Math C067 Independence and Repeated Trials.
|
|
|
- Ann Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math C067 Independence and Repeated Trials. Richard Beigel February 7, 006 Socks. Bill s sock drawer contains 10 red socks, 0 green socks, and 30 blue socks. If Bill removes two socks from his drawer at random, what is the probability that they have the same color? Let E denote the event that both socks have the same color. Let R, G, and B denote the event that the first sock bill picks is red/green/blue respectively. We know: P (R) = 10/60 = 1/6 P (G) = 0/60 = 1/3 P (B) = 30/60 = 1/ P (E R) = 9/59 P (E G) = 19/59 P (E B) = 9/59 Note: the two sock choices are not independent. R, G, and B partition the probability space. So, by the law of total probability, P (E) = P (E R) P (R) + P (E G) P (G) + P (E B) P (B) =
2 Dice. Bill owns a pair of oddly colored 6-sided dice. Each die has 1 red face, green faces, and 3 blue faces. Bill rolls both dice. What is the probability that they both come up the same color? Let E denote the event that both dice come up the same color. Let R, G, B denote the event that that first die comes up red/green/blue respectively. We know P (R) = 1/6 P (G) = /6 = 1/3 P (B) = 3/6 = 1/ the results of the two die rolls are independent R, G, and B partition the probability space. So, by the law of total probability, P (E) = P (E R) P (R) + P (E G) P (G) + P (E B) P (B) = When dealing with repeated independent trials it is conventional to write the results of the trials in order without punctionation, e.g., RR denotes the event that both dice come up red RB denotes the event that the first die comes up red and the second blue BR denotes the event that the first die comes up blue and the second red Using this notation, we would write E = RR GG BB P (E) = P (RR) + P (GG) + P (BB) disjoint events P (E) = P (E)
3 Three Dice. Bill rolls his colored dice 3 times. What is the probability that all three dice are the same color? What is the probability that the three dice are all different colors? Let E denote the event that all three dice are the same color. E = RRR GGG BBB P (E) = P (RRR) + P (GGG) + P (BBB) disjoint events P (E) = P (E) Let E denote the event that the three dice are all different colors. E = RGB RBG BRG BGR GRB GBR P (E) = P (RGB) + P (RBG) + P (BRG) + P (BGR) + P (GRB) + P (GBR) P (E) = P (E) = 1 3 P (E) = P (E) = 1 6 Note: it s only a coincidence that the two probabilities are the same. 3
4 4.49 Let A and B be independent events with p(a) = 0.3 and p(b) = 0.4. Find p(a B), p(a B), P (A B) and p(b A). Because A and B are independent, p(a B) = p(a) p(b) = = 0.1 p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a B) = = Because A and B are independent, p(a B) = p(a) = 0.3. Because A and B are independent, p(b A) = p(b) = Box A contains 5 red marbles and 3 blue marbles. Box B contains red and 3 blue. A marble is drawn at random from each box. (a) Find the probability that both marbles are red. (b) Find the probability that both marbles are red. Solution: Let R 1 denote the event that the first marble is red, B 1 the event that the first marble is blue, R denote the event that the second marble is red, B the event that the second marble is blue. (a) Because the two marbles are chosen randomly from different boxes, their choices are independent. p(r 1 R ) = p(r 1 ) p(r ) independence = = 8 = 1 4 (b) p(r 1 B B 1 R ) = p(r 1 B ) + p(b 1 R ) disjoint events = p(r 1 ) p(b ) + p(b 1 ) p(r ) independence = = =
5 4.51 Let A and B be events with p(a) = 0.3, p(a B) = 0.5, and p(b) = p. Find p if: (a) A and B are disjoint (b) A and B are independent (c) A is a subset of B Solution: p(a), p(b), and p(a B) are always related via the formula p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a B). If we know the other three numbers in the formula, we can solve for p(b). We are given p(a) and p(a B), so it remains for us to figure out p(a B). (a) We are told that A and B are disjoint, i.e., that A B =, so p(a B) = 0. p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a B) 0.5 = p 0 0. = p Alternatively, we could have started this part with the equation p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) because A and B are disjoint 0.5 = p 0. = p (b) We are told that A and B are independent, so p(a B) = P (A) p(b). p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a B) 0.5 = p 0.3 p 0. = 0.7p = p 7 = p (c) We are told that A is a subset of B, so A B = A, so p(a B) = p(a). Alternatively, we could use the formula p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a B) 0.5 = p = p A B = B because A is a subset of B p(a B) = p(b) 0.5 = p 5
