lecture 4, ov 7, 007 Receptor A Knse C Gene G Receptor B Knse D Knse E 3 4 5 TF F 6 Gene H 7 8 Hetunndn
School o Coputer Scence Approte Inerence: Loopy Bele Propgton nd vrnts Prolstc Grphcl Models 0-708 Lecture 4, ov 7, 007 Receptor A Knse C Gene G Receptor B Knse D Knse E 3 4 5 TF F 6 Gene H 7 8 Hetunndn
Chapter 2 Introduction to Algebra. Dr. Chih-Peng Li ( 李 )
 Chpter Introducton to Algebr Dr. Chh-Peng L 李 Outlne Groups Felds Bnry Feld Arthetc Constructon of Glos Feld Bsc Propertes of Glos Feld Coputtons Usng Glos Feld Arthetc Vector Spces Groups 3 Let G be set
Chpter Introducton to Algebr Dr. Chh-Peng L 李 Outlne Groups Felds Bnry Feld Arthetc Constructon of Glos Feld Bsc Propertes of Glos Feld Coputtons Usng Glos Feld Arthetc Vector Spces Groups 3 Let G be set
Chapter Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear Equation
 Chpter.4 Newton-Rphson Method of Solvng Nonlner Equton After redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method formul,. develop the lgorthm of the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chpter.4 Newton-Rphson Method of Solvng Nonlner Equton After redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method formul,. develop the lgorthm of the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chapter Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear Equation
 Chpter 0.04 Newton-Rphson Method o Solvng Nonlner Equton Ater redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method ormul,. develop the lgorthm o the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chpter 0.04 Newton-Rphson Method o Solvng Nonlner Equton Ater redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method ormul,. develop the lgorthm o the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Solubilities and Thermodynamic Properties of SO 2 in Ionic
 Solubltes nd Therodync Propertes of SO n Ionc Lquds Men Jn, Yucu Hou, b Weze Wu, *, Shuhng Ren nd Shdong Tn, L Xo, nd Zhgng Le Stte Key Lbortory of Checl Resource Engneerng, Beng Unversty of Checl Technology,
Solubltes nd Therodync Propertes of SO n Ionc Lquds Men Jn, Yucu Hou, b Weze Wu, *, Shuhng Ren nd Shdong Tn, L Xo, nd Zhgng Le Stte Key Lbortory of Checl Resource Engneerng, Beng Unversty of Checl Technology,
Lecture 3 Camera Models 2 & Camera Calibration. Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometry Lab
 Lecture Cer Models Cer Clbrton rofessor Slvo Svrese Coputtonl Vson nd Geoetry Lb Slvo Svrese Lecture - Jn 7 th, 8 Lecture Cer Models Cer Clbrton Recp of cer odels Cer clbrton proble Cer clbrton wth rdl
Lecture Cer Models Cer Clbrton rofessor Slvo Svrese Coputtonl Vson nd Geoetry Lb Slvo Svrese Lecture - Jn 7 th, 8 Lecture Cer Models Cer Clbrton Recp of cer odels Cer clbrton proble Cer clbrton wth rdl
4. Eccentric axial loading, cross-section core
 . Eccentrc xl lodng, cross-secton core Introducton We re strtng to consder more generl cse when the xl force nd bxl bendng ct smultneousl n the cross-secton of the br. B vrtue of Snt-Vennt s prncple we
. Eccentrc xl lodng, cross-secton core Introducton We re strtng to consder more generl cse when the xl force nd bxl bendng ct smultneousl n the cross-secton of the br. B vrtue of Snt-Vennt s prncple we
Variable time amplitude amplification and quantum algorithms for linear algebra. Andris Ambainis University of Latvia
 Vrble tme mpltude mplfcton nd quntum lgorthms for lner lgebr Andrs Ambns Unversty of Ltv Tlk outlne. ew verson of mpltude mplfcton;. Quntum lgorthm for testng f A s sngulr; 3. Quntum lgorthm for solvng
Vrble tme mpltude mplfcton nd quntum lgorthms for lner lgebr Andrs Ambns Unversty of Ltv Tlk outlne. ew verson of mpltude mplfcton;. Quntum lgorthm for testng f A s sngulr; 3. Quntum lgorthm for solvng
EXPONENT. Section 2.1. Do you see a pattern? Do you see a pattern? Try a) ( ) b) ( ) c) ( ) d)
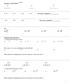 Section. EXPONENT RULES Do ou see pttern? Do ou see pttern? Tr ) ( ) b) ( ) c) ( ) d) Eponent rules strt here:. Epnd the following s bove. ) b) 7 c) d) How n 's re ou ultipling in ech proble? ) b) c) d)
Section. EXPONENT RULES Do ou see pttern? Do ou see pttern? Tr ) ( ) b) ( ) c) ( ) d) Eponent rules strt here:. Epnd the following s bove. ) b) 7 c) d) How n 's re ou ultipling in ech proble? ) b) c) d)
r = cos θ + 1. dt ) dt. (1)
 MTHE 7 Proble Set 5 Solutions (A Crdioid). Let C be the closed curve in R whose polr coordintes (r, θ) stisfy () Sketch the curve C. r = cos θ +. (b) Find pretriztion t (r(t), θ(t)), t [, b], of C in polr
MTHE 7 Proble Set 5 Solutions (A Crdioid). Let C be the closed curve in R whose polr coordintes (r, θ) stisfy () Sketch the curve C. r = cos θ +. (b) Find pretriztion t (r(t), θ(t)), t [, b], of C in polr
Fitting a Polynomial to Heat Capacity as a Function of Temperature for Ag. Mathematical Background Document
 Fttng Polynol to Het Cpcty s Functon of Teperture for Ag. thetcl Bckground Docuent by Theres Jul Zelnsk Deprtent of Chestry, edcl Technology, nd Physcs onouth Unversty West ong Brnch, J 7764-898 tzelns@onouth.edu
Fttng Polynol to Het Cpcty s Functon of Teperture for Ag. thetcl Bckground Docuent by Theres Jul Zelnsk Deprtent of Chestry, edcl Technology, nd Physcs onouth Unversty West ong Brnch, J 7764-898 tzelns@onouth.edu
Rank One Update And the Google Matrix by Al Bernstein Signal Science, LLC
 Introducton Rnk One Updte And the Google Mtrx y Al Bernsten Sgnl Scence, LLC www.sgnlscence.net here re two dfferent wys to perform mtrx multplctons. he frst uses dot product formulton nd the second uses
Introducton Rnk One Updte And the Google Mtrx y Al Bernsten Sgnl Scence, LLC www.sgnlscence.net here re two dfferent wys to perform mtrx multplctons. he frst uses dot product formulton nd the second uses
Introduction to Numerical Integration Part II
 Introducton to umercl Integrton Prt II CS 75/Mth 75 Brn T. Smth, UM, CS Dept. Sprng, 998 4/9/998 qud_ Intro to Gussn Qudrture s eore, the generl tretment chnges the ntegrton prolem to ndng the ntegrl w
Introducton to umercl Integrton Prt II CS 75/Mth 75 Brn T. Smth, UM, CS Dept. Sprng, 998 4/9/998 qud_ Intro to Gussn Qudrture s eore, the generl tretment chnges the ntegrton prolem to ndng the ntegrl w
Math 520 Final Exam Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008
 Mth 520 Finl Exm Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xio/Dums/Liw) Spring 2008 The finl exm will be held on Tuesdy, My 13, 2-5pm in 117 McMilln Wht will be covered The finl exm will cover the mteril from ll of
Mth 520 Finl Exm Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xio/Dums/Liw) Spring 2008 The finl exm will be held on Tuesdy, My 13, 2-5pm in 117 McMilln Wht will be covered The finl exm will cover the mteril from ll of
Two Coefficients of the Dyson Product
 Two Coeffcents of the Dyson Product rxv:07.460v mth.co 7 Nov 007 Lun Lv, Guoce Xn, nd Yue Zhou 3,,3 Center for Combntorcs, LPMC TJKLC Nnk Unversty, Tnjn 30007, P.R. Chn lvlun@cfc.nnk.edu.cn gn@nnk.edu.cn
Two Coeffcents of the Dyson Product rxv:07.460v mth.co 7 Nov 007 Lun Lv, Guoce Xn, nd Yue Zhou 3,,3 Center for Combntorcs, LPMC TJKLC Nnk Unversty, Tnjn 30007, P.R. Chn lvlun@cfc.nnk.edu.cn gn@nnk.edu.cn
ψ ij has the eigenvalue
 Moller Plesset Perturbton Theory In Moller-Plesset (MP) perturbton theory one tes the unperturbed Hmltonn for n tom or molecule s the sum of the one prtcle Foc opertors H F() where the egenfunctons of
Moller Plesset Perturbton Theory In Moller-Plesset (MP) perturbton theory one tes the unperturbed Hmltonn for n tom or molecule s the sum of the one prtcle Foc opertors H F() where the egenfunctons of
Geometric Correction or Georeferencing
 Geoetrc Correcton or Georeferencng GEOREFERENCING: fro ge to p Coordntes on erth: (λ, φ) ge: (, ) p: (, ) rel nteger Trnsfortons (nvolvng deforton): erth-to-ge: χ erth-to-p: ψ (crtogrphc proecton) ge-to-p:
Geoetrc Correcton or Georeferencng GEOREFERENCING: fro ge to p Coordntes on erth: (λ, φ) ge: (, ) p: (, ) rel nteger Trnsfortons (nvolvng deforton): erth-to-ge: χ erth-to-p: ψ (crtogrphc proecton) ge-to-p:
Engineering Tensors. Friday November 16, h30 -Muddy Charles. A BEH430 review session by Thomas Gervais.
 ngneerng Tensors References: BH4 reew sesson b Thoms Gers tgers@mt.ed Long, RR, Mechncs of Solds nd lds, Prentce-Hll, 96, pp - Deen, WD, nlss of trnsport phenomen, Oford, 998, p. 55-56 Goodbod, M, Crtesn
ngneerng Tensors References: BH4 reew sesson b Thoms Gers tgers@mt.ed Long, RR, Mechncs of Solds nd lds, Prentce-Hll, 96, pp - Deen, WD, nlss of trnsport phenomen, Oford, 998, p. 55-56 Goodbod, M, Crtesn
Solutions for Homework #9
 Solutons for Hoewor #9 PROBEM. (P. 3 on page 379 n the note) Consder a sprng ounted rgd bar of total ass and length, to whch an addtonal ass s luped at the rghtost end. he syste has no dapng. Fnd the natural
Solutons for Hoewor #9 PROBEM. (P. 3 on page 379 n the note) Consder a sprng ounted rgd bar of total ass and length, to whch an addtonal ass s luped at the rghtost end. he syste has no dapng. Fnd the natural
HW3, Math 307. CSUF. Spring 2007.
 HW, Mth 7. CSUF. Spring 7. Nsser M. Abbsi Spring 7 Compiled on November 5, 8 t 8:8m public Contents Section.6, problem Section.6, problem Section.6, problem 5 Section.6, problem 7 6 5 Section.6, problem
HW, Mth 7. CSUF. Spring 7. Nsser M. Abbsi Spring 7 Compiled on November 5, 8 t 8:8m public Contents Section.6, problem Section.6, problem Section.6, problem 5 Section.6, problem 7 6 5 Section.6, problem
Review of linear algebra. Nuno Vasconcelos UCSD
 Revew of lner lgebr Nuno Vsconcelos UCSD Vector spces Defnton: vector spce s set H where ddton nd sclr multplcton re defned nd stsf: ) +( + ) (+ )+ 5) λ H 2) + + H 6) 3) H, + 7) λ(λ ) (λλ ) 4) H, - + 8)
Revew of lner lgebr Nuno Vsconcelos UCSD Vector spces Defnton: vector spce s set H where ddton nd sclr multplcton re defned nd stsf: ) +( + ) (+ )+ 5) λ H 2) + + H 6) 3) H, + 7) λ(λ ) (λλ ) 4) H, - + 8)
ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS. The real numbers have the following properties: a b c ab ac
 REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
Lecture 8: Camera Calibration
 Lecture 8: Cer Clbrton rofessor Fe-Fe L Stnford Vson Lb Fe-Fe L 9-Oct- Wht we wll lern tody? Revew cer preters Affne cer odel (roble Set (Q4)) Cer clbrton Vnshng ponts nd lnes (roble Set (Q)) Redng: [F]
Lecture 8: Cer Clbrton rofessor Fe-Fe L Stnford Vson Lb Fe-Fe L 9-Oct- Wht we wll lern tody? Revew cer preters Affne cer odel (roble Set (Q4)) Cer clbrton Vnshng ponts nd lnes (roble Set (Q)) Redng: [F]
Applied Statistics Qualifier Examination
 Appled Sttstcs Qulfer Exmnton Qul_june_8 Fll 8 Instructons: () The exmnton contns 4 Questons. You re to nswer 3 out of 4 of them. () You my use ny books nd clss notes tht you mght fnd helpful n solvng
Appled Sttstcs Qulfer Exmnton Qul_june_8 Fll 8 Instructons: () The exmnton contns 4 Questons. You re to nswer 3 out of 4 of them. () You my use ny books nd clss notes tht you mght fnd helpful n solvng
DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMERICAL METHODS (COS 233-8) Solutions to Assignment 3. x f(x)
 DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMEICAL METHODS (COS -8) Solutons to Assgnment Queston Consder the followng dt: 5 f() 8 7 5 () Set up dfference tble through fourth dfferences. (b) Wht s the mnmum degree tht n nterpoltng
DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMEICAL METHODS (COS -8) Solutons to Assgnment Queston Consder the followng dt: 5 f() 8 7 5 () Set up dfference tble through fourth dfferences. (b) Wht s the mnmum degree tht n nterpoltng
STURM-LIOUVILLE BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS
 STURM-LIOUVILLE BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS Throughout, we let [, b] be bounded intervl in R. C 2 ([, b]) denotes the spce of functions with derivtives of second order continuous up to the endpoints. Cc 2
STURM-LIOUVILLE BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS Throughout, we let [, b] be bounded intervl in R. C 2 ([, b]) denotes the spce of functions with derivtives of second order continuous up to the endpoints. Cc 2
Is there an easy way to find examples of such triples? Why yes! Just look at an ordinary multiplication table to find them!