6 1. Important General Formulas for Computing Ordinary Probabilities. Union (OR) p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a B) Intersection (AND) p(a B) = p(a B) p(b) Complementation (NOT) p(a) = 1 p(a) Law of Total Probability p(a) = p(a B) p(b) + p(a B) p(b). Important Formulas for Independent Events A and B Conditional Probability (independent events) Intersection (independent events) p(a B) = p(a) p(b) Union (independent events) First apply the general formula for union, and then apply the intersection formula for independent events. You will get p(a B) = p(a) + p(b) p(a) p(b) but there is no need to memorize this is a separate formula. 3. Important Formulas for Computing Conditional Probabilities p(a B) = p(a B B) p(a B) = A B / B p(a B) = p(a B)/p(B) Bayes Theorem p(a B) p(b) = p(b A) p(a) 6
Math 511 Exam #1. Show All Work No Calculators
 Math 511 Exam #1 Show All Work No Calculators 1. Suppose that A and B are events in a sample space S and that P(A) = 0.4 and P(B) = 0.6 and P(A B) = 0.3. Suppose too that B, C, and D are mutually independent
Math 511 Exam #1 Show All Work No Calculators 1. Suppose that A and B are events in a sample space S and that P(A) = 0.4 and P(B) = 0.6 and P(A B) = 0.3. Suppose too that B, C, and D are mutually independent
Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes
 Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Probability Review I
 Probability Review I Harvard Math Camp - Econometrics Ashesh Rambachan Summer 2018 Outline Random Experiments The sample space and events σ-algebra and measures Basic probability rules Conditional Probability
Probability Review I Harvard Math Camp - Econometrics Ashesh Rambachan Summer 2018 Outline Random Experiments The sample space and events σ-algebra and measures Basic probability rules Conditional Probability
LECTURE 1. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
 LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
BASICS OF PROBABILITY CHAPTER-1 CS6015-LINEAR ALGEBRA AND RANDOM PROCESSES
 BASICS OF PROBABILITY CHAPTER-1 CS6015-LINEAR ALGEBRA AND RANDOM PROCESSES COMMON TERMS RELATED TO PROBABILITY Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur Probability values are
BASICS OF PROBABILITY CHAPTER-1 CS6015-LINEAR ALGEBRA AND RANDOM PROCESSES COMMON TERMS RELATED TO PROBABILITY Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur Probability values are
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness
 Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of
 Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Math 243 Section 3.1 Introduction to Probability Lab
 Math 243 Section 3.1 Introduction to Probability Lab Overview Why Study Probability? Outcomes, Events, Sample Space, Trials Probabilities and Complements (not) Theoretical vs. Empirical Probability The
Math 243 Section 3.1 Introduction to Probability Lab Overview Why Study Probability? Outcomes, Events, Sample Space, Trials Probabilities and Complements (not) Theoretical vs. Empirical Probability The
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio
 4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
I - Probability. What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring. 1classical probability. 2empirical probability. 3subjective probability
 What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
 Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Bayes Theorem. Jan Kracík. Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava
 Jan Kracík Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava Introduction Bayes theorem fundamental theorem in probability theory named after reverend Thomas Bayes (1701 1761) discovered in Bayes
Jan Kracík Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava Introduction Bayes theorem fundamental theorem in probability theory named after reverend Thomas Bayes (1701 1761) discovered in Bayes
Probability Theory and Applications
 Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Probability and Sample space
 Probability and Sample space We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain but there is a regular distribution of outcomes in a large number of repetitions. The probability of any outcome
Probability and Sample space We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain but there is a regular distribution of outcomes in a large number of repetitions. The probability of any outcome
Compound Events. The event E = E c (the complement of E) is the event consisting of those outcomes which are not in E.
 Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics
 Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
2. Conditional Probability
 ENGG 2430 / ESTR 2004: Probability and Statistics Spring 2019 2. Conditional Probability Andrej Bogdanov Coins game Toss 3 coins. You win if at least two come out heads. S = { HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH,
ENGG 2430 / ESTR 2004: Probability and Statistics Spring 2019 2. Conditional Probability Andrej Bogdanov Coins game Toss 3 coins. You win if at least two come out heads. S = { HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH,
Continuing Probability.
 Continuing Probability. Wrap up: Probability Formalism. Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes Rule Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a uniform probability space: Red
Continuing Probability. Wrap up: Probability Formalism. Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes Rule Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a uniform probability space: Red
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Lecture 9b: Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes' Rule Lecturer: Lale Özkahya
 BBM 205 Discrete Mathematics Hacettepe University http://web.cs.hacettepe.edu.tr/ bbm205 Lecture 9b: Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes' Rule Lecturer: Lale Özkahya Resources: Kenneth
BBM 205 Discrete Mathematics Hacettepe University http://web.cs.hacettepe.edu.tr/ bbm205 Lecture 9b: Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes' Rule Lecturer: Lale Özkahya Resources: Kenneth
Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015
 L645 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015 1 / 34 To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and This is only an introduction; for a fuller understanding, you would
L645 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015 1 / 34 To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and This is only an introduction; for a fuller understanding, you would
Probabilistic models
 Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
CSC Discrete Math I, Spring Discrete Probability
 CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Discrete Probability Probability of an Event Pierre-Simon Laplace s classical theory of probability: Definition of terms: An experiment is a procedure that yields
CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Discrete Probability Probability of an Event Pierre-Simon Laplace s classical theory of probability: Definition of terms: An experiment is a procedure that yields
CINQA Workshop Probability Math 105 Silvia Heubach Department of Mathematics, CSULA Thursday, September 6, 2012
 CINQA Workshop Probability Math 105 Silvia Heubach Department of Mathematics, CSULA Thursday, September 6, 2012 Silvia Heubach/CINQA 2012 Workshop Objectives To familiarize biology faculty with one of
CINQA Workshop Probability Math 105 Silvia Heubach Department of Mathematics, CSULA Thursday, September 6, 2012 Silvia Heubach/CINQA 2012 Workshop Objectives To familiarize biology faculty with one of
Math C067 Bayes Theorem
 Math C067 Bayes Theorem Richard Beigel February 0, 006 Gold and Silver Balls. Bill has three boxes. Their contents are Box 1: Two silver balls Box : One silver ball and one gold ball Box : Two gold balls.
Math C067 Bayes Theorem Richard Beigel February 0, 006 Gold and Silver Balls. Bill has three boxes. Their contents are Box 1: Two silver balls Box : One silver ball and one gold ball Box : Two gold balls.
Chapter 2 PROBABILITY SAMPLE SPACE
 Chapter 2 PROBABILITY Key words: Sample space, sample point, tree diagram, events, complement, union and intersection of an event, mutually exclusive events; Counting techniques: multiplication rule, permutation,
Chapter 2 PROBABILITY Key words: Sample space, sample point, tree diagram, events, complement, union and intersection of an event, mutually exclusive events; Counting techniques: multiplication rule, permutation,
Chapter Summary. 7.1 Discrete Probability 7.2 Probability Theory 7.3 Bayes Theorem 7.4 Expected value and Variance
 Chapter 7 Chapter Summary 7.1 Discrete Probability 7.2 Probability Theory 7.3 Bayes Theorem 7.4 Expected value and Variance Section 7.1 Introduction Probability theory dates back to 1526 when the Italian
Chapter 7 Chapter Summary 7.1 Discrete Probability 7.2 Probability Theory 7.3 Bayes Theorem 7.4 Expected value and Variance Section 7.1 Introduction Probability theory dates back to 1526 when the Italian
Introductory Probability
 Introductory Probability Conditional Probability: Bayes Probabilities Nicholas Nguyen nicholas.nguyen@uky.edu Department of Mathematics UK Agenda Computing Bayes Probabilities Conditional Probability and
Introductory Probability Conditional Probability: Bayes Probabilities Nicholas Nguyen nicholas.nguyen@uky.edu Department of Mathematics UK Agenda Computing Bayes Probabilities Conditional Probability and
Review of Basic Probability
 Review of Basic Probability Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 September 16, 2009 Abstract This document reviews basic discrete
Review of Basic Probability Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 September 16, 2009 Abstract This document reviews basic discrete
1.6/1.7 - Conditional Probability and Bayes Theorem
 1.6/1.7 - Conditional Probability and Bayes Theorem Math 166-502 Blake Boudreaux Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University February 1, 2018 Blake Boudreaux (Texas A&M University) 1.6/1.7 - Conditional