 PUSHING PYTHAGORAS 009 Jmes Tnton A triple of integers ( bc,, ) is clled Pythgoren triple if exmple, some clssic triples re ( 3,4,5 ), ( 5,1,13 ), ( ) fond of ( 0,1,9 ) nd ( 119,10,169 ). + b = c. For
PUSHING PYTHAGORAS 009 Jmes Tnton A triple of integers ( bc,, ) is clled Pythgoren triple if exmple, some clssic triples re ( 3,4,5 ), ( 5,1,13 ), ( ) fond of ( 0,1,9 ) nd ( 119,10,169 ). + b = c. For
Dennis Bricker, 2001 Dept of Industrial Engineering The University of Iowa. MDP: Taxi page 1
 Denns Brcker, 2001 Dept of Industrl Engneerng The Unversty of Iow MDP: Tx pge 1 A tx serves three djcent towns: A, B, nd C. Ech tme the tx dschrges pssenger, the drver must choose from three possble ctons:
Denns Brcker, 2001 Dept of Industrl Engneerng The Unversty of Iow MDP: Tx pge 1 A tx serves three djcent towns: A, B, nd C. Ech tme the tx dschrges pssenger, the drver must choose from three possble ctons:
For convenience, we rewrite m2 s m2 = m m m ; where m is repeted m times. Since xyz = m m m nd jxyj»m, we hve tht the string y is substring of the fir
 CSCI 2400 Models of Computtion, Section 3 Solutions to Homework 4 Problem 1. ll the solutions below refer to the Pumping Lemm of Theorem 4.8, pge 119. () L = f n b l k : k n + lg Let's ssume for contrdiction
CSCI 2400 Models of Computtion, Section 3 Solutions to Homework 4 Problem 1. ll the solutions below refer to the Pumping Lemm of Theorem 4.8, pge 119. () L = f n b l k : k n + lg Let's ssume for contrdiction
Vectors and Tensors. R. Shankar Subramanian. R. Aris, Vectors, Tensors, and the Equations of Fluid Mechanics, Prentice Hall (1962).
 005 Vectors nd Tensors R. Shnkr Subrmnn Good Sources R. rs, Vectors, Tensors, nd the Equtons of Flud Mechncs, Prentce Hll (96). nd ppendces n () R. B. Brd, W. E. Stewrt, nd E. N. Lghtfoot, Trnsport Phenomen,
005 Vectors nd Tensors R. Shnkr Subrmnn Good Sources R. rs, Vectors, Tensors, nd the Equtons of Flud Mechncs, Prentce Hll (96). nd ppendces n () R. B. Brd, W. E. Stewrt, nd E. N. Lghtfoot, Trnsport Phenomen,
Proof that if Voting is Perfect in One Dimension, then the First. Eigenvector Extracted from the Double-Centered Transformed
 Proof tht f Votng s Perfect n One Dmenson, then the Frst Egenvector Extrcted from the Doule-Centered Trnsformed Agreement Score Mtrx hs the Sme Rn Orderng s the True Dt Keth T Poole Unversty of Houston
Proof tht f Votng s Perfect n One Dmenson, then the Frst Egenvector Extrcted from the Doule-Centered Trnsformed Agreement Score Mtrx hs the Sme Rn Orderng s the True Dt Keth T Poole Unversty of Houston
Lecture 4: Piecewise Cubic Interpolation
 Lecture notes on Vrtonl nd Approxmte Methods n Appled Mthemtcs - A Perce UBC Lecture 4: Pecewse Cubc Interpolton Compled 6 August 7 In ths lecture we consder pecewse cubc nterpolton n whch cubc polynoml
Lecture notes on Vrtonl nd Approxmte Methods n Appled Mthemtcs - A Perce UBC Lecture 4: Pecewse Cubc Interpolton Compled 6 August 7 In ths lecture we consder pecewse cubc nterpolton n whch cubc polynoml
Special Relativity and Riemannian Geometry. Department of Mathematical Sciences
 Tutoral Letter 06//018 Specal Relatvty and Reannan Geoetry APM3713 Seester Departent of Matheatcal Scences IMPORTANT INFORMATION: Ths tutoral letter contans the solutons to Assgnent 06. BAR CODE Learn
Tutoral Letter 06//018 Specal Relatvty and Reannan Geoetry APM3713 Seester Departent of Matheatcal Scences IMPORTANT INFORMATION: Ths tutoral letter contans the solutons to Assgnent 06. BAR CODE Learn
Phys101 Lecture 4,5 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Phys101 Lecture 4,5 Dynics: ewton s Lws of Motion Key points: ewton s second lw is vector eqution ction nd rection re cting on different objects ree-ody Digrs riction Inclines Ref: 4-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
Phys101 Lecture 4,5 Dynics: ewton s Lws of Motion Key points: ewton s second lw is vector eqution ction nd rection re cting on different objects ree-ody Digrs riction Inclines Ref: 4-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
CURVE FITTING LEAST SQUARES METHOD
 Nuercl Alss for Egeers Ger Jord Uverst CURVE FITTING Although, the for of fucto represetg phscl sste s kow, the fucto tself ot be kow. Therefore, t s frequetl desred to ft curve to set of dt pots the ssued
Nuercl Alss for Egeers Ger Jord Uverst CURVE FITTING Although, the for of fucto represetg phscl sste s kow, the fucto tself ot be kow. Therefore, t s frequetl desred to ft curve to set of dt pots the ssued
Electrochemical Thermodynamics. Interfaces and Energy Conversion
 CHE465/865, 2006-3, Lecture 6, 18 th Sep., 2006 Electrochemcl Thermodynmcs Interfces nd Energy Converson Where does the energy contrbuton F zϕ dn come from? Frst lw of thermodynmcs (conservton of energy):
CHE465/865, 2006-3, Lecture 6, 18 th Sep., 2006 Electrochemcl Thermodynmcs Interfces nd Energy Converson Where does the energy contrbuton F zϕ dn come from? Frst lw of thermodynmcs (conservton of energy):
Partially Observable Systems. 1 Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) Formalism
 CS294-40 Lernng for Rootcs nd Control Lecture 10-9/30/2008 Lecturer: Peter Aeel Prtlly Oservle Systems Scre: Dvd Nchum Lecture outlne POMDP formlsm Pont-sed vlue terton Glol methods: polytree, enumerton,
CS294-40 Lernng for Rootcs nd Control Lecture 10-9/30/2008 Lecturer: Peter Aeel Prtlly Oservle Systems Scre: Dvd Nchum Lecture outlne POMDP formlsm Pont-sed vlue terton Glol methods: polytree, enumerton,
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sc. Technol., () (), pp. 44-49 Interntonl Journl of Pure nd Appled Scences nd Technolog ISSN 9-67 Avlle onlne t www.jopst.n Reserch Pper Numercl Soluton for Non-Lner Fredholm Integrl
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sc. Technol., () (), pp. 44-49 Interntonl Journl of Pure nd Appled Scences nd Technolog ISSN 9-67 Avlle onlne t www.jopst.n Reserch Pper Numercl Soluton for Non-Lner Fredholm Integrl
Multipoint Analysis for Sibling Pairs. Biostatistics 666 Lecture 18
 Multpont Analyss for Sblng ars Bostatstcs 666 Lecture 8 revously Lnkage analyss wth pars of ndvduals Non-paraetrc BS Methods Maxu Lkelhood BD Based Method ossble Trangle Constrant AS Methods Covered So
Multpont Analyss for Sblng ars Bostatstcs 666 Lecture 8 revously Lnkage analyss wth pars of ndvduals Non-paraetrc BS Methods Maxu Lkelhood BD Based Method ossble Trangle Constrant AS Methods Covered So
GAUSS ELIMINATION. Consider the following system of algebraic linear equations
 Numercl Anlyss for Engneers Germn Jordnn Unversty GAUSS ELIMINATION Consder the followng system of lgebrc lner equtons To solve the bove system usng clsscl methods, equton () s subtrcted from equton ()
Numercl Anlyss for Engneers Germn Jordnn Unversty GAUSS ELIMINATION Consder the followng system of lgebrc lner equtons To solve the bove system usng clsscl methods, equton () s subtrcted from equton ()
Many-Body Calculations of the Isotope Shift
 Mny-Body Clcultons of the Isotope Shft W. R. Johnson Mrch 11, 1 1 Introducton Atomc energy levels re commonly evluted ssumng tht the nucler mss s nfnte. In ths report, we consder correctons to tomc levels
Mny-Body Clcultons of the Isotope Shft W. R. Johnson Mrch 11, 1 1 Introducton Atomc energy levels re commonly evluted ssumng tht the nucler mss s nfnte. In ths report, we consder correctons to tomc levels
Before we can begin Ch. 3 on Radicals, we need to be familiar with perfect squares, cubes, etc. Try and do as many as you can without a calculator!!!
 Nme: Algebr II Honors Pre-Chpter Homework Before we cn begin Ch on Rdicls, we need to be fmilir with perfect squres, cubes, etc Try nd do s mny s you cn without clcultor!!! n The nth root of n n Be ble
Nme: Algebr II Honors Pre-Chpter Homework Before we cn begin Ch on Rdicls, we need to be fmilir with perfect squres, cubes, etc Try nd do s mny s you cn without clcultor!!! n The nth root of n n Be ble
MATRICES AND VECTORS SPACE
 MATRICES AND VECTORS SPACE MATRICES AND MATRIX OPERATIONS SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS DETERMINANTS VECTORS IN -SPACE AND -SPACE GENERAL VECTOR SPACES INNER PRODUCT SPACES EIGENVALUES, EIGENVECTORS LINEAR
MATRICES AND VECTORS SPACE MATRICES AND MATRIX OPERATIONS SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS DETERMINANTS VECTORS IN -SPACE AND -SPACE GENERAL VECTOR SPACES INNER PRODUCT SPACES EIGENVALUES, EIGENVECTORS LINEAR
1. Extend QR downwards to meet the x-axis at U(6, 0). y
 In the digrm, two stright lines re to be drwn through so tht the lines divide the figure OPQRST into pieces of equl re Find the sum of the slopes of the lines R(6, ) S(, ) T(, 0) Determine ll liner functions
In the digrm, two stright lines re to be drwn through so tht the lines divide the figure OPQRST into pieces of equl re Find the sum of the slopes of the lines R(6, ) S(, ) T(, 0) Determine ll liner functions
Grover s Algorithm + Quantum Zeno Effect + Vaidman
 Grover s Algorthm + Quantum Zeno Effect + Vadman CS 294-2 Bomb 10/12/04 Fall 2004 Lecture 11 Grover s algorthm Recall that Grover s algorthm for searchng over a space of sze wors as follows: consder the
Grover s Algorthm + Quantum Zeno Effect + Vadman CS 294-2 Bomb 10/12/04 Fall 2004 Lecture 11 Grover s algorthm Recall that Grover s algorthm for searchng over a space of sze wors as follows: consder the
The Atwood Machine OBJECTIVE INTRODUCTION APPARATUS THEORY
 The Atwood Mchine OBJECTIVE To derive the ening of Newton's second lw of otion s it pplies to the Atwood chine. To explin how ss iblnce cn led to the ccelertion of the syste. To deterine the ccelertion
The Atwood Mchine OBJECTIVE To derive the ening of Newton's second lw of otion s it pplies to the Atwood chine. To explin how ss iblnce cn led to the ccelertion of the syste. To deterine the ccelertion
UCSD Phys 4A Intro Mechanics Winter 2016 Ch 4 Solutions
 USD Phys 4 Intro Mechnics Winter 06 h 4 Solutions 0. () he 0.0 k box restin on the tble hs the free-body dir shown. Its weiht 0.0 k 9.80 s 96 N. Since the box is t rest, the net force on is the box ust
USD Phys 4 Intro Mechnics Winter 06 h 4 Solutions 0. () he 0.0 k box restin on the tble hs the free-body dir shown. Its weiht 0.0 k 9.80 s 96 N. Since the box is t rest, the net force on is the box ust
UNIVERSITY OF IOANNINA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS. M.Sc. in Economics MICROECONOMIC THEORY I. Problem Set II
 Mcroeconomc Theory I UNIVERSITY OF IOANNINA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS MSc n Economcs MICROECONOMIC THEORY I Techng: A Lptns (Note: The number of ndctes exercse s dffculty level) ()True or flse? If V( y )
Mcroeconomc Theory I UNIVERSITY OF IOANNINA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS MSc n Economcs MICROECONOMIC THEORY I Techng: A Lptns (Note: The number of ndctes exercse s dffculty level) ()True or flse? If V( y )
AQA Further Pure 2. Hyperbolic Functions. Section 2: The inverse hyperbolic functions
 Hperbolic Functions Section : The inverse hperbolic functions Notes nd Emples These notes contin subsections on The inverse hperbolic functions Integrtion using the inverse hperbolic functions Logrithmic
Hperbolic Functions Section : The inverse hperbolic functions Notes nd Emples These notes contin subsections on The inverse hperbolic functions Integrtion using the inverse hperbolic functions Logrithmic
Chapter 12 Lyes KADEM [Thermodynamics II] 2007
![Chapter 12 Lyes KADEM [Thermodynamics II] 2007 Chapter 12 Lyes KADEM [Thermodynamics II] 2007](/thumbs/79/79128935.jpg) Chapter 2 Lyes KDEM [Therodynacs II] 2007 Gas Mxtures In ths chapter we wll develop ethods for deternng therodynac propertes of a xture n order to apply the frst law to systes nvolvng xtures. Ths wll be