1.6/1.7 - Conditional Probability and Bayes Theorem Math 166-502 Blake Boudreaux Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University February 1, 2018 Blake Boudreaux (Texas A&M University) 1.6/1.7 - Conditional
Sum and Product Rules
 Sum and Product Rules Exercise. Consider tossing a coin five times. What is the probability of getting the same result on the first two tosses or the last two tosses? Solution. Let E be the event that
Sum and Product Rules Exercise. Consider tossing a coin five times. What is the probability of getting the same result on the first two tosses or the last two tosses? Solution. Let E be the event that
Chapter. Probability
 Chapter 3 Probability Section 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability Section 3.1 Objectives Identify the sample space of a probability experiment Identify simple events Use the Fundamental Counting Principle
Chapter 3 Probability Section 3.1 Basic Concepts of Probability Section 3.1 Objectives Identify the sample space of a probability experiment Identify simple events Use the Fundamental Counting Principle
(6, 1), (5, 2), (4, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5), (1, 6)
 Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
4. Probability of an event A for equally likely outcomes:
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
Topic -2. Probability. Larson & Farber, Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World, 3e 1
 Topic -2 Probability Larson & Farber, Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World, 3e 1 Probability Experiments Experiment : An experiment is an act that can be repeated under given condition. Rolling a
Topic -2 Probability Larson & Farber, Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World, 3e 1 Probability Experiments Experiment : An experiment is an act that can be repeated under given condition. Rolling a
4/17/2012. NE ( ) # of ways an event can happen NS ( ) # of events in the sample space
 I. Vocabulary: A. Outcomes: the things that can happen in a probability experiment B. Sample Space (S): all possible outcomes C. Event (E): one outcome D. Probability of an Event (P(E)): the likelihood
I. Vocabulary: A. Outcomes: the things that can happen in a probability experiment B. Sample Space (S): all possible outcomes C. Event (E): one outcome D. Probability of an Event (P(E)): the likelihood
The Practice of Statistics Third Edition
 The Practice of Statistics Third Edition Chapter 6: Probability and Simulation: The Study of Randomness Copyright 2008 by W. H. Freeman & Company Probability Rules True probability can only be found by
The Practice of Statistics Third Edition Chapter 6: Probability and Simulation: The Study of Randomness Copyright 2008 by W. H. Freeman & Company Probability Rules True probability can only be found by
AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2
 AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2 Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Friday April 10, 2015 Probability: Introduction Probability:
AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2 Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Friday April 10, 2015 Probability: Introduction Probability:
Problem Set 2 Due Feb, 1
 EE126: Probability and Random Processes SP 07 Problem Set 2 Due Feb, 1 Lecturer: Jean C. Walrand GSI: Daniel Preda, Assane Gueye Problem 2.1. Pick 3 balls from an urn containing 15 balls (7 red balls,
EE126: Probability and Random Processes SP 07 Problem Set 2 Due Feb, 1 Lecturer: Jean C. Walrand GSI: Daniel Preda, Assane Gueye Problem 2.1. Pick 3 balls from an urn containing 15 balls (7 red balls,
Properties of Probability
 Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Mathematical Probability
 Mathematical Probability STA 281 Fall 2011 1 Introduction Engineers and scientists are always exposed to data, both in their professional capacities and in everyday activities. The discipline of statistics
Mathematical Probability STA 281 Fall 2011 1 Introduction Engineers and scientists are always exposed to data, both in their professional capacities and in everyday activities. The discipline of statistics
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1
 HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1 Definition 4.1 If an experiment can be repeated under the same condition, its outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, and the collection of its every possible outcome
HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1 Definition 4.1 If an experiment can be repeated under the same condition, its outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, and the collection of its every possible outcome
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 19. Probabilities. CS 441 Discrete mathematics for CS. Probabilities
 CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 19 Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Experiment: a procedure that yields one of the possible outcomes Sample space: a set of possible outcomes
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 19 Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Experiment: a procedure that yields one of the possible outcomes Sample space: a set of possible outcomes
Lecture 1. Chapter 1. (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 ( ). 1. What is Statistics?
 Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
With Question/Answer Animations. Chapter 7
 With Question/Answer Animations Chapter 7 Chapter Summary Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability Theory Bayes Theorem Section 7.1 Section Summary Finite Probability Probabilities of Complements
With Question/Answer Animations Chapter 7 Chapter Summary Introduction to Discrete Probability Probability Theory Bayes Theorem Section 7.1 Section Summary Finite Probability Probabilities of Complements
2.6 Tools for Counting sample points
 2.6 Tools for Counting sample points When the number of simple events in S is too large, manual enumeration of every sample point in S is tedious or even impossible. (Example) If S contains N equiprobable
2.6 Tools for Counting sample points When the number of simple events in S is too large, manual enumeration of every sample point in S is tedious or even impossible. (Example) If S contains N equiprobable
Law of Total Probability and Bayes Rule
 MATH 382 Law of Total Probability and Bayes Rule Dr Neal, WKU Law of Total Probability: Suppose events A 1, A 2,, A n form a partition of Ω That is, the events are mutually disjoint and their union is
MATH 382 Law of Total Probability and Bayes Rule Dr Neal, WKU Law of Total Probability: Suppose events A 1, A 2,, A n form a partition of Ω That is, the events are mutually disjoint and their union is
Topic 2 Probability. Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability
 Topic 2 Probability Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability Random process: a process whose outcome can not be predicted with certainty Examples: rolling
Topic 2 Probability Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability Random process: a process whose outcome can not be predicted with certainty Examples: rolling
the time it takes until a radioactive substance undergoes a decay
 1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
Probabilistic models
 Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Conditional probability
 CHAPTER 4 Conditional probability 4.1. Introduction Suppose there are 200 men, of which 100 are smokers, and 100 women, of which 20 are smokers. What is the probability that a person chosen at random will
CHAPTER 4 Conditional probability 4.1. Introduction Suppose there are 200 men, of which 100 are smokers, and 100 women, of which 20 are smokers. What is the probability that a person chosen at random will
Axioms of Probability
 Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Math Camp. September 16, 2017 Unit 2. MSSM Program Columbia University Dr. Satyajit Bose
 Math Camp September 16, 2017 Unit 2 MSSM Program Columbia University Dr. Satyajit Bose Math Camp Interlude Partial Derivatives Recall:The derivative f'(x) of a function f(x) is the slope of f(x). Alternatively,
Math Camp September 16, 2017 Unit 2 MSSM Program Columbia University Dr. Satyajit Bose Math Camp Interlude Partial Derivatives Recall:The derivative f'(x) of a function f(x) is the slope of f(x). Alternatively,
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 4: Sequential experiments Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: February 2, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Sequential Experiments 3 Total Probability
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 4: Sequential experiments Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: February 2, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Sequential Experiments 3 Total Probability
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15. Lecture 2: Random Experiments. Prof. Vince Calhoun
 ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
Origins of Probability Theory
 1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
1 16.584: INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments.