Chapter 2 Lyes KDEM [Therodynacs II] 2007 Gas Mxtures In ths chapter we wll develop ethods for deternng therodynac propertes of a xture n order to apply the frst law to systes nvolvng xtures. Ths wll be
Multiple view geometry
 EECS 442 Computer vson Multple vew geometry Perspectve Structure from Moton - Perspectve structure from moton prolem - mgutes - lgerc methods - Fctorzton methods - Bundle djustment - Self-clrton Redng:
EECS 442 Computer vson Multple vew geometry Perspectve Structure from Moton - Perspectve structure from moton prolem - mgutes - lgerc methods - Fctorzton methods - Bundle djustment - Self-clrton Redng:
The Schur-Cohn Algorithm
 Modelng, Estmton nd Otml Flterng n Sgnl Processng Mohmed Njm Coyrght 8, ISTE Ltd. Aendx F The Schur-Cohn Algorthm In ths endx, our m s to resent the Schur-Cohn lgorthm [] whch s often used s crteron for
Modelng, Estmton nd Otml Flterng n Sgnl Processng Mohmed Njm Coyrght 8, ISTE Ltd. Aendx F The Schur-Cohn Algorthm In ths endx, our m s to resent the Schur-Cohn lgorthm [] whch s often used s crteron for
STATISTICAL MECHANICS OF THE INVERSE ISING MODEL
 STATISTICAL MECHANICS OF THE INVESE ISING MODEL Muro Cro Supervsors: rof. Mchele Cselle rof. ccrdo Zecchn uly 2009 INTODUCTION SUMMAY OF THE ESENTATION Defnton of the drect nd nverse prole Approton ethods
STATISTICAL MECHANICS OF THE INVESE ISING MODEL Muro Cro Supervsors: rof. Mchele Cselle rof. ccrdo Zecchn uly 2009 INTODUCTION SUMMAY OF THE ESENTATION Defnton of the drect nd nverse prole Approton ethods
List all of the possible rational roots of each equation. Then find all solutions (both real and imaginary) of the equation. 1.
 Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
Numbers Related to Bernoulli-Goss Numbers
 ursh Journl of Anlyss n Nuber heory, 4, Vol., No., -8 Avlble onlne t htt://ubs.sceub.co/tnt///4 Scence n Eucton Publshng OI:.69/tnt---4 Nubers Relte to Bernoull-Goss Nubers Mohe Oul ouh Benough * érteent
ursh Journl of Anlyss n Nuber heory, 4, Vol., No., -8 Avlble onlne t htt://ubs.sceub.co/tnt///4 Scence n Eucton Publshng OI:.69/tnt---4 Nubers Relte to Bernoull-Goss Nubers Mohe Oul ouh Benough * érteent
Math Lecture 23
 Mth 8 - Lecture 3 Dyln Zwick Fll 3 In our lst lecture we delt with solutions to the system: x = Ax where A is n n n mtrix with n distinct eigenvlues. As promised, tody we will del with the question of
Mth 8 - Lecture 3 Dyln Zwick Fll 3 In our lst lecture we delt with solutions to the system: x = Ax where A is n n n mtrix with n distinct eigenvlues. As promised, tody we will del with the question of
13: Diffusion in 2 Energy Groups
 3: Diffusion in Energy Groups B. Rouben McMster University Course EP 4D3/6D3 Nucler Rector Anlysis (Rector Physics) 5 Sept.-Dec. 5 September Contents We study the diffusion eqution in two energy groups
3: Diffusion in Energy Groups B. Rouben McMster University Course EP 4D3/6D3 Nucler Rector Anlysis (Rector Physics) 5 Sept.-Dec. 5 September Contents We study the diffusion eqution in two energy groups
Section 14.3 Arc Length and Curvature
 Section 4.3 Arc Length nd Curvture Clculus on Curves in Spce In this section, we ly the foundtions for describing the movement of n object in spce.. Vector Function Bsics In Clc, formul for rc length in
Section 4.3 Arc Length nd Curvture Clculus on Curves in Spce In this section, we ly the foundtions for describing the movement of n object in spce.. Vector Function Bsics In Clc, formul for rc length in
Definition of Tracking
 Trckng Defnton of Trckng Trckng: Generte some conclusons bout the moton of the scene, objects, or the cmer, gven sequence of mges. Knowng ths moton, predct where thngs re gong to project n the net mge,
Trckng Defnton of Trckng Trckng: Generte some conclusons bout the moton of the scene, objects, or the cmer, gven sequence of mges. Knowng ths moton, predct where thngs re gong to project n the net mge,
STRAND B: NUMBER THEORY
 Mthemtics SKE, Strnd B UNIT B Indices nd Fctors: Tet STRAND B: NUMBER THEORY B Indices nd Fctors Tet Contents Section B. Squres, Cubes, Squre Roots nd Cube Roots B. Inde Nottion B. Fctors B. Prime Fctors,
Mthemtics SKE, Strnd B UNIT B Indices nd Fctors: Tet STRAND B: NUMBER THEORY B Indices nd Fctors Tet Contents Section B. Squres, Cubes, Squre Roots nd Cube Roots B. Inde Nottion B. Fctors B. Prime Fctors,
Convergence Theorems for Two Iterative Methods. A stationary iterative method for solving the linear system: (1.1)
 Conrgnc Thors for Two Itrt Mthods A sttonry trt thod for solng th lnr syst: Ax = b (.) ploys n trton trx B nd constnt ctor c so tht for gn strtng stt x of x for = 2... x Bx c + = +. (.2) For such n trton
Conrgnc Thors for Two Itrt Mthods A sttonry trt thod for solng th lnr syst: Ax = b (.) ploys n trton trx B nd constnt ctor c so tht for gn strtng stt x of x for = 2... x Bx c + = +. (.2) For such n trton
fractions Let s Learn to
 5 simple lgebric frctions corne lens pupil retin Norml vision light focused on the retin concve lens Shortsightedness (myopi) light focused in front of the retin Corrected myopi light focused on the retin
5 simple lgebric frctions corne lens pupil retin Norml vision light focused on the retin concve lens Shortsightedness (myopi) light focused in front of the retin Corrected myopi light focused on the retin
Chapter 1: Fundamentals
 Chpter 1: Fundmentls 1.1 Rel Numbers Types of Rel Numbers: Nturl Numbers: {1, 2, 3,...}; These re the counting numbers. Integers: {... 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}; These re ll the nturl numbers, their negtives,
Chpter 1: Fundmentls 1.1 Rel Numbers Types of Rel Numbers: Nturl Numbers: {1, 2, 3,...}; These re the counting numbers. Integers: {... 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}; These re ll the nturl numbers, their negtives,
? plate in A G in
 Proble (0 ponts): The plstc block shon s bonded to rgd support nd to vertcl plte to hch 0 kp lod P s ppled. Knong tht for the plstc used G = 50 ks, deterne the deflecton of the plte. Gven: G 50 ks, P 0
Proble (0 ponts): The plstc block shon s bonded to rgd support nd to vertcl plte to hch 0 kp lod P s ppled. Knong tht for the plstc used G = 50 ks, deterne the deflecton of the plte. Gven: G 50 ks, P 0
Chapter 5. , r = r 1 r 2 (1) µ = m 1 m 2. r, r 2 = R µ m 2. R(m 1 + m 2 ) + m 2 r = r 1. m 2. r = r 1. R + µ m 1
 Tor Kjellsson Stockholm University Chpter 5 5. Strting with the following informtion: R = m r + m r m + m, r = r r we wnt to derive: µ = m m m + m r = R + µ m r, r = R µ m r 3 = µ m R + r, = µ m R r. 4
Tor Kjellsson Stockholm University Chpter 5 5. Strting with the following informtion: R = m r + m r m + m, r = r r we wnt to derive: µ = m m m + m r = R + µ m r, r = R µ m r 3 = µ m R + r, = µ m R r. 4
Chapter 3 MATRIX. In this chapter: 3.1 MATRIX NOTATION AND TERMINOLOGY
 Chpter 3 MTRIX In this chpter: Definition nd terms Specil Mtrices Mtrix Opertion: Trnspose, Equlity, Sum, Difference, Sclr Multipliction, Mtrix Multipliction, Determinnt, Inverse ppliction of Mtrix in
Chpter 3 MTRIX In this chpter: Definition nd terms Specil Mtrices Mtrix Opertion: Trnspose, Equlity, Sum, Difference, Sclr Multipliction, Mtrix Multipliction, Determinnt, Inverse ppliction of Mtrix in
Variational Techniques for Sturm-Liouville Eigenvalue Problems
 Vritionl Techniques for Sturm-Liouville Eigenvlue Problems Vlerie Cormni Deprtment of Mthemtics nd Sttistics University of Nebrsk, Lincoln Lincoln, NE 68588 Emil: vcormni@mth.unl.edu Rolf Ryhm Deprtment
Vritionl Techniques for Sturm-Liouville Eigenvlue Problems Vlerie Cormni Deprtment of Mthemtics nd Sttistics University of Nebrsk, Lincoln Lincoln, NE 68588 Emil: vcormni@mth.unl.edu Rolf Ryhm Deprtment
Least Squares Fitting of Data
 Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2015. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: January 5, 2015 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2015. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: January 5, 2015 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vectors and Vector Calculus
 ESI 34 tmospherc Dnmcs I Lesson 1 Vectors nd Vector lculus Reference: Schum s Outlne Seres: Mthemtcl Hndbook of Formuls nd Tbles Suggested Redng: Mrtn Secton 1 OORDINTE SYSTEMS n orthonorml coordnte sstem
ESI 34 tmospherc Dnmcs I Lesson 1 Vectors nd Vector lculus Reference: Schum s Outlne Seres: Mthemtcl Hndbook of Formuls nd Tbles Suggested Redng: Mrtn Secton 1 OORDINTE SYSTEMS n orthonorml coordnte sstem
20 MATHEMATICS POLYNOMIALS
 0 MATHEMATICS POLYNOMIALS.1 Introduction In Clss IX, you hve studied polynomils in one vrible nd their degrees. Recll tht if p(x) is polynomil in x, the highest power of x in p(x) is clled the degree of
0 MATHEMATICS POLYNOMIALS.1 Introduction In Clss IX, you hve studied polynomils in one vrible nd their degrees. Recll tht if p(x) is polynomil in x, the highest power of x in p(x) is clled the degree of
Least Squares Fitting of Data
 Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2014. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: February 9, 2008 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2014. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: February 9, 2008 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
Second degree generalized gauss-seidel iteration method for solving linear system of equations. ABSTRACT
 Ethiop. J. Sci. & Technol. 7( 5-, 0 5 Second degree generlized guss-seidel itertion ethod for solving liner syste of equtions Tesfye Keede Bhir Dr University, College of Science, Deprtent of Mthetics tk_ke@yhoo.co
Ethiop. J. Sci. & Technol. 7( 5-, 0 5 Second degree generlized guss-seidel itertion ethod for solving liner syste of equtions Tesfye Keede Bhir Dr University, College of Science, Deprtent of Mthetics tk_ke@yhoo.co
Bernoulli Numbers Jeff Morton
 Bernoulli Numbers Jeff Morton. We re interested in the opertor e t k d k t k, which is to sy k tk. Applying this to some function f E to get e t f d k k tk d k f f + d k k tk dk f, we note tht since f
Bernoulli Numbers Jeff Morton. We re interested in the opertor e t k d k t k, which is to sy k tk. Applying this to some function f E to get e t f d k k tk d k f f + d k k tk dk f, we note tht since f
MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1
 MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integrl Equtions nd the Clculus of Vritions 1 Section 1 Function spces nd opertors Here we gives some brief detils nd definitions, prticulrly relting to opertors. For further
MATH34032: Green s Functions, Integrl Equtions nd the Clculus of Vritions 1 Section 1 Function spces nd opertors Here we gives some brief detils nd definitions, prticulrly relting to opertors. For further
Exponents and Powers
 EXPONENTS AND POWERS 9 Exponents nd Powers CHAPTER. Introduction Do you know? Mss of erth is 5,970,000,000,000, 000, 000, 000, 000 kg. We hve lredy lernt in erlier clss how to write such lrge nubers ore
EXPONENTS AND POWERS 9 Exponents nd Powers CHAPTER. Introduction Do you know? Mss of erth is 5,970,000,000,000, 000, 000, 000, 000 kg. We hve lredy lernt in erlier clss how to write such lrge nubers ore
In Section 5.3 we considered initial value problems for the linear second order equation. y.a/ C ˇy 0.a/ D k 1 (13.1.4)
 678 Chpter 13 Boundry Vlue Problems for Second Order Ordinry Differentil Equtions 13.1 TWO-POINT BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS In Section 5.3 we considered initil vlue problems for the liner second order eqution
678 Chpter 13 Boundry Vlue Problems for Second Order Ordinry Differentil Equtions 13.1 TWO-POINT BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS In Section 5.3 we considered initil vlue problems for the liner second order eqution
Scientific notation is a way of expressing really big numbers or really small numbers.