STAT Chapter 3: Probability
 Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
ECE353: Probability and Random Processes. Lecture 2 - Set Theory
 ECE353: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 2 - Set Theory Xiao Fu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University E-mail: xiao.fu@oregonstate.edu January 10, 2018 Set
ECE353: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 2 - Set Theory Xiao Fu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University E-mail: xiao.fu@oregonstate.edu January 10, 2018 Set
The problem Countable additivity Finite additivity Conglomerability Structure Puzzle. The Measure Problem. Alexander R. Pruss
 The Measure Problem Alexander R. Pruss Department of Philosophy Baylor University July 11, 2013 The problem and the claim There are infinitely many observers (or types of observers, or observations, or
The Measure Problem Alexander R. Pruss Department of Philosophy Baylor University July 11, 2013 The problem and the claim There are infinitely many observers (or types of observers, or observations, or
Math 111, Math & Society. Probability
 Math 111, Math & Society Probability 1 Counting Probability consists in the assignment of likelihoods to the possible outcomes of an experiment, activity, or phenomenon. Correctly calculating probabilities
Math 111, Math & Society Probability 1 Counting Probability consists in the assignment of likelihoods to the possible outcomes of an experiment, activity, or phenomenon. Correctly calculating probabilities
Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a uniform probability space:
 Lecture 16: Continuing Probability Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a uniform probability space: Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a non-uniform probability
Lecture 16: Continuing Probability Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a uniform probability space: Probability Space: Formalism Simplest physical model of a non-uniform probability
Vina Nguyen HSSP July 6, 2008
 Vina Nguyen HSSP July 6, 2008 1 Late registration Claroline class server 2 What are the two types of probability? 3 What are the two types of probability? What is a set? 4 What are the two types of probability?
Vina Nguyen HSSP July 6, 2008 1 Late registration Claroline class server 2 What are the two types of probability? 3 What are the two types of probability? What is a set? 4 What are the two types of probability?
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 3 9/10/2008 CONDITIONING AND INDEPENDENCE
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 3 9/10/2008 CONDITIONING AND INDEPENDENCE Most of the material in this lecture is covered in [Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis] Sections 1.3-1.5
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 3 9/10/2008 CONDITIONING AND INDEPENDENCE Most of the material in this lecture is covered in [Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis] Sections 1.3-1.5
Chapter 5 : Probability. Exercise Sheet. SHilal. 1 P a g e
 1 P a g e experiment ( observing / measuring ) outcomes = results sample space = set of all outcomes events = subset of outcomes If we collect all outcomes we are forming a sample space If we collect some
1 P a g e experiment ( observing / measuring ) outcomes = results sample space = set of all outcomes events = subset of outcomes If we collect all outcomes we are forming a sample space If we collect some
Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes. Set Operations and Relations. Venn Diagram 2.1. Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes
 Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability. Elements of Probability. Conditional probability. Sequential Calculation of Probability
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Lecture Lecture 5
 Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that the event will occur.
 Chapter 5 This chapter introduces probability to quantify randomness. Section 5.1: How Can Probability Quantify Randomness? The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that
Chapter 5 This chapter introduces probability to quantify randomness. Section 5.1: How Can Probability Quantify Randomness? The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that
= 2 5 Note how we need to be somewhat careful with how we define the total number of outcomes in b) and d). We will return to this later.
 PROBABILITY MATH CIRCLE (ADVANCED /27/203 The likelyhood of something (usually called an event happening is called the probability. Probability (informal: We can calculate probability using a ratio: want
PROBABILITY MATH CIRCLE (ADVANCED /27/203 The likelyhood of something (usually called an event happening is called the probability. Probability (informal: We can calculate probability using a ratio: want
Chapter 2 Probability
 Basic Axioms and properties Chapter 2 Probability 1. 0 Pr(A) 1 2. Pr(S) = 1 3. A B Pr(A) Pr(B) 4. Pr(φ ) = 0 5. If A and B are disjoint i.e. A B φ P( A B) = P(A) + P(B). 6. For any two events A and B,
Basic Axioms and properties Chapter 2 Probability 1. 0 Pr(A) 1 2. Pr(S) = 1 3. A B Pr(A) Pr(B) 4. Pr(φ ) = 0 5. If A and B are disjoint i.e. A B φ P( A B) = P(A) + P(B). 6. For any two events A and B,
Set/deck of playing cards. Spades Hearts Diamonds Clubs
 TC Mathematics S2 Coins Die dice Tale Head Set/deck of playing cards Spades Hearts Diamonds Clubs TC Mathematics S2 PROBABILITIES : intuitive? Experiment tossing a coin Event it s a head Probability 1/2
TC Mathematics S2 Coins Die dice Tale Head Set/deck of playing cards Spades Hearts Diamonds Clubs TC Mathematics S2 PROBABILITIES : intuitive? Experiment tossing a coin Event it s a head Probability 1/2
Lecture 6 Probability
 Lecture 6 Probability Example: When you toss a coin, there are only two possible outcomes, heads and tails. What if we toss a coin 4 times? Figure below shows the results of tossing a coin 5000 times twice.