 Scientific Nottion (Stndrd form) Scientific nottion is wy of expressing relly big numbers or relly smll numbers. It is most often used in scientific clcultions where the nlysis must be very precise. Scientific
Scientific Nottion (Stndrd form) Scientific nottion is wy of expressing relly big numbers or relly smll numbers. It is most often used in scientific clcultions where the nlysis must be very precise. Scientific
approaches as n becomes larger and larger. Since e > 1, the graph of the natural exponential function is as below
 . Eponentil nd rithmic functions.1 Eponentil Functions A function of the form f() =, > 0, 1 is clled n eponentil function. Its domin is the set of ll rel f ( 1) numbers. For n eponentil function f we hve.
. Eponentil nd rithmic functions.1 Eponentil Functions A function of the form f() =, > 0, 1 is clled n eponentil function. Its domin is the set of ll rel f ( 1) numbers. For n eponentil function f we hve.
Least squares. Václav Hlaváč. Czech Technical University in Prague
 Lest squres Václv Hlváč Czech echncl Unversty n Prgue hlvc@fel.cvut.cz http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~hlvc Courtesy: Fred Pghn nd J.P. Lews, SIGGRAPH 2007 Course; Outlne 2 Lner regresson Geometry of lest-squres
Lest squres Václv Hlváč Czech echncl Unversty n Prgue hlvc@fel.cvut.cz http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~hlvc Courtesy: Fred Pghn nd J.P. Lews, SIGGRAPH 2007 Course; Outlne 2 Lner regresson Geometry of lest-squres
Analysis of Geometric, Zernike and United Moment Invariants Techniques Based on Intra-class Evaluation
 0 Ffth Interntonl Conference on Intellgent Systes, odellng nd Sulton Anlyss of Geoetrc, ernke nd Unted oent Invrnts Technques Bsed on Intr-clss Evluton ohd Wf srudn *, Shhrul z Ykob, Roze Rzf Othn, Iszdy
0 Ffth Interntonl Conference on Intellgent Systes, odellng nd Sulton Anlyss of Geoetrc, ernke nd Unted oent Invrnts Technques Bsed on Intr-clss Evluton ohd Wf srudn *, Shhrul z Ykob, Roze Rzf Othn, Iszdy
OXFORD H i g h e r E d u c a t i o n Oxford University Press, All rights reserved.
 Renshw: Mths for Econoics nswers to dditionl exercises Exercise.. Given: nd B 5 Find: () + B + B 7 8 (b) (c) (d) (e) B B B + B T B (where 8 B 6 B 6 8 B + B T denotes the trnspose of ) T 8 B 5 (f) (g) B
Renshw: Mths for Econoics nswers to dditionl exercises Exercise.. Given: nd B 5 Find: () + B + B 7 8 (b) (c) (d) (e) B B B + B T B (where 8 B 6 B 6 8 B + B T denotes the trnspose of ) T 8 B 5 (f) (g) B
PHYS 601 HW3 Solution
 3.1 Norl force using Lgrnge ultiplier Using the center of the hoop s origin, we will describe the position of the prticle with conventionl polr coordintes. The Lgrngin is therefore L = 1 2 ṙ2 + 1 2 r2
3.1 Norl force using Lgrnge ultiplier Using the center of the hoop s origin, we will describe the position of the prticle with conventionl polr coordintes. The Lgrngin is therefore L = 1 2 ṙ2 + 1 2 r2
Chapter 13. Gas Mixtures. Study Guide in PowerPoint. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th edition by Yunus A. Çengel and Michael A.
 Chapter 3 Gas Mxtures Study Gude n PowerPont to accopany Therodynacs: An Engneerng Approach, 5th edton by Yunus A. Çengel and Mchael A. Boles The dscussons n ths chapter are restrcted to nonreactve deal-gas
Chapter 3 Gas Mxtures Study Gude n PowerPont to accopany Therodynacs: An Engneerng Approach, 5th edton by Yunus A. Çengel and Mchael A. Boles The dscussons n ths chapter are restrcted to nonreactve deal-gas
Math 270A: Numerical Linear Algebra
 Mth 70A: Numericl Liner Algebr Instructor: Michel Holst Fll Qurter 014 Homework Assignment #3 Due Give to TA t lest few dys before finl if you wnt feedbck. Exercise 3.1. (The Bsic Liner Method for Liner
Mth 70A: Numericl Liner Algebr Instructor: Michel Holst Fll Qurter 014 Homework Assignment #3 Due Give to TA t lest few dys before finl if you wnt feedbck. Exercise 3.1. (The Bsic Liner Method for Liner
FUNDAMENTALS ON ALGEBRA MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS
 Dol Bgyoko (0 FUNDAMENTALS ON ALGEBRA MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS Introducton Expressons of the form P(x o + x + x + + n x n re clled polynomls The coeffcents o,, n re ndependent of x nd the exponents 0,,,
Dol Bgyoko (0 FUNDAMENTALS ON ALGEBRA MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS Introducton Expressons of the form P(x o + x + x + + n x n re clled polynomls The coeffcents o,, n re ndependent of x nd the exponents 0,,,
Inner-product spaces
 Inner-product spces Definition: Let V be rel or complex liner spce over F (here R or C). An inner product is n opertion between two elements of V which results in sclr. It is denoted by u, v nd stisfies:
Inner-product spces Definition: Let V be rel or complex liner spce over F (here R or C). An inner product is n opertion between two elements of V which results in sclr. It is denoted by u, v nd stisfies:
1.2. Linear Variable Coefficient Equations. y + b "! = a y + b " Remark: The case b = 0 and a non-constant can be solved with the same idea as above.
 1 12 Liner Vrible Coefficient Equtions Section Objective(s): Review: Constnt Coefficient Equtions Solving Vrible Coefficient Equtions The Integrting Fctor Method The Bernoulli Eqution 121 Review: Constnt
1 12 Liner Vrible Coefficient Equtions Section Objective(s): Review: Constnt Coefficient Equtions Solving Vrible Coefficient Equtions The Integrting Fctor Method The Bernoulli Eqution 121 Review: Constnt
VECTORS VECTORS VECTORS VECTORS. 2. Vector Representation. 1. Definition. 3. Types of Vectors. 5. Vector Operations I. 4. Equal and Opposite Vectors
 1. Defnton A vetor s n entt tht m represent phsl quntt tht hs mgntude nd dreton s opposed to slr tht ls dreton.. Vetor Representton A vetor n e represented grphll n rrow. The length of the rrow s the mgntude
1. Defnton A vetor s n entt tht m represent phsl quntt tht hs mgntude nd dreton s opposed to slr tht ls dreton.. Vetor Representton A vetor n e represented grphll n rrow. The length of the rrow s the mgntude
Exam 2, Mathematics 4701, Section ETY6 6:05 pm 7:40 pm, March 31, 2016, IH-1105 Instructor: Attila Máté 1
 Exm, Mthemtics 471, Section ETY6 6:5 pm 7:4 pm, Mrch 1, 16, IH-115 Instructor: Attil Máté 1 17 copies 1. ) Stte the usul sufficient condition for the fixed-point itertion to converge when solving the eqution
Exm, Mthemtics 471, Section ETY6 6:5 pm 7:4 pm, Mrch 1, 16, IH-115 Instructor: Attil Máté 1 17 copies 1. ) Stte the usul sufficient condition for the fixed-point itertion to converge when solving the eqution
Lecture 22: Logic Synthesis (1)
 Lecture 22: Logc Synthess (1) Sldes courtesy o Demng Chen Some sldes Courtesy o Pro. J. Cong o UCLA Outlne Redng Synthess nd optmzton o dgtl crcuts, G. De Mchel, 1994, Secton 2.5-2.5.1 Overvew Boolen lgebr
Lecture 22: Logc Synthess (1) Sldes courtesy o Demng Chen Some sldes Courtesy o Pro. J. Cong o UCLA Outlne Redng Synthess nd optmzton o dgtl crcuts, G. De Mchel, 1994, Secton 2.5-2.5.1 Overvew Boolen lgebr
Quadrilateral et Hexahedral Pseudo-conform Finite Elements
 Qurlterl et Heerl seuo-conform Fnte Elements E. DUBACH R. LUCE J.M. THOMAS Lbortore e Mtémtques Applquées UMR 5 u Frnce GDR MoMs Métoes Numérques pour les Flues. rs écembre 6 Wt s te problem? Loss of conergence
Qurlterl et Heerl seuo-conform Fnte Elements E. DUBACH R. LUCE J.M. THOMAS Lbortore e Mtémtques Applquées UMR 5 u Frnce GDR MoMs Métoes Numérques pour les Flues. rs écembre 6 Wt s te problem? Loss of conergence
Investigation phase in case of Bragg coupling
 Journl of Th-Qr Unversty No.3 Vol.4 December/008 Investgton phse n cse of Brgg couplng Hder K. Mouhmd Deprtment of Physcs, College of Scence, Th-Qr, Unv. Mouhmd H. Abdullh Deprtment of Physcs, College
Journl of Th-Qr Unversty No.3 Vol.4 December/008 Investgton phse n cse of Brgg couplng Hder K. Mouhmd Deprtment of Physcs, College of Scence, Th-Qr, Unv. Mouhmd H. Abdullh Deprtment of Physcs, College
Review of Linear Algebra
 PGE 30: Forulto d Soluto Geosstes Egeerg Dr. Blhoff Sprg 0 Revew of Ler Alger Chpter 7 of Nuercl Methods wth MATLAB, Gerld Recktewld Vector s ordered set of rel (or cople) uers rrged s row or colu sclr
PGE 30: Forulto d Soluto Geosstes Egeerg Dr. Blhoff Sprg 0 Revew of Ler Alger Chpter 7 of Nuercl Methods wth MATLAB, Gerld Recktewld Vector s ordered set of rel (or cople) uers rrged s row or colu sclr
Regulated functions and the regulated integral
 Regulted functions nd the regulted integrl Jordn Bell jordn.bell@gmil.com Deprtment of Mthemtics University of Toronto April 3 2014 1 Regulted functions nd step functions Let = [ b] nd let X be normed
Regulted functions nd the regulted integrl Jordn Bell jordn.bell@gmil.com Deprtment of Mthemtics University of Toronto April 3 2014 1 Regulted functions nd step functions Let = [ b] nd let X be normed
Trigonometry. Trigonometry. Solutions. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 223, 224, 245.
 Trgonometry Trgonometry Solutons Currulum Redy CMMG:, 4, 4 www.mthlets.om Trgonometry Solutons Bss Pge questons. Identfy f the followng trngles re rght ngled or not. Trngles,, d, e re rght ngled ndted
Trgonometry Trgonometry Solutons Currulum Redy CMMG:, 4, 4 www.mthlets.om Trgonometry Solutons Bss Pge questons. Identfy f the followng trngles re rght ngled or not. Trngles,, d, e re rght ngled ndted
September 13 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Computer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprtment Mechnicl Engineering 5A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll Ticket: 5966 Instructor: Lrry Cretto Septemer Homework Solutions. Are
College of Engineering nd Computer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprtment Mechnicl Engineering 5A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll Ticket: 5966 Instructor: Lrry Cretto Septemer Homework Solutions. Are
Regular Language. Nonregular Languages The Pumping Lemma. The pumping lemma. Regular Language. The pumping lemma. Infinitely long words 3/17/15
 Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