Lecture 6 Probability Example: When you toss a coin, there are only two possible outcomes, heads and tails. What if we toss a coin 4 times? Figure below shows the results of tossing a coin 5000 times twice.
Prelim 1 (10 8)!8! = 10 9 = 45. (b) How many ways can it be done if the first three questions are required? 2 = 21
 Math 1105 Fall 010 J.T. Gene Hwang, Instructor Robyn Miller, T.A. Prelim 1 Instructions This is a closed book exam. Graphing calculators are not permitted. Solutions should be written in your blue book
Math 1105 Fall 010 J.T. Gene Hwang, Instructor Robyn Miller, T.A. Prelim 1 Instructions This is a closed book exam. Graphing calculators are not permitted. Solutions should be written in your blue book
Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Lecture Outline October 18, 2018
 Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Lecture Outline October 18, 2018 The Total Probability Theorem. Consider events E and F. Consider a sample point ω E. Observe that ω belongs to either F or
Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Lecture Outline October 18, 2018 The Total Probability Theorem. Consider events E and F. Consider a sample point ω E. Observe that ω belongs to either F or
Probability and Independence Terri Bittner, Ph.D.
 Probability and Independence Terri Bittner, Ph.D. The concept of independence is often confusing for students. This brief paper will cover the basics, and will explain the difference between independent
Probability and Independence Terri Bittner, Ph.D. The concept of independence is often confusing for students. This brief paper will cover the basics, and will explain the difference between independent
Probability Basics Review
 CS70: Jean Walrand: Lecture 16 Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes Rule Probability Basics Review Setup: Set notation review A B A [ B A \ B 1 Probability Basics Review 2 Events 3 Conditional
CS70: Jean Walrand: Lecture 16 Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes Rule Probability Basics Review Setup: Set notation review A B A [ B A \ B 1 Probability Basics Review 2 Events 3 Conditional
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]
![Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision]](/thumbs/93/111285649.jpg) Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
Part (A): Review of Probability [Statistics I revision] 1 Definition of Probability 1.1 Experiment An experiment is any procedure whose outcome is uncertain ffl toss a coin ffl throw a die ffl buy a lottery
Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability
 Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability Sta102 / BME102 January 25, 2016 Colin Rundel Axioms of Probability What does it mean to say that: The probability of flipping a coin and getting heads is 1/2? 3 What
Lecture 3 - Axioms of Probability Sta102 / BME102 January 25, 2016 Colin Rundel Axioms of Probability What does it mean to say that: The probability of flipping a coin and getting heads is 1/2? 3 What
CS70: Jean Walrand: Lecture 16.
 CS70: Jean Walrand: Lecture 16. Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes Rule 1. Probability Basics Review 2. Events 3. Conditional Probability 4. Independence of Events 5. Bayes Rule Probability
CS70: Jean Walrand: Lecture 16. Events, Conditional Probability, Independence, Bayes Rule 1. Probability Basics Review 2. Events 3. Conditional Probability 4. Independence of Events 5. Bayes Rule Probability
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability
 Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
1. Consider a random independent sample of size 712 from a distribution with the following pdf. c 1+x. f(x) =
 1. Consider a random independent sample of size 712 from a distribution with the following pdf f(x) = c 1+x 0
1. Consider a random independent sample of size 712 from a distribution with the following pdf f(x) = c 1+x 0
Outline Conditional Probability The Law of Total Probability and Bayes Theorem Independent Events. Week 4 Classical Probability, Part II
 Week 4 Classical Probability, Part II Week 4 Objectives This week we continue covering topics from classical probability. The notion of conditional probability is presented first. Important results/tools
Week 4 Classical Probability, Part II Week 4 Objectives This week we continue covering topics from classical probability. The notion of conditional probability is presented first. Important results/tools
2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY
 IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
PERMUTATIONS, COMBINATIONS AND DISCRETE PROBABILITY
 Friends, we continue the discussion with fundamentals of discrete probability in the second session of third chapter of our course in Discrete Mathematics. The conditional probability and Baye s theorem
Friends, we continue the discussion with fundamentals of discrete probability in the second session of third chapter of our course in Discrete Mathematics. The conditional probability and Baye s theorem
Combinatorics and probability
 Combinatorics and probability Maths 4 th ESO José Jaime Noguera 1 Organizing data: tree diagrams Draw the tree diagram for the problem: You have 3 seats and three people Andrea (A), Bob (B) and Carol (C).
Combinatorics and probability Maths 4 th ESO José Jaime Noguera 1 Organizing data: tree diagrams Draw the tree diagram for the problem: You have 3 seats and three people Andrea (A), Bob (B) and Carol (C).
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14 Introduction One of the key properties of coin flips is independence: if you flip a fair coin ten times and get ten
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14 Introduction One of the key properties of coin flips is independence: if you flip a fair coin ten times and get ten
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page α 2 θ 1 u 3. wear coat. θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ 1 = cold u 3 = brrr!
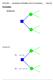 ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
The enumeration of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space, denoted S. E.g.: S={head, tail}
 Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
PROBABILITY THEORY. Prof. S. J. Soni. Assistant Professor Computer Engg. Department SPCE, Visnagar
 PROBABILITY THEORY By Prof. S. J. Soni Assistant Professor Computer Engg. Department SPCE, Visnagar Introduction Signals whose values at any instant t are determined by their analytical or graphical description
PROBABILITY THEORY By Prof. S. J. Soni Assistant Professor Computer Engg. Department SPCE, Visnagar Introduction Signals whose values at any instant t are determined by their analytical or graphical description
Lecture 3: Probability
 Lecture 3: Probability 28th of October 2015 Lecture 3: Probability 28th of October 2015 1 / 36 Summary of previous lecture Define chance experiment, sample space and event Introduce the concept of the
Lecture 3: Probability 28th of October 2015 Lecture 3: Probability 28th of October 2015 1 / 36 Summary of previous lecture Define chance experiment, sample space and event Introduce the concept of the
Probability Theory. Introduction to Probability Theory. Principles of Counting Examples. Principles of Counting. Probability spaces.
 Probability Theory To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and probability Introduction to Probability Theory L645 Advanced NLP Autumn 2009 This is only an introduction; for
Probability Theory To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and probability Introduction to Probability Theory L645 Advanced NLP Autumn 2009 This is only an introduction; for
{ } all possible outcomes of the procedure. There are 8 ways this procedure can happen.
 Probability with the 3-Kids Procedure Statistics Procedures and Events Definition A procedure is something that produces an outcome. When a procedure produces an outcome, it s called a trial or a run of
Probability with the 3-Kids Procedure Statistics Procedures and Events Definition A procedure is something that produces an outcome. When a procedure produces an outcome, it s called a trial or a run of
Term Definition Example Random Phenomena
 UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Probabilities Course Learning Outcomes for Unit VI Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Apply mathematical principles used in real-world situations. 1.1 Demonstrate
UNIT VI STUDY GUIDE Probabilities Course Learning Outcomes for Unit VI Upon completion of this unit, students should be able to: 1. Apply mathematical principles used in real-world situations. 1.1 Demonstrate
Statistical Theory 1
 Statistical Theory 1 Set Theory and Probability Paolo Bautista September 12, 2017 Set Theory We start by defining terms in Set Theory which will be used in the following sections. Definition 1 A set is
Statistical Theory 1 Set Theory and Probability Paolo Bautista September 12, 2017 Set Theory We start by defining terms in Set Theory which will be used in the following sections. Definition 1 A set is
4. Suppose that we roll two die and let X be equal to the maximum of the two rolls. Find P (X {1, 3, 5}) and draw the PMF for X.
 Math 10B with Professor Stankova Worksheet, Midterm #2; Wednesday, 3/21/2018 GSI name: Roy Zhao 1 Problems 1.1 Bayes Theorem 1. Suppose a test is 99% accurate and 1% of people have a disease. What is the
Math 10B with Professor Stankova Worksheet, Midterm #2; Wednesday, 3/21/2018 GSI name: Roy Zhao 1 Problems 1.1 Bayes Theorem 1. Suppose a test is 99% accurate and 1% of people have a disease. What is the
